6b5c924ba77b857fa8206c36d9bf5498.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41
 MS Project Management Development & Management of Complex Projects Course Code - 706 Procurement Process & Documents Lecture # 31
MS Project Management Development & Management of Complex Projects Course Code - 706 Procurement Process & Documents Lecture # 31
 Summary of Previous Lecture In previous Lecture, we have discussed about Ø Ø Procurement management Tools & Techniques Bidding types Procurement in general
Summary of Previous Lecture In previous Lecture, we have discussed about Ø Ø Procurement management Tools & Techniques Bidding types Procurement in general
 PROCUREMENT IN GENERAL Procurement means acquisition of Contractors/Consultants for execution of works or provision of services / goods / machinery / plant / equipment etc. as required through the legal instrument of entering into a contract. The process of procurement in general include following tasks: Ø Ø Ø Prequalification of Contractors / Consultants. Invitation of Bids / Request for Proposals. Preparation / Review of Bidding Documents. Opening / Evaluation of Bids / Proposals. Award of Work Execution of Contract Agreement. There are mandatory procedures to be followed for all government or donor/funded procurements. The purpose of these procedures is to ensure that all procurements are conducted in a fair and transparent manner. It also brings with it value for money to the executing agency alongwith efficient and cost effective procurement proceeds.
PROCUREMENT IN GENERAL Procurement means acquisition of Contractors/Consultants for execution of works or provision of services / goods / machinery / plant / equipment etc. as required through the legal instrument of entering into a contract. The process of procurement in general include following tasks: Ø Ø Ø Prequalification of Contractors / Consultants. Invitation of Bids / Request for Proposals. Preparation / Review of Bidding Documents. Opening / Evaluation of Bids / Proposals. Award of Work Execution of Contract Agreement. There are mandatory procedures to be followed for all government or donor/funded procurements. The purpose of these procedures is to ensure that all procurements are conducted in a fair and transparent manner. It also brings with it value for money to the executing agency alongwith efficient and cost effective procurement proceeds.
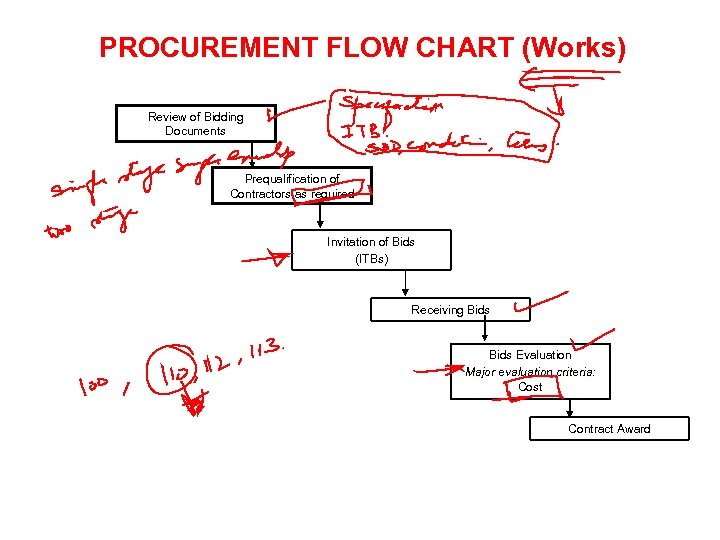 PROCUREMENT FLOW CHART (Works) Review of Bidding Documents Prequalification of Contractors as required Invitation of Bids (ITBs) Receiving Bids Evaluation Major evaluation criteria: Cost Contract Award
PROCUREMENT FLOW CHART (Works) Review of Bidding Documents Prequalification of Contractors as required Invitation of Bids (ITBs) Receiving Bids Evaluation Major evaluation criteria: Cost Contract Award
 PREQUALIFICATION (Works) To ensure that bids are submitted only by the firms that have the necessary qualification in terms of: ü Eligibility ü Experience ü Financial capacity ü Pending Litigation to undertake the work for which bids are to be invited. It is made sure that only technically and financially capable firms having adequate managerial capability are invited to submit their bids.
PREQUALIFICATION (Works) To ensure that bids are submitted only by the firms that have the necessary qualification in terms of: ü Eligibility ü Experience ü Financial capacity ü Pending Litigation to undertake the work for which bids are to be invited. It is made sure that only technically and financially capable firms having adequate managerial capability are invited to submit their bids.
 EVALUATION OF BIDS (Works) Bid evaluation committee prepares a detailed report on the evaluation and comparison of the bids. This report is signed by each member of the committee. Evaluation is carried out as under: ü The work has been administratively approved & technically sanctioned. ü Financial concurrence exists. ü The bids are also checked arithmetically. ü The bids are being received through wide publicity in press and website. ü The bids as a whole or the rates quoted for a individual items are reasonable. ü The bids conform to the provisions of tender documents as responsive.
EVALUATION OF BIDS (Works) Bid evaluation committee prepares a detailed report on the evaluation and comparison of the bids. This report is signed by each member of the committee. Evaluation is carried out as under: ü The work has been administratively approved & technically sanctioned. ü Financial concurrence exists. ü The bids are also checked arithmetically. ü The bids are being received through wide publicity in press and website. ü The bids as a whole or the rates quoted for a individual items are reasonable. ü The bids conform to the provisions of tender documents as responsive.
 EVALUATION OF BIDS (Works) onsive ü The bids conform to the provisions of tender documents as responsive. provisions of documents. ü The lowest bid is reasonably in line with the Engineer’s Estimate. ü Methodology of execution of work proposed in bid is in conformity. The evaluation report along with comparative statements and recommendations is submitted to Tender Acceptance Committee for review, concurrence and signature. Some times bid evaluation is followed by negotiations if so permitted by the competent authority or the donor agency concerned. Award of Work The case for Award of Work is put up to Competent Authority for approval.
EVALUATION OF BIDS (Works) onsive ü The bids conform to the provisions of tender documents as responsive. provisions of documents. ü The lowest bid is reasonably in line with the Engineer’s Estimate. ü Methodology of execution of work proposed in bid is in conformity. The evaluation report along with comparative statements and recommendations is submitted to Tender Acceptance Committee for review, concurrence and signature. Some times bid evaluation is followed by negotiations if so permitted by the competent authority or the donor agency concerned. Award of Work The case for Award of Work is put up to Competent Authority for approval.
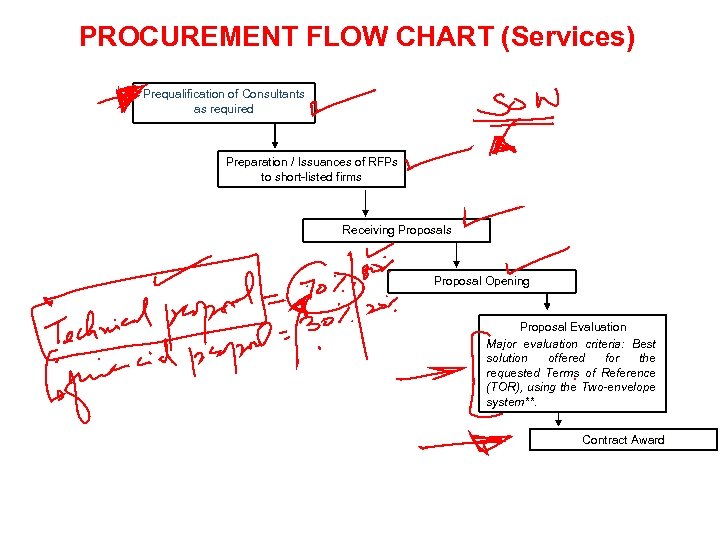 PROCUREMENT FLOW CHART (Services) Prequalification of Consultants as required Preparation / Issuances of RFPs to short-listed firms Receiving Proposals Proposal Opening Proposal Evaluation Major evaluation criteria: Best solution offered for the requested Terms of Reference (TOR), using the Two-envelope system**. Contract Award
PROCUREMENT FLOW CHART (Services) Prequalification of Consultants as required Preparation / Issuances of RFPs to short-listed firms Receiving Proposals Proposal Opening Proposal Evaluation Major evaluation criteria: Best solution offered for the requested Terms of Reference (TOR), using the Two-envelope system**. Contract Award
 1. PQ PROCESS • Prequalification of Consultants based on Public Regulatory Authority Rules – 2004 is initiated after seeking administrative approval by Competent Authority. • PQ notice to be published in Newspapers and displayed on Websites of Procurement Regulatory Authority as well as the relevant authority. • Requirements of PQ. Ø Specific Experience of the firm. Ø List of permanent technical staff with full address employed by the firm. Ø Registration certificate of Pakistan Engineering Council in relevant category and discipline duly updated. Ø Facilities available with consultants to perform their functions effectively Ø Affidavit on stamp paper properly attested by the oath commissioner, to the effect that the firm has neither been blacklisted nor any contract rescinded in the past for non-fulfillment of contractual obligations
1. PQ PROCESS • Prequalification of Consultants based on Public Regulatory Authority Rules – 2004 is initiated after seeking administrative approval by Competent Authority. • PQ notice to be published in Newspapers and displayed on Websites of Procurement Regulatory Authority as well as the relevant authority. • Requirements of PQ. Ø Specific Experience of the firm. Ø List of permanent technical staff with full address employed by the firm. Ø Registration certificate of Pakistan Engineering Council in relevant category and discipline duly updated. Ø Facilities available with consultants to perform their functions effectively Ø Affidavit on stamp paper properly attested by the oath commissioner, to the effect that the firm has neither been blacklisted nor any contract rescinded in the past for non-fulfillment of contractual obligations
 2. INVITATION TO CONSULTANTS The prequalified bidders to be invited to submit their proposals on single stage two envelope system along with issuance of Request for Proposal (RFP). This RFP provides all instructions necessary to submit the bid by the pre-qualified consultants and consists of: Letter of invitation Scope of Work Technical Proposal – Standard forms Financial Proposal – Standard forms Terms of Reference (TOR) Evaluation Criteria • Proposals invited on single stage two envelope system in which technical proposals and financial proposals submitted in two sealed envelopes. • Proposals are to be submitted after 2 weeks (minimum) for National Competitive Bidding and 4 weeks for International Competitive Bidding.
2. INVITATION TO CONSULTANTS The prequalified bidders to be invited to submit their proposals on single stage two envelope system along with issuance of Request for Proposal (RFP). This RFP provides all instructions necessary to submit the bid by the pre-qualified consultants and consists of: Letter of invitation Scope of Work Technical Proposal – Standard forms Financial Proposal – Standard forms Terms of Reference (TOR) Evaluation Criteria • Proposals invited on single stage two envelope system in which technical proposals and financial proposals submitted in two sealed envelopes. • Proposals are to be submitted after 2 weeks (minimum) for National Competitive Bidding and 4 weeks for International Competitive Bidding.
 3. SUBMISSION OF PROPOSALS & OPENING OF TECHNICAL PROPOSAL • The proposals are received on the due date by an Evaluation Committee of officials as constituted under relevant codes. • The technical proposals are first opened and evaluated to select proposals on technical ground as per criteria provided in the RFP. • The Evaluation Committee grade Technical Proposals and prepare a Technical Proposal Evaluation Report for submission to competent forum for approval.
3. SUBMISSION OF PROPOSALS & OPENING OF TECHNICAL PROPOSAL • The proposals are received on the due date by an Evaluation Committee of officials as constituted under relevant codes. • The technical proposals are first opened and evaluated to select proposals on technical ground as per criteria provided in the RFP. • The Evaluation Committee grade Technical Proposals and prepare a Technical Proposal Evaluation Report for submission to competent forum for approval.
 4. OPENING OF FINANCIAL PROPOSALS • After finalization of the grading of technical proposal, the financial proposals are opened as the next step. • The Financial Proposals are opened as per relevant provisions of law. As per this, three technically top proposals are considered only for opening of their financial proposals.
4. OPENING OF FINANCIAL PROPOSALS • After finalization of the grading of technical proposal, the financial proposals are opened as the next step. • The Financial Proposals are opened as per relevant provisions of law. As per this, three technically top proposals are considered only for opening of their financial proposals.
 EVALUATION OF PROPOSALS (Services) Evaluation Committee prepares a detailed report on the evaluation and comparison of the proposals. Here normally single-stage twoenvelope bidding system is adopted. The committee first examine the technical proposals and only those having qualified this only are considered for opening of the financial proposals. This is followed by negotiations with ranked No. 1 firm to negotiate all terms and to conclude a binding contract. This also include review of scope of work plan etc. and subsequently contract amount is finalized on the basis of agreed work plan and man-months. The conclusion of successful negotiation results in the preparation of draft agreement and is submitted for approval to the concerned appropriate forum. After obtaining approval, the final contract agreement is signed and issued to all concerned.
EVALUATION OF PROPOSALS (Services) Evaluation Committee prepares a detailed report on the evaluation and comparison of the proposals. Here normally single-stage twoenvelope bidding system is adopted. The committee first examine the technical proposals and only those having qualified this only are considered for opening of the financial proposals. This is followed by negotiations with ranked No. 1 firm to negotiate all terms and to conclude a binding contract. This also include review of scope of work plan etc. and subsequently contract amount is finalized on the basis of agreed work plan and man-months. The conclusion of successful negotiation results in the preparation of draft agreement and is submitted for approval to the concerned appropriate forum. After obtaining approval, the final contract agreement is signed and issued to all concerned.
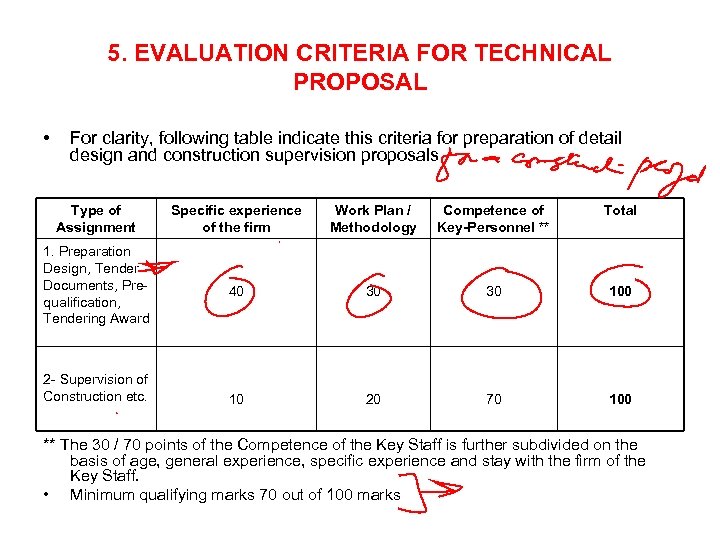 5. EVALUATION CRITERIA FOR TECHNICAL PROPOSAL • For clarity, following table indicate this criteria for preparation of detail design and construction supervision proposals Type of Assignment Specific experience of the firm Work Plan / Methodology Competence of Key-Personnel ** Total 1. Preparation Design, Tender Documents, Prequalification, Tendering Award 40 30 30 10 20 70 100 2 - Supervision of Construction etc. ** The 30 / 70 points of the Competence of the Key Staff is further subdivided on the basis of age, general experience, specific experience and stay with the firm of the Key Staff. • Minimum qualifying marks 70 out of 100 marks
5. EVALUATION CRITERIA FOR TECHNICAL PROPOSAL • For clarity, following table indicate this criteria for preparation of detail design and construction supervision proposals Type of Assignment Specific experience of the firm Work Plan / Methodology Competence of Key-Personnel ** Total 1. Preparation Design, Tender Documents, Prequalification, Tendering Award 40 30 30 10 20 70 100 2 - Supervision of Construction etc. ** The 30 / 70 points of the Competence of the Key Staff is further subdivided on the basis of age, general experience, specific experience and stay with the firm of the Key Staff. • Minimum qualifying marks 70 out of 100 marks
 6. NEGOTIATIONS • The negotiations are conducted after a review of cost break up PROVIDED BY THE CONSULTANT in standard forms in the RFP on the basis of lowest offer received from the bidders technically qualified (top three).
6. NEGOTIATIONS • The negotiations are conducted after a review of cost break up PROVIDED BY THE CONSULTANT in standard forms in the RFP on the basis of lowest offer received from the bidders technically qualified (top three).
 7. AWARD OF WORK • The evaluation Committee deliberate upon results of negotiation meetings and prepares a report for the approval of competent authority. • After approval of Competent Authority, a letter of Acceptance, is issued to the Consultant along with a draft contract for review, concurrence and finalization.
7. AWARD OF WORK • The evaluation Committee deliberate upon results of negotiation meetings and prepares a report for the approval of competent authority. • After approval of Competent Authority, a letter of Acceptance, is issued to the Consultant along with a draft contract for review, concurrence and finalization.
 Eligibility Limitation for Participation – Ideally only by bidders' capability to fulfill the contract Exceptions – Compliance with Relevant laws and rules (blacklisting) – Conflict of interest (i. e. , party has interests that could improperly influence that party’s performance of official duties or responsibilities, contractual obligations, or compliance with law) – Government owned enterprises (unless they are legally and financially autonomous, operate under principles of commercial law and not dependent on executing agency) – Declaration of ineligibility by regulatory bodies
Eligibility Limitation for Participation – Ideally only by bidders' capability to fulfill the contract Exceptions – Compliance with Relevant laws and rules (blacklisting) – Conflict of interest (i. e. , party has interests that could improperly influence that party’s performance of official duties or responsibilities, contractual obligations, or compliance with law) – Government owned enterprises (unless they are legally and financially autonomous, operate under principles of commercial law and not dependent on executing agency) – Declaration of ineligibility by regulatory bodies
 Eligibility – Case Study 1 Bids for a road project in China included a requirement for a telecommunications system. One bidder, a Chinese contractor, offered equipment that was manufactured in South Africa. The value of this item was 5. 2% of the total bid price. South Africa is not a member country of the Donor Agency. How should this bid be treated?
Eligibility – Case Study 1 Bids for a road project in China included a requirement for a telecommunications system. One bidder, a Chinese contractor, offered equipment that was manufactured in South Africa. The value of this item was 5. 2% of the total bid price. South Africa is not a member country of the Donor Agency. How should this bid be treated?
 Eligibility – Case Study 2 Donor Agency investigated the relationship between two bidders for a contract in India. Each of the two companies submitted bids for the same contract as separate companies with different names. The investigation found that the companies both had the same head office address and that the owners were brothers, living at the same address. How should this bid be treated?
Eligibility – Case Study 2 Donor Agency investigated the relationship between two bidders for a contract in India. Each of the two companies submitted bids for the same contract as separate companies with different names. The investigation found that the companies both had the same head office address and that the owners were brothers, living at the same address. How should this bid be treated?
 Eligibility – Case Study 3 An American company bid for the supply of fabricated steel poles, which it manufactures at its factory in the United States. It obtained the steel from Mexico. USA is a member country of the Donor Agency. Mexico is not. How should this bid be treated?
Eligibility – Case Study 3 An American company bid for the supply of fabricated steel poles, which it manufactures at its factory in the United States. It obtained the steel from Mexico. USA is a member country of the Donor Agency. Mexico is not. How should this bid be treated?
 Eligibility – Case Study 4 A bidder is owned and managed by Americans and manufactures widgets at its factory in the United States. The company has incorporated in the Cayman Islands for tax purposes. How should this bid be treated?
Eligibility – Case Study 4 A bidder is owned and managed by Americans and manufactures widgets at its factory in the United States. The company has incorporated in the Cayman Islands for tax purposes. How should this bid be treated?
 Misprocurement If Procurement is not carried out as agreed, the client will. . . declare mis-procurement. . . cancel corresponding portion of financing. . . exercise other remedies If appropriate, Donor Agency may permit rebidding
Misprocurement If Procurement is not carried out as agreed, the client will. . . declare mis-procurement. . . cancel corresponding portion of financing. . . exercise other remedies If appropriate, Donor Agency may permit rebidding
 Fraud and Corruption Corrupt Practice the offering, giving, receiving, or soliciting, directly or indirectly, anything of value to influence improperly the actions of another party (e. g. bribery, kickbacks, extortion, bid manipulation) Fraudulent Practice action or omission, including a misrepresentation, that knowingly or recklessly misleads, or attempts to mislead, a party to obtain a financial or other benefit or to avoid an obligation (e. g. , false bid security/bank guarantees, work certificates, financial statements) Collusive Practice an arrangement between two or more parties designed to achieve an improper purpose, including influencing improperly the actions of another party (e. g. leaking of bid information, rigged specifications) Coercive Practice impairing or harming, or threatening to impair or harm, directly or indirectly, any party or its property to influence improperly the actions of a party
Fraud and Corruption Corrupt Practice the offering, giving, receiving, or soliciting, directly or indirectly, anything of value to influence improperly the actions of another party (e. g. bribery, kickbacks, extortion, bid manipulation) Fraudulent Practice action or omission, including a misrepresentation, that knowingly or recklessly misleads, or attempts to mislead, a party to obtain a financial or other benefit or to avoid an obligation (e. g. , false bid security/bank guarantees, work certificates, financial statements) Collusive Practice an arrangement between two or more parties designed to achieve an improper purpose, including influencing improperly the actions of another party (e. g. leaking of bid information, rigged specifications) Coercive Practice impairing or harming, or threatening to impair or harm, directly or indirectly, any party or its property to influence improperly the actions of a party
 Procurement Plan Preparation
Procurement Plan Preparation
 Procurement Plan Features § Executing Agency shall prepare its Procurement Plan for approval before project execution § Procurement Plan should specify: § Number and size of packages for Supply, Works, Design-Supply-Install (Turnkey), Consulting Services § Timing (Advertisement, Closing Date, Contract Award) § Procurement Method (ICB, LIB, NCB, Shopping, etc. ) § ICB Bidding Procedures § Employer / Donor’s Review Procedures (Post or Prior review) § Modifications Procedures to National Competitive Bidding
Procurement Plan Features § Executing Agency shall prepare its Procurement Plan for approval before project execution § Procurement Plan should specify: § Number and size of packages for Supply, Works, Design-Supply-Install (Turnkey), Consulting Services § Timing (Advertisement, Closing Date, Contract Award) § Procurement Method (ICB, LIB, NCB, Shopping, etc. ) § ICB Bidding Procedures § Employer / Donor’s Review Procedures (Post or Prior review) § Modifications Procedures to National Competitive Bidding
 Sound Procurement Planning Requires Understanding of Historical Levels of Competition in the Market § § § § Difference between contract award price, final contract amount and engineer’s estimate Comparison between engineer’s estimate and contract award prices with rates in other countries for off-the-shelf items Number of bids submitted by, and contracts awarded to, international bidders Percentage of bids submitted that were responsive Reasons why bids were rejected Percentage of bidders who were qualified but did not submit bids Percentage of bidders who purchased bidding documents but did not submit bids
Sound Procurement Planning Requires Understanding of Historical Levels of Competition in the Market § § § § Difference between contract award price, final contract amount and engineer’s estimate Comparison between engineer’s estimate and contract award prices with rates in other countries for off-the-shelf items Number of bids submitted by, and contracts awarded to, international bidders Percentage of bids submitted that were responsive Reasons why bids were rejected Percentage of bidders who were qualified but did not submit bids Percentage of bidders who purchased bidding documents but did not submit bids
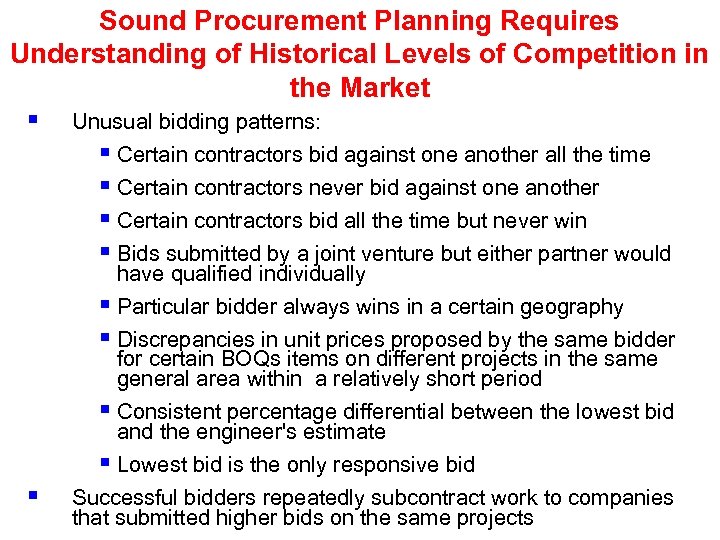 Sound Procurement Planning Requires Understanding of Historical Levels of Competition in the Market § Unusual bidding patterns: § Certain contractors bid against one another all the time § Certain contractors never bid against one another § Certain contractors bid all the time but never win § Bids submitted by a joint venture but either partner would § have qualified individually § Particular bidder always wins in a certain geography § Discrepancies in unit prices proposed by the same bidder for certain BOQs items on different projects in the same general area within a relatively short period § Consistent percentage differential between the lowest bid and the engineer's estimate § Lowest bid is the only responsive bid Successful bidders repeatedly subcontract work to companies that submitted higher bids on the same projects
Sound Procurement Planning Requires Understanding of Historical Levels of Competition in the Market § Unusual bidding patterns: § Certain contractors bid against one another all the time § Certain contractors never bid against one another § Certain contractors bid all the time but never win § Bids submitted by a joint venture but either partner would § have qualified individually § Particular bidder always wins in a certain geography § Discrepancies in unit prices proposed by the same bidder for certain BOQs items on different projects in the same general area within a relatively short period § Consistent percentage differential between the lowest bid and the engineer's estimate § Lowest bid is the only responsive bid Successful bidders repeatedly subcontract work to companies that submitted higher bids on the same projects
 Sound Procurement Planning Requires Understanding of Constraints and Preferences of Market Players § § § § § High financial and experience requirements Tight bid preparation and completion/delivery periods High bid security requirement High barriers to entry for new entrants (licensing requirements, security concerns, health risks) Poor reputation of executing agency Site location Packaging together of unrelated goods/works Difficulty obtaining relevant information when preparing bids (e. g. material availability, equipment availability, local labor, market prices, tax laws, visa and licensing requirements) Lack of bidder understanding of pipeline of future opportunities
Sound Procurement Planning Requires Understanding of Constraints and Preferences of Market Players § § § § § High financial and experience requirements Tight bid preparation and completion/delivery periods High bid security requirement High barriers to entry for new entrants (licensing requirements, security concerns, health risks) Poor reputation of executing agency Site location Packaging together of unrelated goods/works Difficulty obtaining relevant information when preparing bids (e. g. material availability, equipment availability, local labor, market prices, tax laws, visa and licensing requirements) Lack of bidder understanding of pipeline of future opportunities
 Sound Procurement Planning Requires Understanding of Executing Agency’s Capacity Executing Agencies should assess their ability to award and administer contracts § § § Staff: procurement staffing levels Skills: procurement skills gap mapping, training Structure: centralized procurement units, composition of bid evaluation committees Systems: target setting, performance monitoring, review and approval processes, storage of procurement documents and records, accountability, incentives Shared Values: organizational culture, values
Sound Procurement Planning Requires Understanding of Executing Agency’s Capacity Executing Agencies should assess their ability to award and administer contracts § § § Staff: procurement staffing levels Skills: procurement skills gap mapping, training Structure: centralized procurement units, composition of bid evaluation committees Systems: target setting, performance monitoring, review and approval processes, storage of procurement documents and records, accountability, incentives Shared Values: organizational culture, values
 BIDDING DOCUMENTS Basics Purpose • to inform about the scope of contract • to advise on procedures for bid preparation and submission • to inform on criteria and methods for bid evaluation and award of contract • to inform on conditions of contract Responsibility The employer is responsible for preparing and issuing the bidding documents Standard Bidding Documents (SBDs) These are available on relevant websites
BIDDING DOCUMENTS Basics Purpose • to inform about the scope of contract • to advise on procedures for bid preparation and submission • to inform on criteria and methods for bid evaluation and award of contract • to inform on conditions of contract Responsibility The employer is responsible for preparing and issuing the bidding documents Standard Bidding Documents (SBDs) These are available on relevant websites
 BIDDING DOCUMENTS Basics Clarity Bidding Documents must … – be comprehensive in scope and clear in content – describe works to be done, or goods to be procured, including place and period of delivery and installation – indicate methods, terms and conditions of bid evaluation – clearly state the conditions of contract and other requirements that the bidders must comply with
BIDDING DOCUMENTS Basics Clarity Bidding Documents must … – be comprehensive in scope and clear in content – describe works to be done, or goods to be procured, including place and period of delivery and installation – indicate methods, terms and conditions of bid evaluation – clearly state the conditions of contract and other requirements that the bidders must comply with
 BIDDING DOCUMENTS Basics Language English is the working language for many employers, therefore procurement related documents must be in English for most of projects Reference to Financer / Sponsor • Reference to Financer / sponsor is deemed mandatory for contracts wholly or partially financed • Purpose is to inform bidders that procurement is subject to which policies and procedures
BIDDING DOCUMENTS Basics Language English is the working language for many employers, therefore procurement related documents must be in English for most of projects Reference to Financer / Sponsor • Reference to Financer / sponsor is deemed mandatory for contracts wholly or partially financed • Purpose is to inform bidders that procurement is subject to which policies and procedures
 BIDDING DOCUMENTS Outline and Components Part I: Bidding Procedures Section 1. Instruction to Bidders Section 2. Bid Data Sheet Section 3. Evaluation and Qualification Criteria Section 4. Bidding Forms Section 5. Eligible Countries Part II: Requirements Section 6. Supply or Works Requirements Part III: Contract Section 7. General Conditions of Contract Section 8. Particular Conditions of Contract Section 9. Contract Forms
BIDDING DOCUMENTS Outline and Components Part I: Bidding Procedures Section 1. Instruction to Bidders Section 2. Bid Data Sheet Section 3. Evaluation and Qualification Criteria Section 4. Bidding Forms Section 5. Eligible Countries Part II: Requirements Section 6. Supply or Works Requirements Part III: Contract Section 7. General Conditions of Contract Section 8. Particular Conditions of Contract Section 9. Contract Forms
 BIDDING DOCUMENTS 1. Instructions to Bidders (ITB) Purpose to specify general procedures that regulate the bidding process Contents standard clauses that have been designed to remain unchanged and to be used without modifying their text
BIDDING DOCUMENTS 1. Instructions to Bidders (ITB) Purpose to specify general procedures that regulate the bidding process Contents standard clauses that have been designed to remain unchanged and to be used without modifying their text
 BIDDING DOCUMENTS 2. Bid Data Sheet (BDS) Purpose to provide information specific to a particular bidding process in order to supplement the information or requirements of Section I Content clauses which are numbered with the same numbers as the corresponding clauses of Section I. - Instruction to Bidders
BIDDING DOCUMENTS 2. Bid Data Sheet (BDS) Purpose to provide information specific to a particular bidding process in order to supplement the information or requirements of Section I Content clauses which are numbered with the same numbers as the corresponding clauses of Section I. - Instruction to Bidders
 BIDDING DOCUMENTS ITB and BDS Content A. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. General Scope of Bids * Source of Funds * Corrupt Practices Eligible Bidders Eligible Goods & Related Services * B. 6. 7. 8. Contents Of Bidding Document Sections of the BD Clarification of the BD * Amendment of the BD C. Preparation Of Bids 9. Cost of Bidding 10. Language of Bid * 11. Documents Comprising the Bid * 12. Bid Submission Sheet and Price Schedules 13. Alternative Bids * 14. Bid Prices and Discounts * 15. Currencies of Bids * 16. Documents Establishing the Eligibility of the Bidder 17. Documents Establishing the Eligibility of the Goods and Related Services 18. Documents Establishing the Conformity of the Goods and Related Services to the BD
BIDDING DOCUMENTS ITB and BDS Content A. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. General Scope of Bids * Source of Funds * Corrupt Practices Eligible Bidders Eligible Goods & Related Services * B. 6. 7. 8. Contents Of Bidding Document Sections of the BD Clarification of the BD * Amendment of the BD C. Preparation Of Bids 9. Cost of Bidding 10. Language of Bid * 11. Documents Comprising the Bid * 12. Bid Submission Sheet and Price Schedules 13. Alternative Bids * 14. Bid Prices and Discounts * 15. Currencies of Bids * 16. Documents Establishing the Eligibility of the Bidder 17. Documents Establishing the Eligibility of the Goods and Related Services 18. Documents Establishing the Conformity of the Goods and Related Services to the BD
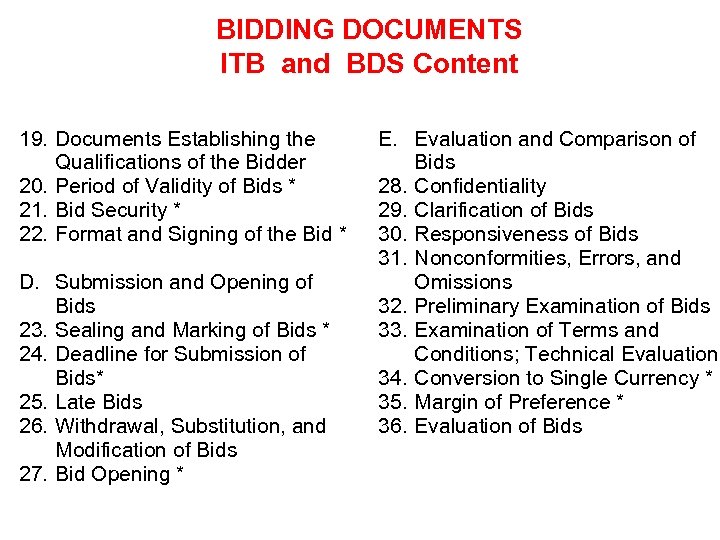 BIDDING DOCUMENTS ITB and BDS Content 19. Documents Establishing the Qualifications of the Bidder 20. Period of Validity of Bids * 21. Bid Security * 22. Format and Signing of the Bid * D. Submission and Opening of Bids 23. Sealing and Marking of Bids * 24. Deadline for Submission of Bids* 25. Late Bids 26. Withdrawal, Substitution, and Modification of Bids 27. Bid Opening * E. Evaluation and Comparison of Bids 28. Confidentiality 29. Clarification of Bids 30. Responsiveness of Bids 31. Nonconformities, Errors, and Omissions 32. Preliminary Examination of Bids 33. Examination of Terms and Conditions; Technical Evaluation 34. Conversion to Single Currency * 35. Margin of Preference * 36. Evaluation of Bids
BIDDING DOCUMENTS ITB and BDS Content 19. Documents Establishing the Qualifications of the Bidder 20. Period of Validity of Bids * 21. Bid Security * 22. Format and Signing of the Bid * D. Submission and Opening of Bids 23. Sealing and Marking of Bids * 24. Deadline for Submission of Bids* 25. Late Bids 26. Withdrawal, Substitution, and Modification of Bids 27. Bid Opening * E. Evaluation and Comparison of Bids 28. Confidentiality 29. Clarification of Bids 30. Responsiveness of Bids 31. Nonconformities, Errors, and Omissions 32. Preliminary Examination of Bids 33. Examination of Terms and Conditions; Technical Evaluation 34. Conversion to Single Currency * 35. Margin of Preference * 36. Evaluation of Bids
 BIDDING DOCUMENTS ITB and BDS Content 37. Comparison of Bids 38. Postqualification of the Bidder 39. Purchaser’s Right to Accept Any Bid, and to Reject Any or All Bids F. Award of Contract 40. Award Criteria 41. Purchaser’s Right to Vary Quantities at the Time of Award * 42. Notification of Award 43. Signing of Contract 44. Performance Security
BIDDING DOCUMENTS ITB and BDS Content 37. Comparison of Bids 38. Postqualification of the Bidder 39. Purchaser’s Right to Accept Any Bid, and to Reject Any or All Bids F. Award of Contract 40. Award Criteria 41. Purchaser’s Right to Vary Quantities at the Time of Award * 42. Notification of Award 43. Signing of Contract 44. Performance Security
 Summary of This Lecture In this Lecture, we have discussed about Ø Ø Ø Procurement process for Works Procurement process for services Eligibility Procurement plan preparation Bid documents outlines
Summary of This Lecture In this Lecture, we have discussed about Ø Ø Ø Procurement process for Works Procurement process for services Eligibility Procurement plan preparation Bid documents outlines
 End Note Being good is easy, what is difficult is being just.
End Note Being good is easy, what is difficult is being just.
 THANK YOU!
THANK YOU!


