 MSU & Skol. Tech Mitosis
MSU & Skol. Tech Mitosis
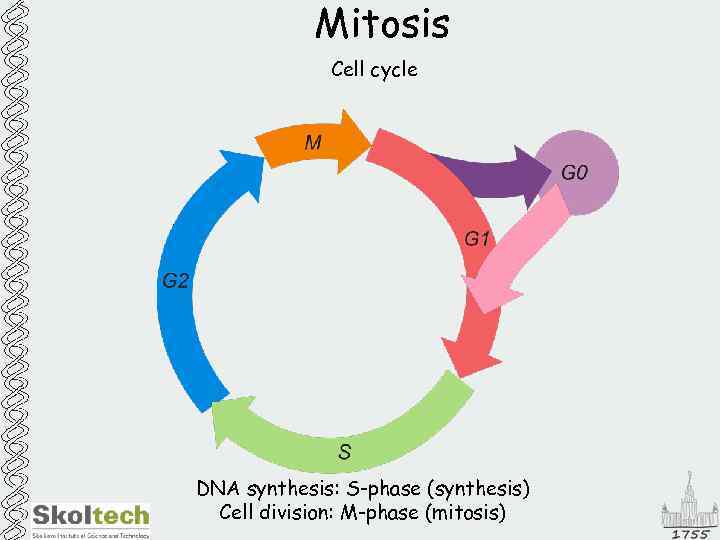 Mitosis Cell cycle DNA synthesis: S-phase (synthesis) Cell division: M-phase (mitosis)
Mitosis Cell cycle DNA synthesis: S-phase (synthesis) Cell division: M-phase (mitosis)
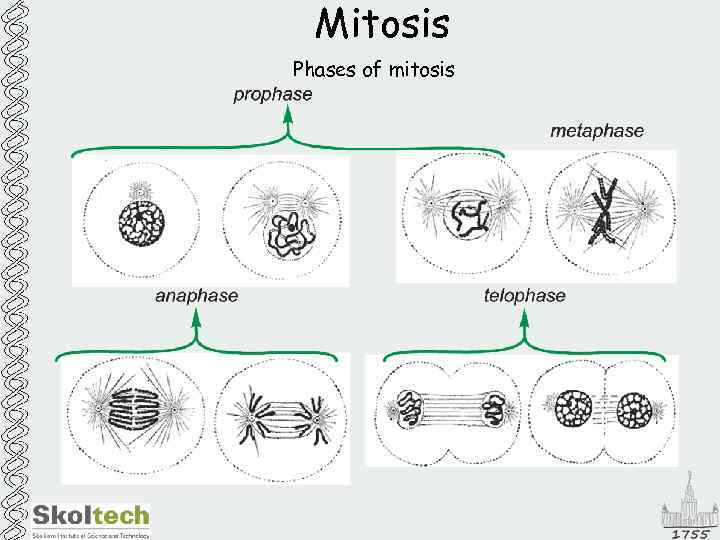 Mitosis Phases of mitosis
Mitosis Phases of mitosis
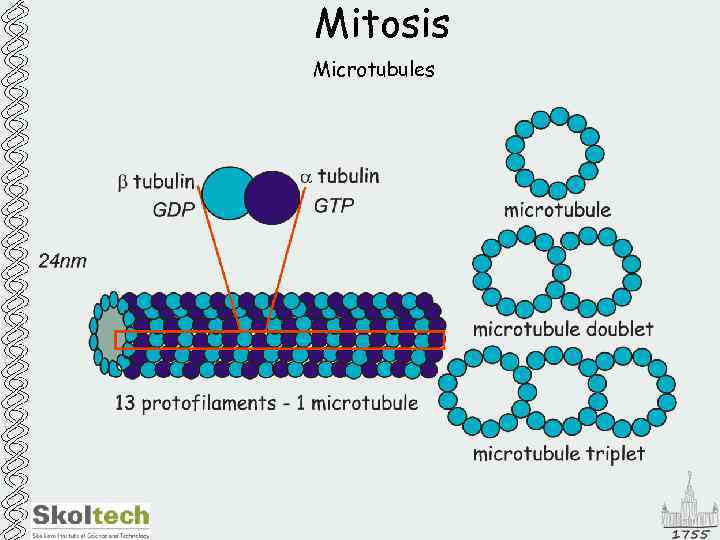 Mitosis Microtubules
Mitosis Microtubules
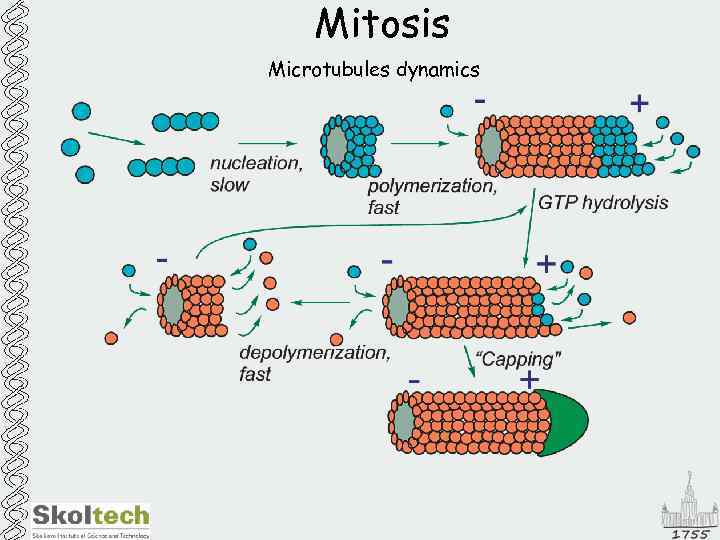 Mitosis Microtubules dynamics
Mitosis Microtubules dynamics
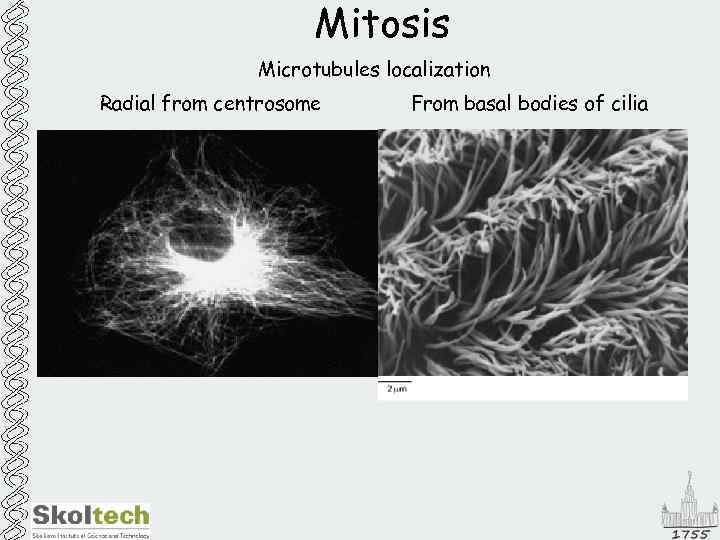 Mitosis Microtubules localization Radial from centrosome From basal bodies of cilia
Mitosis Microtubules localization Radial from centrosome From basal bodies of cilia
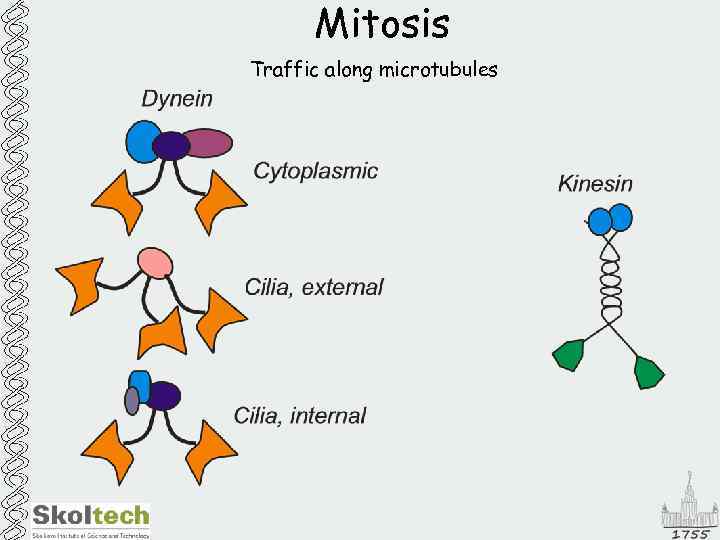 Mitosis Traffic along microtubules
Mitosis Traffic along microtubules
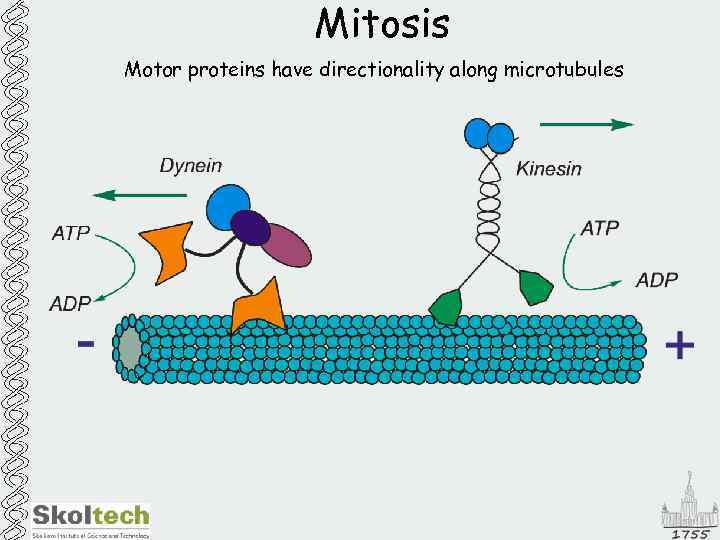 Mitosis Motor proteins have directionality along microtubules
Mitosis Motor proteins have directionality along microtubules
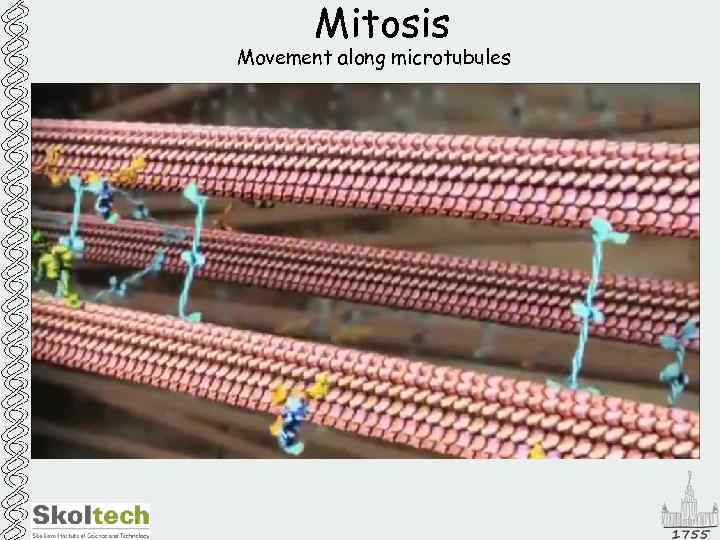 Mitosis Movement along microtubules
Mitosis Movement along microtubules
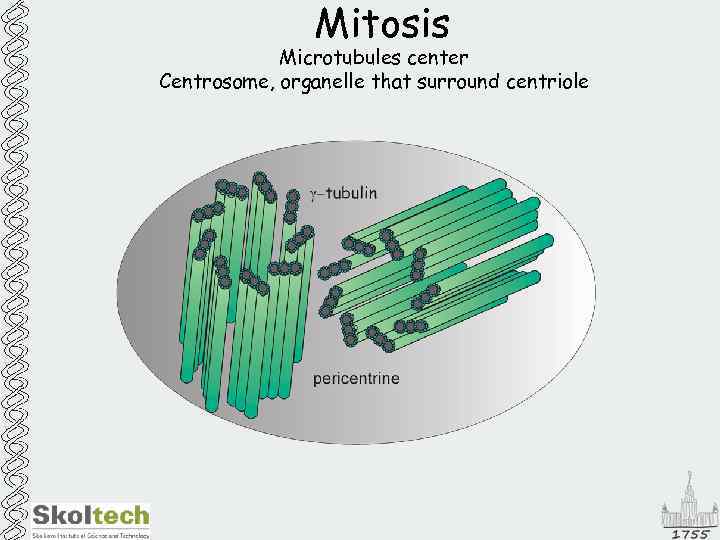 Mitosis Microtubules center Centrosome, organelle that surround centriole
Mitosis Microtubules center Centrosome, organelle that surround centriole
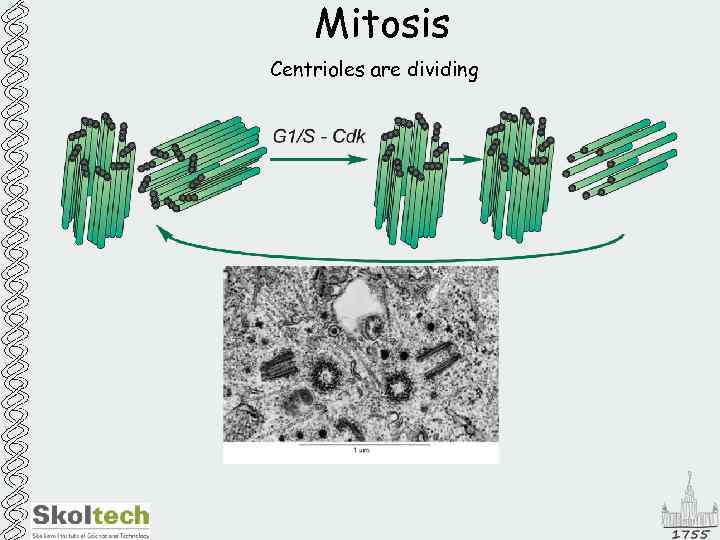 Mitosis Centrioles are dividing
Mitosis Centrioles are dividing
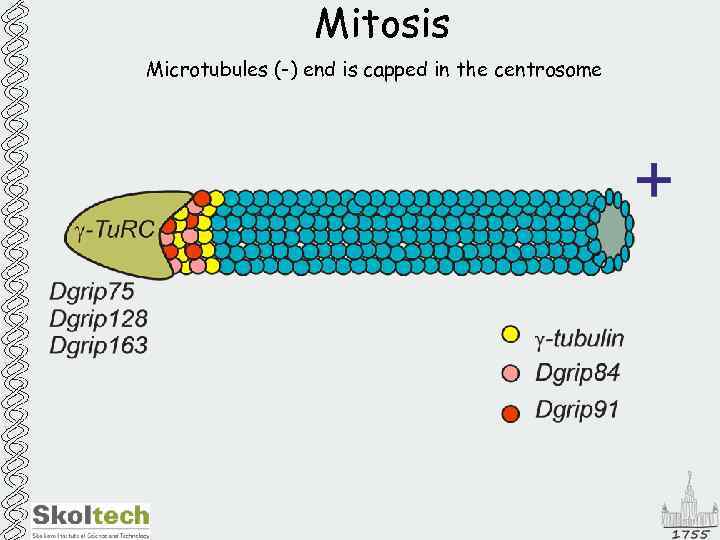 Mitosis Microtubules (-) end is capped in the centrosome
Mitosis Microtubules (-) end is capped in the centrosome
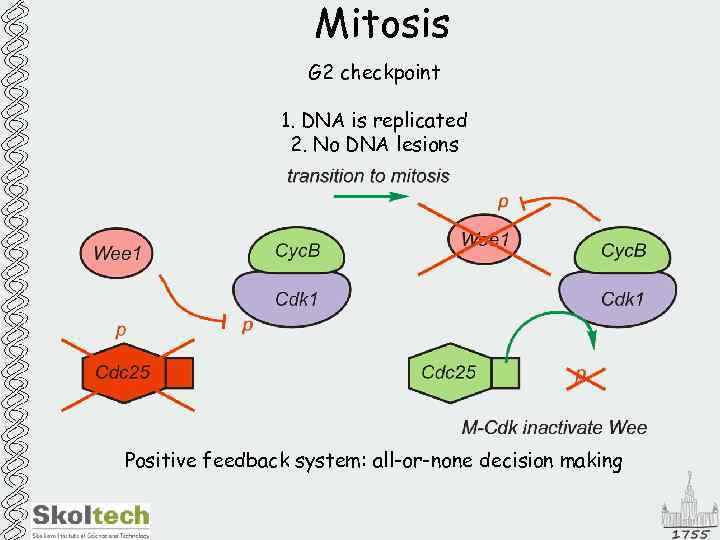 Mitosis G 2 checkpoint 1. DNA is replicated 2. No DNA lesions Positive feedback system: all-or-none decision making
Mitosis G 2 checkpoint 1. DNA is replicated 2. No DNA lesions Positive feedback system: all-or-none decision making
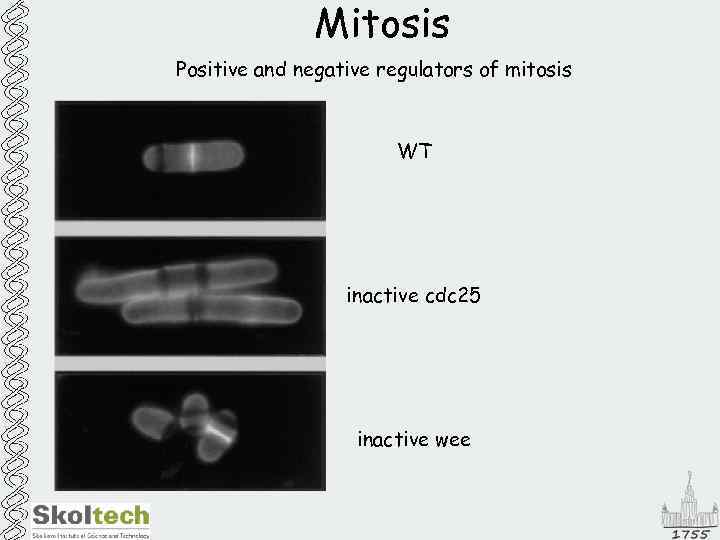 Mitosis Positive and negative regulators of mitosis WT inactive cdc 25 inactive wee
Mitosis Positive and negative regulators of mitosis WT inactive cdc 25 inactive wee
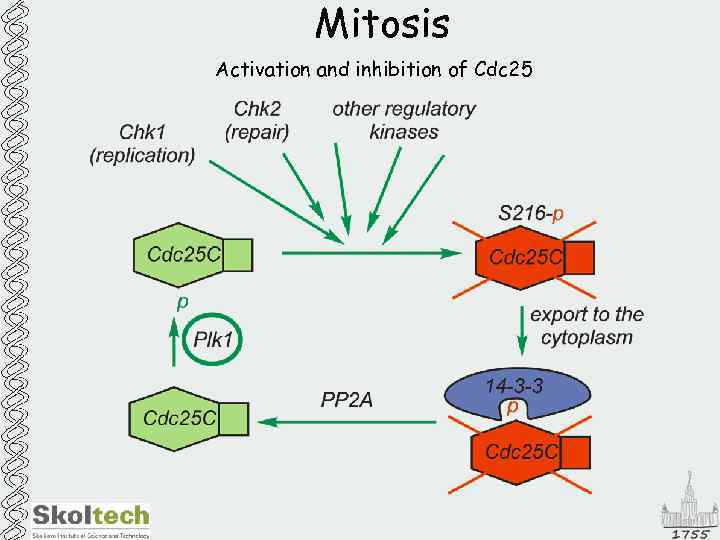 Mitosis Activation and inhibition of Cdc 25
Mitosis Activation and inhibition of Cdc 25
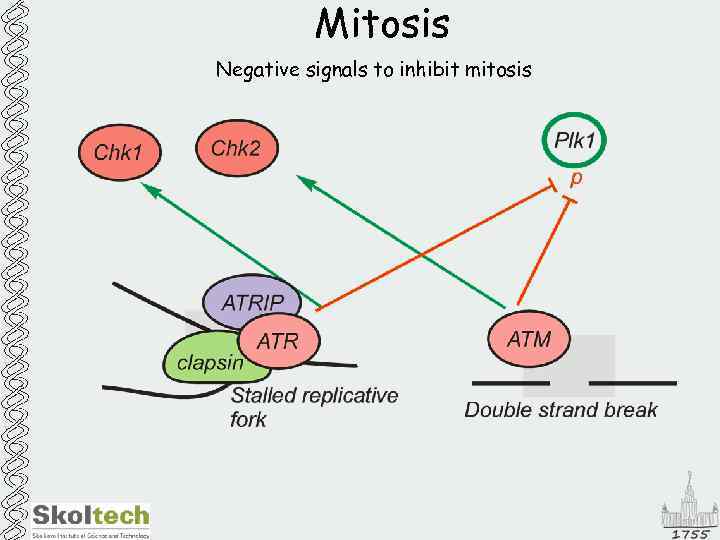 Mitosis Negative signals to inhibit mitosis
Mitosis Negative signals to inhibit mitosis
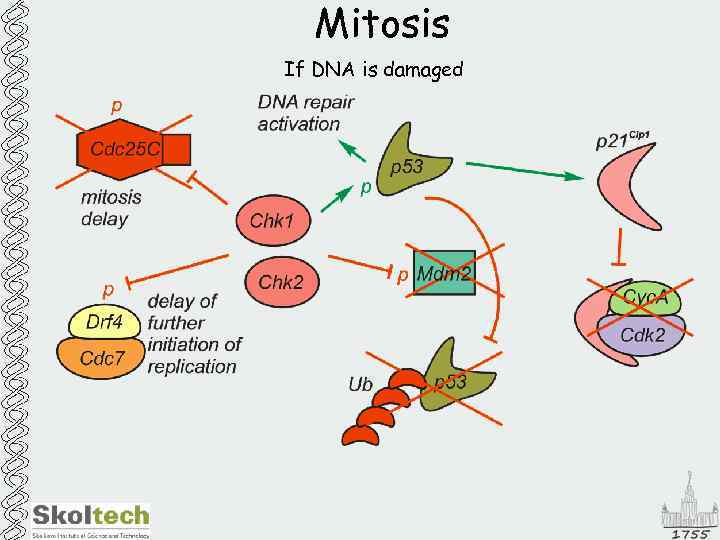 Mitosis If DNA is damaged
Mitosis If DNA is damaged
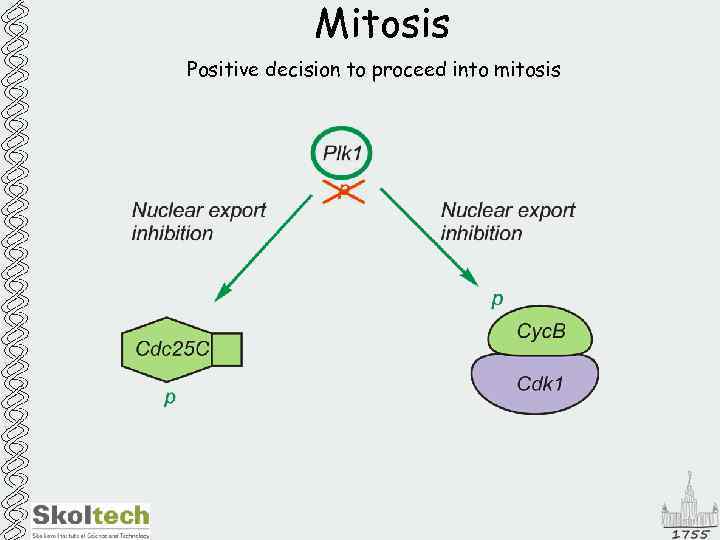 Mitosis Positive decision to proceed into mitosis
Mitosis Positive decision to proceed into mitosis
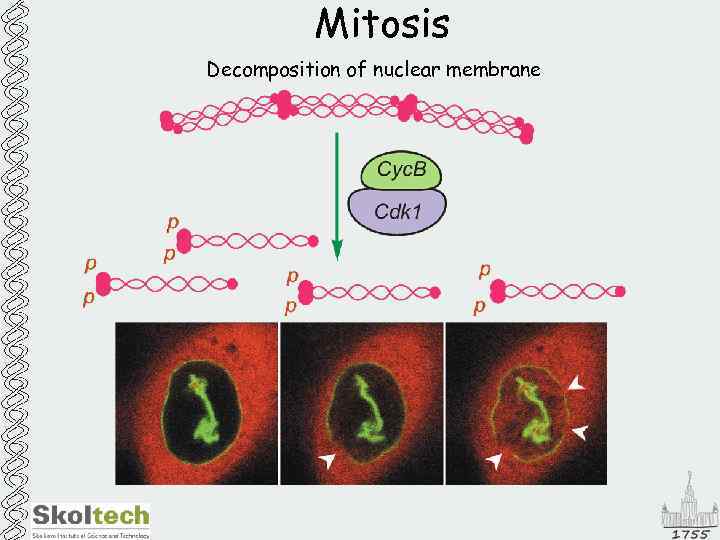 Mitosis Decomposition of nuclear membrane
Mitosis Decomposition of nuclear membrane
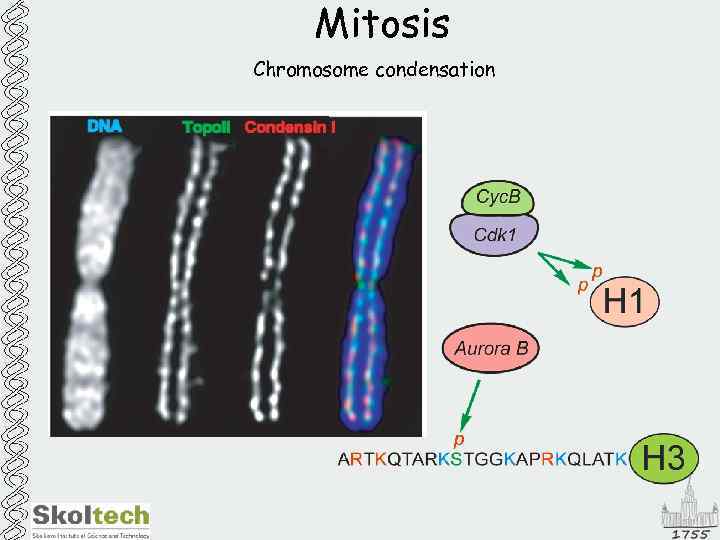 Mitosis Chromosome condensation
Mitosis Chromosome condensation
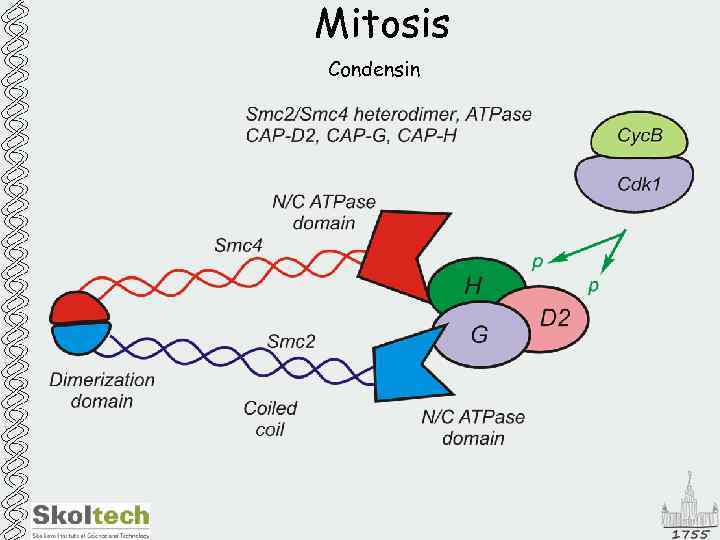 Mitosis Condensin
Mitosis Condensin
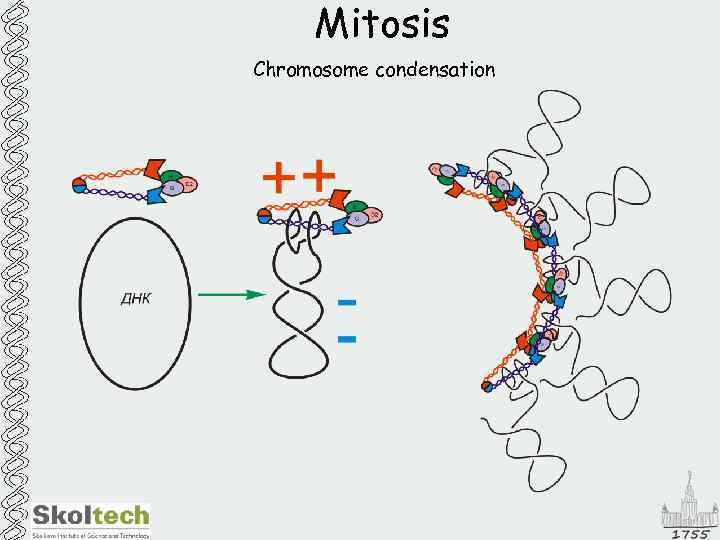 Mitosis Chromosome condensation
Mitosis Chromosome condensation
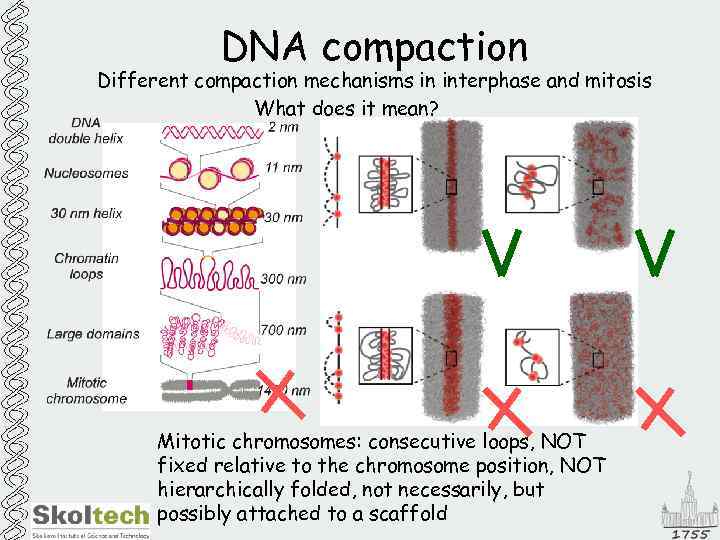 DNA compaction Different compaction mechanisms in interphase and mitosis What does it mean? Mitotic chromosomes: consecutive loops, NOT fixed relative to the chromosome position, NOT hierarchically folded, not necessarily, but possibly attached to a scaffold
DNA compaction Different compaction mechanisms in interphase and mitosis What does it mean? Mitotic chromosomes: consecutive loops, NOT fixed relative to the chromosome position, NOT hierarchically folded, not necessarily, but possibly attached to a scaffold
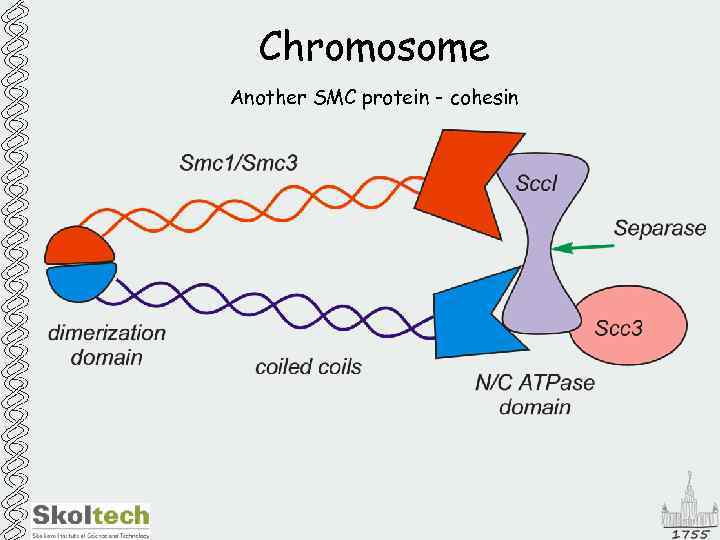 Chromosome Another SMC protein - cohesin
Chromosome Another SMC protein - cohesin
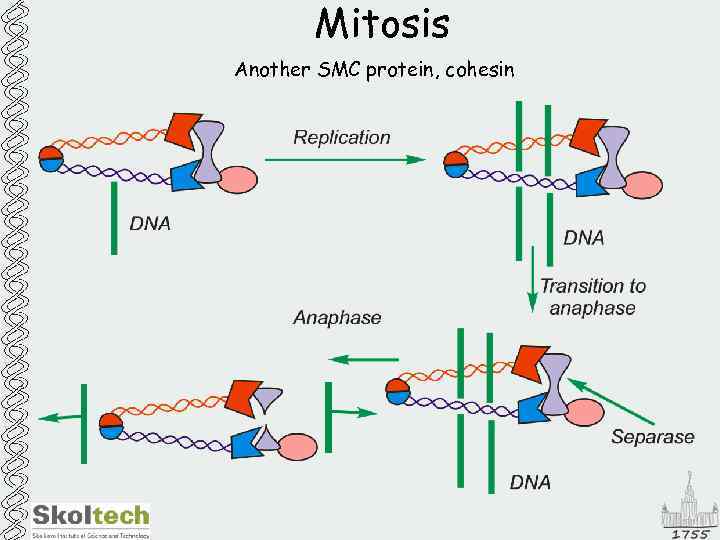 Mitosis Another SMC protein, cohesin
Mitosis Another SMC protein, cohesin
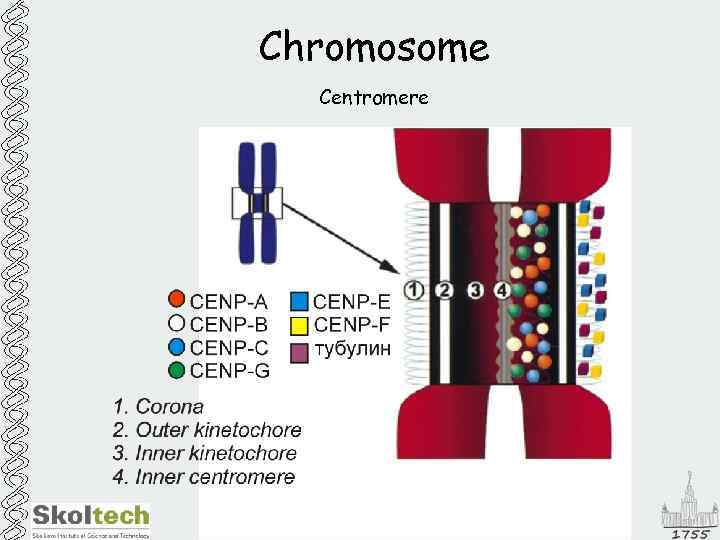 Chromosome Centromere
Chromosome Centromere
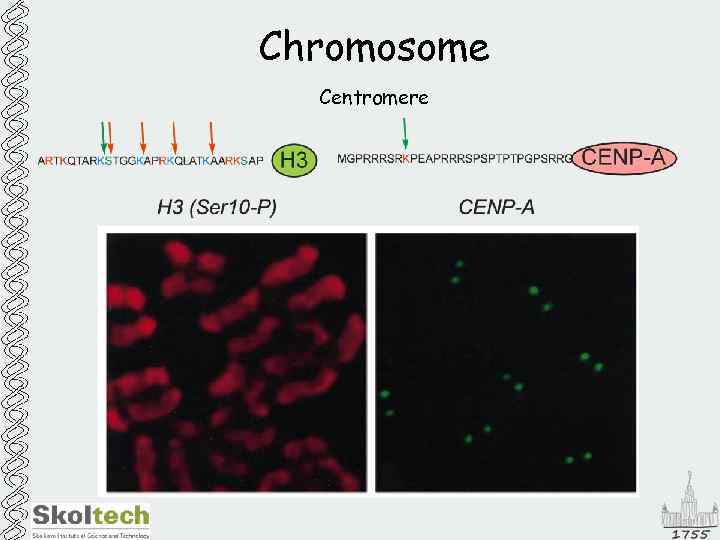 Chromosome Centromere
Chromosome Centromere
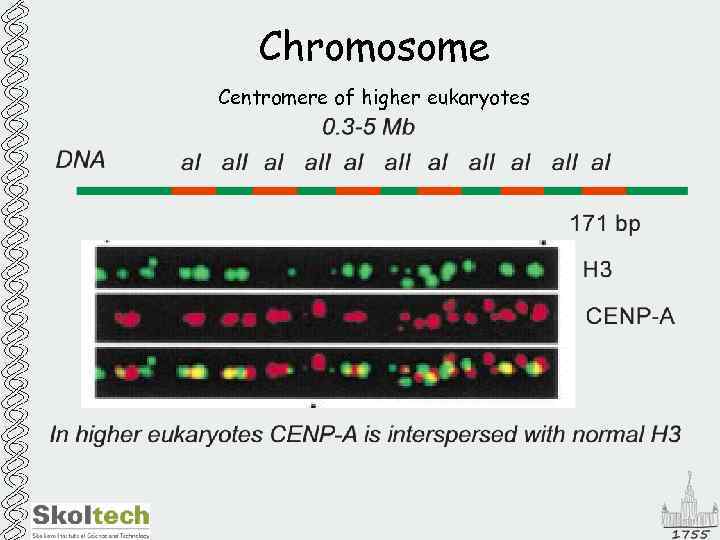 Chromosome Centromere of higher eukaryotes
Chromosome Centromere of higher eukaryotes
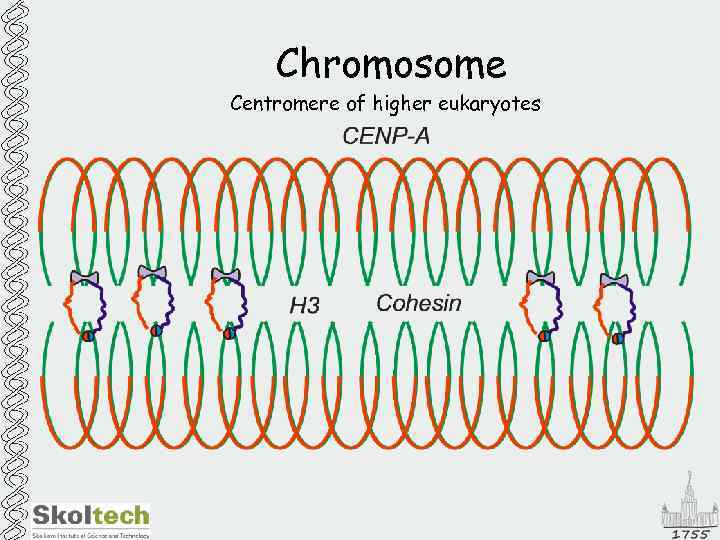 Chromosome Centromere of higher eukaryotes
Chromosome Centromere of higher eukaryotes
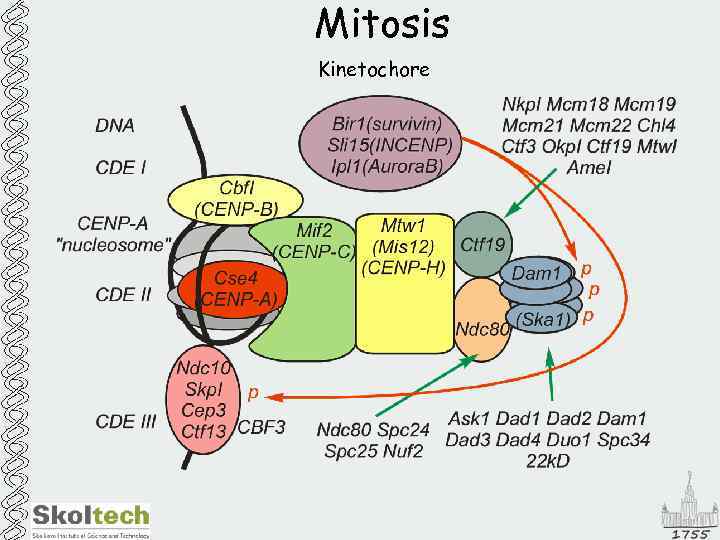 Mitosis Kinetochore
Mitosis Kinetochore
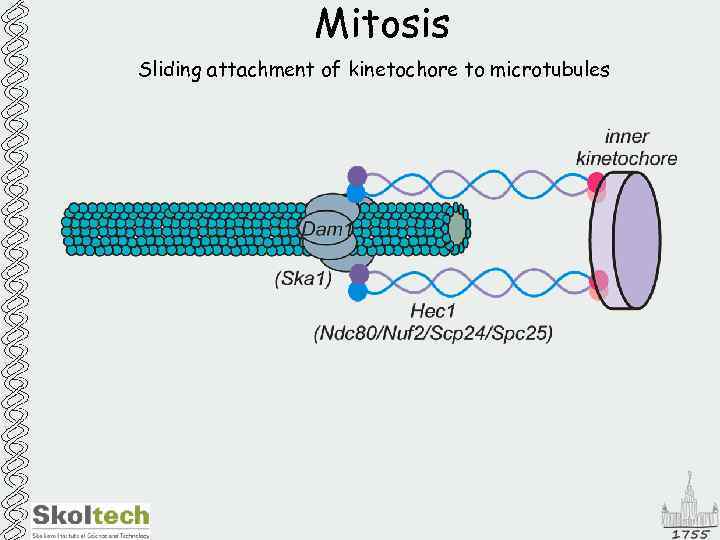 Mitosis Sliding attachment of kinetochore to microtubules
Mitosis Sliding attachment of kinetochore to microtubules
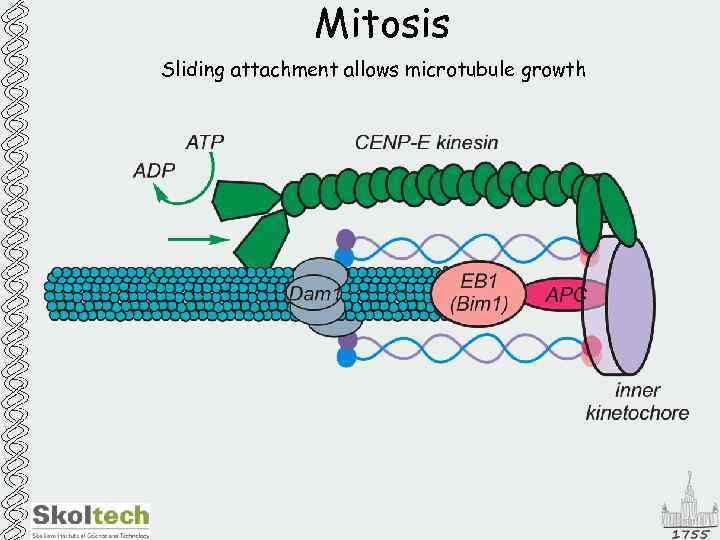 Mitosis Sliding attachment allows microtubule growth
Mitosis Sliding attachment allows microtubule growth
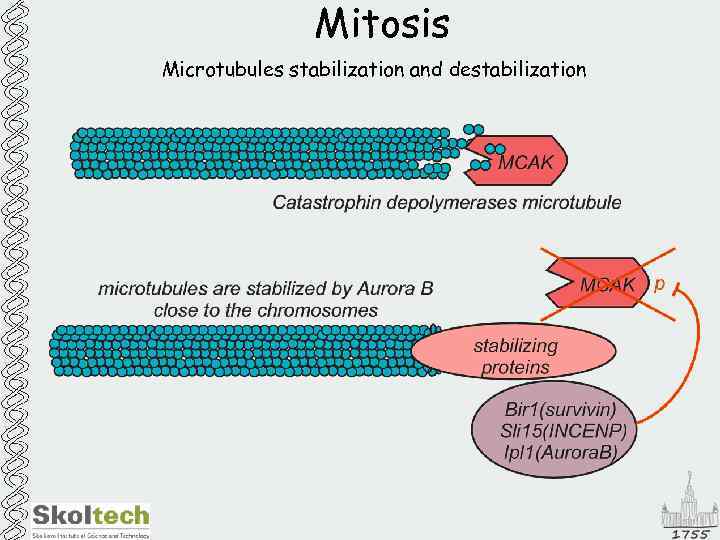 Mitosis Microtubules stabilization and destabilization
Mitosis Microtubules stabilization and destabilization
 Mitosis Cell cycle
Mitosis Cell cycle
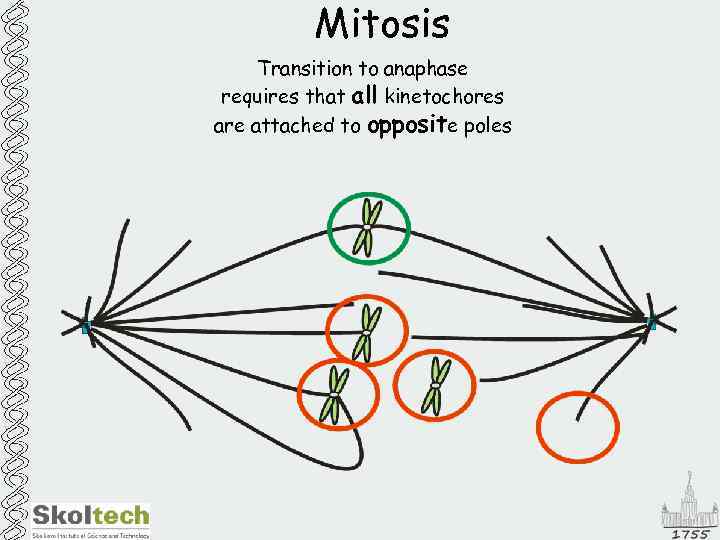 Mitosis Transition to anaphase requires that all kinetochores are attached to opposite poles
Mitosis Transition to anaphase requires that all kinetochores are attached to opposite poles
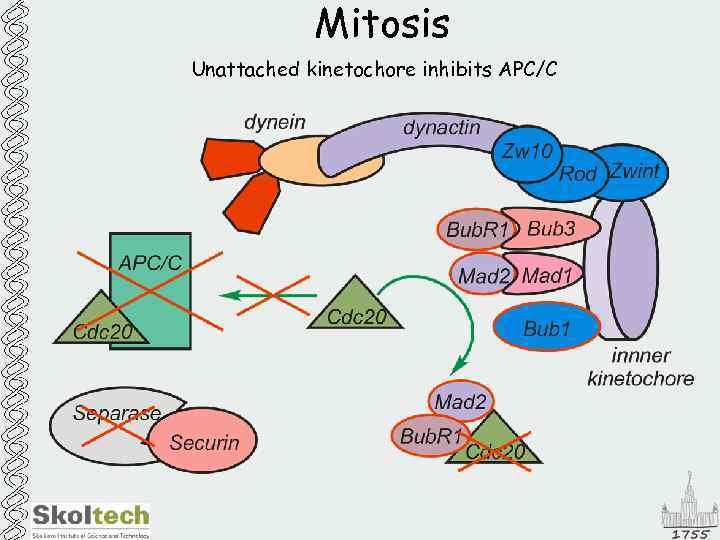 Mitosis Unattached kinetochore inhibits APC/C
Mitosis Unattached kinetochore inhibits APC/C
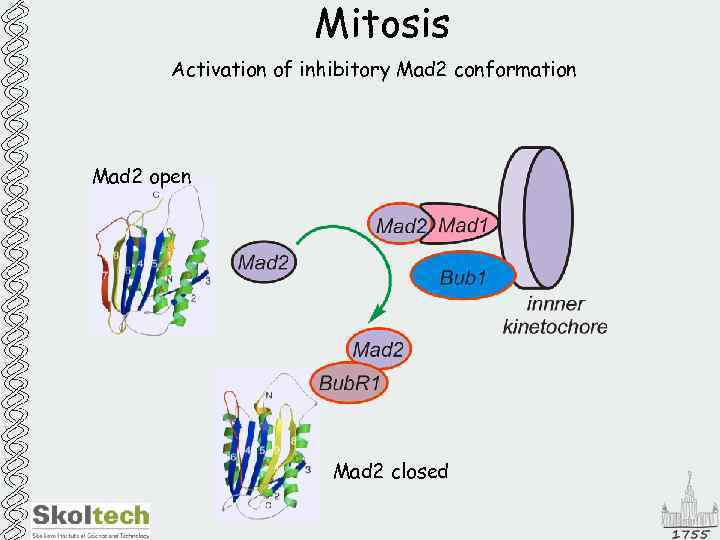 Mitosis Activation of inhibitory Mad 2 conformation Mad 2 open Mad 2 closed
Mitosis Activation of inhibitory Mad 2 conformation Mad 2 open Mad 2 closed
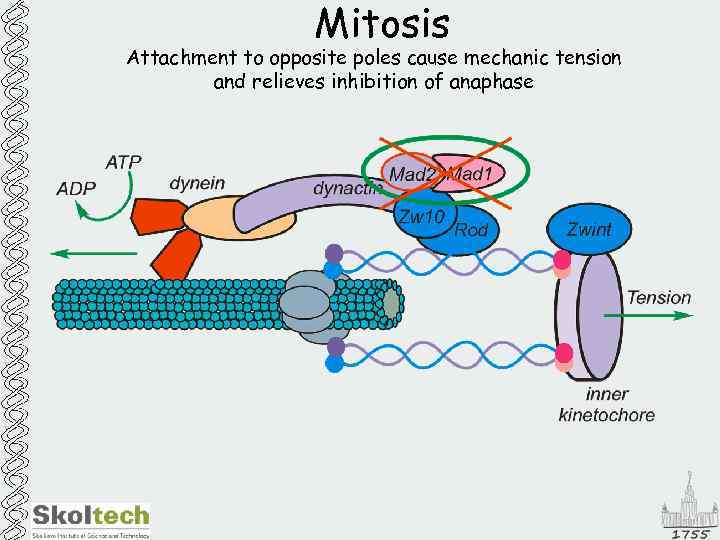 Mitosis Attachment to opposite poles cause mechanic tension and relieves inhibition of anaphase
Mitosis Attachment to opposite poles cause mechanic tension and relieves inhibition of anaphase
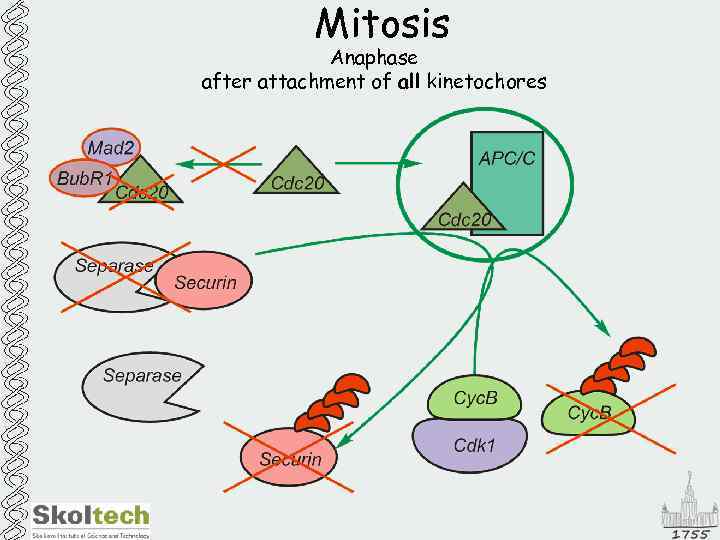 Mitosis Anaphase after attachment of all kinetochores
Mitosis Anaphase after attachment of all kinetochores
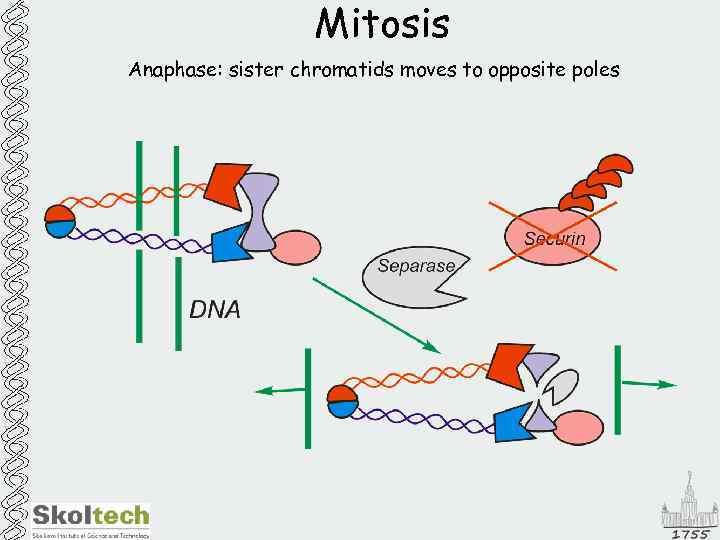 Mitosis Anaphase: sister chromatids moves to opposite poles
Mitosis Anaphase: sister chromatids moves to opposite poles
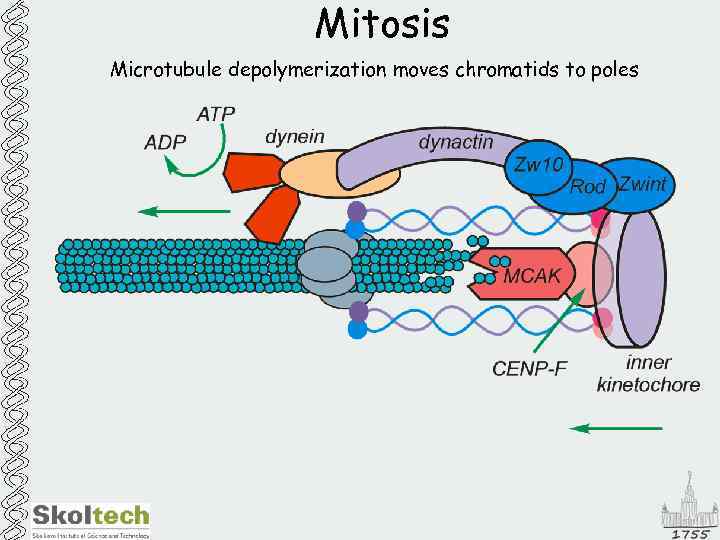 Mitosis Microtubule depolymerization moves chromatids to poles
Mitosis Microtubule depolymerization moves chromatids to poles
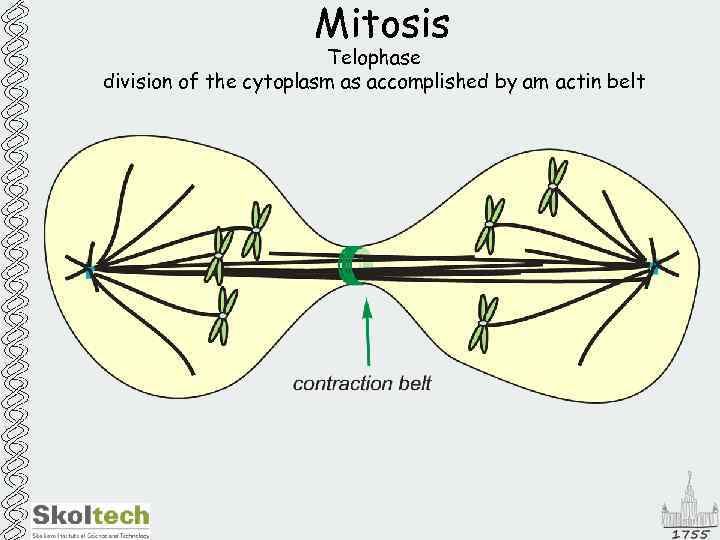 Mitosis Telophase division of the cytoplasm as accomplished by am actin belt
Mitosis Telophase division of the cytoplasm as accomplished by am actin belt
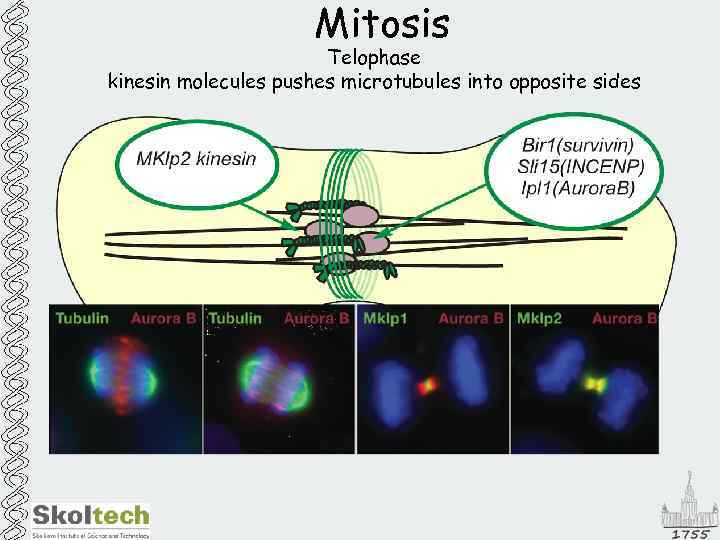 Mitosis Telophase kinesin molecules pushes microtubules into opposite sides
Mitosis Telophase kinesin molecules pushes microtubules into opposite sides
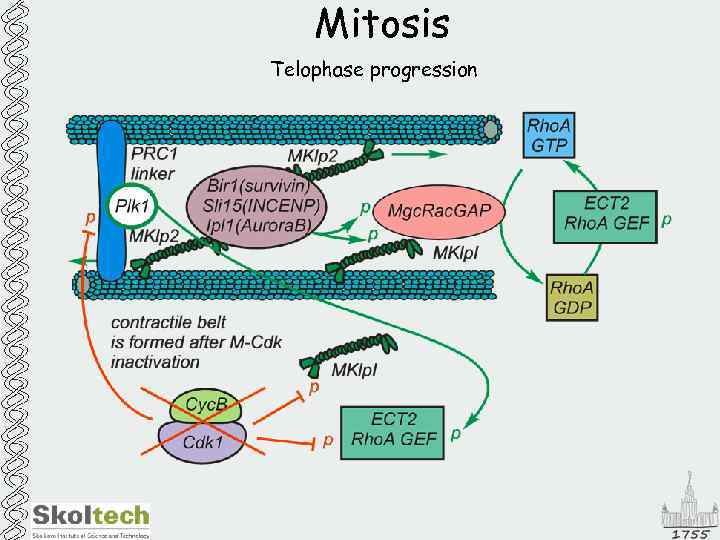 Mitosis Telophase progression
Mitosis Telophase progression
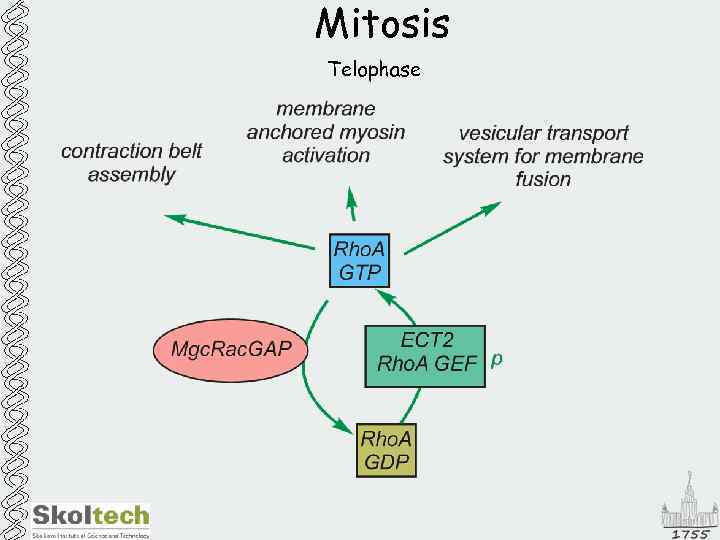 Mitosis Telophase
Mitosis Telophase


