9. Replication eukaryotes.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 MSU & Skol. Tech Replication eukaryotes
MSU & Skol. Tech Replication eukaryotes
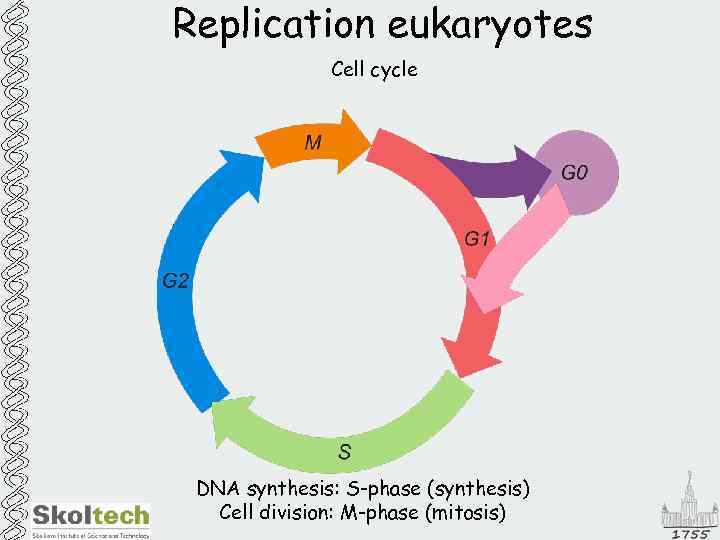 Replication eukaryotes Cell cycle DNA synthesis: S-phase (synthesis) Cell division: M-phase (mitosis)
Replication eukaryotes Cell cycle DNA synthesis: S-phase (synthesis) Cell division: M-phase (mitosis)
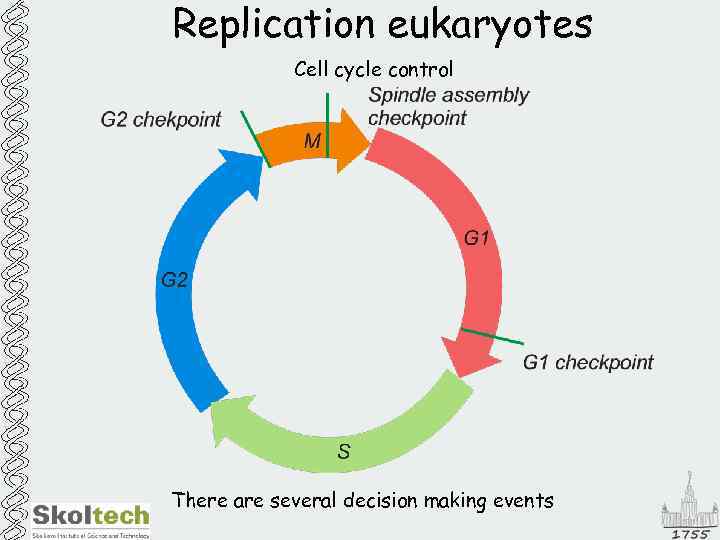 Replication eukaryotes Cell cycle control There are several decision making events
Replication eukaryotes Cell cycle control There are several decision making events
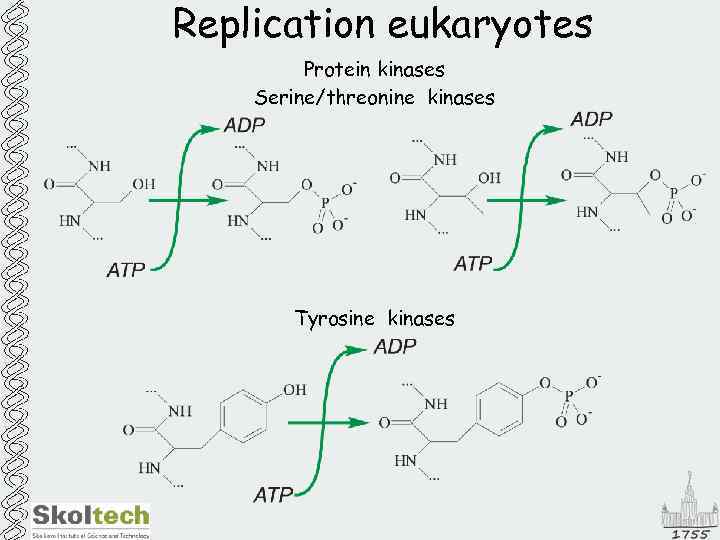 Replication eukaryotes Protein kinases Serine/threonine kinases Tyrosine kinases
Replication eukaryotes Protein kinases Serine/threonine kinases Tyrosine kinases
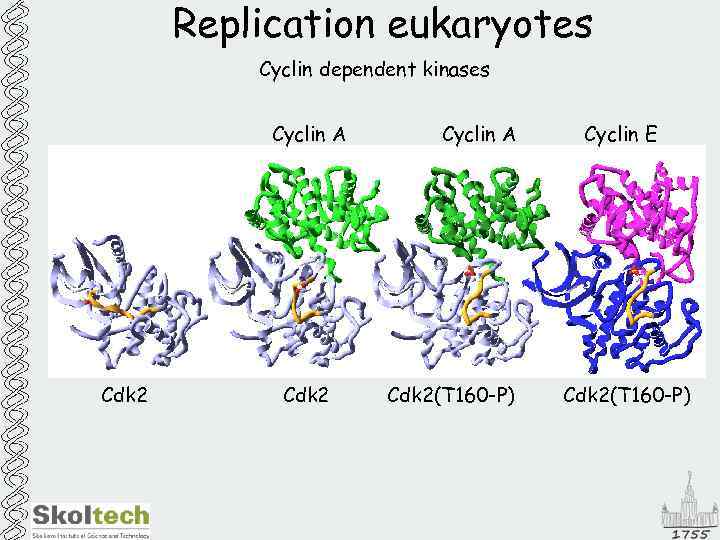 Replication eukaryotes Cyclin dependent kinases Cyclin A Cdk 2(T 160 -P) Cyclin E Cdk 2(T 160 -P)
Replication eukaryotes Cyclin dependent kinases Cyclin A Cdk 2(T 160 -P) Cyclin E Cdk 2(T 160 -P)
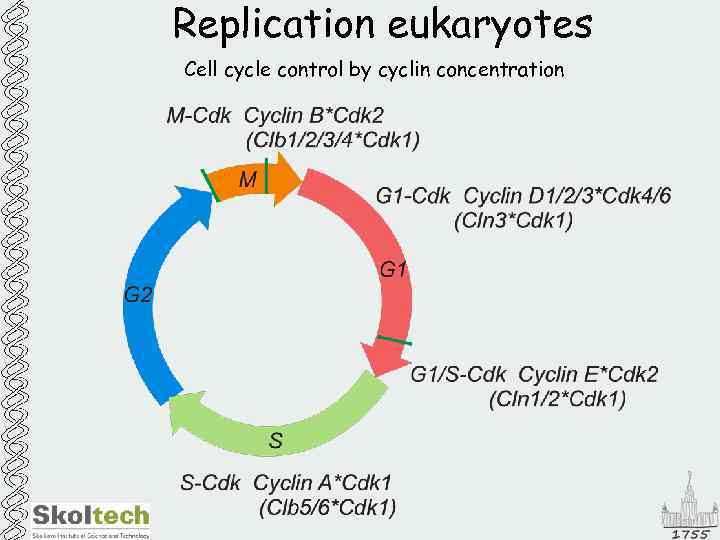 Replication eukaryotes Cell cycle control by cyclin concentration
Replication eukaryotes Cell cycle control by cyclin concentration
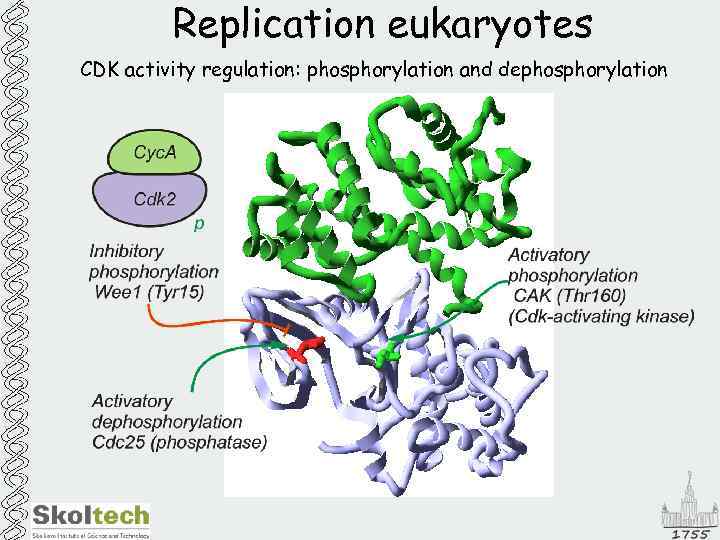 Replication eukaryotes CDK activity regulation: phosphorylation and dephosphorylation
Replication eukaryotes CDK activity regulation: phosphorylation and dephosphorylation
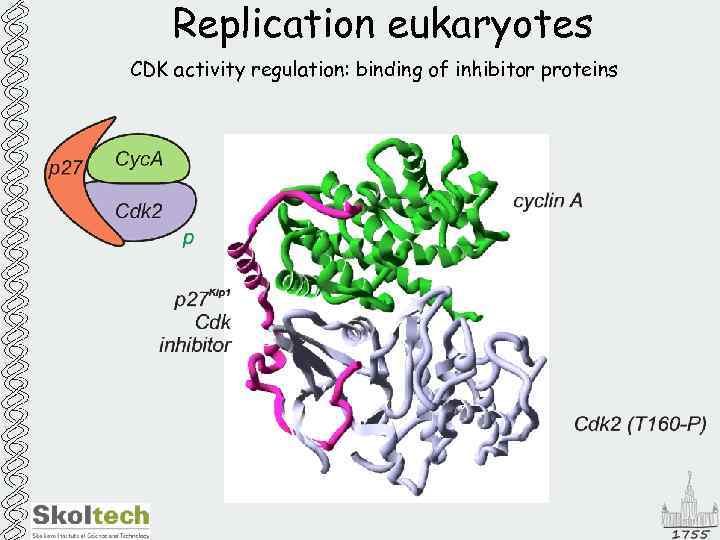 Replication eukaryotes CDK activity regulation: binding of inhibitor proteins
Replication eukaryotes CDK activity regulation: binding of inhibitor proteins
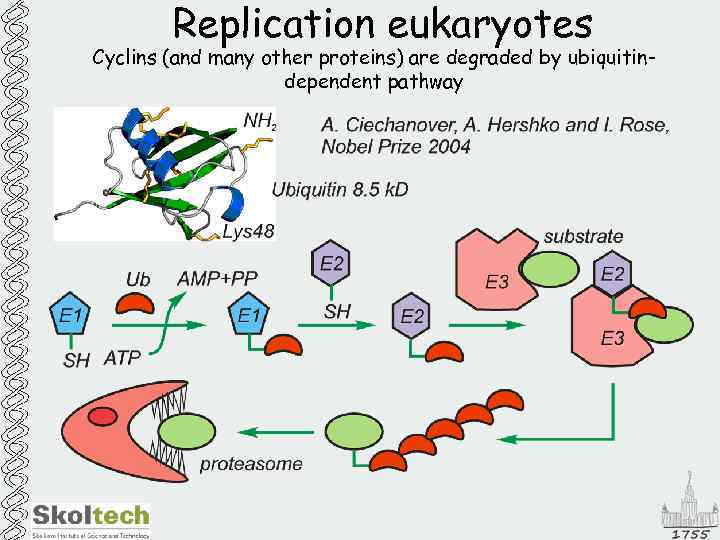 Replication eukaryotes Cyclins (and many other proteins) are degraded by ubiquitindependent pathway
Replication eukaryotes Cyclins (and many other proteins) are degraded by ubiquitindependent pathway
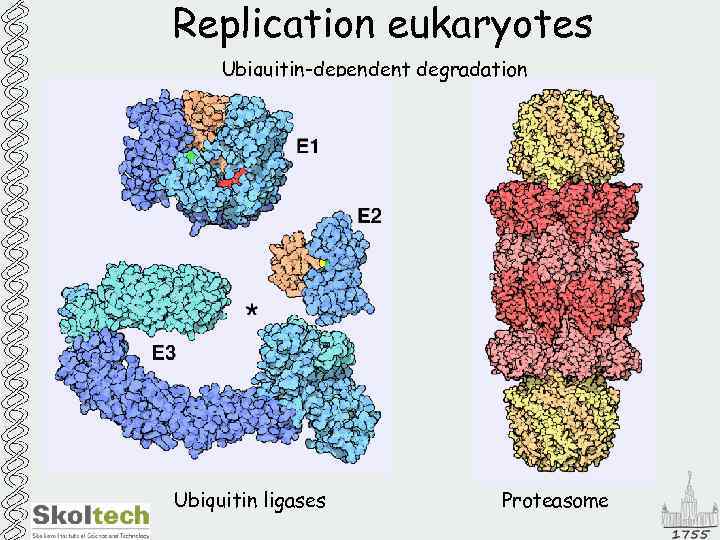 Replication eukaryotes Ubiquitin-dependent degradation Ubiquitin ligases Proteasome
Replication eukaryotes Ubiquitin-dependent degradation Ubiquitin ligases Proteasome
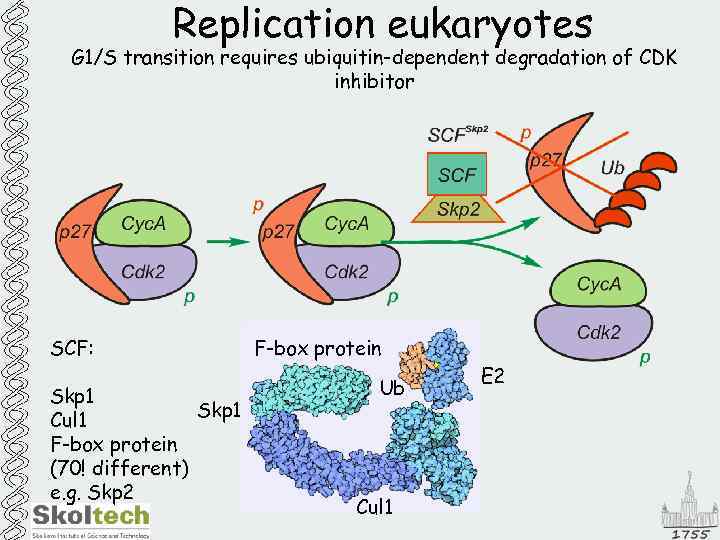 Replication eukaryotes G 1/S transition requires ubiquitin-dependent degradation of CDK inhibitor SCF: Skp 1 Cul 1 F-box protein (70! different) e. g. Skp 2 F-box protein Ub Cul 1 E 2
Replication eukaryotes G 1/S transition requires ubiquitin-dependent degradation of CDK inhibitor SCF: Skp 1 Cul 1 F-box protein (70! different) e. g. Skp 2 F-box protein Ub Cul 1 E 2
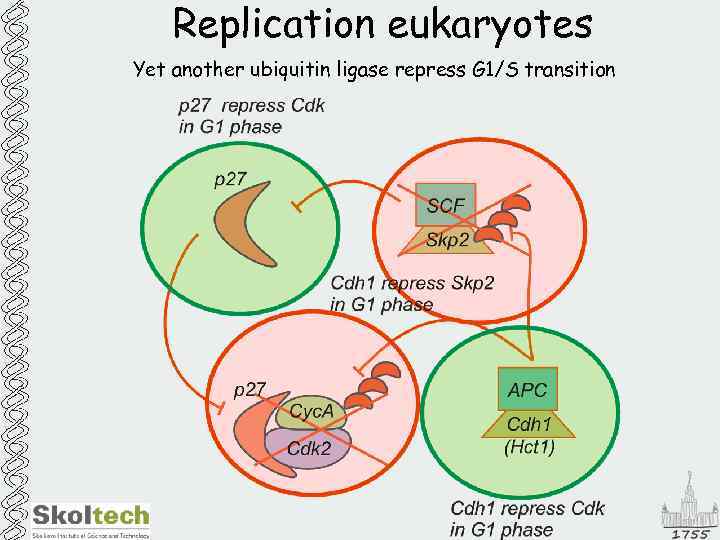 Replication eukaryotes Yet another ubiquitin ligase repress G 1/S transition
Replication eukaryotes Yet another ubiquitin ligase repress G 1/S transition
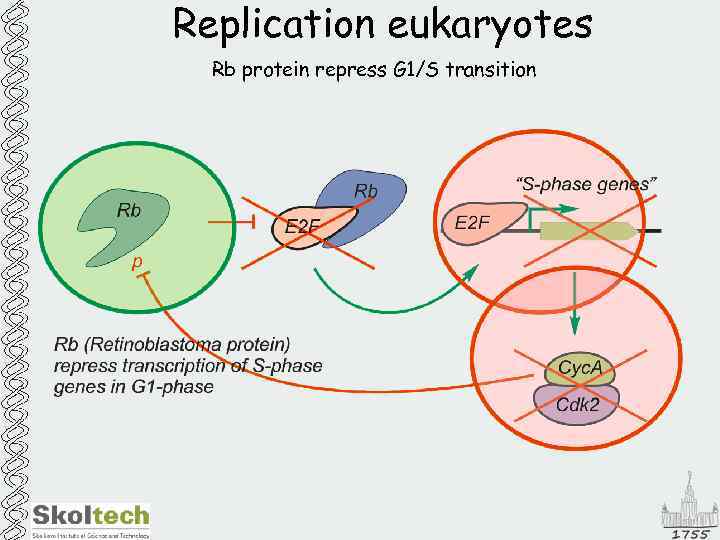 Replication eukaryotes Rb protein repress G 1/S transition
Replication eukaryotes Rb protein repress G 1/S transition
 Replication eukaryotes G 1/S checkpoint
Replication eukaryotes G 1/S checkpoint
 Replication eukaryotes Decision to enter S-phase Yeast cells: Cell size Nutrient availability Mammalian cells: Activation signals (growth factors) Inhibitory signals Adhesion to a proper surface Contact inhibition DNA damage
Replication eukaryotes Decision to enter S-phase Yeast cells: Cell size Nutrient availability Mammalian cells: Activation signals (growth factors) Inhibitory signals Adhesion to a proper surface Contact inhibition DNA damage
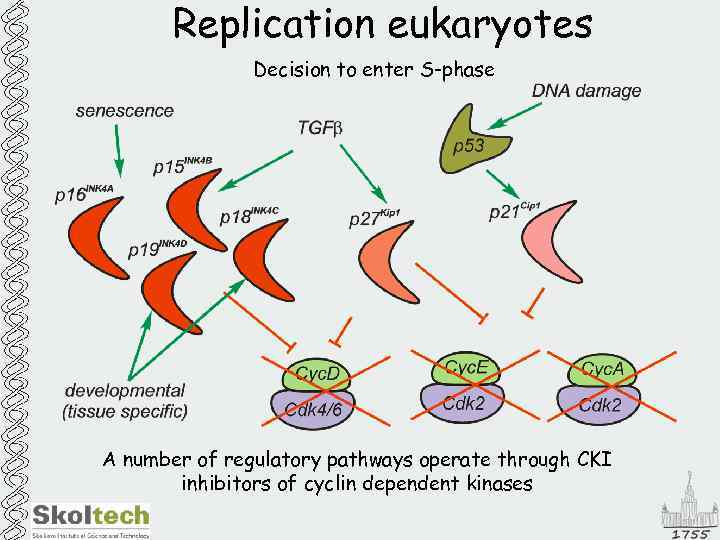 Replication eukaryotes Decision to enter S-phase A number of regulatory pathways operate through CKI inhibitors of cyclin dependent kinases
Replication eukaryotes Decision to enter S-phase A number of regulatory pathways operate through CKI inhibitors of cyclin dependent kinases
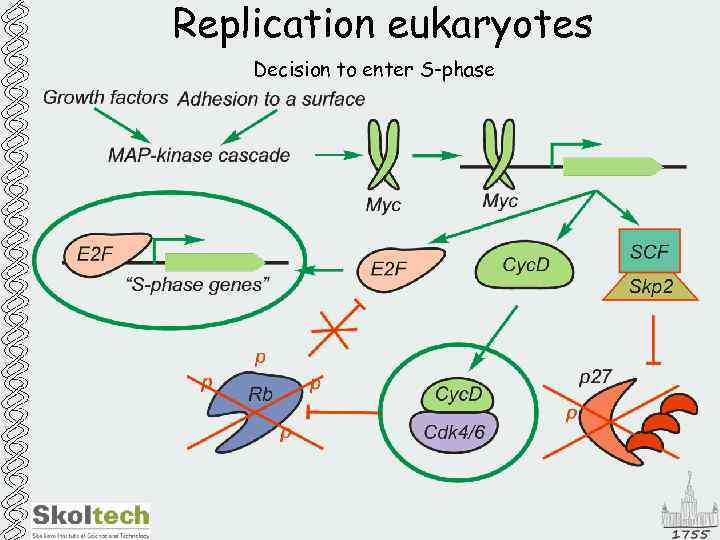 Replication eukaryotes Decision to enter S-phase
Replication eukaryotes Decision to enter S-phase
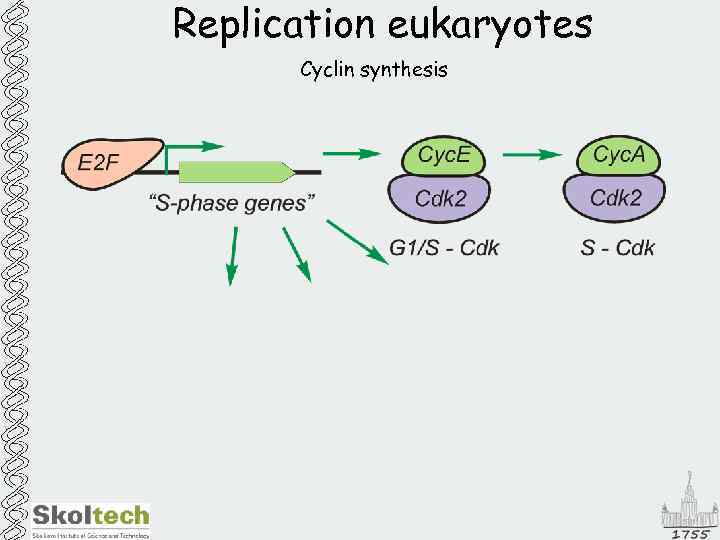 Replication eukaryotes Cyclin synthesis
Replication eukaryotes Cyclin synthesis
 Replication eukaryotes Initiation of replication Organism Genome Number of origins E. coli 4. 6 Mb 1 Yeast 12 Mb 350 Human 3 000 Mb 10 000 -1 000 ? Origins should fire once in an S-phase
Replication eukaryotes Initiation of replication Organism Genome Number of origins E. coli 4. 6 Mb 1 Yeast 12 Mb 350 Human 3 000 Mb 10 000 -1 000 ? Origins should fire once in an S-phase
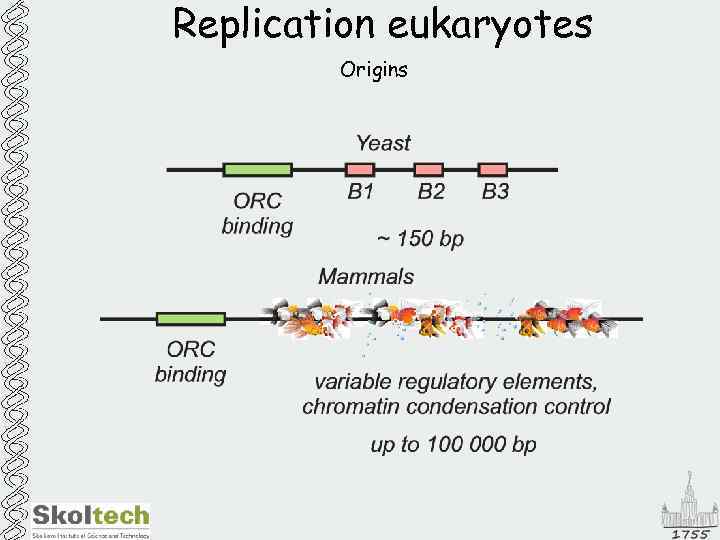 Replication eukaryotes Origins
Replication eukaryotes Origins
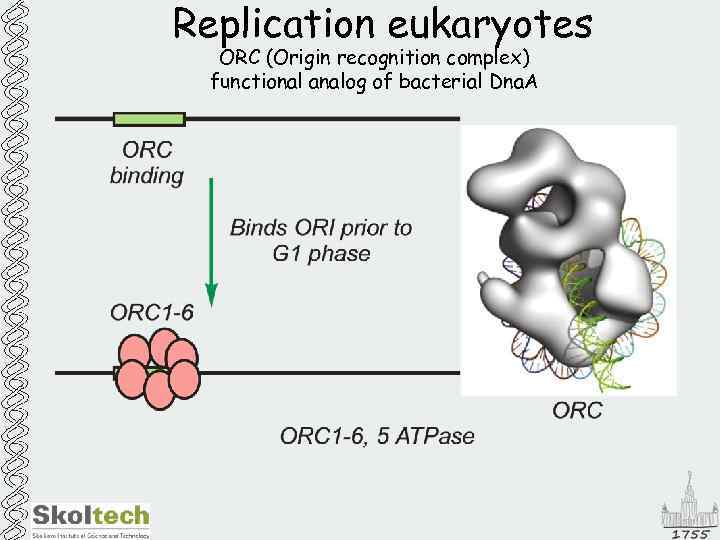 Replication eukaryotes ORC (Origin recognition complex) functional analog of bacterial Dna. A
Replication eukaryotes ORC (Origin recognition complex) functional analog of bacterial Dna. A
 Replication eukaryotes ORC (Origin recognition complex) functional analog of bacterial Dna. A
Replication eukaryotes ORC (Origin recognition complex) functional analog of bacterial Dna. A
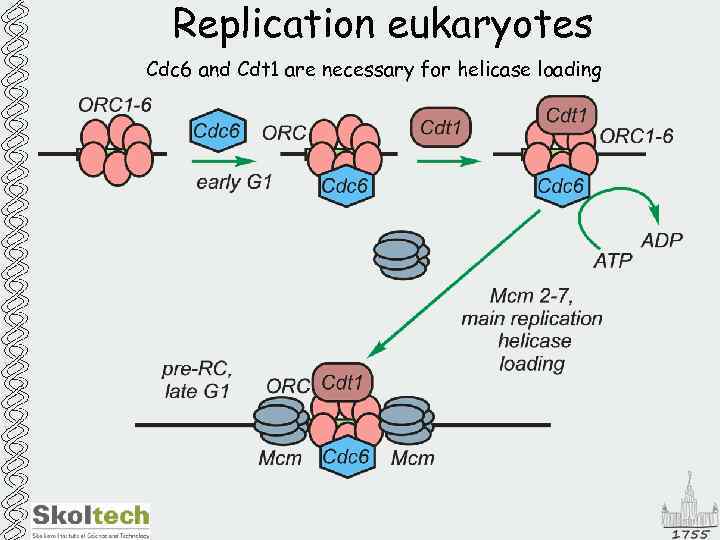 Replication eukaryotes Cdc 6 and Cdt 1 are necessary for helicase loading
Replication eukaryotes Cdc 6 and Cdt 1 are necessary for helicase loading
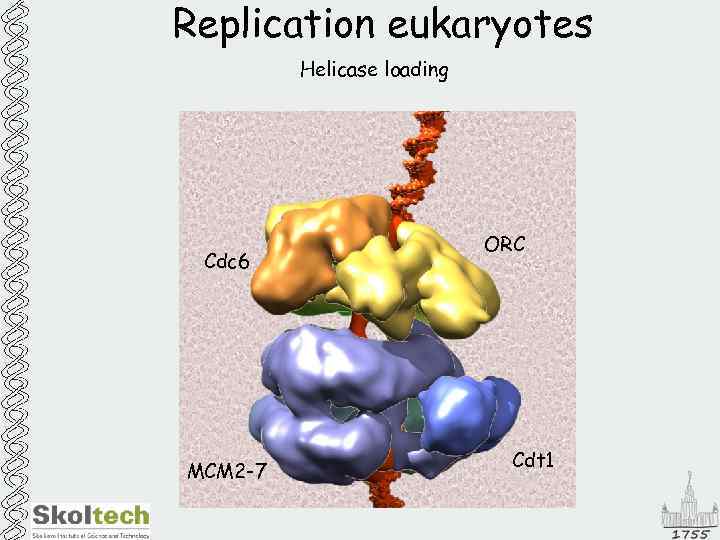 Replication eukaryotes Helicase loading Cdc 6 MCM 2 -7 ORC Cdt 1
Replication eukaryotes Helicase loading Cdc 6 MCM 2 -7 ORC Cdt 1
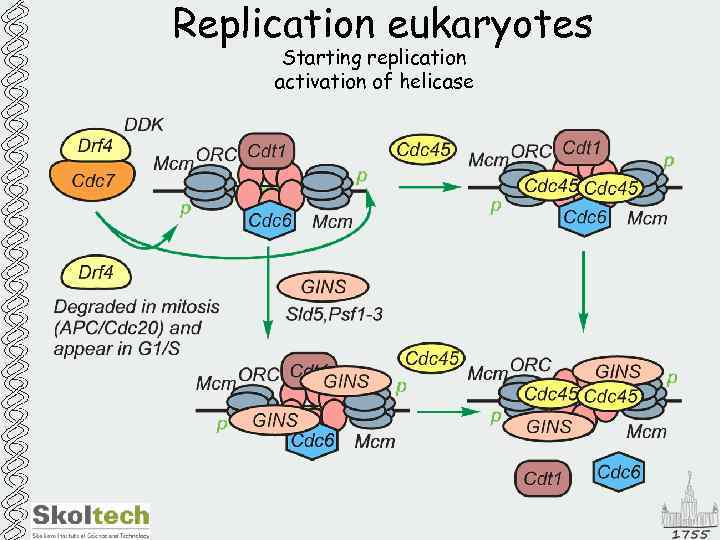 Replication eukaryotes Starting replication activation of helicase
Replication eukaryotes Starting replication activation of helicase
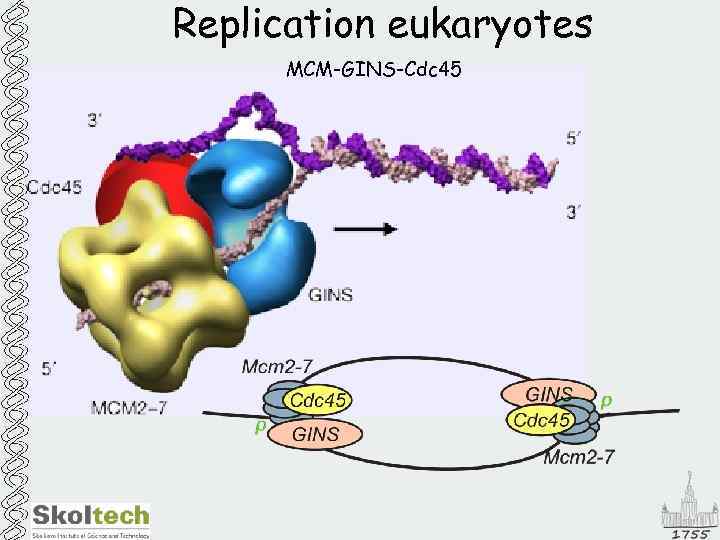 Replication eukaryotes MCM-GINS-Cdc 45
Replication eukaryotes MCM-GINS-Cdc 45
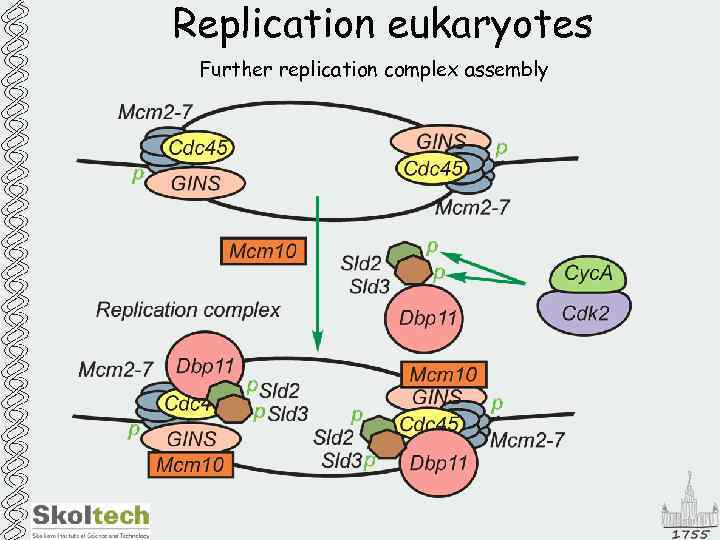 Replication eukaryotes Further replication complex assembly
Replication eukaryotes Further replication complex assembly
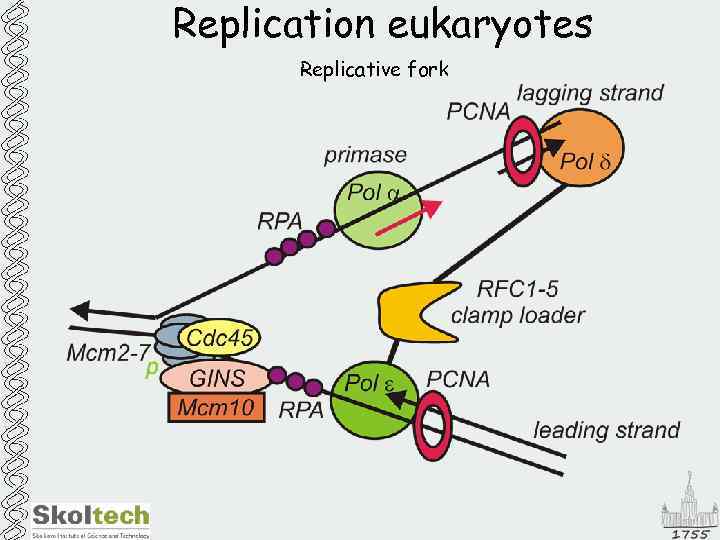 Replication eukaryotes Replicative fork
Replication eukaryotes Replicative fork
 Replication eukaryotes DNA polymerases adegbzhi k - Replicative Primase subunit Replicative lagging strand Replicative leading strand Mitochondrial Reparative High fidelity, low processivity, BER Low fidelity, TT dimer reading Low fidelity, meiotic Low fidelity
Replication eukaryotes DNA polymerases adegbzhi k - Replicative Primase subunit Replicative lagging strand Replicative leading strand Mitochondrial Reparative High fidelity, low processivity, BER Low fidelity, TT dimer reading Low fidelity, meiotic Low fidelity
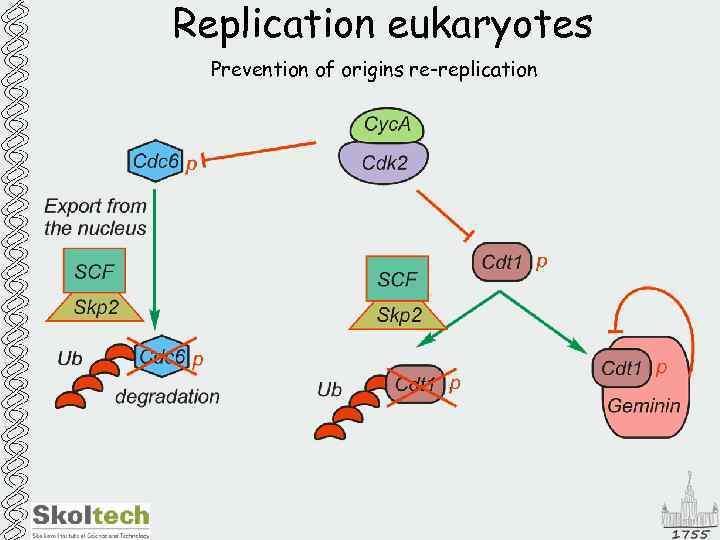 Replication eukaryotes Prevention of origins re-replication
Replication eukaryotes Prevention of origins re-replication
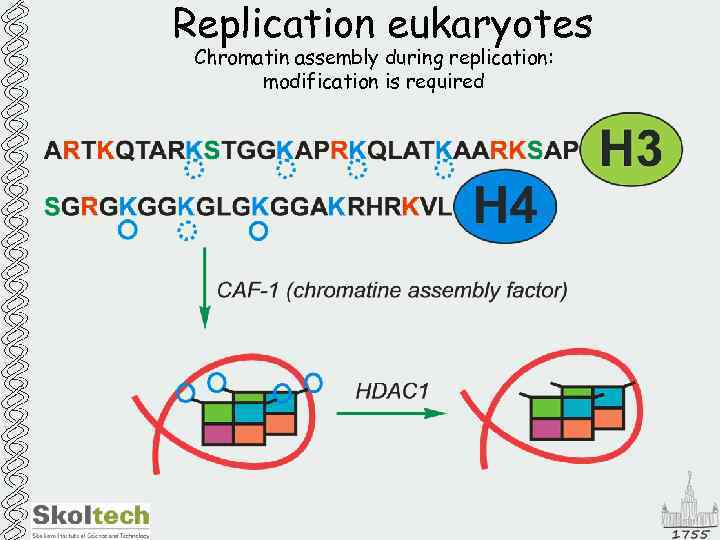 Replication eukaryotes Chromatin assembly during replication: modification is required
Replication eukaryotes Chromatin assembly during replication: modification is required
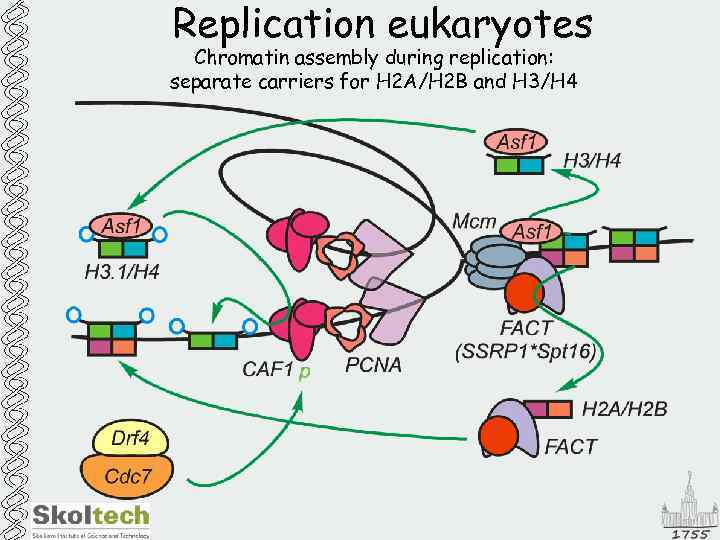 Replication eukaryotes Chromatin assembly during replication: separate carriers for H 2 A/H 2 B and H 3/H 4
Replication eukaryotes Chromatin assembly during replication: separate carriers for H 2 A/H 2 B and H 3/H 4


