Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly 11 Copyright © 2012













monopolistic_competition_and_oligopoly.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly 11 Copyright © 2012 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly 11 Copyright © 2012 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. McGraw-Hill/Irwin
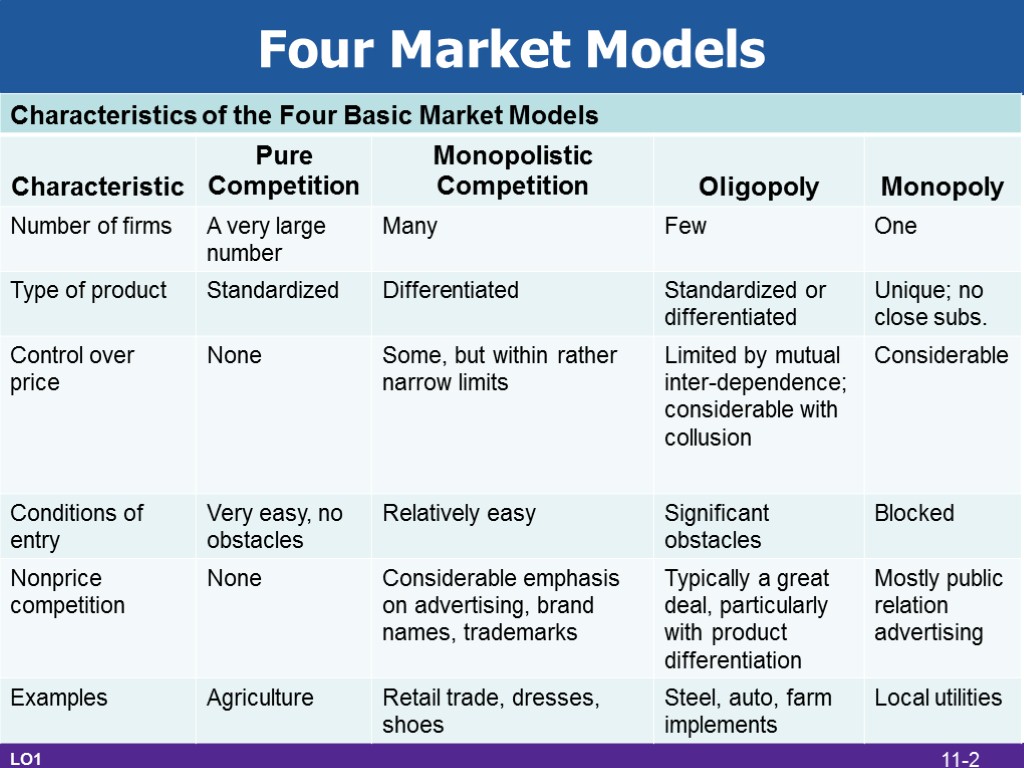
 Four Market Models LO1 11-2
Four Market Models LO1 11-2
 Monopolistic Competition Relatively large number of sellers Differentiated products Easy entry and exit Advertising LO1 11-3
Monopolistic Competition Relatively large number of sellers Differentiated products Easy entry and exit Advertising LO1 11-3
 Monopolistically Competitive Industry concentration Measured by: Four-firm concentration ratios Percentage of 4 largest firms Herfindahl index Sum of squared market shares LO1 4-Firm CR = Output of four largest firms Total output in the industry HI = (%S1)2 + (%S2)2 + (%S3)2 + …. + (%Sn)2 11-4
Monopolistically Competitive Industry concentration Measured by: Four-firm concentration ratios Percentage of 4 largest firms Herfindahl index Sum of squared market shares LO1 4-Firm CR = Output of four largest firms Total output in the industry HI = (%S1)2 + (%S2)2 + (%S3)2 + …. + (%Sn)2 11-4
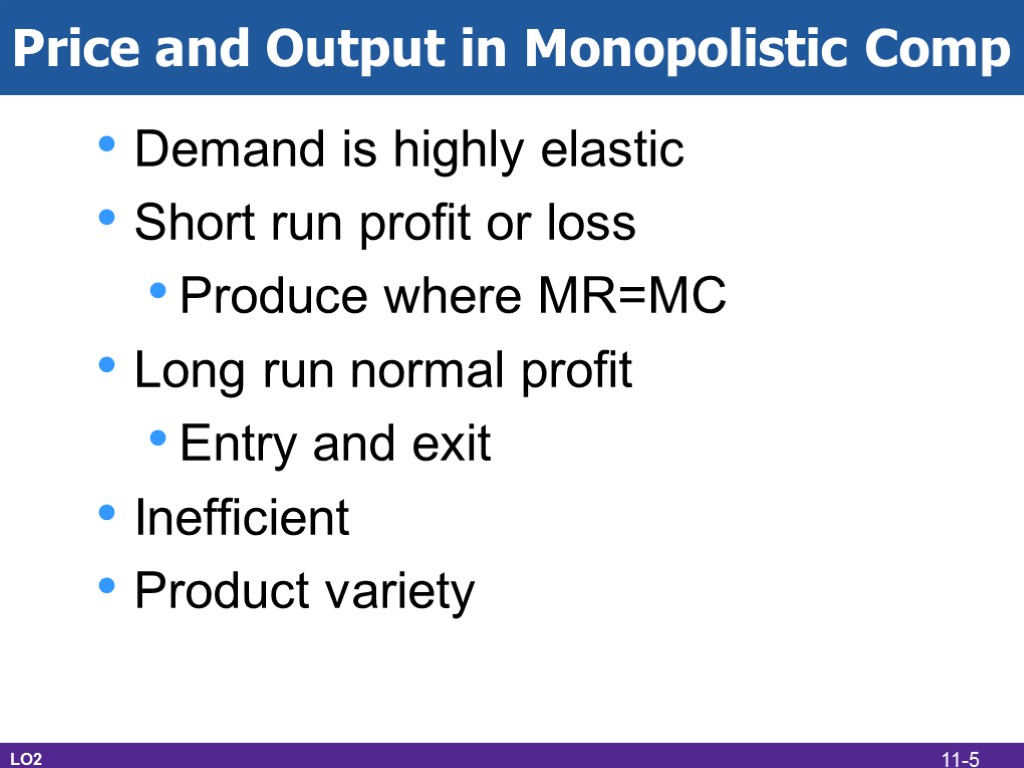
 Price and Output in Monopolistic Comp Demand is highly elastic Short run profit or loss Produce where MR=MC Long run normal profit Entry and exit Inefficient Product variety LO2 11-5
Price and Output in Monopolistic Comp Demand is highly elastic Short run profit or loss Produce where MR=MC Long run normal profit Entry and exit Inefficient Product variety LO2 11-5
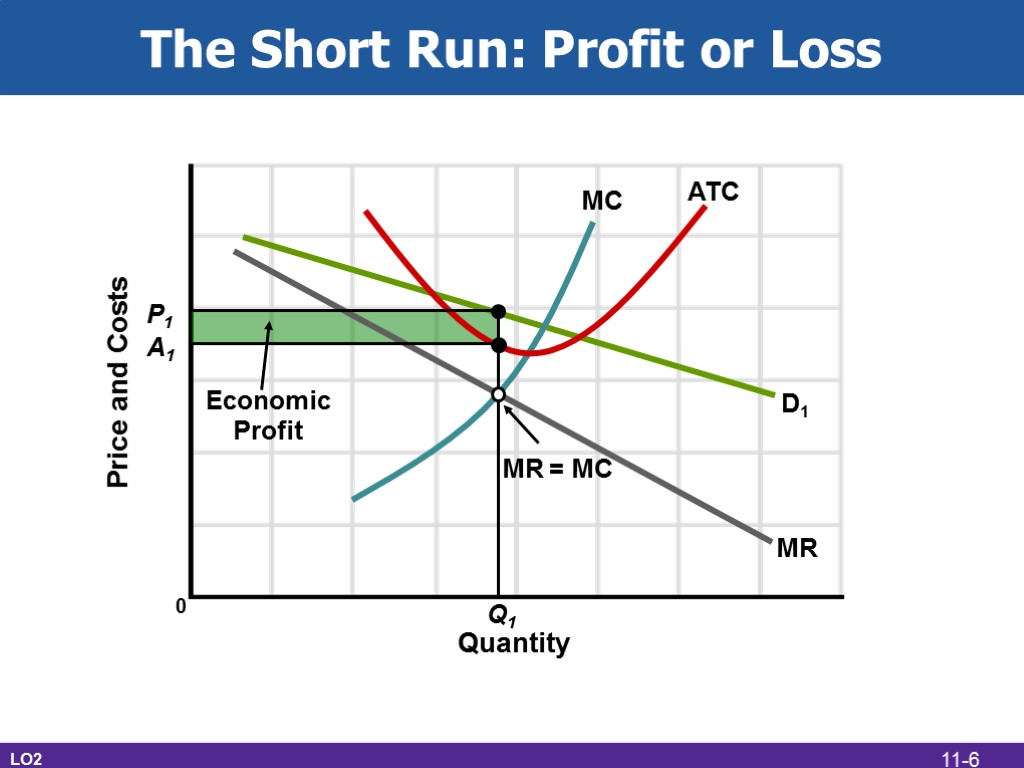
 The Short Run: Profit or Loss LO2 Quantity Price and Costs MR = MC MC MR D1 ATC Economic Profit Q1 A1 P1 0 11-6
The Short Run: Profit or Loss LO2 Quantity Price and Costs MR = MC MC MR D1 ATC Economic Profit Q1 A1 P1 0 11-6
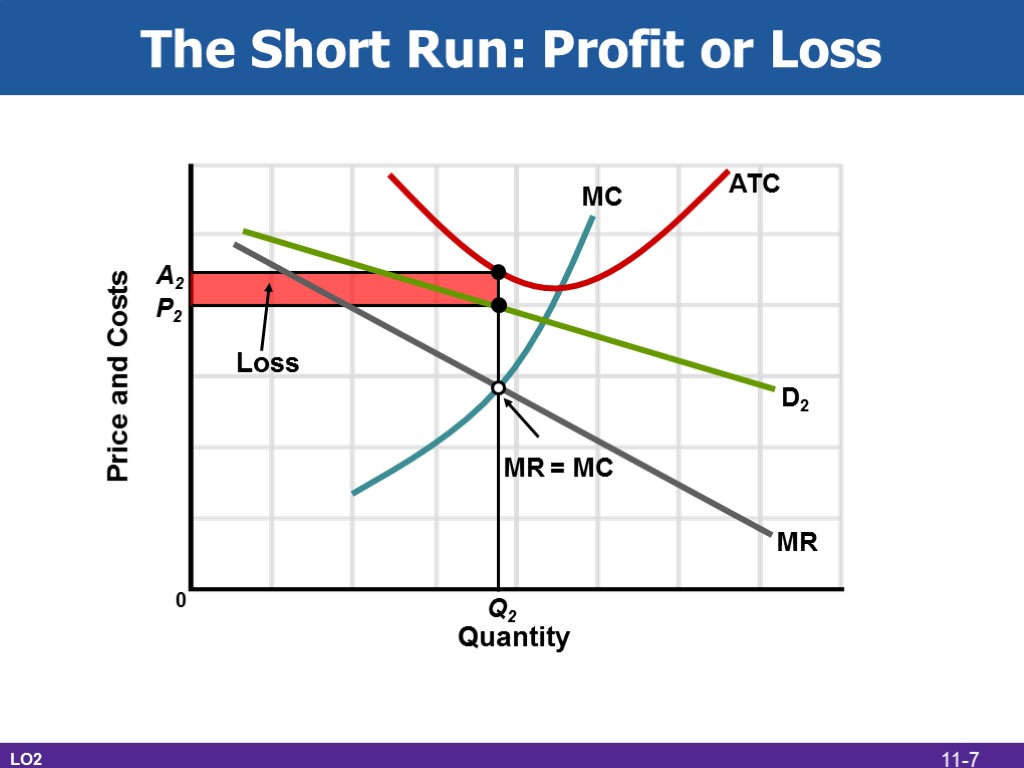
 The Short Run: Profit or Loss LO2 Quantity Price and Costs MC MR D2 ATC Loss Q2 A2 P2 0 MR = MC 11-7
The Short Run: Profit or Loss LO2 Quantity Price and Costs MC MR D2 ATC Loss Q2 A2 P2 0 MR = MC 11-7
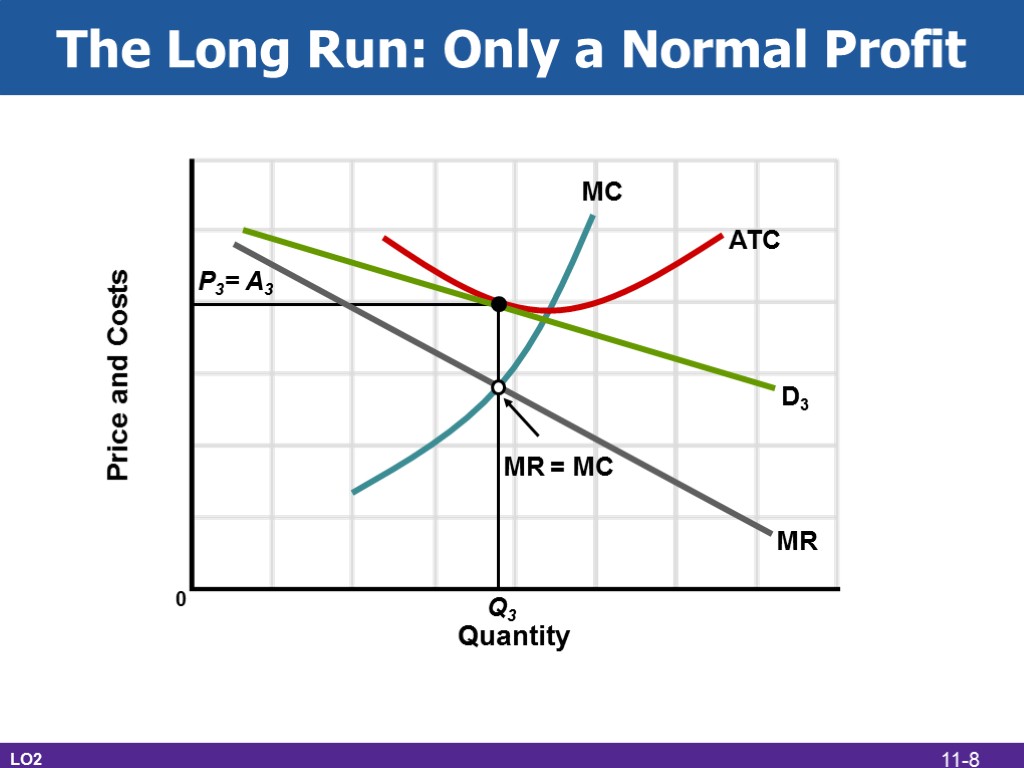
 The Long Run: Only a Normal Profit LO2 Quantity Price and Costs MC MR D3 ATC Q3 P3= A3 0 MR = MC 11-8
The Long Run: Only a Normal Profit LO2 Quantity Price and Costs MC MR D3 ATC Q3 P3= A3 0 MR = MC 11-8
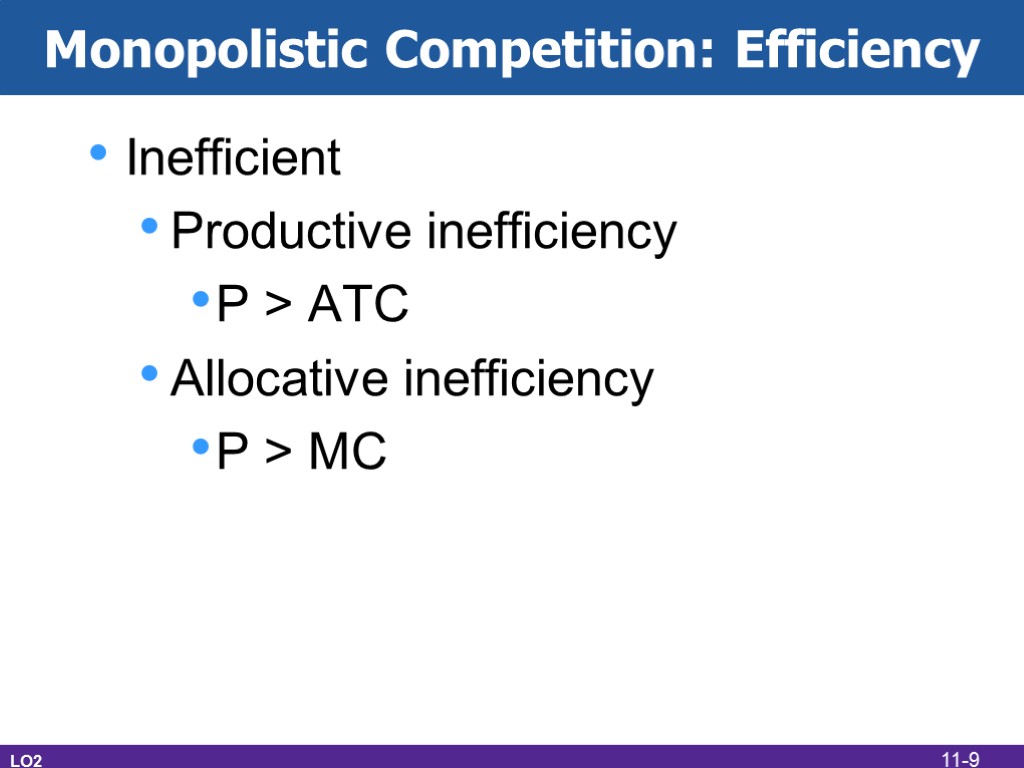
 Monopolistic Competition: Efficiency Inefficient Productive inefficiency P > ATC Allocative inefficiency P > MC LO2 11-9
Monopolistic Competition: Efficiency Inefficient Productive inefficiency P > ATC Allocative inefficiency P > MC LO2 11-9
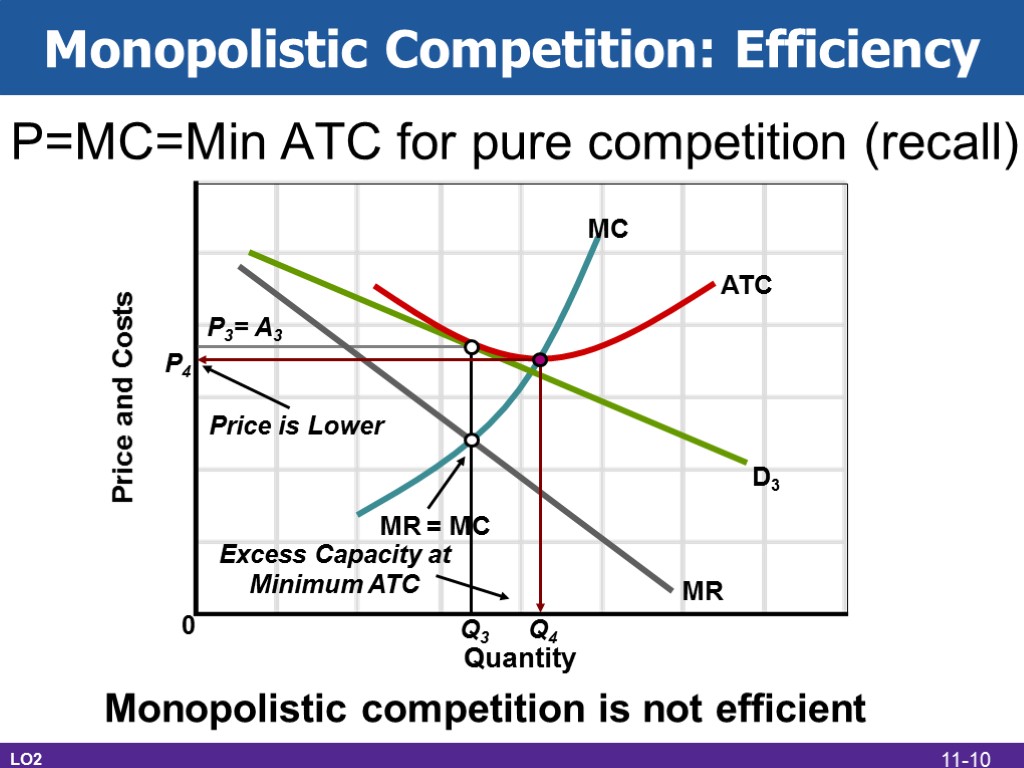
 Monopolistic Competition: Efficiency LO2 P=MC=Min ATC for pure competition (recall) P4 Q4 Price is Lower Excess Capacity at Minimum ATC Monopolistic competition is not efficient 11-10
Monopolistic Competition: Efficiency LO2 P=MC=Min ATC for pure competition (recall) P4 Q4 Price is Lower Excess Capacity at Minimum ATC Monopolistic competition is not efficient 11-10
 Product Variety The firm constantly manages price, product, and advertising Better product differentiation Better advertising The consumer benefits by greater array of choices and better products Types and styles Brands and quality LO2 11-11
Product Variety The firm constantly manages price, product, and advertising Better product differentiation Better advertising The consumer benefits by greater array of choices and better products Types and styles Brands and quality LO2 11-11
 Oligopoly A few large producers Homogeneous or differentiated products Limited control over price Mutual interdependence Strategic behavior Entry barriers Mergers LO3 11-12
Oligopoly A few large producers Homogeneous or differentiated products Limited control over price Mutual interdependence Strategic behavior Entry barriers Mergers LO3 11-12
 Oligopolistic Industries Four-firm concentration ratio 40% or more to be oligopoly Shortcomings Localized markets Inter-industry competition World price Dominant firms LO3 11-13
Oligopolistic Industries Four-firm concentration ratio 40% or more to be oligopoly Shortcomings Localized markets Inter-industry competition World price Dominant firms LO3 11-13
 Game Theory Overview Oligopolies display strategic pricing behavior Mutual interdependence Collusion Incentive to cheat Prisoner’s dilemma LO4 11-14
Game Theory Overview Oligopolies display strategic pricing behavior Mutual interdependence Collusion Incentive to cheat Prisoner’s dilemma LO4 11-14
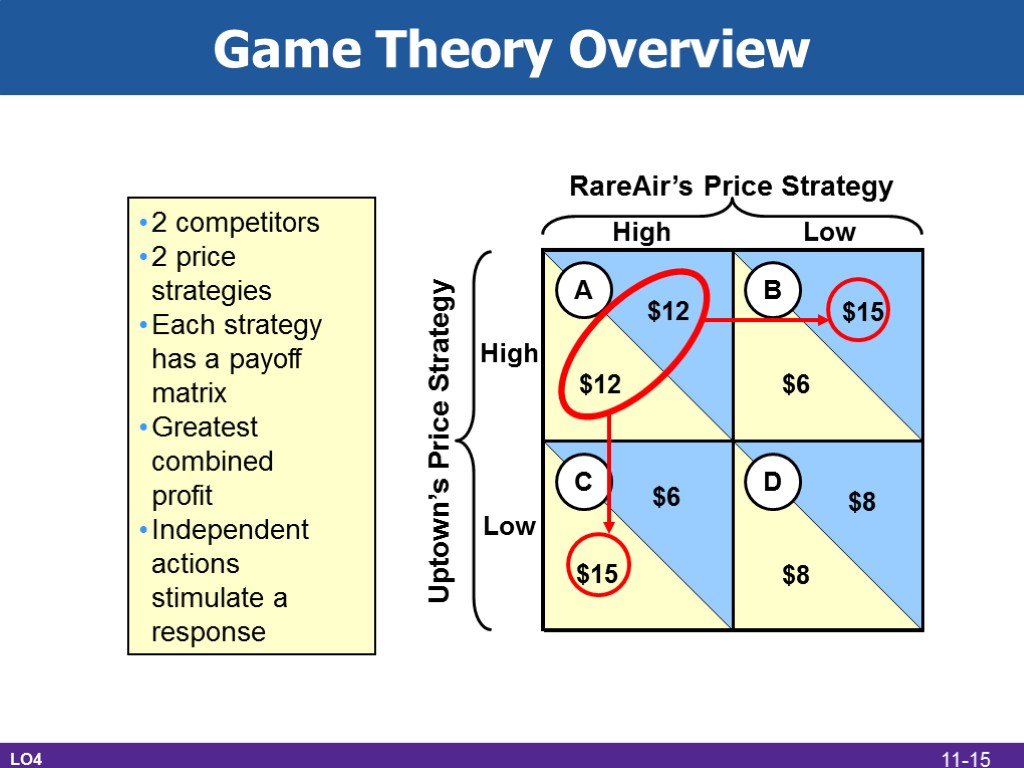
 Game Theory Overview LO4 RareAir’s Price Strategy Uptown’s Price Strategy A B C D $12 $12 $15 $6 $8 $8 $6 $15 High High Low Low 2 competitors 2 price strategies Each strategy has a payoff matrix Greatest combined profit Independent actions stimulate a response 11-15
Game Theory Overview LO4 RareAir’s Price Strategy Uptown’s Price Strategy A B C D $12 $12 $15 $6 $8 $8 $6 $15 High High Low Low 2 competitors 2 price strategies Each strategy has a payoff matrix Greatest combined profit Independent actions stimulate a response 11-15
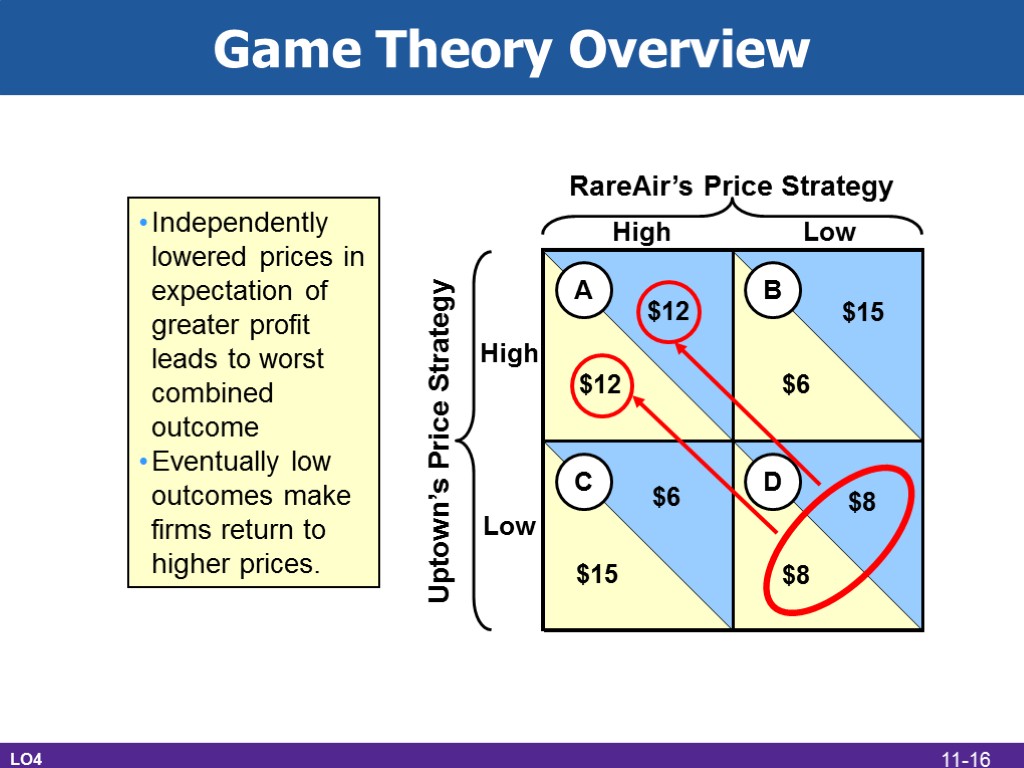
 Game Theory Overview LO4 RareAir’s Price Strategy Uptown’s Price Strategy A B C D $12 $12 $15 $6 $8 $8 $6 $15 High High Low Low Independently lowered prices in expectation of greater profit leads to worst combined outcome Eventually low outcomes make firms return to higher prices. 11-16
Game Theory Overview LO4 RareAir’s Price Strategy Uptown’s Price Strategy A B C D $12 $12 $15 $6 $8 $8 $6 $15 High High Low Low Independently lowered prices in expectation of greater profit leads to worst combined outcome Eventually low outcomes make firms return to higher prices. 11-16
 Three Oligopoly Models Kinked-demand curve Collusive pricing Price leadership Reasons for 3 models Diversity of oligopolies Complications of interdependence LO5 11-17
Three Oligopoly Models Kinked-demand curve Collusive pricing Price leadership Reasons for 3 models Diversity of oligopolies Complications of interdependence LO5 11-17
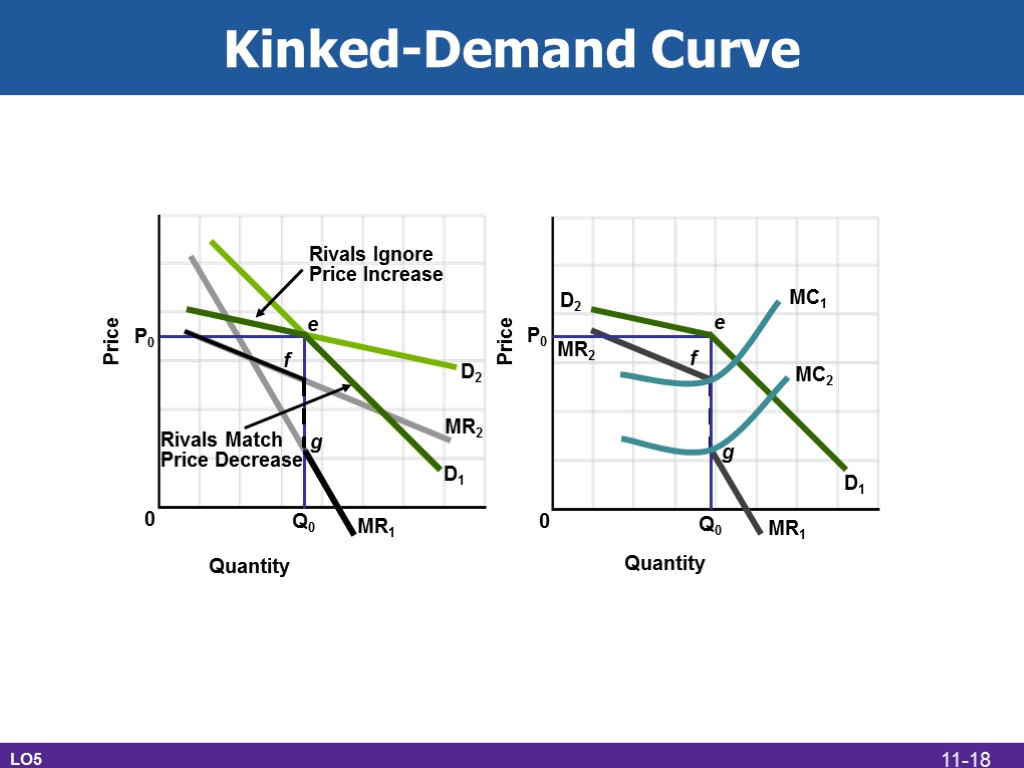
 Kinked-Demand Curve LO5 P0 MR2 D2 D1 MR1 e f g Rivals Ignore Price Increase Rivals Match Price Decrease Q0 MR2 D2 D1 MR1 Q0 MC1 MC2 P0 e f g Price Price Quantity Quantity 0 0 11-18
Kinked-Demand Curve LO5 P0 MR2 D2 D1 MR1 e f g Rivals Ignore Price Increase Rivals Match Price Decrease Q0 MR2 D2 D1 MR1 Q0 MC1 MC2 P0 e f g Price Price Quantity Quantity 0 0 11-18
 Kinked-Demand Curve Criticisms Explains inflexibility, not price Prices are not that rigid Price wars LO6 11-19
Kinked-Demand Curve Criticisms Explains inflexibility, not price Prices are not that rigid Price wars LO6 11-19
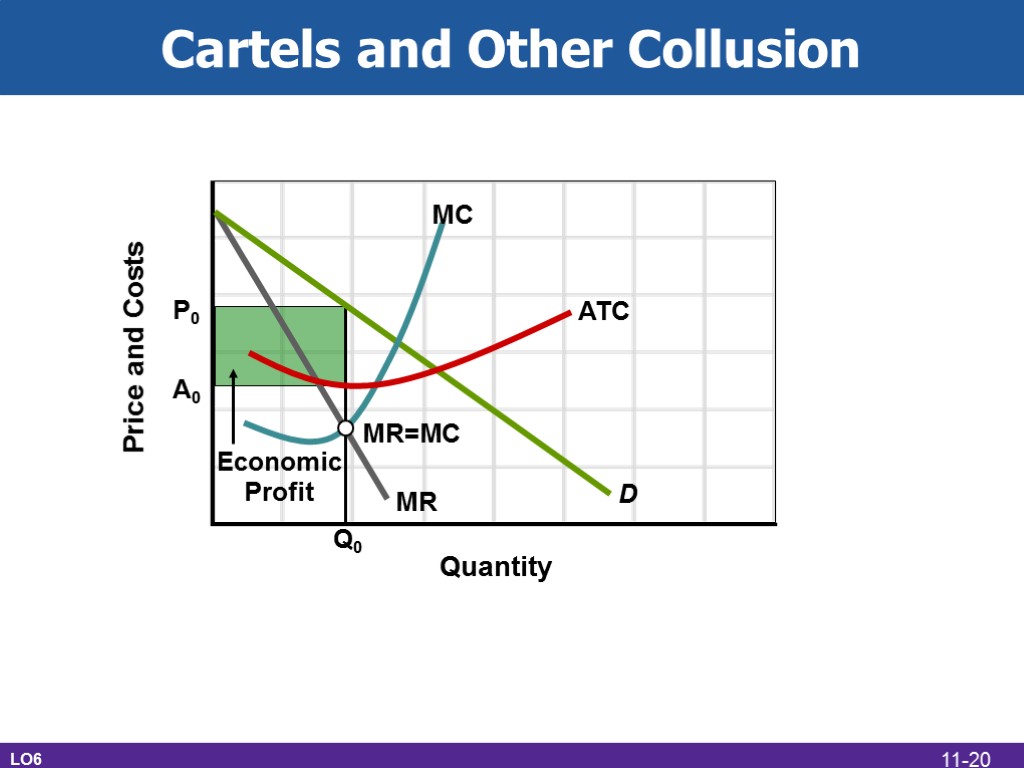
 Cartels and Other Collusion LO6 D MR=MC ATC MC MR P0 A0 Q0 Economic Profit 11-20
Cartels and Other Collusion LO6 D MR=MC ATC MC MR P0 A0 Q0 Economic Profit 11-20
 Overt Collusion Cartels - a group of firms or nations that collude Formally agreeing to the price Sets output levels for members Collusion is illegal in the United States OPEC LO6 11-21
Overt Collusion Cartels - a group of firms or nations that collude Formally agreeing to the price Sets output levels for members Collusion is illegal in the United States OPEC LO6 11-21
 Obstacles to Collusion Demand and cost differences Number of firms Cheating Recession New entrants Legal obstacles LO6 11-22
Obstacles to Collusion Demand and cost differences Number of firms Cheating Recession New entrants Legal obstacles LO6 11-22
 Price Leadership Model Price Leadership Dominant firm initiates price changes Other firms follow the leader Use limit pricing to block entry of new firms Possible price war LO6 11-23
Price Leadership Model Price Leadership Dominant firm initiates price changes Other firms follow the leader Use limit pricing to block entry of new firms Possible price war LO6 11-23
 Oligopoly and Advertising Prevalent to compete with product development and advertising Less easily duplicated than a price change Financially able to advertise LO7 11-24
Oligopoly and Advertising Prevalent to compete with product development and advertising Less easily duplicated than a price change Financially able to advertise LO7 11-24
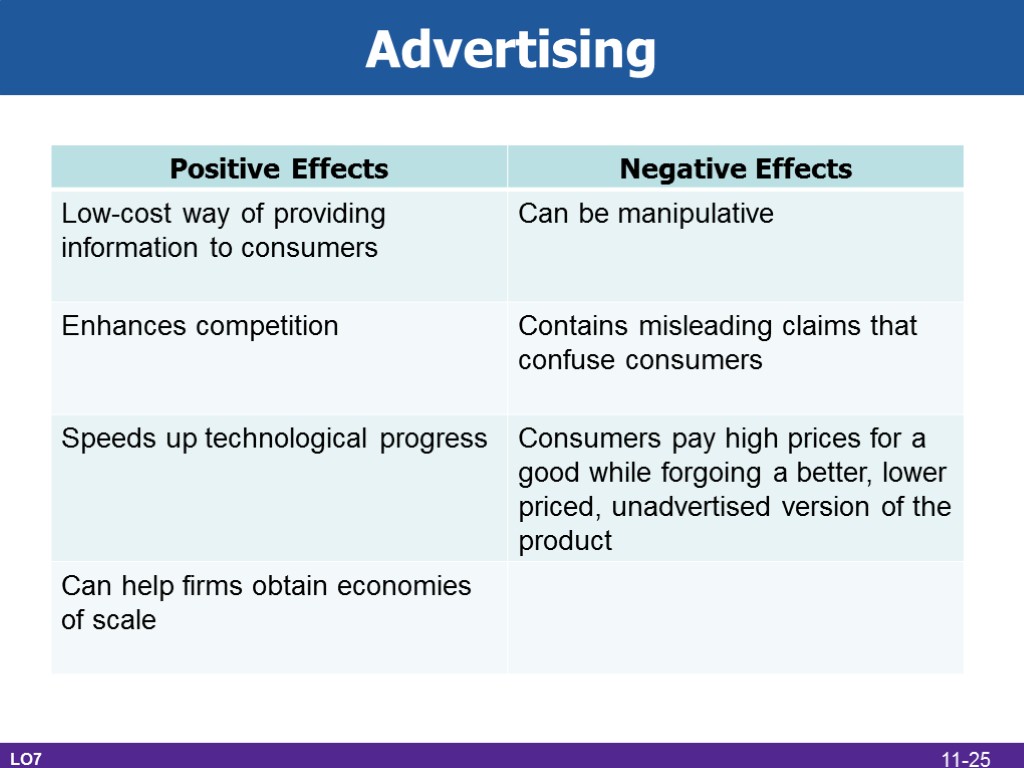
 Advertising LO7 11-25
Advertising LO7 11-25
 Oligopoly and Efficiency Oligopolies are inefficient Productively inefficient P > minATC Allocatively inefficient P > MC Qualifications Increased foreign competition Limit pricing Technological advance LO7 11-26
Oligopoly and Efficiency Oligopolies are inefficient Productively inefficient P > minATC Allocatively inefficient P > MC Qualifications Increased foreign competition Limit pricing Technological advance LO7 11-26

