9728f2832a556f45c98a32b411d99bbb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39
 MORE CONCEPTS
MORE CONCEPTS
 Central Processing Unit (CPU) Designed to process instructions ALU arithmetic logic unit CU control unit
Central Processing Unit (CPU) Designed to process instructions ALU arithmetic logic unit CU control unit
 Memory RAM Random Access Memory ROM Read Only Memory
Memory RAM Random Access Memory ROM Read Only Memory
 RAM Random Access Memory Temporary (volatile) holding area for data, application software and operating system Less storage than disk Capacity measured in MB (128 - 256 MB) Speed in nanoseconds
RAM Random Access Memory Temporary (volatile) holding area for data, application software and operating system Less storage than disk Capacity measured in MB (128 - 256 MB) Speed in nanoseconds
 ROM Read-Only Memory Permanent on a chip from manufacturer Holds computer start up routine, which are hard-wired instructions
ROM Read-Only Memory Permanent on a chip from manufacturer Holds computer start up routine, which are hard-wired instructions
 Digital Data Representation The form in which information is conceived, manipulated and recorded on a digital device. Uses discrete digits/electronic signals 1, 0 (bits - binary digits) - On/Off - Yes/No - Byte = 8 bits = 1 character
Digital Data Representation The form in which information is conceived, manipulated and recorded on a digital device. Uses discrete digits/electronic signals 1, 0 (bits - binary digits) - On/Off - Yes/No - Byte = 8 bits = 1 character
 Coding Systems Depends on computer ASCII (7 bits) Extended ASCII (8 bits - current PCs) EBCDIC (8 bits - older IBM machines ) Unicode (16 bits - good for languages - future)
Coding Systems Depends on computer ASCII (7 bits) Extended ASCII (8 bits - current PCs) EBCDIC (8 bits - older IBM machines ) Unicode (16 bits - good for languages - future)
 Quantifying Bytes and Bits Bit = b Nibble = Half of a byte Byte = B Kilobyte (KB) (1024 bytes) Megabyte (MB) (Million bytes) Gigabyte (GB) (Billion bytes) Terabyte (TB) (Trillion bytes)
Quantifying Bytes and Bits Bit = b Nibble = Half of a byte Byte = B Kilobyte (KB) (1024 bytes) Megabyte (MB) (Million bytes) Gigabyte (GB) (Billion bytes) Terabyte (TB) (Trillion bytes)
 Modem Internet Connections Dial-up connection via modem (56 K) Cable modems Network card and cable modem required Always-on and 25 times faster than dial-up
Modem Internet Connections Dial-up connection via modem (56 K) Cable modems Network card and cable modem required Always-on and 25 times faster than dial-up
 Faster Internet Connections ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network) 64 K or 128 K Always-on and expensive DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) and x. DSL Up to 125 times faster than dialup DSS (Digital Satellite Service) 500 K Need proximity to a telephone switching station
Faster Internet Connections ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network) 64 K or 128 K Always-on and expensive DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) and x. DSL Up to 125 times faster than dialup DSS (Digital Satellite Service) 500 K Need proximity to a telephone switching station
 E-mail Basics Account = Mailbox Message userid@computer Attachment ASCII vs HTML format Netiquette
E-mail Basics Account = Mailbox Message userid@computer Attachment ASCII vs HTML format Netiquette
 E-mail System E-mail servers Store-and-forward technology Types POP (Post Office Protocol) used via ISP IMAP (Internet Messaging Access Protocol) Web-based like Hotmail
E-mail System E-mail servers Store-and-forward technology Types POP (Post Office Protocol) used via ISP IMAP (Internet Messaging Access Protocol) Web-based like Hotmail
 Software Categories Application Software System Software
Software Categories Application Software System Software
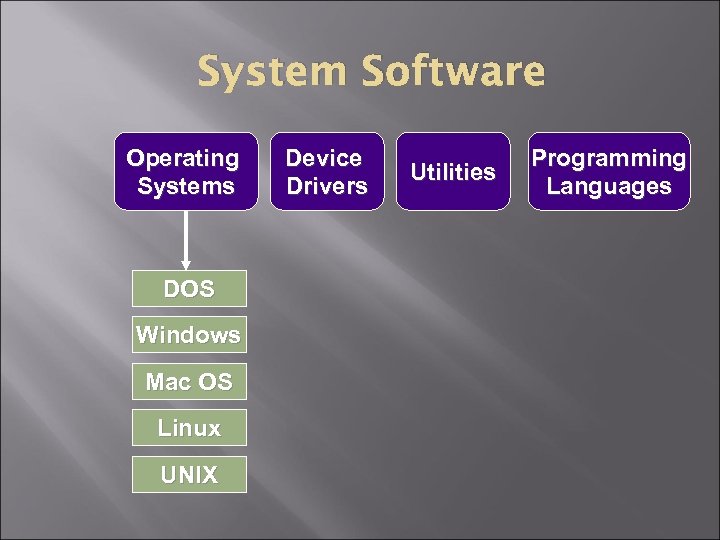 System Software Operating Systems DOS Windows Mac OS Linux UNIX Device Drivers Utilities Programming Languages
System Software Operating Systems DOS Windows Mac OS Linux UNIX Device Drivers Utilities Programming Languages
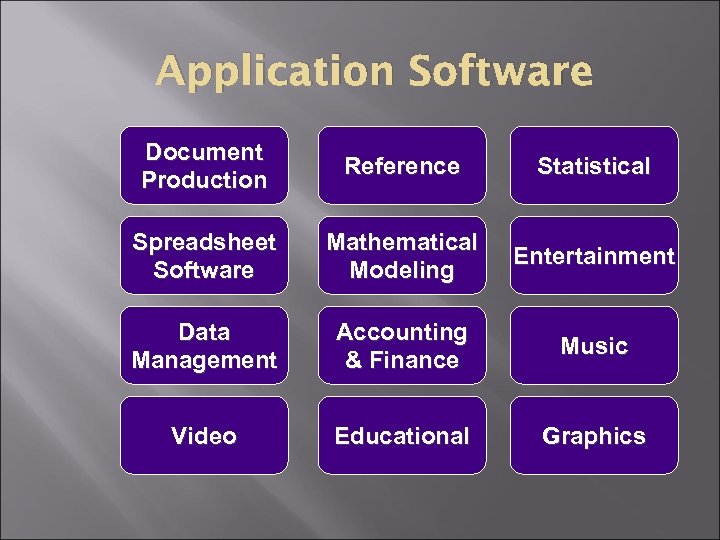 Application Software Document Production Reference Statistical Spreadsheet Software Mathematical Modeling Entertainment Data Management Accounting & Finance Music Video Educational Graphics
Application Software Document Production Reference Statistical Spreadsheet Software Mathematical Modeling Entertainment Data Management Accounting & Finance Music Video Educational Graphics
 Software Topics Computer program Support module main executable program (. exe) called by the program (. dll) Data module Example: a dictionary file or a file that is not supplied by the user
Software Topics Computer program Support module main executable program (. exe) called by the program (. dll) Data module Example: a dictionary file or a file that is not supplied by the user
 How Computers Interpret Software Computer languages Source code High-level languages: COBOL, C++, Java Machine language Compiler Creates object code in single batch Interpreter Converts one instruction at a time Common with web-based scripts (part of web page)
How Computers Interpret Software Computer languages Source code High-level languages: COBOL, C++, Java Machine language Compiler Creates object code in single batch Interpreter Converts one instruction at a time Common with web-based scripts (part of web page)
 Operating Systems Interacts with application software, device drivers & hardware to manage computers resources Multitasking CTRL-ALT-DEL GUI graphical user interface Utilities
Operating Systems Interacts with application software, device drivers & hardware to manage computers resources Multitasking CTRL-ALT-DEL GUI graphical user interface Utilities
 License vs. Copyright Software License: a legal contract that defines the ways in which you may use a computer program. Copyright: a form of legal protection that grants the author of an original work an exclusive right to copy, distribute, sell and modify that work. Software piracy For contract to take effect: Open a shrink-wrap license product Agree to an installation agreement
License vs. Copyright Software License: a legal contract that defines the ways in which you may use a computer program. Copyright: a form of legal protection that grants the author of an original work an exclusive right to copy, distribute, sell and modify that work. Software piracy For contract to take effect: Open a shrink-wrap license product Agree to an installation agreement
 Types of Copyright Protections Shareware: try before you buy on the honor system Freeware: no fee - can use, but not alter or sell Open Source: uncompiled source code that can be changed - sold or free Public Domain: can be copied, altered and resold
Types of Copyright Protections Shareware: try before you buy on the honor system Freeware: no fee - can use, but not alter or sell Open Source: uncompiled source code that can be changed - sold or free Public Domain: can be copied, altered and resold
 Tech. Talk: Boot Process Power up ROM runs bootstrap program POST (Power-on self-test) Identifies and checks peripherals ROM loads operating system from hard disk into RAM Checks configuration and customization startup routines Safe Mode if this process is not successful
Tech. Talk: Boot Process Power up ROM runs bootstrap program POST (Power-on self-test) Identifies and checks peripherals ROM loads operating system from hard disk into RAM Checks configuration and customization startup routines Safe Mode if this process is not successful
 Computer File Characteristics A collection of data on a storage medium Filename conventions Filename extension . txt . jpg . exe . doc
Computer File Characteristics A collection of data on a storage medium Filename conventions Filename extension . txt . jpg . exe . doc
 File Locations Device drive letters A: C: D: Directory Root Directory (C: ) Subdirectory or folder (C: Documents) File specification or Path File size and date C: MusicReggaeMarley One Love. mp 3 Drive letter Primary folder Secondary folder Filename extension
File Locations Device drive letters A: C: D: Directory Root Directory (C: ) Subdirectory or folder (C: Documents) File specification or Path File size and date C: MusicReggaeMarley One Love. mp 3 Drive letter Primary folder Secondary folder Filename extension
 Deleting Files Move to Recycle Bin in Windows Undelete Empty Bin
Deleting Files Move to Recycle Bin in Windows Undelete Empty Bin
 File Management Helps you organize your computer files File/Save and File/Open Utilities like Windows Explorer or MAC Finder list, find, move, copy, delete, rename Save vs. Save As
File Management Helps you organize your computer files File/Save and File/Open Utilities like Windows Explorer or MAC Finder list, find, move, copy, delete, rename Save vs. Save As
 Logical File Storage Filing cabinet model Metaphor to help you visualize files on a storage device Windows Explorer Folder hierarchy
Logical File Storage Filing cabinet model Metaphor to help you visualize files on a storage device Windows Explorer Folder hierarchy
 Physical File Storage medium formatted into tracks /sectors electronically File system keeps track of names and file locations. FAT (File Allocation Table) on each disk keeps track of where all files are. If damaged, you lose everything.
Physical File Storage medium formatted into tracks /sectors electronically File system keeps track of names and file locations. FAT (File Allocation Table) on each disk keeps track of where all files are. If damaged, you lose everything.
 Storage Technology Storage Medium: disk, tape, CD, DVD Storage Device: disk drives, CD drives holds data mechanical device Storage = Medium + Device
Storage Technology Storage Medium: disk, tape, CD, DVD Storage Device: disk drives, CD drives holds data mechanical device Storage = Medium + Device
 Storage Process Data copied from storage device to RAM Processed in RAM volatile (temporary) high speed storage Data copied back to storage medium (permanent) Storing data is writing/saving file Retrieving data is reading/loading/opening file
Storage Process Data copied from storage device to RAM Processed in RAM volatile (temporary) high speed storage Data copied back to storage medium (permanent) Storing data is writing/saving file Retrieving data is reading/loading/opening file
 Magnetic Storage Magnetizes microscopic particles on medium surface Permanent, but modifiable Hard disk, floppy disk, zip disk and tape Read-write head Not very durable
Magnetic Storage Magnetizes microscopic particles on medium surface Permanent, but modifiable Hard disk, floppy disk, zip disk and tape Read-write head Not very durable
 Optical Storage Stores data as microscopic light and dark spots on disk surface Pits and lands Uses laser lights More durable
Optical Storage Stores data as microscopic light and dark spots on disk surface Pits and lands Uses laser lights More durable
 Comparing Storage Devices Versatility Durability versatile devices can access data from several different media; i. e. , DVD drive – data DVDs, DVD movies, audio CDs, etc. mishandling, environmental factors Speed access time milliseconds (ms – thousandths of a second) random versus sequential access
Comparing Storage Devices Versatility Durability versatile devices can access data from several different media; i. e. , DVD drive – data DVDs, DVD movies, audio CDs, etc. mishandling, environmental factors Speed access time milliseconds (ms – thousandths of a second) random versus sequential access
 Floppy Disk Technology Most common 3 ½” 1. 44 MB (1, 440, 000 bytes) Write protect window Others zip disks (100 MB and 250 MB) Super. Disks (120 MB) Compatibility
Floppy Disk Technology Most common 3 ½” 1. 44 MB (1, 440, 000 bytes) Write protect window Others zip disks (100 MB and 250 MB) Super. Disks (120 MB) Compatibility
 CD Technology CD-ROM: Compact Disk Read-Only Memory CD-R: Compact Disk Recordable manufactured; cannot change; up to 680 MB; more durable you record; cannot be erased or modified CD-RW: Compact Disk Rewritable you record; can erase and modify
CD Technology CD-ROM: Compact Disk Read-Only Memory CD-R: Compact Disk Recordable manufactured; cannot change; up to 680 MB; more durable you record; cannot be erased or modified CD-RW: Compact Disk Rewritable you record; can erase and modify
 DVD Technology Digital Video Disk originally an alternative to VCR Manufactured Can play CD-ROM and most CD-Rs and CD-RWs
DVD Technology Digital Video Disk originally an alternative to VCR Manufactured Can play CD-ROM and most CD-Rs and CD-RWs
 Solid State Storage USB flash drive Compact. Flash (CF) cards Multi. Media cards (MMC) high-end digital cameras Smaller; mobile phones, pagers, cameras Secure. Digital (SD) cards MP 3 storage
Solid State Storage USB flash drive Compact. Flash (CF) cards Multi. Media cards (MMC) high-end digital cameras Smaller; mobile phones, pagers, cameras Secure. Digital (SD) cards MP 3 storage
 Display Device Image Quality Screen size (13” to 21”) horizontal and vertical pixels displayed on the screen 640 x 480, 800 x 600, 1024 x 768 (higher is better) measured diagonally viewable image size (vis) Dot pitch measure of image clarity smaller is better Resolution Color depth (or bit depth) number of colors that can be displayed 24 -bit (true color) = millions of colors
Display Device Image Quality Screen size (13” to 21”) horizontal and vertical pixels displayed on the screen 640 x 480, 800 x 600, 1024 x 768 (higher is better) measured diagonally viewable image size (vis) Dot pitch measure of image clarity smaller is better Resolution Color depth (or bit depth) number of colors that can be displayed 24 -bit (true color) = millions of colors
 Printer Comparison Criteria Resolution (dpi) Materials cost Speed (ppm or cps) Quality versus Price
Printer Comparison Criteria Resolution (dpi) Materials cost Speed (ppm or cps) Quality versus Price
 Peripherals device driver Plug and Play (Pn. P)
Peripherals device driver Plug and Play (Pn. P)


