1b55765920e2a3c8092ad1a9a2702e5b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 68
 MS Studies Ch. 5 Secession & Civil War
MS Studies Ch. 5 Secession & Civil War
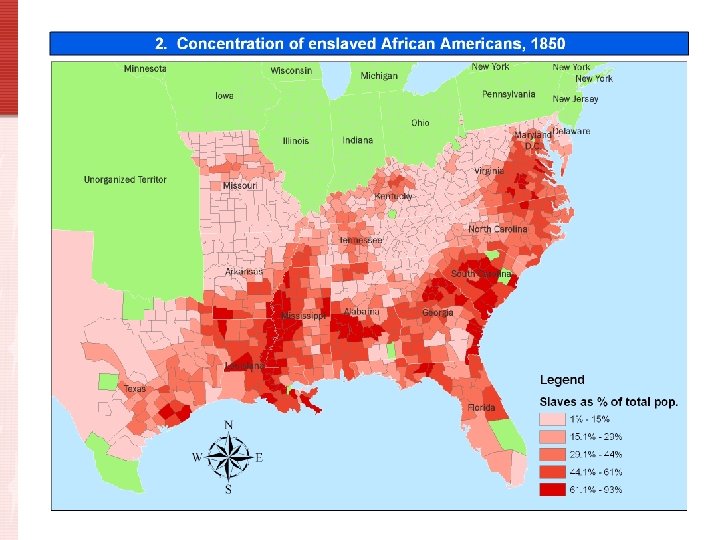
 Slavery • Slavery was viewed as a potential problem dating back to the drafting of the U. S. Constitution • By 1819, slavery was the primary political issue in the U. S.
Slavery • Slavery was viewed as a potential problem dating back to the drafting of the U. S. Constitution • By 1819, slavery was the primary political issue in the U. S.
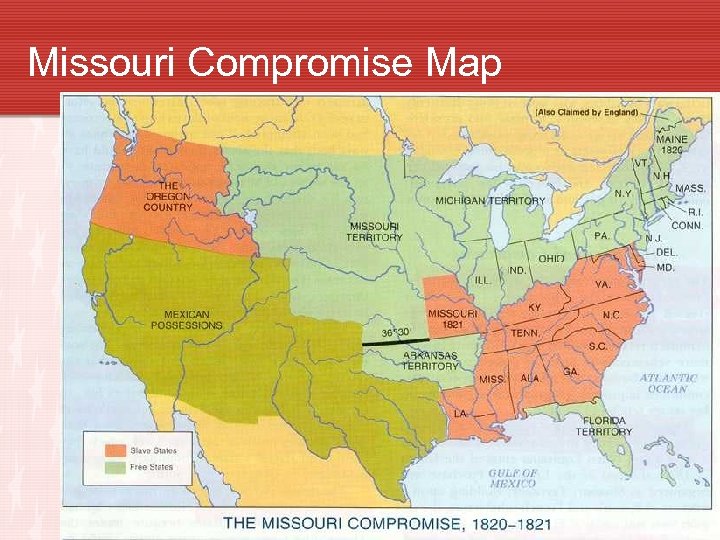
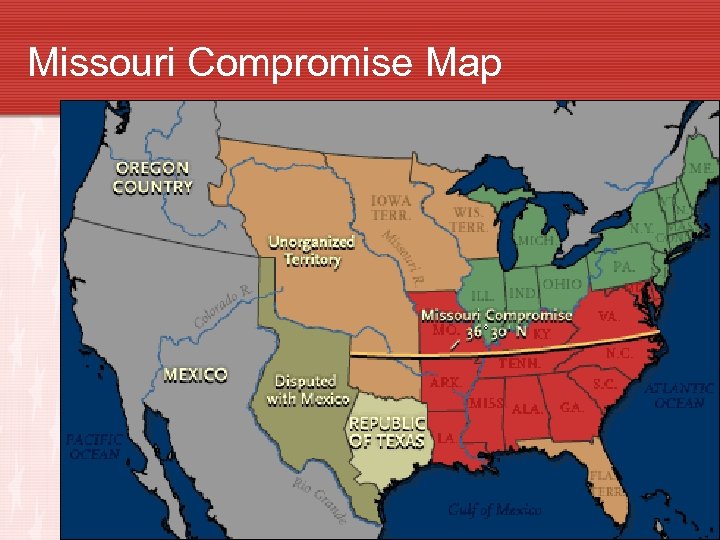
 The Missouri Compromise • 1819 U. S. had 22 states. 11 free states. 11 slave states • Free State – State that did not allow slavery • Slave State – State that did allow slavery • Missouri applied for statehood as a slave state • Intense debates erupted in U. S. Congress • Missouri Compromise was created. • Missouri was admitted as slave state • Maine admitted as a free state • Slavery forbidden in the remainder of the Louisiana Purchase north of 36° 30’ N
The Missouri Compromise • 1819 U. S. had 22 states. 11 free states. 11 slave states • Free State – State that did not allow slavery • Slave State – State that did allow slavery • Missouri applied for statehood as a slave state • Intense debates erupted in U. S. Congress • Missouri Compromise was created. • Missouri was admitted as slave state • Maine admitted as a free state • Slavery forbidden in the remainder of the Louisiana Purchase north of 36° 30’ N
 Missouri Compromise Map
Missouri Compromise Map
 Missouri Compromise Map
Missouri Compromise Map
 Antislavery Movement • 1817 American Colonization Society formed. Offered to send free blacks back to Africa (Liberia) • MS Colonization Society formed 1831. • Many people wanted to end slavery, but no person knew the proper way.
Antislavery Movement • 1817 American Colonization Society formed. Offered to send free blacks back to Africa (Liberia) • MS Colonization Society formed 1831. • Many people wanted to end slavery, but no person knew the proper way.
 Nullification Crisis & States’ Rights • States’ Rights – the principle that the rights of the individual state should prevail over the rights of the federal government. • Many southerners believed deeply in states’ rights • 1832 South Carolina challenged the U. S. tariff saying that they had the right as a state to nullify this U. S. law. • S. Carolina threatened to secede • A compromise reduced the tariff, but a law was passed that denied the states the right to nullify a national law • Mississippians were divided on this issue.
Nullification Crisis & States’ Rights • States’ Rights – the principle that the rights of the individual state should prevail over the rights of the federal government. • Many southerners believed deeply in states’ rights • 1832 South Carolina challenged the U. S. tariff saying that they had the right as a state to nullify this U. S. law. • S. Carolina threatened to secede • A compromise reduced the tariff, but a law was passed that denied the states the right to nullify a national law • Mississippians were divided on this issue.

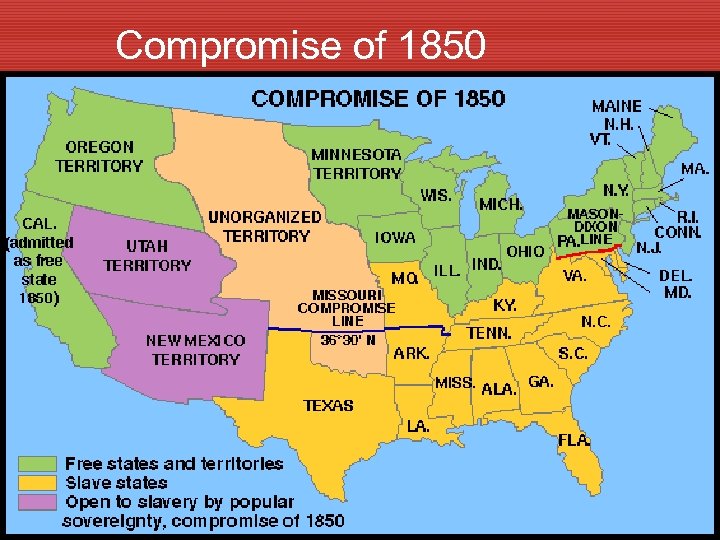
 The Compromise of 1850 • 1846 U. S. gained new lands from Mexico and the Missouri Compromise did not apply to them. • By 1850 California was ready for statehood & wanted to be free. • Issue was raised “FREE or SLAVE” • Compromise of 1850 solved the issue • California admitted as free state • Slavery in new territories would be determined by Popular Sovereignty (means a vote by those living there) • South got a stronger fugitive slave law
The Compromise of 1850 • 1846 U. S. gained new lands from Mexico and the Missouri Compromise did not apply to them. • By 1850 California was ready for statehood & wanted to be free. • Issue was raised “FREE or SLAVE” • Compromise of 1850 solved the issue • California admitted as free state • Slavery in new territories would be determined by Popular Sovereignty (means a vote by those living there) • South got a stronger fugitive slave law
 Compromise of 1850
Compromise of 1850
 Slavery Issues • Kansas-Nebraska Act passed 1854 • Said Pop. Sovereignty would decide slavery issue • Led to violence and wars known as “Bleeding Kansas” or “Border War” • 1854 Republican Party created to stop expansion of slavery • 1857 Supreme Court rules that Dred Scott was property and that slavery could expand into territories. • 1859 John Brown leads a raid against an armory at Harper’s Ferry Virginia. • He hoped to start a slave revolt, but he was captured and executed
Slavery Issues • Kansas-Nebraska Act passed 1854 • Said Pop. Sovereignty would decide slavery issue • Led to violence and wars known as “Bleeding Kansas” or “Border War” • 1854 Republican Party created to stop expansion of slavery • 1857 Supreme Court rules that Dred Scott was property and that slavery could expand into territories. • 1859 John Brown leads a raid against an armory at Harper’s Ferry Virginia. • He hoped to start a slave revolt, but he was captured and executed
 John Brown
John Brown
 Dred Scott
Dred Scott
 Harper’s Ferry
Harper’s Ferry
 MS & Secession • Mississippians were divided. They loved the U. S. , but also loved slavery. • Secession (withdrawal from the Union) was not accepted by most Mississippians during the 1850’s. They wanted U. S. Congress to protect slavery • By 1859 most Mississippians felt like secession was the only answer to the slave question.
MS & Secession • Mississippians were divided. They loved the U. S. , but also loved slavery. • Secession (withdrawal from the Union) was not accepted by most Mississippians during the 1850’s. They wanted U. S. Congress to protect slavery • By 1859 most Mississippians felt like secession was the only answer to the slave question.
 1860 Presidential Election • Democrats divided • Southern Democrats nominated John C. Breckinridge (U. S. Vice President) • Northern Democrats nominated Stephen Douglas • Constitution Party nominated John Bell • Republican Party nominated Abraham Lincoln • Lincoln won the election (Breckenridge carried the south)
1860 Presidential Election • Democrats divided • Southern Democrats nominated John C. Breckinridge (U. S. Vice President) • Northern Democrats nominated Stephen Douglas • Constitution Party nominated John Bell • Republican Party nominated Abraham Lincoln • Lincoln won the election (Breckenridge carried the south)
 Election of 1860 Candidates Abraham Lincoln (Republican) John C. Breckinridge (Southern Democrats) John Bell (Constitutional Party) Stephen A. Douglas (Northern Democrats)
Election of 1860 Candidates Abraham Lincoln (Republican) John C. Breckinridge (Southern Democrats) John Bell (Constitutional Party) Stephen A. Douglas (Northern Democrats)
 Secession • Dec. 20, 1860 South Carolina seceded from the union • MS called a state convention. • MS delegates voted 84 – 15 in favor of secession • Jan. 9, 1861 MS became 2 nd state to secede from the Union • AL, GA, FL, LA, & TX followed. • Feb. 1861 delegates from each state met in Montgomery, AL and formed the Confederate States of America (new government) • Jefferson Davis was selected as the President & Montgomery, AL was the capital • When VA seceded from the Union, the capital was moved to Richmond, VA.
Secession • Dec. 20, 1860 South Carolina seceded from the union • MS called a state convention. • MS delegates voted 84 – 15 in favor of secession • Jan. 9, 1861 MS became 2 nd state to secede from the Union • AL, GA, FL, LA, & TX followed. • Feb. 1861 delegates from each state met in Montgomery, AL and formed the Confederate States of America (new government) • Jefferson Davis was selected as the President & Montgomery, AL was the capital • When VA seceded from the Union, the capital was moved to Richmond, VA.
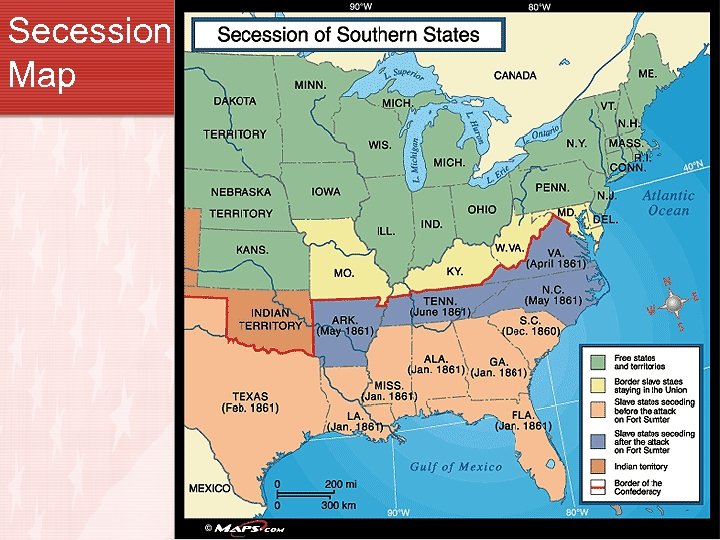 Secession Map
Secession Map
 Jefferson Davis
Jefferson Davis
 Confederate Flags Confederate Flag 1861 -1863 Confederate Flag 1865 Confederate Navy Jack Confederate Flag 1863 -1865 Confederate Battle Flag
Confederate Flags Confederate Flag 1861 -1863 Confederate Flag 1865 Confederate Navy Jack Confederate Flag 1863 -1865 Confederate Battle Flag
 War Begins • April 1861, Confederate forces fire on Fort Sumter in Charleston, South Carolina when a resupply is attempted. • President Lincoln called for troops to put down the rebellion. • VA, NC, TN, & AR seceded. • Both sides thought they could win • South had better leaders & thought foreign nations would support them • North had more people and resources than the south.
War Begins • April 1861, Confederate forces fire on Fort Sumter in Charleston, South Carolina when a resupply is attempted. • President Lincoln called for troops to put down the rebellion. • VA, NC, TN, & AR seceded. • Both sides thought they could win • South had better leaders & thought foreign nations would support them • North had more people and resources than the south.
 Fort Sumter War Begins
Fort Sumter War Begins
 Fort Sumter Aftermath
Fort Sumter Aftermath
 U. S. Leaders
U. S. Leaders
 Confederate Leaders Jefferson Davis Gen. Robert E. Lee (Eastern Front) Gen. Albert Johnston (Western Front)
Confederate Leaders Jefferson Davis Gen. Robert E. Lee (Eastern Front) Gen. Albert Johnston (Western Front)
 MS River • The MS River was a key component to the Union’s success during the war. • Gen. Ulysses S. Grant commanded Union forces in the West • Gen. Albert Sidney Johnston commanded Confederate troops in the West. • March 1862 Gen. Johnston is defending Corinth, MS. Gen. Grant has a fort at Shiloh (TN).
MS River • The MS River was a key component to the Union’s success during the war. • Gen. Ulysses S. Grant commanded Union forces in the West • Gen. Albert Sidney Johnston commanded Confederate troops in the West. • March 1862 Gen. Johnston is defending Corinth, MS. Gen. Grant has a fort at Shiloh (TN).
 Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant
 Confederate encampment at Corinth
Confederate encampment at Corinth


 Battle of Shiloh • Johnston attacks grant on April 6 beginning the Battle of Shiloh. Johnston is killed during the battle. • Gen. P. G. T. Beauregard takes command of southern forces. South advances on Day 1, but on Day 2 reinforced Union forces cause a Confederate retreat back to Corinth. • Shiloh was the bloodiest battle of the war to that point. • Corinth & Memphis were later abandoned by the Confederates.
Battle of Shiloh • Johnston attacks grant on April 6 beginning the Battle of Shiloh. Johnston is killed during the battle. • Gen. P. G. T. Beauregard takes command of southern forces. South advances on Day 1, but on Day 2 reinforced Union forces cause a Confederate retreat back to Corinth. • Shiloh was the bloodiest battle of the war to that point. • Corinth & Memphis were later abandoned by the Confederates.
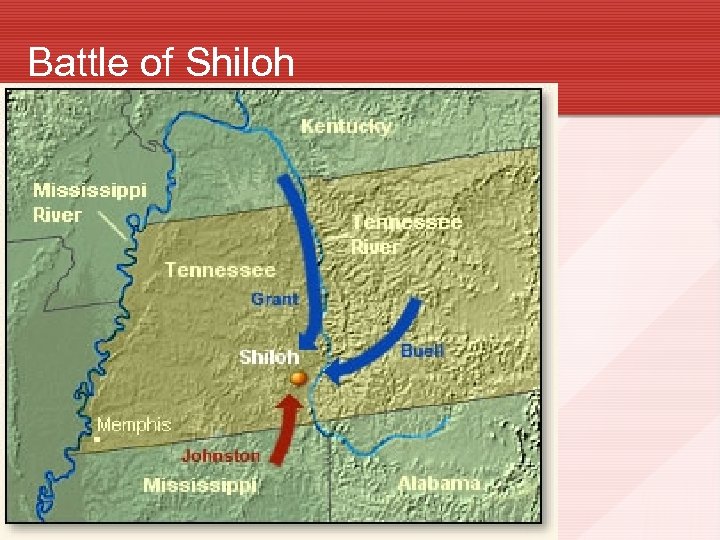 Battle of Shiloh
Battle of Shiloh
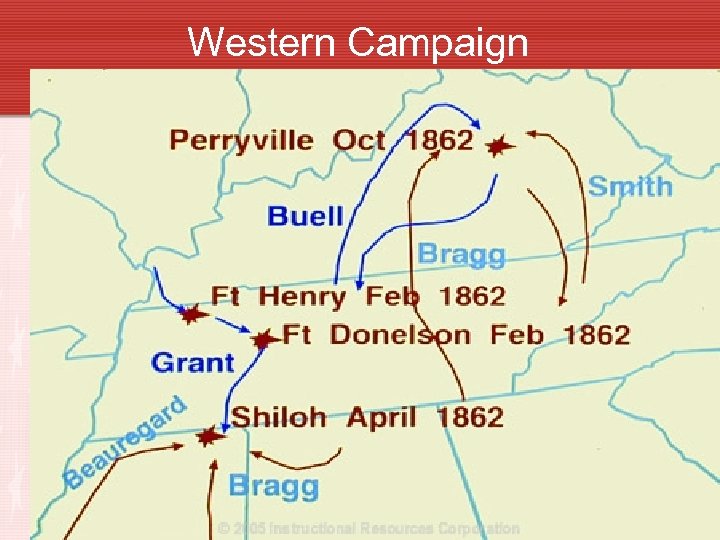 Western Campaign
Western Campaign
 Battle of Shiloh
Battle of Shiloh
 Battle for Vicksburg • Vicksburg was vital. It sat within a great curve in the MS River. The city was well fortified and sat atop high bluffs. • Vicksburg was a key supply point for the Confederacy. • Union tried to dig a canal on the LA side of the river to avoid Vicksburg. This failed. • Dec. 1862 Union Gen. William Tecumseh Sherman begins a direct attack against Vicksburg from the North. Attack Fails
Battle for Vicksburg • Vicksburg was vital. It sat within a great curve in the MS River. The city was well fortified and sat atop high bluffs. • Vicksburg was a key supply point for the Confederacy. • Union tried to dig a canal on the LA side of the river to avoid Vicksburg. This failed. • Dec. 1862 Union Gen. William Tecumseh Sherman begins a direct attack against Vicksburg from the North. Attack Fails
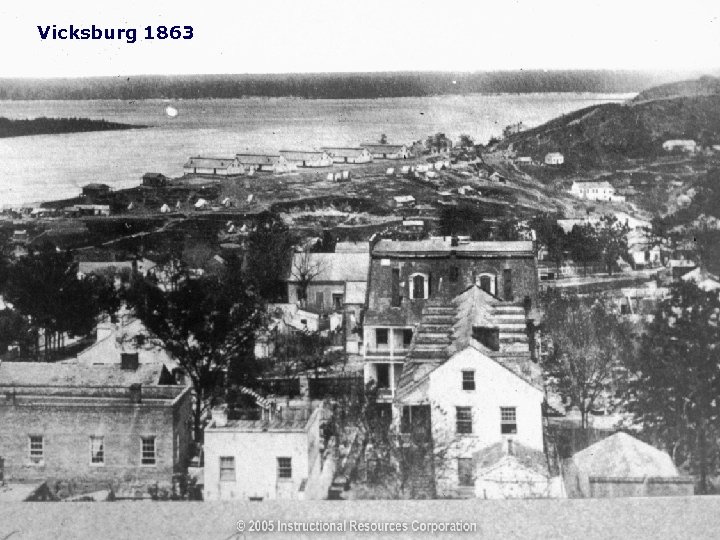 Vicksburg 1863
Vicksburg 1863
 Battle for Vicksburg (Cont. ) • Grant tries to dig a canal to bypass Vicksburg, but this fails due to Confederate Artillery fire. • Grant moves his forces south of Vicksburg through LA. • Grant attacked & captured Jackson, MS in May 1863 & then led a direct attack on Vicksburg. • Vicksburg was surrounded, but numerous attacks failed • Grant laid siege to Vicksburg for 6 weeks • Vicksburg fell July 4, 1863 (same day as Gettysburg victory)
Battle for Vicksburg (Cont. ) • Grant tries to dig a canal to bypass Vicksburg, but this fails due to Confederate Artillery fire. • Grant moves his forces south of Vicksburg through LA. • Grant attacked & captured Jackson, MS in May 1863 & then led a direct attack on Vicksburg. • Vicksburg was surrounded, but numerous attacks failed • Grant laid siege to Vicksburg for 6 weeks • Vicksburg fell July 4, 1863 (same day as Gettysburg victory)
 Vicksburg, MS
Vicksburg, MS
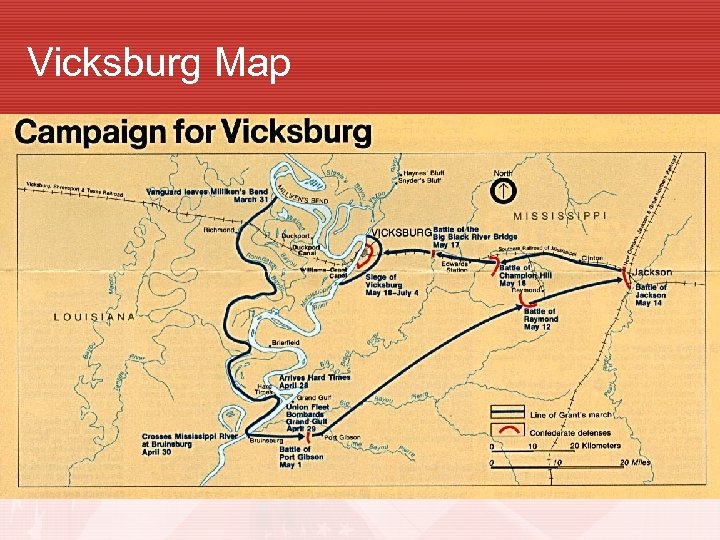 Vicksburg Map
Vicksburg Map
 Union blockade at Vicksburg
Union blockade at Vicksburg
 Union soldiers at Vicksburg
Union soldiers at Vicksburg
 Vicksburg National Cemetery
Vicksburg National Cemetery
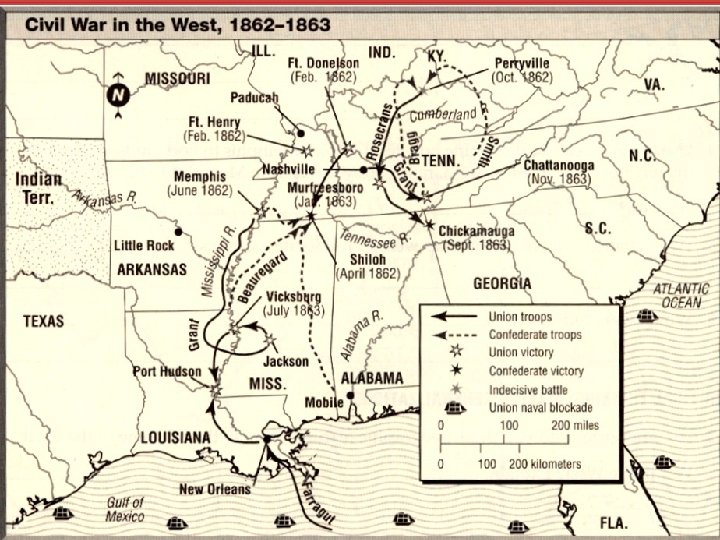
 After Vicksburg • Grant named Commander of all Union Forces • General William T. Sherman commands Union troops in the West • Sherman captured Meridian, MS in Feb. 1864 (RR Depot) • Sherman moved on to Chattanooga • Sherman kept MS Generals Nathan Bedford Forrest and Stephen Lee off of his supply lines by constantly raiding North & East MS • Late 1864 Sherman makes his famous “March to the Sea” (from Atlanta to Savannah, GA)
After Vicksburg • Grant named Commander of all Union Forces • General William T. Sherman commands Union troops in the West • Sherman captured Meridian, MS in Feb. 1864 (RR Depot) • Sherman moved on to Chattanooga • Sherman kept MS Generals Nathan Bedford Forrest and Stephen Lee off of his supply lines by constantly raiding North & East MS • Late 1864 Sherman makes his famous “March to the Sea” (from Atlanta to Savannah, GA)
 Battle of Chattanooga & Chickamagua
Battle of Chattanooga & Chickamagua
 Atlanta Gen. William Tecumseh Sherman
Atlanta Gen. William Tecumseh Sherman
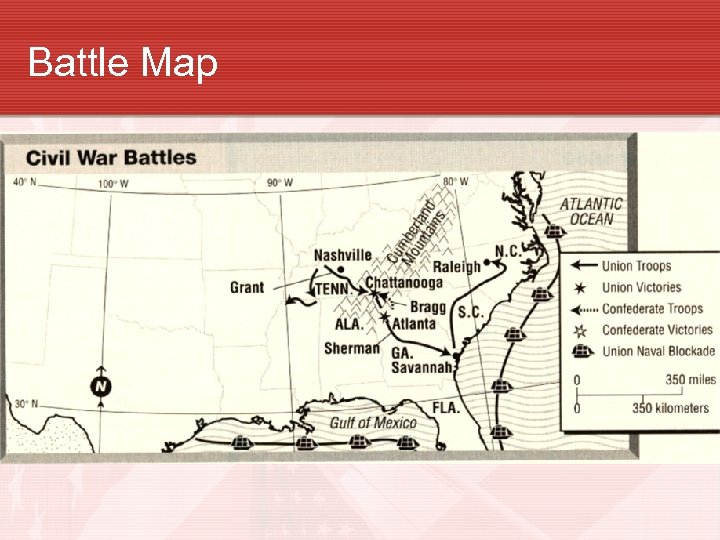 Battle Map
Battle Map
 Fort Massachusetts (Ship Island)
Fort Massachusetts (Ship Island)
 War Ends • March 1865 Richmond, VA falls to the Union. • April 1865 Robert E. Lee surrenders at Appomattox Court House, VA • MS & AL troops surrendered on May 4, 1865 at Citronelle, AL • Jefferson Davis was captured on May 10, 1865 in Irwinville, GA
War Ends • March 1865 Richmond, VA falls to the Union. • April 1865 Robert E. Lee surrenders at Appomattox Court House, VA • MS & AL troops surrendered on May 4, 1865 at Citronelle, AL • Jefferson Davis was captured on May 10, 1865 in Irwinville, GA
 Lee Surrender
Lee Surrender
 Mclean House
Mclean House
 Washington D. C. after the War
Washington D. C. after the War
 MS Numbers • 80, 000 Mississippians fought for the Confederacy • About 500 Mississippians fought for the Union Army • 17, 000 MS slaves or freedmen fought for the Union Army • MS had about 27, 000 dead at the end of the Civil War.
MS Numbers • 80, 000 Mississippians fought for the Confederacy • About 500 Mississippians fought for the Union Army • 17, 000 MS slaves or freedmen fought for the Union Army • MS had about 27, 000 dead at the end of the Civil War.
 9 th Mississippi Infantry
9 th Mississippi Infantry
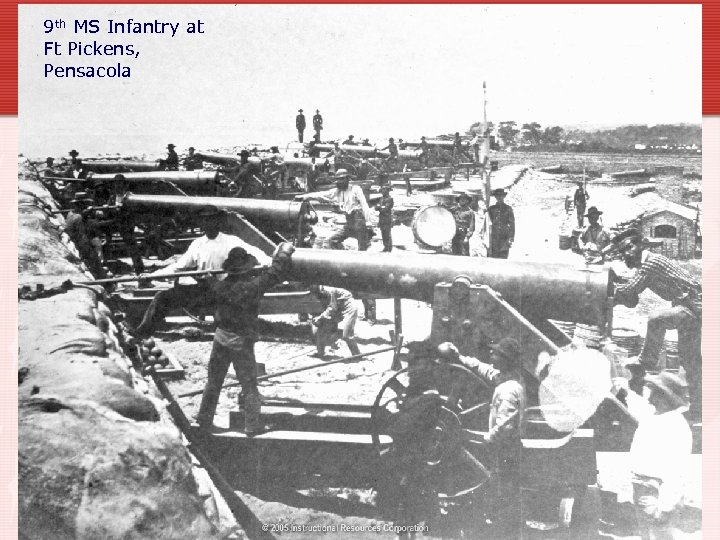 9 th MS Infantry at Ft Pickens, Pensacola
9 th MS Infantry at Ft Pickens, Pensacola
 • Private James Madison Moore, Company A, 14 th Regiment, Mississippi Consolidated Infantry
• Private James Madison Moore, Company A, 14 th Regiment, Mississippi Consolidated Infantry


 MS’s Homefront • Those at home did what they could • Men joined the service • Women made uniforms or were nurses • Everyone supported the state or opposed in silence • MS tried to have normal politics but it was impossible. • Money became worthless in the south. • People did not have • Candle wax, salt, coffee & tea (corn, okra, sweet potatoes used instead), • Slave Revolts were feared • Union Soldiers took what they wanted and in many cases destroyed everything else.
MS’s Homefront • Those at home did what they could • Men joined the service • Women made uniforms or were nurses • Everyone supported the state or opposed in silence • MS tried to have normal politics but it was impossible. • Money became worthless in the south. • People did not have • Candle wax, salt, coffee & tea (corn, okra, sweet potatoes used instead), • Slave Revolts were feared • Union Soldiers took what they wanted and in many cases destroyed everything else.
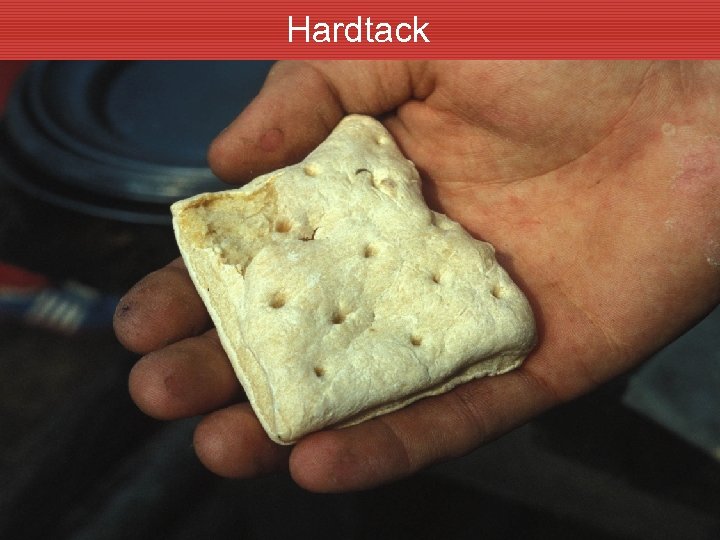 Hardtack
Hardtack
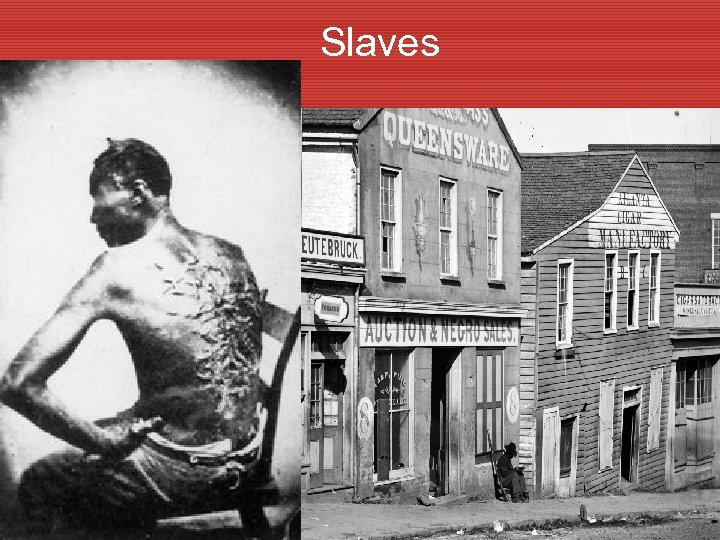
 End of Slavery • During war many southern blacks fled to Union army camps. • Some stayed on the Plantations • Blacks joined Union army and mainly performed labor roles. • By end of war blacks were actively fighting for the Union • Blacks were paid less and usually given menial tasks. • 1862 Emancipation Proclamation issued. Freed slaves in the seceding states. • Dec. 1865 13 th Amendment abolished slavery
End of Slavery • During war many southern blacks fled to Union army camps. • Some stayed on the Plantations • Blacks joined Union army and mainly performed labor roles. • By end of war blacks were actively fighting for the Union • Blacks were paid less and usually given menial tasks. • 1862 Emancipation Proclamation issued. Freed slaves in the seceding states. • Dec. 1865 13 th Amendment abolished slavery
 Slaves
Slaves
 Slaves
Slaves
 Slaves
Slaves
 Emancipation Proclamation
Emancipation Proclamation
 13 th Amendment (from Harper’s Weekly) SCENE IN THE HOUSE ON THE PASSAGE OF THE PROPOSITION TO AMEND THE CONSTITUTION, JANUARY 31, 1865.
13 th Amendment (from Harper’s Weekly) SCENE IN THE HOUSE ON THE PASSAGE OF THE PROPOSITION TO AMEND THE CONSTITUTION, JANUARY 31, 1865.


