 MSU & Skol. Tech Restriction/modification
MSU & Skol. Tech Restriction/modification
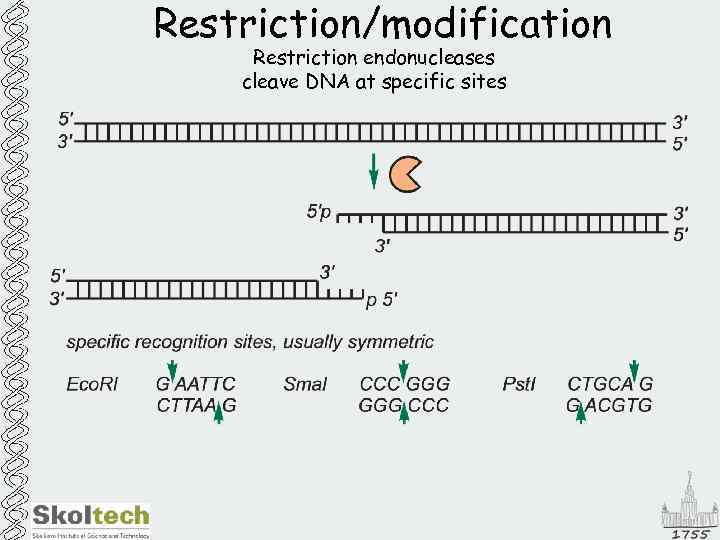 Restriction/modification Restriction endonucleases cleave DNA at specific sites
Restriction/modification Restriction endonucleases cleave DNA at specific sites
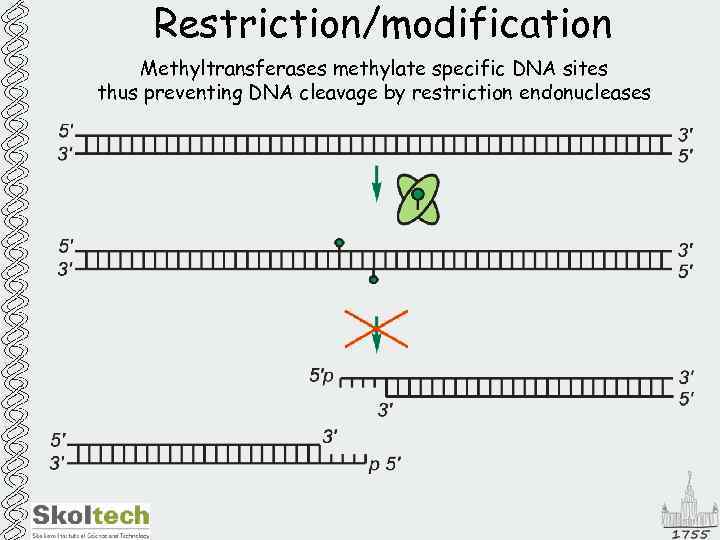 Restriction/modification Methyltransferases methylate specific DNA sites thus preventing DNA cleavage by restriction endonucleases
Restriction/modification Methyltransferases methylate specific DNA sites thus preventing DNA cleavage by restriction endonucleases
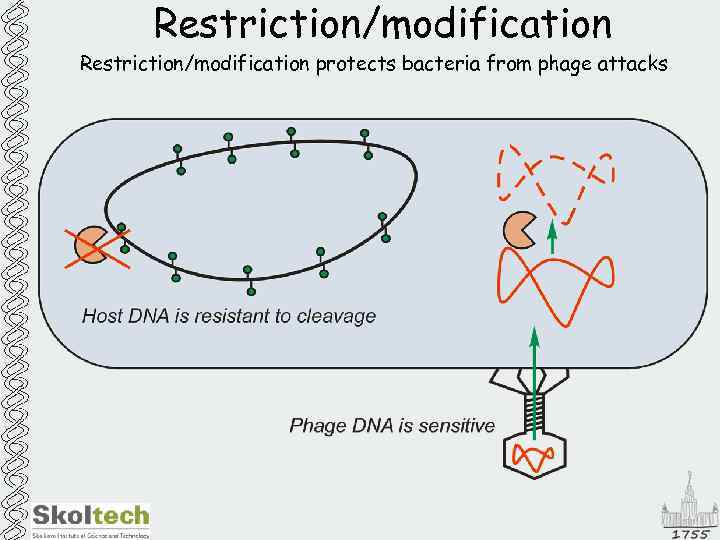 Restriction/modification protects bacteria from phage attacks
Restriction/modification protects bacteria from phage attacks
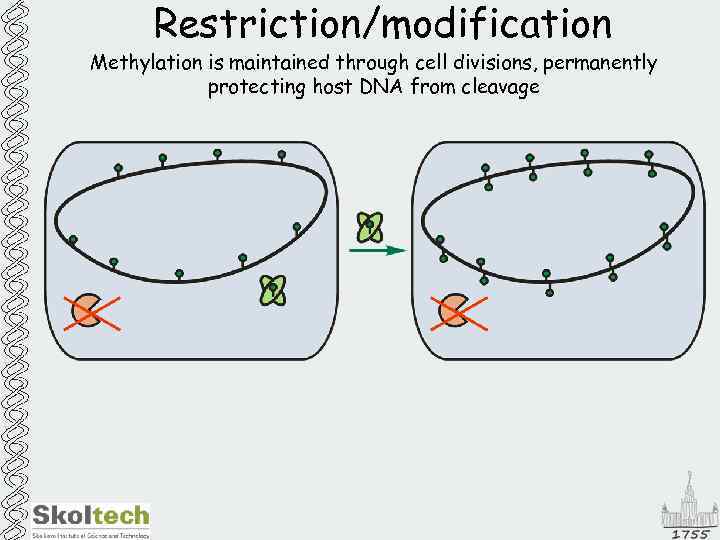 Restriction/modification Methylation is maintained through cell divisions, permanently protecting host DNA from cleavage
Restriction/modification Methylation is maintained through cell divisions, permanently protecting host DNA from cleavage
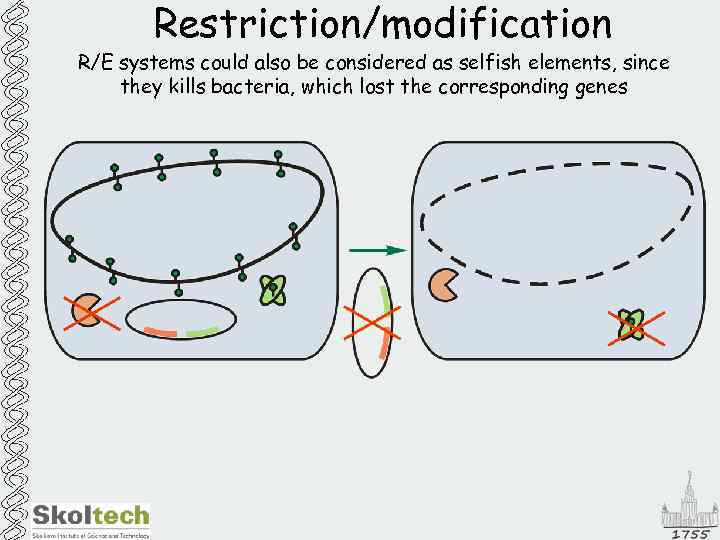 Restriction/modification R/E systems could also be considered as selfish elements, since they kills bacteria, which lost the corresponding genes
Restriction/modification R/E systems could also be considered as selfish elements, since they kills bacteria, which lost the corresponding genes
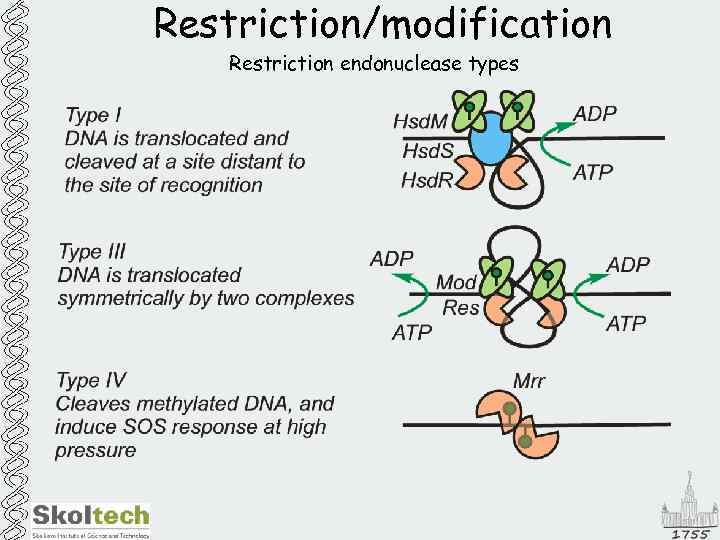 Restriction/modification Restriction endonuclease types
Restriction/modification Restriction endonuclease types
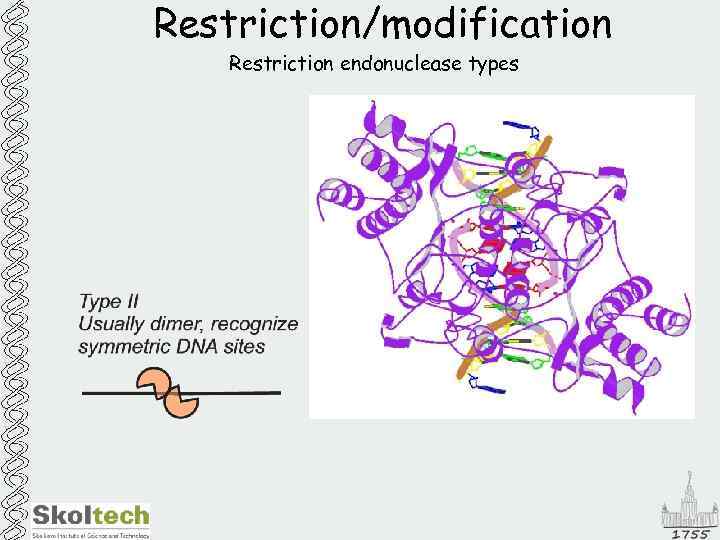 Restriction/modification Restriction endonuclease types
Restriction/modification Restriction endonuclease types
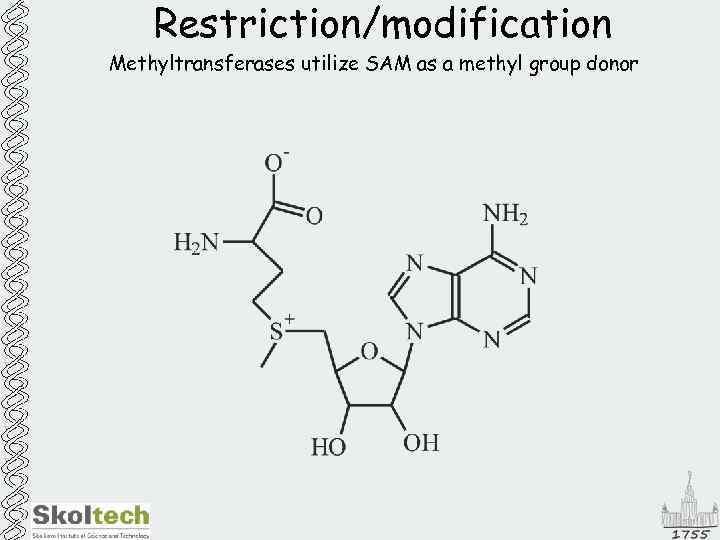 Restriction/modification Methyltransferases utilize SAM as a methyl group donor
Restriction/modification Methyltransferases utilize SAM as a methyl group donor
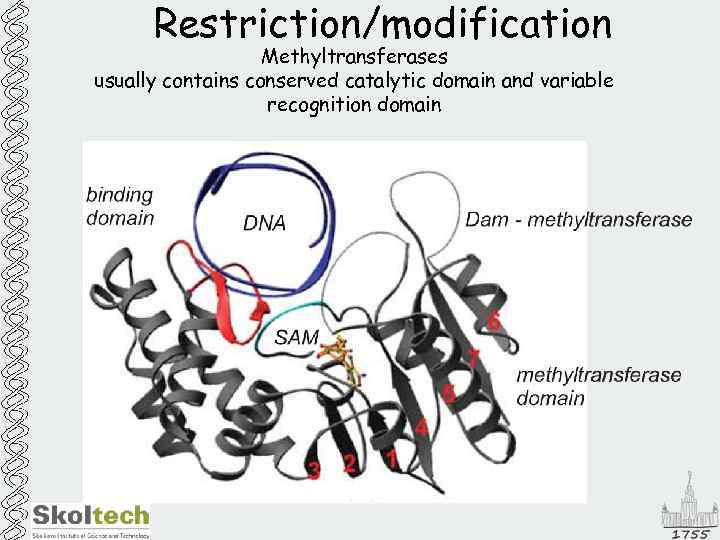 Restriction/modification Methyltransferases usually contains conserved catalytic domain and variable recognition domain
Restriction/modification Methyltransferases usually contains conserved catalytic domain and variable recognition domain
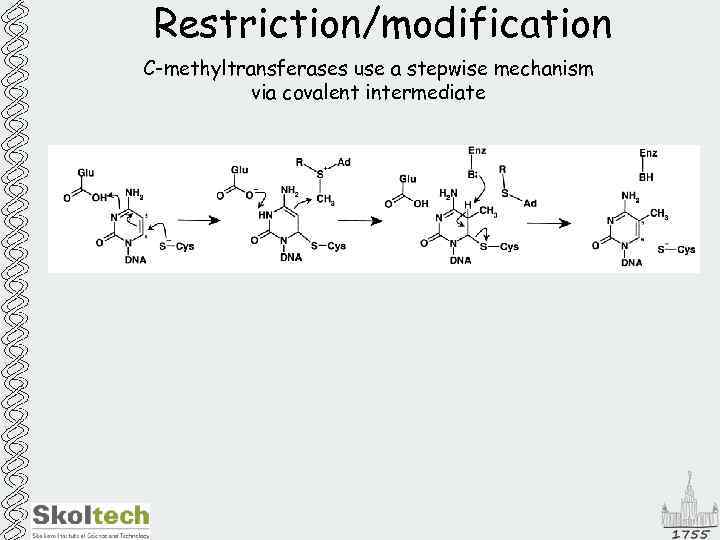 Restriction/modification C-methyltransferases use a stepwise mechanism via covalent intermediate
Restriction/modification C-methyltransferases use a stepwise mechanism via covalent intermediate
 Restriction/modification Regulation of R/E systems Aims of regulation 1. Methyltransferase should appear first to protect host DNA 2. Restriction nuclease expression should follow that of methyltransferase 3. In a steady state methyltransferase shouldn’t be in a too much excess (not to methylate phage DNA)
Restriction/modification Regulation of R/E systems Aims of regulation 1. Methyltransferase should appear first to protect host DNA 2. Restriction nuclease expression should follow that of methyltransferase 3. In a steady state methyltransferase shouldn’t be in a too much excess (not to methylate phage DNA)
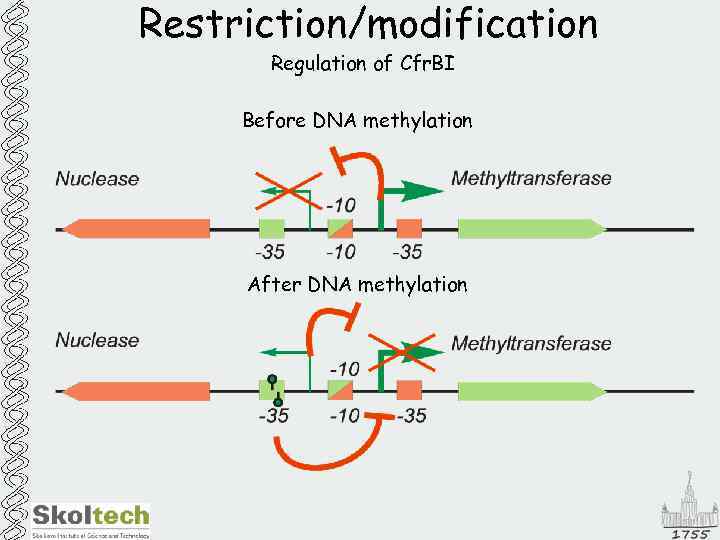 Restriction/modification Regulation of Cfr. BI Before DNA methylation After DNA methylation
Restriction/modification Regulation of Cfr. BI Before DNA methylation After DNA methylation
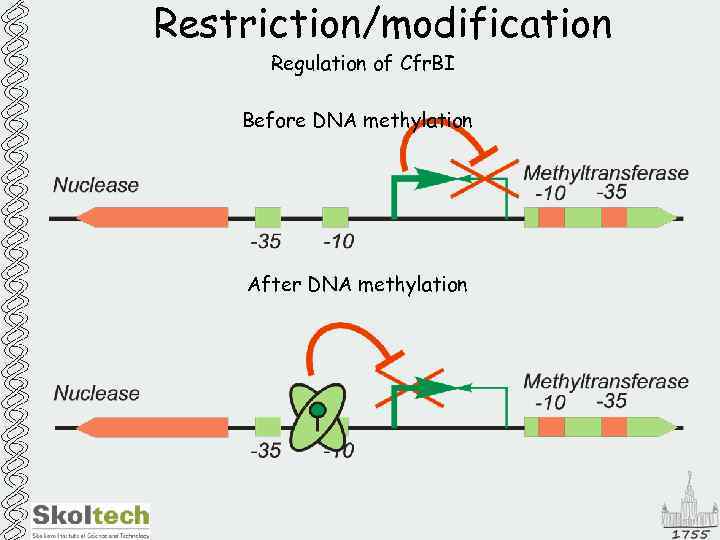 Restriction/modification Regulation of Cfr. BI Before DNA methylation After DNA methylation
Restriction/modification Regulation of Cfr. BI Before DNA methylation After DNA methylation
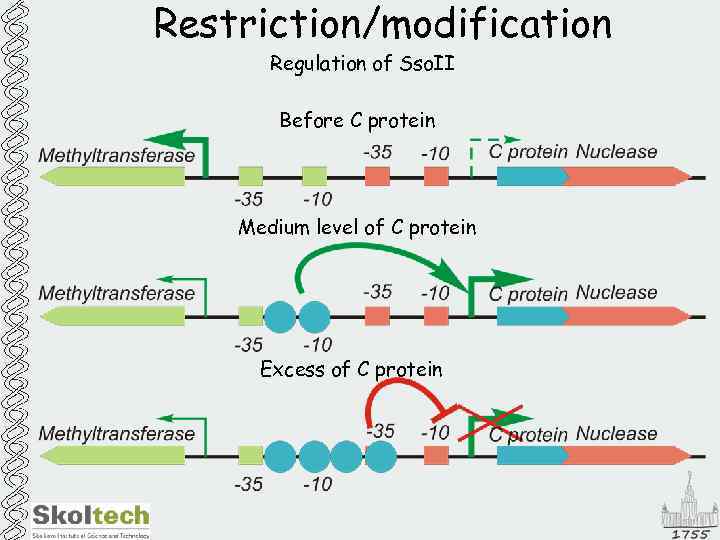 Restriction/modification Regulation of Sso. II Before C protein Medium level of C protein Excess of C protein
Restriction/modification Regulation of Sso. II Before C protein Medium level of C protein Excess of C protein
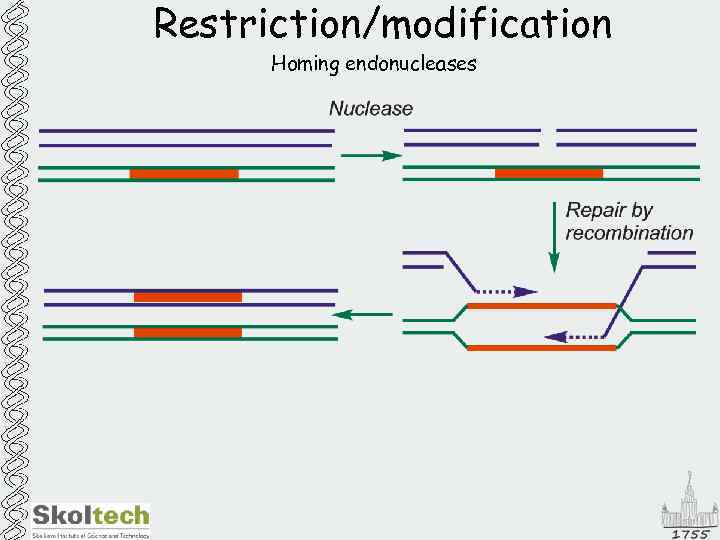 Restriction/modification Homing endonucleases
Restriction/modification Homing endonucleases
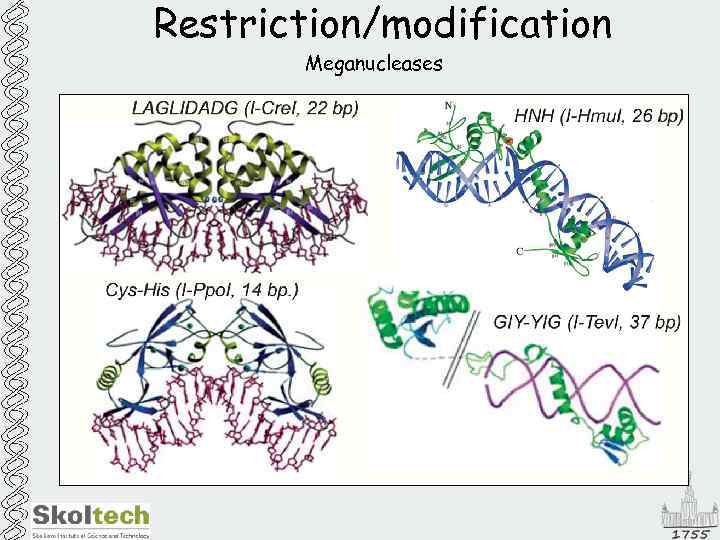 Restriction/modification Meganucleases
Restriction/modification Meganucleases
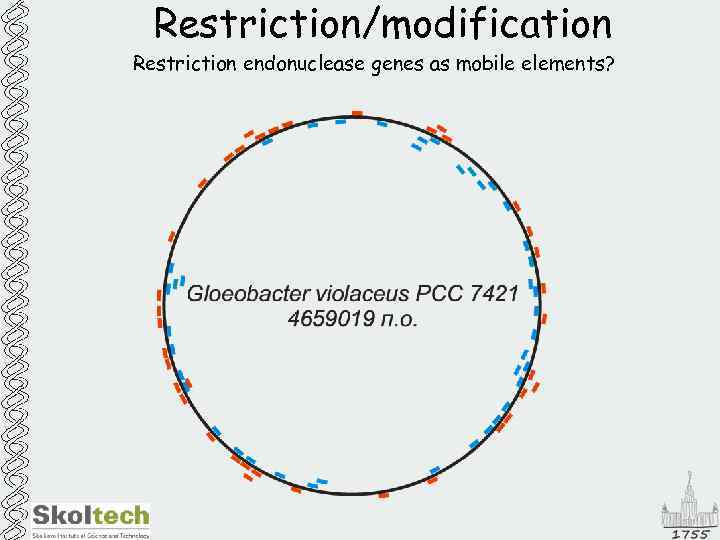 Restriction/modification Restriction endonuclease genes as mobile elements?
Restriction/modification Restriction endonuclease genes as mobile elements?
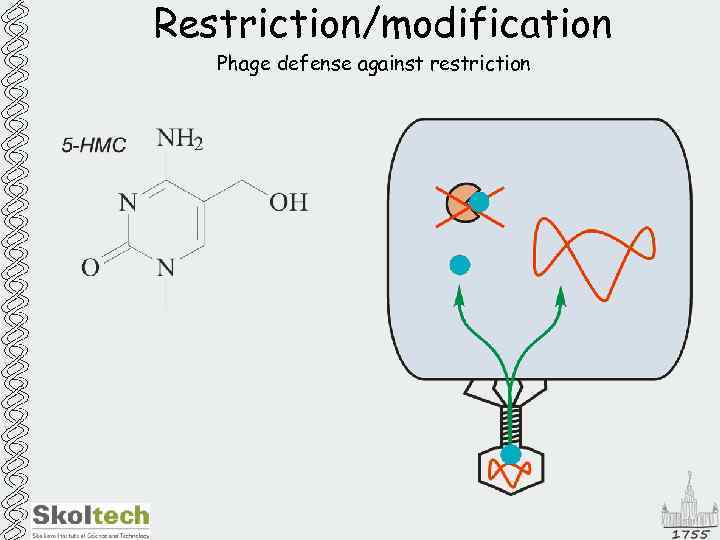 Restriction/modification Phage defense against restriction
Restriction/modification Phage defense against restriction
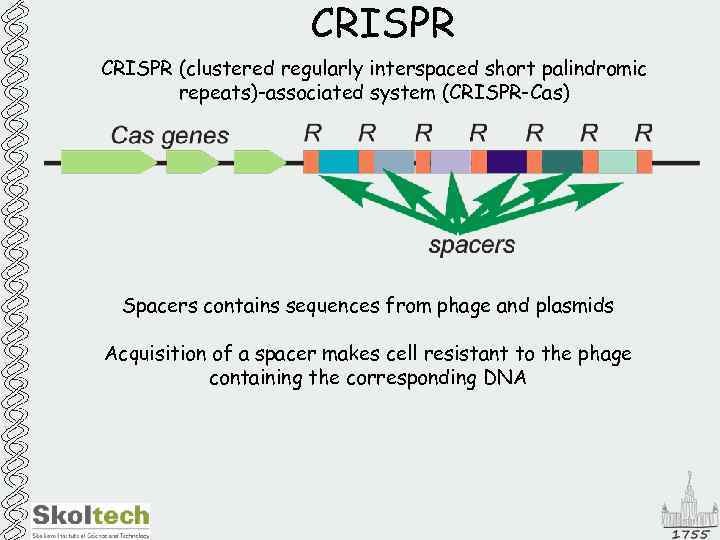 CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats)-associated system (CRISPR-Cas) Spacers contains sequences from phage and plasmids Acquisition of a spacer makes cell resistant to the phage containing the corresponding DNA
CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats)-associated system (CRISPR-Cas) Spacers contains sequences from phage and plasmids Acquisition of a spacer makes cell resistant to the phage containing the corresponding DNA
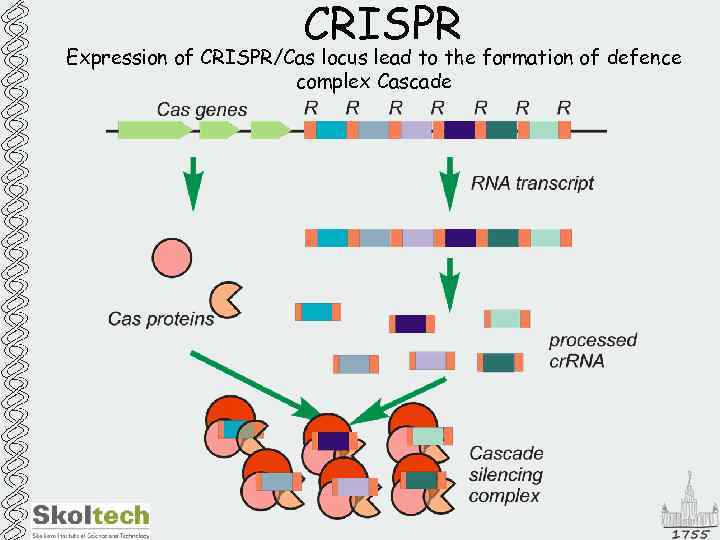 CRISPR Expression of CRISPR/Cas locus lead to the formation of defence complex Cascade
CRISPR Expression of CRISPR/Cas locus lead to the formation of defence complex Cascade
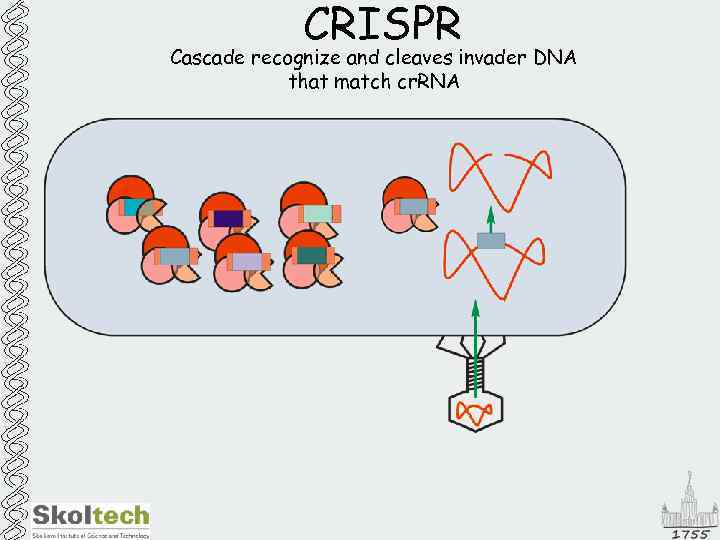 CRISPR Cascade recognize and cleaves invader DNA that match cr. RNA
CRISPR Cascade recognize and cleaves invader DNA that match cr. RNA
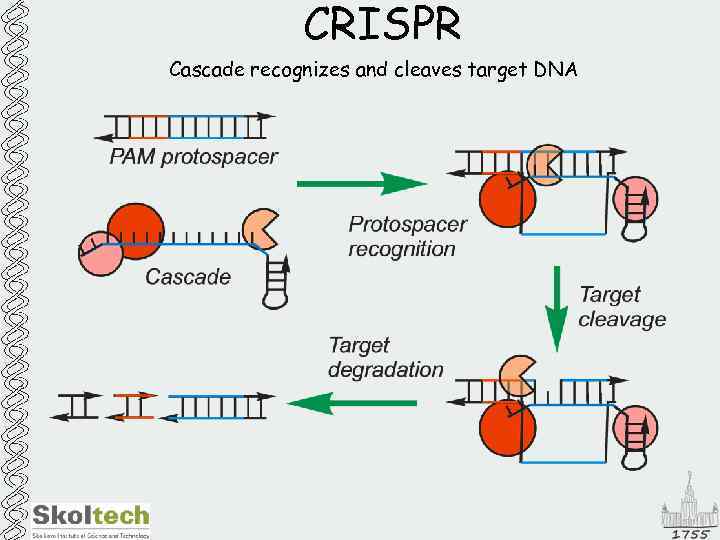 CRISPR Cascade recognizes and cleaves target DNA
CRISPR Cascade recognizes and cleaves target DNA