50292813cc69a8b155c994c2c81a3d35.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15
 MP 3 Overview John Ehrhardt Elena Silenok CSE 228 – Spring 03
MP 3 Overview John Ehrhardt Elena Silenok CSE 228 – Spring 03
 Where did MP 3 come from? l In 1987 the Fraunhofer IIS (Institut Integreierte Schaltungen) started work on audio encoding l In 1991 with Prof. Deiter Seitzler from the University of Erlangen they devised a very powerful algorithm that was standardized as ISO-MPEG Audio Layer-3
Where did MP 3 come from? l In 1987 the Fraunhofer IIS (Institut Integreierte Schaltungen) started work on audio encoding l In 1991 with Prof. Deiter Seitzler from the University of Erlangen they devised a very powerful algorithm that was standardized as ISO-MPEG Audio Layer-3
 Why “MP 3” and what is MP 3? l Windows introduced the. mp 3 file extension for MPEG-1 Layer III encoder and decoder software l Files encoded with the MPEG-2 lower sampling rate extension of Layer III are also known as mp 3 s
Why “MP 3” and what is MP 3? l Windows introduced the. mp 3 file extension for MPEG-1 Layer III encoder and decoder software l Files encoded with the MPEG-2 lower sampling rate extension of Layer III are also known as mp 3 s
 MPEG Audio In MPEG audio, one may achieve a typical data reduction of 1: 4 by Layer 1 (corresponds to 384 kbps for a stereo signal), 1: 6. . . 1: 8 by Layer 2 (corresponds to 256. . 192 kbps for a stereo signal), 1: 10. . . 1: 12 by Layer 3 (corresponds to 128. . 112 kbps for a stereo signal), While maintaining CD quality sound.
MPEG Audio In MPEG audio, one may achieve a typical data reduction of 1: 4 by Layer 1 (corresponds to 384 kbps for a stereo signal), 1: 6. . . 1: 8 by Layer 2 (corresponds to 256. . 192 kbps for a stereo signal), 1: 10. . . 1: 12 by Layer 3 (corresponds to 128. . 112 kbps for a stereo signal), While maintaining CD quality sound.
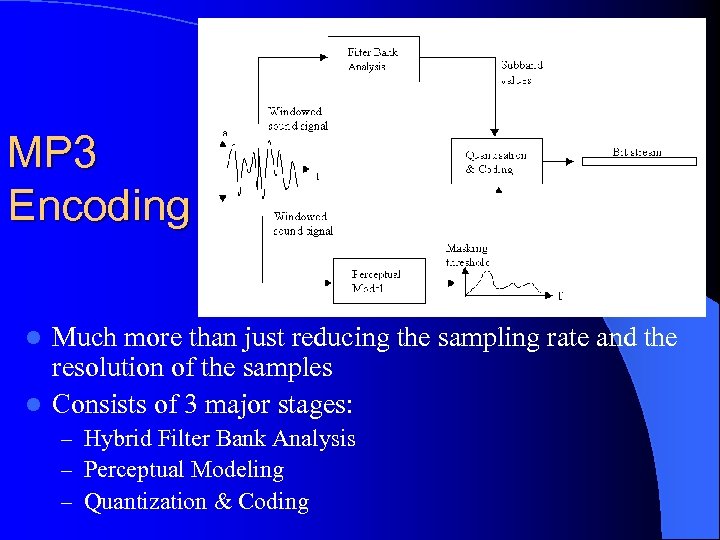 MP 3 Encoding Much more than just reducing the sampling rate and the resolution of the samples l Consists of 3 major stages: l – Hybrid Filter Bank Analysis – Perceptual Modeling – Quantization & Coding
MP 3 Encoding Much more than just reducing the sampling rate and the resolution of the samples l Consists of 3 major stages: l – Hybrid Filter Bank Analysis – Perceptual Modeling – Quantization & Coding
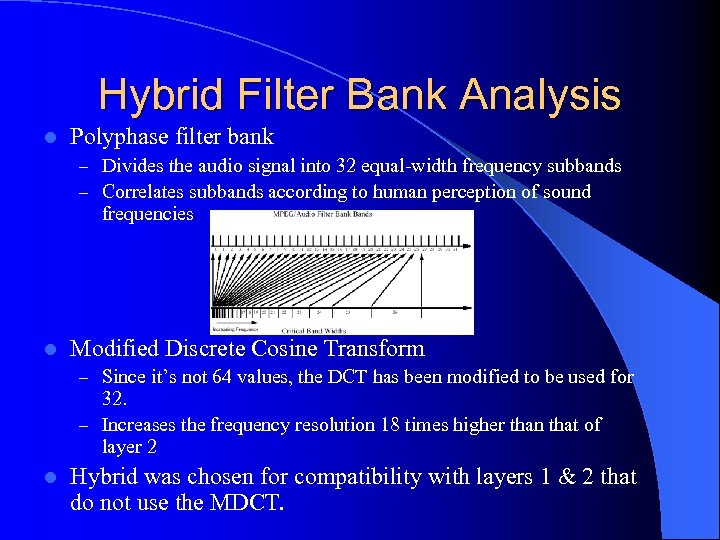 Hybrid Filter Bank Analysis l Polyphase filter bank – Divides the audio signal into 32 equal-width frequency subbands – Correlates subbands according to human perception of sound frequencies l Modified Discrete Cosine Transform – Since it’s not 64 values, the DCT has been modified to be used for 32. – Increases the frequency resolution 18 times higher than that of layer 2 l Hybrid was chosen for compatibility with layers 1 & 2 that do not use the MDCT.
Hybrid Filter Bank Analysis l Polyphase filter bank – Divides the audio signal into 32 equal-width frequency subbands – Correlates subbands according to human perception of sound frequencies l Modified Discrete Cosine Transform – Since it’s not 64 values, the DCT has been modified to be used for 32. – Increases the frequency resolution 18 times higher than that of layer 2 l Hybrid was chosen for compatibility with layers 1 & 2 that do not use the MDCT.
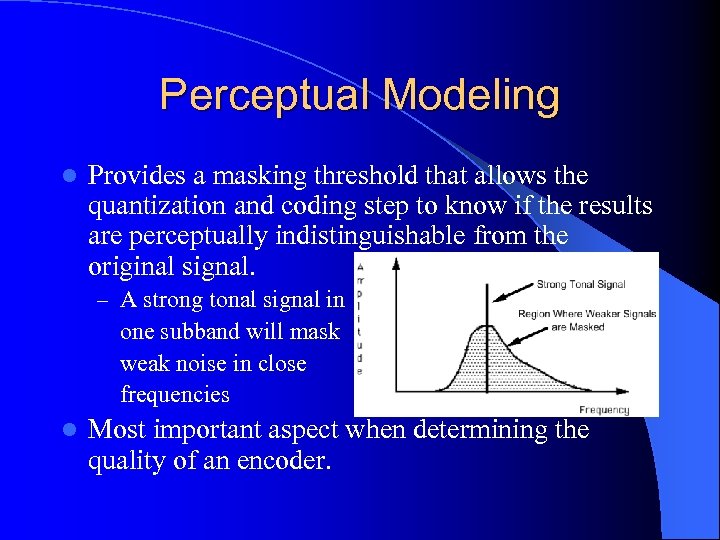 Perceptual Modeling l Provides a masking threshold that allows the quantization and coding step to know if the results are perceptually indistinguishable from the original signal. – A strong tonal signal in one subband will mask weak noise in close frequencies l Most important aspect when determining the quality of an encoder.
Perceptual Modeling l Provides a masking threshold that allows the quantization and coding step to know if the results are perceptually indistinguishable from the original signal. – A strong tonal signal in one subband will mask weak noise in close frequencies l Most important aspect when determining the quality of an encoder.
 Quantization & Coding l Quantization – Power-law: larger values have less accuracy – Huffman coding l Coding – Attempts to quantize the resulting MDCT from the Filter Bank at level that meets both the bitrate and the masking requirements – Huffman Coding and Quantization level provide feedback for bitrate – Scale factors for each subband are adjusted until they meet the masking threshold.
Quantization & Coding l Quantization – Power-law: larger values have less accuracy – Huffman coding l Coding – Attempts to quantize the resulting MDCT from the Filter Bank at level that meets both the bitrate and the masking requirements – Huffman Coding and Quantization level provide feedback for bitrate – Scale factors for each subband are adjusted until they meet the masking threshold.
 Bitstream Layout Divided into 1152 samples per block l One block is encoded within one MPEG-1 audio frame (header and data. ) l Header (First 4 bytes of a frame) l – No file header – Contains: Frame Sync, MPEG Layer, Sampling Frequency, Number of Channels, CRC, etc. – Variable bit rate mp 3’s switch bitrate between frames
Bitstream Layout Divided into 1152 samples per block l One block is encoded within one MPEG-1 audio frame (header and data. ) l Header (First 4 bytes of a frame) l – No file header – Contains: Frame Sync, MPEG Layer, Sampling Frequency, Number of Channels, CRC, etc. – Variable bit rate mp 3’s switch bitrate between frames
 Audio Tag: ID 3 v 1 l Contains information about the artist, title, published year, genre, etc. l The last 128 bytes of the MPEG audio file. l ID 3 v 2 much more complicated – See www. id 3. org for more details
Audio Tag: ID 3 v 1 l Contains information about the artist, title, published year, genre, etc. l The last 128 bytes of the MPEG audio file. l ID 3 v 2 much more complicated – See www. id 3. org for more details
 Watermarking l Set of secondary digital data embedded in the primary digital media l Provides ownership protection, copy control, fingerprinting, authentication, and control over information l Robust vs. fragile, invisible vs. visible, public vs. private (detection w/ or w/o the original unmarked image)
Watermarking l Set of secondary digital data embedded in the primary digital media l Provides ownership protection, copy control, fingerprinting, authentication, and control over information l Robust vs. fragile, invisible vs. visible, public vs. private (detection w/ or w/o the original unmarked image)
 Current State of MP 3 l 3 million of MP 3 tracks downloaded every day (International Federation of Phonographic Industries) – mostly pirated l Forrester Research says MP 3/other online music sales have reached 7% by 2003 $1. 1 bn a year l MP 3 alternative launched in December 1998: the Secure Digital Music Initiative
Current State of MP 3 l 3 million of MP 3 tracks downloaded every day (International Federation of Phonographic Industries) – mostly pirated l Forrester Research says MP 3/other online music sales have reached 7% by 2003 $1. 1 bn a year l MP 3 alternative launched in December 1998: the Secure Digital Music Initiative
 Secure Digital Music Initiative l Started in 1998, currently over 200 members l Spearheaded by RIAA, IFPI, RIAJ and major recording companies l SDMI intended to secure music in all forms, across all delivery channels l 2 phases, to finally incorporate dual watermarking or other protection scheme
Secure Digital Music Initiative l Started in 1998, currently over 200 members l Spearheaded by RIAA, IFPI, RIAJ and major recording companies l SDMI intended to secure music in all forms, across all delivery channels l 2 phases, to finally incorporate dual watermarking or other protection scheme
 References l l l http: //www. stanford. edu/~udara/SOCO/lossy/mp 3 http: //www. iis. fraunhofer. de/amm/techinf/layer 3/inde x. html http: //www. tnt. unihannover. de/project/mpeg/audio/faq/mpeg 1. html http: //www. dv. co. yu/mpgscript/mpeghdr. htm “MP 3 And AAC Explained, ” Karlheinz Brandenburg, Fraunhofer Institute for Integrated Circuits Fh. G-IIS A, Erlangen, Germany http: //www. sdmi. org
References l l l http: //www. stanford. edu/~udara/SOCO/lossy/mp 3 http: //www. iis. fraunhofer. de/amm/techinf/layer 3/inde x. html http: //www. tnt. unihannover. de/project/mpeg/audio/faq/mpeg 1. html http: //www. dv. co. yu/mpgscript/mpeghdr. htm “MP 3 And AAC Explained, ” Karlheinz Brandenburg, Fraunhofer Institute for Integrated Circuits Fh. G-IIS A, Erlangen, Germany http: //www. sdmi. org
 Thank you for your attention!
Thank you for your attention!


