d6dca579341d76d3421d8624d35b54fc.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36
 MSK Train the Trainer 2 Clinical Application of Low Back Pain Cases www. pspbc. ca
MSK Train the Trainer 2 Clinical Application of Low Back Pain Cases www. pspbc. ca
 Faculty/Presenter Disclosure Speaker’s Name: Speaker’s Name Relationships with commercial interests: - Grants/Research Support: Pharma. Corp ABC - Speakers Bureau/Honoraria: XYZ Biopharmaceuticals Ltd - Consulting Fees: Med. X Group Inc. - Other: Employee of XYZ Hospital Group 2
Faculty/Presenter Disclosure Speaker’s Name: Speaker’s Name Relationships with commercial interests: - Grants/Research Support: Pharma. Corp ABC - Speakers Bureau/Honoraria: XYZ Biopharmaceuticals Ltd - Consulting Fees: Med. X Group Inc. - Other: Employee of XYZ Hospital Group 2
![Disclosure of Commercial Support This program has received financial support from [organization name] in Disclosure of Commercial Support This program has received financial support from [organization name] in](https://present5.com/presentation/d6dca579341d76d3421d8624d35b54fc/image-3.jpg) Disclosure of Commercial Support This program has received financial support from [organization name] in the form of [describe support here – e. g. educational grant]. This program has received in-kind support from [organization name] in the form of [describe the support here – e. g. logistical support]. Potential for conflict(s) of interest: - [Speaker/Faculty name] has received [payment/funding, etc. ] from [organization supporting this program AND/OR organization whose product(s) are being discussed in this program]. - [Supporting organization name] [developed/licenses/distributes/benefits from the sale of, etc. ] a product that will be discussed in this program: [enter generic and brand name here]. 3
Disclosure of Commercial Support This program has received financial support from [organization name] in the form of [describe support here – e. g. educational grant]. This program has received in-kind support from [organization name] in the form of [describe the support here – e. g. logistical support]. Potential for conflict(s) of interest: - [Speaker/Faculty name] has received [payment/funding, etc. ] from [organization supporting this program AND/OR organization whose product(s) are being discussed in this program]. - [Supporting organization name] [developed/licenses/distributes/benefits from the sale of, etc. ] a product that will be discussed in this program: [enter generic and brand name here]. 3
 Mitigating Potential Bias [Explain how potential sources of bias identified in slides 1 and 2 have been mitigated]. Refer to “Quick Tips” document 4
Mitigating Potential Bias [Explain how potential sources of bias identified in slides 1 and 2 have been mitigated]. Refer to “Quick Tips” document 4
 Certification § Up to 21 Mainpro+ Certified credits for GPs awarded upon completion of: › All 3 Learning Sessions (NOTE: Credits and payment will be based on the exact number of hours in session) › At least 1 Action Period › The Post-Activity Reflective Questionnaire (2 months after LS 3) § Up to 10. 5 Section 1 credits for Specialists › All 3 Learning Sessions (NOTE: Credits and payment will be based on the exact number of hours in session) › The Post-Activity Reflective Questionnaire (2 months after LS 3) 5
Certification § Up to 21 Mainpro+ Certified credits for GPs awarded upon completion of: › All 3 Learning Sessions (NOTE: Credits and payment will be based on the exact number of hours in session) › At least 1 Action Period › The Post-Activity Reflective Questionnaire (2 months after LS 3) § Up to 10. 5 Section 1 credits for Specialists › All 3 Learning Sessions (NOTE: Credits and payment will be based on the exact number of hours in session) › The Post-Activity Reflective Questionnaire (2 months after LS 3) 5
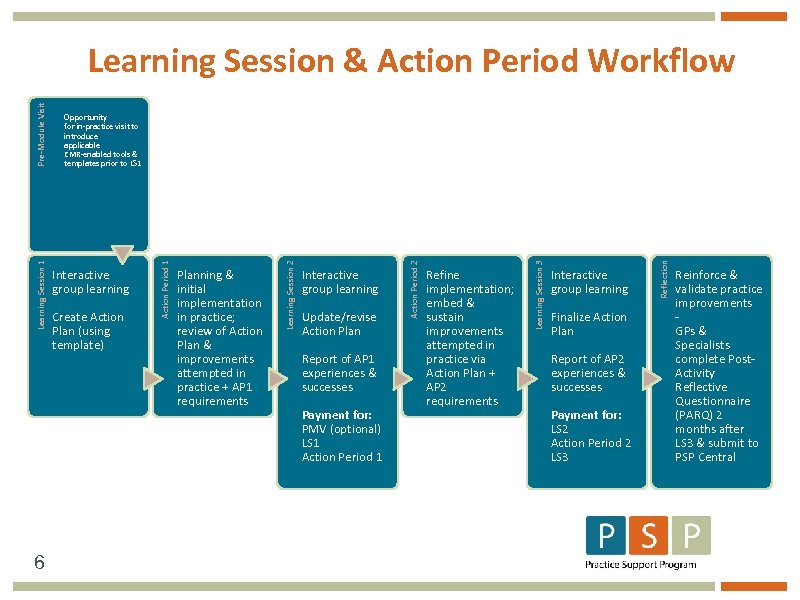 6 Update/revise Action Plan Report of AP 1 experiences & successes Payment for: PMV (optional) LS 1 Action Period 1 Refine implementation; embed & sustain improvements attempted in practice via Action Plan + AP 2 requirements Interactive group learning Finalize Action Plan Report of AP 2 experiences & successes Payment for: LS 2 Action Period 2 LS 3 Reflection Interactive group learning Learning Session 3 Create Action Plan (using template) Planning & initial implementation in practice; review of Action Plan & improvements attempted in practice + AP 1 requirements Action Period 2 Interactive group learning Learning Session 2 Opportunity for in-practice visit to introduce applicable EMR-enabled tools & templates prior to LS 1 Action Period 1 Learning Session 1 Pre-Module Visit Learning Session & Action Period Workflow Reinforce & validate practice improvements GPs & Specialists complete Post. Activity Reflective Questionnaire (PARQ) 2 months after LS 3 & submit to PSP Central
6 Update/revise Action Plan Report of AP 1 experiences & successes Payment for: PMV (optional) LS 1 Action Period 1 Refine implementation; embed & sustain improvements attempted in practice via Action Plan + AP 2 requirements Interactive group learning Finalize Action Plan Report of AP 2 experiences & successes Payment for: LS 2 Action Period 2 LS 3 Reflection Interactive group learning Learning Session 3 Create Action Plan (using template) Planning & initial implementation in practice; review of Action Plan & improvements attempted in practice + AP 1 requirements Action Period 2 Interactive group learning Learning Session 2 Opportunity for in-practice visit to introduce applicable EMR-enabled tools & templates prior to LS 1 Action Period 1 Learning Session 1 Pre-Module Visit Learning Session & Action Period Workflow Reinforce & validate practice improvements GPs & Specialists complete Post. Activity Reflective Questionnaire (PARQ) 2 months after LS 3 & submit to PSP Central
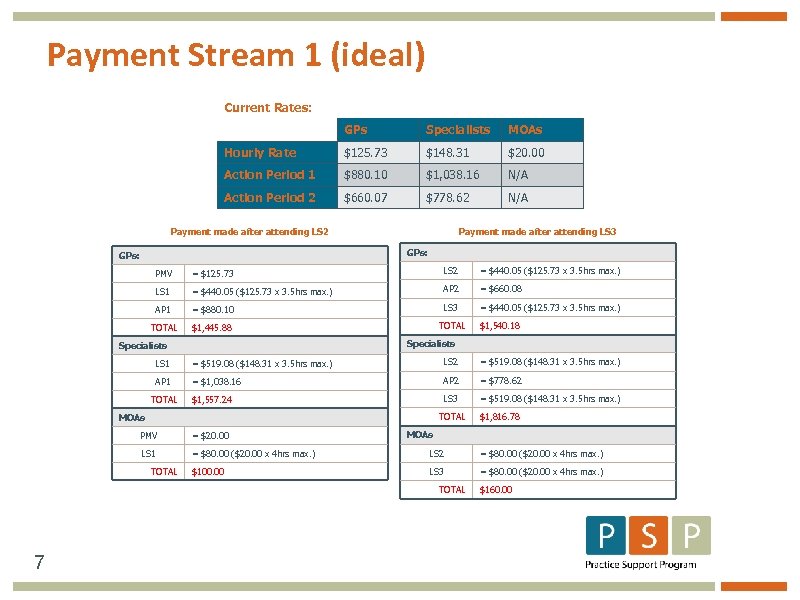 Payment Stream 1 (ideal) Current Rates: GPs Specialists MOAs Hourly Rate $125. 73 $148. 31 $20. 00 Action Period 1 $880. 10 $1, 038. 16 N/A Action Period 2 $660. 07 $778. 62 N/A Payment made after attending LS 2 Payment made after attending LS 3 GPs: PMV = $125. 73 LS 2 = $440. 05 ($125. 73 x 3. 5 hrs max. ) LS 1 = $440. 05 ($125. 73 x 3. 5 hrs max. ) AP 2 = $660. 08 AP 1 = $880. 10 LS 3 = $440. 05 ($125. 73 x 3. 5 hrs max. ) TOTAL $1, 445. 88 TOTAL $1, 540. 18 Specialists LS 1 = $519. 08 ($148. 31 x 3. 5 hrs max. ) LS 2 = $519. 08 ($148. 31 x 3. 5 hrs max. ) AP 1 = $1, 038. 16 AP 2 = $778. 62 $1, 557. 24 LS 3 = $519. 08 ($148. 31 x 3. 5 hrs max. ) TOTAL MOAs $1, 816. 78 MOAs PMV = $20. 00 LS 1 = $80. 00 ($20. 00 x 4 hrs max. ) LS 2 = $80. 00 ($20. 00 x 4 hrs max. ) $100. 00 LS 3 = $80. 00 ($20. 00 x 4 hrs max. ) TOTAL 7 $160. 00
Payment Stream 1 (ideal) Current Rates: GPs Specialists MOAs Hourly Rate $125. 73 $148. 31 $20. 00 Action Period 1 $880. 10 $1, 038. 16 N/A Action Period 2 $660. 07 $778. 62 N/A Payment made after attending LS 2 Payment made after attending LS 3 GPs: PMV = $125. 73 LS 2 = $440. 05 ($125. 73 x 3. 5 hrs max. ) LS 1 = $440. 05 ($125. 73 x 3. 5 hrs max. ) AP 2 = $660. 08 AP 1 = $880. 10 LS 3 = $440. 05 ($125. 73 x 3. 5 hrs max. ) TOTAL $1, 445. 88 TOTAL $1, 540. 18 Specialists LS 1 = $519. 08 ($148. 31 x 3. 5 hrs max. ) LS 2 = $519. 08 ($148. 31 x 3. 5 hrs max. ) AP 1 = $1, 038. 16 AP 2 = $778. 62 $1, 557. 24 LS 3 = $519. 08 ($148. 31 x 3. 5 hrs max. ) TOTAL MOAs $1, 816. 78 MOAs PMV = $20. 00 LS 1 = $80. 00 ($20. 00 x 4 hrs max. ) LS 2 = $80. 00 ($20. 00 x 4 hrs max. ) $100. 00 LS 3 = $80. 00 ($20. 00 x 4 hrs max. ) TOTAL 7 $160. 00
 Cases
Cases
 Case Discussions § § Consolidate Learning Apply Concepts Reality Test Readiness to Teach 9
Case Discussions § § Consolidate Learning Apply Concepts Reality Test Readiness to Teach 9
 Primary Care Provider § § § § § Dealing with complex and chronic LBP Patient expectations for MRI & referrals Psychosocial patient needs Lack of patient educational resources Lack of tools in guideline recommendations Work related restrictions Medication (Opioid Management) Lack of funded therapy Unsure of exercise Prescription 10
Primary Care Provider § § § § § Dealing with complex and chronic LBP Patient expectations for MRI & referrals Psychosocial patient needs Lack of patient educational resources Lack of tools in guideline recommendations Work related restrictions Medication (Opioid Management) Lack of funded therapy Unsure of exercise Prescription 10
 Patient Barriers § Lack of understanding of rationale for investigations and specialist referral § Lack of self-management strategies § Request for more medications § Request for time off work § Lack of understanding of urgent symptoms versus pain § Lack of education on etiology of low back pain § Access to medical appointments 11
Patient Barriers § Lack of understanding of rationale for investigations and specialist referral § Lack of self-management strategies § Request for more medications § Request for time off work § Lack of understanding of urgent symptoms versus pain § Lack of education on etiology of low back pain § Access to medical appointments 11
 Approach to Low Back Pain 1. History is Key to Diagnosis 2. Physical Examination 3. Treatment response
Approach to Low Back Pain 1. History is Key to Diagnosis 2. Physical Examination 3. Treatment response
 Pete the Pilot A 41 year-old airline pilot has a five month history of left low back pain radiating from the top of the left buttock around the hip and into his left groin. He first noticed the pain after finishing a trans-Atlantic flight and it has gradually gotten worse. Although the symptoms do vary in intensity he has not been completely pain free at any time in the past few months. His pain has stopped him from coaching his son’s hockey team and has limited his activities around the house. He has started using a laxative to combat increasing constipation
Pete the Pilot A 41 year-old airline pilot has a five month history of left low back pain radiating from the top of the left buttock around the hip and into his left groin. He first noticed the pain after finishing a trans-Atlantic flight and it has gradually gotten worse. Although the symptoms do vary in intensity he has not been completely pain free at any time in the past few months. His pain has stopped him from coaching his son’s hockey team and has limited his activities around the house. He has started using a laxative to combat increasing constipation
 High Yield Questions • • Where is the Pain Intermittent or Constant Worse with Bending Red Flags ?
High Yield Questions • • Where is the Pain Intermittent or Constant Worse with Bending Red Flags ?
 Predictions • What Pattern? • What do you expect on Physical Exam? • Investigations? • Referrals ? • Management
Predictions • What Pattern? • What do you expect on Physical Exam? • Investigations? • Referrals ? • Management
 Physical Examination All back movements are significantly restricted. Both flexion and extension while standing reproduce his left sided back pain. The pain prevents him from performing a single passive prone extension. Lying in a supine knees-to-chest position with his legs up on a chair gives some relief. Straight leg raising is about 70 degrees bilaterally with the reproduction of his typical pain. Motor testing is hampered by the spinal stiffness and back pain. There seems to be a generalized weakness in both lower limbs. Reflexes in the upper and lower limbs are normal. The plantar reflex is down-going. Sensation, including the saddle area, is normal
Physical Examination All back movements are significantly restricted. Both flexion and extension while standing reproduce his left sided back pain. The pain prevents him from performing a single passive prone extension. Lying in a supine knees-to-chest position with his legs up on a chair gives some relief. Straight leg raising is about 70 degrees bilaterally with the reproduction of his typical pain. Motor testing is hampered by the spinal stiffness and back pain. There seems to be a generalized weakness in both lower limbs. Reflexes in the upper and lower limbs are normal. The plantar reflex is down-going. Sensation, including the saddle area, is normal
 Can you perform a Physical Exam Movement Exam Straight Leg Raise Motor Testing
Can you perform a Physical Exam Movement Exam Straight Leg Raise Motor Testing
 Management Pattern Rest Positions Recovery Activities Decrease Pain, Increase Function
Management Pattern Rest Positions Recovery Activities Decrease Pain, Increase Function
 Katie the Cashier A 32 year- old woman who works at the checkout counter in a supermarket gives a seven week history of pain in the left buttock and thigh. She states that about two months ago the pain began in the left buttock but that about three weeks ago it shifted into her leg. She now has pain in both areas but the thigh pain is more severe. She cannot recall any event that might have triggered the pain or the change in location. Her symptoms are aggravated by sitting and are reduced by lying on her back. The pain has become so intense that she has not been able to work for the past three weeks. There is a burning discomfort involving most of the left foot
Katie the Cashier A 32 year- old woman who works at the checkout counter in a supermarket gives a seven week history of pain in the left buttock and thigh. She states that about two months ago the pain began in the left buttock but that about three weeks ago it shifted into her leg. She now has pain in both areas but the thigh pain is more severe. She cannot recall any event that might have triggered the pain or the change in location. Her symptoms are aggravated by sitting and are reduced by lying on her back. The pain has become so intense that she has not been able to work for the past three weeks. There is a burning discomfort involving most of the left foot
 High Yield Questions • Pattern recognition questions • Yellow Flag Questions • Functional Questions
High Yield Questions • Pattern recognition questions • Yellow Flag Questions • Functional Questions
 Predictions • What Pattern? • What do you expect on Physical Exam? • Investigations? • Referrals ? • Management
Predictions • What Pattern? • What do you expect on Physical Exam? • Investigations? • Referrals ? • Management
 On physical examination the patient has a marked left trunk shift. Left straight leg raising at 50 degrees produces both the left buttock and thigh pain. The “Z” lie position decreases the pain but does not eliminate it completely. There are no changes in the power or reflexes in either leg. She can feel light touch over all of the left foot. Saddle sensation and the plantar responses are normal
On physical examination the patient has a marked left trunk shift. Left straight leg raising at 50 degrees produces both the left buttock and thigh pain. The “Z” lie position decreases the pain but does not eliminate it completely. There are no changes in the power or reflexes in either leg. She can feel light touch over all of the left foot. Saddle sensation and the plantar responses are normal
 Will you modify you examination? Positions Pain Levels Repetitions Verifying Tests for Neurological Deficits
Will you modify you examination? Positions Pain Levels Repetitions Verifying Tests for Neurological Deficits
 Management Pattern Pain Management Referrals +/- Investigations Restrictions
Management Pattern Pain Management Referrals +/- Investigations Restrictions
 Cam the Contractor A 48 -year-old contractor reports four months of pain across the low back at the top of the pelvis, more severe on the right side. His symptoms began while he was installing ceiling tile and were severe enough to make him stop. He describes his pain as constant but is aware that there are brief periods of complete pain relief when he lies in a fetal position. The pain returns as soon as he moves. He prefers to sit slumped forward rather than to stand. There is occasional pain radiation into the right leg to just below the knee.
Cam the Contractor A 48 -year-old contractor reports four months of pain across the low back at the top of the pelvis, more severe on the right side. His symptoms began while he was installing ceiling tile and were severe enough to make him stop. He describes his pain as constant but is aware that there are brief periods of complete pain relief when he lies in a fetal position. The pain returns as soon as he moves. He prefers to sit slumped forward rather than to stand. There is occasional pain radiation into the right leg to just below the knee.
 High Yield Questions • Pattern Possibilities • What about his job? • Leg Pain Symptoms - Referred - Radicular
High Yield Questions • Pattern Possibilities • What about his job? • Leg Pain Symptoms - Referred - Radicular
 Predictions Back or Leg Dominant? Examination Hypothesis Management Plan
Predictions Back or Leg Dominant? Examination Hypothesis Management Plan
 Physical Examination On examination in standing there is no change in the back pain with repeated flexion , 3/10. While a single extension increases his pain immediately to 6/10. Both passive prone lumbar extension and supine passive right straight leg raising produce the typical back pain. The remaining neurological examination is normal. He has mild left groin pain with passive hip internal rotation.
Physical Examination On examination in standing there is no change in the back pain with repeated flexion , 3/10. While a single extension increases his pain immediately to 6/10. Both passive prone lumbar extension and supine passive right straight leg raising produce the typical back pain. The remaining neurological examination is normal. He has mild left groin pain with passive hip internal rotation.
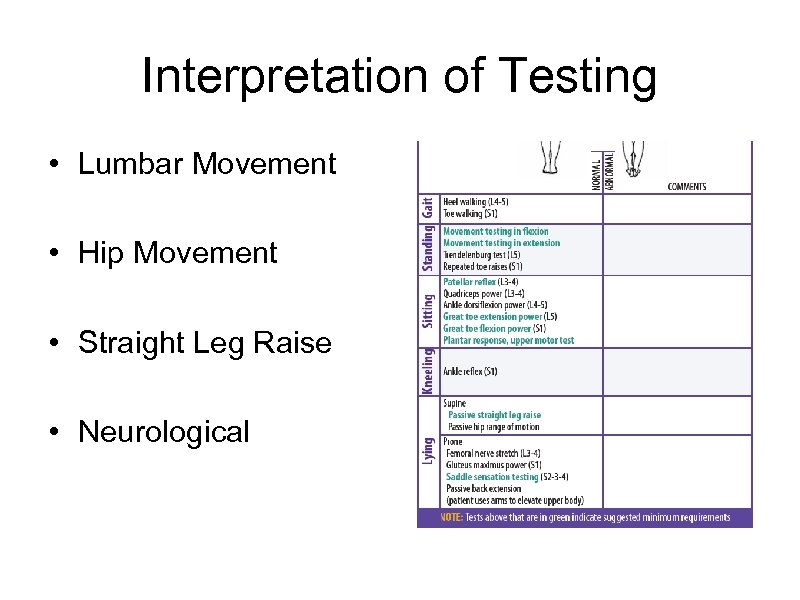 Interpretation of Testing • Lumbar Movement • Hip Movement • Straight Leg Raise • Neurological
Interpretation of Testing • Lumbar Movement • Hip Movement • Straight Leg Raise • Neurological
 Management Pattern Self Management Strategies Activity and Work Advice
Management Pattern Self Management Strategies Activity and Work Advice
 Katrina the Chef A 60 year-old chef has a chief complaint of left posterior thigh pain after walking for more than 15 minutes. This is making it difficult for her to continue to work in the kitchen of an exclusive Italian restaurant. She has suffered constant low back pain for about ten years which has not responded to chiropractic manipulation, physiotherapy modalities or massage therapy. She is often stiff for 20 minutes in the morning. The leg pain began three years ago after she was involved in a rear end collision and is getting progressively worse. To continue working she must sit down frequently and draw up her left knee, which gives total but only short term relief from her leg complaints.
Katrina the Chef A 60 year-old chef has a chief complaint of left posterior thigh pain after walking for more than 15 minutes. This is making it difficult for her to continue to work in the kitchen of an exclusive Italian restaurant. She has suffered constant low back pain for about ten years which has not responded to chiropractic manipulation, physiotherapy modalities or massage therapy. She is often stiff for 20 minutes in the morning. The leg pain began three years ago after she was involved in a rear end collision and is getting progressively worse. To continue working she must sit down frequently and draw up her left knee, which gives total but only short term relief from her leg complaints.
 High Yield History • Red Flags • Risk of Chronicity • Inflammatory
High Yield History • Red Flags • Risk of Chronicity • Inflammatory
 Predictions What Pattern? What examination techniques and why? What tools are most useful ?
Predictions What Pattern? What examination techniques and why? What tools are most useful ?
 Physical Examination Repetitive flexion in standing increases the back pain but does not produce pain in the thigh. Her symptoms don’t change with repeated standing extensions. Straight leg raising on the left at 90 degrees causes back pain only. Motor power is 4/5 in the left ankle dorsiflexiors and left EHL. The Trendelenburg test is asymmetrical. The remaining motor, reflex and sensory tests are unremarkable. There are no upper motor findings
Physical Examination Repetitive flexion in standing increases the back pain but does not produce pain in the thigh. Her symptoms don’t change with repeated standing extensions. Straight leg raising on the left at 90 degrees causes back pain only. Motor power is 4/5 in the left ankle dorsiflexiors and left EHL. The Trendelenburg test is asymmetrical. The remaining motor, reflex and sensory tests are unremarkable. There are no upper motor findings
 Management • What pattern and why? • Would you prescribe therapy? • Would you investigate or refer? • How would you handle patient expectations?
Management • What pattern and why? • Would you prescribe therapy? • Would you investigate or refer? • How would you handle patient expectations?
 Summary • • • Practice makes perfect History is key for role modelling Anticipate your examination Interpret your examination findings Connect to Management
Summary • • • Practice makes perfect History is key for role modelling Anticipate your examination Interpret your examination findings Connect to Management


