4f7f2d4600684a0cd2032651096ec6f4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 Motivational Interviewing: A Strategy to Reduce Resistance to change Robert P. Schwartz, M. D. Department of Pediatrics Wake Forest University School of Medicine Winston-Salem, NC July 28, 2012
Motivational Interviewing: A Strategy to Reduce Resistance to change Robert P. Schwartz, M. D. Department of Pediatrics Wake Forest University School of Medicine Winston-Salem, NC July 28, 2012
 Faculty Disclosure Information “I have no relevant financial relationship with the manufacturer(s) of any commercial product(s) and/or provider of commercial services discussed in this CME activity. ” “I do not intend to discuss an unapproved/investigative use of a commercial product/device in my presentation. ” July 28, 2012
Faculty Disclosure Information “I have no relevant financial relationship with the manufacturer(s) of any commercial product(s) and/or provider of commercial services discussed in this CME activity. ” “I do not intend to discuss an unapproved/investigative use of a commercial product/device in my presentation. ” July 28, 2012
 Definition of Motivational Interviewing Patient-centered guiding style for enhancing motivation to change by exploring and resolving ambivalence. Miller WR, Rollnick S. Motivational Interviewing: Preparing People for Change. 2 nd ed. New York: Guilford Press; 2002. July 28, 2012
Definition of Motivational Interviewing Patient-centered guiding style for enhancing motivation to change by exploring and resolving ambivalence. Miller WR, Rollnick S. Motivational Interviewing: Preparing People for Change. 2 nd ed. New York: Guilford Press; 2002. July 28, 2012
 Four Guiding Principles of MI Resist arguing and persuasion Understand your patient’s motivations Listen to your patient Empower your patient July 28, 2012
Four Guiding Principles of MI Resist arguing and persuasion Understand your patient’s motivations Listen to your patient Empower your patient July 28, 2012
 Three Communication Styles • Following- listening, understanding • Guiding-deciding • Directing- advising, informing Rollnick S, Miller WR, Butler CC. Motivational Interviewing in Health Care. Guilford Press; 2008 July 28, 2012
Three Communication Styles • Following- listening, understanding • Guiding-deciding • Directing- advising, informing Rollnick S, Miller WR, Butler CC. Motivational Interviewing in Health Care. Guilford Press; 2008 July 28, 2012
 Motivational Interviewing: What it’s Not • Not arguing that a person has a problem and needs to change. • Not offering advice without patient’s permission. • Not doing most of talking. • Not giving a “prescription”. July 28, 2012
Motivational Interviewing: What it’s Not • Not arguing that a person has a problem and needs to change. • Not offering advice without patient’s permission. • Not doing most of talking. • Not giving a “prescription”. July 28, 2012
 MI: Tools of Trade • • Agenda setting Getting permission Asking open-ended (starting) questions Using reflective listening July 28, 2012
MI: Tools of Trade • • Agenda setting Getting permission Asking open-ended (starting) questions Using reflective listening July 28, 2012
 MI: Tools of Trade • Considering the pros and cons • Eliciting “change talk” (importance and confidence) • Summarizing July 28, 2012
MI: Tools of Trade • Considering the pros and cons • Eliciting “change talk” (importance and confidence) • Summarizing July 28, 2012
 Open-Ended Questions (get the ball rolling) • Can’t be answered yes/no • Use patient’s own words • Not biased or judgmental July 28, 2012
Open-Ended Questions (get the ball rolling) • Can’t be answered yes/no • Use patient’s own words • Not biased or judgmental July 28, 2012
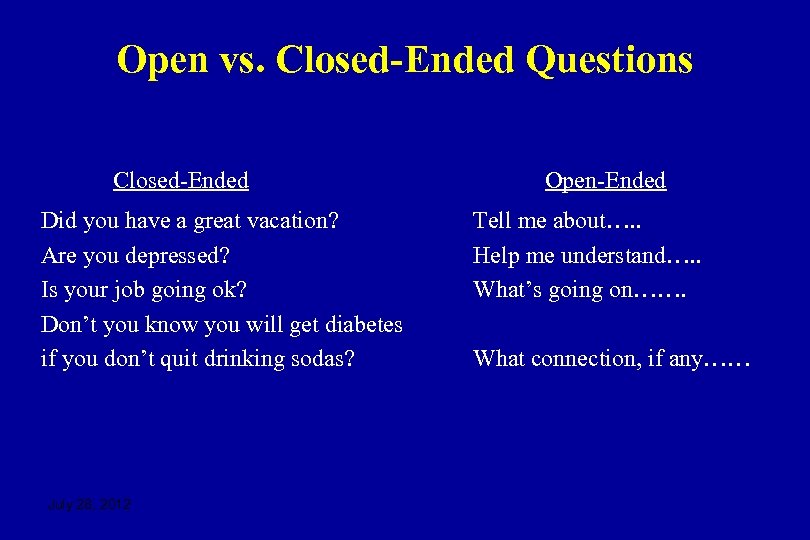 Open vs. Closed-Ended Questions Closed-Ended Did you have a great vacation? Are you depressed? Is your job going ok? Don’t you know you will get diabetes if you don’t quit drinking sodas? July 28, 2012 Open-Ended Tell me about…. . Help me understand…. . What’s going on……. What connection, if any……
Open vs. Closed-Ended Questions Closed-Ended Did you have a great vacation? Are you depressed? Is your job going ok? Don’t you know you will get diabetes if you don’t quit drinking sodas? July 28, 2012 Open-Ended Tell me about…. . Help me understand…. . What’s going on……. What connection, if any……
 Open vs Closed-Ended Questions Do you feel like your weight is a problem? Are you upset when your child doesn’t clean his plate? Will not buying sodas increase stress in your house? Do you think your son watches too much TV? Will Sarah be angry if you say no to eating at Mc. Donalds? July 28, 2012
Open vs Closed-Ended Questions Do you feel like your weight is a problem? Are you upset when your child doesn’t clean his plate? Will not buying sodas increase stress in your house? Do you think your son watches too much TV? Will Sarah be angry if you say no to eating at Mc. Donalds? July 28, 2012
 Reflective Listening (keep the ball rolling) • Restate and rephrase • Statement of understanding (clarifies meaning) • Builds rapport and keeps patient talking July 28, 2012
Reflective Listening (keep the ball rolling) • Restate and rephrase • Statement of understanding (clarifies meaning) • Builds rapport and keeps patient talking July 28, 2012
 Universal Safe Reflections • It sounds like you are feeling……. . • It sounds like you are not happy with…. • It sounds like you are having trouble with…. . As you improve, you can truncate the reflection… • You’re not ready to…. • You’re having a problem with…. • You’re feeling that…. • It’s been difficult for you…. • You are frustrated…. July 28, 2012
Universal Safe Reflections • It sounds like you are feeling……. . • It sounds like you are not happy with…. • It sounds like you are having trouble with…. . As you improve, you can truncate the reflection… • You’re not ready to…. • You’re having a problem with…. • You’re feeling that…. • It’s been difficult for you…. • You are frustrated…. July 28, 2012
 TELEVISION I know TV is bad for him, but I need some peace and quiet in the house. I am a single mom. I don’t have a lot of help. Having him watch TV let’s me get my housework and schoolwork done. He is happy, content, and frankly, I don’t have to worry about entertaining him. REFLECTION………… July 28, 2012
TELEVISION I know TV is bad for him, but I need some peace and quiet in the house. I am a single mom. I don’t have a lot of help. Having him watch TV let’s me get my housework and schoolwork done. He is happy, content, and frankly, I don’t have to worry about entertaining him. REFLECTION………… July 28, 2012
 Reflections A. Letting him watch TV gives you time to get your work done. B. It can be exhausting having to entertain him all the time. C. You would like for him to watch less TV. D. You don’t have to worry about him when he is watching TV. E. On one hand you need some free time to get things done. On the other hand you are concerned about the amount of time he spends watching TV. July 28, 2012
Reflections A. Letting him watch TV gives you time to get your work done. B. It can be exhausting having to entertain him all the time. C. You would like for him to watch less TV. D. You don’t have to worry about him when he is watching TV. E. On one hand you need some free time to get things done. On the other hand you are concerned about the amount of time he spends watching TV. July 28, 2012
 You don’t have to hit a home run. Just get your bat on the ball. July 28, 2012
You don’t have to hit a home run. Just get your bat on the ball. July 28, 2012
 PROS and CONS • Could you tell me some things you like about ____ • What things are not so good about _____ • What might happen if you don’t change? July 28, 2012
PROS and CONS • Could you tell me some things you like about ____ • What things are not so good about _____ • What might happen if you don’t change? July 28, 2012
 Providing Information • • Ask for permission Provide nothing but the facts. Let patient interpret it. Elicit-Provide-Elicit “Would it be okay if I shared information with you? ” Provide the information. “What does this mean to you? ” July 28, 2012
Providing Information • • Ask for permission Provide nothing but the facts. Let patient interpret it. Elicit-Provide-Elicit “Would it be okay if I shared information with you? ” Provide the information. “What does this mean to you? ” July 28, 2012
 Importance and Confidence IMPORTANCE On a scale of 0 to 10, with 10 being the highest, how important is it for you to change (INSERT BEHAVIOR)? 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Not at all Somewhat Very CONFIDENCE On a scale of 0 to 10 assuming you wanted to change (INSERT BEHAVIOR), how confident are you that you can do it? 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Not at all Somewhat Very PROBE 1: Why did you not choose a lower number? July 28, PROBE 2012 What would it take to get you to a higher number? 2:
Importance and Confidence IMPORTANCE On a scale of 0 to 10, with 10 being the highest, how important is it for you to change (INSERT BEHAVIOR)? 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Not at all Somewhat Very CONFIDENCE On a scale of 0 to 10 assuming you wanted to change (INSERT BEHAVIOR), how confident are you that you can do it? 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Not at all Somewhat Very PROBE 1: Why did you not choose a lower number? July 28, PROBE 2012 What would it take to get you to a higher number? 2:
 Summarizing and Closing the Deal “ If it’s ok, I would like to go over what we have discussed today. ” • Summarize pros and cons of change. • Closure – “What do you think might be a first step? ” If ambivalent: “Would it be okay if I shared some strategies that have worked for other families? ” If not ready to change: “It seems that you are not ready to make a change at this time. Perhaps, if it is ok with you, we can discuss this again at your next visit. ” July 28, 2012
Summarizing and Closing the Deal “ If it’s ok, I would like to go over what we have discussed today. ” • Summarize pros and cons of change. • Closure – “What do you think might be a first step? ” If ambivalent: “Would it be okay if I shared some strategies that have worked for other families? ” If not ready to change: “It seems that you are not ready to make a change at this time. Perhaps, if it is ok with you, we can discuss this again at your next visit. ” July 28, 2012
 Changes in Practice After Attending this Session 1. I will use open-ended questions and reflections when counseling my patients about behavior change. 2. I will use the importance and confidence scales in assessing my patient’s readiness for behavior change. July 28, 2012
Changes in Practice After Attending this Session 1. I will use open-ended questions and reflections when counseling my patients about behavior change. 2. I will use the importance and confidence scales in assessing my patient’s readiness for behavior change. July 28, 2012
 Motivational Interviewing References Journal Articles: 1. Erickson S, Gerstle M, Feldstein SW. Brief interventions and motivational interviewing with children, adolescents, and their parents in pediatric healthcare settings. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 2005; 159: 1173 -1180. 2. Rollnick S, Butler CC, Mc. Cambridge J, Kinnersly P, Elwyn G, Resnicow K. Consultations about changing behavior. BMJ 2005; 331: 961 -963. 3. Schwartz RP. Motivational Interviewing (Patient-Centered Counseling) to Address Childhood Obesity. Pediatric Annals 2010; 39: 154 -158. Books: 1. Rollnick S, Miller WR, Butler CC. Motivational Interviewing in Health Care: Helping Patients Change Behavior. New York: Guilford Press; 2008. 2. Schwartz RP. Motivational Interviewing. In Tanski S, Garfunkel LC, Duncan PM, Weitzman M, ed. Performing Preventive Services. A Bright Futures Handbook. American Academy of Pediatrics 2011; 175 -177. Online: http: //www. motivationalinterviewing. org July 28, 2012
Motivational Interviewing References Journal Articles: 1. Erickson S, Gerstle M, Feldstein SW. Brief interventions and motivational interviewing with children, adolescents, and their parents in pediatric healthcare settings. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 2005; 159: 1173 -1180. 2. Rollnick S, Butler CC, Mc. Cambridge J, Kinnersly P, Elwyn G, Resnicow K. Consultations about changing behavior. BMJ 2005; 331: 961 -963. 3. Schwartz RP. Motivational Interviewing (Patient-Centered Counseling) to Address Childhood Obesity. Pediatric Annals 2010; 39: 154 -158. Books: 1. Rollnick S, Miller WR, Butler CC. Motivational Interviewing in Health Care: Helping Patients Change Behavior. New York: Guilford Press; 2008. 2. Schwartz RP. Motivational Interviewing. In Tanski S, Garfunkel LC, Duncan PM, Weitzman M, ed. Performing Preventive Services. A Bright Futures Handbook. American Academy of Pediatrics 2011; 175 -177. Online: http: //www. motivationalinterviewing. org July 28, 2012
 It’s up to you! July 28, 2012
It’s up to you! July 28, 2012


