 Morphology The Noun
Morphology The Noun
 Definition Noun is a word expressing, expressing a: – A living being (e. g. a man, a woman) – A lifeless thing (e. g. a pen) – Abstract ideas (love, friendship)
Definition Noun is a word expressing, expressing a: – A living being (e. g. a man, a woman) – A lifeless thing (e. g. a pen) – Abstract ideas (love, friendship)
 Characteristics • Most nouns have two nouns: singular and plural (e. g. a cat – cats) • Most nouns have two cases: the common case and possessive case. e. g. Andrew and his car. (c. c. ) Andrew’s car. (p. c. )
Characteristics • Most nouns have two nouns: singular and plural (e. g. a cat – cats) • Most nouns have two cases: the common case and possessive case. e. g. Andrew and his car. (c. c. ) Andrew’s car. (p. c. )
 Characteristics • According to the morphological structure: - simple (pen, dog) - derivative – have prefixes and suffixes – revolution, explanation. - compound (copybook, blackboard)
Characteristics • According to the morphological structure: - simple (pen, dog) - derivative – have prefixes and suffixes – revolution, explanation. - compound (copybook, blackboard)
 The Plural of Nouns English countable nouns have two numbers^ singular and plural 1. Regular Formation: A cat – cats A dog – dogs A bee – bees A fox – foxes
The Plural of Nouns English countable nouns have two numbers^ singular and plural 1. Regular Formation: A cat – cats A dog – dogs A bee – bees A fox – foxes
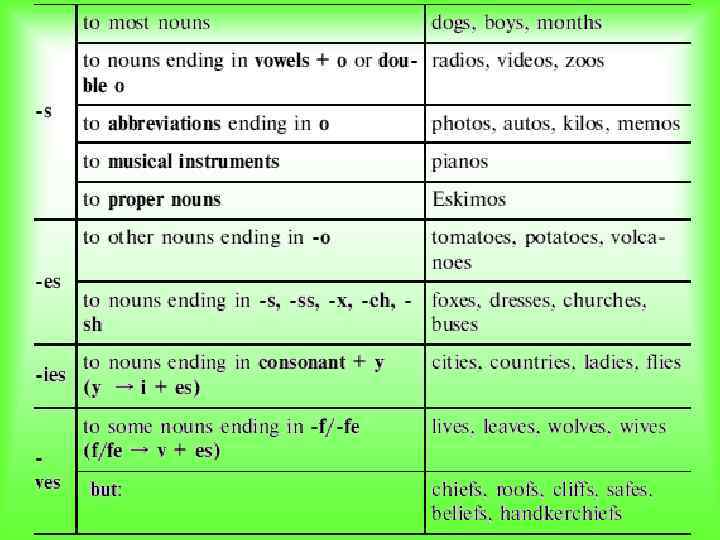
 The Plural of Nouns A) By changing a vowel B) By adding the suffix –en C) The plural form is similar to the singular form
The Plural of Nouns A) By changing a vowel B) By adding the suffix –en C) The plural form is similar to the singular form
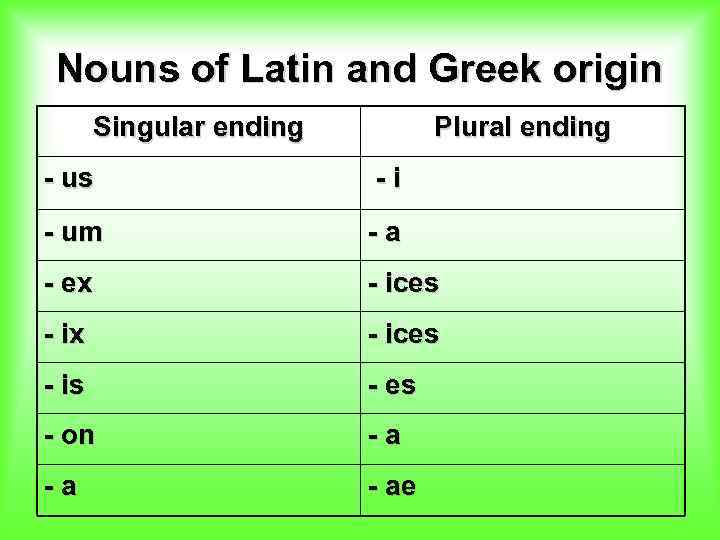 Nouns of Latin and Greek origin Singular ending Plural ending - us -i - um -a - ex - ices - is - es - on -a -a - ae
Nouns of Latin and Greek origin Singular ending Plural ending - us -i - um -a - ex - ices - is - es - on -a -a - ae
 E. g. a stimulus – stimuli a datum – data an index – indices
E. g. a stimulus – stimuli a datum – data an index – indices
 The Plural of Compound Nouns
The Plural of Compound Nouns
 Uncountable Nouns (Singular Only) The most common uncountable nouns are: • Mass nouns: fluids (blood, tea, etc), solids (bread, nouns china, fish etc), gasses (air, oxygen, smoke, smog, etc), particles (corn, flour, hair, salt, sand, etc). • Subjects of study: chemistry, economics, literature, study mathematics, physics, etc. • Languages: Chinese, English, French, etc. Languages • Games: billiards, chess, golf, soccer, tennis, etc. Games • Diseases: flu, measles, etc. Diseases • Natural phenomena: darkness, hail, humidity, etc. phenomena
Uncountable Nouns (Singular Only) The most common uncountable nouns are: • Mass nouns: fluids (blood, tea, etc), solids (bread, nouns china, fish etc), gasses (air, oxygen, smoke, smog, etc), particles (corn, flour, hair, salt, sand, etc). • Subjects of study: chemistry, economics, literature, study mathematics, physics, etc. • Languages: Chinese, English, French, etc. Languages • Games: billiards, chess, golf, soccer, tennis, etc. Games • Diseases: flu, measles, etc. Diseases • Natural phenomena: darkness, hail, humidity, etc. phenomena
 Uncountable Nouns (Singular Only) • Some abstract nouns: advice, anger, nouns applause, behaviour, business, courage, education, homework, information, intelligence, knowledge, luck, music, news, peace, truth, wealth, work, etc. news • Collective nouns: baggage, furniture, nouns jewellery, luggage, machinery, money stationery, etc.
Uncountable Nouns (Singular Only) • Some abstract nouns: advice, anger, nouns applause, behaviour, business, courage, education, homework, information, intelligence, knowledge, luck, music, news, peace, truth, wealth, work, etc. news • Collective nouns: baggage, furniture, nouns jewellery, luggage, machinery, money stationery, etc.
 Note!!! • Many uncountable nouns can be made countable by adding a partitive “a piece of”: a piece of information (advice)
Note!!! • Many uncountable nouns can be made countable by adding a partitive “a piece of”: a piece of information (advice)
 Nouns used in the Plural only • • • garments (trousers, etc), tools (scissors, etc), instruments (binoculars, compasses, spectacles, etc), • nouns such as: arms, clothes, earnings, as people, police, stairs, surroundings, etc. police
Nouns used in the Plural only • • • garments (trousers, etc), tools (scissors, etc), instruments (binoculars, compasses, spectacles, etc), • nouns such as: arms, clothes, earnings, as people, police, stairs, surroundings, etc. police
 Note !!! • The uncountable nouns used only in the Plural can be made countable by a particle – “a pair of” – a pair of glasses etc.
Note !!! • The uncountable nouns used only in the Plural can be made countable by a particle – “a pair of” – a pair of glasses etc.
 Group nouns refer to a group of people. • These nouns can take either a singular or a plural verb depending on whether we see the group as a whole or as individuals. Such group nouns are: army, audience, class, club, committee, company, council, crew, crowd, headquarters, family, jury, government, press, public, staff, team, etc.
Group nouns refer to a group of people. • These nouns can take either a singular or a plural verb depending on whether we see the group as a whole or as individuals. Such group nouns are: army, audience, class, club, committee, company, council, crew, crowd, headquarters, family, jury, government, press, public, staff, team, etc.
 Note!!! • With expressions of duration, distance or money meaning ‘a whole amount’ we use a singular verb: E. g. Two years is long to wait. Three miles is a long way to go. Nine thousand pounds is a high price to pay.
Note!!! • With expressions of duration, distance or money meaning ‘a whole amount’ we use a singular verb: E. g. Two years is long to wait. Three miles is a long way to go. Nine thousand pounds is a high price to pay.


