 MSU & Skol. Tech DNA repair
MSU & Skol. Tech DNA repair
 DNA repair pathways 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Direct reversal Base excision repair (BER) Nucleotides excision repair (NER) Mismatch repair (MMR) Trans-lesion synthesis (SOS-response) Repair via recombination Double strand break repair
DNA repair pathways 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Direct reversal Base excision repair (BER) Nucleotides excision repair (NER) Mismatch repair (MMR) Trans-lesion synthesis (SOS-response) Repair via recombination Double strand break repair
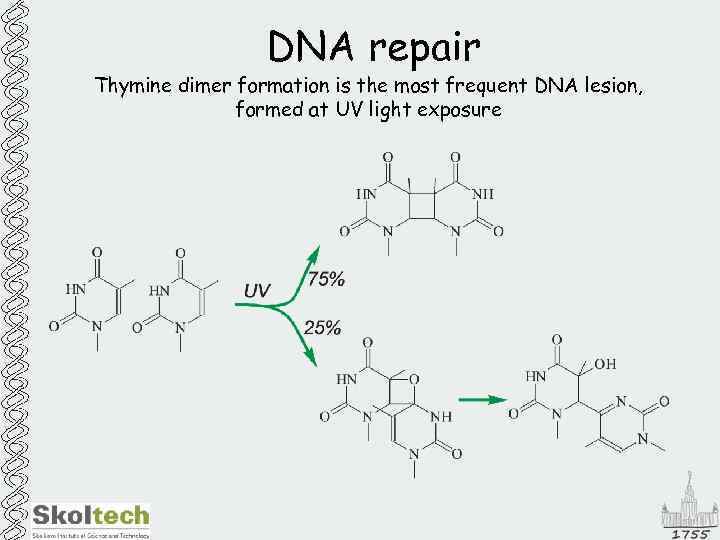 DNA repair Thymine dimer formation is the most frequent DNA lesion, formed at UV light exposure
DNA repair Thymine dimer formation is the most frequent DNA lesion, formed at UV light exposure
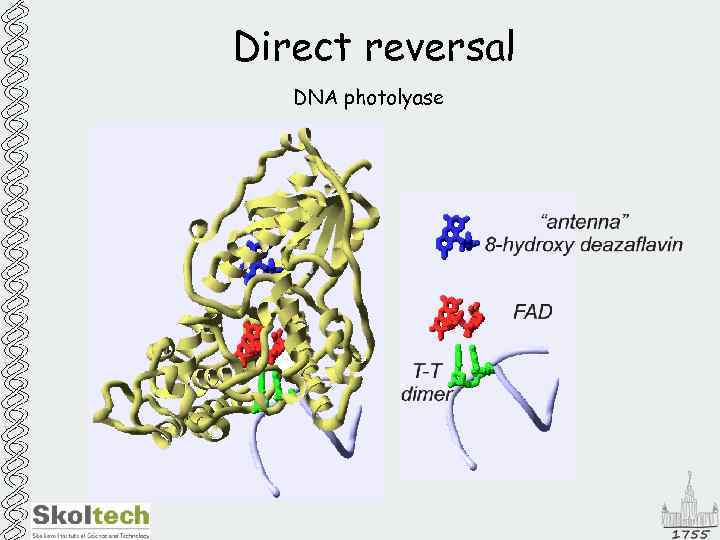 Direct reversal DNA photolyase
Direct reversal DNA photolyase
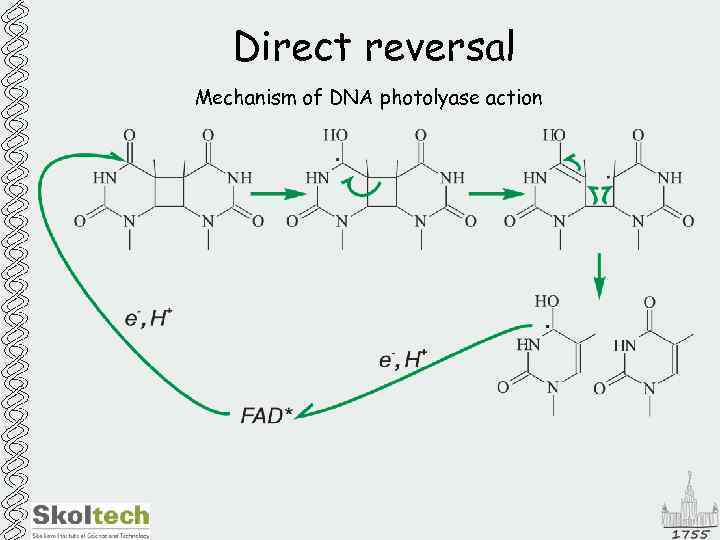 Direct reversal Mechanism of DNA photolyase action
Direct reversal Mechanism of DNA photolyase action
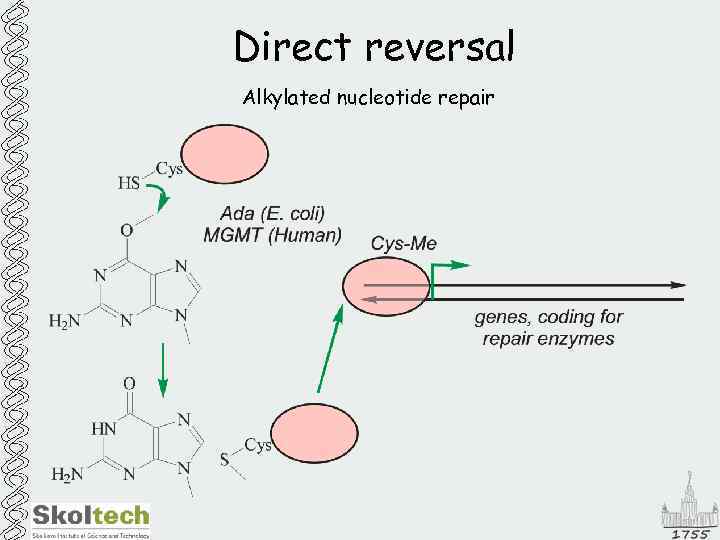 Direct reversal Alkylated nucleotide repair
Direct reversal Alkylated nucleotide repair
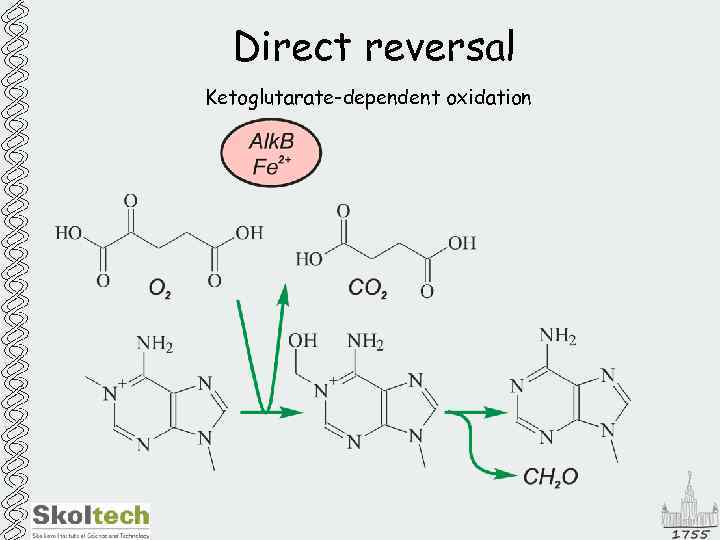 Direct reversal Ketoglutarate-dependent oxidation
Direct reversal Ketoglutarate-dependent oxidation
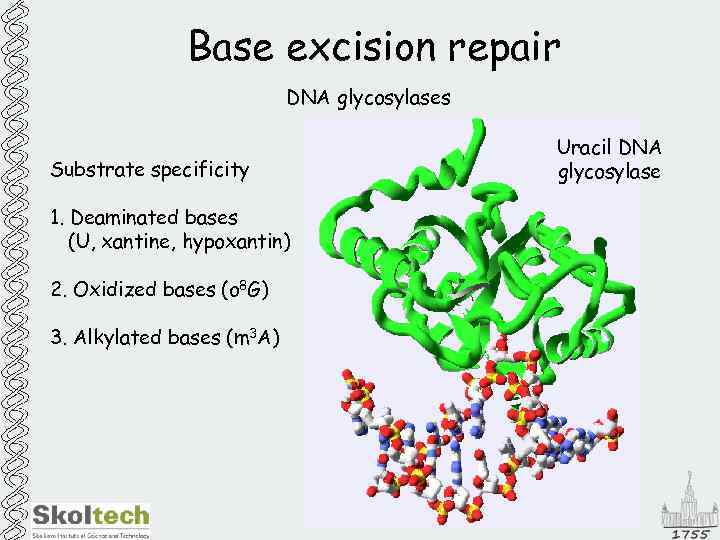 Base excision repair DNA glycosylases Substrate specificity 1. Deaminated bases (U, xantine, hypoxantin) 2. Oxidized bases (o 8 G) 3. Alkylated bases (m 3 A) Uracil DNA glycosylase
Base excision repair DNA glycosylases Substrate specificity 1. Deaminated bases (U, xantine, hypoxantin) 2. Oxidized bases (o 8 G) 3. Alkylated bases (m 3 A) Uracil DNA glycosylase
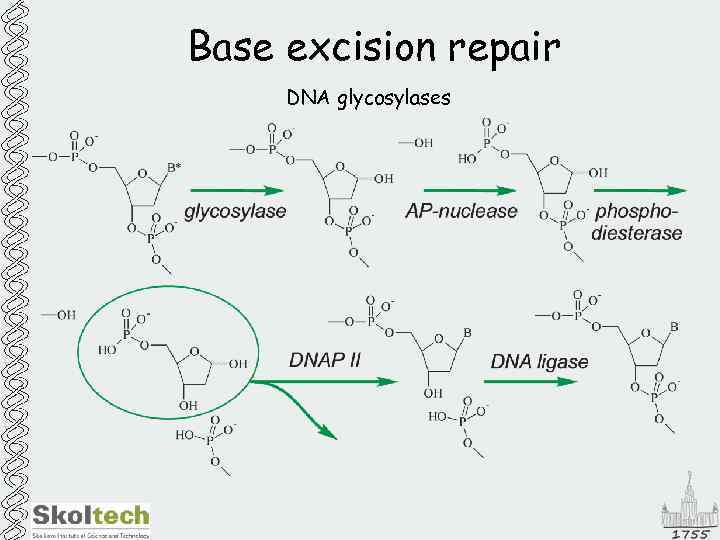 Base excision repair DNA glycosylases
Base excision repair DNA glycosylases
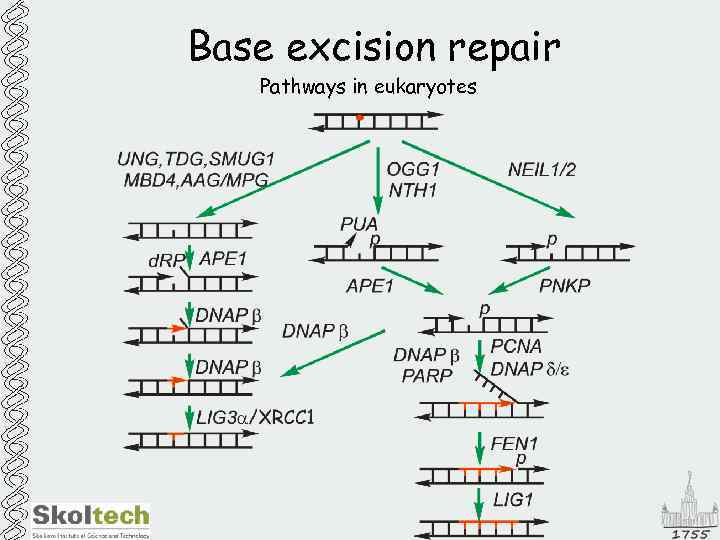 Base excision repair Pathways in eukaryotes
Base excision repair Pathways in eukaryotes
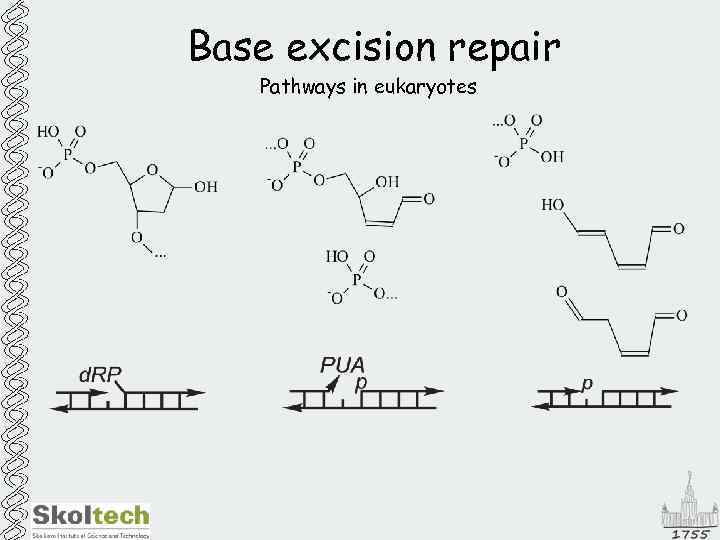 Base excision repair Pathways in eukaryotes
Base excision repair Pathways in eukaryotes
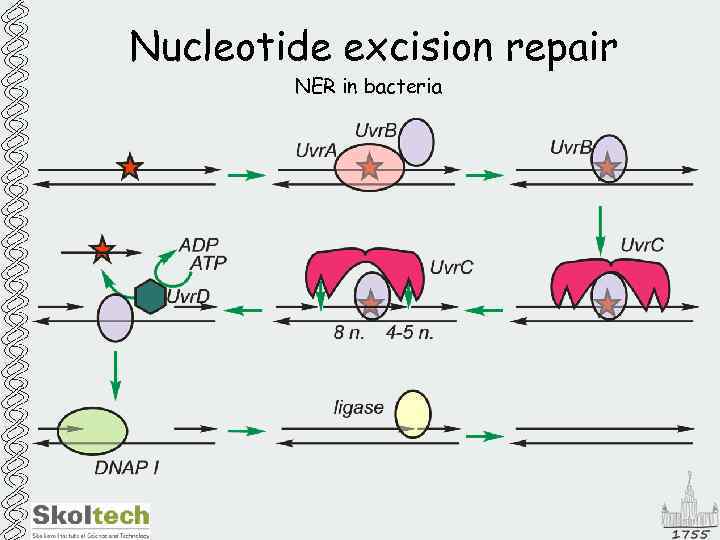 Nucleotide excision repair NER in bacteria
Nucleotide excision repair NER in bacteria
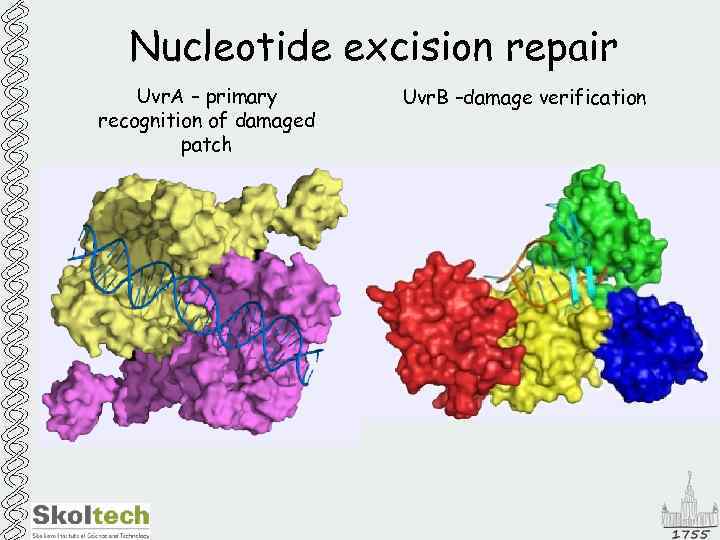 Nucleotide excision repair Uvr. A – primary recognition of damaged patch Uvr. B –damage verification
Nucleotide excision repair Uvr. A – primary recognition of damaged patch Uvr. B –damage verification
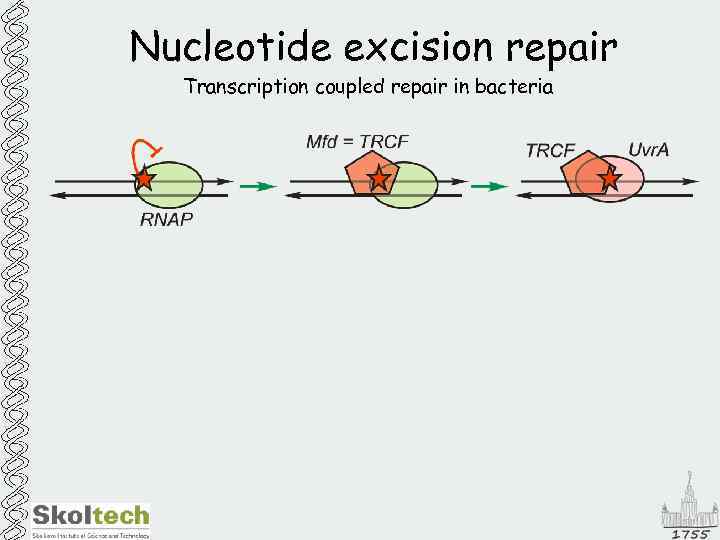 Nucleotide excision repair Transcription coupled repair in bacteria
Nucleotide excision repair Transcription coupled repair in bacteria
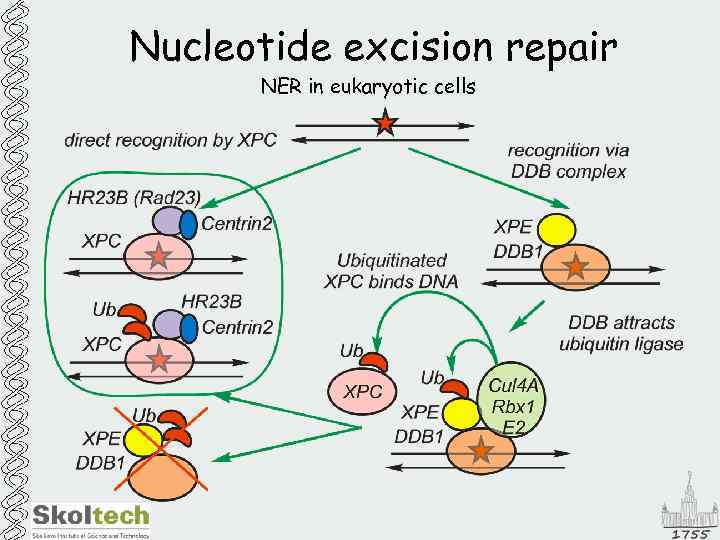 Nucleotide excision repair NER in eukaryotic cells
Nucleotide excision repair NER in eukaryotic cells
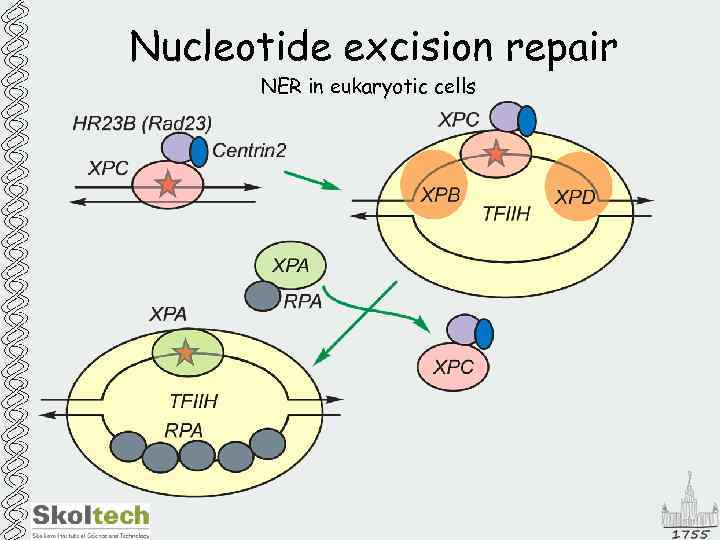 Nucleotide excision repair NER in eukaryotic cells
Nucleotide excision repair NER in eukaryotic cells
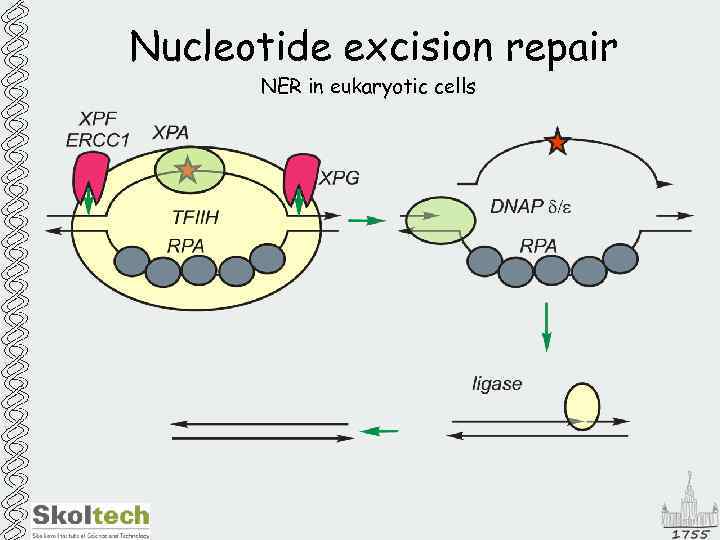 Nucleotide excision repair NER in eukaryotic cells
Nucleotide excision repair NER in eukaryotic cells
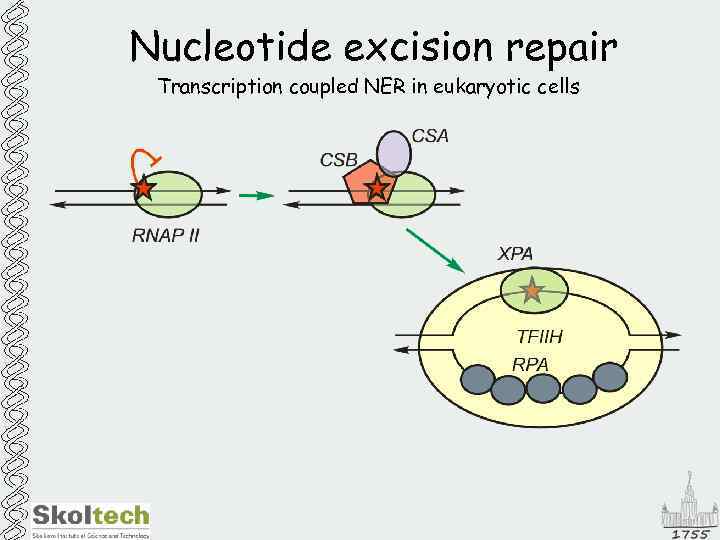 Nucleotide excision repair Transcription coupled NER in eukaryotic cells
Nucleotide excision repair Transcription coupled NER in eukaryotic cells
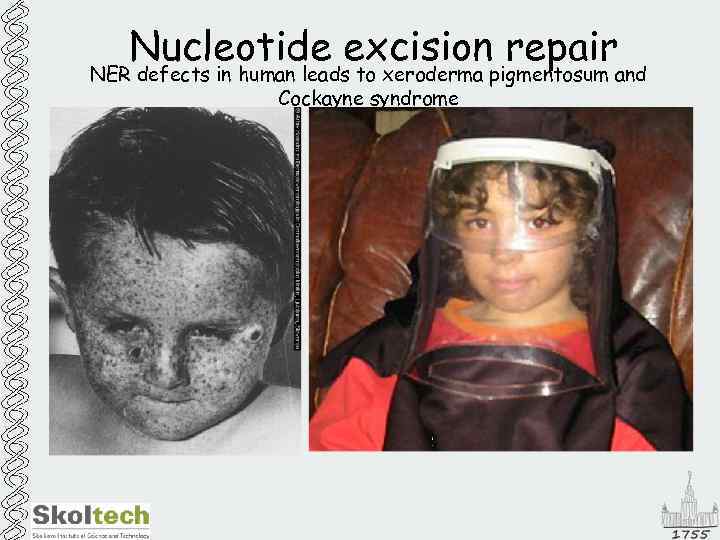 Nucleotide excision repair NER defects in human leads to xeroderma pigmentosum and Cockayne syndrome
Nucleotide excision repair NER defects in human leads to xeroderma pigmentosum and Cockayne syndrome
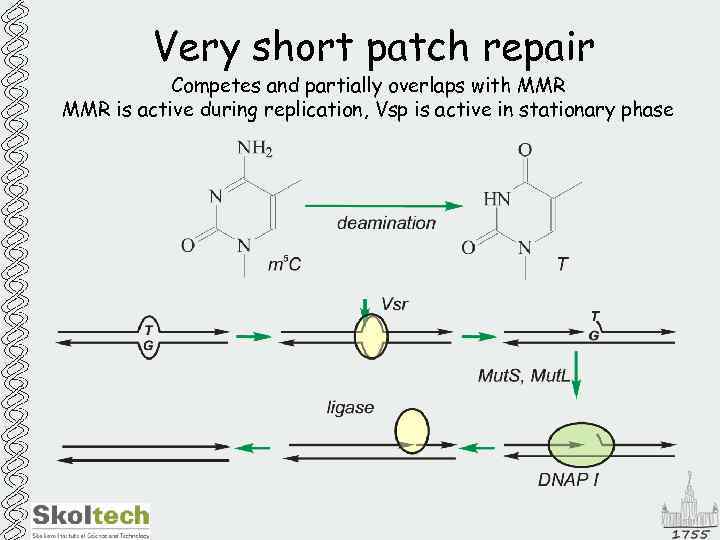 Very short patch repair Competes and partially overlaps with MMR is active during replication, Vsp is active in stationary phase
Very short patch repair Competes and partially overlaps with MMR is active during replication, Vsp is active in stationary phase
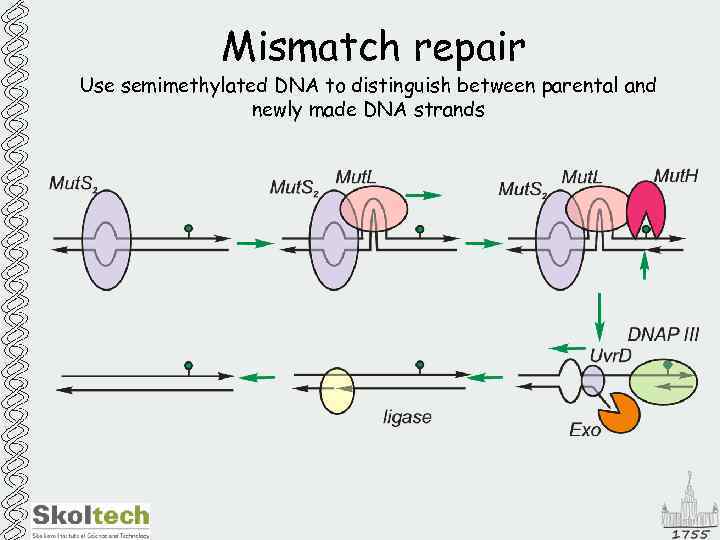 Mismatch repair Use semimethylated DNA to distinguish between parental and newly made DNA strands
Mismatch repair Use semimethylated DNA to distinguish between parental and newly made DNA strands
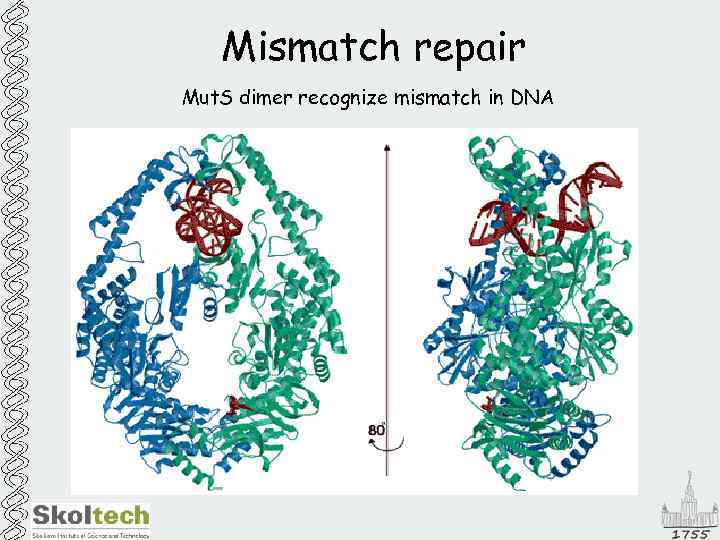 Mismatch repair Mut. S dimer recognize mismatch in DNA
Mismatch repair Mut. S dimer recognize mismatch in DNA
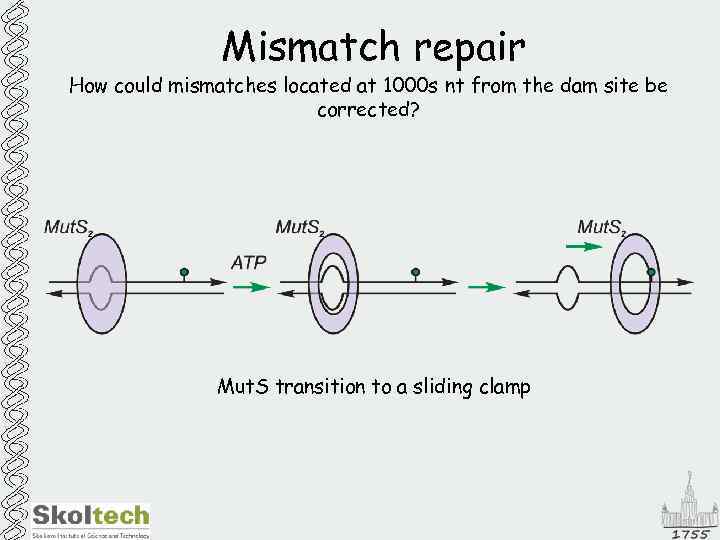 Mismatch repair How could mismatches located at 1000 s nt from the dam site be corrected? Mut. S transition to a sliding clamp
Mismatch repair How could mismatches located at 1000 s nt from the dam site be corrected? Mut. S transition to a sliding clamp
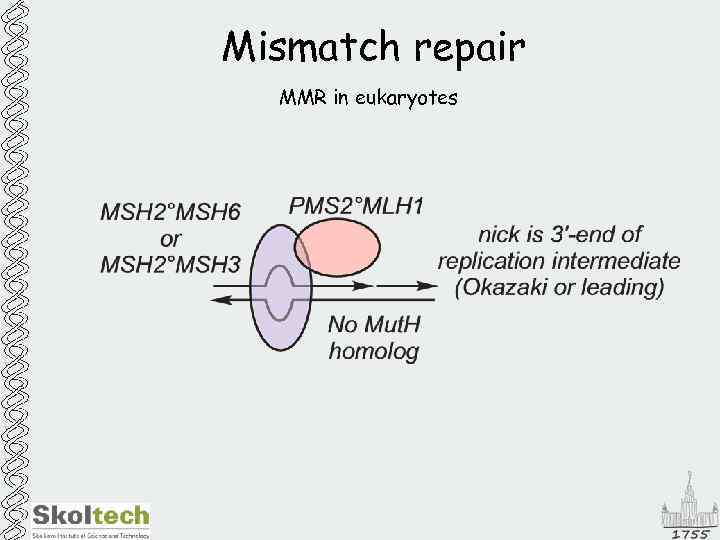 Mismatch repair MMR in eukaryotes
Mismatch repair MMR in eukaryotes
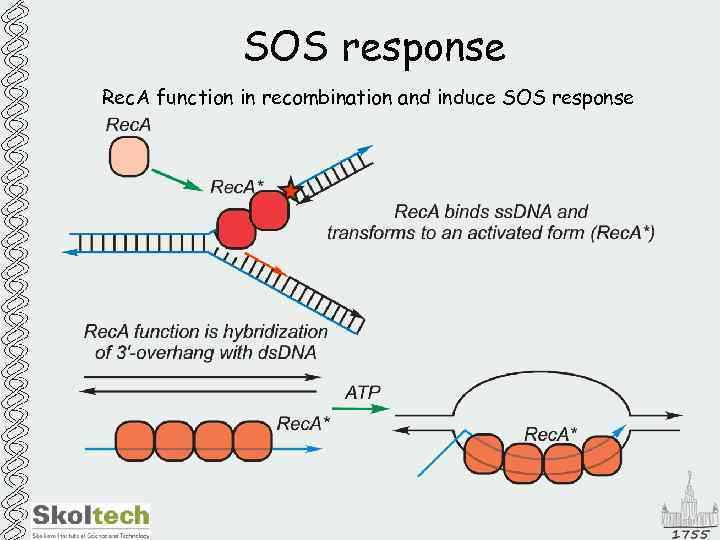 SOS response Rec. A function in recombination and induce SOS response
SOS response Rec. A function in recombination and induce SOS response
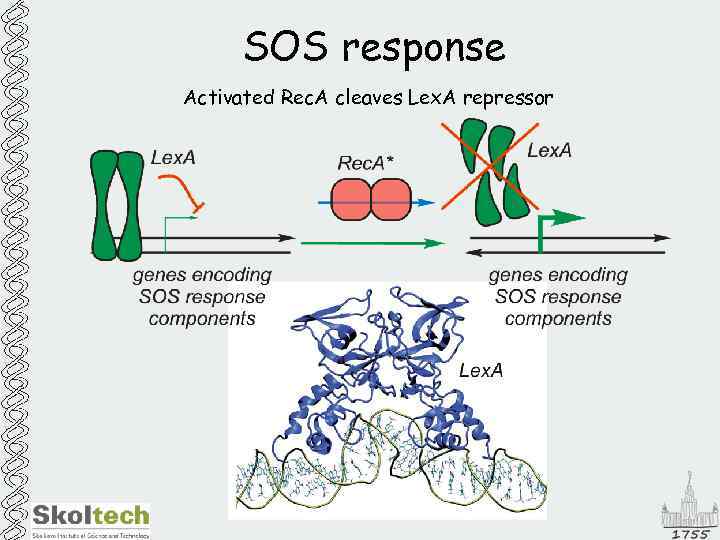 SOS response Activated Rec. A cleaves Lex. A repressor
SOS response Activated Rec. A cleaves Lex. A repressor
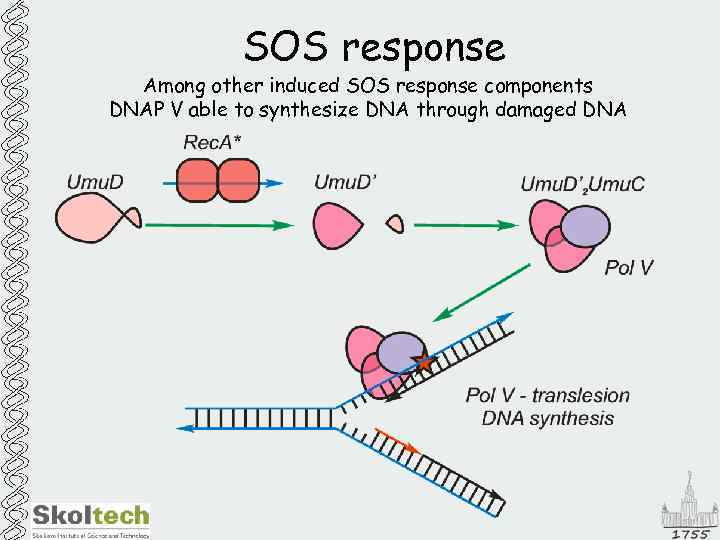 SOS response Among other induced SOS response components DNAP V able to synthesize DNA through damaged DNA
SOS response Among other induced SOS response components DNAP V able to synthesize DNA through damaged DNA
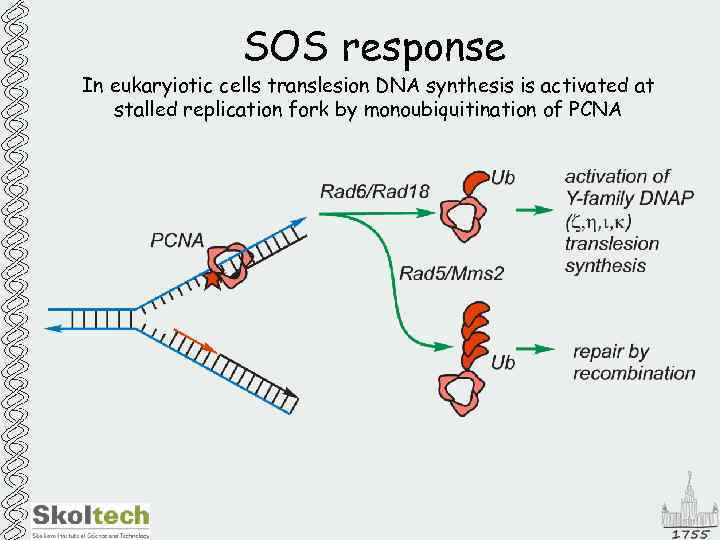 SOS response In eukaryiotic cells translesion DNA synthesis is activated at stalled replication fork by monoubiquitination of PCNA
SOS response In eukaryiotic cells translesion DNA synthesis is activated at stalled replication fork by monoubiquitination of PCNA
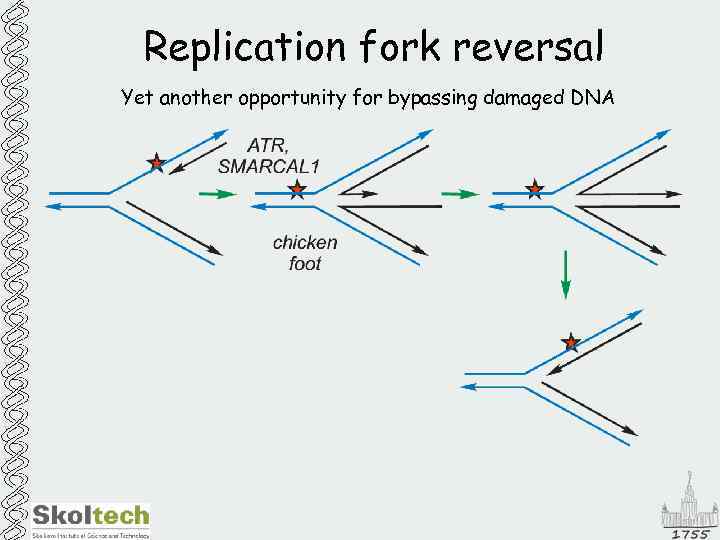 Replication fork reversal Yet another opportunity for bypassing damaged DNA
Replication fork reversal Yet another opportunity for bypassing damaged DNA
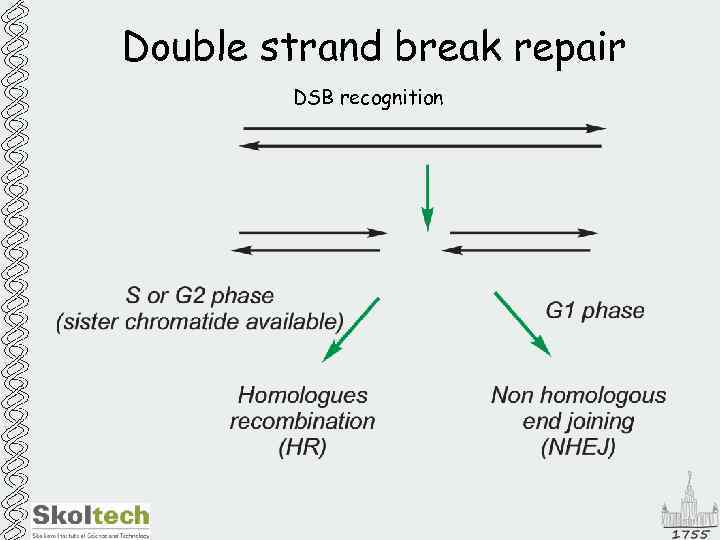 Double strand break repair DSB recognition
Double strand break repair DSB recognition
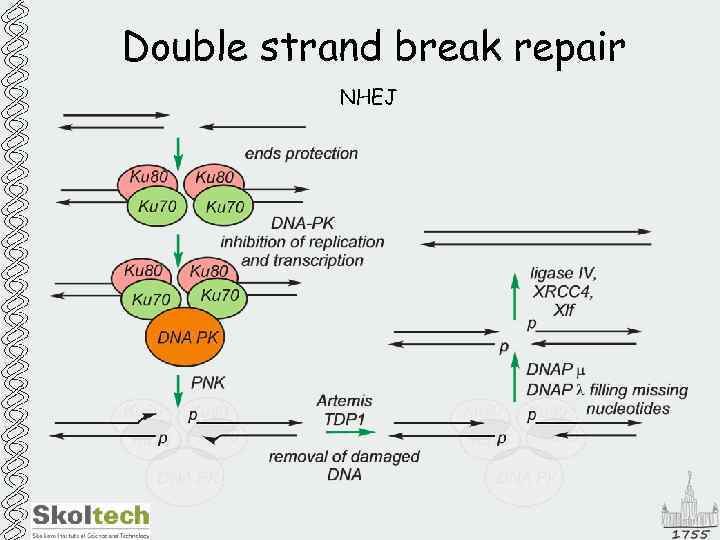 Double strand break repair NHEJ
Double strand break repair NHEJ