b83570b7534e33c9ed4d8d9b7ffb8b75.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 155
 MSDP Training May 5, 2009 Day One Presented by MHSACM, DMH, DPH/BSAS 1
MSDP Training May 5, 2009 Day One Presented by MHSACM, DMH, DPH/BSAS 1
 Welcome and Introductions Presented by MHSACM, DMH, DPH/BSAS 2
Welcome and Introductions Presented by MHSACM, DMH, DPH/BSAS 2
 Presenters • • • Jordan Oshlag, LICSW, Vice President of Operations, Community Healthlink, Inc. Vic Di. Gravio, CEO, MHSACM David Lloyd, President, M. T. M. Services & Senior National Council Consultant Stephanie Sladen, LICSW, Asst. Vice President: Outpatient Mental Health & Substance Abuse Services, Health & Education Services, Inc. Bill Schmelter, Ph. D. , M. T. M. Services & National Council Consultant Kathleen Janssen, BSN, RN, MS, Director of Quality Management, Riverside Community Care Joe Passeneau, LMHC, Director of Health Record Review and Audit, MBHP Marcia Webster, Consultant to The Transformation Center Susan Schneider, Member of MOAR
Presenters • • • Jordan Oshlag, LICSW, Vice President of Operations, Community Healthlink, Inc. Vic Di. Gravio, CEO, MHSACM David Lloyd, President, M. T. M. Services & Senior National Council Consultant Stephanie Sladen, LICSW, Asst. Vice President: Outpatient Mental Health & Substance Abuse Services, Health & Education Services, Inc. Bill Schmelter, Ph. D. , M. T. M. Services & National Council Consultant Kathleen Janssen, BSN, RN, MS, Director of Quality Management, Riverside Community Care Joe Passeneau, LMHC, Director of Health Record Review and Audit, MBHP Marcia Webster, Consultant to The Transformation Center Susan Schneider, Member of MOAR
 Thank you! • • DMH DPH/BSAS MHSACM MBHP CHD Presenters Countless volunteers
Thank you! • • DMH DPH/BSAS MHSACM MBHP CHD Presenters Countless volunteers
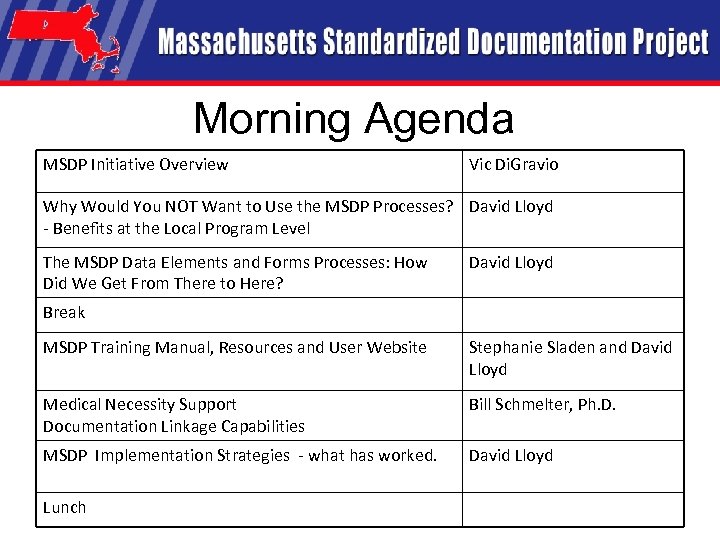 Morning Agenda MSDP Initiative Overview Vic Di. Gravio Why Would You NOT Want to Use the MSDP Processes? David Lloyd - Benefits at the Local Program Level The MSDP Data Elements and Forms Processes: How Did We Get From There to Here? David Lloyd Break MSDP Training Manual, Resources and User Website Stephanie Sladen and David Lloyd Medical Necessity Support Documentation Linkage Capabilities Bill Schmelter, Ph. D. MSDP Implementation Strategies - what has worked. David Lloyd Lunch
Morning Agenda MSDP Initiative Overview Vic Di. Gravio Why Would You NOT Want to Use the MSDP Processes? David Lloyd - Benefits at the Local Program Level The MSDP Data Elements and Forms Processes: How Did We Get From There to Here? David Lloyd Break MSDP Training Manual, Resources and User Website Stephanie Sladen and David Lloyd Medical Necessity Support Documentation Linkage Capabilities Bill Schmelter, Ph. D. MSDP Implementation Strategies - what has worked. David Lloyd Lunch
 MSDP - Overview • Terms -
MSDP - Overview • Terms -
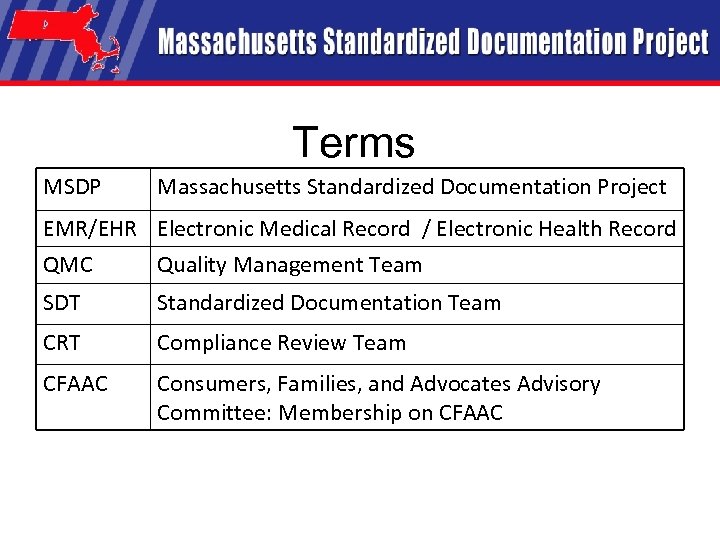 Terms MSDP Massachusetts Standardized Documentation Project EMR/EHR Electronic Medical Record / Electronic Health Record QMC Quality Management Team SDT Standardized Documentation Team CRT Compliance Review Team CFAAC Consumers, Families, and Advocates Advisory Committee: Membership on CFAAC
Terms MSDP Massachusetts Standardized Documentation Project EMR/EHR Electronic Medical Record / Electronic Health Record QMC Quality Management Team SDT Standardized Documentation Team CRT Compliance Review Team CFAAC Consumers, Families, and Advocates Advisory Committee: Membership on CFAAC
 More terms CBFS Community Based Flexible Support Services CBHI Children’s Behavioral Health Initiative Recovery Orientated Person Centered RAC Recovery Audit Contractor Program
More terms CBFS Community Based Flexible Support Services CBHI Children’s Behavioral Health Initiative Recovery Orientated Person Centered RAC Recovery Audit Contractor Program
 Paradigm Shift
Paradigm Shift
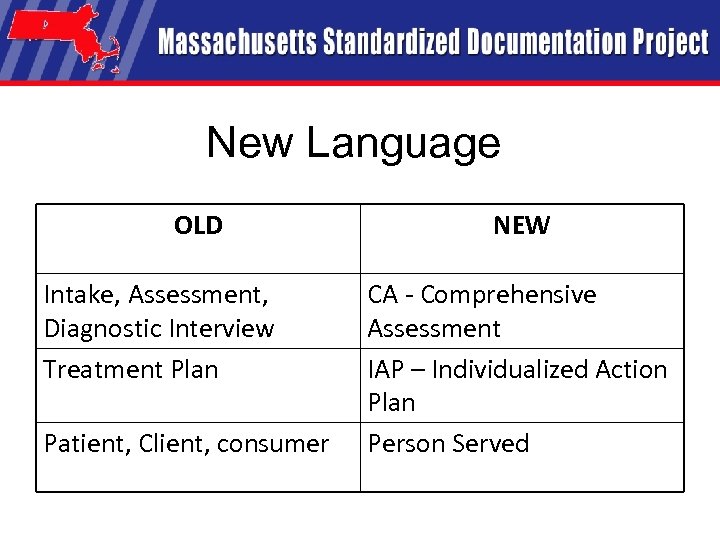 New Language OLD Intake, Assessment, Diagnostic Interview Treatment Plan Patient, Client, consumer NEW CA - Comprehensive Assessment IAP – Individualized Action Plan Person Served
New Language OLD Intake, Assessment, Diagnostic Interview Treatment Plan Patient, Client, consumer NEW CA - Comprehensive Assessment IAP – Individualized Action Plan Person Served
 MSDP Initiative Overview A New Direction… Leading the Way! Vic Di. Gravio, CEO, MHSACM
MSDP Initiative Overview A New Direction… Leading the Way! Vic Di. Gravio, CEO, MHSACM
 Purpose of the MSDP Initiative • Conceived as part of MHSACM e-Health Initiative • Sub-committee process in Fall 2006 identified need to bring order/structure to how providers document care • Essential interim step in transition from paper to electronic based records- “e. Health Readiness” 12
Purpose of the MSDP Initiative • Conceived as part of MHSACM e-Health Initiative • Sub-committee process in Fall 2006 identified need to bring order/structure to how providers document care • Essential interim step in transition from paper to electronic based records- “e. Health Readiness” 12
 Goals of MSDP Develop standardized set of clinical forms that will lead to: • Improved quality of patient care • Increased compliance • More efficient business practices 13
Goals of MSDP Develop standardized set of clinical forms that will lead to: • Improved quality of patient care • Increased compliance • More efficient business practices 13
 MSDP Initiative Stakeholders • • Mental Health and Substance Abuse Corporations of Massachusetts (MHSACM) Executive Office of Health and Human Services (EOHHS) Department of Mental Health (DMH) Mass. Health Department of Public Health Bureau of Substance Abuse Services DPH/BSAS Massachusetts Behavioral Health Partnership (MBHP) Medicaid Carve Out Medicaid Managed Care Organizations (MMCOs): – BMC Health. Net, – Neighborhood Health Plan, – Fallon Community Health Plan – Network Health. Consumer/Families and Advocate Organizations: – National Alliance for the Mentally Ill of Massachusetts (NAMI) – The Consumer Quality Initiative (CQI) – Massachusetts Organization for Addiction Recovery (MOAR) – Massachusetts People/Patients Organized for Wellness, Empowerment and Rights (M-Power) 14
MSDP Initiative Stakeholders • • Mental Health and Substance Abuse Corporations of Massachusetts (MHSACM) Executive Office of Health and Human Services (EOHHS) Department of Mental Health (DMH) Mass. Health Department of Public Health Bureau of Substance Abuse Services DPH/BSAS Massachusetts Behavioral Health Partnership (MBHP) Medicaid Carve Out Medicaid Managed Care Organizations (MMCOs): – BMC Health. Net, – Neighborhood Health Plan, – Fallon Community Health Plan – Network Health. Consumer/Families and Advocate Organizations: – National Alliance for the Mentally Ill of Massachusetts (NAMI) – The Consumer Quality Initiative (CQI) – Massachusetts Organization for Addiction Recovery (MOAR) – Massachusetts People/Patients Organized for Wellness, Empowerment and Rights (M-Power) 14
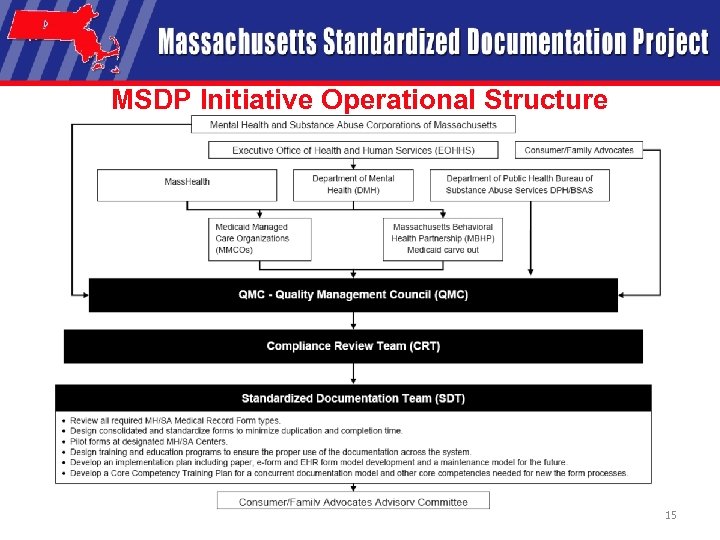 MSDP Initiative Operational Structure 15
MSDP Initiative Operational Structure 15
 Why Would You Not Want to Use the MSDP Processes? – Benefits at the Local Program Level Presented by: David Lloyd, President M. T. M. Services
Why Would You Not Want to Use the MSDP Processes? – Benefits at the Local Program Level Presented by: David Lloyd, President M. T. M. Services
 Benefits of Participating • Quality of Care Benefits – Promotes consistent assessment, planning & service documentation – Person-Centered and Strengths focus – Recovery/Resiliency focus – Promotes Information Sharing • Promotes effective collaboration with other providers & shared terminology for use by different disciplines – Less room for error; Decision support Presented by: David Lloyd, MTM Services 17
Benefits of Participating • Quality of Care Benefits – Promotes consistent assessment, planning & service documentation – Person-Centered and Strengths focus – Recovery/Resiliency focus – Promotes Information Sharing • Promotes effective collaboration with other providers & shared terminology for use by different disciplines – Less room for error; Decision support Presented by: David Lloyd, MTM Services 17
 Benefits of Participating • Business Benefits – Compliant with Federal Mandate for Electronic Health Records by 2014 & a wide variety of regulatory and payer requirements • Protection against federal audits – Wide array of funders/payers support this initiative – Enhances Measurement & Outcomes Focus 18
Benefits of Participating • Business Benefits – Compliant with Federal Mandate for Electronic Health Records by 2014 & a wide variety of regulatory and payer requirements • Protection against federal audits – Wide array of funders/payers support this initiative – Enhances Measurement & Outcomes Focus 18
 Benefits of Participating • Financial Benefits – Free training and forms – Compliant with a wide variety of regulatory and payer requirements • Some protection against federal audits – Saves time and money • Reduces redundancy in collecting information • Concurrent documentation possible – Standardized revisions and updates in future 19
Benefits of Participating • Financial Benefits – Free training and forms – Compliant with a wide variety of regulatory and payer requirements • Some protection against federal audits – Saves time and money • Reduces redundancy in collecting information • Concurrent documentation possible – Standardized revisions and updates in future 19
 Statewide MSDP Pilot Study Completed: • Twenty-six MHSACM member provider agencies submitted a request to participate in the MSDP Pilot Study in March and April 2008. • A total of 70 different local programs at these member agencies representing twenty-six different statewide funded program types participated 20
Statewide MSDP Pilot Study Completed: • Twenty-six MHSACM member provider agencies submitted a request to participate in the MSDP Pilot Study in March and April 2008. • A total of 70 different local programs at these member agencies representing twenty-six different statewide funded program types participated 20
 Evaluation Levels and Tools • Program Level Evaluations – Completed after local pilot trainings – Assessed Local Program Pilot Training and “Kickoff” • Evaluate quality of training and supports received • Evaluate success of agency training – One evaluation per program participating in the pilot 21
Evaluation Levels and Tools • Program Level Evaluations – Completed after local pilot trainings – Assessed Local Program Pilot Training and “Kickoff” • Evaluate quality of training and supports received • Evaluate success of agency training – One evaluation per program participating in the pilot 21
 Evaluations Levels and Tools • Direct Staff Form “Mark-up” Process – Completed during pilot study – Evaluation of pilot forms – Notations made directly on blank forms by participating program staff – Each participating staff member required to mark up one form for each mandatory type piloted • Direct staff members’ chance to influence the final product • Commented on form layout, data elements, spacing issues, etc. 22
Evaluations Levels and Tools • Direct Staff Form “Mark-up” Process – Completed during pilot study – Evaluation of pilot forms – Notations made directly on blank forms by participating program staff – Each participating staff member required to mark up one form for each mandatory type piloted • Direct staff members’ chance to influence the final product • Commented on form layout, data elements, spacing issues, etc. 22
 Program Evaluation Focus Areas 1. Identified of how many times each pilot form/process was used by direct care staff during the pilot study. 2. Evaluated to what extent each pilot form used collected the data elements direct care staff need to do their job well 3. Evaluated to what extent each pilot form used contained unnecessary data elements 4. Evaluated to what extent each pilot form supported compliance with regulations and payer requirements (DMH, MBHP, Medicare, MCOs, CMS, etc) 23
Program Evaluation Focus Areas 1. Identified of how many times each pilot form/process was used by direct care staff during the pilot study. 2. Evaluated to what extent each pilot form used collected the data elements direct care staff need to do their job well 3. Evaluated to what extent each pilot form used contained unnecessary data elements 4. Evaluated to what extent each pilot form supported compliance with regulations and payer requirements (DMH, MBHP, Medicare, MCOs, CMS, etc) 23
 Program Evaluation Focus Areas 5. Evaluated to what extent each pilot form used supported compliance with accrediting body standards (CARF, JCAHO, COA, NCQA, etc) 6. Evaluated to what extent each pilot form used supported a ‘Person Centered, Recovery Oriented” approach to services 7. Evaluated the overall clinical flow/ clinical content of the MSDP forms/documentation processes 8. Compared each new pilot form used with the equivalent form being used just prior to the pilot in terms of support for quality clinical/ recovery focused services 9. Evaluated to what extent the pilot forms used unnecessarily collected information more than once 24
Program Evaluation Focus Areas 5. Evaluated to what extent each pilot form used supported compliance with accrediting body standards (CARF, JCAHO, COA, NCQA, etc) 6. Evaluated to what extent each pilot form used supported a ‘Person Centered, Recovery Oriented” approach to services 7. Evaluated the overall clinical flow/ clinical content of the MSDP forms/documentation processes 8. Compared each new pilot form used with the equivalent form being used just prior to the pilot in terms of support for quality clinical/ recovery focused services 9. Evaluated to what extent the pilot forms used unnecessarily collected information more than once 24
 Ongoing Support for the MSDP Process • EHR Vendor Certification Process to help ensure that the EHR product you purchase is compliant with the MSDP data elements • Data mapping for all forms/processes has been completed and will be used to develop gap analysis between the EHR vendor’s data elements and the data elements identified as required in the MSDP process for each form type 25
Ongoing Support for the MSDP Process • EHR Vendor Certification Process to help ensure that the EHR product you purchase is compliant with the MSDP data elements • Data mapping for all forms/processes has been completed and will be used to develop gap analysis between the EHR vendor’s data elements and the data elements identified as required in the MSDP process for each form type 25
 Presented by: David Lloyd, MTM Services 26
Presented by: David Lloyd, MTM Services 26
 Ongoing Support for the MSDP Process • Ongoing Annual Review of the MSDP processes and manuals to ensure continued compliance with revised standards • Eliminates local costly efforts to revise and maintain forms/training manuals 27
Ongoing Support for the MSDP Process • Ongoing Annual Review of the MSDP processes and manuals to ensure continued compliance with revised standards • Eliminates local costly efforts to revise and maintain forms/training manuals 27
 MSDP Data Elements and Forms Processes: How Did We Get From There to Here? Presented by: David Lloyd, President M. T. M. Services
MSDP Data Elements and Forms Processes: How Did We Get From There to Here? Presented by: David Lloyd, President M. T. M. Services
 MSDP Scope of Work • The identified scope of work for the MSDP includes documentation requirements for services identified below: – All Department of Mental Health community services – Medicaid Mental Health acute services, regardless of health plan, carve out or Fee For Service status – Services purchased by the Bureau of Substance Abuse Services – Substance Abuse services purchased by Medicaid – EATS, CBATS and Supported Education and Employment Services are included in the scope of work for the project. – Programs that do not have an individual record will not be included in the scope of work (i. e. , Disaster Response, Training, Trauma Response, Consultation Programs, etc. ) 29
MSDP Scope of Work • The identified scope of work for the MSDP includes documentation requirements for services identified below: – All Department of Mental Health community services – Medicaid Mental Health acute services, regardless of health plan, carve out or Fee For Service status – Services purchased by the Bureau of Substance Abuse Services – Substance Abuse services purchased by Medicaid – EATS, CBATS and Supported Education and Employment Services are included in the scope of work for the project. – Programs that do not have an individual record will not be included in the scope of work (i. e. , Disaster Response, Training, Trauma Response, Consultation Programs, etc. ) 29
 MSDP Project Management Model • The Project Management Model used in the MSDP Initiative includes: – – – – Empowered Project Teams 70% Super Majority Decision Making Compliance Grid Development Statewide Pilot Study of all developed processes/data elements Three levels of evaluation Training Manual Development Implementation Training Plan Development 30
MSDP Project Management Model • The Project Management Model used in the MSDP Initiative includes: – – – – Empowered Project Teams 70% Super Majority Decision Making Compliance Grid Development Statewide Pilot Study of all developed processes/data elements Three levels of evaluation Training Manual Development Implementation Training Plan Development 30
 MSDP Project Management Scope of Work 1. Develop the data elements necessary in each clinical form type to support an integrated standardize documentation approach statewide based on Ohio’s SOQIC standardized documentation initiative refocused to Massachusetts requirements 2. Develop a data element dictionary and cross walk for all data elements in each form type 3. Provide compliance review to ensure the created form processes meet applicable state, federal and national accreditation requirements/standards 4. Develop a statewide documentation training manual based on the model used in the SOQIC initiative in Ohio 5. Use the MH/SA providers’ technical assessment level survey completed by MHSACM to develop interim documentation solutions for community providers based on possible paper processes, electronic forms and/or EHR specifications 6. Provide technical assistance for the development of an RFP to select a vendor to create EHR specifications for application statewide with all vendor types (i. e. , XML code model, etc. ) 7. Provide training to support the documentation model and data elements developed to facilitate an understanding of how to use the new processes to support: – – – Medical Necessity linkage requirements Recovery/Rehabilitation service delivery focus Move to more fidelity between “what we do, versus what we write” 31
MSDP Project Management Scope of Work 1. Develop the data elements necessary in each clinical form type to support an integrated standardize documentation approach statewide based on Ohio’s SOQIC standardized documentation initiative refocused to Massachusetts requirements 2. Develop a data element dictionary and cross walk for all data elements in each form type 3. Provide compliance review to ensure the created form processes meet applicable state, federal and national accreditation requirements/standards 4. Develop a statewide documentation training manual based on the model used in the SOQIC initiative in Ohio 5. Use the MH/SA providers’ technical assessment level survey completed by MHSACM to develop interim documentation solutions for community providers based on possible paper processes, electronic forms and/or EHR specifications 6. Provide technical assistance for the development of an RFP to select a vendor to create EHR specifications for application statewide with all vendor types (i. e. , XML code model, etc. ) 7. Provide training to support the documentation model and data elements developed to facilitate an understanding of how to use the new processes to support: – – – Medical Necessity linkage requirements Recovery/Rehabilitation service delivery focus Move to more fidelity between “what we do, versus what we write” 31
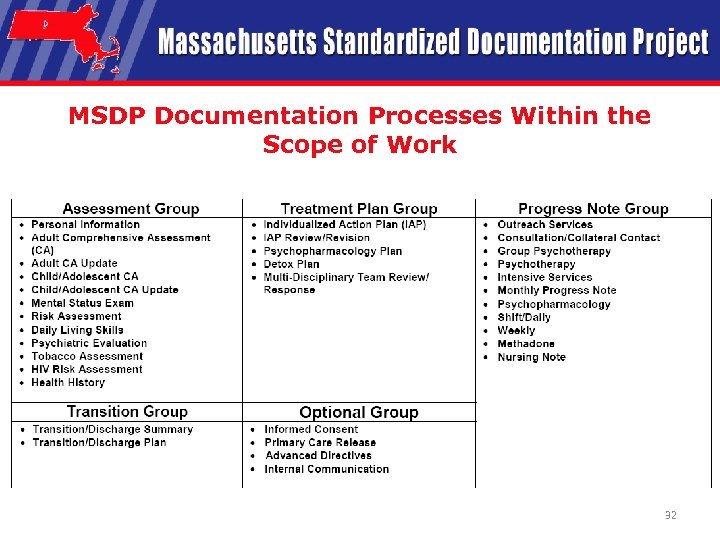 MSDP Documentation Processes Within the Scope of Work 32
MSDP Documentation Processes Within the Scope of Work 32
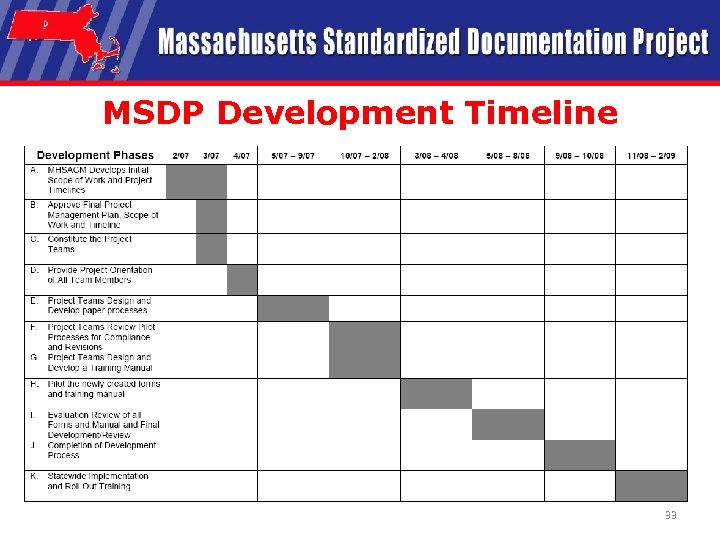 MSDP Development Timeline 33
MSDP Development Timeline 33
 Decision-Making Process to Support Core Organizational Principles The following decision-making process that was utilized for the MSDP Initiative: • Primary emphasis will be placed on gaining consensus and support from all stakeholders • Preliminary straw votes will be taken to determine the position of QMC, Compliance Review and Project Team members on specific issues/initiatives • If consensus cannot be reached in a reasonable time frame, then a final vote will be taken with a super majority (70% of members attending the meeting) being required to act on any issues/initiative that needs leadership. • The minutes will accurately reflect the vote of members. 34
Decision-Making Process to Support Core Organizational Principles The following decision-making process that was utilized for the MSDP Initiative: • Primary emphasis will be placed on gaining consensus and support from all stakeholders • Preliminary straw votes will be taken to determine the position of QMC, Compliance Review and Project Team members on specific issues/initiatives • If consensus cannot be reached in a reasonable time frame, then a final vote will be taken with a super majority (70% of members attending the meeting) being required to act on any issues/initiative that needs leadership. • The minutes will accurately reflect the vote of members. 34
 Empowered Team Membership and Scope of Work • Quality Management Council: Membership on the QMC consists of: • • • Eight representatives from MHSACM, two representatives from EOHHS, two representatives from DMH, two representatives from Mass. Health, two representatives DPH/BSAS, two representatives of consumers, family members, and/or advocates and two at large members will be selected and empowered to represent stakeholders. A MHSACM Senior Administrator will serve as the Chair of the QMC to facilitate the business activities of the Council. A consultation team member will serve as facilitator consultant to the QMC. Guides the project and is charged with ensuring data element development and implementation occurs 35
Empowered Team Membership and Scope of Work • Quality Management Council: Membership on the QMC consists of: • • • Eight representatives from MHSACM, two representatives from EOHHS, two representatives from DMH, two representatives from Mass. Health, two representatives DPH/BSAS, two representatives of consumers, family members, and/or advocates and two at large members will be selected and empowered to represent stakeholders. A MHSACM Senior Administrator will serve as the Chair of the QMC to facilitate the business activities of the Council. A consultation team member will serve as facilitator consultant to the QMC. Guides the project and is charged with ensuring data element development and implementation occurs 35
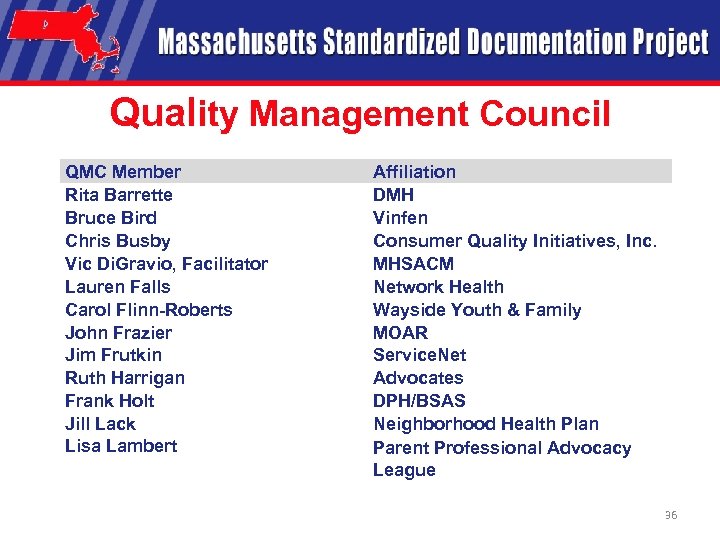 Quality Management Council QMC Member Rita Barrette Bruce Bird Chris Busby Vic Di. Gravio, Facilitator Lauren Falls Carol Flinn-Roberts John Frazier Jim Frutkin Ruth Harrigan Frank Holt Jill Lack Lisa Lambert Affiliation DMH Vinfen Consumer Quality Initiatives, Inc. MHSACM Network Health Wayside Youth & Family MOAR Service. Net Advocates DPH/BSAS Neighborhood Health Plan Parent Professional Advocacy League 36
Quality Management Council QMC Member Rita Barrette Bruce Bird Chris Busby Vic Di. Gravio, Facilitator Lauren Falls Carol Flinn-Roberts John Frazier Jim Frutkin Ruth Harrigan Frank Holt Jill Lack Lisa Lambert Affiliation DMH Vinfen Consumer Quality Initiatives, Inc. MHSACM Network Health Wayside Youth & Family MOAR Service. Net Advocates DPH/BSAS Neighborhood Health Plan Parent Professional Advocacy League 36
 Quality Management Council (Cont’d) QMC Member Pat Lawrence Marsha Medalie Jackie Moore Daniel Mumbauer Divya Narayan John Nestor Kevin Norton Paul O'Shea Elizabeth Ross-Wong Susan Schneider Ronnie Springer Scott Taberner Kathy Wilson Affiliation NAMI MA/Family Member/Advocate Riverside Community Care North Suffolk Mental Health High Point Treatment Center EOHHS Amesbury Psychological Center CAB Health & Recovery Health & Education Services, Inc. BMC Health. Net Plan Member of MOAR Bay Cove Human Services MBHP Behavioral Health Network 37
Quality Management Council (Cont’d) QMC Member Pat Lawrence Marsha Medalie Jackie Moore Daniel Mumbauer Divya Narayan John Nestor Kevin Norton Paul O'Shea Elizabeth Ross-Wong Susan Schneider Ronnie Springer Scott Taberner Kathy Wilson Affiliation NAMI MA/Family Member/Advocate Riverside Community Care North Suffolk Mental Health High Point Treatment Center EOHHS Amesbury Psychological Center CAB Health & Recovery Health & Education Services, Inc. BMC Health. Net Plan Member of MOAR Bay Cove Human Services MBHP Behavioral Health Network 37
 Empowered Team Membership and Scope of Work • Compliance Review Team: Membership on the CRT consists of fourteen members and be comprised of representatives each from: • • MHSACM, EOHHS, DMH, Mass. Health, DPH/BSAS, MMCOs and MBHP who have experience and expertise with HIPAA, CMS Corporate Compliance, state and federal standards, and JCAHO, CARF and COA Accreditation compliance. The CRT will be required to provide a full review all data element recommendations developed by the Project Teams to confirm full compliance with all HIPAA, CMS Corporate Compliance, state/federal requirements and Accreditation standards. 38
Empowered Team Membership and Scope of Work • Compliance Review Team: Membership on the CRT consists of fourteen members and be comprised of representatives each from: • • MHSACM, EOHHS, DMH, Mass. Health, DPH/BSAS, MMCOs and MBHP who have experience and expertise with HIPAA, CMS Corporate Compliance, state and federal standards, and JCAHO, CARF and COA Accreditation compliance. The CRT will be required to provide a full review all data element recommendations developed by the Project Teams to confirm full compliance with all HIPAA, CMS Corporate Compliance, state/federal requirements and Accreditation standards. 38
 Compliance Review Team CRT Member Paul Acford Grace Beason Madeline Becker Judith Boardman Craig Gaudette Jim Haughey Jane Eckert Kathy Janssen, Facilitator Carol Kress Fran Markle Marcy Morgenbesser Christine Paschal Michele Savage Michael Wagner Affiliation Beacon Health Department of Mental Health Vinfen Health & Education Services, Inc. Advocates Behavioral Health Network MSPCC Riverside Community Care MBHP High Point Treatment Center Network Health Wayside Youth & Family Bay Cove Human Services North Suffolk Mental Health 39
Compliance Review Team CRT Member Paul Acford Grace Beason Madeline Becker Judith Boardman Craig Gaudette Jim Haughey Jane Eckert Kathy Janssen, Facilitator Carol Kress Fran Markle Marcy Morgenbesser Christine Paschal Michele Savage Michael Wagner Affiliation Beacon Health Department of Mental Health Vinfen Health & Education Services, Inc. Advocates Behavioral Health Network MSPCC Riverside Community Care MBHP High Point Treatment Center Network Health Wayside Youth & Family Bay Cove Human Services North Suffolk Mental Health 39
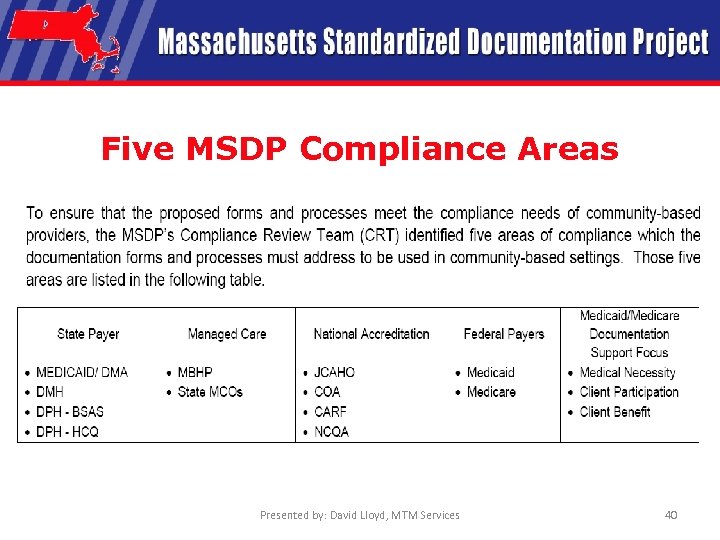 Five MSDP Compliance Areas Presented by: David Lloyd, MTM Services 40
Five MSDP Compliance Areas Presented by: David Lloyd, MTM Services 40
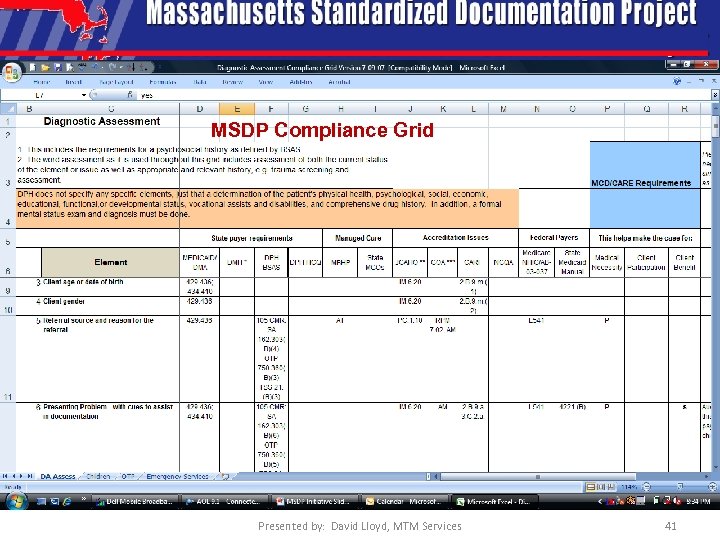 MSDP Compliance Grid Presented by: David Lloyd, MTM Services 41
MSDP Compliance Grid Presented by: David Lloyd, MTM Services 41
 Empowered Team Membership and Scope of Work • Standardized Documentation Team: Membership on the SDT consists of fourteen members comprised of representatives each from: • • MHSACM, EOHHS, DMH, Mass. Health, DPH/BSAS, MMCOs and MBHP who have experience and expertise with clinical documentation for all levels of MH/SA services contained in the scope of work The SDT will develop new documentation models, protocols and processes, pilot the newly developed models, send recommendations to the CRT for compliance review and submit reviewed recommendations to the QMC for approval and implementation. 42
Empowered Team Membership and Scope of Work • Standardized Documentation Team: Membership on the SDT consists of fourteen members comprised of representatives each from: • • MHSACM, EOHHS, DMH, Mass. Health, DPH/BSAS, MMCOs and MBHP who have experience and expertise with clinical documentation for all levels of MH/SA services contained in the scope of work The SDT will develop new documentation models, protocols and processes, pilot the newly developed models, send recommendations to the CRT for compliance review and submit reviewed recommendations to the QMC for approval and implementation. 42
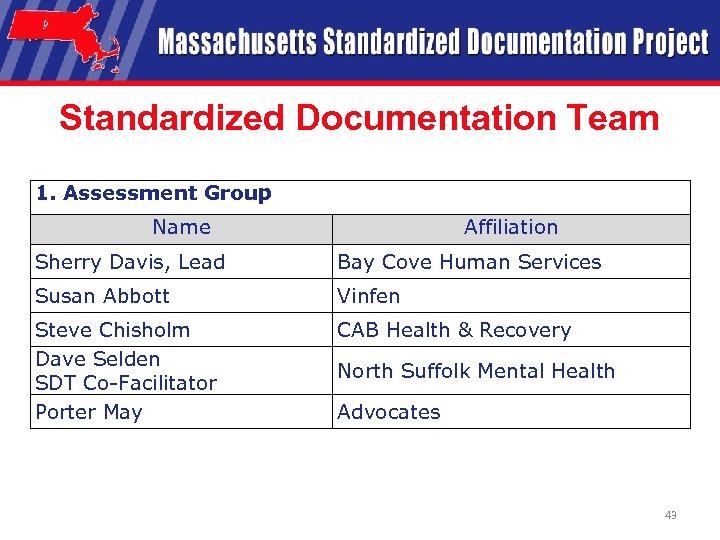 Standardized Documentation Team 1. Assessment Group Name Affiliation Sherry Davis, Lead Bay Cove Human Services Susan Abbott Vinfen Steve Chisholm Dave Selden SDT Co-Facilitator Porter May CAB Health & Recovery North Suffolk Mental Health Advocates 43
Standardized Documentation Team 1. Assessment Group Name Affiliation Sherry Davis, Lead Bay Cove Human Services Susan Abbott Vinfen Steve Chisholm Dave Selden SDT Co-Facilitator Porter May CAB Health & Recovery North Suffolk Mental Health Advocates 43
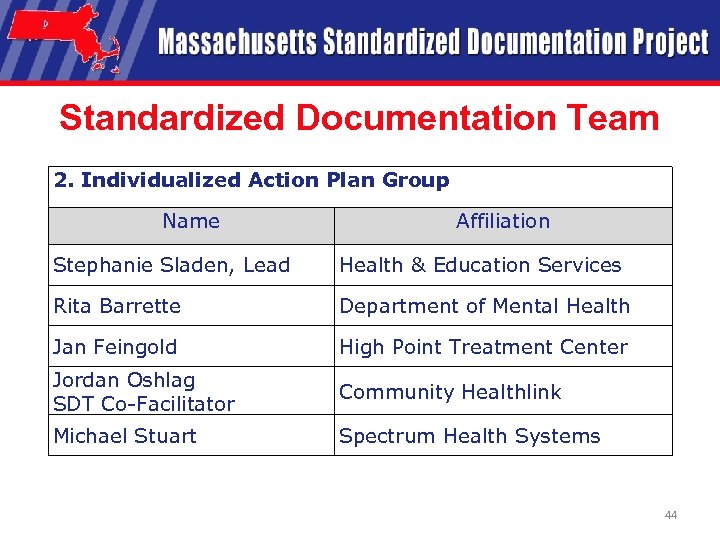 Standardized Documentation Team 2. Individualized Action Plan Group Name Affiliation Stephanie Sladen, Lead Health & Education Services Rita Barrette Department of Mental Health Jan Feingold High Point Treatment Center Jordan Oshlag SDT Co-Facilitator Community Healthlink Michael Stuart Spectrum Health Systems 44
Standardized Documentation Team 2. Individualized Action Plan Group Name Affiliation Stephanie Sladen, Lead Health & Education Services Rita Barrette Department of Mental Health Jan Feingold High Point Treatment Center Jordan Oshlag SDT Co-Facilitator Community Healthlink Michael Stuart Spectrum Health Systems 44
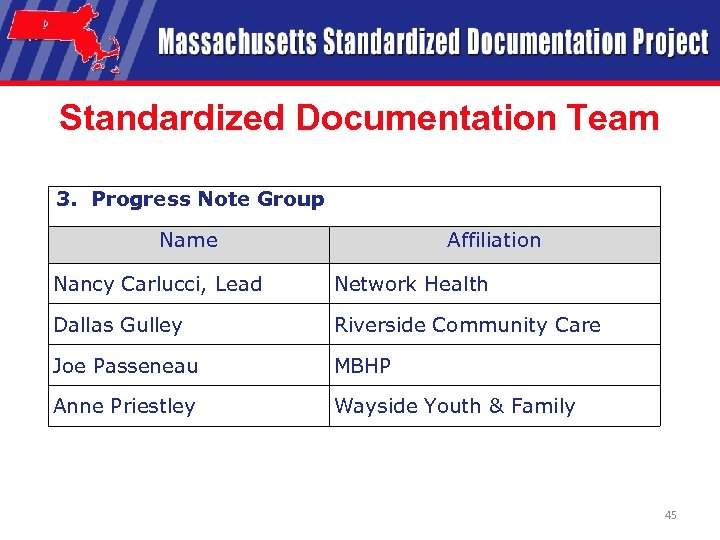 Standardized Documentation Team 3. Progress Note Group Name Affiliation Nancy Carlucci, Lead Network Health Dallas Gulley Riverside Community Care Joe Passeneau MBHP Anne Priestley Wayside Youth & Family 45
Standardized Documentation Team 3. Progress Note Group Name Affiliation Nancy Carlucci, Lead Network Health Dallas Gulley Riverside Community Care Joe Passeneau MBHP Anne Priestley Wayside Youth & Family 45
 Empowered Team Membership and Scope of Work • Consumers, Families, and Advocates Advisory Committee: Membership on CFAAC consists of ten representatives from statewide consumer and advocacy agencies/groups/individuals. • CFAAC is to provide feedback to the SDT regarding documentation needs of consumers/families and review all documentation processes developed by SDT prior to piloting. 46
Empowered Team Membership and Scope of Work • Consumers, Families, and Advocates Advisory Committee: Membership on CFAAC consists of ten representatives from statewide consumer and advocacy agencies/groups/individuals. • CFAAC is to provide feedback to the SDT regarding documentation needs of consumers/families and review all documentation processes developed by SDT prior to piloting. 46
 CFAAC Membership CFAAC Member Affiliation Karl Ackerman Transcom Chris Busby Consumer Quality Initiatives, Inc. Deborah Delman Transformation Center Maryanne Frangules MOAR Project Coordinator John Frazier MOAR Phil Hadley NAMI Massachusetts Lisa Halpern Vinfen Pat Lawrence NAMI MA/Family Member/Advocate Susan Schneider, Facilitator Member of MOAR Judith Siggins Learn to Cope 47
CFAAC Membership CFAAC Member Affiliation Karl Ackerman Transcom Chris Busby Consumer Quality Initiatives, Inc. Deborah Delman Transformation Center Maryanne Frangules MOAR Project Coordinator John Frazier MOAR Phil Hadley NAMI Massachusetts Lisa Halpern Vinfen Pat Lawrence NAMI MA/Family Member/Advocate Susan Schneider, Facilitator Member of MOAR Judith Siggins Learn to Cope 47
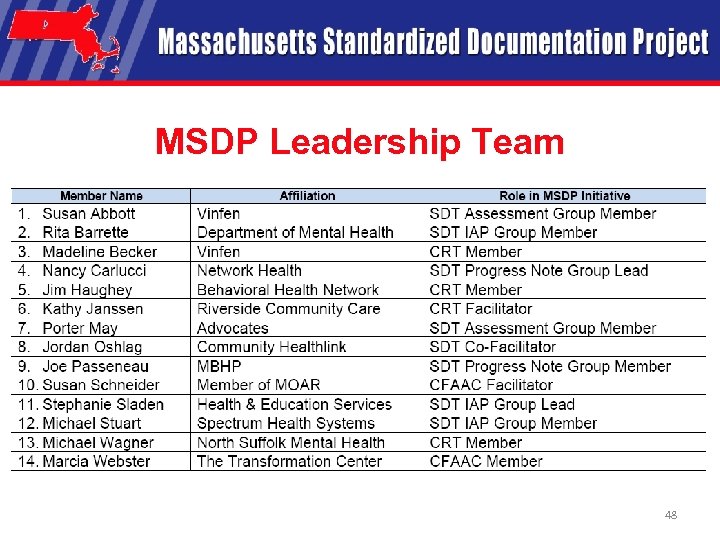 MSDP Leadership Team 48
MSDP Leadership Team 48
 Break
Break
 MSDP Training Manual, Resources and User Website Presented by: Stephanie Sladen MSDP Leadership Team David Lloyd, President M. T. M. Services
MSDP Training Manual, Resources and User Website Presented by: Stephanie Sladen MSDP Leadership Team David Lloyd, President M. T. M. Services
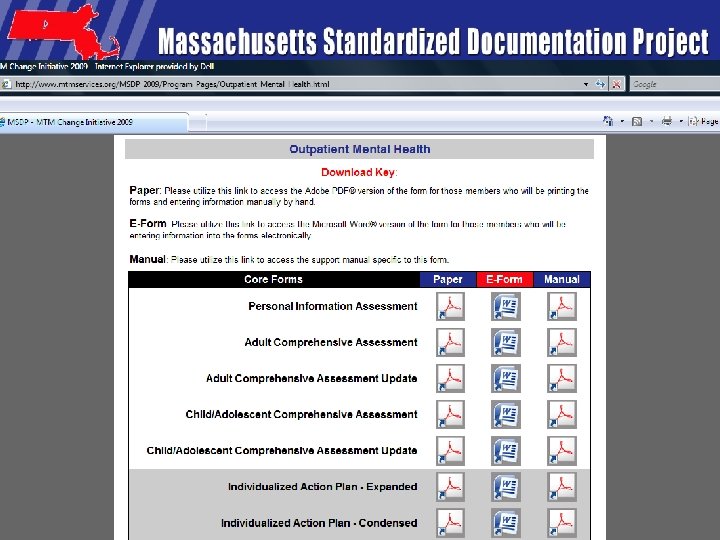
 Access to Forms/Manuals • Each Provider Program will be provided all of the following files electronically via the MSDP Website: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. MSDP User Training Manual Electronic Version of each MSDP Form type PDF Version of each MSDP Form Type MSDP Compliance Grids MSDP Training Power. Point Slides 51
Access to Forms/Manuals • Each Provider Program will be provided all of the following files electronically via the MSDP Website: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. MSDP User Training Manual Electronic Version of each MSDP Form type PDF Version of each MSDP Form Type MSDP Compliance Grids MSDP Training Power. Point Slides 51
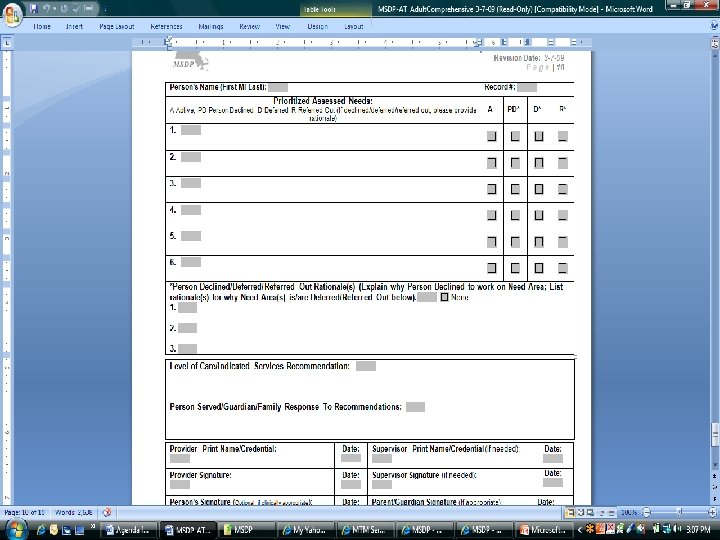
 MSDP User Training Manual • • • Section 1: Simplifying and Standardizing the Mental Health/Substance Abuse Treatment Process. Contains background information about the MSDP effort, the forms development process, and the benefits MSDP documentation processes provide. Also, this section provides specific information regarding Medical Necessity, payer, signature and compliance requirements and a discussion of a person-centered Recovery/ Resiliency approach to services. Section 2: Using the MSDP Assessment Group Documentation Processes/Forms. This section provides a sample of each Assessment form type, guidelines for the use of each form, and instructions for completion of the forms, including definitions for each data field. Section 3: Using the MSDP Individualized Action Plan (IAP) Group Documentation Processes/Forms. This section provides a sample of each Action Plan Group form type, guidelines for the use of each form, and instructions for completion of the forms, including definitions for each data field. Section 4: Using the MSDP Progress Note Group Documentation Processes/Forms. This section provides a sample of each Progress Note form type, guidelines for the use of each form, and instructions for completion of the forms, including definitions for each data field. Section 5: Appendix This section contains supporting reference information. 52
MSDP User Training Manual • • • Section 1: Simplifying and Standardizing the Mental Health/Substance Abuse Treatment Process. Contains background information about the MSDP effort, the forms development process, and the benefits MSDP documentation processes provide. Also, this section provides specific information regarding Medical Necessity, payer, signature and compliance requirements and a discussion of a person-centered Recovery/ Resiliency approach to services. Section 2: Using the MSDP Assessment Group Documentation Processes/Forms. This section provides a sample of each Assessment form type, guidelines for the use of each form, and instructions for completion of the forms, including definitions for each data field. Section 3: Using the MSDP Individualized Action Plan (IAP) Group Documentation Processes/Forms. This section provides a sample of each Action Plan Group form type, guidelines for the use of each form, and instructions for completion of the forms, including definitions for each data field. Section 4: Using the MSDP Progress Note Group Documentation Processes/Forms. This section provides a sample of each Progress Note form type, guidelines for the use of each form, and instructions for completion of the forms, including definitions for each data field. Section 5: Appendix This section contains supporting reference information. 52
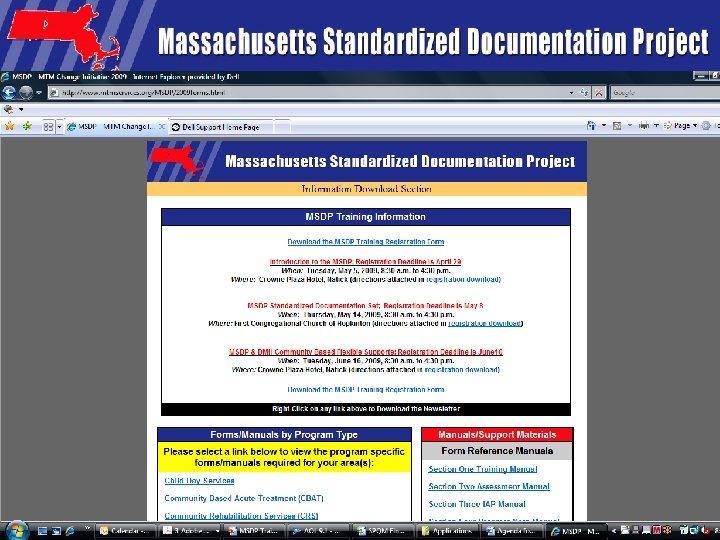
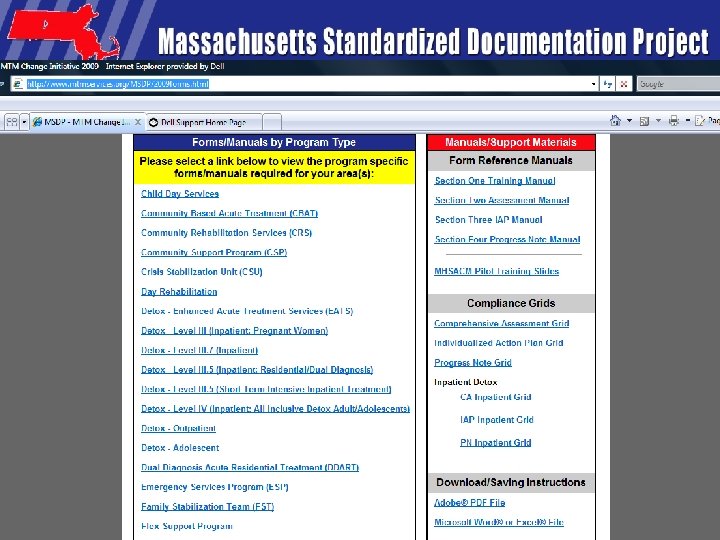
 Case Studies • Adolescent • Adult • Where located – MSDP Web site http: //www. mtmservices. org/MSDP/2009 forms. html
Case Studies • Adolescent • Adult • Where located – MSDP Web site http: //www. mtmservices. org/MSDP/2009 forms. html
 Presented by: David Lloyd, MTM Services 54
Presented by: David Lloyd, MTM Services 54
 Presented by: David Lloyd, MTM Services 55
Presented by: David Lloyd, MTM Services 55
 Presented by: David Lloyd, MTM Services 56
Presented by: David Lloyd, MTM Services 56
 57
57
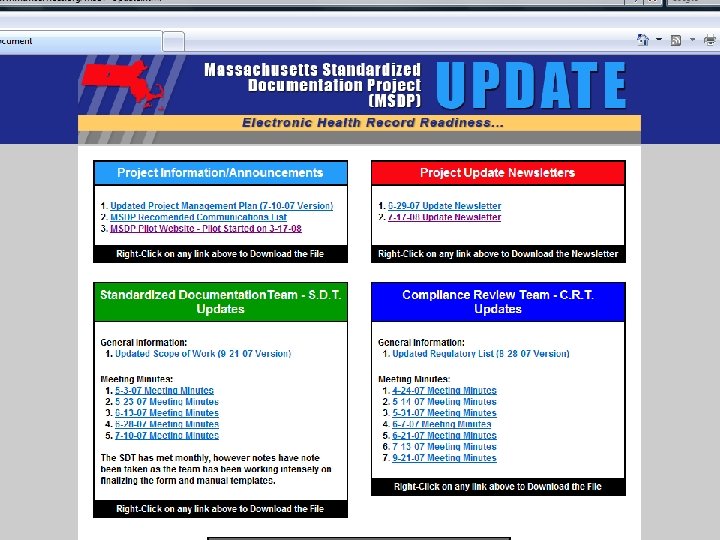
 Stakeholder Information Provided via E -Mailed UPDATES Presented by: Vic Di. Gravio and David Lloyd 58
Stakeholder Information Provided via E -Mailed UPDATES Presented by: Vic Di. Gravio and David Lloyd 58
 MSDP Forms and Manual Website • Each of the MSDP 2009 version of the paper forms, eforms and manuals can be downloaded by program type at the website: • http: //www. mtmservices. org/MSDP/2009 forms. html • MSDP UPDATE Website: http: //www. mtmservices. org/MSDP-Update. html • Technical Assistance will be provided by the MSDP Leadership Team. Email at MSDPHelp@Earthlink. net 59
MSDP Forms and Manual Website • Each of the MSDP 2009 version of the paper forms, eforms and manuals can be downloaded by program type at the website: • http: //www. mtmservices. org/MSDP/2009 forms. html • MSDP UPDATE Website: http: //www. mtmservices. org/MSDP-Update. html • Technical Assistance will be provided by the MSDP Leadership Team. Email at MSDPHelp@Earthlink. net 59
 Medical Necessity Support Documentation Linkage Capabilities Bill Schmelter Ph. D 60
Medical Necessity Support Documentation Linkage Capabilities Bill Schmelter Ph. D 60
 Medical Necessity “The type, intensity and duration of an intervention as provided by a qualified practitioner and ordered by a qualified practitioner in the current action plan is needed to prevent worsening and/or produce improvement of symptoms, behaviors and/or functioning level related to an approved diagnosis and assessed needs” 61
Medical Necessity “The type, intensity and duration of an intervention as provided by a qualified practitioner and ordered by a qualified practitioner in the current action plan is needed to prevent worsening and/or produce improvement of symptoms, behaviors and/or functioning level related to an approved diagnosis and assessed needs” 61
 Medical Necessity – Auditor View Provided Service • Appropriately Qualified Practitioner • Clinically Appropriate and Allowed Services • At appropriate Intensity and Duration As Prescribed in • Individualized Action Plan Designed to • To improve functioning, symptoms and/or behaviors or prevent their worsening Based on • An Approved Diagnosis and Assessed Needs 62
Medical Necessity – Auditor View Provided Service • Appropriately Qualified Practitioner • Clinically Appropriate and Allowed Services • At appropriate Intensity and Duration As Prescribed in • Individualized Action Plan Designed to • To improve functioning, symptoms and/or behaviors or prevent their worsening Based on • An Approved Diagnosis and Assessed Needs 62
 Documentation Linkage “The Golden Thread” Assessment Data: Diagnoses - Assessed Needs – Service Recommendations Individual Action Plan Goals Individual Action Plan Objectives Interventions and Services Progress Notes 63
Documentation Linkage “The Golden Thread” Assessment Data: Diagnoses - Assessed Needs – Service Recommendations Individual Action Plan Goals Individual Action Plan Objectives Interventions and Services Progress Notes 63
 Presented by David Lloyd, MSDP Project Manager 64
Presented by David Lloyd, MSDP Project Manager 64
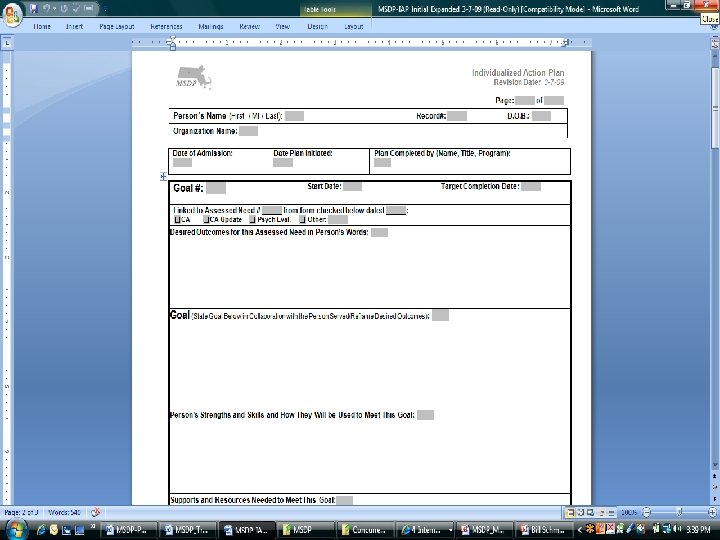 Presented by David Lloyd, MSDP Project Manager 65
Presented by David Lloyd, MSDP Project Manager 65
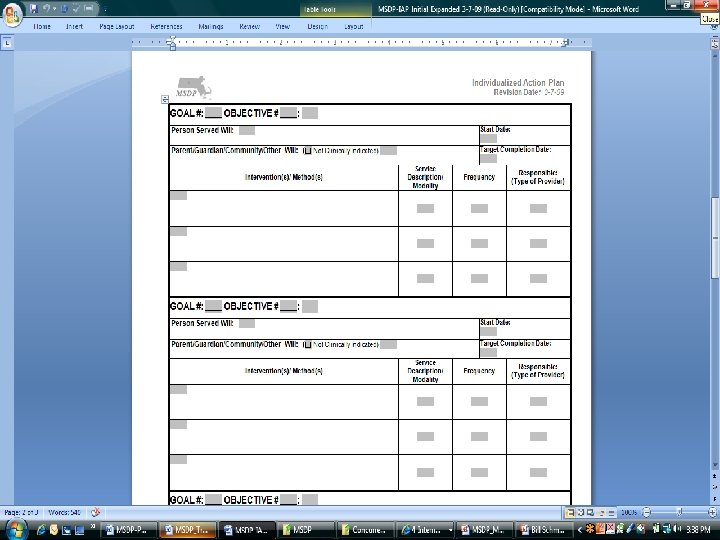 Presented by David Lloyd, MSDP Project Manager 66
Presented by David Lloyd, MSDP Project Manager 66
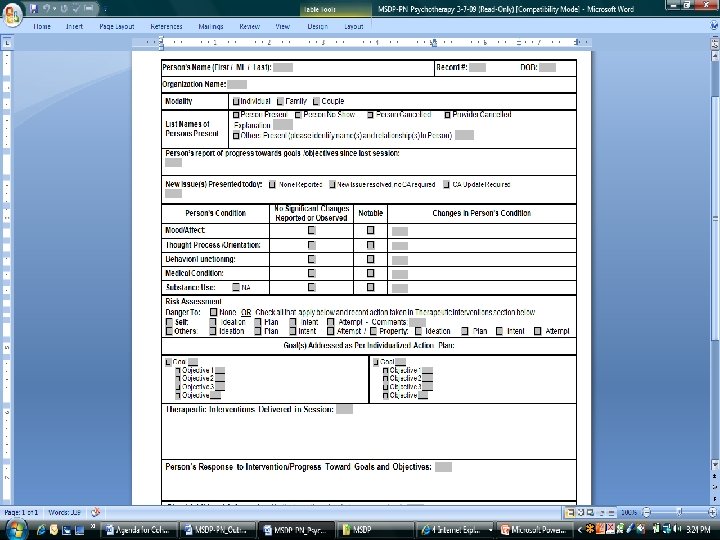 Presented by David Lloyd, MSDP Project Manager 67
Presented by David Lloyd, MSDP Project Manager 67
 MSDP Implementation Strategies Presented by: David Lloyd, President M. T. M. Services
MSDP Implementation Strategies Presented by: David Lloyd, President M. T. M. Services
 The Change Rules Have Changed… • Behavioral healthcare community providers are facing an increased emphasis on delivering services that support rehabilitation/recovery, outcome based quality services, compliance, performance based funding, and change management requirements like no other time in our industry’s history. • The MSDP Documentation Process is a SOLUTION… 69
The Change Rules Have Changed… • Behavioral healthcare community providers are facing an increased emphasis on delivering services that support rehabilitation/recovery, outcome based quality services, compliance, performance based funding, and change management requirements like no other time in our industry’s history. • The MSDP Documentation Process is a SOLUTION… 69
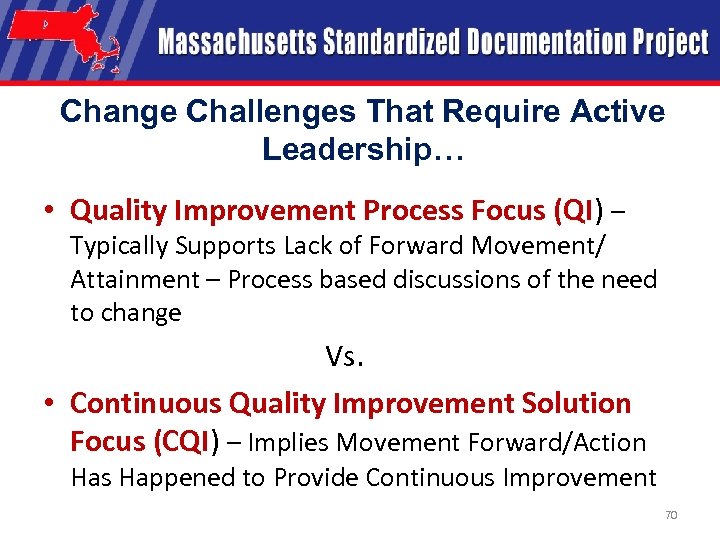 Change Challenges That Require Active Leadership… • Quality Improvement Process Focus (QI) – Typically Supports Lack of Forward Movement/ Attainment – Process based discussions of the need to change Vs. • Continuous Quality Improvement Solution Focus (CQI) – Implies Movement Forward/Action Has Happened to Provide Continuous Improvement 70
Change Challenges That Require Active Leadership… • Quality Improvement Process Focus (QI) – Typically Supports Lack of Forward Movement/ Attainment – Process based discussions of the need to change Vs. • Continuous Quality Improvement Solution Focus (CQI) – Implies Movement Forward/Action Has Happened to Provide Continuous Improvement 70
 Key CQI Pre-Implementation Evaluation Areas 1. 2. 3. 4. How many styles/processes of Diagnostic Assessments, Service/Action Plans, Progress Notes, etc. are currently being used by staff in the Organization? What is the level of “ownership” in the current processes/documentation models? Emotional response level from staff when faced with change needs Willingness/support of Senior Managers to move forward 71
Key CQI Pre-Implementation Evaluation Areas 1. 2. 3. 4. How many styles/processes of Diagnostic Assessments, Service/Action Plans, Progress Notes, etc. are currently being used by staff in the Organization? What is the level of “ownership” in the current processes/documentation models? Emotional response level from staff when faced with change needs Willingness/support of Senior Managers to move forward 71
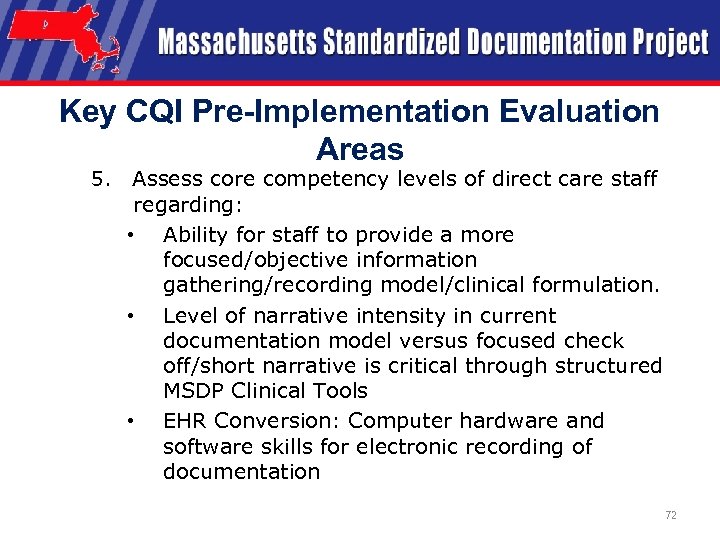 Key CQI Pre-Implementation Evaluation Areas 5. Assess core competency levels of direct care staff regarding: • Ability for staff to provide a more focused/objective information gathering/recording model/clinical formulation. • Level of narrative intensity in current documentation model versus focused check off/short narrative is critical through structured MSDP Clinical Tools • EHR Conversion: Computer hardware and software skills for electronic recording of documentation 72
Key CQI Pre-Implementation Evaluation Areas 5. Assess core competency levels of direct care staff regarding: • Ability for staff to provide a more focused/objective information gathering/recording model/clinical formulation. • Level of narrative intensity in current documentation model versus focused check off/short narrative is critical through structured MSDP Clinical Tools • EHR Conversion: Computer hardware and software skills for electronic recording of documentation 72
 Top Eight MSDP Implementation Challenges 1. Change Itself… Change is hard “We’ve always done it another way. ” “I like my way better. ” Individualized documentation perspectives and professional pride – Lack of understanding of WHY we should change – Big changes might affect competencies of some staff – Concern that the MSDP forms will not keep up with accreditation changes – – 73
Top Eight MSDP Implementation Challenges 1. Change Itself… Change is hard “We’ve always done it another way. ” “I like my way better. ” Individualized documentation perspectives and professional pride – Lack of understanding of WHY we should change – Big changes might affect competencies of some staff – Concern that the MSDP forms will not keep up with accreditation changes – – 73
 Top Eight MSDP Implementation Challenges 2. Training costs/Learning curve/Productivity issues – Initially it takes more time to use new forms – Don’t know where to find info or where to put info in the forms – New forms might alter some internal processes – Training is needed to adapt to new forms system 74
Top Eight MSDP Implementation Challenges 2. Training costs/Learning curve/Productivity issues – Initially it takes more time to use new forms – Don’t know where to find info or where to put info in the forms – New forms might alter some internal processes – Training is needed to adapt to new forms system 74
 Top Eight MSDP Implementation Challenges 3. Lack of commitment by top management – Perception that this is something we have to do, that this is being done to us, rather than looking for how it helps us. – Focus on rules, requirements and mandates – Lack of recognition of the changing business climate (increased scrutiny) – Focus on the perception that this will cost us money to implement, not seeing the potential for saving $$ 75
Top Eight MSDP Implementation Challenges 3. Lack of commitment by top management – Perception that this is something we have to do, that this is being done to us, rather than looking for how it helps us. – Focus on rules, requirements and mandates – Lack of recognition of the changing business climate (increased scrutiny) – Focus on the perception that this will cost us money to implement, not seeing the potential for saving $$ 75
 Top Eight MSDP Implementation Challenges 4. Forms don’t accommodate everyone’s current way of doing business – Asking clinicians to code billing strips on Progress Notes – Person Served name and # at the top of page, not the bottom – Some info on CA we’ve always put on Demographic form or Health History form, etc. – At first, clinical staff disagreed with the CA 76
Top Eight MSDP Implementation Challenges 4. Forms don’t accommodate everyone’s current way of doing business – Asking clinicians to code billing strips on Progress Notes – Person Served name and # at the top of page, not the bottom – Some info on CA we’ve always put on Demographic form or Health History form, etc. – At first, clinical staff disagreed with the CA 76
 Top Eight MSDP Implementation Challenges 5. New processes – Lack of understanding of important linkages necessary in the documentation – A CA Update and IAP Review/Revision processes are not understood – Lack of recognition that new forms will require some processes to be changed or reinvented – Need to look at whole system of documentation rather than just pieces and focus on integration of services and documentation 77
Top Eight MSDP Implementation Challenges 5. New processes – Lack of understanding of important linkages necessary in the documentation – A CA Update and IAP Review/Revision processes are not understood – Lack of recognition that new forms will require some processes to be changed or reinvented – Need to look at whole system of documentation rather than just pieces and focus on integration of services and documentation 77
 Top Eight MSDP Implementation Challenges 6. Technology issues – Investments in current systems – Costs to make changes in current systems – Forms don’t accommodate our existing business model; need to be integrated into how we do business 78
Top Eight MSDP Implementation Challenges 6. Technology issues – Investments in current systems – Costs to make changes in current systems – Forms don’t accommodate our existing business model; need to be integrated into how we do business 78
 Top Eight MSDP Implementation Challenges 7. Issues with the forms themselves – – Not enough space to write on the forms No lines in the text boxes We can’t change the forms They are not in our local software which I know and love (They are in WORD!) 79
Top Eight MSDP Implementation Challenges 7. Issues with the forms themselves – – Not enough space to write on the forms No lines in the text boxes We can’t change the forms They are not in our local software which I know and love (They are in WORD!) 79
 Top Eight MSDP Implementation Challenges 8. Incorporating a recovery culture – Shifting from a culture of doing for clients to a culture of empowering persons served – Lack of understanding what recovery/ resiliency is – Lack of understanding the Medicaid rehabilitation option 80
Top Eight MSDP Implementation Challenges 8. Incorporating a recovery culture – Shifting from a culture of doing for clients to a culture of empowering persons served – Lack of understanding what recovery/ resiliency is – Lack of understanding the Medicaid rehabilitation option 80
 Acceptance Levels of Change Process • Keep in mind the stages of acceptance of change staff typically go through with this process: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Denial Negotiation Anger (Blaming) Drop Out Acceptance of the need to change 81
Acceptance Levels of Change Process • Keep in mind the stages of acceptance of change staff typically go through with this process: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Denial Negotiation Anger (Blaming) Drop Out Acceptance of the need to change 81
 Key Challenges To Address before Implementation of MSDP Forms Begins 1. 2. 3. The trainer needs to believe in the MSDP documentation process and come across to the staff that way – Select Trainers that really believe MSDP process is a positive change. Be aware of individualized documentation perspectives and professional pride Be aware big change may affect the competency of some staff – Plan ahead to provide core competency training (i. e. , Motivational Interviewing, Objective Recording Using Structured Form Process, etc. ) 82
Key Challenges To Address before Implementation of MSDP Forms Begins 1. 2. 3. The trainer needs to believe in the MSDP documentation process and come across to the staff that way – Select Trainers that really believe MSDP process is a positive change. Be aware of individualized documentation perspectives and professional pride Be aware big change may affect the competency of some staff – Plan ahead to provide core competency training (i. e. , Motivational Interviewing, Objective Recording Using Structured Form Process, etc. ) 82
 Key Challenges To Address before Implementation of MSDP Begins 4. 5. 6. Change is hard for some to accept – may need to provide an enhanced Coaching/Mentoring Supervision Model during implementation Management of an agency needs to feel confident and support the documentation processes if the agency is going to implement– need buy in of top management Initially will need to do a closer review of quality of notes and clinical forms 83
Key Challenges To Address before Implementation of MSDP Begins 4. 5. 6. Change is hard for some to accept – may need to provide an enhanced Coaching/Mentoring Supervision Model during implementation Management of an agency needs to feel confident and support the documentation processes if the agency is going to implement– need buy in of top management Initially will need to do a closer review of quality of notes and clinical forms 83
 Some Identified Solution Focus Areas to Assist Focus on MSDP Forms are a “Tool not a rule”. As a tool it can address compliance and audit concerns. 2. Focus on what MSDP documentation can do FOR staff instead of what it will do TO staff. Look for the potential benefits. Talk about the benefits. Continue to remind staff that MSDP documentation: 1. – Meets all three national accreditation standards (JCAHO, CARF and COA) – Provides available documentation solution without having to develop local form design efforts – Prepares us to move towards electronic medical records 3. Senior management/leadership need to be visibly proactive about the MSDP forms. Communicate, communicate, communicate. Share “learnings”, “aha’s” and success stories 84
Some Identified Solution Focus Areas to Assist Focus on MSDP Forms are a “Tool not a rule”. As a tool it can address compliance and audit concerns. 2. Focus on what MSDP documentation can do FOR staff instead of what it will do TO staff. Look for the potential benefits. Talk about the benefits. Continue to remind staff that MSDP documentation: 1. – Meets all three national accreditation standards (JCAHO, CARF and COA) – Provides available documentation solution without having to develop local form design efforts – Prepares us to move towards electronic medical records 3. Senior management/leadership need to be visibly proactive about the MSDP forms. Communicate, communicate, communicate. Share “learnings”, “aha’s” and success stories 84
 Some Identified Solution Focus Areas to Assist in Implementation of MSDP Forms 4. 5. 6. Be proactive about training and re-training needs (i. e. , schedule additional core competency support). Provide coaching sessions on documentation. Develop and provide to staff a written implementation plan including a change management strategy. Whether you decide to implement one form at a time or a group of forms (i. e. Progress notes), or all the forms at once, be planful about the approach. Provide training and support. Develop post implementation monitoring and coaching plans. Tie monitoring to CQI efforts. 85
Some Identified Solution Focus Areas to Assist in Implementation of MSDP Forms 4. 5. 6. Be proactive about training and re-training needs (i. e. , schedule additional core competency support). Provide coaching sessions on documentation. Develop and provide to staff a written implementation plan including a change management strategy. Whether you decide to implement one form at a time or a group of forms (i. e. Progress notes), or all the forms at once, be planful about the approach. Provide training and support. Develop post implementation monitoring and coaching plans. Tie monitoring to CQI efforts. 85
 Some Identified Solution Focus Areas to Assist in Implementation of MSDP Forms 7. 8. 9. With staff, look at processes that could be improved and how the transition to MSDP forms can help improve them. View MSDP implementation as an opportunity to take a look at the things that are problematic in your system and perhaps make changes. Use MSDP data for internal process Improvements. Try the MSDP e-forms. Talk to your software vendor about integrating the forms into your systems (Several vendors are in the process). Try each form at least 7 times and then keep track of issues, problems, suggestions for improvement. 86
Some Identified Solution Focus Areas to Assist in Implementation of MSDP Forms 7. 8. 9. With staff, look at processes that could be improved and how the transition to MSDP forms can help improve them. View MSDP implementation as an opportunity to take a look at the things that are problematic in your system and perhaps make changes. Use MSDP data for internal process Improvements. Try the MSDP e-forms. Talk to your software vendor about integrating the forms into your systems (Several vendors are in the process). Try each form at least 7 times and then keep track of issues, problems, suggestions for improvement. 86
 Implementation Timeframes and Supports • Establish a completion date before the initiative begins. • Develop a full implementation plan with action work plans to ensure operational readiness. • Recommend a pre-announced evaluation process to ensure all feedback regarding implementation process is given consideration 87
Implementation Timeframes and Supports • Establish a completion date before the initiative begins. • Develop a full implementation plan with action work plans to ensure operational readiness. • Recommend a pre-announced evaluation process to ensure all feedback regarding implementation process is given consideration 87
 MSDP 88
MSDP 88
 89
89
 Lunch • Questions on Index Cards
Lunch • Questions on Index Cards
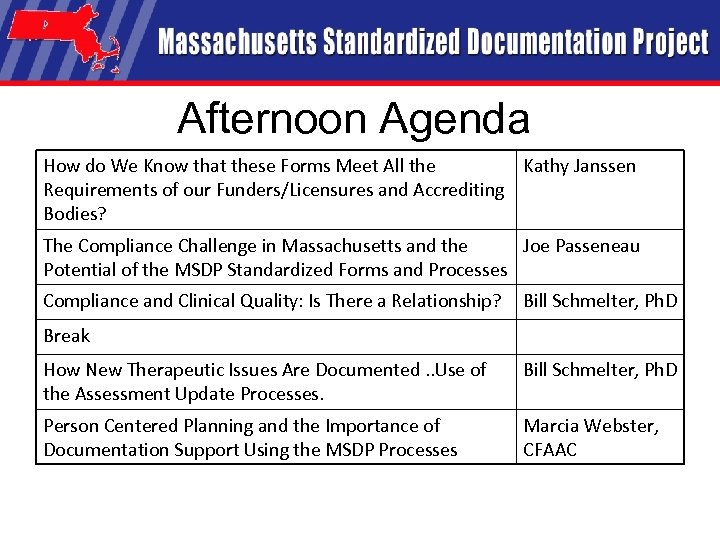 Afternoon Agenda How do We Know that these Forms Meet All the Kathy Janssen Requirements of our Funders/Licensures and Accrediting Bodies? The Compliance Challenge in Massachusetts and the Joe Passeneau Potential of the MSDP Standardized Forms and Processes Compliance and Clinical Quality: Is There a Relationship? Bill Schmelter, Ph. D Break How New Therapeutic Issues Are Documented. . Use of the Assessment Update Processes. Bill Schmelter, Ph. D Person Centered Planning and the Importance of Documentation Support Using the MSDP Processes Marcia Webster, CFAAC
Afternoon Agenda How do We Know that these Forms Meet All the Kathy Janssen Requirements of our Funders/Licensures and Accrediting Bodies? The Compliance Challenge in Massachusetts and the Joe Passeneau Potential of the MSDP Standardized Forms and Processes Compliance and Clinical Quality: Is There a Relationship? Bill Schmelter, Ph. D Break How New Therapeutic Issues Are Documented. . Use of the Assessment Update Processes. Bill Schmelter, Ph. D Person Centered Planning and the Importance of Documentation Support Using the MSDP Processes Marcia Webster, CFAAC
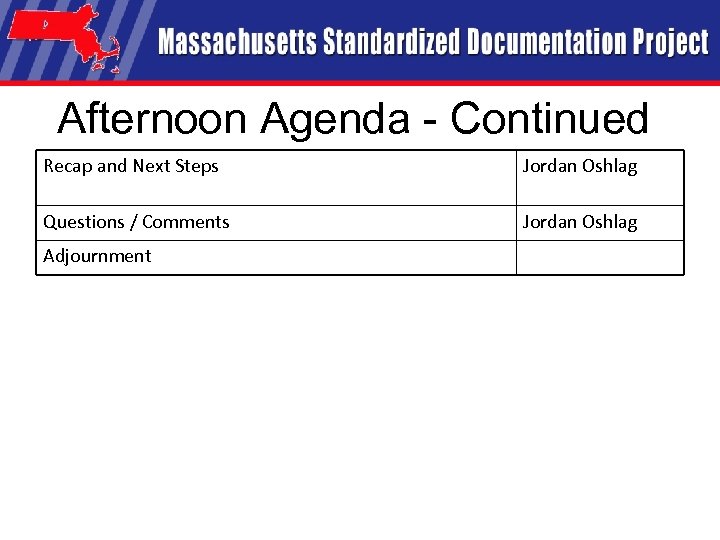 Afternoon Agenda - Continued Recap and Next Steps Jordan Oshlag Questions / Comments Jordan Oshlag Adjournment
Afternoon Agenda - Continued Recap and Next Steps Jordan Oshlag Questions / Comments Jordan Oshlag Adjournment
 How do We Know that these Forms Meet All the Requirements of our Funders/Licensures and Accrediting Bodies? Presenter: Kathleen Janssen, BSN, RN, MS, Director of Quality Management, Riverside Community Care
How do We Know that these Forms Meet All the Requirements of our Funders/Licensures and Accrediting Bodies? Presenter: Kathleen Janssen, BSN, RN, MS, Director of Quality Management, Riverside Community Care
 Compliance Review Team Beason, Grace Department of Mental Health Becker, Madeline Vinfen Boardman, Judith Health & Education Services, Inc. Gaudette, Craig Advocates Haughey, Jim Behavioral Health Network Eckert, Jane MSPCC Janssen, Kathy Riverside Community Care Kress, Carol MBHP Markle, Fran High Point Treatment Center Morgenbesser, Marcy. Network Health Paschal, Christine Wayside Youth & Family Savage, Michele Baycove Human Services Thompson, Doug Beacon Health Wagner, Michael North Suffolk Mental Health 94
Compliance Review Team Beason, Grace Department of Mental Health Becker, Madeline Vinfen Boardman, Judith Health & Education Services, Inc. Gaudette, Craig Advocates Haughey, Jim Behavioral Health Network Eckert, Jane MSPCC Janssen, Kathy Riverside Community Care Kress, Carol MBHP Markle, Fran High Point Treatment Center Morgenbesser, Marcy. Network Health Paschal, Christine Wayside Youth & Family Savage, Michele Baycove Human Services Thompson, Doug Beacon Health Wagner, Michael North Suffolk Mental Health 94
 List of Programs in MSDP Child Day Services Community Based Acute Treatment (CBAT) Community Rehabilitation Services (CRS) Community Support Program (CSP) Crisis Stabilization Unity (CSU) Day Rehabilitation Detox – Enhanced Acute Treatment Services (EATS) Detox – Level III (Inpatient: Pregnant Women) Detox – Level III. 7 (Inpatient) Detox – Level III. 5 (Inpatient: Residential/Dual Diagnosis) Detox – Level III. 5 (Short Term Intensive Inpatient Treatment) Detox – Level IV (Inpatient: All Inclusive Detox Adult/Adolescents) 95
List of Programs in MSDP Child Day Services Community Based Acute Treatment (CBAT) Community Rehabilitation Services (CRS) Community Support Program (CSP) Crisis Stabilization Unity (CSU) Day Rehabilitation Detox – Enhanced Acute Treatment Services (EATS) Detox – Level III (Inpatient: Pregnant Women) Detox – Level III. 7 (Inpatient) Detox – Level III. 5 (Inpatient: Residential/Dual Diagnosis) Detox – Level III. 5 (Short Term Intensive Inpatient Treatment) Detox – Level IV (Inpatient: All Inclusive Detox Adult/Adolescents) 95
 List of Programs in MSDP (con’t) Detox – Outpatient Detox – Adolescent Dual Diagnosis Acute Residential Treatment (DDART) Emergency Service Program (ESP) Family Stabilization Team (FST) Flex Support Program Intensive Outpatient Program – Substance Abuse (IOP) Intensive Residential Treatment Program Intensive Community Based Acute Treatment (ICBAT) Opiate Treatment Program Outpatient Mental Health Outpatient Substance Use Disorder 96
List of Programs in MSDP (con’t) Detox – Outpatient Detox – Adolescent Dual Diagnosis Acute Residential Treatment (DDART) Emergency Service Program (ESP) Family Stabilization Team (FST) Flex Support Program Intensive Outpatient Program – Substance Abuse (IOP) Intensive Residential Treatment Program Intensive Community Based Acute Treatment (ICBAT) Opiate Treatment Program Outpatient Mental Health Outpatient Substance Use Disorder 96
 List of Programs in MSDP (con’t) Partial Hospitalization Program (PHP) Program of Assertive Community Treatment (PACT) Psychiatric Day Treatment Rehabilitative Treatment in the Community (RTC) Residential Services – Adult DMH Residential Services – Adult DPH Residential Services – Child/Adolescent DMH Residential Services – Child/Adolescent DPH Respite Structured Outpatient Addiction Program (SOAP) Transitional Support Services (TSS) 97
List of Programs in MSDP (con’t) Partial Hospitalization Program (PHP) Program of Assertive Community Treatment (PACT) Psychiatric Day Treatment Rehabilitative Treatment in the Community (RTC) Residential Services – Adult DMH Residential Services – Adult DPH Residential Services – Child/Adolescent DMH Residential Services – Child/Adolescent DPH Respite Structured Outpatient Addiction Program (SOAP) Transitional Support Services (TSS) 97
 List of Regulators / Licensers / Accrediting Bodies - MSDP Beacon Health: • Documentation Review Tool • BHS FCHP Manual • BHS NHP Manual DHHS Regs: • DHHS Program Memo AB 03037 MH • DHHS SMD Letter Rehab Option DMA Regs: • DMA 130 CMR 429. 400: MH Center Manual • 130450 -275: Resident Regs • 130 CMR 433 -428 Docs • 130 CMR 418 -400 • 130 CMR 417: Day Tx • 130 CMR 450. 100 98
List of Regulators / Licensers / Accrediting Bodies - MSDP Beacon Health: • Documentation Review Tool • BHS FCHP Manual • BHS NHP Manual DHHS Regs: • DHHS Program Memo AB 03037 MH • DHHS SMD Letter Rehab Option DMA Regs: • DMA 130 CMR 429. 400: MH Center Manual • 130450 -275: Resident Regs • 130 CMR 433 -428 Docs • 130 CMR 418 -400 • 130 CMR 417: Day Tx • 130 CMR 450. 100 98
 List of Regulators / Licensers / Accrediting Bodies - MSDP DMH Regs: • DMH 104 CMR 28. 00 Licensing and Operations for Community Programs • 104 CMR 29. 00 Service Planning • Risk Management Policies: Informed Consent for Psychotropic Medications/ECT Therapy • Comprehensive Assessment Requirements DPH Regs: • DPH 104 CMR 27 • 105 CMR 140. 000 • 105 CMR 160 Detox • 105 CMR 161 STIIT • 105 CMR 162 SA/OT/PT • 105 CMR 750 Drug Tx Programs 99
List of Regulators / Licensers / Accrediting Bodies - MSDP DMH Regs: • DMH 104 CMR 28. 00 Licensing and Operations for Community Programs • 104 CMR 29. 00 Service Planning • Risk Management Policies: Informed Consent for Psychotropic Medications/ECT Therapy • Comprehensive Assessment Requirements DPH Regs: • DPH 104 CMR 27 • 105 CMR 140. 000 • 105 CMR 160 Detox • 105 CMR 161 STIIT • 105 CMR 162 SA/OT/PT • 105 CMR 750 Drug Tx Programs 99
 List of Regulators / Licensers / Accrediting Bodies - MSDP DMH Regs (con’t): • 105 CMR 165 Halfway House • Family Substance Abuse Shelter Guidelines • Transitional Support MBHP • MBHP Audit Tool • OT/PT Perf Specs • SOAP Documentation Requirements • CBATICBAT Performance Specs • Inpatient Acute Mental Health Performance Specs • Level 4 Detox for Co-occuring Disorders Performance Specs • Medically Monitored Detox ATS Performance Specs 100
List of Regulators / Licensers / Accrediting Bodies - MSDP DMH Regs (con’t): • 105 CMR 165 Halfway House • Family Substance Abuse Shelter Guidelines • Transitional Support MBHP • MBHP Audit Tool • OT/PT Perf Specs • SOAP Documentation Requirements • CBATICBAT Performance Specs • Inpatient Acute Mental Health Performance Specs • Level 4 Detox for Co-occuring Disorders Performance Specs • Medically Monitored Detox ATS Performance Specs 100
 List of Regulators / Licensers / Accrediting Bodies - MSDP Network Health Regs: • Network Health Chart Review Tool NHIC Regs: • NHIC (L 13492) Health Behav Ass Tx • L 3159 Diag Assess • L 3162 Psycho Pharm • L 3187 ECT • L 3203 Neuro Psy Test • L 3220 Group Tx • L 3239 Ind Tx • L 3242 Interactive Ind Tx • Article 90862 • Transmit Psychotherapy Notes • Transmit Psych Tests 101
List of Regulators / Licensers / Accrediting Bodies - MSDP Network Health Regs: • Network Health Chart Review Tool NHIC Regs: • NHIC (L 13492) Health Behav Ass Tx • L 3159 Diag Assess • L 3162 Psycho Pharm • L 3187 ECT • L 3203 Neuro Psy Test • L 3220 Group Tx • L 3239 Ind Tx • L 3242 Interactive Ind Tx • Article 90862 • Transmit Psychotherapy Notes • Transmit Psych Tests 101
 List of Regulators / Licensers / Accrediting Bodies - MSDP Federal Medicaid Regs: • Federal States Medicaid Manual 2500 A Doc • States Medicaid Manual 4221 Psych OTPT • States Medicaid Manual 4320 Clinic Federal Opiod Regs: • 42 CFR 812 Opiod Tx • 42 CFR 8. 1221 CFR 291 Opiod Tx JCAHO CARF COA NCQA 102
List of Regulators / Licensers / Accrediting Bodies - MSDP Federal Medicaid Regs: • Federal States Medicaid Manual 2500 A Doc • States Medicaid Manual 4221 Psych OTPT • States Medicaid Manual 4320 Clinic Federal Opiod Regs: • 42 CFR 812 Opiod Tx • 42 CFR 8. 1221 CFR 291 Opiod Tx JCAHO CARF COA NCQA 102
 Compliance Grids Compliance Girds SDT – Form Creation CRT – Form Review
Compliance Grids Compliance Girds SDT – Form Creation CRT – Form Review
 Compliance Reviews • MHSACM Compliance Committee
Compliance Reviews • MHSACM Compliance Committee
 The Compliance Challenge in Massachusetts and the Potential of the MSDP Standardized Forms and Processes Joseph Passeneau, Ed. M, LMHC Director of Health Record Review and Audit Massachusetts Behavioral Health Partnership 105
The Compliance Challenge in Massachusetts and the Potential of the MSDP Standardized Forms and Processes Joseph Passeneau, Ed. M, LMHC Director of Health Record Review and Audit Massachusetts Behavioral Health Partnership 105
 In 2001, MBHP Began Quality Initiative: Statewide Record Review Since then: • Over 29, 000 records reviewed; • More than 1, 900 MA site visits; • Recovered more than $950, 000. 106
In 2001, MBHP Began Quality Initiative: Statewide Record Review Since then: • Over 29, 000 records reviewed; • More than 1, 900 MA site visits; • Recovered more than $950, 000. 106
 State of Behavioral Health Records in Massachusetts : 2001 107
State of Behavioral Health Records in Massachusetts : 2001 107
 In 2001, we found isolated examples of superior documentation. Generally, however, record keeping: • • Low Priority; Poor Quality; Confusing Forms / Terminology; Multiplicity of Forms. 108
In 2001, we found isolated examples of superior documentation. Generally, however, record keeping: • • Low Priority; Poor Quality; Confusing Forms / Terminology; Multiplicity of Forms. 108
 Recovery of Payment: Administrative Issues • Missing Records / Notes; • Notes Do Not Match Paid Claims; • Exceed Authorization Parameters; • Illegible.
Recovery of Payment: Administrative Issues • Missing Records / Notes; • Notes Do Not Match Paid Claims; • Exceed Authorization Parameters; • Illegible.
 Recovery of Payment: Medical Necessity Issues As found in a record: “played tiddly-winks, he got a score of 2600, told him it was the highest I ever saw. He was happy and I was happy. Plan: return next week. ”
Recovery of Payment: Medical Necessity Issues As found in a record: “played tiddly-winks, he got a score of 2600, told him it was the highest I ever saw. He was happy and I was happy. Plan: return next week. ”
 When Clinical Forms are Not Standardized: • Labor-Intensive Form Revision Process • Staff Training • Difficulty Reconciling Payer Requirements • Existence Of Multiple Forms, Same Facility • Frustration
When Clinical Forms are Not Standardized: • Labor-Intensive Form Revision Process • Staff Training • Difficulty Reconciling Payer Requirements • Existence Of Multiple Forms, Same Facility • Frustration
 Is it an exaggeration… to say that across the state, there at least 1, 000 versions of each sheet of paper, for each form?
Is it an exaggeration… to say that across the state, there at least 1, 000 versions of each sheet of paper, for each form?
 Lack of Standardization, At What Cost? 8 most common clinical forms per OP record*: – Personal Info. Assess. (1 p) – Comp. Assessment (4 pp) – Individ. Action Plan (1 p) – Progress Note: therapy (1 p) – Progress Note: group (1 p) – MDT Review (2 pp) – Discharge Summary (1 p) – Psychopharm. Eval. (2 pp) TOTALS: *8 forms = 13 pages @ 1, 000 versions = 13, 000 pages = 26 reams = 2. 6 cases of paper 8 MSDP Forms: 1 version, 23 pages
Lack of Standardization, At What Cost? 8 most common clinical forms per OP record*: – Personal Info. Assess. (1 p) – Comp. Assessment (4 pp) – Individ. Action Plan (1 p) – Progress Note: therapy (1 p) – Progress Note: group (1 p) – MDT Review (2 pp) – Discharge Summary (1 p) – Psychopharm. Eval. (2 pp) TOTALS: *8 forms = 13 pages @ 1, 000 versions = 13, 000 pages = 26 reams = 2. 6 cases of paper 8 MSDP Forms: 1 version, 23 pages
 Advice from The Joint Commission “When the problems/need statements are well written, the development of care goals and objectives is easy. If problems/need statements are vague and unclear, the development of observable care goals and objectives is laborious or impossible. Staff attitudes about the wastefulness of documentation then become self-reinforcing. ” A Practical Guide to Documentation in Behavioral Health Care, 2 nd Edition, The Joint Commission, 2002, p. 64
Advice from The Joint Commission “When the problems/need statements are well written, the development of care goals and objectives is easy. If problems/need statements are vague and unclear, the development of observable care goals and objectives is laborious or impossible. Staff attitudes about the wastefulness of documentation then become self-reinforcing. ” A Practical Guide to Documentation in Behavioral Health Care, 2 nd Edition, The Joint Commission, 2002, p. 64
 MSDP Forms are Tools • All tools take time to learn. • They are not substitutes for professional judgment and are not perfect. • Designed to: – – – Clearly Identify Assessed Needs Decrease Confusion Fix Documentation Problems Address Risk Management Document Quality of Services
MSDP Forms are Tools • All tools take time to learn. • They are not substitutes for professional judgment and are not perfect. • Designed to: – – – Clearly Identify Assessed Needs Decrease Confusion Fix Documentation Problems Address Risk Management Document Quality of Services
 The Potential of MSDP Forms Designed to bring clarity to roles of: ØPerson Served, ØProvider, ØPayer, in the documentation of behavioral health services.
The Potential of MSDP Forms Designed to bring clarity to roles of: ØPerson Served, ØProvider, ØPayer, in the documentation of behavioral health services.
 Compliance and Clinical Quality Is There a Relationship? Bill Schmelter Ph. D 117
Compliance and Clinical Quality Is There a Relationship? Bill Schmelter Ph. D 117
 Compliance and Quality • Is Compliance Related to Quality? – Strongly – Moderately – Poorly 118
Compliance and Quality • Is Compliance Related to Quality? – Strongly – Moderately – Poorly 118
 Compliance and Quality • Is compliance effort and cost proportional to the clinical benefit? – Yes – No 119
Compliance and Quality • Is compliance effort and cost proportional to the clinical benefit? – Yes – No 119
 Compliance and Quality • Let’s throw out the paper! 120
Compliance and Quality • Let’s throw out the paper! 120
 Compliance and Quality Where is The Real “Golden” Thread? Person Centered Process Paperwork Process A. Assessing with the Person A. Completing Assessment Form B. Planning with the Person B. Completing the Service Plan C. Working with the Person C. Writing Progress Notes 121
Compliance and Quality Where is The Real “Golden” Thread? Person Centered Process Paperwork Process A. Assessing with the Person A. Completing Assessment Form B. Planning with the Person B. Completing the Service Plan C. Working with the Person C. Writing Progress Notes 121
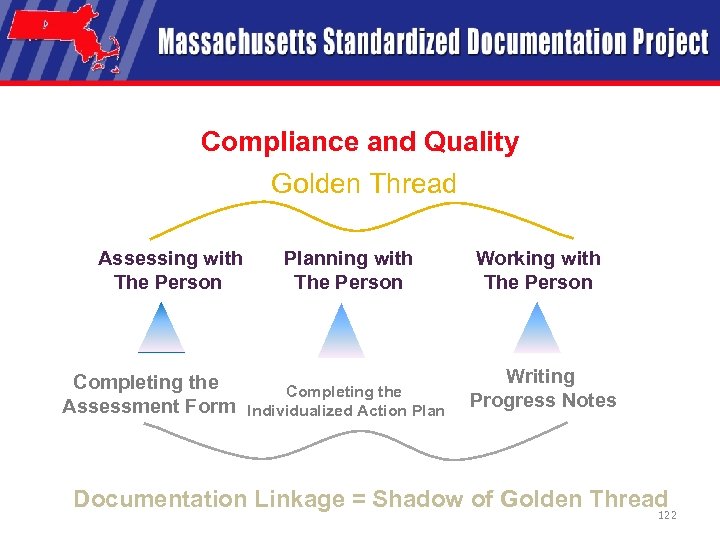 Compliance and Quality Golden Thread Assessing with The Person Completing the Assessment Form Planning with The Person Completing the Individualized Action Plan Working with The Person Writing Progress Notes Documentation Linkage = Shadow of Golden Thread 122
Compliance and Quality Golden Thread Assessing with The Person Completing the Assessment Form Planning with The Person Completing the Individualized Action Plan Working with The Person Writing Progress Notes Documentation Linkage = Shadow of Golden Thread 122
 Compliance and Quality Assumption ? ? “We do good work… We just don’t document well. ” 123
Compliance and Quality Assumption ? ? “We do good work… We just don’t document well. ” 123
 Compliance and Quality How much of the Behavioral Health System’s problem with compliance audits is due to documentation? 124
Compliance and Quality How much of the Behavioral Health System’s problem with compliance audits is due to documentation? 124
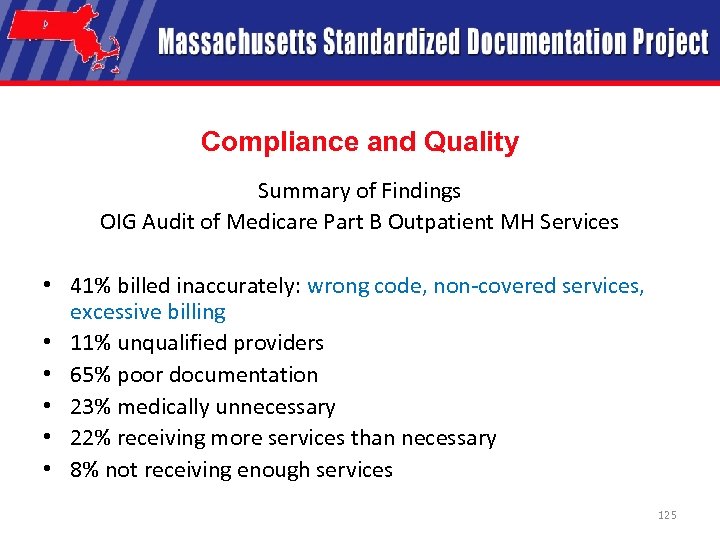 Compliance and Quality Summary of Findings OIG Audit of Medicare Part B Outpatient MH Services • 41% billed inaccurately: wrong code, non-covered services, excessive billing • 11% unqualified providers • 65% poor documentation • 23% medically unnecessary • 22% receiving more services than necessary • 8% not receiving enough services 125
Compliance and Quality Summary of Findings OIG Audit of Medicare Part B Outpatient MH Services • 41% billed inaccurately: wrong code, non-covered services, excessive billing • 11% unqualified providers • 65% poor documentation • 23% medically unnecessary • 22% receiving more services than necessary • 8% not receiving enough services 125
 Compliance and Quality Is Our Documentation Worthwhile? Worthwhile Documentation Models Should Support: • Quality – Person Centered Services and Positive Outcomes • Compliance • Efficiency 126
Compliance and Quality Is Our Documentation Worthwhile? Worthwhile Documentation Models Should Support: • Quality – Person Centered Services and Positive Outcomes • Compliance • Efficiency 126
 Compliance and Quality If our documentation was Worthwhile we would not resent doing it! 127
Compliance and Quality If our documentation was Worthwhile we would not resent doing it! 127
 Compliance and Quality Do we miss the point? Examples: • Strengths of person served • Relationship between assessment information, planned services and services provided • Misplaced person centeredness 128
Compliance and Quality Do we miss the point? Examples: • Strengths of person served • Relationship between assessment information, planned services and services provided • Misplaced person centeredness 128
 Compliance and Quality • Documentation should just be an accurate account of what we do • The goal is effective and compliant interventions (positive outcomes) • We should not need to Bend our documentation to meet compliance standards • Our documentation forms and processes should help guide quality services 129
Compliance and Quality • Documentation should just be an accurate account of what we do • The goal is effective and compliant interventions (positive outcomes) • We should not need to Bend our documentation to meet compliance standards • Our documentation forms and processes should help guide quality services 129
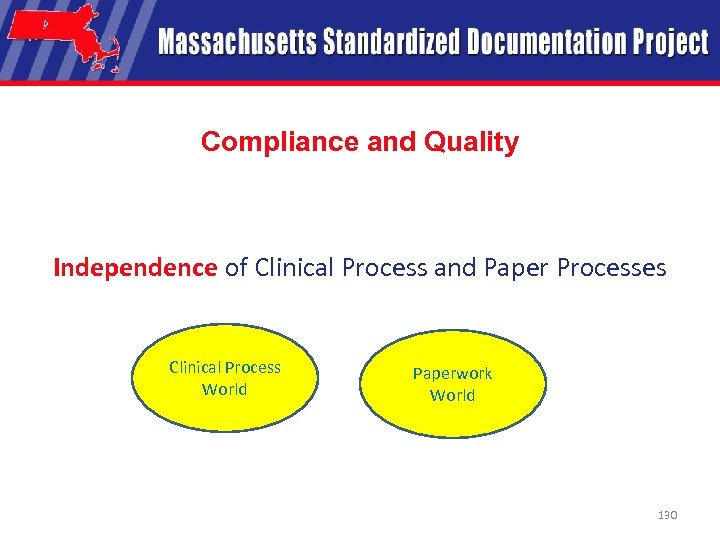 Compliance and Quality Independence of Clinical Process and Paper Processes Clinical Process World Paperwork World 130
Compliance and Quality Independence of Clinical Process and Paper Processes Clinical Process World Paperwork World 130
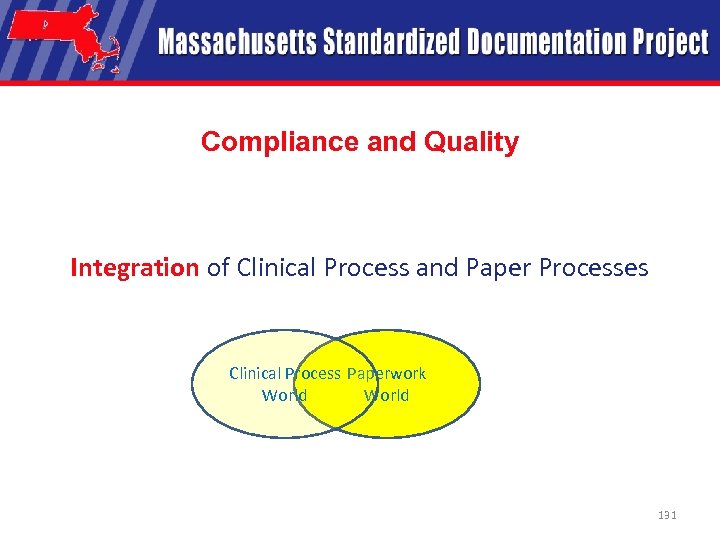 Compliance and Quality Integration of Clinical Process and Paper Processes Clinical Process Paperwork World 131
Compliance and Quality Integration of Clinical Process and Paper Processes Clinical Process Paperwork World 131
 Compliance and Quality Integration of Clinical Process and Paper Processes Clinical Process/ Documentation 132
Compliance and Quality Integration of Clinical Process and Paper Processes Clinical Process/ Documentation 132
 Compliance and Quality The MSDP Forms and Processes Provide a High Level of Support for Worthwhile Documentation • Support for Quality - Person Centered Services and Positive Outcomes • Compliance • Efficiency As long as we don’t miss the point ! 133
Compliance and Quality The MSDP Forms and Processes Provide a High Level of Support for Worthwhile Documentation • Support for Quality - Person Centered Services and Positive Outcomes • Compliance • Efficiency As long as we don’t miss the point ! 133
 Break
Break
 How New Therapeutic Issues Are Documented. . Use of the Assessment Update Processes. . Bill Schmelter Ph. D 135
How New Therapeutic Issues Are Documented. . Use of the Assessment Update Processes. . Bill Schmelter Ph. D 135
 How New Therapeutic Issues Are Documented • What do we do when new therapeutic issues are identified? 136
How New Therapeutic Issues Are Documented • What do we do when new therapeutic issues are identified? 136
 How New Therapeutic Issues Are Documented • Cannot document new information in progress notes only if it has implications for services! • Cannot wait until scheduled Assessment Update or Action Plan Review/Update! 137
How New Therapeutic Issues Are Documented • Cannot document new information in progress notes only if it has implications for services! • Cannot wait until scheduled Assessment Update or Action Plan Review/Update! 137
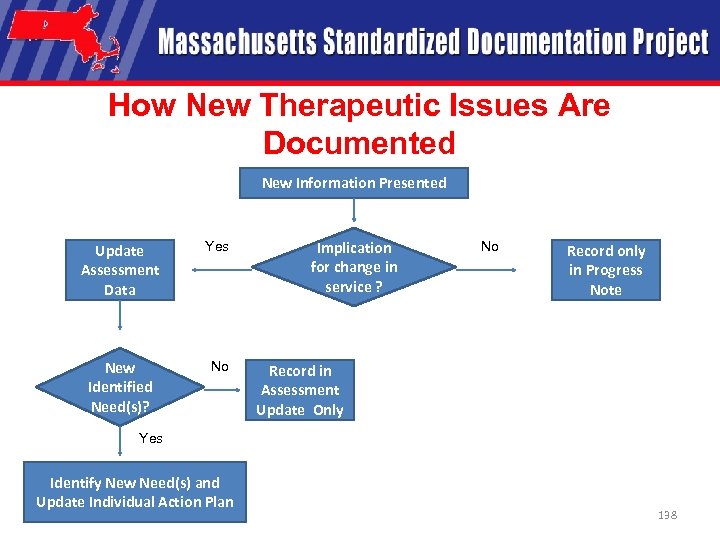 How New Therapeutic Issues Are Documented New Information Presented Update Assessment Data Yes New Identified Need(s)? No Implication for change in service ? No Record only in Progress Note Record in Assessment Update Only Yes Identify New Need(s) and Update Individual Action Plan 138
How New Therapeutic Issues Are Documented New Information Presented Update Assessment Data Yes New Identified Need(s)? No Implication for change in service ? No Record only in Progress Note Record in Assessment Update Only Yes Identify New Need(s) and Update Individual Action Plan 138
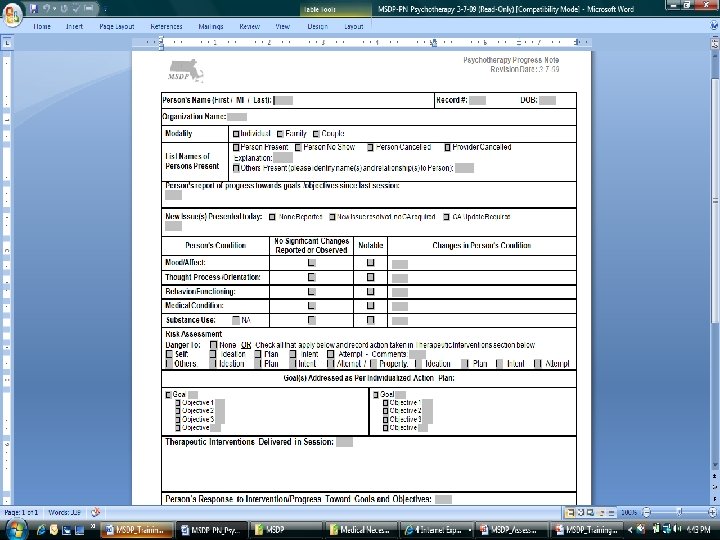 Presented by David Lloyd, MSDP Project Manager 139
Presented by David Lloyd, MSDP Project Manager 139
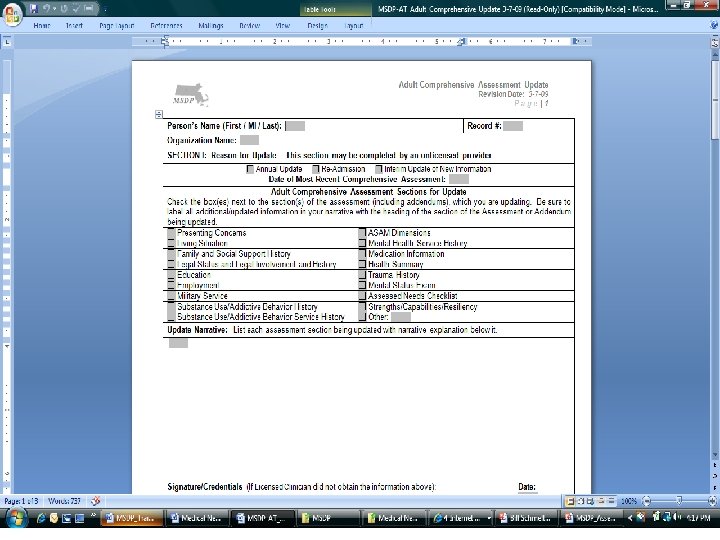 Presented by David Lloyd, MSDP Project Manager 140
Presented by David Lloyd, MSDP Project Manager 140
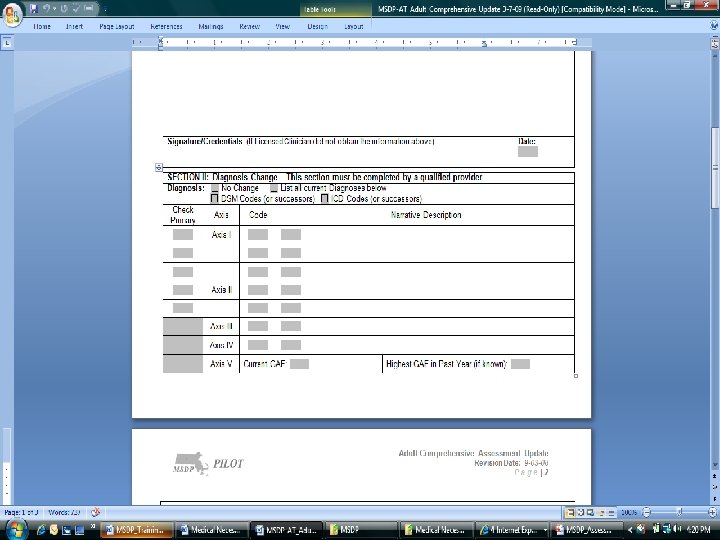 Presented by David Lloyd, MSDP Project Manager 141
Presented by David Lloyd, MSDP Project Manager 141
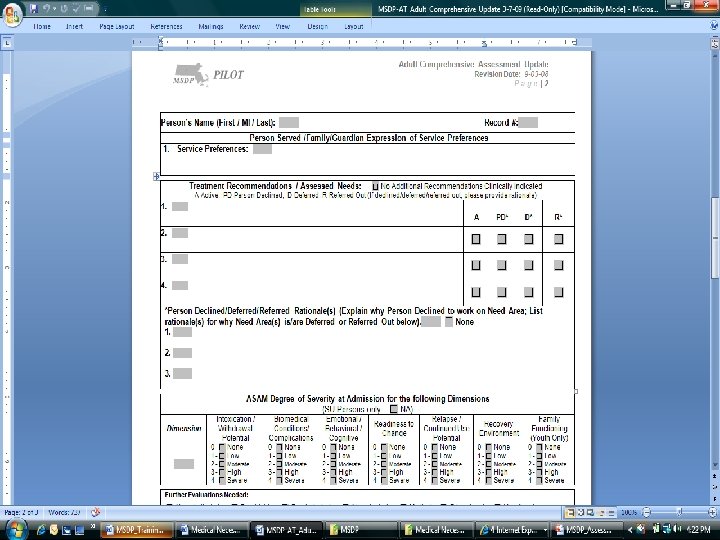 Presented by David Lloyd, MSDP Project Manager 142
Presented by David Lloyd, MSDP Project Manager 142
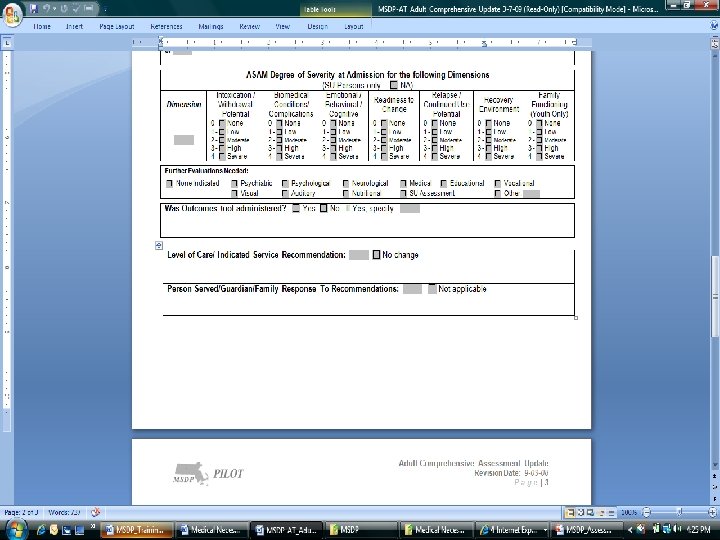 Presented by David Lloyd, MSDP Project Manager 143
Presented by David Lloyd, MSDP Project Manager 143
 Person Centered Planning and the Importance of Documentation Support Using the MSDP Processes Presenters: Marcia Webster, CFAAC Susan Schneider, MOAR
Person Centered Planning and the Importance of Documentation Support Using the MSDP Processes Presenters: Marcia Webster, CFAAC Susan Schneider, MOAR
 Documentation that Supports People and their Recovery Standardized forms and processes can help you do work that is: 1. Increasingly, energized and driven by the person or family you want to support. 2. Oriented toward recovery. 3. Sustainable over time and with limited resources. 145
Documentation that Supports People and their Recovery Standardized forms and processes can help you do work that is: 1. Increasingly, energized and driven by the person or family you want to support. 2. Oriented toward recovery. 3. Sustainable over time and with limited resources. 145
 Person-Centered, Person-Driven “Language, structures and decisions that are driven and fueled by the person using services, the whole of the person, are essential to effective care [and support]. ” p. 28, MSDP Training Manual 146
Person-Centered, Person-Driven “Language, structures and decisions that are driven and fueled by the person using services, the whole of the person, are essential to effective care [and support]. ” p. 28, MSDP Training Manual 146
 Concurrent Documentation: The next frontier in person-driven practice “Last month there was a huge reduction in my ‘no show’ rating and to me, that’s an indication that my clients like my attention and my approach. . . Ninety-five per cent of the time I leave work on time - I could never do that before [I started completing notes in session]. ” Catherine A. Main, MSW, LCSW, SOQIC (Ohio) Documentation Process Implementation Manual p. 62 147
Concurrent Documentation: The next frontier in person-driven practice “Last month there was a huge reduction in my ‘no show’ rating and to me, that’s an indication that my clients like my attention and my approach. . . Ninety-five per cent of the time I leave work on time - I could never do that before [I started completing notes in session]. ” Catherine A. Main, MSW, LCSW, SOQIC (Ohio) Documentation Process Implementation Manual p. 62 147
 Recovery-oriented Documentation “The concept of recovery emphasizes a person’s capacity to have hope and lead a meaningful life, and suggests that treatment can be guided by attention to life goals and ambitions. ” The American Psychiatric Association, 2005 148
Recovery-oriented Documentation “The concept of recovery emphasizes a person’s capacity to have hope and lead a meaningful life, and suggests that treatment can be guided by attention to life goals and ambitions. ” The American Psychiatric Association, 2005 148
 Recovery and Peer Support Practitioners, Researchers and Writers to explore. . . • • • Bill Anthony, Boston University, MA Mary Ellen Copeland, VT Pat Deegan, MA Dan Fisher, The Empowerment Center, MA Larry Fricks, GA Ed Knight, Value Options, CO Renee Kopache, OH Shery Mead, NH Mark Ragins, The Village, CA Peggy Swarbrick, NJ-CSP Nowhere near a complete list! 149
Recovery and Peer Support Practitioners, Researchers and Writers to explore. . . • • • Bill Anthony, Boston University, MA Mary Ellen Copeland, VT Pat Deegan, MA Dan Fisher, The Empowerment Center, MA Larry Fricks, GA Ed Knight, Value Options, CO Renee Kopache, OH Shery Mead, NH Mark Ragins, The Village, CA Peggy Swarbrick, NJ-CSP Nowhere near a complete list! 149
 Sustainable Documentation • Establishing a goal and pursuing a purpose over time and in the context of local community. • Answers the question “what happened? ” instead of “what is wrong? ”. • Affirms the individual’s power, control and connections in the present and future. 150
Sustainable Documentation • Establishing a goal and pursuing a purpose over time and in the context of local community. • Answers the question “what happened? ” instead of “what is wrong? ”. • Affirms the individual’s power, control and connections in the present and future. 150
 Role Play! Person-Centered Recovery-Oriented Sustainable Assumes individual is. . . Questions elicit. . . Language is. . . • Whole • Capable • Unique • Worthy • Strength, skills • Hope, desires • Connection • Support, resources • Precise • Human • Person-first • Future oriented 151
Role Play! Person-Centered Recovery-Oriented Sustainable Assumes individual is. . . Questions elicit. . . Language is. . . • Whole • Capable • Unique • Worthy • Strength, skills • Hope, desires • Connection • Support, resources • Precise • Human • Person-first • Future oriented 151
 Documentation that Supports People and their Recovery • Marcia Webster, The Transformation Center marciaw@transformation-center. org 413 -626 -6968 • Susan Schneider susan. shr@gmail. com 617 -429 -7398 152
Documentation that Supports People and their Recovery • Marcia Webster, The Transformation Center marciaw@transformation-center. org 413 -626 -6968 • Susan Schneider susan. shr@gmail. com 617 -429 -7398 152
 Recap and Next Steps
Recap and Next Steps
 Questions / Comments
Questions / Comments
 Adjournment
Adjournment


