3cbd411103470ae351401efbd633c10f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41
 MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 Introduction to electrical circuits terminology and machine sectorisation M. Zerlauth, CO-MI + many slides from various colleagues (KH, Rudiger, Paul, …) 1
MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 Introduction to electrical circuits terminology and machine sectorisation M. Zerlauth, CO-MI + many slides from various colleagues (KH, Rudiger, Paul, …) 1
 Outline è Yesterdays presentation of KH – Dangers in electrical circuits – Stored energies – Quenches – Components of electrical circuits è Machine sectorisation and naming conventions – Basics – Electrical Circuits – The concept of Powering Subsectors è Electrical Circuit terminology and concepts MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 – Naming conventions – Electrical Circuit components – Circuit Types – LHC Layout Database 2
Outline è Yesterdays presentation of KH – Dangers in electrical circuits – Stored energies – Quenches – Components of electrical circuits è Machine sectorisation and naming conventions – Basics – Electrical Circuits – The concept of Powering Subsectors è Electrical Circuit terminology and concepts MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 – Naming conventions – Electrical Circuit components – Circuit Types – LHC Layout Database 2
 MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 Machine Sectorisation and naming conventions 3
MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 Machine Sectorisation and naming conventions 3
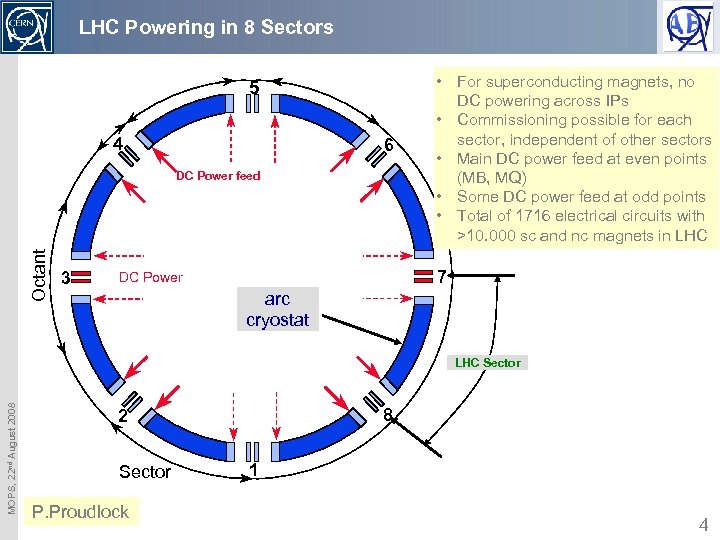 LHC Powering in 8 Sectors 5 4 6 Octant DC Power feed 3 • For superconducting magnets, no DC powering across IPs • Commissioning possible for each sector, independent of other sectors • Main DC power feed at even points (MB, MQ) • Some DC power feed at odd points • Total of 1716 electrical circuits with >10. 000 sc and nc magnets in LHC 7 DC Power arc cryostat MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 LHC Sector 8 2 Sector P. Proudlock 1 4
LHC Powering in 8 Sectors 5 4 6 Octant DC Power feed 3 • For superconducting magnets, no DC powering across IPs • Commissioning possible for each sector, independent of other sectors • Main DC power feed at even points (MB, MQ) • Some DC power feed at odd points • Total of 1716 electrical circuits with >10. 000 sc and nc magnets in LHC 7 DC Power arc cryostat MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 LHC Sector 8 2 Sector P. Proudlock 1 4
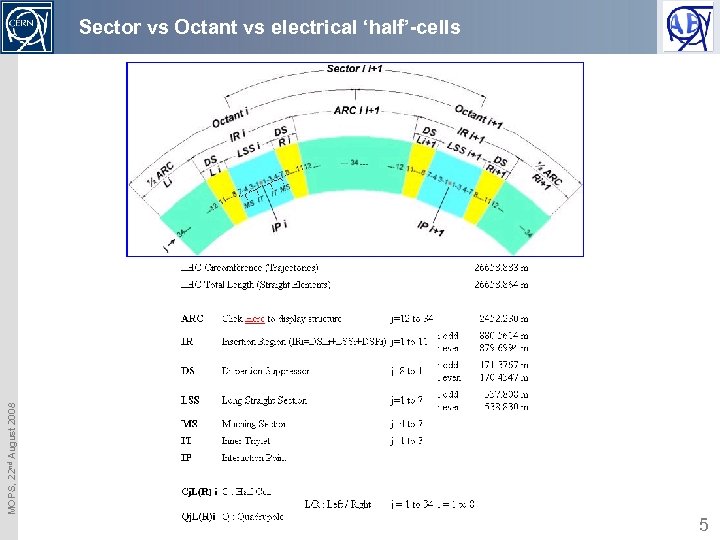 MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 Sector vs Octant vs electrical ‘half’-cells 5
MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 Sector vs Octant vs electrical ‘half’-cells 5
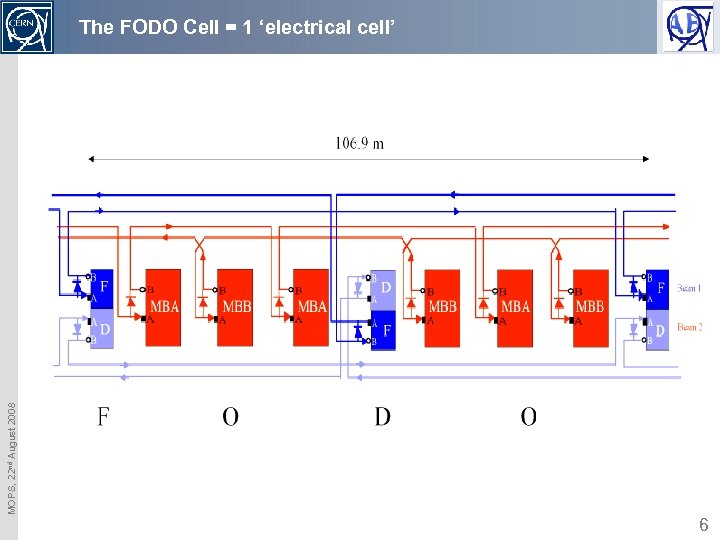 MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 The FODO Cell = 1 ‘electrical cell’ 6
MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 The FODO Cell = 1 ‘electrical cell’ 6
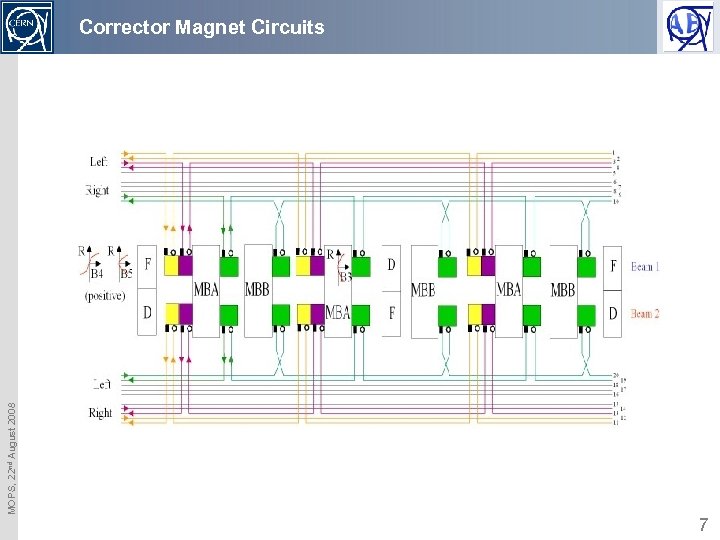 MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 Corrector Magnet Circuits 7
MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 Corrector Magnet Circuits 7
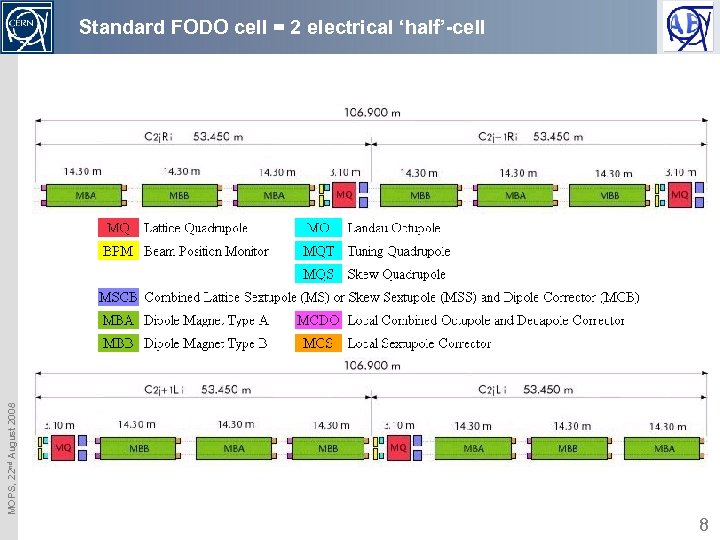 MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 Standard FODO cell = 2 electrical ‘half’-cell 8
MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 Standard FODO cell = 2 electrical ‘half’-cell 8
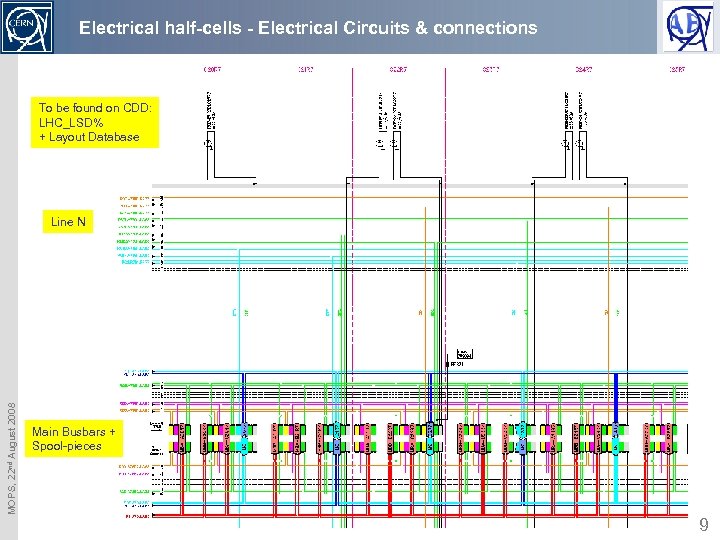 Electrical half-cells - Electrical Circuits & connections To be found on CDD: LHC_LSD% + Layout Database MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 Line N Main Busbars + Spool-pieces 9
Electrical half-cells - Electrical Circuits & connections To be found on CDD: LHC_LSD% + Layout Database MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 Line N Main Busbars + Spool-pieces 9
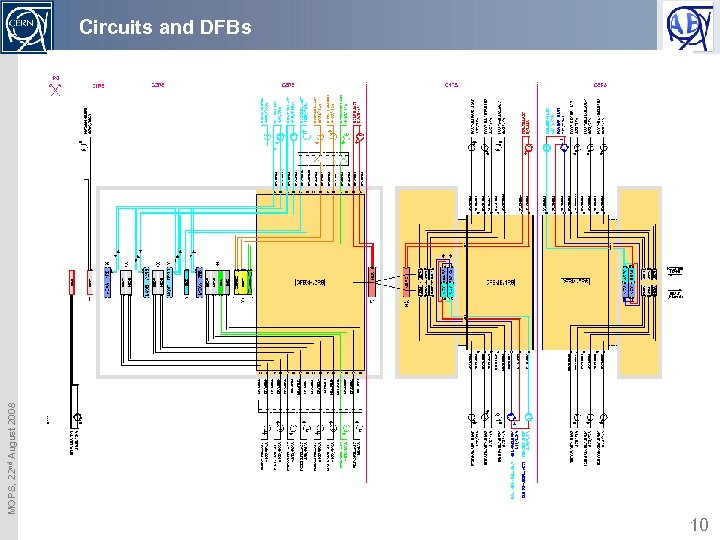 MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 Circuits and DFBs 10
MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 Circuits and DFBs 10
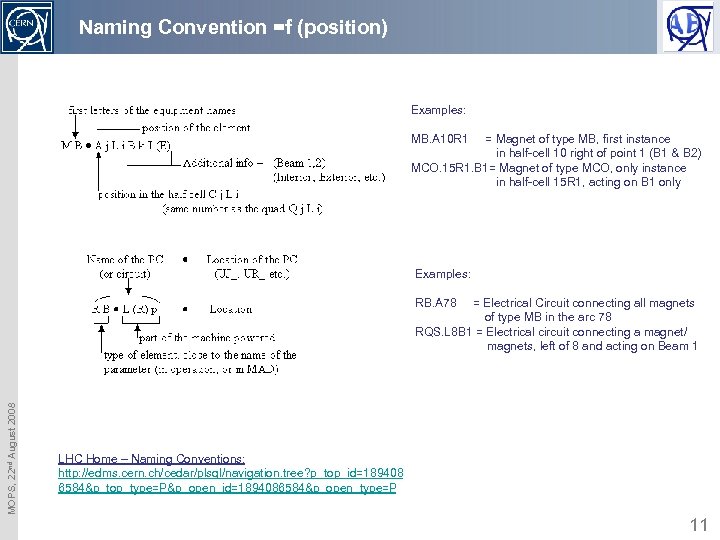 Naming Convention =f (position) Examples: MB. A 10 R 1 = Magnet of type MB, first instance in half-cell 10 right of point 1 (B 1 & B 2) MCO. 15 R 1. B 1= Magnet of type MCO, only instance in half-cell 15 R 1, acting on B 1 only Examples: = Electrical Circuit connecting all magnets of type MB in the arc 78 RQS. L 8 B 1 = Electrical circuit connecting a magnet/ magnets, left of 8 and acting on Beam 1 MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 RB. A 78 LHC Home – Naming Conventions: http: //edms. cern. ch/cedar/plsql/navigation. tree? p_top_id=189408 6584&p_top_type=P&p_open_id=1894086584&p_open_type=P 11
Naming Convention =f (position) Examples: MB. A 10 R 1 = Magnet of type MB, first instance in half-cell 10 right of point 1 (B 1 & B 2) MCO. 15 R 1. B 1= Magnet of type MCO, only instance in half-cell 15 R 1, acting on B 1 only Examples: = Electrical Circuit connecting all magnets of type MB in the arc 78 RQS. L 8 B 1 = Electrical circuit connecting a magnet/ magnets, left of 8 and acting on Beam 1 MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 RB. A 78 LHC Home – Naming Conventions: http: //edms. cern. ch/cedar/plsql/navigation. tree? p_top_id=189408 6584&p_top_type=P&p_open_id=1894086584&p_open_type=P 11
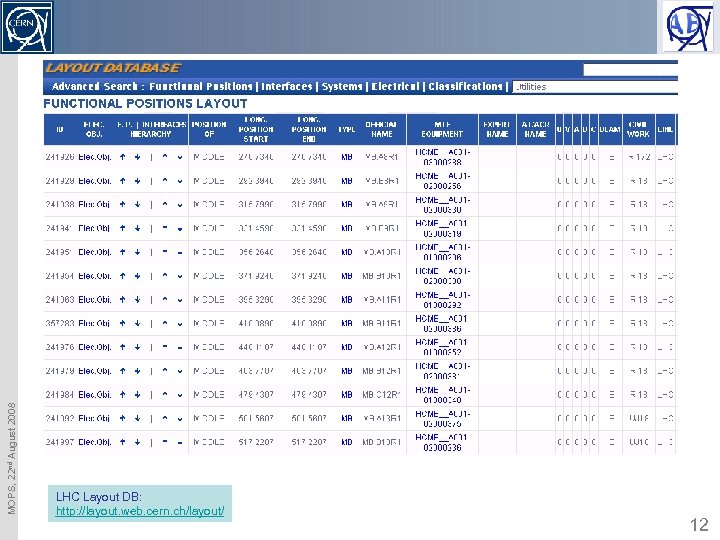 MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 LHC Layout DB: http: //layout. web. cern. ch/layout/ 12
MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 LHC Layout DB: http: //layout. web. cern. ch/layout/ 12
 Sectorisation across systems MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 ¨ Different sectorisation chosen by different systems, as the machine can be seen from different angles (mechanical, beam physics, electrical powering, cryogenics, vacuum…) ¨ Most important configuration for magnet powering (and current HWC) is the POWERING SUBSECTOR LHC-D-ES-0002 v. 1. 0 13
Sectorisation across systems MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 ¨ Different sectorisation chosen by different systems, as the machine can be seen from different angles (mechanical, beam physics, electrical powering, cryogenics, vacuum…) ¨ Most important configuration for magnet powering (and current HWC) is the POWERING SUBSECTOR LHC-D-ES-0002 v. 1. 0 13
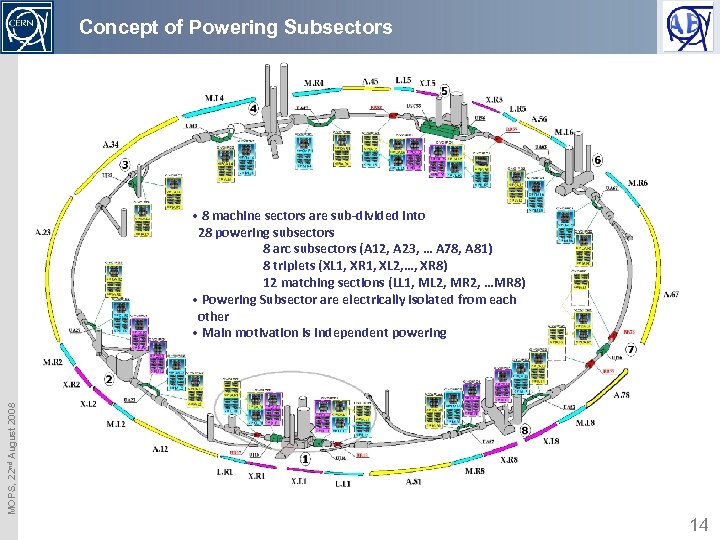 Concept of Powering Subsectors MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 • 8 machine sectors are sub-divided into 28 powering subsectors 8 arc subsectors (A 12, A 23, … A 78, A 81) 8 triplets (XL 1, XR 1, XL 2, …, XR 8) 12 matching sections (LL 1, ML 2, MR 2, …MR 8) • Powering Subsector are electrically isolated from each other • Main motivation is independent powering 14
Concept of Powering Subsectors MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 • 8 machine sectors are sub-divided into 28 powering subsectors 8 arc subsectors (A 12, A 23, … A 78, A 81) 8 triplets (XL 1, XR 1, XL 2, …, XR 8) 12 matching sections (LL 1, ML 2, MR 2, …MR 8) • Powering Subsector are electrically isolated from each other • Main motivation is independent powering 14
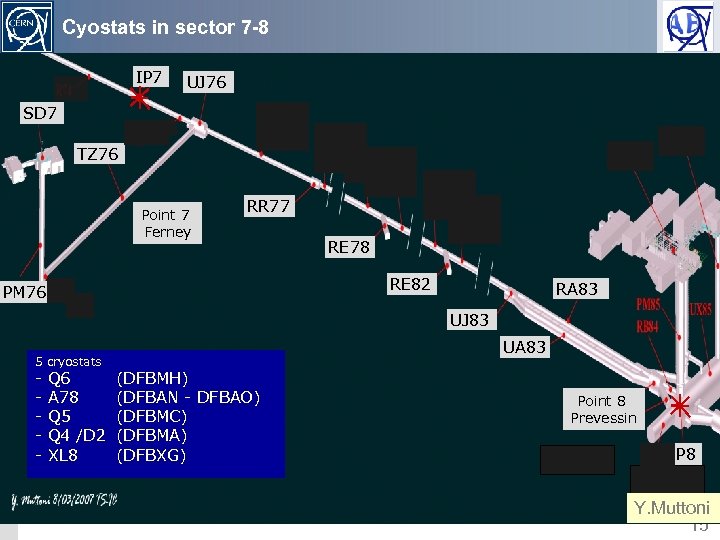 Cyostats in sector 7 -8 IP 7 UJ 76 SD 7 TZ 76 Point 7 Ferney RR 77 RE 78 RE 82 PM 76 RA 83 UJ 83 MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 5 cryostats - Q 6 A 78 Q 5 Q 4 /D 2 XL 8 UA 83 (DFBMH) (DFBAN - DFBAO) (DFBMC) (DFBMA) (DFBXG) Point 8 Prevessin IP 8 Y. Muttoni 15
Cyostats in sector 7 -8 IP 7 UJ 76 SD 7 TZ 76 Point 7 Ferney RR 77 RE 78 RE 82 PM 76 RA 83 UJ 83 MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 5 cryostats - Q 6 A 78 Q 5 Q 4 /D 2 XL 8 UA 83 (DFBMH) (DFBAN - DFBAO) (DFBMC) (DFBMA) (DFBXG) Point 8 Prevessin IP 8 Y. Muttoni 15
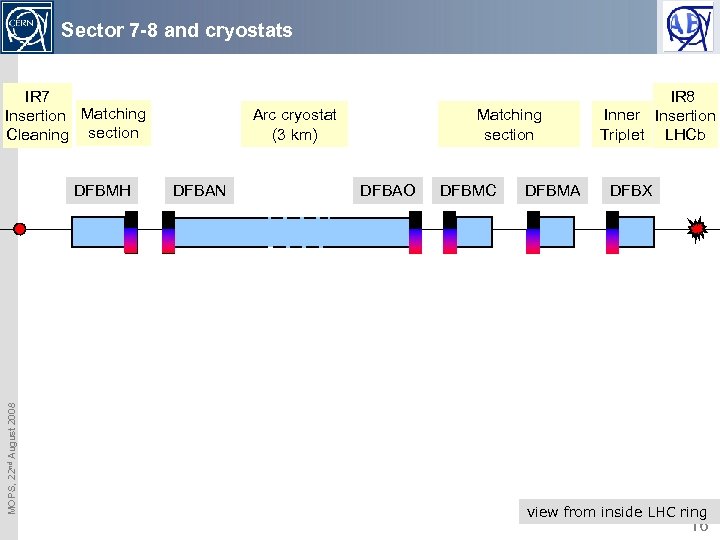 Sector 7 -8 and cryostats IR 7 Insertion Matching Cleaning section MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 DFBMH Arc cryostat (3 km) DFBAN Matching section DFBAO DFBMC DFBMA IR 8 Inner Insertion Triplet LHCb DFBX view from inside LHC ring 16
Sector 7 -8 and cryostats IR 7 Insertion Matching Cleaning section MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 DFBMH Arc cryostat (3 km) DFBAN Matching section DFBAO DFBMC DFBMA IR 8 Inner Insertion Triplet LHCb DFBX view from inside LHC ring 16
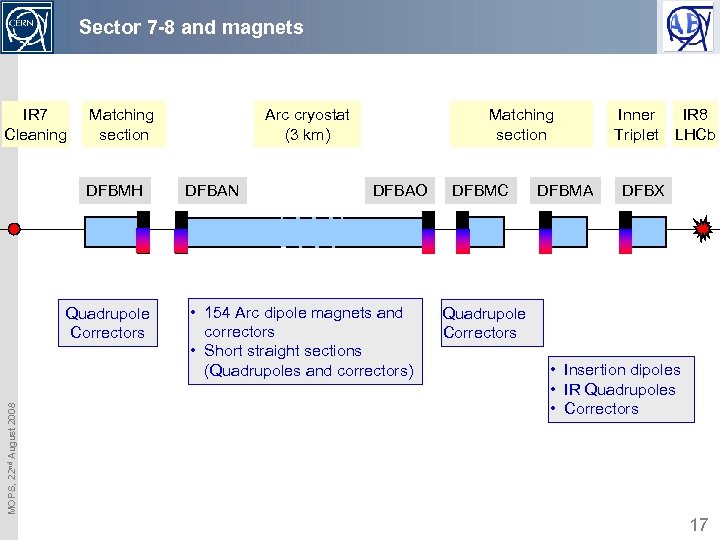 Sector 7 -8 and magnets IR 7 Cleaning Matching section DFBMH MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 Quadrupole Correctors Arc cryostat (3 km) DFBAN Matching section DFBAO • 154 Arc dipole magnets and correctors • Short straight sections (Quadrupoles and correctors) DFBMC DFBMA Inner Triplet IR 8 LHCb DFBX Quadrupole Correctors • Insertion dipoles • IR Quadrupoles • Correctors 17
Sector 7 -8 and magnets IR 7 Cleaning Matching section DFBMH MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 Quadrupole Correctors Arc cryostat (3 km) DFBAN Matching section DFBAO • 154 Arc dipole magnets and correctors • Short straight sections (Quadrupoles and correctors) DFBMC DFBMA Inner Triplet IR 8 LHCb DFBX Quadrupole Correctors • Insertion dipoles • IR Quadrupoles • Correctors 17
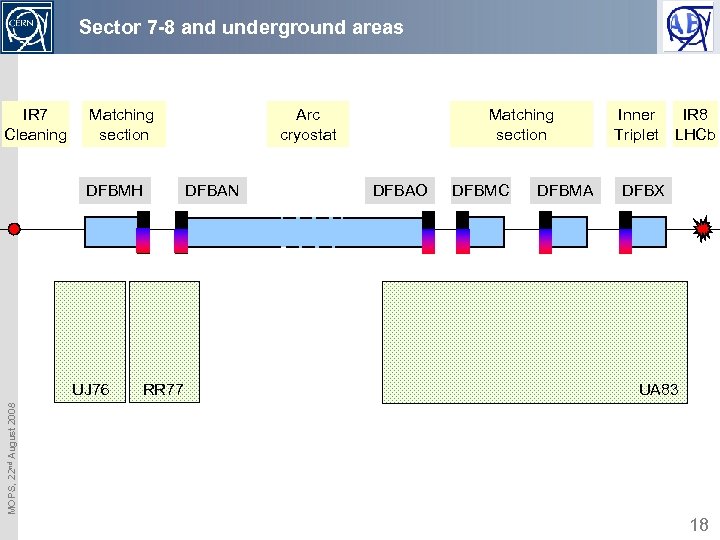 Sector 7 -8 and underground areas IR 7 Cleaning Matching section DFBMH RR 77 DFBAN Matching section DFBAO DFBMC DFBMA Inner Triplet IR 8 LHCb DFBX UA 83 MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 UJ 76 Arc cryostat 18
Sector 7 -8 and underground areas IR 7 Cleaning Matching section DFBMH RR 77 DFBAN Matching section DFBAO DFBMC DFBMA Inner Triplet IR 8 LHCb DFBX UA 83 MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 UJ 76 Arc cryostat 18
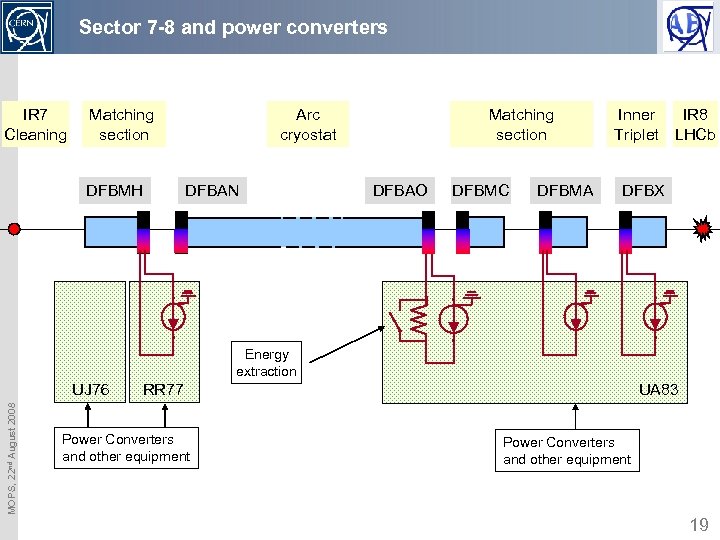 Sector 7 -8 and power converters IR 7 Cleaning Matching section DFBMH Arc cryostat DFBAN Matching section DFBAO DFBMC DFBMA Inner Triplet IR 8 LHCb DFBX Energy extraction MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 UJ 76 RR 77 Power Converters and other equipment UA 83 Power Converters and other equipment 19
Sector 7 -8 and power converters IR 7 Cleaning Matching section DFBMH Arc cryostat DFBAN Matching section DFBAO DFBMC DFBMA Inner Triplet IR 8 LHCb DFBX Energy extraction MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 UJ 76 RR 77 Power Converters and other equipment UA 83 Power Converters and other equipment 19
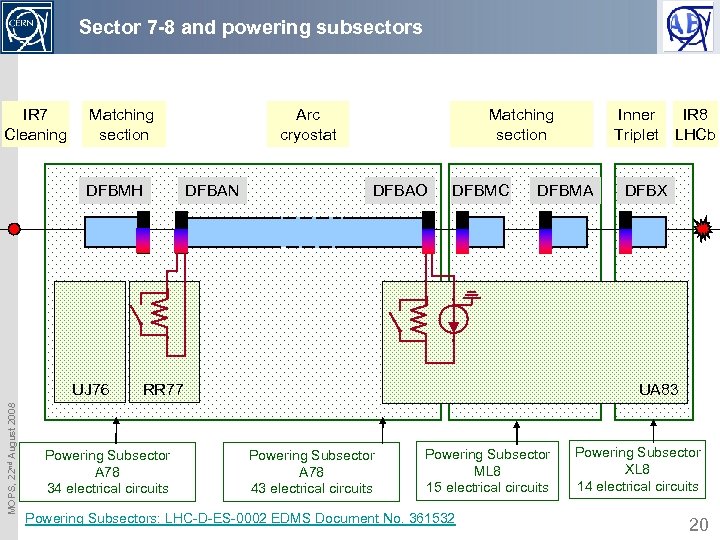 Sector 7 -8 and powering subsectors IR 7 Cleaning Matching section DFBMH MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 UJ 76 Arc cryostat DFBAN Matching section DFBAO DFBMC DFBMA RR 77 Powering Subsector A 78 34 electrical circuits Inner Triplet IR 8 LHCb DFBX UA 83 Powering Subsector A 78 43 electrical circuits Powering Subsector ML 8 15 electrical circuits Powering Subsectors: LHC-D-ES-0002 EDMS Document No. 361532 Powering Subsector XL 8 14 electrical circuits 20
Sector 7 -8 and powering subsectors IR 7 Cleaning Matching section DFBMH MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 UJ 76 Arc cryostat DFBAN Matching section DFBAO DFBMC DFBMA RR 77 Powering Subsector A 78 34 electrical circuits Inner Triplet IR 8 LHCb DFBX UA 83 Powering Subsector A 78 43 electrical circuits Powering Subsector ML 8 15 electrical circuits Powering Subsectors: LHC-D-ES-0002 EDMS Document No. 361532 Powering Subsector XL 8 14 electrical circuits 20
 MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 Electrical Circuits and Terminology 21
MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 Electrical Circuits and Terminology 21
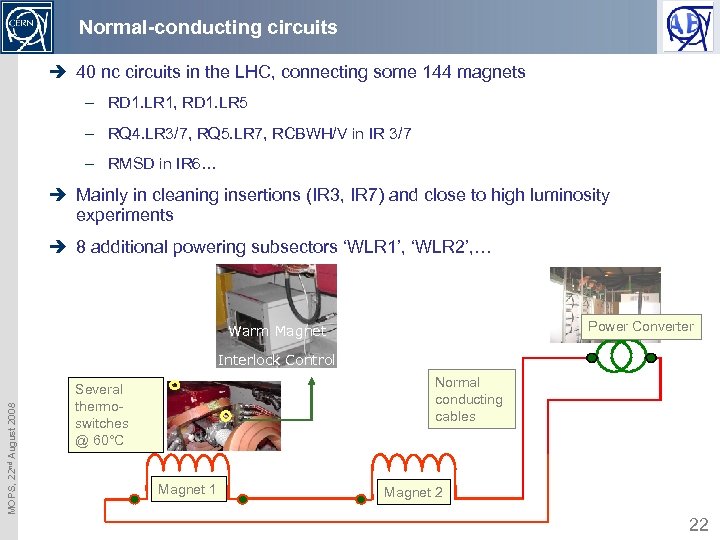 Normal-conducting circuits è 40 nc circuits in the LHC, connecting some 144 magnets – RD 1. LR 1, RD 1. LR 5 – RQ 4. LR 3/7, RQ 5. LR 7, RCBWH/V in IR 3/7 – RMSD in IR 6… è Mainly in cleaning insertions (IR 3, IR 7) and close to high luminosity experiments è 8 additional powering subsectors ‘WLR 1’, ‘WLR 2’, … Power Converter Warm Magnet MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 Interlock Controller Normal conducting cables Several thermoswitches @ 60°C Magnet 1 Magnet 2 22
Normal-conducting circuits è 40 nc circuits in the LHC, connecting some 144 magnets – RD 1. LR 1, RD 1. LR 5 – RQ 4. LR 3/7, RQ 5. LR 7, RCBWH/V in IR 3/7 – RMSD in IR 6… è Mainly in cleaning insertions (IR 3, IR 7) and close to high luminosity experiments è 8 additional powering subsectors ‘WLR 1’, ‘WLR 2’, … Power Converter Warm Magnet MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 Interlock Controller Normal conducting cables Several thermoswitches @ 60°C Magnet 1 Magnet 2 22
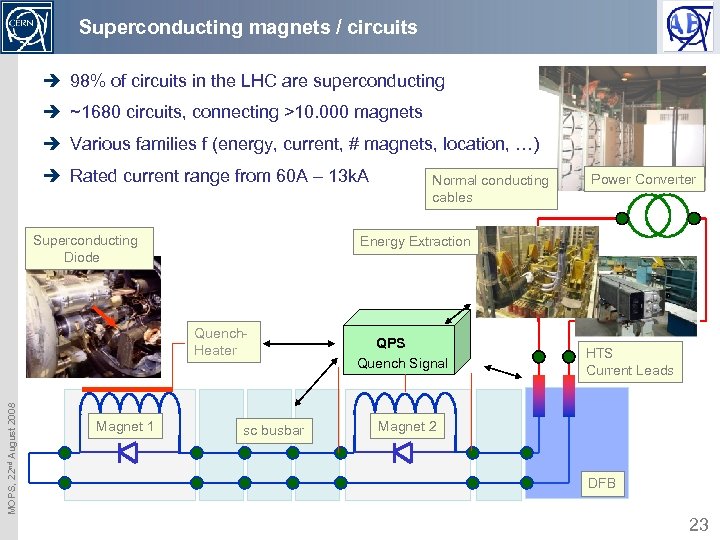 Superconducting magnets / circuits è 98% of circuits in the LHC are superconducting è ~1680 circuits, connecting >10. 000 magnets è Various families f (energy, current, # magnets, location, …) è Rated current range from 60 A – 13 k. A Superconducting Diode MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 Power Converter Energy Extraction Quench. Heater Magnet 1 Normal conducting cables sc busbar QPS Quench Signal HTS Current Leads Magnet 2 DFB 23
Superconducting magnets / circuits è 98% of circuits in the LHC are superconducting è ~1680 circuits, connecting >10. 000 magnets è Various families f (energy, current, # magnets, location, …) è Rated current range from 60 A – 13 k. A Superconducting Diode MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 Power Converter Energy Extraction Quench. Heater Magnet 1 Normal conducting cables sc busbar QPS Quench Signal HTS Current Leads Magnet 2 DFB 23
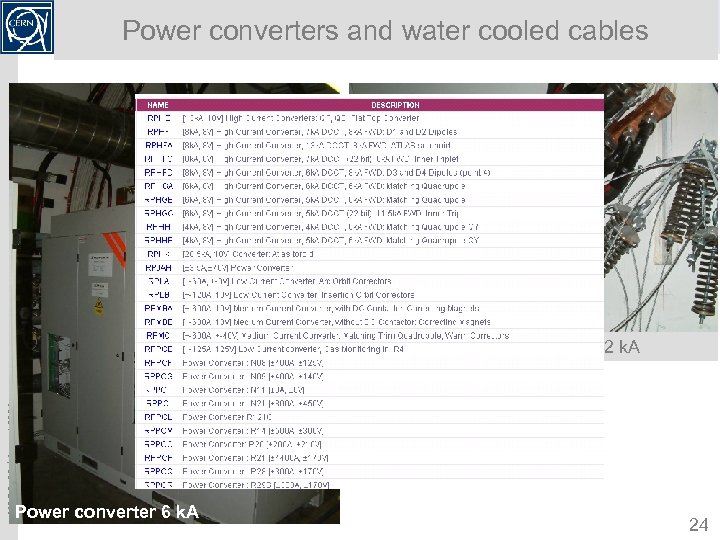 Power converters and water cooled cables MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 Water cooled cables 12 k. A Power converter 6 k. A 24
Power converters and water cooled cables MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 Water cooled cables 12 k. A Power converter 6 k. A 24
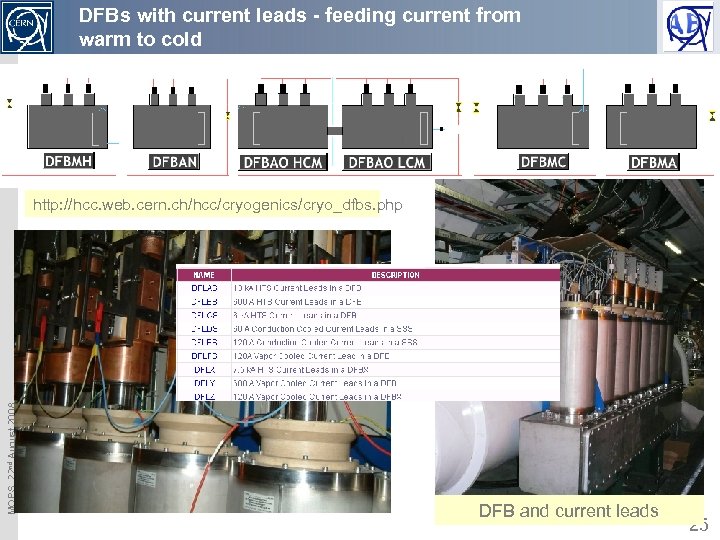 DFBs with current leads - feeding current from warm to cold MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 http: //hcc. web. cern. ch/hcc/cryogenics/cryo_dfbs. php DFB and current leads 25
DFBs with current leads - feeding current from warm to cold MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 http: //hcc. web. cern. ch/hcc/cryogenics/cryo_dfbs. php DFB and current leads 25
 MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 Cryogenic Feed Box with HTc Current Leads 26
MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 Cryogenic Feed Box with HTc Current Leads 26
 MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 Cryogenic Connection 27
MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 Cryogenic Connection 27
 MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 Installation of the Cryogenic Transfer Line 28
MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 Installation of the Cryogenic Transfer Line 28
 Energy extraction resistors MB Energy extraction switch house 12 k. A è 32 DQR/DQS systems (13 k. A for 8 RB, 24 RQD/F circuits) MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 è 202 DQEMC systems (600 A circuits) Diode for 12 k. A Energy extraction switch 12 k. A 29
Energy extraction resistors MB Energy extraction switch house 12 k. A è 32 DQR/DQS systems (13 k. A for 8 RB, 24 RQD/F circuits) MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 è 202 DQEMC systems (600 A circuits) Diode for 12 k. A Energy extraction switch 12 k. A 29
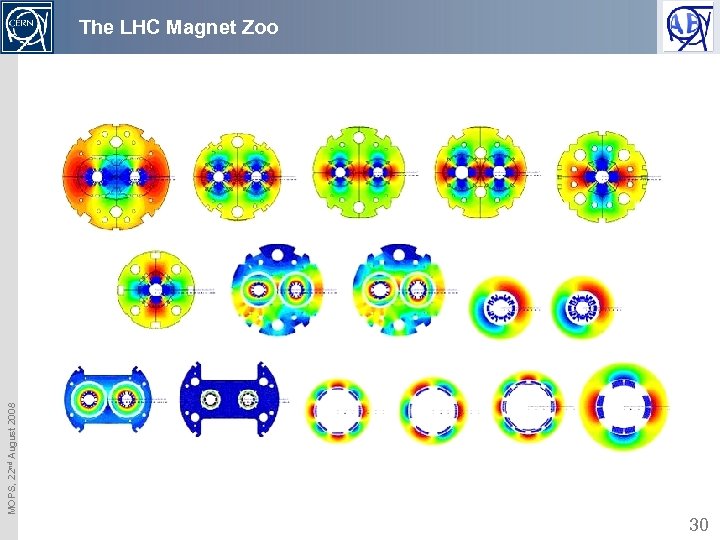 MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 The LHC Magnet Zoo 30
MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 The LHC Magnet Zoo 30
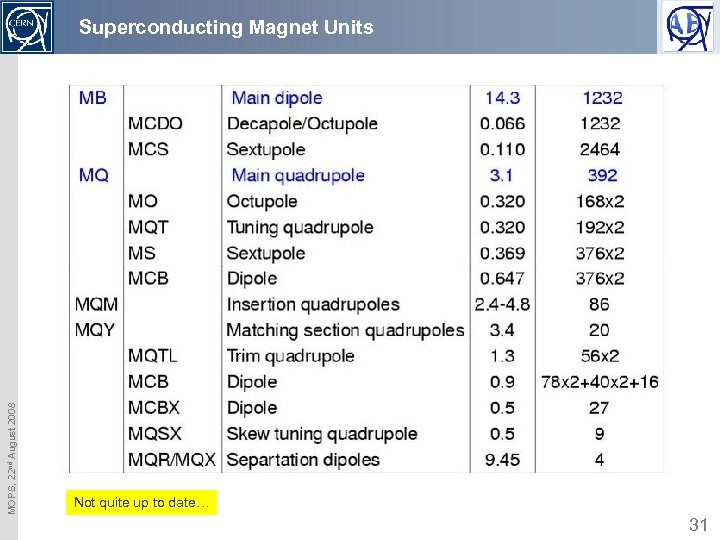 MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 Superconducting Magnet Units Not quite up to date… 31
MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 Superconducting Magnet Units Not quite up to date… 31
 Magnet inventory è 1232 main dipole magnets powered in series with the same strength – to make it around the LHC è 752 orbit corrector magnets powered individually – to ensure that the beam follows the design orbit (within about 0. 5 mm), è Focusing and defocusing quadrupole magnets powered in series – to keep beam size limited è Lattice sextupole magnets powered in series – to correct the trajectories for off-energy particles, è Multipole-corrector magnets (sextupoles, decapoles, octupoles, . . . ) MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 – to correct field imperfections, to suppress instabilities, etc. , powered in series è Corrector magnets to adjust essential beam parameters (quadrupoles) è Insertion dipole and quadrupole magnets – to ensure beam crossing / increase the interbeam distance / focus beams for experiments etc. http: //edms. cern. ch/cedar/plsql/navigation. tree? top=1459088716 32
Magnet inventory è 1232 main dipole magnets powered in series with the same strength – to make it around the LHC è 752 orbit corrector magnets powered individually – to ensure that the beam follows the design orbit (within about 0. 5 mm), è Focusing and defocusing quadrupole magnets powered in series – to keep beam size limited è Lattice sextupole magnets powered in series – to correct the trajectories for off-energy particles, è Multipole-corrector magnets (sextupoles, decapoles, octupoles, . . . ) MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 – to correct field imperfections, to suppress instabilities, etc. , powered in series è Corrector magnets to adjust essential beam parameters (quadrupoles) è Insertion dipole and quadrupole magnets – to ensure beam crossing / increase the interbeam distance / focus beams for experiments etc. http: //edms. cern. ch/cedar/plsql/navigation. tree? top=1459088716 32
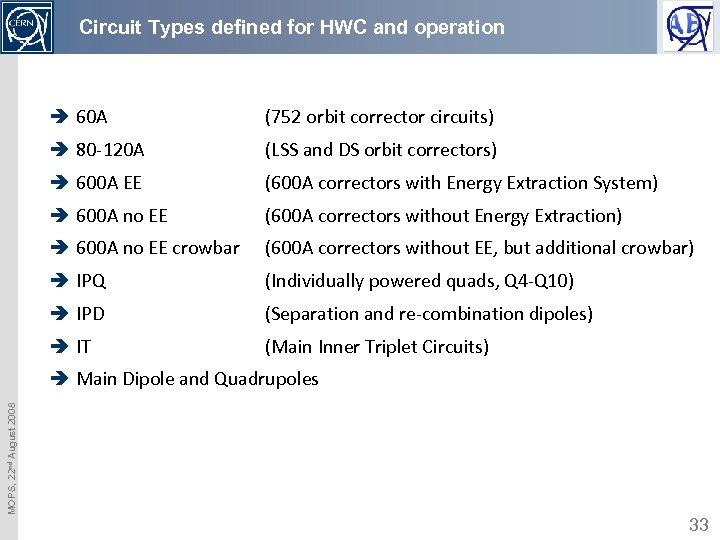 Circuit Types defined for HWC and operation è 60 A (752 orbit corrector circuits) è 80 -120 A (LSS and DS orbit correctors) è 600 A EE (600 A correctors with Energy Extraction System) è 600 A no EE (600 A correctors without Energy Extraction) è 600 A no EE crowbar (600 A correctors without EE, but additional crowbar) è IPQ (Individually powered quads, Q 4 -Q 10) è IPD (Separation and re-combination dipoles) è IT (Main Inner Triplet Circuits) MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 è Main Dipole and Quadrupoles 33
Circuit Types defined for HWC and operation è 60 A (752 orbit corrector circuits) è 80 -120 A (LSS and DS orbit correctors) è 600 A EE (600 A correctors with Energy Extraction System) è 600 A no EE (600 A correctors without Energy Extraction) è 600 A no EE crowbar (600 A correctors without EE, but additional crowbar) è IPQ (Individually powered quads, Q 4 -Q 10) è IPD (Separation and re-combination dipoles) è IT (Main Inner Triplet Circuits) MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 è Main Dipole and Quadrupoles 33
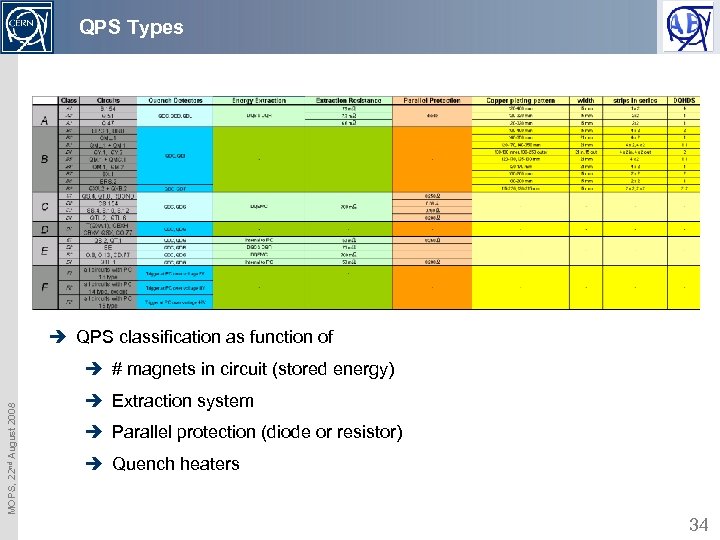 QPS Types è QPS classification as function of MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 è # magnets in circuit (stored energy) è Extraction system è Parallel protection (diode or resistor) è Quench heaters 34
QPS Types è QPS classification as function of MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 è # magnets in circuit (stored energy) è Extraction system è Parallel protection (diode or resistor) è Quench heaters 34
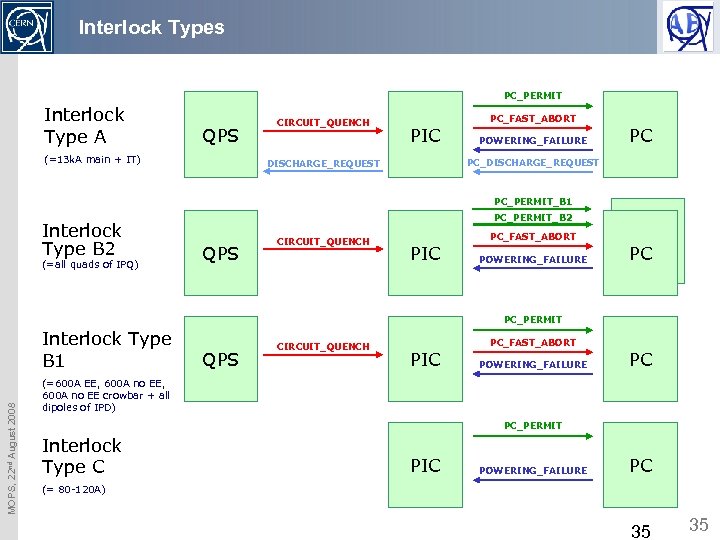 Interlock Types PC_PERMIT Interlock Type A QPS (=13 k. A main + IT) CIRCUIT_QUENCH PC_FAST_ABORT PIC POWERING_FAILURE PC PC_DISCHARGE_REQUEST PC_PERMIT_B 1 Interlock Type B 2 (=all quads of IPQ) PC_PERMIT_B 2 QPS CIRCUIT_QUENCH PC_FAST_ABORT PIC POWERING_FAILURE PC PC PC_PERMIT MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 Interlock Type B 1 QPS CIRCUIT_QUENCH PC_FAST_ABORT PIC POWERING_FAILURE PC (=600 A EE, 600 A no EE crowbar + all dipoles of IPD) PC_PERMIT Interlock Type C PIC POWERING_FAILURE PC (= 80 -120 A) 35 35
Interlock Types PC_PERMIT Interlock Type A QPS (=13 k. A main + IT) CIRCUIT_QUENCH PC_FAST_ABORT PIC POWERING_FAILURE PC PC_DISCHARGE_REQUEST PC_PERMIT_B 1 Interlock Type B 2 (=all quads of IPQ) PC_PERMIT_B 2 QPS CIRCUIT_QUENCH PC_FAST_ABORT PIC POWERING_FAILURE PC PC PC_PERMIT MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 Interlock Type B 1 QPS CIRCUIT_QUENCH PC_FAST_ABORT PIC POWERING_FAILURE PC (=600 A EE, 600 A no EE crowbar + all dipoles of IPD) PC_PERMIT Interlock Type C PIC POWERING_FAILURE PC (= 80 -120 A) 35 35
 Types of electrical circuits è A: main dipoles (8), main quadrupoles (16), triplet quadrupoles (8) – extraction of the energy stored in the magnets when requested by the Power Converter in case of failure is performed by the QPS è B: magnets equipped with QPS – B 2: insertion quadrupoles using MQM / MQY (3. 9 k. A – 5. 8 k. A) – B 1: insertion dipoles (4. 6 k. A-6. 2 k. A) and most 600 A corrector magnets – extraction of the energy stored in the magnets not required in case of Power Converter failure – B 1: electrical circuits with one Power Converter MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 – B 2: electrical circuits with two Power Converters è C: dipole corrector magnets in the insertions and other circuits with corrector magnets with little stored energy (60 A, 80 A and 120 A) – connection to Powering Interlock Controller è D: orbit dipole corrector magnets in the arcs (60 A) – no connection to Powering Interlock Controller 36 36
Types of electrical circuits è A: main dipoles (8), main quadrupoles (16), triplet quadrupoles (8) – extraction of the energy stored in the magnets when requested by the Power Converter in case of failure is performed by the QPS è B: magnets equipped with QPS – B 2: insertion quadrupoles using MQM / MQY (3. 9 k. A – 5. 8 k. A) – B 1: insertion dipoles (4. 6 k. A-6. 2 k. A) and most 600 A corrector magnets – extraction of the energy stored in the magnets not required in case of Power Converter failure – B 1: electrical circuits with one Power Converter MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 – B 2: electrical circuits with two Power Converters è C: dipole corrector magnets in the insertions and other circuits with corrector magnets with little stored energy (60 A, 80 A and 120 A) – connection to Powering Interlock Controller è D: orbit dipole corrector magnets in the arcs (60 A) – no connection to Powering Interlock Controller 36 36
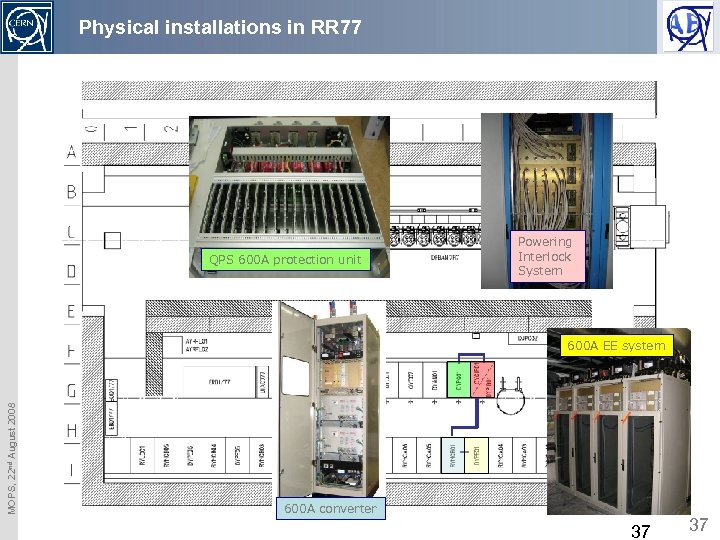 Physical installations in RR 77 QPS 600 A protection unit Powering Interlock System MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 600 A EE system 600 A converter 37 37
Physical installations in RR 77 QPS 600 A protection unit Powering Interlock System MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 600 A EE system 600 A converter 37 37
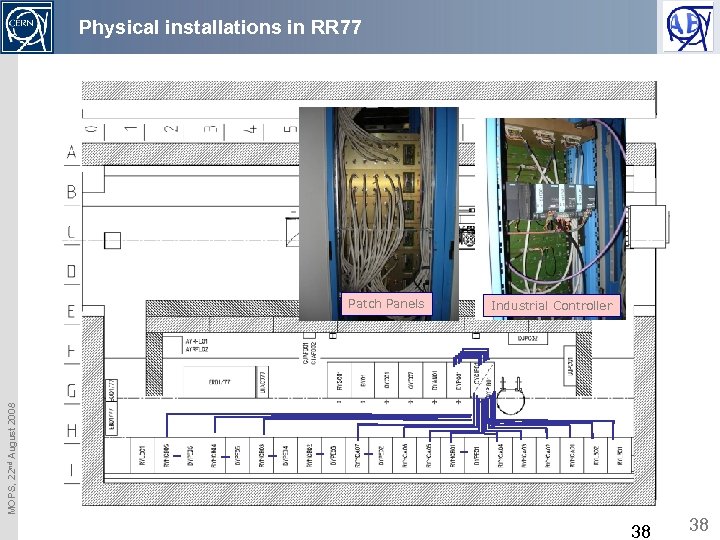 Physical installations in RR 77 Industrial Controller MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 Patch Panels 38 38
Physical installations in RR 77 Industrial Controller MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 Patch Panels 38 38
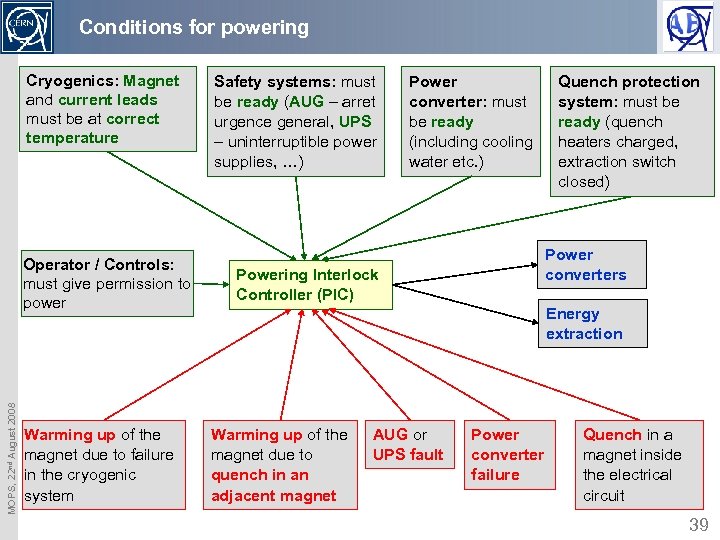 Conditions for powering Cryogenics: Magnet and current leads must be at correct temperature MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 Operator / Controls: must give permission to power Warming up of the magnet due to failure in the cryogenic system Safety systems: must be ready (AUG – arret urgence general, UPS – uninterruptible power supplies, …) Power converter: must be ready (including cooling water etc. ) Quench protection system: must be ready (quench heaters charged, extraction switch closed) Power converters Powering Interlock Controller (PIC) Energy extraction Warming up of the magnet due to quench in an adjacent magnet AUG or UPS fault Power converter failure Quench in a magnet inside the electrical circuit 39
Conditions for powering Cryogenics: Magnet and current leads must be at correct temperature MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 Operator / Controls: must give permission to power Warming up of the magnet due to failure in the cryogenic system Safety systems: must be ready (AUG – arret urgence general, UPS – uninterruptible power supplies, …) Power converter: must be ready (including cooling water etc. ) Quench protection system: must be ready (quench heaters charged, extraction switch closed) Power converters Powering Interlock Controller (PIC) Energy extraction Warming up of the magnet due to quench in an adjacent magnet AUG or UPS fault Power converter failure Quench in a magnet inside the electrical circuit 39
 Layout DB All this can also be found and browsed in detail in the LHC Layout DB: MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 http: //layout. web. cern. ch/layout/ 40
Layout DB All this can also be found and browsed in detail in the LHC Layout DB: MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 http: //layout. web. cern. ch/layout/ 40
 Thanks a lot for your attention MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 Questions? 41
Thanks a lot for your attention MOPS, 22 nd August 2008 Questions? 41


