89d74693729c64d10480d8f4e657e00c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 64
 • Motivation • Education • Implementation Pharmaceuticals IEC-61508 Implementing a Compliance Program
• Motivation • Education • Implementation Pharmaceuticals IEC-61508 Implementing a Compliance Program
 Pharmaceuticals Overview
Pharmaceuticals Overview
 Pharmaceuticals Overview
Pharmaceuticals Overview
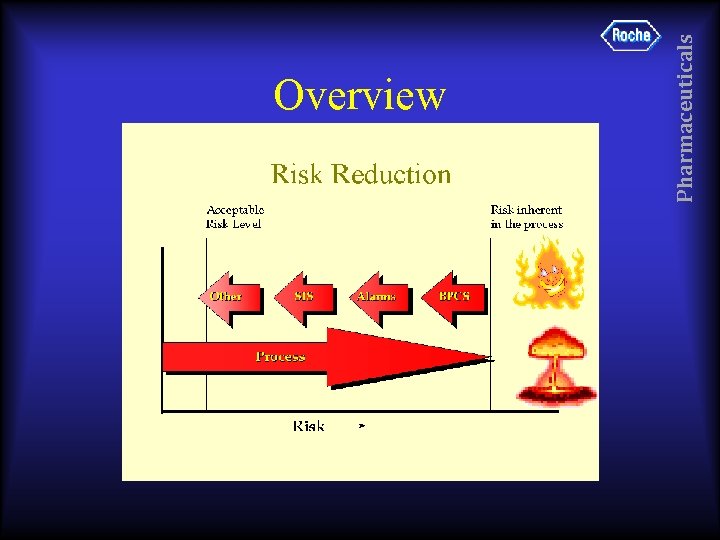 Pharmaceuticals Overview
Pharmaceuticals Overview
 • Do you or your company believe in the infallibility of Engineered systems? Pharmaceuticals Motivation
• Do you or your company believe in the infallibility of Engineered systems? Pharmaceuticals Motivation
 • Roche Ireland does not have this delusion • 25 + years operational experience • Including some close calls • Reality has motivated out safety culture. Pharmaceuticals Motivation
• Roche Ireland does not have this delusion • 25 + years operational experience • Including some close calls • Reality has motivated out safety culture. Pharmaceuticals Motivation
 Much of the rest of this presentation has been generated from training presentations given in Roche Ireland to • Management • Process Engineering • Instrument / Electrical Engineering Pharmaceuticals Education
Much of the rest of this presentation has been generated from training presentations given in Roche Ireland to • Management • Process Engineering • Instrument / Electrical Engineering Pharmaceuticals Education
 Need to educate yourself : • Guidelines for Safe Automation of Chemical Processes {CCPS/AICh. E} • ISA S 84 • Functional Safety, {Smith & Simpson} • IBC conferences • Various WWW resources (exida/ sis-tech etc) Pharmaceuticals Education
Need to educate yourself : • Guidelines for Safe Automation of Chemical Processes {CCPS/AICh. E} • ISA S 84 • Functional Safety, {Smith & Simpson} • IBC conferences • Various WWW resources (exida/ sis-tech etc) Pharmaceuticals Education
 • Functional safety of electrical / electronic & programmable electronic safety-related systems. • Critical Protective equipment - Safety Instrumented Systems Pharmaceuticals IEC-61508, SOP 973
• Functional safety of electrical / electronic & programmable electronic safety-related systems. • Critical Protective equipment - Safety Instrumented Systems Pharmaceuticals IEC-61508, SOP 973
 n Safety requires protection from hazards of different causes (movement, heat, radiation, el. shock, etc. ) n “Functional Safety” means protection from hazards due to incorrect functioning. . heat Protection against. . . electrical shock . . . hazards due to incorrect function . . . radiation Pharmaceuticals IEC-61508, SOP 973
n Safety requires protection from hazards of different causes (movement, heat, radiation, el. shock, etc. ) n “Functional Safety” means protection from hazards due to incorrect functioning. . heat Protection against. . . electrical shock . . . hazards due to incorrect function . . . radiation Pharmaceuticals IEC-61508, SOP 973
 • • • Process Engineers: Instrument/Electrical Designers: Mechanical Engineering Commissioning: - Extra Effort Documentation : - Extra Effort Pharmaceuticals IEC-61508 Will Effect:
• • • Process Engineers: Instrument/Electrical Designers: Mechanical Engineering Commissioning: - Extra Effort Documentation : - Extra Effort Pharmaceuticals IEC-61508 Will Effect:
 • • Not legislation Meets ‘Reasonably practicable’ duty Health, safety & welfare at Work act, 1989 Have to put in place a compliance program. Pharmaceuticals IEC-61508 is legally vague
• • Not legislation Meets ‘Reasonably practicable’ duty Health, safety & welfare at Work act, 1989 Have to put in place a compliance program. Pharmaceuticals IEC-61508 is legally vague
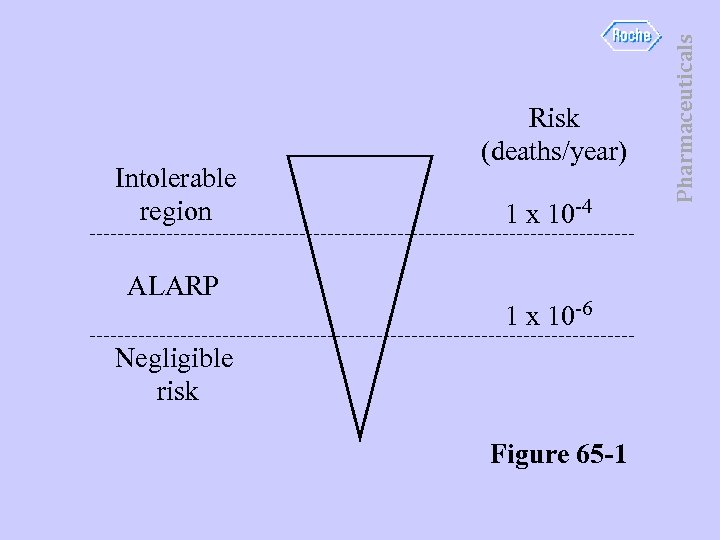 ALARP 1 x 10 -4 1 x 10 -6 Negligible risk Figure 65 -1 Pharmaceuticals Intolerable region Risk (deaths/year)
ALARP 1 x 10 -4 1 x 10 -6 Negligible risk Figure 65 -1 Pharmaceuticals Intolerable region Risk (deaths/year)
 • • • As low as reasonably practicable. IEC 61508 based on ALARP concept. ALARP concerns region of risk. Risk is an emotive and irrational thing. Commonly accepted values are: upper limit 1 x 10 -4 deaths per year lower limit 1 x 10 -6 deaths per year Pharmaceuticals RISK Reduction - ALARP
• • • As low as reasonably practicable. IEC 61508 based on ALARP concept. ALARP concerns region of risk. Risk is an emotive and irrational thing. Commonly accepted values are: upper limit 1 x 10 -4 deaths per year lower limit 1 x 10 -6 deaths per year Pharmaceuticals RISK Reduction - ALARP
 • ISA S 84 life cycle depicted in Fig 65 -3. • ISA S 84 focuses on Box 9 of IEC 61508. Pharmaceuticals Safety life cycle - milestone approach
• ISA S 84 life cycle depicted in Fig 65 -3. • ISA S 84 focuses on Box 9 of IEC 61508. Pharmaceuticals Safety life cycle - milestone approach
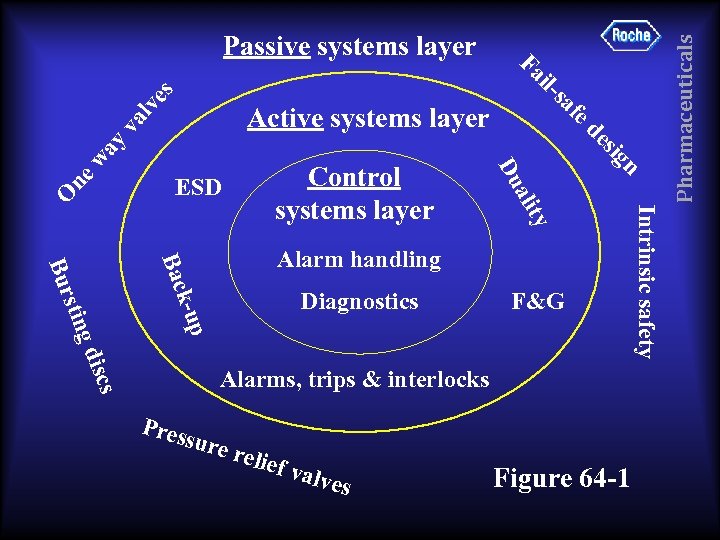 F&G p k-u Diagnostics Alarms, trips & interlocks Pres sure relie f val ves Figure 64 -1 Intrinsic safety ty Bac scs g di stin Bur Alarm handling Pharmaceuticals va y wa ne O n ali Control systems layer Du ESD ig es ed af Active systems layer s il. Fa lv es Passive systems layer
F&G p k-u Diagnostics Alarms, trips & interlocks Pres sure relie f val ves Figure 64 -1 Intrinsic safety ty Bac scs g di stin Bur Alarm handling Pharmaceuticals va y wa ne O n ali Control systems layer Du ESD ig es ed af Active systems layer s il. Fa lv es Passive systems layer
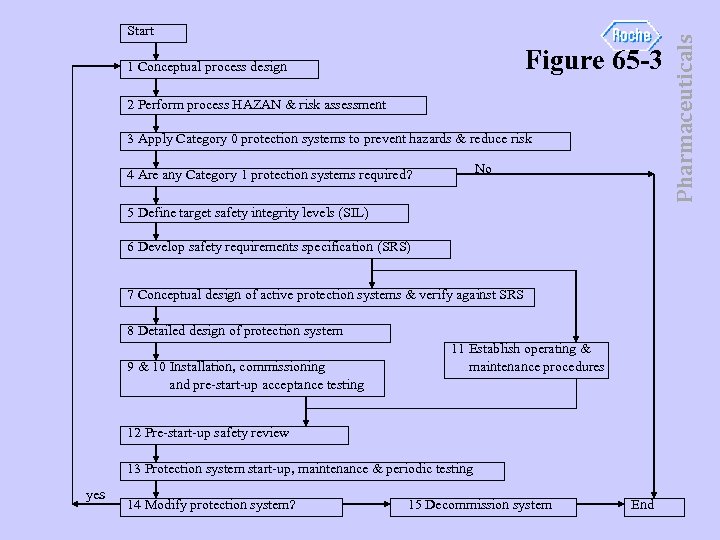 Figure 65 -3 1 Conceptual process design 2 Perform process HAZAN & risk assessment 3 Apply Category 0 protection systems to prevent hazards & reduce risk No 4 Are any Category 1 protection systems required? 5 Define target safety integrity levels (SIL) 6 Develop safety requirements specification (SRS) 7 Conceptual design of active protection systems & verify against SRS 8 Detailed design of protection system 9 & 10 Installation, commissioning and pre-start-up acceptance testing 11 Establish operating & maintenance procedures 12 Pre-start-up safety review 13 Protection system start-up, maintenance & periodic testing yes 14 Modify protection system? 15 Decommission system End Pharmaceuticals Start
Figure 65 -3 1 Conceptual process design 2 Perform process HAZAN & risk assessment 3 Apply Category 0 protection systems to prevent hazards & reduce risk No 4 Are any Category 1 protection systems required? 5 Define target safety integrity levels (SIL) 6 Develop safety requirements specification (SRS) 7 Conceptual design of active protection systems & verify against SRS 8 Detailed design of protection system 9 & 10 Installation, commissioning and pre-start-up acceptance testing 11 Establish operating & maintenance procedures 12 Pre-start-up safety review 13 Protection system start-up, maintenance & periodic testing yes 14 Modify protection system? 15 Decommission system End Pharmaceuticals Start
 • First Stage of realisation of high-integrity safety instrumented systems • Modified PHA • Feeds into SRS • Based on good process data & good process judgement. Pharmaceuticals Process Engineering
• First Stage of realisation of high-integrity safety instrumented systems • Modified PHA • Feeds into SRS • Based on good process data & good process judgement. Pharmaceuticals Process Engineering
 • • • Carius Tube test for decomposition Pressure Dewar Calorimetry Understanding of Exotherms Knowledge of onset temperatures {Chilworth} Pharmaceuticals Process Chemistry
• • • Carius Tube test for decomposition Pressure Dewar Calorimetry Understanding of Exotherms Knowledge of onset temperatures {Chilworth} Pharmaceuticals Process Chemistry
 • Good process judgement. • Hazop • Margins of safety Pharmaceuticals Process Engineering
• Good process judgement. • Hazop • Margins of safety Pharmaceuticals Process Engineering
 • Reactant being transferred in from Reactor 1 without agitation could accumulate & react in a sudden, violent manner. • Reactor 2 Inlet valve 205 should OPEN only if agitator ON Pharmaceuticals Hazard identification, Interlock Identification
• Reactant being transferred in from Reactor 1 without agitation could accumulate & react in a sudden, violent manner. • Reactor 2 Inlet valve 205 should OPEN only if agitator ON Pharmaceuticals Hazard identification, Interlock Identification
 • Simplified Technique. • MIL Std 882 Pharmaceuticals Hazard identification, Interlock Identification
• Simplified Technique. • MIL Std 882 Pharmaceuticals Hazard identification, Interlock Identification
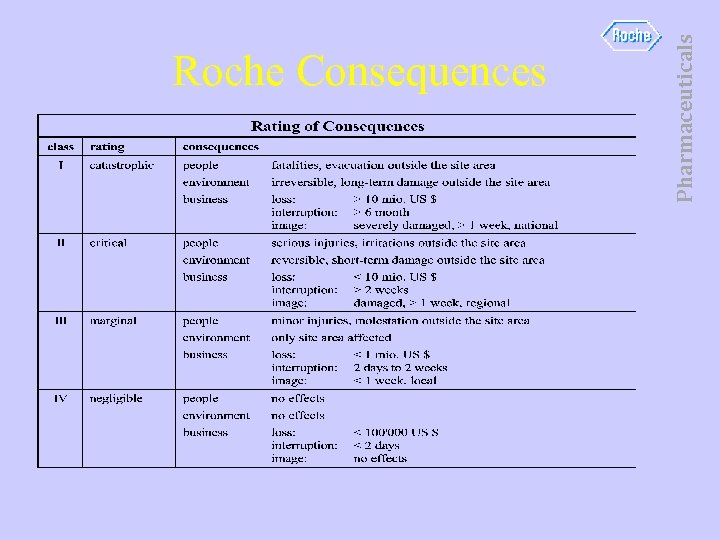
 • Consequence of this is overpressure, loss of batch, over-temperature, possible destruction of vessel. • 1 week downtime to recover. • Fatality or Serious injury unlikely. • Critical • (C 2) Pharmaceuticals Consequences
• Consequence of this is overpressure, loss of batch, over-temperature, possible destruction of vessel. • 1 week downtime to recover. • Fatality or Serious injury unlikely. • Critical • (C 2) Pharmaceuticals Consequences
 • Building is continually occupied • (F 2) Pharmaceuticals Occupancy factor
• Building is continually occupied • (F 2) Pharmaceuticals Occupancy factor
 • There is quite a good chance of an operator observing that something is going wrong & intervening successfully. • (P 1) Pharmaceuticals Manual Avoidance factor
• There is quite a good chance of an operator observing that something is going wrong & intervening successfully. • (P 1) Pharmaceuticals Manual Avoidance factor
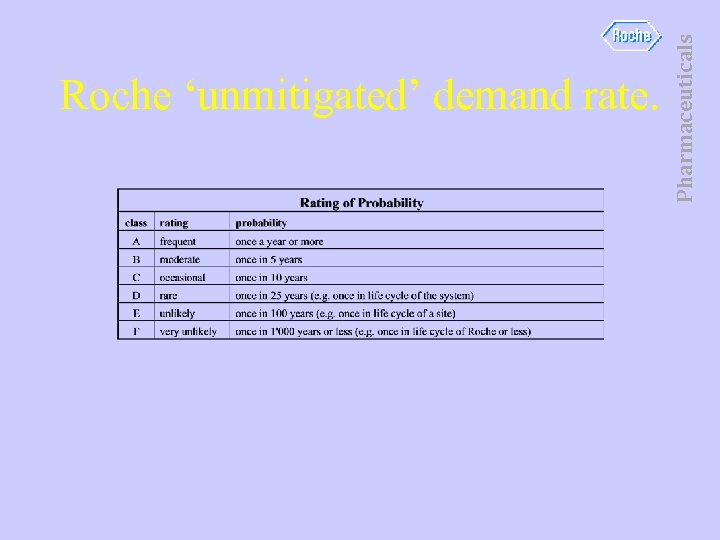
 • • • Likely to occur once every 5 years. Occasional The process is DCS automated. DCS is not a SIS – no SIL rating. DCS control reduces frequency of Unmitigated Demand. • (W 2) Pharmaceuticals Unmitigated demand rate.
• • • Likely to occur once every 5 years. Occasional The process is DCS automated. DCS is not a SIS – no SIL rating. DCS control reduces frequency of Unmitigated Demand. • (W 2) Pharmaceuticals Unmitigated demand rate.
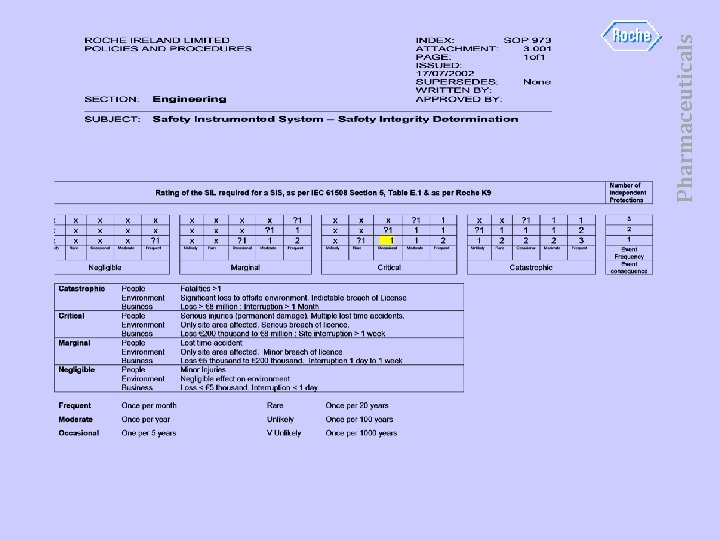
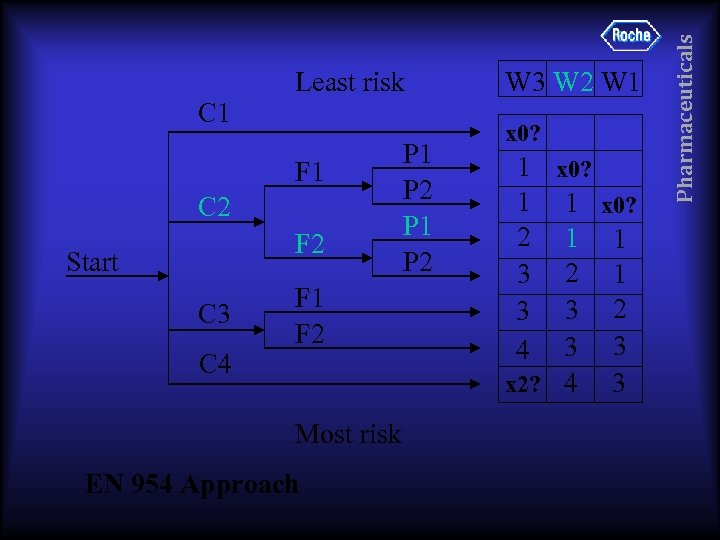 C 1 F 1 C 2 F 2 Start C 3 C 4 F 1 F 2 Most risk EN 954 Approach P 1 P 2 W 3 W 2 W 1 x 0? 1 1 x 0? 2 1 1 3 2 1 3 3 2 4 3 3 x 2? 4 3 Pharmaceuticals Least risk
C 1 F 1 C 2 F 2 Start C 3 C 4 F 1 F 2 Most risk EN 954 Approach P 1 P 2 W 3 W 2 W 1 x 0? 1 1 x 0? 2 1 1 3 2 1 3 3 2 4 3 3 x 2? 4 3 Pharmaceuticals Least risk
 Pharmaceuticals
Pharmaceuticals
 Pharmaceuticals Roche Consequences
Pharmaceuticals Roche Consequences
 Pharmaceuticals Roche ‘unmitigated’ demand rate.
Pharmaceuticals Roche ‘unmitigated’ demand rate.
 • Second Stage of realisation of high-integrity safety instrumented systems • Modified Instrument design • Modified Instrument Commissioning • Feeds into SRS Pharmaceuticals Instrument / Electrical Design
• Second Stage of realisation of high-integrity safety instrumented systems • Modified Instrument design • Modified Instrument Commissioning • Feeds into SRS Pharmaceuticals Instrument / Electrical Design
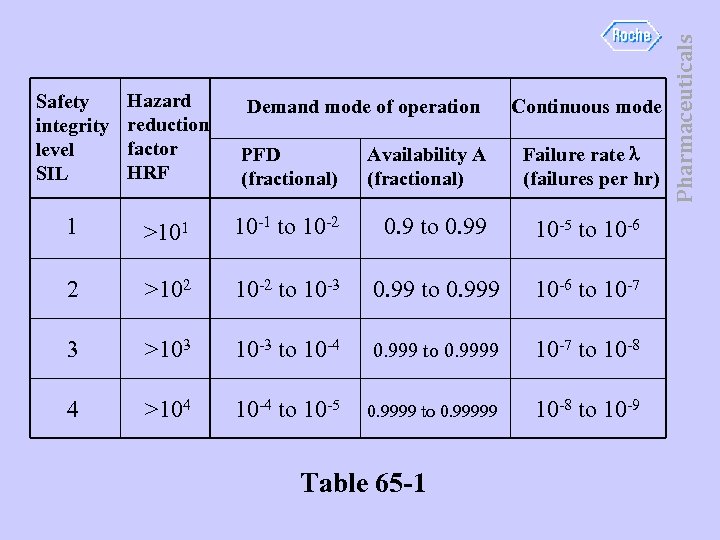 Hazard reduction factor HRF PFD (fractional) Availability A (fractional) 1 >101 10 -1 to 10 -2 0. 9 to 0. 99 10 -5 to 10 -6 2 >102 10 -2 to 10 -3 0. 99 to 0. 999 10 -6 to 10 -7 3 >103 10 -3 to 10 -4 0. 999 to 0. 9999 10 -7 to 10 -8 4 >104 10 -4 to 10 -5 0. 9999 to 0. 99999 10 -8 to 10 -9 Demand mode of operation Table 65 -1 Continuous mode Failure rate (failures per hr) Pharmaceuticals Safety integrity level SIL
Hazard reduction factor HRF PFD (fractional) Availability A (fractional) 1 >101 10 -1 to 10 -2 0. 9 to 0. 99 10 -5 to 10 -6 2 >102 10 -2 to 10 -3 0. 99 to 0. 999 10 -6 to 10 -7 3 >103 10 -3 to 10 -4 0. 999 to 0. 9999 10 -7 to 10 -8 4 >104 10 -4 to 10 -5 0. 9999 to 0. 99999 10 -8 to 10 -9 Demand mode of operation Table 65 -1 Continuous mode Failure rate (failures per hr) Pharmaceuticals Safety integrity level SIL
 • SIL value is measure of quality of protection system, end to end. • System has to be designed, specified, built and maintained to that standard. • Proof testing at regular intervals • Conformance assessment for safety systems Pharmaceuticals Equipment implications
• SIL value is measure of quality of protection system, end to end. • System has to be designed, specified, built and maintained to that standard. • Proof testing at regular intervals • Conformance assessment for safety systems Pharmaceuticals Equipment implications
 • • Simplified Equation ISA-TR 84. 00. 02 -2002 Part 2 Equation B. 34 – Rare event approximation “Adequate” for SIL 1 or 2, where the plant is well controlled, well maintained, understood process, conservative engineering with good mechanical integrity Pharmaceuticals PFD Calculation
• • Simplified Equation ISA-TR 84. 00. 02 -2002 Part 2 Equation B. 34 – Rare event approximation “Adequate” for SIL 1 or 2, where the plant is well controlled, well maintained, understood process, conservative engineering with good mechanical integrity Pharmaceuticals PFD Calculation
 • MTBF = Mean (Average) time between failures • Information provided by vendor. • MTBF = 86 Years Pharmaceuticals PFD Calc. Motion Sensor
• MTBF = Mean (Average) time between failures • Information provided by vendor. • MTBF = 86 Years Pharmaceuticals PFD Calc. Motion Sensor
 Failures can be • fail to danger (Falsely shows agitator moving)or • fail to safe (Falsely shows agitator stopped) • Aim of good design is to maximise fail to safe, minimise fail to danger. The failure mode split is the percentage in the fail to danger category. • Failure mode split =. 1 (SA estimate) Pharmaceuticals PFD Calc. Motion Sensor
Failures can be • fail to danger (Falsely shows agitator moving)or • fail to safe (Falsely shows agitator stopped) • Aim of good design is to maximise fail to safe, minimise fail to danger. The failure mode split is the percentage in the fail to danger category. • Failure mode split =. 1 (SA estimate) Pharmaceuticals PFD Calc. Motion Sensor
 • Proof test interval = 1 year (8760 hours) • Time between re-tests of the interlock. • Need to be genuine tests Pharmaceuticals PFD Calc. Motion Sensor
• Proof test interval = 1 year (8760 hours) • Time between re-tests of the interlock. • Need to be genuine tests Pharmaceuticals PFD Calc. Motion Sensor
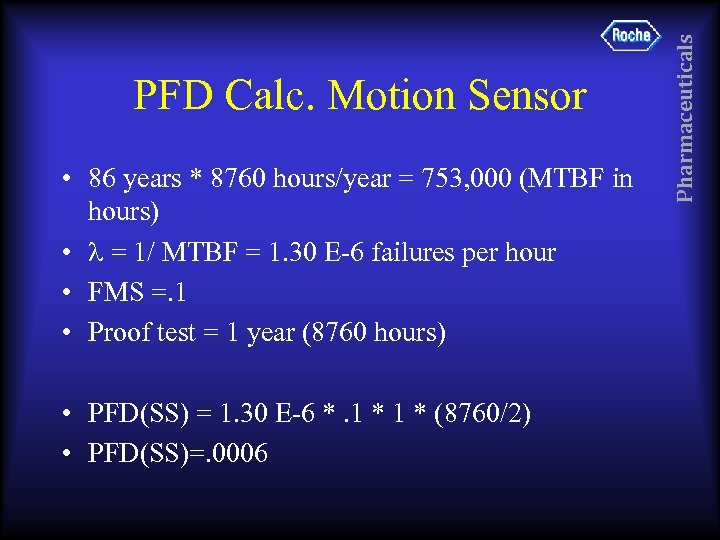 • 86 years * 8760 hours/year = 753, 000 (MTBF in hours) • = 1/ MTBF = 1. 30 E-6 failures per hour • FMS =. 1 • Proof test = 1 year (8760 hours) • PFD(SS) = 1. 30 E-6 *. 1 * (8760/2) • PFD(SS)=. 0006 Pharmaceuticals PFD Calc. Motion Sensor
• 86 years * 8760 hours/year = 753, 000 (MTBF in hours) • = 1/ MTBF = 1. 30 E-6 failures per hour • FMS =. 1 • Proof test = 1 year (8760 hours) • PFD(SS) = 1. 30 E-6 *. 1 * (8760/2) • PFD(SS)=. 0006 Pharmaceuticals PFD Calc. Motion Sensor
 • MTBF = 4 Years • Failure mode split =. 4 • Proof test interval = 1 year (8760 hours) = 1/ MTBF = 2. 87 E-5 failures per hour PFD(B 6) = 2. 87 E-5 *. 4 * 1 * (8760/2) • PFD(B 6)=. 0500 Pharmaceuticals PFD Calc. Barrier 6
• MTBF = 4 Years • Failure mode split =. 4 • Proof test interval = 1 year (8760 hours) = 1/ MTBF = 2. 87 E-5 failures per hour PFD(B 6) = 2. 87 E-5 *. 4 * 1 * (8760/2) • PFD(B 6)=. 0500 Pharmaceuticals PFD Calc. Barrier 6
 • MTBF = 100 Years • Failure mode split =. 01 • Proof test interval = 1 year (8760 hours) = 1/ MTBF = 1. 14 E-6 failures per hour PFD(R 5) = 1. 14 E-6 *. 01 * (8760/2) • PFD(R 5)=. 00005 Pharmaceuticals PFD Calc. Relay 5
• MTBF = 100 Years • Failure mode split =. 01 • Proof test interval = 1 year (8760 hours) = 1/ MTBF = 1. 14 E-6 failures per hour PFD(R 5) = 1. 14 E-6 *. 01 * (8760/2) • PFD(R 5)=. 00005 Pharmaceuticals PFD Calc. Relay 5
 • MTBF = 10 Years • Failure mode split =. 9 • Proof test interval = 1 day (24 hours) = 1/ MTBF = 1. 14 E-5 failures per hour PFD(MB) = 1. 14 E-5 *. 9 * 1 * (24/2) • PFD(MB)=. 001242 Pharmaceuticals PFD Calc. Main Barrier
• MTBF = 10 Years • Failure mode split =. 9 • Proof test interval = 1 day (24 hours) = 1/ MTBF = 1. 14 E-5 failures per hour PFD(MB) = 1. 14 E-5 *. 9 * 1 * (24/2) • PFD(MB)=. 001242 Pharmaceuticals PFD Calc. Main Barrier
 • MTBF = 10 Years • Failure mode split =. 4 • Proof test interval = 1 day (24 hours) = 1/ MTBF = 1. 14 E-5 failures per hour PFD(SOL) = 1. 14 E-5 *. 4 * 1 * (24/2) • PFD(SOL)=. 00006 Pharmaceuticals PFD Calc. Solenoid
• MTBF = 10 Years • Failure mode split =. 4 • Proof test interval = 1 day (24 hours) = 1/ MTBF = 1. 14 E-5 failures per hour PFD(SOL) = 1. 14 E-5 *. 4 * 1 * (24/2) • PFD(SOL)=. 00006 Pharmaceuticals PFD Calc. Solenoid
 • MTBF = 10 Years • Failure mode split =. 2 • Proof test interval = 1 day (24 hours) = 1/ MTBF = 1. 14 E-5 failures per hour PFD(VA) = 1. 14 E-5 *. 2 * 1 * (24/2) • PFD(VA)=. 00003 Pharmaceuticals PFD Calc. Valve & Actuator
• MTBF = 10 Years • Failure mode split =. 2 • Proof test interval = 1 day (24 hours) = 1/ MTBF = 1. 14 E-5 failures per hour PFD(VA) = 1. 14 E-5 *. 2 * 1 * (24/2) • PFD(VA)=. 00003 Pharmaceuticals PFD Calc. Valve & Actuator
 • • PFD(VA)=. 00003 PFD(SOL)=. 00006 PFD(MB)=. 00124 PFD(R 5)=. 00005 PFD(B 6)=. 0500 PFD(SS)=. 0006 PFD =. 052 => SIL 1 Pharmaceuticals PFD Calc. Overall
• • PFD(VA)=. 00003 PFD(SOL)=. 00006 PFD(MB)=. 00124 PFD(R 5)=. 00005 PFD(B 6)=. 0500 PFD(SS)=. 0006 PFD =. 052 => SIL 1 Pharmaceuticals PFD Calc. Overall
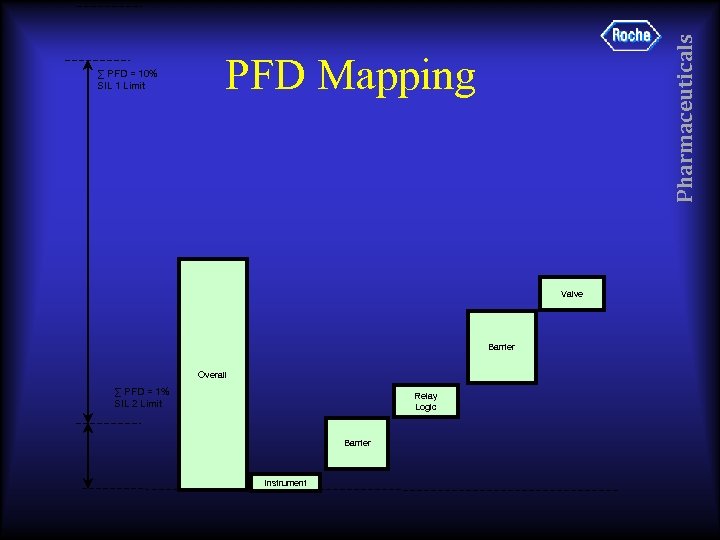 Pharmaceuticals ∑ PFD = 10% SIL 1 Limit PFD Mapping Valve Barrier Overall ∑ PFD = 1% SIL 2 Limit Relay Logic Barrier Instrument
Pharmaceuticals ∑ PFD = 10% SIL 1 Limit PFD Mapping Valve Barrier Overall ∑ PFD = 1% SIL 2 Limit Relay Logic Barrier Instrument
 • Elements in series: USYS Ui 62 -16 Elements in parallel: USYS Ui -17 • Common cause failure: SYS = IND + . MAX -18 • Voting systems: UKOON n. Uk -19 • For more complex systems – Fault Tree Analysis using ISA-TR 84. 00. 02 -2002 Part 3. • “Probabilistic Risk Assesment” – Henley, E J Pharmaceuticals PFD Calc. Issues
• Elements in series: USYS Ui 62 -16 Elements in parallel: USYS Ui -17 • Common cause failure: SYS = IND + . MAX -18 • Voting systems: UKOON n. Uk -19 • For more complex systems – Fault Tree Analysis using ISA-TR 84. 00. 02 -2002 Part 3. • “Probabilistic Risk Assesment” – Henley, E J Pharmaceuticals PFD Calc. Issues
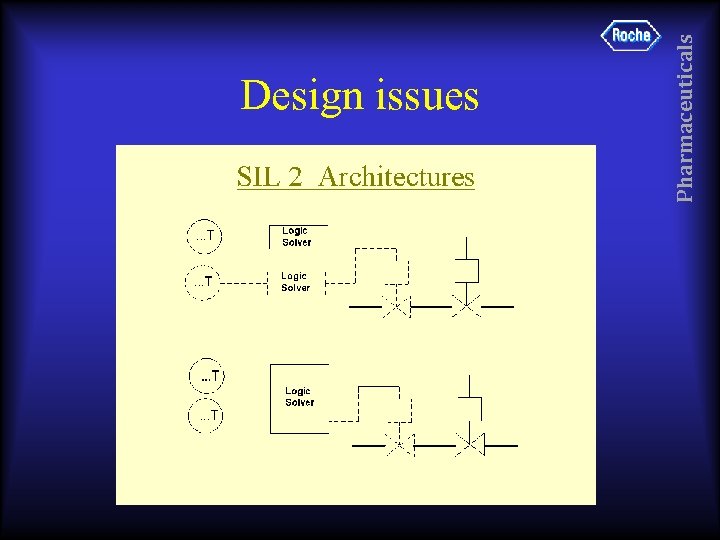
 • Roche have decided that valve & actuator may be shared for SIL 1 only. • SIS & BPCS share barrier, solenoid, actuator & Valve. This is not recommended • Solenoid has local SMO, which might be OK for normal operation, but not for SIS. Pharmaceuticals Design issues
• Roche have decided that valve & actuator may be shared for SIL 1 only. • SIS & BPCS share barrier, solenoid, actuator & Valve. This is not recommended • Solenoid has local SMO, which might be OK for normal operation, but not for SIS. Pharmaceuticals Design issues
 Pharmaceuticals Design issues
Pharmaceuticals Design issues
 • #####-# type barrier not recommended (TTL Logic switching – independent energy source) • No clear indication on loop sheet or in field of safety critical nature of instruments Pharmaceuticals Design issues
• #####-# type barrier not recommended (TTL Logic switching – independent energy source) • No clear indication on loop sheet or in field of safety critical nature of instruments Pharmaceuticals Design issues
 • Design of periodic re-test method is the instrument designers responsibility. • This would help facilitate periodic testing • Loop sheet to indicate safety critical nature of instruments Pharmaceuticals Design issues
• Design of periodic re-test method is the instrument designers responsibility. • This would help facilitate periodic testing • Loop sheet to indicate safety critical nature of instruments Pharmaceuticals Design issues
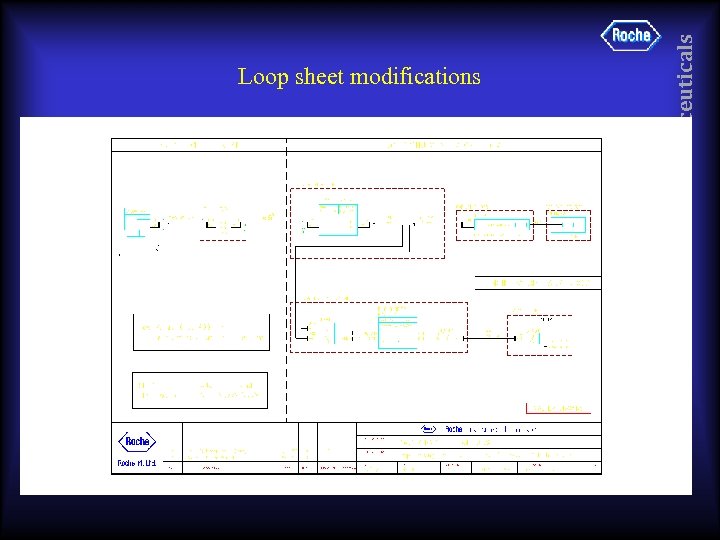
 • SIS to actuate solenoid in panel, which controls air supply to Shutoff Valve & Control Valve • High energy panel mount solenoid, not IS pilot operated solenoid => more ‘suitable’ for SIS • Control Valve should have positioner suitable for SIS Pharmaceuticals Improvement suggestions
• SIS to actuate solenoid in panel, which controls air supply to Shutoff Valve & Control Valve • High energy panel mount solenoid, not IS pilot operated solenoid => more ‘suitable’ for SIS • Control Valve should have positioner suitable for SIS Pharmaceuticals Improvement suggestions
 Pharmaceuticals Loop sheet modifications
Pharmaceuticals Loop sheet modifications
 • IQ / OQ + Proof testing of the safety function • Validation of the retest method • Loop sheet to indicate safety critical nature of instruments • Field marking Pharmaceuticals Commissioning Aspects
• IQ / OQ + Proof testing of the safety function • Validation of the retest method • Loop sheet to indicate safety critical nature of instruments • Field marking Pharmaceuticals Commissioning Aspects
 • Supplier might have correctly designed safety Engineering. • That does not mean it reaches standard. • Modified Instrument/Electrical design • Modified Instrument/Electrical Commissioning • Feeds into SRS Pharmaceuticals Machine / Package Design
• Supplier might have correctly designed safety Engineering. • That does not mean it reaches standard. • Modified Instrument/Electrical design • Modified Instrument/Electrical Commissioning • Feeds into SRS Pharmaceuticals Machine / Package Design
 • • E Ex d motor – Surface temperature limits Variable Speed Drive. Never below 10 Hz Always with Thermistor Protection Pharmaceuticals Machine / Package Design
• • E Ex d motor – Surface temperature limits Variable Speed Drive. Never below 10 Hz Always with Thermistor Protection Pharmaceuticals Machine / Package Design
 Pharmaceuticals Machine / Package Design
Pharmaceuticals Machine / Package Design
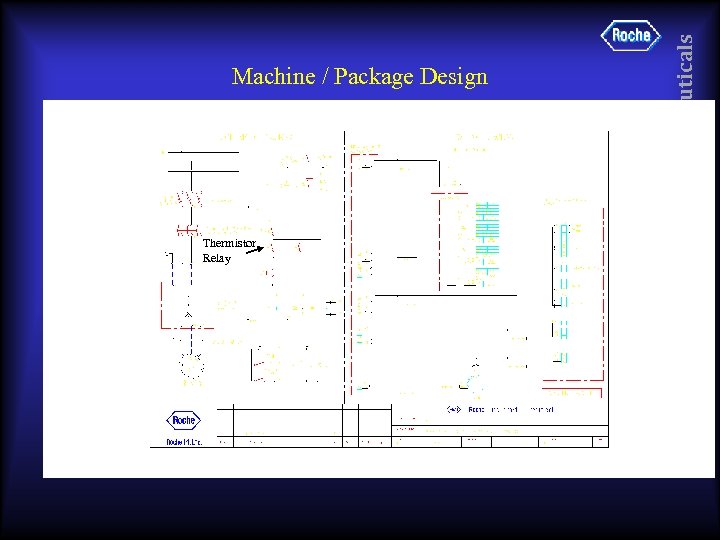 Thermistor Relay Pharmaceuticals Machine / Package Design
Thermistor Relay Pharmaceuticals Machine / Package Design
 Pharmaceuticals Maintenance • Vital part of ensuring safety function remains intact. • Will have to retest interlocks on a periodic basis. • Will need to follow methods set out during Instrument/Electrical design stage. • Care required in effecting changes to the loop when in use.
Pharmaceuticals Maintenance • Vital part of ensuring safety function remains intact. • Will have to retest interlocks on a periodic basis. • Will need to follow methods set out during Instrument/Electrical design stage. • Care required in effecting changes to the loop when in use.
 • Document which brings together the design thread. • Started by the Process Engineering group • Continued by the Instrument / Electrical engineering group • Reviewed by Safety Engineering group. • Live document until pre-start safety review. Pharmaceuticals Safety Requirements Spec
• Document which brings together the design thread. • Started by the Process Engineering group • Continued by the Instrument / Electrical engineering group • Reviewed by Safety Engineering group. • Live document until pre-start safety review. Pharmaceuticals Safety Requirements Spec
 • Different way of thinking Defence in Depth Layers of Protection • Risk Analysis • Basic Statistics • Fault Tree Analysis Pharmaceuticals New skills
• Different way of thinking Defence in Depth Layers of Protection • Risk Analysis • Basic Statistics • Fault Tree Analysis Pharmaceuticals New skills
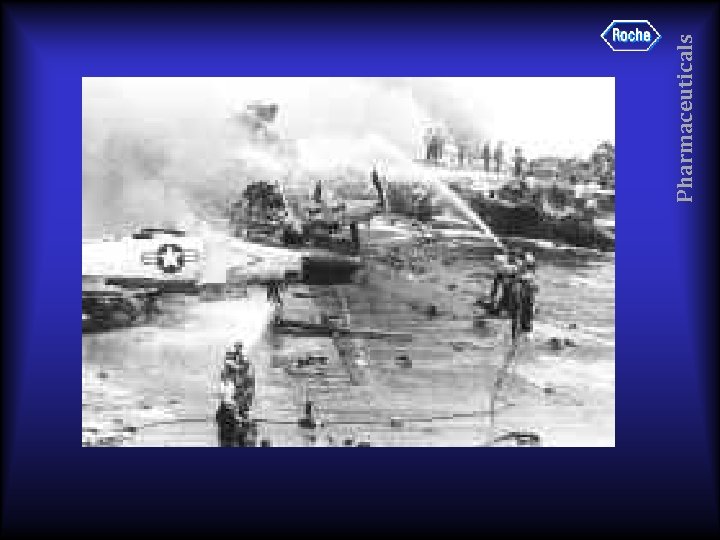
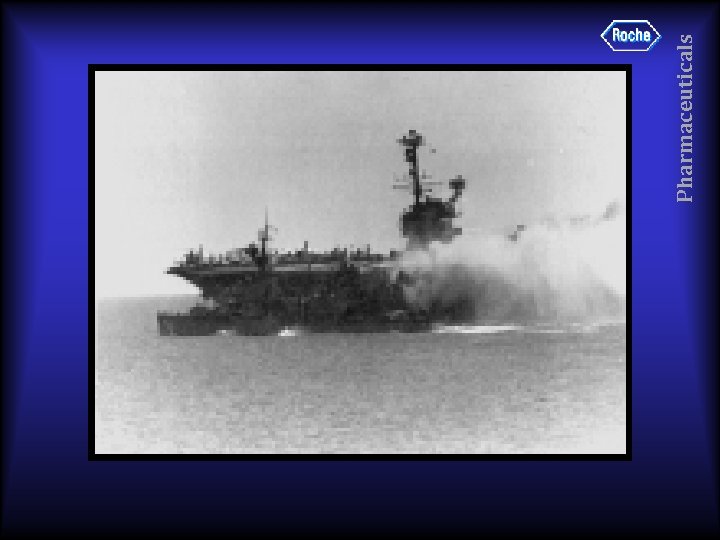
 Pharmaceuticals 6 June 1967
Pharmaceuticals 6 June 1967
 Pharmaceuticals
Pharmaceuticals
 Pharmaceuticals
Pharmaceuticals
 Pharmaceuticals
Pharmaceuticals


