e535985284e77c3881720246afe788ec.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 Mouse Model Neuro-Facial Dysmorphology: Translational & Treatment Studies Progress since September 1, 2007 Feng C. Zhou Charles Goodlett Yun Liang Shiaofen Fang Bruce Anthony
Mouse Model Neuro-Facial Dysmorphology: Translational & Treatment Studies Progress since September 1, 2007 Feng C. Zhou Charles Goodlett Yun Liang Shiaofen Fang Bruce Anthony
 Specific Aims • Aim 1. To advance the understanding of sources of variation in abnormal facial development induced by prenatal alcohol exposure as a function of the dose and developmental timing of alcohol exposure in a C 57 BL/6 mouse model. • Aim 2. To determine longitudinally the extent of brain structural and neuro-facial abnormalities as a function of the dose and developmental stage of alcohol exposure. • Aim 3. To determine the extent to which the Neurotrophic peptides NAP/SAL will provide long-term protection against alcohol-induced neuro-facial dysmorphology and neurobehavioral deficits.
Specific Aims • Aim 1. To advance the understanding of sources of variation in abnormal facial development induced by prenatal alcohol exposure as a function of the dose and developmental timing of alcohol exposure in a C 57 BL/6 mouse model. • Aim 2. To determine longitudinally the extent of brain structural and neuro-facial abnormalities as a function of the dose and developmental stage of alcohol exposure. • Aim 3. To determine the extent to which the Neurotrophic peptides NAP/SAL will provide long-term protection against alcohol-induced neuro-facial dysmorphology and neurobehavioral deficits.
 1. Mouse Model for Dose and Timing of Alcohol Exposure • Standardization of C 57 BL 6 mice lines from Halan and Jackson breeder used in Drs. Zhou and Sulik’s laboratories (a) Drinking level—Bruce Anthony (b) Teratogenesis – Scott Parnell
1. Mouse Model for Dose and Timing of Alcohol Exposure • Standardization of C 57 BL 6 mice lines from Halan and Jackson breeder used in Drs. Zhou and Sulik’s laboratories (a) Drinking level—Bruce Anthony (b) Teratogenesis – Scott Parnell
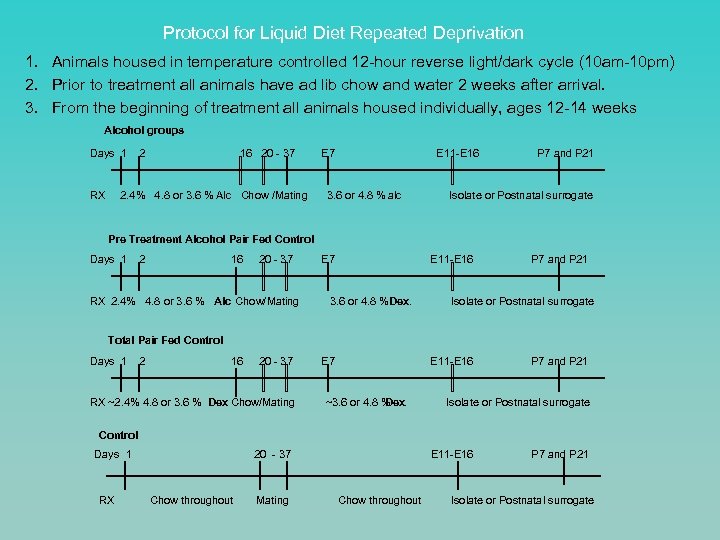 Protocol for Liquid Diet Repeated Deprivation 1. Animals housed in temperature controlled 12 -hour reverse light/dark cycle (10 am-10 pm) 2. Prior to treatment all animals have ad lib chow and water 2 weeks after arrival. 3. From the beginning of treatment all animals housed individually, ages 12 -14 weeks Alcohol groups Days 1 2 16 20 - 37 E 7 E 11 -E 16 P 7 and P 21 RX 2. 4% 4. 8 or 3. 6 % Alc Chow /Mating 3. 6 or 4. 8 % alc Isolate or Postnatal surrogate Pre Treatment Alcohol Pair Fed Control Days 1 2 16 20 - 37 E 7 E 11 -E 16 P 7 and P 21 RX 2. 4% 4. 8 or 3. 6 % Alc Chow/Mating 3. 6 or 4. 8 % ex. Isolate or Postnatal surrogate D Total Pair Fed Control Days 1 2 16 20 - 37 E 7 E 11 -E 16 P 7 and P 21 RX ~2. 4% 4. 8 or 3. 6 % Dex Chow/Mating ~3. 6 or 4. 8 % Dex. Isolate or Postnatal surrogate Control Days 1 20 - 37 E 11 -E 16 P 7 and P 21 RX Chow throughout Mating Chow throughout Isolate or Postnatal surrogate
Protocol for Liquid Diet Repeated Deprivation 1. Animals housed in temperature controlled 12 -hour reverse light/dark cycle (10 am-10 pm) 2. Prior to treatment all animals have ad lib chow and water 2 weeks after arrival. 3. From the beginning of treatment all animals housed individually, ages 12 -14 weeks Alcohol groups Days 1 2 16 20 - 37 E 7 E 11 -E 16 P 7 and P 21 RX 2. 4% 4. 8 or 3. 6 % Alc Chow /Mating 3. 6 or 4. 8 % alc Isolate or Postnatal surrogate Pre Treatment Alcohol Pair Fed Control Days 1 2 16 20 - 37 E 7 E 11 -E 16 P 7 and P 21 RX 2. 4% 4. 8 or 3. 6 % Alc Chow/Mating 3. 6 or 4. 8 % ex. Isolate or Postnatal surrogate D Total Pair Fed Control Days 1 2 16 20 - 37 E 7 E 11 -E 16 P 7 and P 21 RX ~2. 4% 4. 8 or 3. 6 % Dex Chow/Mating ~3. 6 or 4. 8 % Dex. Isolate or Postnatal surrogate Control Days 1 20 - 37 E 11 -E 16 P 7 and P 21 RX Chow throughout Mating Chow throughout Isolate or Postnatal surrogate
 ** * * **** Mating Harlan C 57 Bl/6 Jackson C 57 Bl/6 Mating Treatment Paradigm 1. Pre treatment 2. 4% (x 2 days) then 4. 8 % 14 days. 2. 16 day deprivation and mating 3. E 7 -E 18 4. 8% Alc Averages: Harlan pre depreviation 26. 6 Avg daily Harlan post deprivation 26. 6 Avg daily Jax pre deprivation Jax post deprivation 22. 6 Avg daily 22. 4 Avg Daily * Statistical Significant N=6
** * * **** Mating Harlan C 57 Bl/6 Jackson C 57 Bl/6 Mating Treatment Paradigm 1. Pre treatment 2. 4% (x 2 days) then 4. 8 % 14 days. 2. 16 day deprivation and mating 3. E 7 -E 18 4. 8% Alc Averages: Harlan pre depreviation 26. 6 Avg daily Harlan post deprivation 26. 6 Avg daily Jax pre deprivation Jax post deprivation 22. 6 Avg daily 22. 4 Avg Daily * Statistical Significant N=6
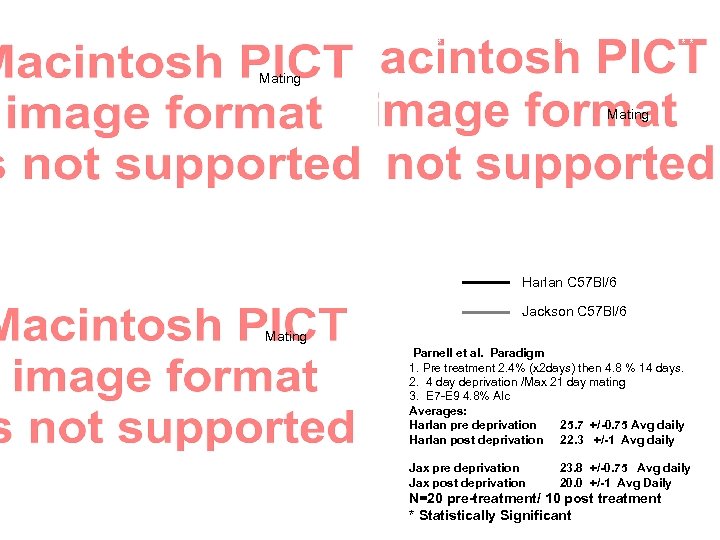 * * * * * Mating * * * * * Harlan C 57 Bl/6 Jackson C 57 Bl/6 Mating Parnell et al. Paradigm 1. Pre treatment 2. 4% (x 2 days) then 4. 8 % 14 days. 2. 4 day deprivation /Max 21 day mating 3. E 7 -E 9 4. 8% Alc Averages: Harlan pre deprivation 25. 7 +/-0. 75 Avg daily Harlan post deprivation 22. 3 +/-1 Avg daily Jax pre deprivation Jax post deprivation 23. 8 +/-0. 75 Avg daily 20. 0 +/-1 Avg Daily N=20 pre-treatment/ 10 post treatment * Statistically Significant
* * * * * Mating * * * * * Harlan C 57 Bl/6 Jackson C 57 Bl/6 Mating Parnell et al. Paradigm 1. Pre treatment 2. 4% (x 2 days) then 4. 8 % 14 days. 2. 4 day deprivation /Max 21 day mating 3. E 7 -E 9 4. 8% Alc Averages: Harlan pre deprivation 25. 7 +/-0. 75 Avg daily Harlan post deprivation 22. 3 +/-1 Avg daily Jax pre deprivation Jax post deprivation 23. 8 +/-0. 75 Avg daily 20. 0 +/-1 Avg Daily N=20 pre-treatment/ 10 post treatment * Statistically Significant
 2. Facial dysmorph. Analysis A. Microvideo imaging analysis Moving from 2 D to 3 D --- Shiaofen Fang B. Micro. CT imaging analysis ---Yun Liang
2. Facial dysmorph. Analysis A. Microvideo imaging analysis Moving from 2 D to 3 D --- Shiaofen Fang B. Micro. CT imaging analysis ---Yun Liang
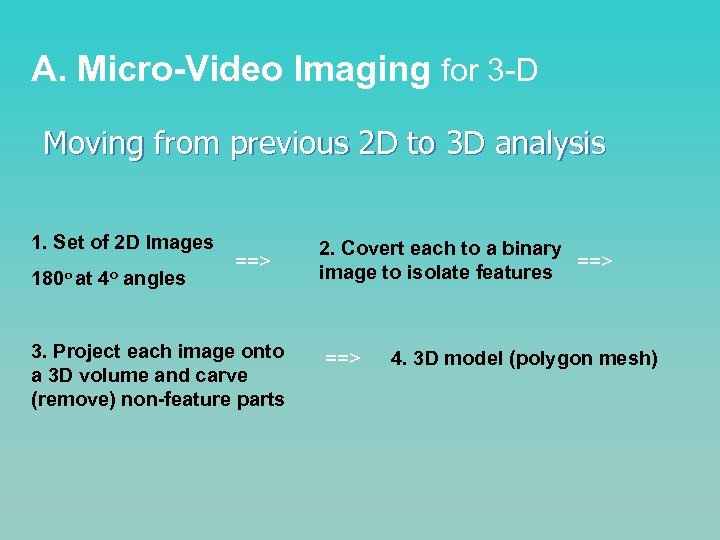 A. Micro-Video Imaging for 3 -D Moving from previous 2 D to 3 D analysis 1. Set of 2 D Images 180 o at 4 o angles ==> 3. Project each image onto a 3 D volume and carve (remove) non-feature parts 2. Covert each to a binary ==> image to isolate features ==> 4. 3 D model (polygon mesh)
A. Micro-Video Imaging for 3 -D Moving from previous 2 D to 3 D analysis 1. Set of 2 D Images 180 o at 4 o angles ==> 3. Project each image onto a 3 D volume and carve (remove) non-feature parts 2. Covert each to a binary ==> image to isolate features ==> 4. 3 D model (polygon mesh)
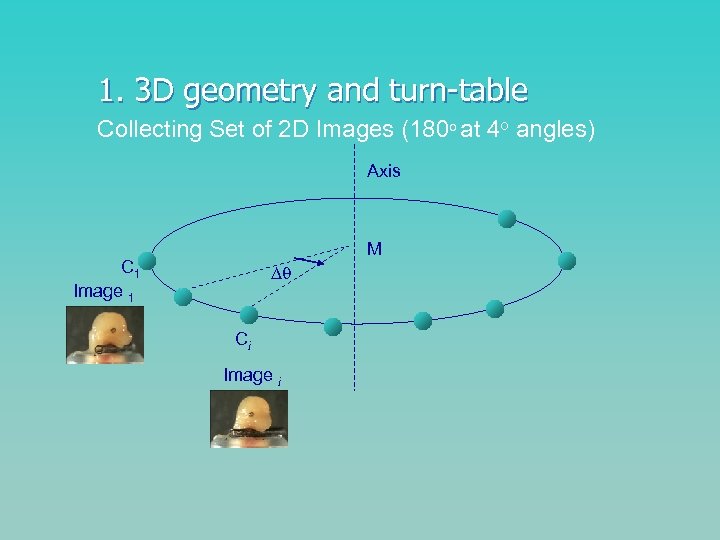 1. 3 D geometry and turn-table Collecting Set of 2 D Images (180 o at 4 o angles) Axis M C 1 Image 1 Ci Image i
1. 3 D geometry and turn-table Collecting Set of 2 D Images (180 o at 4 o angles) Axis M C 1 Image 1 Ci Image i
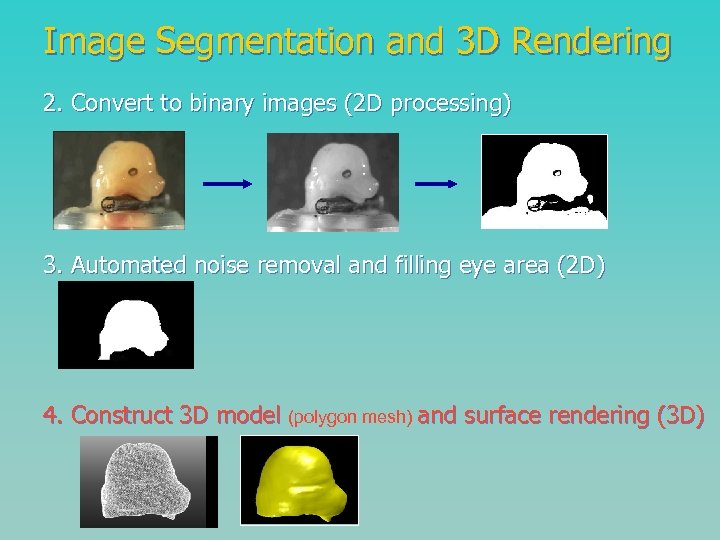 Image Segmentation and 3 D Rendering 2. Convert to binary images (2 D processing) 3. Automated noise removal and filling eye area (2 D) 4. Construct 3 D model (polygon mesh) and surface rendering (3 D)
Image Segmentation and 3 D Rendering 2. Convert to binary images (2 D processing) 3. Automated noise removal and filling eye area (2 D) 4. Construct 3 D model (polygon mesh) and surface rendering (3 D)
 Improvements in Microvideo 1. New rotor for Implementation of step motor a. Exact definition of degree changes b. Control of angle progression in capture 2. Images scaled within software a. To ensure proper aspect ratio b. To maintain optimal dimensions software allows 3. Projection algorithm re-done a. Projection done with built-in functions for consistency and quality assurance between users.
Improvements in Microvideo 1. New rotor for Implementation of step motor a. Exact definition of degree changes b. Control of angle progression in capture 2. Images scaled within software a. To ensure proper aspect ratio b. To maintain optimal dimensions software allows 3. Projection algorithm re-done a. Projection done with built-in functions for consistency and quality assurance between users.
 B. Micro-CT for Craniofacial Analysis —including facial & skeletal imaging co-registration • Evaluate facial and cranial bone dysmorphology in postnatal mice (P 7 and P 21) using 3 D images obtained by a Micro-CT. • Identify anthropometric geometries and features to differentiate subjects with alcohol exposure. • Correlative studies of facial and skeletal features
B. Micro-CT for Craniofacial Analysis —including facial & skeletal imaging co-registration • Evaluate facial and cranial bone dysmorphology in postnatal mice (P 7 and P 21) using 3 D images obtained by a Micro-CT. • Identify anthropometric geometries and features to differentiate subjects with alcohol exposure. • Correlative studies of facial and skeletal features
 Components of Micro. CT System Imaging Volume Detector X-Ray Source EVS RS-9
Components of Micro. CT System Imaging Volume Detector X-Ray Source EVS RS-9
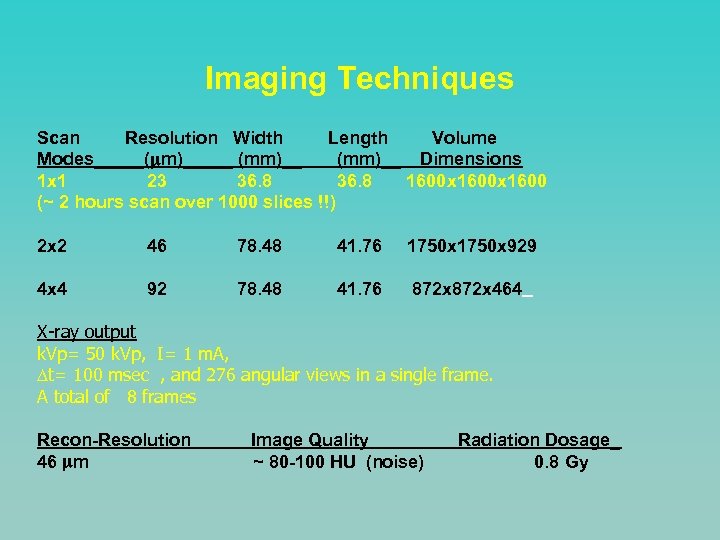 Imaging Techniques Scan Resolution Width Length Volume Modes_____( m)_____ (mm)__ Dimensions 1 x 1 23 36. 8 1600 x 1600 (~ 2 hours scan over 1000 slices !!) 2 x 2 46 78. 48 41. 76 1750 x 929 4 x 4 92 78. 48 41. 76 872 x 464 X-ray output k. Vp= 50 k. Vp, I= 1 m. A, t= 100 msec , and 276 angular views in a single frame. A total of 8 frames Recon-Resolution 46 m Image Quality ~ 80 -100 HU (noise) Radiation Dosage_ 0. 8 Gy
Imaging Techniques Scan Resolution Width Length Volume Modes_____( m)_____ (mm)__ Dimensions 1 x 1 23 36. 8 1600 x 1600 (~ 2 hours scan over 1000 slices !!) 2 x 2 46 78. 48 41. 76 1750 x 929 4 x 4 92 78. 48 41. 76 872 x 464 X-ray output k. Vp= 50 k. Vp, I= 1 m. A, t= 100 msec , and 276 angular views in a single frame. A total of 8 frames Recon-Resolution 46 m Image Quality ~ 80 -100 HU (noise) Radiation Dosage_ 0. 8 Gy
 Micro. CT Study Procedure Subjects: P 7 and P 21 C 57 BL/6 mice, Control vs Liquid Alcohol diet treated. Anesthesia: an induction chamber with Isoflurane levels of 1. 5 % at a initially flow rate of 0. 8 -1. 2 liter/min followed by a maintenance Isoflurane rate of 0. 5 liter/min. CT number Calibration: QA phantom with water, air, acyrilc, bone (SB 3) inserts Image Analysis: (1) Semi-automatic: Segmentation of skull with thresholding, followed by manually refining in slice-by-slice way; (2) Volume rendering (shaded-surface-display); (3) Metric measurement with volume/slice relating tool. Analyzed using “Mx. View” (courtesy of Philips Medical Systems).
Micro. CT Study Procedure Subjects: P 7 and P 21 C 57 BL/6 mice, Control vs Liquid Alcohol diet treated. Anesthesia: an induction chamber with Isoflurane levels of 1. 5 % at a initially flow rate of 0. 8 -1. 2 liter/min followed by a maintenance Isoflurane rate of 0. 5 liter/min. CT number Calibration: QA phantom with water, air, acyrilc, bone (SB 3) inserts Image Analysis: (1) Semi-automatic: Segmentation of skull with thresholding, followed by manually refining in slice-by-slice way; (2) Volume rendering (shaded-surface-display); (3) Metric measurement with volume/slice relating tool. Analyzed using “Mx. View” (courtesy of Philips Medical Systems).
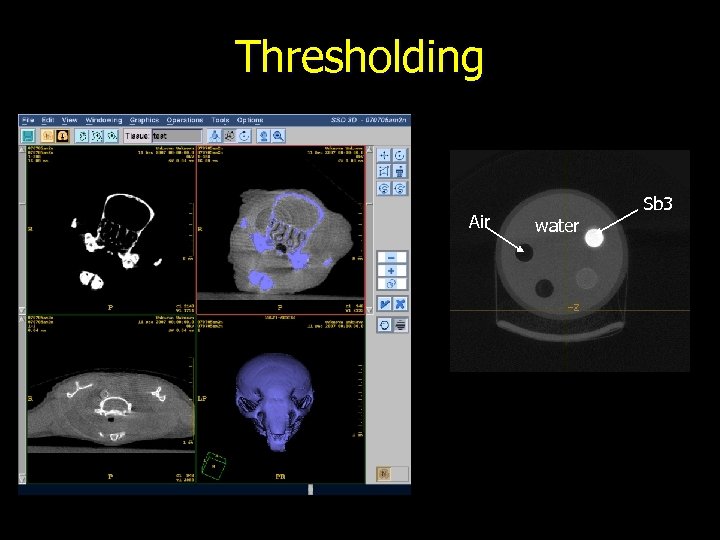 Thresholding Air water QA Phantom Sb 3
Thresholding Air water QA Phantom Sb 3
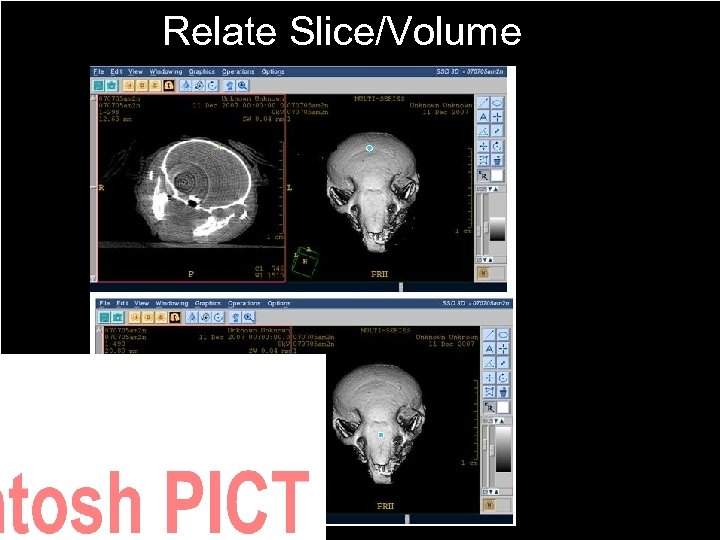 Relate Slice/Volume
Relate Slice/Volume
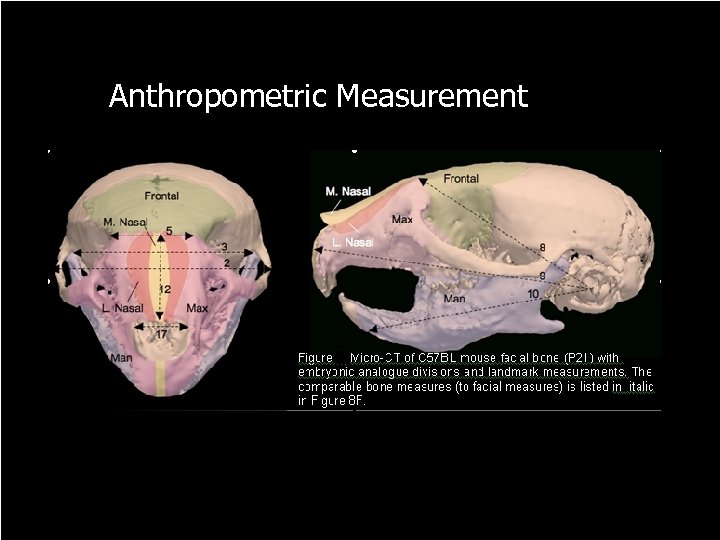 Anthropometric Measurement
Anthropometric Measurement
 Comparative analysis
Comparative analysis
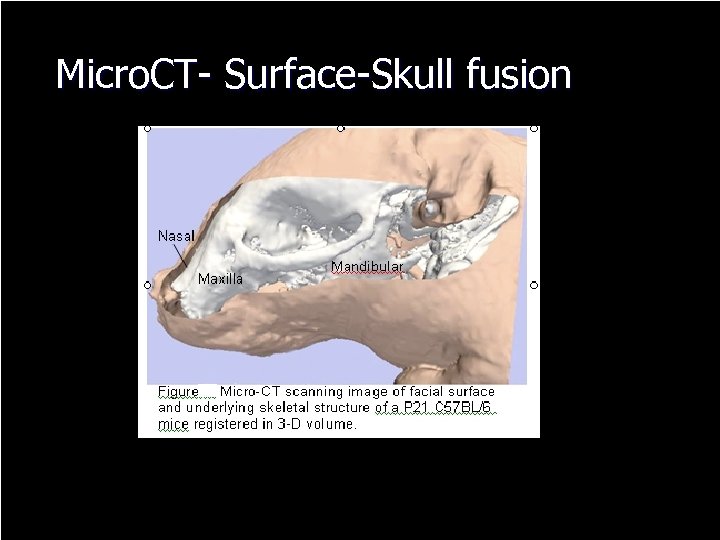 Micro. CT- Surface-Skull fusion
Micro. CT- Surface-Skull fusion
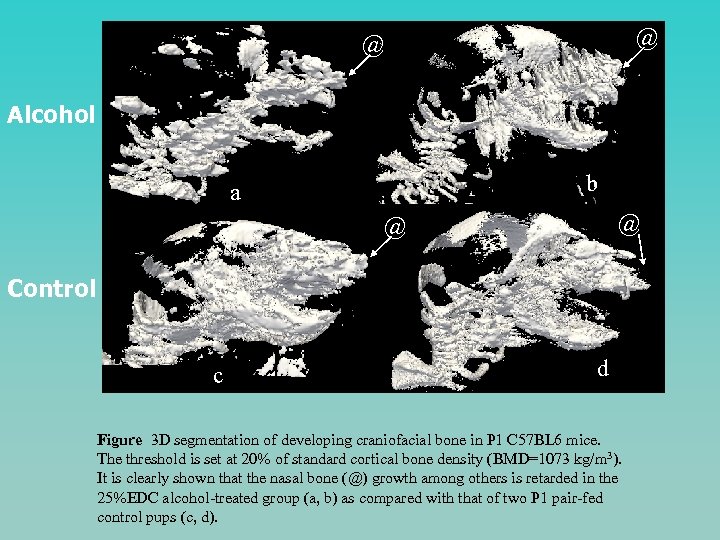 @ @ Alcohol b a @ @ Control c d Figure 3 D segmentation of developing craniofacial bone in P 1 C 57 BL 6 mice. The threshold is set at 20% of standard cortical bone density (BMD=1073 kg/m 3). It is clearly shown that the nasal bone (@) growth among others is retarded in the 25%EDC alcohol-treated group (a, b) as compared with that of two P 1 pair-fed control pups (c, d).
@ @ Alcohol b a @ @ Control c d Figure 3 D segmentation of developing craniofacial bone in P 1 C 57 BL 6 mice. The threshold is set at 20% of standard cortical bone density (BMD=1073 kg/m 3). It is clearly shown that the nasal bone (@) growth among others is retarded in the 25%EDC alcohol-treated group (a, b) as compared with that of two P 1 pair-fed control pups (c, d).
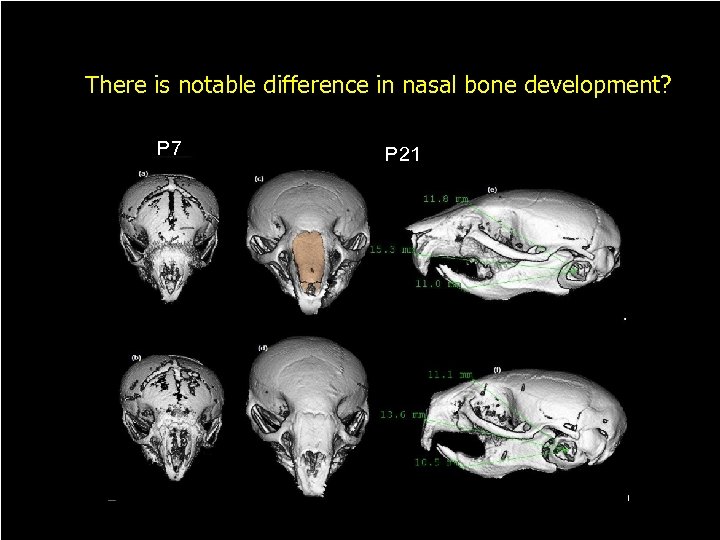 There is notable difference in nasal bone development? P 7 P 21
There is notable difference in nasal bone development? P 7 P 21


