2aeff0919b3d0954613c628bb5158fd0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41
 Mortality Workshop - IRIS Health Statistics User Group – 24/04/2015 Claudia Wells Head of Mortality Analysis Office for National Statistics
Mortality Workshop - IRIS Health Statistics User Group – 24/04/2015 Claudia Wells Head of Mortality Analysis Office for National Statistics
 Plan for the morning 11: 05 – 11: 15 IRIS for cause of death coding 11: 15 – 11: 25 Death certification reform 11: 25 – 12: 00 Breakout sessions 12: 00 – 12: 30 Feedback and discussion
Plan for the morning 11: 05 – 11: 15 IRIS for cause of death coding 11: 15 – 11: 25 Death certification reform 11: 25 – 12: 00 Breakout sessions 12: 00 – 12: 30 Feedback and discussion
 What is IRIS?
What is IRIS?
 What is IRIS? • Software used to code cause of death to a package called IRIS (version 2013). • The development of IRIS was supported by Eurostat (the statistical office of the European Union) and managed by the IRIS Institute hosted by the German Institute of Medical Documentation and Information in Cologne. • Provide a common mortality coding system that can be used for coding death certificates, written in any language, according to ICD mortality coding rules and instructions. • The use of the IRIS software will help to improve the international comparability of mortality statistics. • Currently IRIS uses components of the NCHS Mortality Medical Data System (MMDS) to code the causes of death
What is IRIS? • Software used to code cause of death to a package called IRIS (version 2013). • The development of IRIS was supported by Eurostat (the statistical office of the European Union) and managed by the IRIS Institute hosted by the German Institute of Medical Documentation and Information in Cologne. • Provide a common mortality coding system that can be used for coding death certificates, written in any language, according to ICD mortality coding rules and instructions. • The use of the IRIS software will help to improve the international comparability of mortality statistics. • Currently IRIS uses components of the NCHS Mortality Medical Data System (MMDS) to code the causes of death
 Main changes introduced with IRIS • IRIS includes major updates to the ICD-10 approved by WHO - including significant changes to the use of codes within the neoplasms chapter. • Control of the English IRIS data dictionary • Changes to the way drug mentions are coded • For stillbirths and neonatal deaths, any maternal condition mentioned on the death certificate will be coded to chapter XVI (certain conditions originating in the perinatal period).
Main changes introduced with IRIS • IRIS includes major updates to the ICD-10 approved by WHO - including significant changes to the use of codes within the neoplasms chapter. • Control of the English IRIS data dictionary • Changes to the way drug mentions are coded • For stillbirths and neonatal deaths, any maternal condition mentioned on the death certificate will be coded to chapter XVI (certain conditions originating in the perinatal period).
 Dual coding • 2012 registrations, (excluding neonates) • Records were selected from each quarter to avoid seasonal influences • Weeks around public holidays were excluded • 38, 718 records (7. 8 per cent) selected for dual coding
Dual coding • 2012 registrations, (excluding neonates) • Records were selected from each quarter to avoid seasonal influences • Weeks around public holidays were excluded • 38, 718 records (7. 8 per cent) selected for dual coding
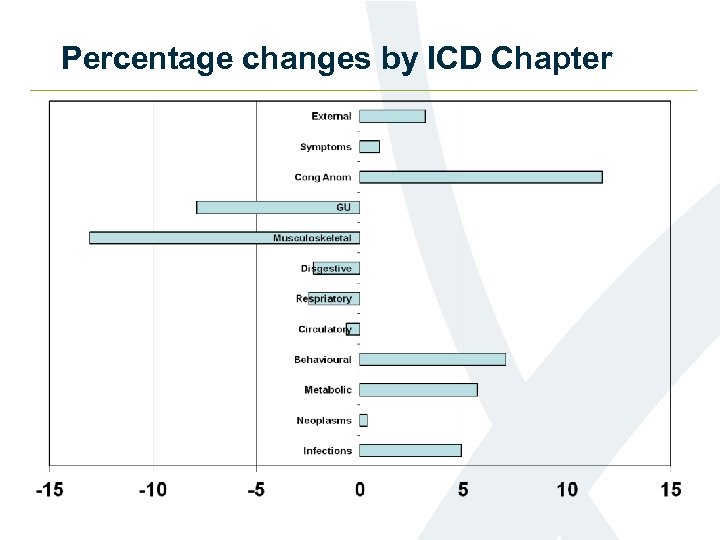 Percentage changes by ICD Chapter
Percentage changes by ICD Chapter
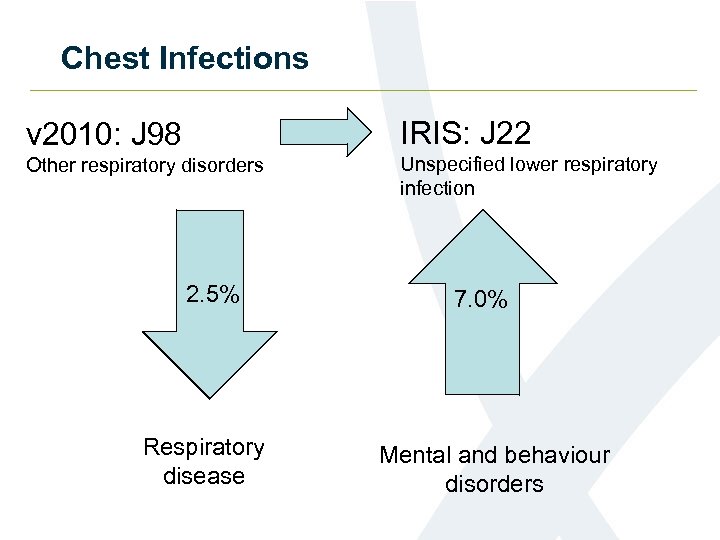 Chest Infections v 2010: J 98 IRIS: J 22 Other respiratory disorders Unspecified lower respiratory infection 2. 5% Respiratory disease 7. 0% Mental and behaviour disorders
Chest Infections v 2010: J 98 IRIS: J 22 Other respiratory disorders Unspecified lower respiratory infection 2. 5% Respiratory disease 7. 0% Mental and behaviour disorders
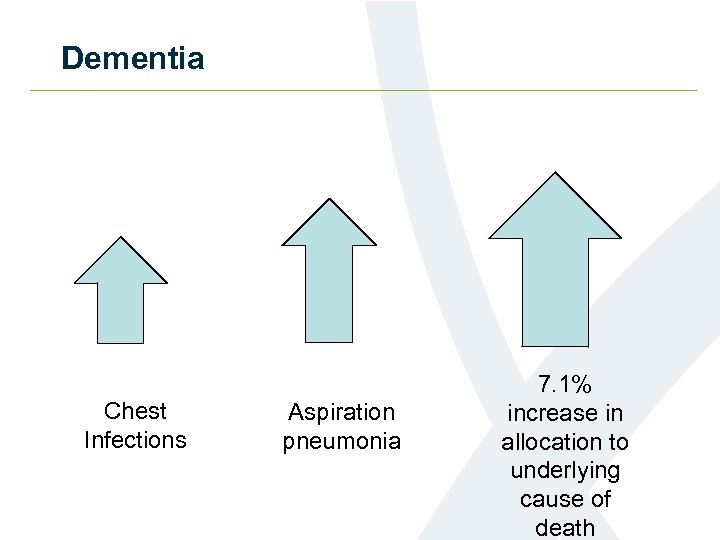 Dementia Chest Infections Aspiration pneumonia 7. 1% increase in allocation to underlying cause of death
Dementia Chest Infections Aspiration pneumonia 7. 1% increase in allocation to underlying cause of death
 Other significant changes • Certain infectious and parasitic diseases • Up 4. 9 % • Movement of deaths involving sepsis/septicaemia
Other significant changes • Certain infectious and parasitic diseases • Up 4. 9 % • Movement of deaths involving sepsis/septicaemia
 Other significant changes • Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases increased by 5. 7% • Diabetes increased by 6. 8%
Other significant changes • Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases increased by 5. 7% • Diabetes increased by 6. 8%
 Where to get more information • Statistical Bulletin and underlying data: www. ons. gov. uk/ons/rel/subnational-health 3/impact-of-the-implementation-of-iris-software-foricd-10 -cause-of-death-coding-on-mortality-statistics/england-wales/index. html • Information Note: www. ons. gov. uk/ons/guide-method/user-guidance/health-and-life-events/Changes-to-cause-of -death-coding-in-England-Wales/index. html
Where to get more information • Statistical Bulletin and underlying data: www. ons. gov. uk/ons/rel/subnational-health 3/impact-of-the-implementation-of-iris-software-foricd-10 -cause-of-death-coding-on-mortality-statistics/england-wales/index. html • Information Note: www. ons. gov. uk/ons/guide-method/user-guidance/health-and-life-events/Changes-to-cause-of -death-coding-in-England-Wales/index. html
 What about stillbirths and neonatal deaths • An English dictionary of terms specifically for stillbirths and neonatal deaths • Automatic coding using the same system as deaths >28 days • Requires a change in coding for stillbirths and neonatal deaths • Assigns an underlying cause of death
What about stillbirths and neonatal deaths • An English dictionary of terms specifically for stillbirths and neonatal deaths • Automatic coding using the same system as deaths >28 days • Requires a change in coding for stillbirths and neonatal deaths • Assigns an underlying cause of death
 Neonatal and stillbirth death certificate Duration a. Main diseases or conditions in infant/fetus . . . . b. Other diseases or conditions in infant/fetus . . . . c. Main maternal diseases or conditions affecting infant/ fetus . . . . d. Other maternal diseases or conditions affecting infant/ fetus. . . . . e. Other relevant causes . . . . .
Neonatal and stillbirth death certificate Duration a. Main diseases or conditions in infant/fetus . . . . b. Other diseases or conditions in infant/fetus . . . . c. Main maternal diseases or conditions affecting infant/ fetus . . . . d. Other maternal diseases or conditions affecting infant/ fetus. . . . . e. Other relevant causes . . . . .
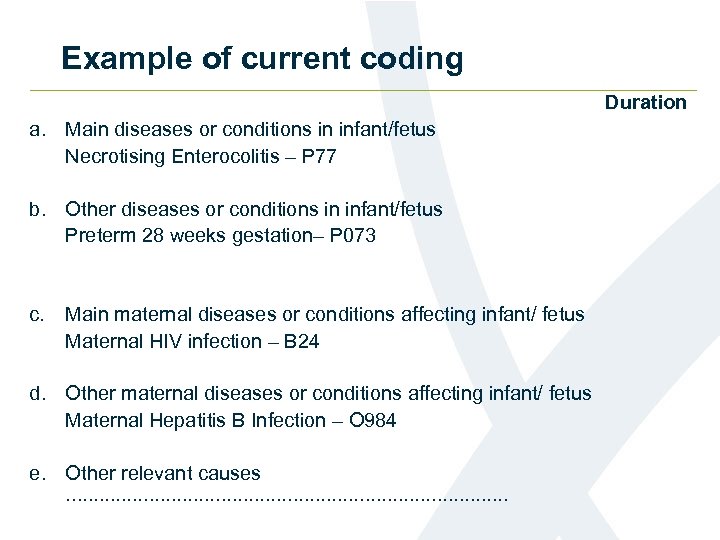 Example of current coding Duration a. Main diseases or conditions in infant/fetus Necrotising Enterocolitis – P 77 b. Other diseases or conditions in infant/fetus Preterm 28 weeks gestation– P 073 c. Main maternal diseases or conditions affecting infant/ fetus Maternal HIV infection – B 24 d. Other maternal diseases or conditions affecting infant/ fetus Maternal Hepatitis B Infection – O 984 e. Other relevant causes . . . . .
Example of current coding Duration a. Main diseases or conditions in infant/fetus Necrotising Enterocolitis – P 77 b. Other diseases or conditions in infant/fetus Preterm 28 weeks gestation– P 073 c. Main maternal diseases or conditions affecting infant/ fetus Maternal HIV infection – B 24 d. Other maternal diseases or conditions affecting infant/ fetus Maternal Hepatitis B Infection – O 984 e. Other relevant causes . . . . .
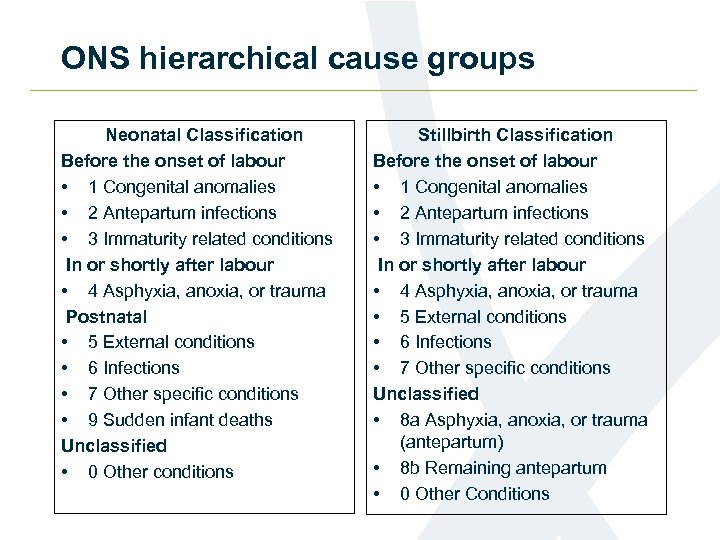 ONS hierarchical cause groups Neonatal Classification Before the onset of labour • 1 Congenital anomalies • 2 Antepartum infections • 3 Immaturity related conditions In or shortly after labour • 4 Asphyxia, anoxia, or trauma Postnatal • 5 External conditions • 6 Infections • 7 Other specific conditions • 9 Sudden infant deaths Unclassified • 0 Other conditions Stillbirth Classification Before the onset of labour • 1 Congenital anomalies • 2 Antepartum infections • 3 Immaturity related conditions In or shortly after labour • 4 Asphyxia, anoxia, or trauma • 5 External conditions • 6 Infections • 7 Other specific conditions Unclassified • 8 a Asphyxia, anoxia, or trauma (antepartum) • 8 b Remaining antepartum • 0 Other Conditions
ONS hierarchical cause groups Neonatal Classification Before the onset of labour • 1 Congenital anomalies • 2 Antepartum infections • 3 Immaturity related conditions In or shortly after labour • 4 Asphyxia, anoxia, or trauma Postnatal • 5 External conditions • 6 Infections • 7 Other specific conditions • 9 Sudden infant deaths Unclassified • 0 Other conditions Stillbirth Classification Before the onset of labour • 1 Congenital anomalies • 2 Antepartum infections • 3 Immaturity related conditions In or shortly after labour • 4 Asphyxia, anoxia, or trauma • 5 External conditions • 6 Infections • 7 Other specific conditions Unclassified • 8 a Asphyxia, anoxia, or trauma (antepartum) • 8 b Remaining antepartum • 0 Other Conditions
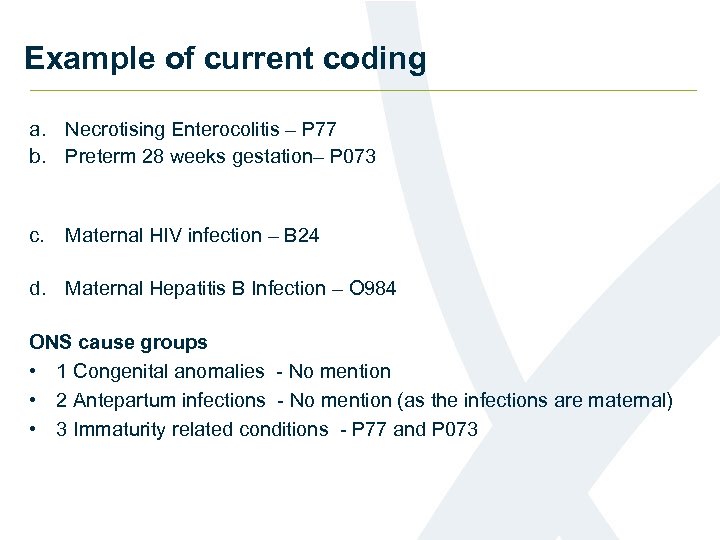 Example of current coding a. Necrotising Enterocolitis – P 77 b. Preterm 28 weeks gestation– P 073 c. Maternal HIV infection – B 24 d. Maternal Hepatitis B Infection – O 984 ONS cause groups • 1 Congenital anomalies - No mention • 2 Antepartum infections - No mention (as the infections are maternal) • 3 Immaturity related conditions - P 77 and P 073
Example of current coding a. Necrotising Enterocolitis – P 77 b. Preterm 28 weeks gestation– P 073 c. Maternal HIV infection – B 24 d. Maternal Hepatitis B Infection – O 984 ONS cause groups • 1 Congenital anomalies - No mention • 2 Antepartum infections - No mention (as the infections are maternal) • 3 Immaturity related conditions - P 77 and P 073
 Analysis of IRIS coded data • Developing English language dictionary • Events that occurred in 2010 • 2014 Neonatal deaths, 3712 Stillbirths 1. ONS cause group based on IRIS coded mentions 2. ONS cause group based on IRIS coded underlying cause of death
Analysis of IRIS coded data • Developing English language dictionary • Events that occurred in 2010 • 2014 Neonatal deaths, 3712 Stillbirths 1. ONS cause group based on IRIS coded mentions 2. ONS cause group based on IRIS coded underlying cause of death
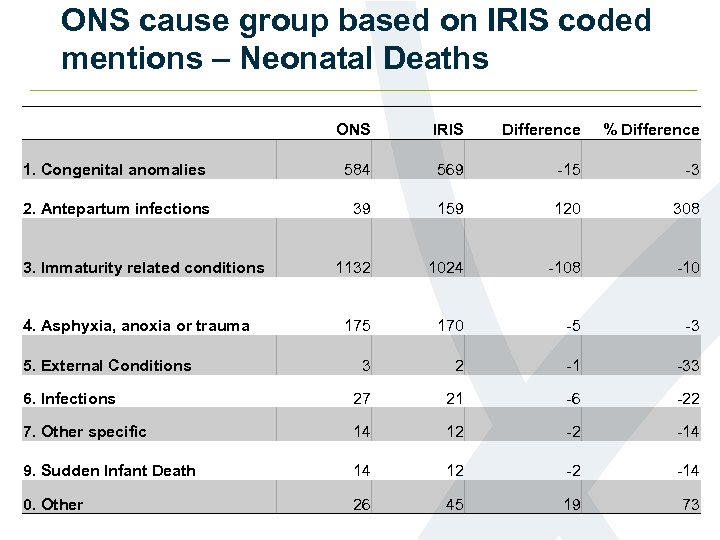 ONS cause group based on IRIS coded mentions – Neonatal Deaths ONS IRIS Difference % Difference 1. Congenital anomalies 584 569 -15 -3 2. Antepartum infections 39 159 120 308 1132 1024 -108 -10 175 170 -5 -3 3 2 -1 -33 6. Infections 27 21 -6 -22 7. Other specific 14 12 -2 -14 9. Sudden Infant Death 14 12 -2 -14 0. Other 26 45 19 73 3. Immaturity related conditions 4. Asphyxia, anoxia or trauma 5. External Conditions
ONS cause group based on IRIS coded mentions – Neonatal Deaths ONS IRIS Difference % Difference 1. Congenital anomalies 584 569 -15 -3 2. Antepartum infections 39 159 120 308 1132 1024 -108 -10 175 170 -5 -3 3 2 -1 -33 6. Infections 27 21 -6 -22 7. Other specific 14 12 -2 -14 9. Sudden Infant Death 14 12 -2 -14 0. Other 26 45 19 73 3. Immaturity related conditions 4. Asphyxia, anoxia or trauma 5. External Conditions
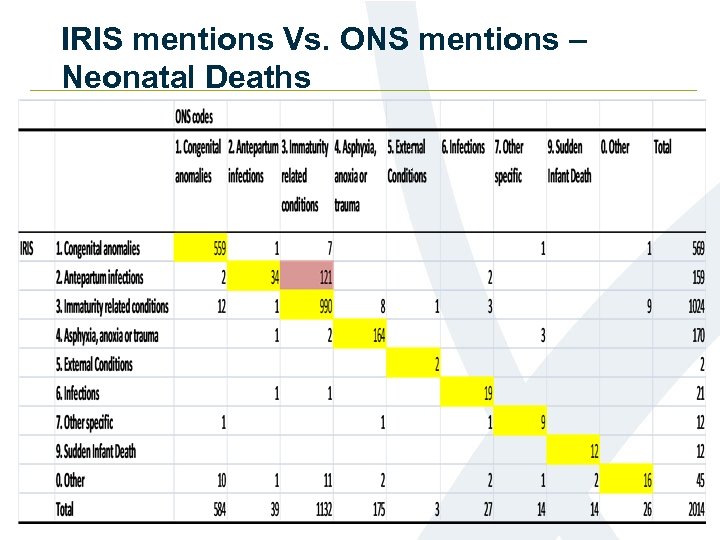 IRIS mentions Vs. ONS mentions – Neonatal Deaths
IRIS mentions Vs. ONS mentions – Neonatal Deaths
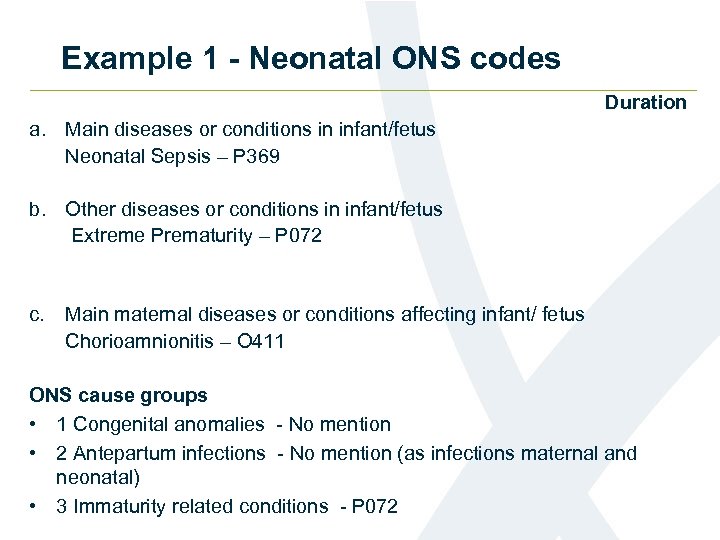 Example 1 - Neonatal ONS codes Duration a. Main diseases or conditions in infant/fetus Neonatal Sepsis – P 369 b. Other diseases or conditions in infant/fetus Extreme Prematurity – P 072 c. Main maternal diseases or conditions affecting infant/ fetus Chorioamnionitis – O 411 ONS cause groups • 1 Congenital anomalies - No mention • 2 Antepartum infections - No mention (as infections maternal and neonatal) • 3 Immaturity related conditions - P 072
Example 1 - Neonatal ONS codes Duration a. Main diseases or conditions in infant/fetus Neonatal Sepsis – P 369 b. Other diseases or conditions in infant/fetus Extreme Prematurity – P 072 c. Main maternal diseases or conditions affecting infant/ fetus Chorioamnionitis – O 411 ONS cause groups • 1 Congenital anomalies - No mention • 2 Antepartum infections - No mention (as infections maternal and neonatal) • 3 Immaturity related conditions - P 072
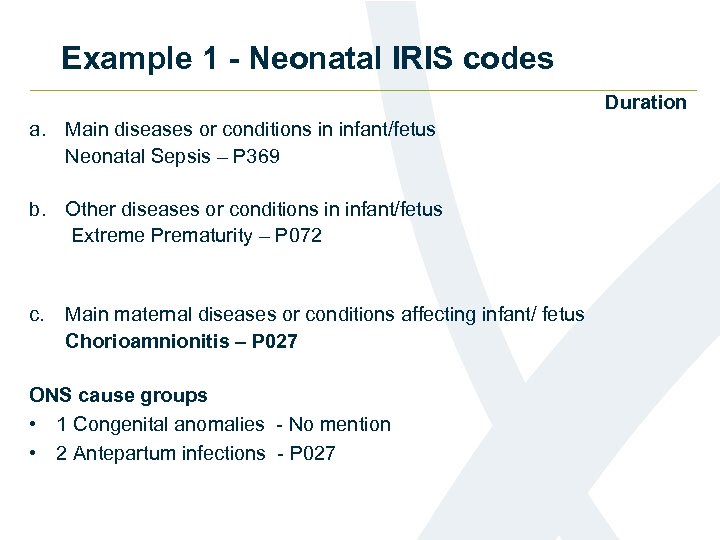 Example 1 - Neonatal IRIS codes Duration a. Main diseases or conditions in infant/fetus Neonatal Sepsis – P 369 b. Other diseases or conditions in infant/fetus Extreme Prematurity – P 072 c. Main maternal diseases or conditions affecting infant/ fetus Chorioamnionitis – P 027 ONS cause groups • 1 Congenital anomalies - No mention • 2 Antepartum infections - P 027
Example 1 - Neonatal IRIS codes Duration a. Main diseases or conditions in infant/fetus Neonatal Sepsis – P 369 b. Other diseases or conditions in infant/fetus Extreme Prematurity – P 072 c. Main maternal diseases or conditions affecting infant/ fetus Chorioamnionitis – P 027 ONS cause groups • 1 Congenital anomalies - No mention • 2 Antepartum infections - P 027
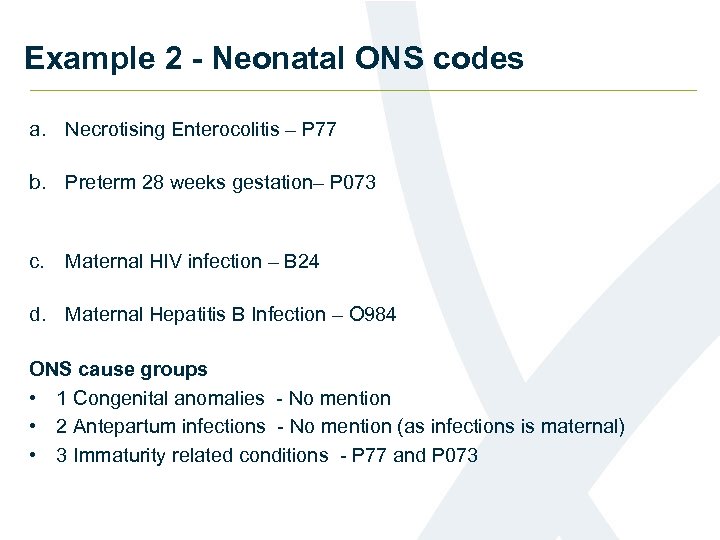 Example 2 - Neonatal ONS codes a. Necrotising Enterocolitis – P 77 b. Preterm 28 weeks gestation– P 073 c. Maternal HIV infection – B 24 d. Maternal Hepatitis B Infection – O 984 ONS cause groups • 1 Congenital anomalies - No mention • 2 Antepartum infections - No mention (as infections is maternal) • 3 Immaturity related conditions - P 77 and P 073
Example 2 - Neonatal ONS codes a. Necrotising Enterocolitis – P 77 b. Preterm 28 weeks gestation– P 073 c. Maternal HIV infection – B 24 d. Maternal Hepatitis B Infection – O 984 ONS cause groups • 1 Congenital anomalies - No mention • 2 Antepartum infections - No mention (as infections is maternal) • 3 Immaturity related conditions - P 77 and P 073
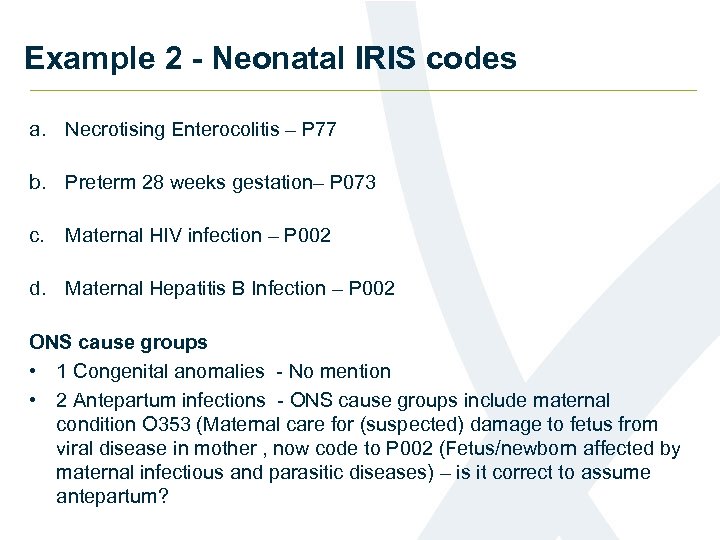 Example 2 - Neonatal IRIS codes a. Necrotising Enterocolitis – P 77 b. Preterm 28 weeks gestation– P 073 c. Maternal HIV infection – P 002 d. Maternal Hepatitis B Infection – P 002 ONS cause groups • 1 Congenital anomalies - No mention • 2 Antepartum infections - ONS cause groups include maternal condition O 353 (Maternal care for (suspected) damage to fetus from viral disease in mother , now code to P 002 (Fetus/newborn affected by maternal infectious and parasitic diseases) – is it correct to assume antepartum?
Example 2 - Neonatal IRIS codes a. Necrotising Enterocolitis – P 77 b. Preterm 28 weeks gestation– P 073 c. Maternal HIV infection – P 002 d. Maternal Hepatitis B Infection – P 002 ONS cause groups • 1 Congenital anomalies - No mention • 2 Antepartum infections - ONS cause groups include maternal condition O 353 (Maternal care for (suspected) damage to fetus from viral disease in mother , now code to P 002 (Fetus/newborn affected by maternal infectious and parasitic diseases) – is it correct to assume antepartum?
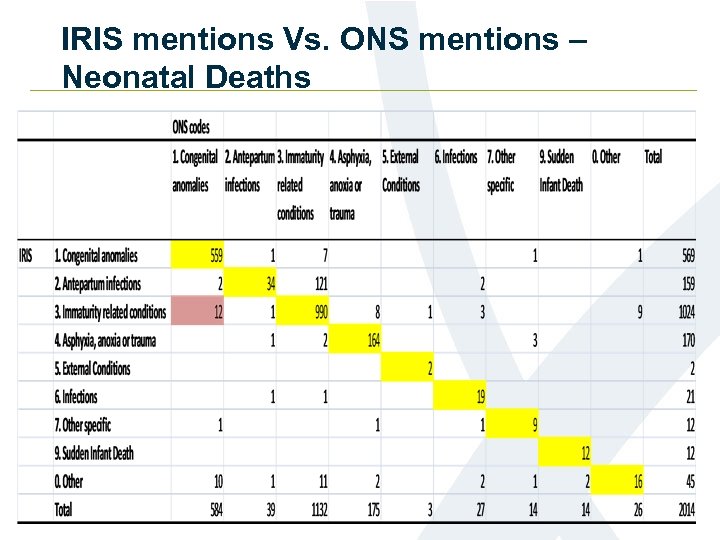 IRIS mentions Vs. ONS mentions – Neonatal Deaths
IRIS mentions Vs. ONS mentions – Neonatal Deaths
 Congenital Anomalies to Immaturity • Majority mentioned Q 33. 6 Hypoplasia and dysplasia of lung • Converted to P 28. 0 in IRIS Hypoplasia associated with short gestation • Majority but not all recorded mentioned prematurity of some degree
Congenital Anomalies to Immaturity • Majority mentioned Q 33. 6 Hypoplasia and dysplasia of lung • Converted to P 28. 0 in IRIS Hypoplasia associated with short gestation • Majority but not all recorded mentioned prematurity of some degree
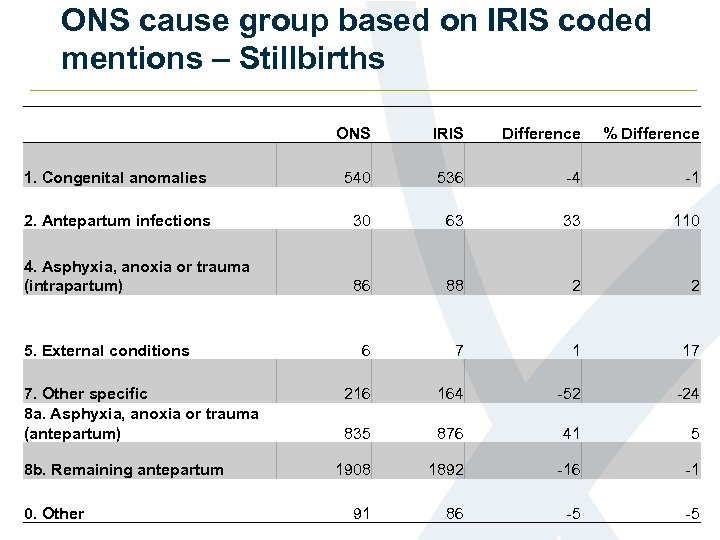 ONS cause group based on IRIS coded mentions – Stillbirths ONS IRIS Difference % Difference 1. Congenital anomalies 540 536 -4 -1 2. Antepartum infections 30 63 33 110 4. Asphyxia, anoxia or trauma (intrapartum) 86 88 2 2 6 7 1 17 216 164 -52 -24 835 876 41 5 1908 1892 -16 -1 91 86 -5 -5 5. External conditions 7. Other specific 8 a. Asphyxia, anoxia or trauma (antepartum) 8 b. Remaining antepartum 0. Other
ONS cause group based on IRIS coded mentions – Stillbirths ONS IRIS Difference % Difference 1. Congenital anomalies 540 536 -4 -1 2. Antepartum infections 30 63 33 110 4. Asphyxia, anoxia or trauma (intrapartum) 86 88 2 2 6 7 1 17 216 164 -52 -24 835 876 41 5 1908 1892 -16 -1 91 86 -5 -5 5. External conditions 7. Other specific 8 a. Asphyxia, anoxia or trauma (antepartum) 8 b. Remaining antepartum 0. Other
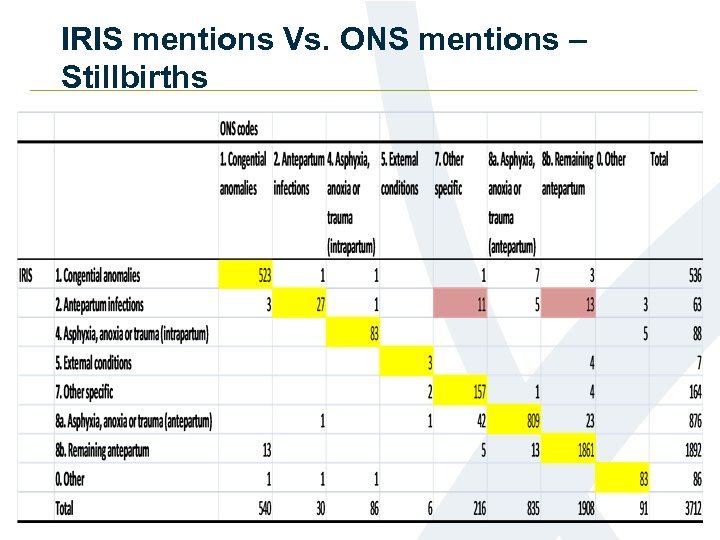 IRIS mentions Vs. ONS mentions – Stillbirths
IRIS mentions Vs. ONS mentions – Stillbirths
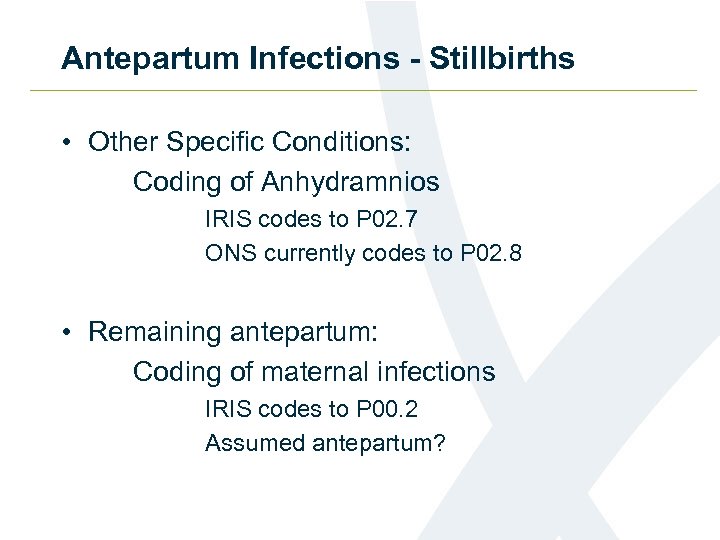 Antepartum Infections - Stillbirths • Other Specific Conditions: Coding of Anhydramnios IRIS codes to P 02. 7 ONS currently codes to P 02. 8 • Remaining antepartum: Coding of maternal infections IRIS codes to P 00. 2 Assumed antepartum?
Antepartum Infections - Stillbirths • Other Specific Conditions: Coding of Anhydramnios IRIS codes to P 02. 7 ONS currently codes to P 02. 8 • Remaining antepartum: Coding of maternal infections IRIS codes to P 00. 2 Assumed antepartum?
 Further work • Implications for UK data • Publication of dual coded data • Publication of mapping document • Publication of the stillbirth and neonatal cause of death dictionaries
Further work • Implications for UK data • Publication of dual coded data • Publication of mapping document • Publication of the stillbirth and neonatal cause of death dictionaries
 Talking/Discussion points • How to we balance maintaining an accurate internationally comparable classification with monitoring trends over time? • What do you need in terms of impact analysis? • Do you use the ONS hierarchical cause groups (Wigglesworth codes)?
Talking/Discussion points • How to we balance maintaining an accurate internationally comparable classification with monitoring trends over time? • What do you need in terms of impact analysis? • Do you use the ONS hierarchical cause groups (Wigglesworth codes)?
 Death Certification Reform • Harold Shipman (GP) certified the deaths of 250 victims without challenge • Inquiry into Shipman's crimes in 2004 recommend: • All deaths that do not require investigation by a coroner will undergo the independent scrutiny of a locally appointed Medical Examiner • Independent and proportionate scrutiny of relevant health records, examining the deceased person’s body (in most cases) and in all cases discussing the death with a relative or other appropriate person.
Death Certification Reform • Harold Shipman (GP) certified the deaths of 250 victims without challenge • Inquiry into Shipman's crimes in 2004 recommend: • All deaths that do not require investigation by a coroner will undergo the independent scrutiny of a locally appointed Medical Examiner • Independent and proportionate scrutiny of relevant health records, examining the deceased person’s body (in most cases) and in all cases discussing the death with a relative or other appropriate person.
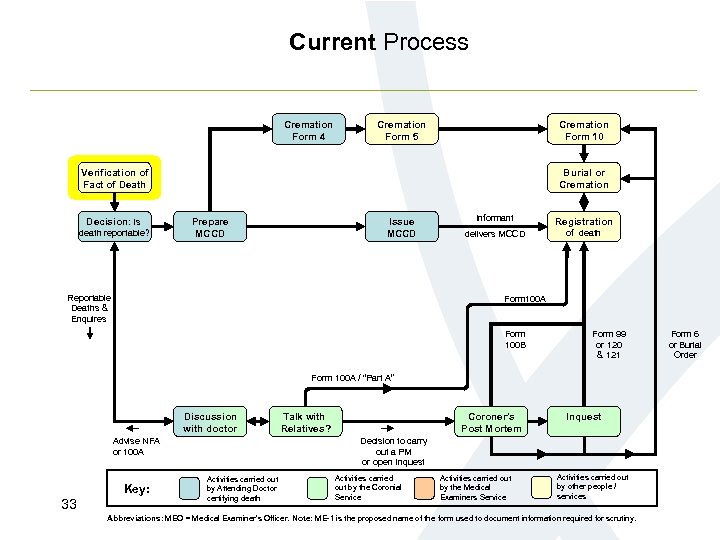 Current Process Cremation Form 4 Cremation Form 5 Cremation Form 10 Verification of Fact of Death Decision: is death reportable? Burial or Cremation Prepare MCCD Issue MCCD Reportable Deaths & Enquires Informant Registration delivers MCCD of death Form 100 A Form 100 B Form 99 or 120 & 121 Form 100 A / “Part A” Discussion with doctor Advise NFA or 100 A Key: 33 Talk with Relatives? Coroner’s Post Mortem Inquest Decision to carry out a PM or open Inquest Activities carried out by Attending Doctor certifying death Activities carried out by the Coronial Service Activities carried out by the Medical Examiners Service Activities carried out by other people / services Abbreviations: MEO = Medical Examiner’s Officer. Note: ME-1 is the proposed name of the form used to document information required for scrutiny. Form 6 or Burial Order
Current Process Cremation Form 4 Cremation Form 5 Cremation Form 10 Verification of Fact of Death Decision: is death reportable? Burial or Cremation Prepare MCCD Issue MCCD Reportable Deaths & Enquires Informant Registration delivers MCCD of death Form 100 A Form 100 B Form 99 or 120 & 121 Form 100 A / “Part A” Discussion with doctor Advise NFA or 100 A Key: 33 Talk with Relatives? Coroner’s Post Mortem Inquest Decision to carry out a PM or open Inquest Activities carried out by Attending Doctor certifying death Activities carried out by the Coronial Service Activities carried out by the Medical Examiners Service Activities carried out by other people / services Abbreviations: MEO = Medical Examiner’s Officer. Note: ME-1 is the proposed name of the form used to document information required for scrutiny. Form 6 or Burial Order
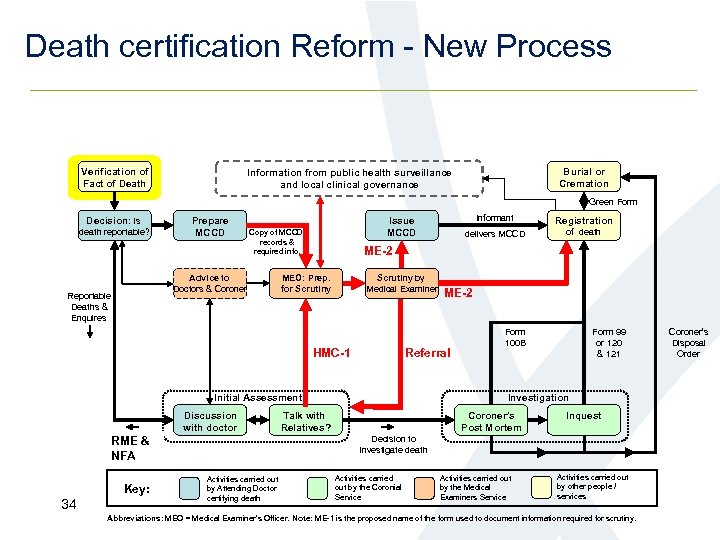 Death certification Reform - New Process Verification of Fact of Death Burial or Cremation Information from public health surveillance and local clinical governance Green Form Decision: is death reportable? Prepare MCCD Advice to Doctors & Coroner Reportable Deaths & Enquires MEO: Prep. for Scrutiny by Medical Examiner Key: 34 delivers MCCD of death ME-2 Referral Initial Assessment Advise NFA RME & or 100 A NFA Registration ME-2 HMC-1 Discussion with doctor Informant Issue MCCD Copy of MCCD, records & required info. Form 100 B Form 99 or 120 & 121 Investigation Talk with Relatives? Coroner’s Post Mortem Inquest Decision to carry Decision to investigate death out a PM or open Inquest Activities carried out by Attending Doctor certifying death Activities carried out by the Coronial Service Activities carried out by the Medical Examiners Service Activities carried out by other people / services Abbreviations: MEO = Medical Examiner’s Officer. Note: ME-1 is the proposed name of the form used to document information required for scrutiny. Coroner’s Disposal Order
Death certification Reform - New Process Verification of Fact of Death Burial or Cremation Information from public health surveillance and local clinical governance Green Form Decision: is death reportable? Prepare MCCD Advice to Doctors & Coroner Reportable Deaths & Enquires MEO: Prep. for Scrutiny by Medical Examiner Key: 34 delivers MCCD of death ME-2 Referral Initial Assessment Advise NFA RME & or 100 A NFA Registration ME-2 HMC-1 Discussion with doctor Informant Issue MCCD Copy of MCCD, records & required info. Form 100 B Form 99 or 120 & 121 Investigation Talk with Relatives? Coroner’s Post Mortem Inquest Decision to carry Decision to investigate death out a PM or open Inquest Activities carried out by Attending Doctor certifying death Activities carried out by the Coronial Service Activities carried out by the Medical Examiners Service Activities carried out by other people / services Abbreviations: MEO = Medical Examiner’s Officer. Note: ME-1 is the proposed name of the form used to document information required for scrutiny. Coroner’s Disposal Order
 Death Certification reform pilots • The new process was piloted by the in six areas across England Wales, commencing in 2008. • Office for National Statistics (ONS) carried out a case study investigating records from five of the six pilot areas. • The cause(s) of death proposed initially by the certifying medical practitioner and also the confirmed cause(s) of death following medical examiner scrutiny of the deceased’s medical history and hospital notes.
Death Certification reform pilots • The new process was piloted by the in six areas across England Wales, commencing in 2008. • Office for National Statistics (ONS) carried out a case study investigating records from five of the six pilot areas. • The cause(s) of death proposed initially by the certifying medical practitioner and also the confirmed cause(s) of death following medical examiner scrutiny of the deceased’s medical history and hospital notes.
 Impact • More likely to add supplementary information to the death certificate. • This often led to more conditions being mentioned and to the order in which they were presented on the cause of death certificate being altered. • As a result there was a change to the underlying cause of death in 22 per cent of cases.
Impact • More likely to add supplementary information to the death certificate. • This often led to more conditions being mentioned and to the order in which they were presented on the cause of death certificate being altered. • As a result there was a change to the underlying cause of death in 22 per cent of cases.
 Impact by cause • 1 % more death certificates with an underlying cause of cancer • 6 % increase the proportion of deaths that were attributed to diseases of the circulatory system • 7% decrease in deaths attributed to a respiratory disease • In general, more conditions were mentioned on the death certificate as a result of scrutiny by medical examiners
Impact by cause • 1 % more death certificates with an underlying cause of cancer • 6 % increase the proportion of deaths that were attributed to diseases of the circulatory system • 7% decrease in deaths attributed to a respiratory disease • In general, more conditions were mentioned on the death certificate as a result of scrutiny by medical examiners
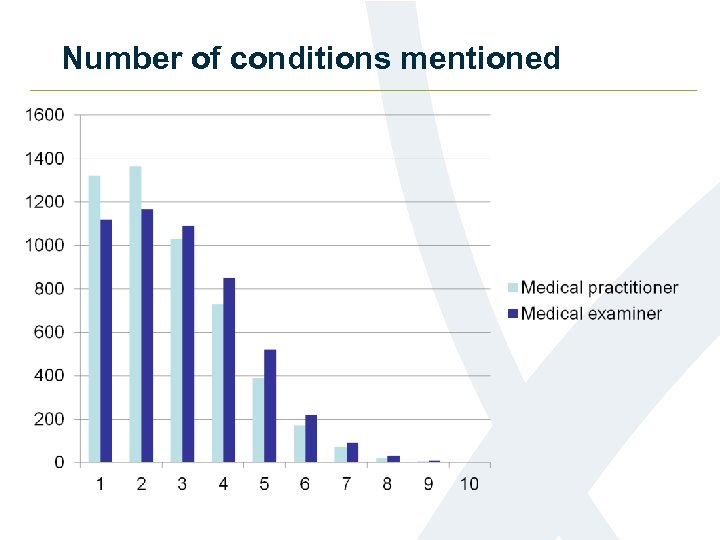 Number of conditions mentioned
Number of conditions mentioned
 Implementation timetable - UK • Scotland are due to implement in April 2015 • England, Wales and Northern Ireland – implementation has be delayed until further consultation can be carried out. Will not be until after May 2015
Implementation timetable - UK • Scotland are due to implement in April 2015 • England, Wales and Northern Ireland – implementation has be delayed until further consultation can be carried out. Will not be until after May 2015
 Where to get more information • Statistical Bulletin and underlying data: http: //www. ons. gov. uk/ons/rel/subnational-health 2/death-certification-reform---a-case-study-on -the-potential-impact-on-mortality-statistics/england-wales/index. html
Where to get more information • Statistical Bulletin and underlying data: http: //www. ons. gov. uk/ons/rel/subnational-health 2/death-certification-reform---a-case-study-on -the-potential-impact-on-mortality-statistics/england-wales/index. html
 Thanks! Any questions? Contact: mortality@ons. gsi. gov. uk
Thanks! Any questions? Contact: mortality@ons. gsi. gov. uk


