Monolithic optical cavities with low thermal noise and












06_simpozium_kolachevskiy.ppt
- Размер: 15.0 Мб
- Автор:
- Количество слайдов: 31
Описание презентации Monolithic optical cavities with low thermal noise and по слайдам
 Monolithic optical cavities with low thermal noise and perspectives for laser frequency stabilization N. Kolachevsky, K. Khavarova, A. Gribov, N. Zadnov, S. Sluysarev
Monolithic optical cavities with low thermal noise and perspectives for laser frequency stabilization N. Kolachevsky, K. Khavarova, A. Gribov, N. Zadnov, S. Sluysarev
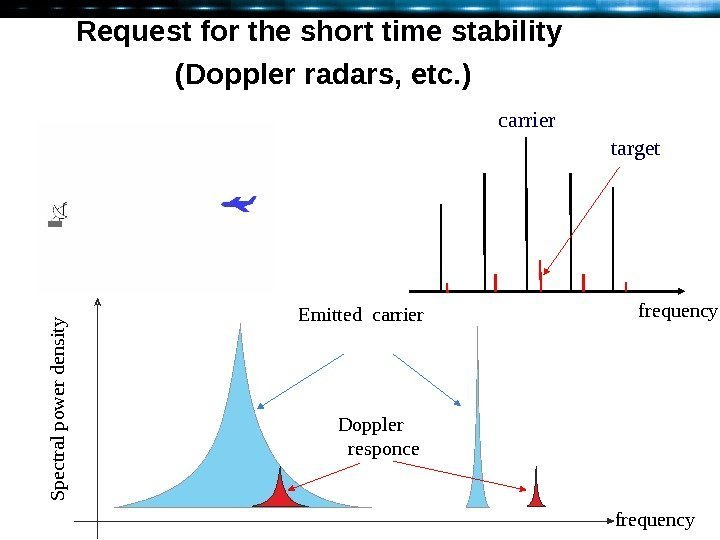
 Request for the short time stability ( Doppler radars, etc. ) carrier target frequency. S p ectral p ow er d en sity. Emitted carrier Doppler responce
Request for the short time stability ( Doppler radars, etc. ) carrier target frequency. S p ectral p ow er d en sity. Emitted carrier Doppler responce
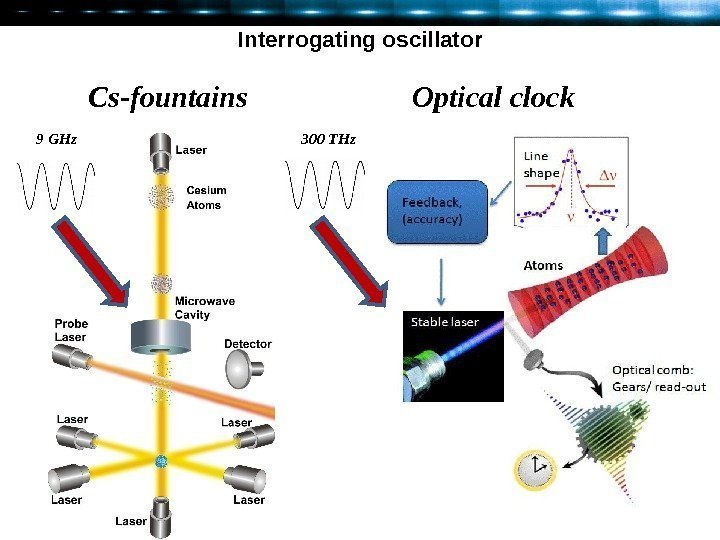
 Interrogating oscillator Cs-fountains Optical clock 9 GHz 300 THz
Interrogating oscillator Cs-fountains Optical clock 9 GHz 300 THz
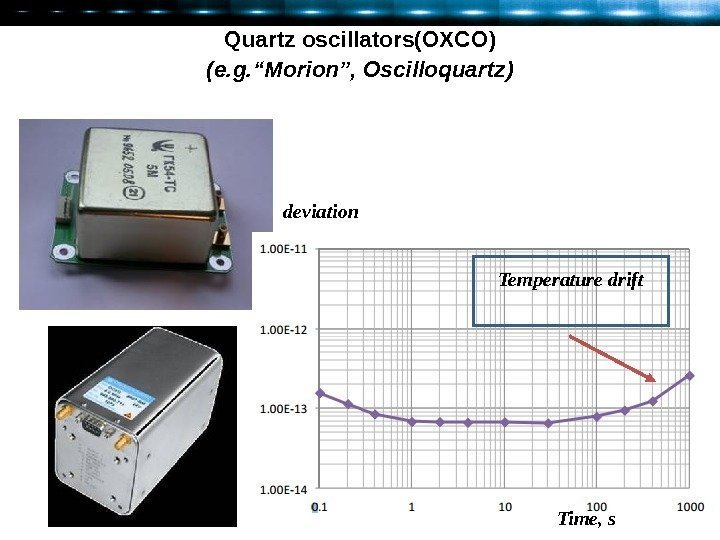
 Quartz oscillators ( OXCO ) ( e. g. “Morion”, Oscilloquartz ) Temperature drift Time, sdeviation
Quartz oscillators ( OXCO ) ( e. g. “Morion”, Oscilloquartz ) Temperature drift Time, sdeviation
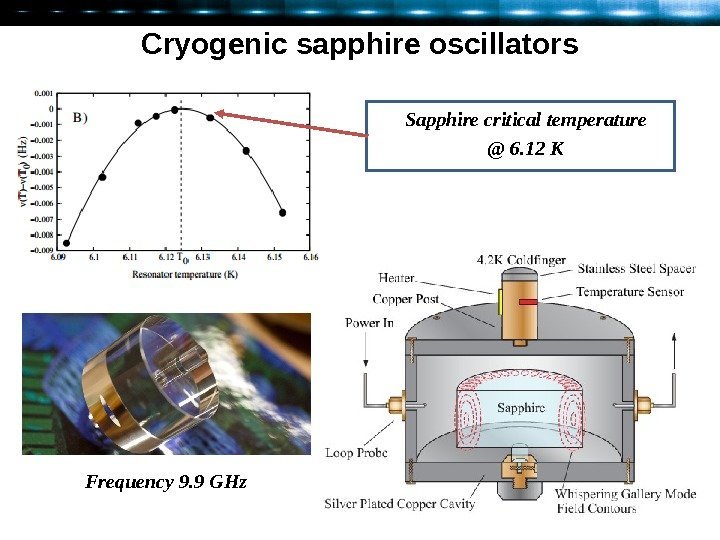
 Cryogenic sapphire oscillators Sapphire critical temperature @ 6. 12 К Frequency 9. 9 GHz
Cryogenic sapphire oscillators Sapphire critical temperature @ 6. 12 К Frequency 9. 9 GHz
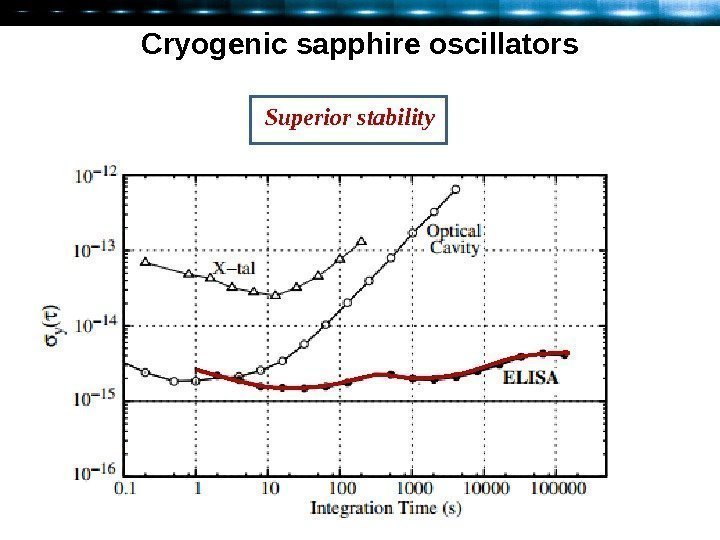
 Cryogenic sapphire oscillators Superior stability
Cryogenic sapphire oscillators Superior stability
 University of Western Australia How to lower the instability further?
University of Western Australia How to lower the instability further?
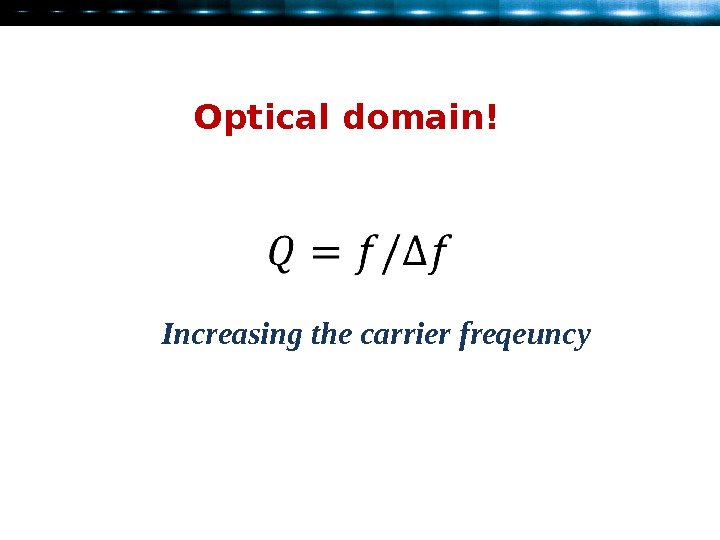
 Optical domain ! Increasing the carrier freqeuncy
Optical domain ! Increasing the carrier freqeuncy
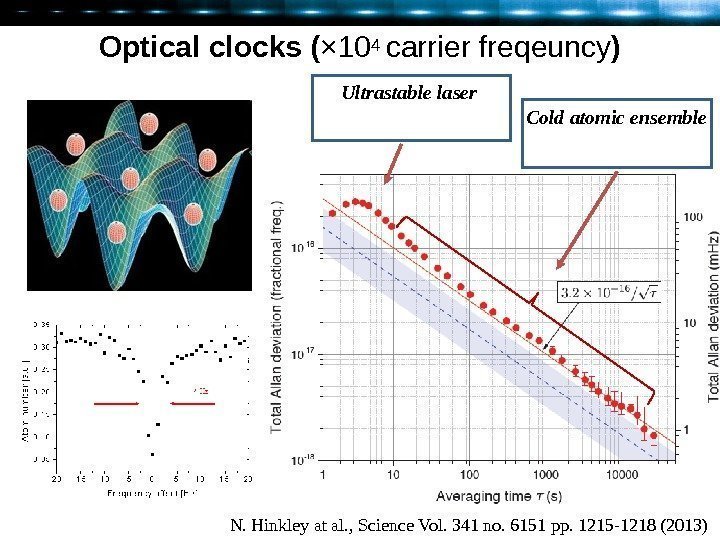
 N. Hinkley at al. , Science Vol. 341 no. 6151 pp. 1215 -1218 (2013)Optical clocks ( × 104 carrier freqeuncy ) Ultrastable laser Cold atomic ensemble
N. Hinkley at al. , Science Vol. 341 no. 6151 pp. 1215 -1218 (2013)Optical clocks ( × 104 carrier freqeuncy ) Ultrastable laser Cold atomic ensemble
 The problem is solved: optical clocks with laser-cooled atoms (ions) provide necessary specifications for instability and accuracy. How about technological aspects ? ? ? • Bulky and very sensitive to adjustment: laser cooling, trapping in the lattice, reading the clock transition • From 5 to 10 laser systems are required. Lasers are yet much less robust compared to microwave components.
The problem is solved: optical clocks with laser-cooled atoms (ions) provide necessary specifications for instability and accuracy. How about technological aspects ? ? ? • Bulky and very sensitive to adjustment: laser cooling, trapping in the lattice, reading the clock transition • From 5 to 10 laser systems are required. Lasers are yet much less robust compared to microwave components.
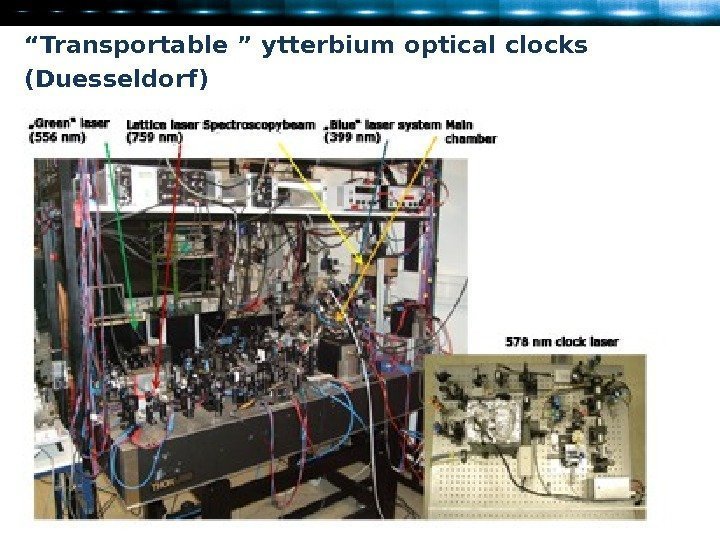
 “ Transportable ” ytterbium optical clocks ( Duesseldorf )
“ Transportable ” ytterbium optical clocks ( Duesseldorf )
 • One needs a compact setup with minimal number of robust laser systems • One can restrict requirements for the short/long term instabitliy to 10 -1 6 — 10 —
• One needs a compact setup with minimal number of robust laser systems • One can restrict requirements for the short/long term instabitliy to 10 -1 6 — 10 —
 A laser locked to the passive optical cavity Limitations? Vladimir Braginsky dream: 10 -20 !
A laser locked to the passive optical cavity Limitations? Vladimir Braginsky dream: 10 -20 !
 Stabilized lasers at LPI • Compact systems based on ULE glass cavitites • Room temperature operation ( critical point T с 300 K ) • Vibration compensation
Stabilized lasers at LPI • Compact systems based on ULE glass cavitites • Room temperature operation ( critical point T с 300 K ) • Vibration compensation
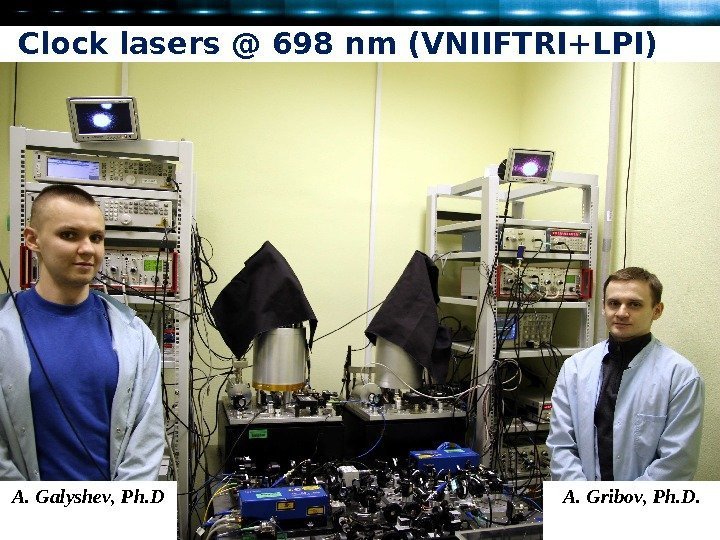
 Clock lasers @ 6 98 nm (VNIIFTRI+LPI) A. Galyshev , Ph. D A. Gribov , Ph. D.
Clock lasers @ 6 98 nm (VNIIFTRI+LPI) A. Galyshev , Ph. D A. Gribov , Ph. D.
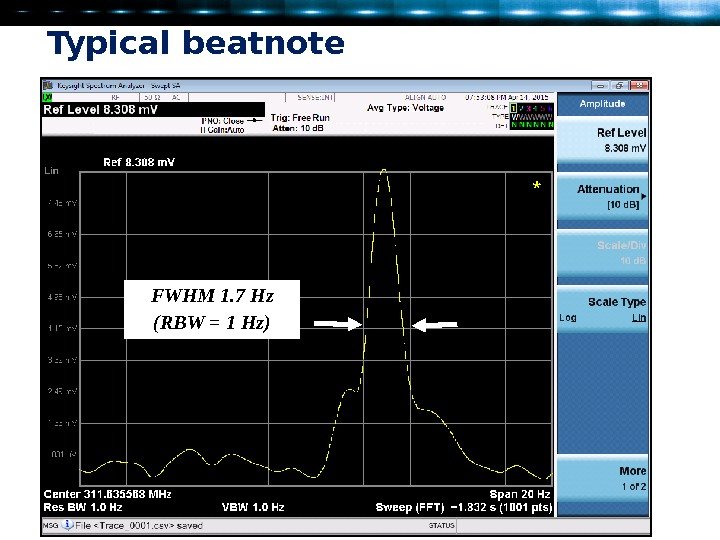
 Typical beatnote FWHM 1. 7 Hz ( RBW = 1 Hz )
Typical beatnote FWHM 1. 7 Hz ( RBW = 1 Hz )
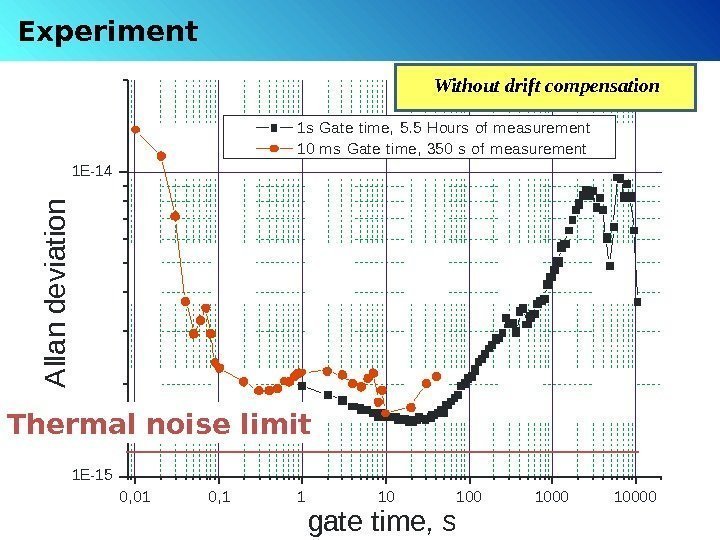
 Experiment 0, 01 0, 1 1 10 100001 E-151 E-14 1 s Gat e t im e, 5. 5 Hours of meas urem ent 10 m s Gat e t im e, 350 s of m eas urem ent gate time, s. A lla n d e v ia tio n. Thermal noise limit Without drift compensation
Experiment 0, 01 0, 1 1 10 100001 E-151 E-14 1 s Gat e t im e, 5. 5 Hours of meas urem ent 10 m s Gat e t im e, 350 s of m eas urem ent gate time, s. A lla n d e v ia tio n. Thermal noise limit Without drift compensation
 Instability sources: 1) Thermal noise ( fundamental ) 2) Aging of composite materials ( + technical noise )
Instability sources: 1) Thermal noise ( fundamental ) 2) Aging of composite materials ( + technical noise )
 Nature of thermal noisel l Random Brownian motion of mirror surfaces due to thermal excitation of vibrational modes l
Nature of thermal noisel l Random Brownian motion of mirror surfaces due to thermal excitation of vibrational modes l
 Thermal noise of ULE cavity Multilayer dielectric structure 0 ( ) 2 1 1 coating mirror coat sub S S d w 17 ( ) 5. 4 10 coat. S f f m Hz Spectral density 6 10 10 мd 25 coat spacer Material losses Thickness of the coating
Thermal noise of ULE cavity Multilayer dielectric structure 0 ( ) 2 1 1 coating mirror coat sub S S d w 17 ( ) 5. 4 10 coat. S f f m Hz Spectral density 6 10 10 мd 25 coat spacer Material losses Thickness of the coating
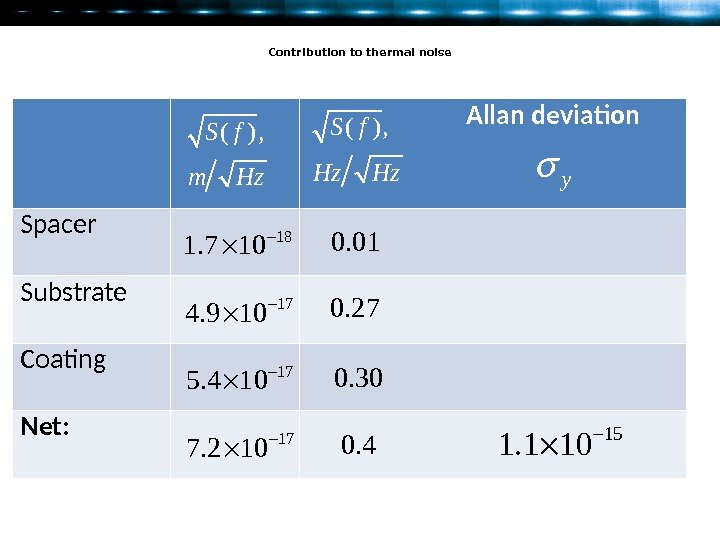
 Contribution to thermal noise Allan deviation Spacer Substrate Coating Net: ( ) , S f m Hz ( ) , S f Hz Hz 18 1. 7 10 17 4. 9 10 17 5. 4 10 17 7. 2 10 0. 4 0. 30 0. 27 0. 01 y 15 1.
Contribution to thermal noise Allan deviation Spacer Substrate Coating Net: ( ) , S f m Hz ( ) , S f Hz Hz 18 1. 7 10 17 4. 9 10 17 5. 4 10 17 7. 2 10 0. 4 0. 30 0. 27 0. 01 y 15 1.
 How to improve stability? • Lowering the temperature • Crystalline materials
How to improve stability? • Lowering the temperature • Crystalline materials
 Fritz Riehle, PTB The first silicon cavity
Fritz Riehle, PTB The first silicon cavity
 Silicon — Optical material for — Critical temperature 124 К — Low mechanical losses — High thermal conductivity ( ULE× 100)7 10 1200 nm
Silicon — Optical material for — Critical temperature 124 К — Low mechanical losses — High thermal conductivity ( ULE× 100)7 10 1200 nm
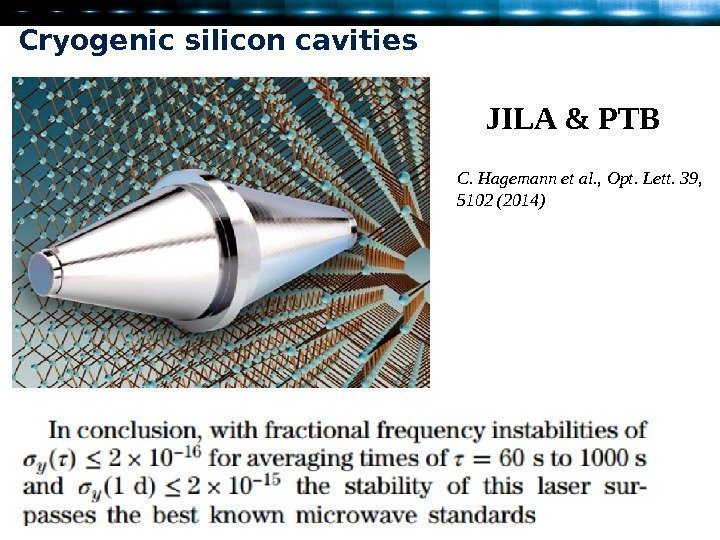
 Cryogenic silicon cavities JILA & PTB C. Hagemann et al. , Opt. Lett. 39, 5102 (2014)
Cryogenic silicon cavities JILA & PTB C. Hagemann et al. , Opt. Lett. 39, 5102 (2014)
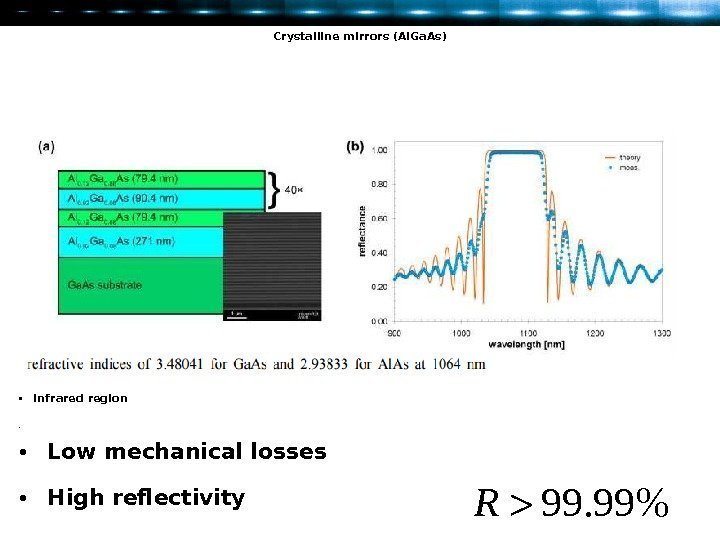
 Crystalline mirrors (Al. Ga. As) • Infrared region • 99. 99%R • Low mechanical losses • High reflectivity
Crystalline mirrors (Al. Ga. As) • Infrared region • 99. 99%R • Low mechanical losses • High reflectivity
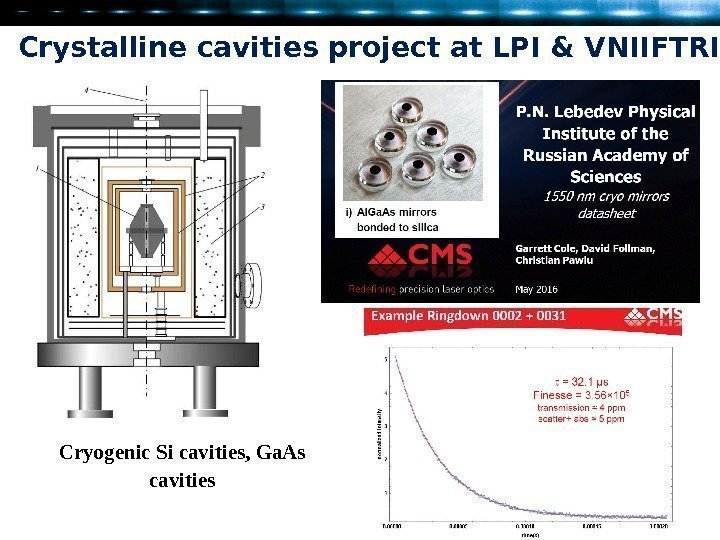
 Crystalline cavities project at LPI & VNIIFTRI Cryogenic Si cavities, Ga. As cavities
Crystalline cavities project at LPI & VNIIFTRI Cryogenic Si cavities, Ga. As cavities
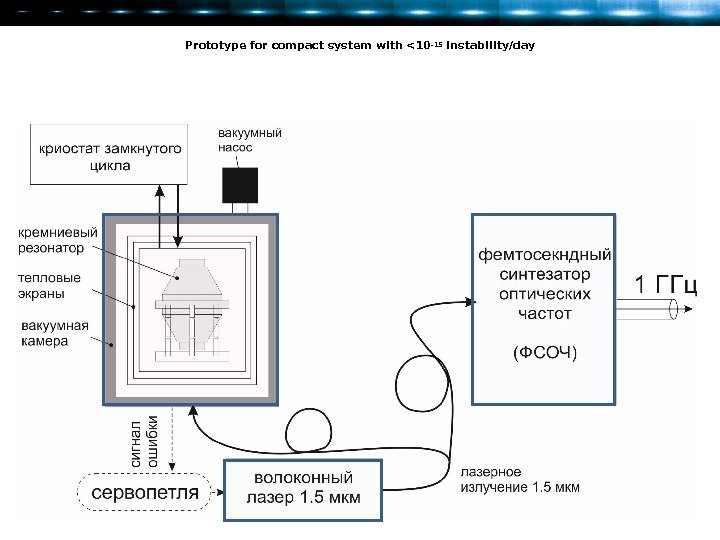
 Prototype for compact system with <10 -15 instability/day
Prototype for compact system with <10 -15 instability/day
 Laser source Fiber laser @ 1. 5 m LASUS system
Laser source Fiber laser @ 1. 5 m LASUS system
 Space-specified frequency comb FOKUS (Menlo Systems)
Space-specified frequency comb FOKUS (Menlo Systems)
 Conclusion/outlook • Microwave systems with <10 -15 instability in 1 second are already commercially available (Menlo Systems) • Space-specified systems may appear on 5 -year horizon • Optical-to-microwave systems with 10 -16 — 10 -15 instability will be available based on crystalline/cryogenic technologies • Strong competition to H-masers on 10 -year horizon
Conclusion/outlook • Microwave systems with <10 -15 instability in 1 second are already commercially available (Menlo Systems) • Space-specified systems may appear on 5 -year horizon • Optical-to-microwave systems with 10 -16 — 10 -15 instability will be available based on crystalline/cryogenic technologies • Strong competition to H-masers on 10 -year horizon

