f4ab89a994a086080bdf275170ee5d18.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 50
 MS Studies Ch. 6 Reconstruction & Transition
MS Studies Ch. 6 Reconstruction & Transition
 After The War • MS went from very wealthy to ruins – Cities, roads, bridges, towns, buildings, all were destroyed • 1/3 of white males were killed or injured during the war • 400, 000 freedmen (former slaves) now existed – Homeless, uneducated, jobless • MS social order was gone – Blacks Free – Whites had hard time accepting them as equal Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 2
After The War • MS went from very wealthy to ruins – Cities, roads, bridges, towns, buildings, all were destroyed • 1/3 of white males were killed or injured during the war • 400, 000 freedmen (former slaves) now existed – Homeless, uneducated, jobless • MS social order was gone – Blacks Free – Whites had hard time accepting them as equal Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 2
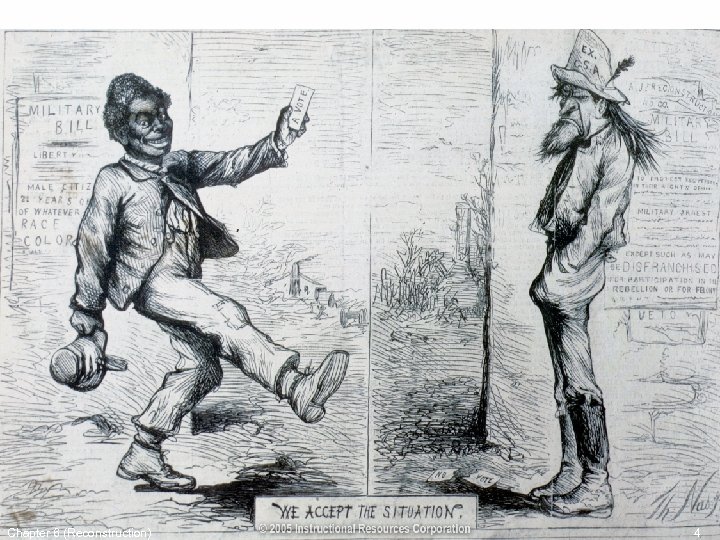
 Freed Slaves • Freedmen’s Bureau – created to help slaves find food, shelter, work, & assimilate to freedom. • Rumors stated that every black male would receive 40 acres of land a mule. This never happens. • Most land confiscated during the war was returned to the owners. Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 3
Freed Slaves • Freedmen’s Bureau – created to help slaves find food, shelter, work, & assimilate to freedom. • Rumors stated that every black male would receive 40 acres of land a mule. This never happens. • Most land confiscated during the war was returned to the owners. Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 3
 Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 4
Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 4
 Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 5
Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 5
 Presidential Reconstruction • Lincoln’s Plan for Reconstruction – All Southerners, except high ranking Conf. officials, would be pardoned after signing oath of loyalty – 10% of people signed oath, they could create a state gov. and be readmitted. • Johnson’s Plan for Reconstruction – Same as Lincoln’s except high ranking military & Conf. officials and those owning more than $20, 000 worth of property were not pardoned. • Congress wanted tougher requirements & pressured Johnson to add the following. – States must repeal Secession Ordinances – Void their War Debt – Ratify 13 th Amendment Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 6
Presidential Reconstruction • Lincoln’s Plan for Reconstruction – All Southerners, except high ranking Conf. officials, would be pardoned after signing oath of loyalty – 10% of people signed oath, they could create a state gov. and be readmitted. • Johnson’s Plan for Reconstruction – Same as Lincoln’s except high ranking military & Conf. officials and those owning more than $20, 000 worth of property were not pardoned. • Congress wanted tougher requirements & pressured Johnson to add the following. – States must repeal Secession Ordinances – Void their War Debt – Ratify 13 th Amendment Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 6
 Lincoln & Johnson Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 7
Lincoln & Johnson Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 7
 Constitutional Conv. 1865 • William L. Sharkey named temp. Governor by Pres. Johnson • MS was first to hold Conv. & everyone was watching • 300 men met on Aug. 14, 1865. Most were pre-war leaders • They created a government just like the one before the war. • Blacks were not given voting rights • Most white Mississippians agreed with this Convention. Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 8
Constitutional Conv. 1865 • William L. Sharkey named temp. Governor by Pres. Johnson • MS was first to hold Conv. & everyone was watching • 300 men met on Aug. 14, 1865. Most were pre-war leaders • They created a government just like the one before the war. • Blacks were not given voting rights • Most white Mississippians agreed with this Convention. Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 8
 William Sharkey Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 9
William Sharkey Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 9
 • Herschel Johnson led the state constitutional convention in 1865 Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 10
• Herschel Johnson led the state constitutional convention in 1865 Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 10
 MS’s Post War Government • Benjamin Humphreys elected Governor (Conf. General) • Most elected officials had served in the Confederate Government & refused to grant blacks rights • Legislature passed the Black Codes to control blacks – Black marriages legal, blacks could sue in court. – Interracial marriage illegal, blacks can’t testify against whites – Blacks could rent or lease land in cities or towns – Blacks had to have employment contracts and were arrested if they broke the contract. – Blacks could not carry firearms or weapons, and could not assemble w/o permission – Jailed blacks could be rented out to anyone that paid their jail fine. Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 11
MS’s Post War Government • Benjamin Humphreys elected Governor (Conf. General) • Most elected officials had served in the Confederate Government & refused to grant blacks rights • Legislature passed the Black Codes to control blacks – Black marriages legal, blacks could sue in court. – Interracial marriage illegal, blacks can’t testify against whites – Blacks could rent or lease land in cities or towns – Blacks had to have employment contracts and were arrested if they broke the contract. – Blacks could not carry firearms or weapons, and could not assemble w/o permission – Jailed blacks could be rented out to anyone that paid their jail fine. Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 11
 Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 12
Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 12
 Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 13
Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 13
 Benjamin Humphreys Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 14
Benjamin Humphreys Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 14
 U. S. Congress • U. S. Congress refused to seat MS Representatives & passed the 14 th Amendment. – 14 th Amendment guaranteed all people their rights “white or black” • March 2, 1867 Congress passed the Reconstruction Act. – South divided into 5 Military districts and readmission to the Union was much stricter. • MS was in the 4 th district and Major Gen. Edward O. Ord became military governor in MS. Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 15
U. S. Congress • U. S. Congress refused to seat MS Representatives & passed the 14 th Amendment. – 14 th Amendment guaranteed all people their rights “white or black” • March 2, 1867 Congress passed the Reconstruction Act. – South divided into 5 Military districts and readmission to the Union was much stricter. • MS was in the 4 th district and Major Gen. Edward O. Ord became military governor in MS. Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 15
 14 th Amendment Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 16
14 th Amendment Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 16
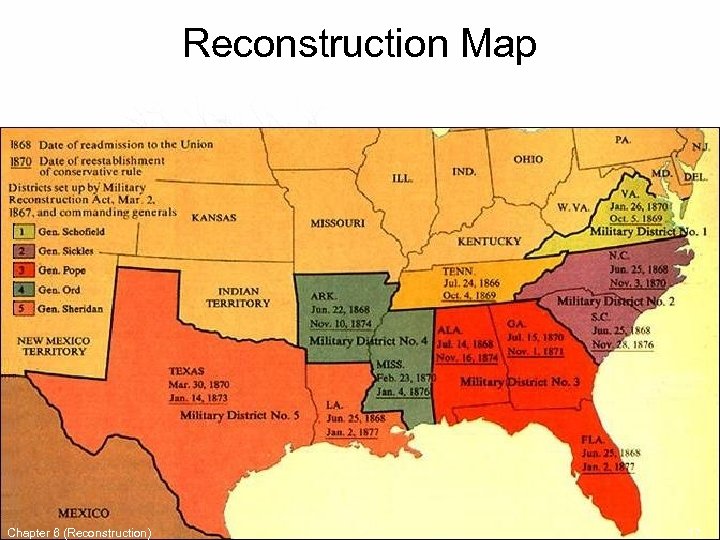 Reconstruction Map Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 17
Reconstruction Map Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 17
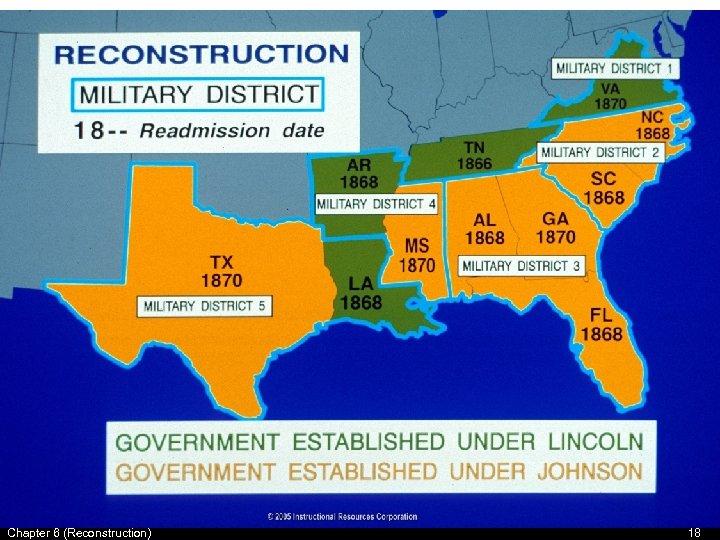 Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 18
Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 18
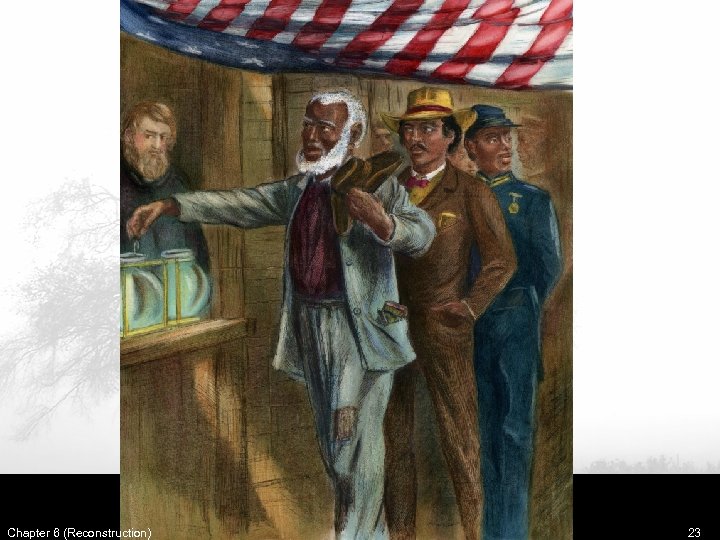
 MS During Reconstruction • All eligible males registered to vote regardless of race • MS Politics included – Democrats – White southerners that didn’t support black rights – Republicans – Whites and blacks that supported black rights. – Scalawags – Southerners that supported the Republican Party – Carpetbaggers – northern whites that were Republicans and moved to MS. • The Republican Party used their majority of votes (black & white) to call for a new state constitutional convention Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 19
MS During Reconstruction • All eligible males registered to vote regardless of race • MS Politics included – Democrats – White southerners that didn’t support black rights – Republicans – Whites and blacks that supported black rights. – Scalawags – Southerners that supported the Republican Party – Carpetbaggers – northern whites that were Republicans and moved to MS. • The Republican Party used their majority of votes (black & white) to call for a new state constitutional convention Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 19
 Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 20
Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 20
 Carpetbagger Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 21
Carpetbagger Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 21
 Constitution of 1868 • 100 delegates. 17 black, 29 scalawags, 25 carpetbaggers, 17 Democrats • They created the states 3 rd & most democratic constitution. – – – Universal Male Suffrage granted Free Public Education Ages 6 -18 No discrimination in public transportation Property qualification for voting or holding office eliminated. Property rights granted to women Disfranchises all person who supported secession and helped Confederacy – Whites had to sign oath stating “all men are created equal” • This constitution failed to ratify due to the disenfranchising clause & equality oath. These were eliminated by Pres. Ulysses S. Grant in 1869 & the Constitution was ratified. Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 22
Constitution of 1868 • 100 delegates. 17 black, 29 scalawags, 25 carpetbaggers, 17 Democrats • They created the states 3 rd & most democratic constitution. – – – Universal Male Suffrage granted Free Public Education Ages 6 -18 No discrimination in public transportation Property qualification for voting or holding office eliminated. Property rights granted to women Disfranchises all person who supported secession and helped Confederacy – Whites had to sign oath stating “all men are created equal” • This constitution failed to ratify due to the disenfranchising clause & equality oath. These were eliminated by Pres. Ulysses S. Grant in 1869 & the Constitution was ratified. Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 22
 Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 23
Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 23
 President Ulysses S. Grant Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 24
President Ulysses S. Grant Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 24
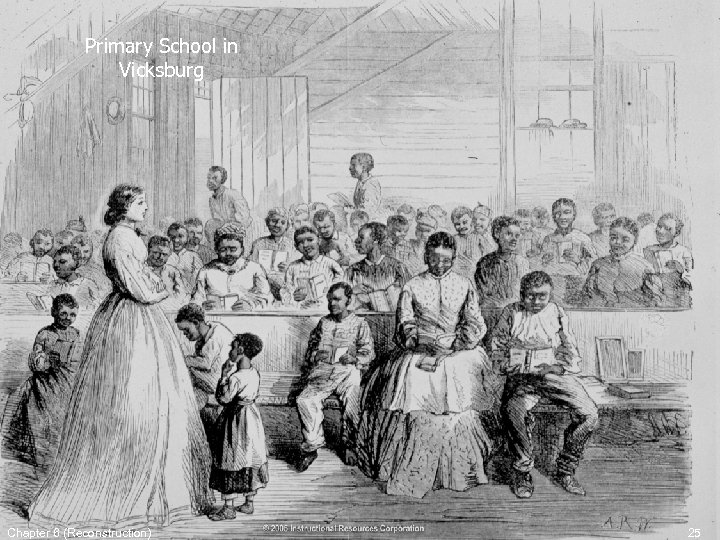 Primary School in Vicksburg Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 25
Primary School in Vicksburg Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 25
 Freedmen school Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 26
Freedmen school Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 26
 Republican Rule • • Republicans ruled MS 1869 James Alcorn elected governor. Republicans had majority in legislature State ratified 14 th & 15 th amendments & was readmitted to the Union Feb. 23, 1870. • Hiram Revels (black) filled Jefferson Davis’ unexpired Senate term & Adelbert Ames was elected to the other. – Revels is the first black in the U. S. Senate • Ames defeated Alcorn for governor in 1873 Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 27
Republican Rule • • Republicans ruled MS 1869 James Alcorn elected governor. Republicans had majority in legislature State ratified 14 th & 15 th amendments & was readmitted to the Union Feb. 23, 1870. • Hiram Revels (black) filled Jefferson Davis’ unexpired Senate term & Adelbert Ames was elected to the other. – Revels is the first black in the U. S. Senate • Ames defeated Alcorn for governor in 1873 Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 27
 James Alcorn Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 28
James Alcorn Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 28
 • Aldelbert Ames replaced James Alcorn as governor in 1873. He was Union General in Civil War. Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 29
• Aldelbert Ames replaced James Alcorn as governor in 1873. He was Union General in Civil War. Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 29
 Hiram Revels Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 30
Hiram Revels Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 30
 Adelbert Ames Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 31
Adelbert Ames Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 31
 Black Political Power • Blacks served as early as 1868 in political roles • 1868 Benjamin Montgomery became justice of the peace. Believed to be first black to hold public office in MS • Many blacks served in the MS House and Senate. • A. K. Davis elected Lt. Governor in 1873 • John Lynch served as MS’s only black member in the U. S. House of Reps. • Blanche K. Bruce of MS was the first black elected to the U. S. Senate and the first to serve a full term. Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 32
Black Political Power • Blacks served as early as 1868 in political roles • 1868 Benjamin Montgomery became justice of the peace. Believed to be first black to hold public office in MS • Many blacks served in the MS House and Senate. • A. K. Davis elected Lt. Governor in 1873 • John Lynch served as MS’s only black member in the U. S. House of Reps. • Blanche K. Bruce of MS was the first black elected to the U. S. Senate and the first to serve a full term. Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 32
 John R. Lynch Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 33
John R. Lynch Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 33
 Blanche K. Bruce Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 34
Blanche K. Bruce Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 34
 1 st African Americans in Congress Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 35
1 st African Americans in Congress Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 35
 Education • Const. of 1868 created free public schools (tax based) • State supported them with funding and elected a state superintendent who appointed county superintendents. • The following was created – – – – University of MS expanded 1871 Alcorn State College (black only) 1877 MS A & M (later MS State) MS University for Women 1884 Jackson State 1877 Millsaps College 1892 Mississippi College 1892 Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 36
Education • Const. of 1868 created free public schools (tax based) • State supported them with funding and elected a state superintendent who appointed county superintendents. • The following was created – – – – University of MS expanded 1871 Alcorn State College (black only) 1877 MS A & M (later MS State) MS University for Women 1884 Jackson State 1877 Millsaps College 1892 Mississippi College 1892 Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 36
 University of MS Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 37
University of MS Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 37
 Alcorn College Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 38
Alcorn College Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 38
 MS University for Women Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 39
MS University for Women Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 39
 Millsaps College Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 40
Millsaps College Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 40
 Mississippi College Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 41
Mississippi College Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 41
 End of Republican Rule • From the beginning of Reconstruction, white Democrats were trying to regain political power in MS • Those that wanted to return control of the state to the Democrats were called Redeemers • The election of 1875 was the turning point – White Republicans were threatened with violence and becoming a social outcast if they didn’t become Democrat – Blacks were driven from voting poles with violence, or forced to vote Democrat by their employers. – The Ku Klux Klan (KKK) was the terror group used to intimidate voters. • Democrats won 4 of 6 Congressional seats, and claimed the majority in the State Congress • Republican Senators were later replaced by Democrats • Republican Governor Adelbert Ames was threatened w/ impeachment and resigned. Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 42
End of Republican Rule • From the beginning of Reconstruction, white Democrats were trying to regain political power in MS • Those that wanted to return control of the state to the Democrats were called Redeemers • The election of 1875 was the turning point – White Republicans were threatened with violence and becoming a social outcast if they didn’t become Democrat – Blacks were driven from voting poles with violence, or forced to vote Democrat by their employers. – The Ku Klux Klan (KKK) was the terror group used to intimidate voters. • Democrats won 4 of 6 Congressional seats, and claimed the majority in the State Congress • Republican Senators were later replaced by Democrats • Republican Governor Adelbert Ames was threatened w/ impeachment and resigned. Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 42
 Ku Klux Klan (KKK) Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 43
Ku Klux Klan (KKK) Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 43
 Ku Klux Klan (KKK) Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 44
Ku Klux Klan (KKK) Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 44
 KKK March on Washington D. C. Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 45
KKK March on Washington D. C. Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 45
 Presidential Election of 1876 • Dem. Candidate Samuel Tilden & Repub. Candidate Rutherford B. Hayes • No candidate won a majority. Some electoral votes were contested. • Commission was formed to pick a winner. • Southern Democrats used a filibuster (continuous speechmaking to delay action) to slow the commission. – Democrats agreed to stop the filibuster and support Hayes, if Hayes promised to withdraw troops from the South • Hayes won the election & military occupation ended Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 46
Presidential Election of 1876 • Dem. Candidate Samuel Tilden & Repub. Candidate Rutherford B. Hayes • No candidate won a majority. Some electoral votes were contested. • Commission was formed to pick a winner. • Southern Democrats used a filibuster (continuous speechmaking to delay action) to slow the commission. – Democrats agreed to stop the filibuster and support Hayes, if Hayes promised to withdraw troops from the South • Hayes won the election & military occupation ended Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 46
 Rutherford Hayes & Samuel Tilden Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 47
Rutherford Hayes & Samuel Tilden Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 47
 Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 48
Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 48
 Constitution of 1890 • MS called Constitutional convention in 1890 • MS reapportioned (redrew district lines) to give white majorities power over black populated areas • Met in Jackson in Aug. 1890 • One black (Isaiah Montgomery) attended • Constitution said – Voters had to • • Register at least 4 months before election Live in the state for 2 years before voting Pay a $2 poll tax Pass Literacy Test. Had to read any section of the state constitution or “understand it when read to them”. This was the understanding clause • Black voters dropped from 142, 000 to 8, 615 Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 49
Constitution of 1890 • MS called Constitutional convention in 1890 • MS reapportioned (redrew district lines) to give white majorities power over black populated areas • Met in Jackson in Aug. 1890 • One black (Isaiah Montgomery) attended • Constitution said – Voters had to • • Register at least 4 months before election Live in the state for 2 years before voting Pay a $2 poll tax Pass Literacy Test. Had to read any section of the state constitution or “understand it when read to them”. This was the understanding clause • Black voters dropped from 142, 000 to 8, 615 Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 49
 Isaiah Montgomery Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 50
Isaiah Montgomery Chapter 6 (Reconstruction) 50


