73dbfb659bbae395b4f0ccaab4549cdd.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 51
 Monitoring The Human Condition Study - 2009 ** TRENDS ** Presented By: Warren Smith, Data Analyst Barnstable County Dept. of Human Services June 25, 2009 1
Monitoring The Human Condition Study - 2009 ** TRENDS ** Presented By: Warren Smith, Data Analyst Barnstable County Dept. of Human Services June 25, 2009 1
 Background • Monitoring The Human Condition on Cape Cod Study: – – – – Health & Human Services Needs Assessment Annual Cape Cod Community Survey Findings Five Years of Data (2004 -2008) Latest US Census Statistics Findings Report in April Findings Presented at May HHSAC Meeting TRENDS Report in June 2
Background • Monitoring The Human Condition on Cape Cod Study: – – – – Health & Human Services Needs Assessment Annual Cape Cod Community Survey Findings Five Years of Data (2004 -2008) Latest US Census Statistics Findings Report in April Findings Presented at May HHSAC Meeting TRENDS Report in June 2
 Today’s Presentation • Demographic Trends • Affordability Trends: – Trade-Offs – Central Issues • Trends in Eleven Key Areas: – Statistically-significant changes 3
Today’s Presentation • Demographic Trends • Affordability Trends: – Trade-Offs – Central Issues • Trends in Eleven Key Areas: – Statistically-significant changes 3
 Trends in Eleven Key Areas 1. Food/Nutrition 2. Housing 3. Leisure Time/Recreation 4. Medical/Dental 5. Mental Health 6. Overweight/Obesity 7. Childcare 8. Legal Assistance 9. Transportation 10. Discrimination 11. Work/Employment 4
Trends in Eleven Key Areas 1. Food/Nutrition 2. Housing 3. Leisure Time/Recreation 4. Medical/Dental 5. Mental Health 6. Overweight/Obesity 7. Childcare 8. Legal Assistance 9. Transportation 10. Discrimination 11. Work/Employment 4
 Key Demographic Trends ** Changes in the Population ** 5
Key Demographic Trends ** Changes in the Population ** 5
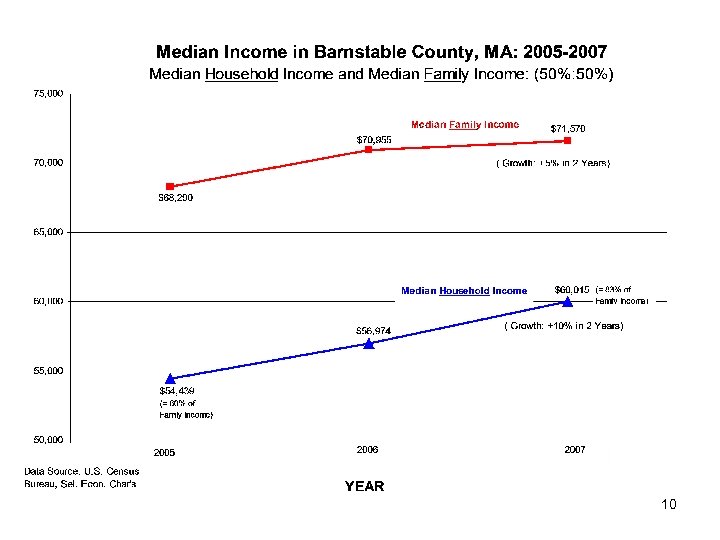
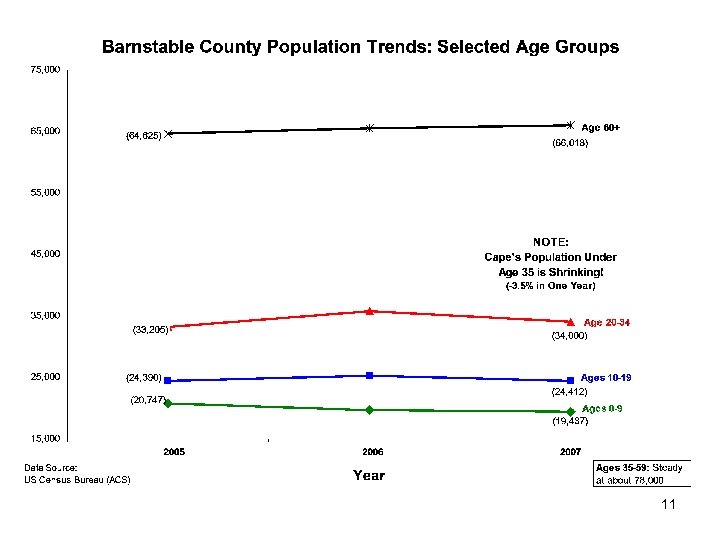
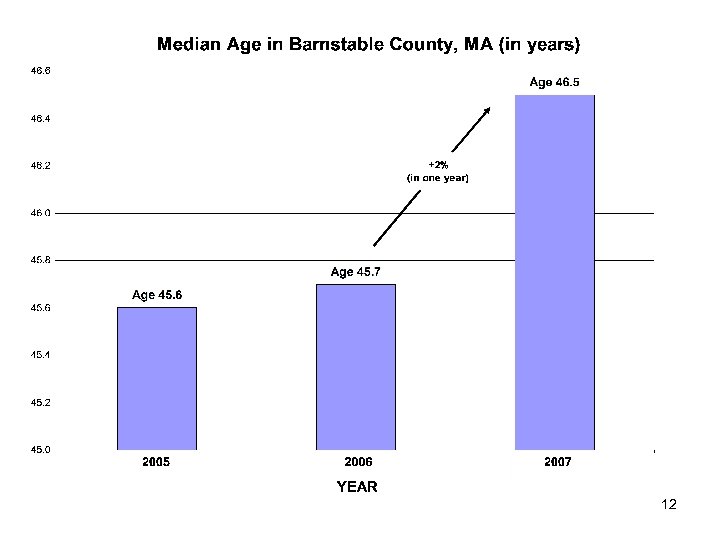
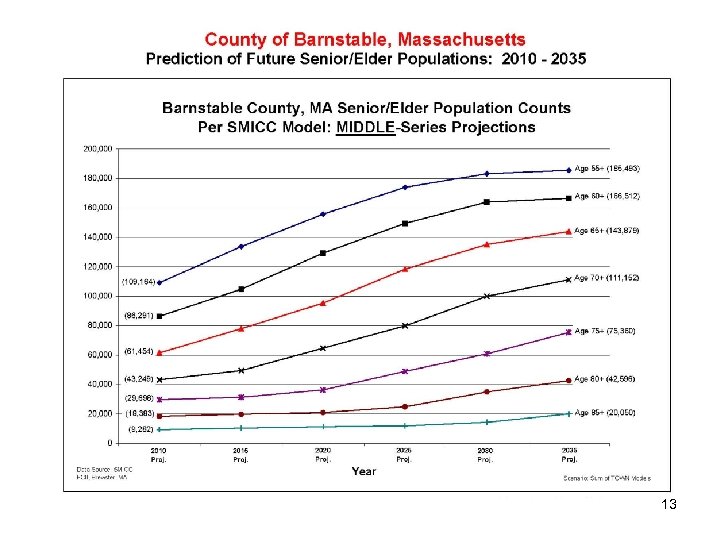
 Population Changes • • Births Public School Enrollment Child Poverty Median Income Age Distributions Median Age Future Projections (Seniors/Elders) 6
Population Changes • • Births Public School Enrollment Child Poverty Median Income Age Distributions Median Age Future Projections (Seniors/Elders) 6
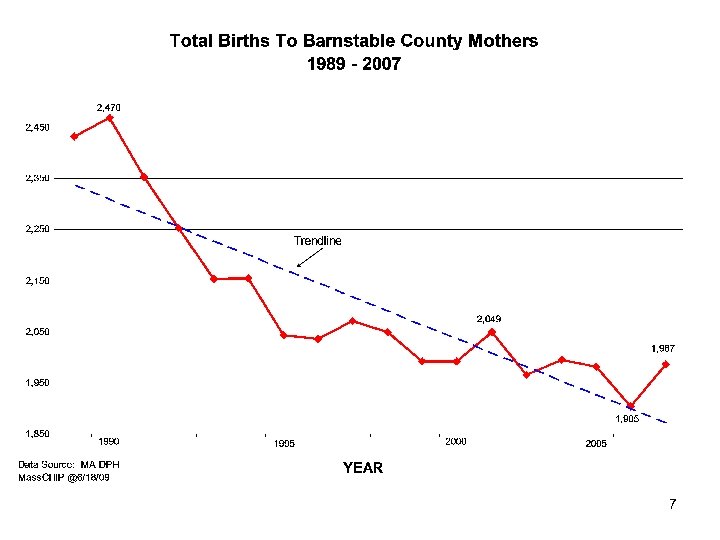 7
7
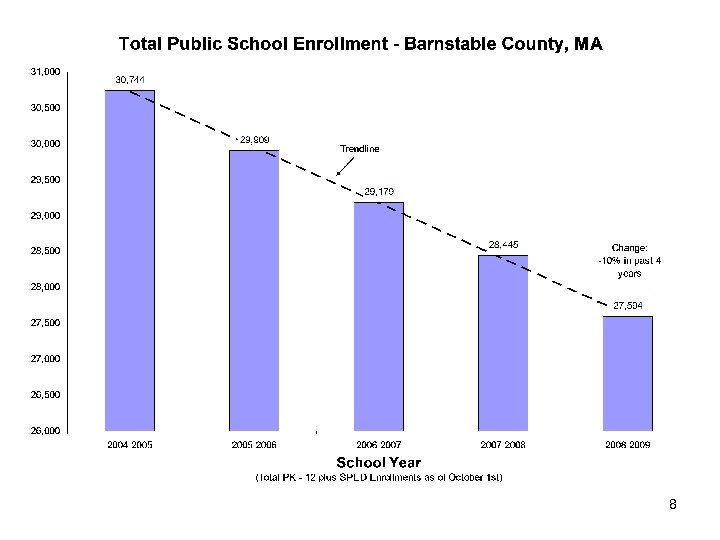 8
8
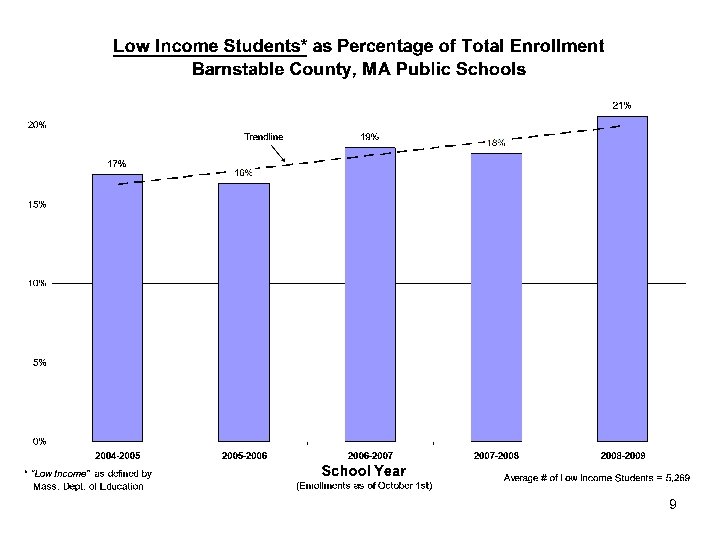 9
9
 10
10
 11
11
 12
12
 13
13
 Notes: 14
Notes: 14
 Trends in Human Need on Cape Cod 15
Trends in Human Need on Cape Cod 15
 Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs 16
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs 16
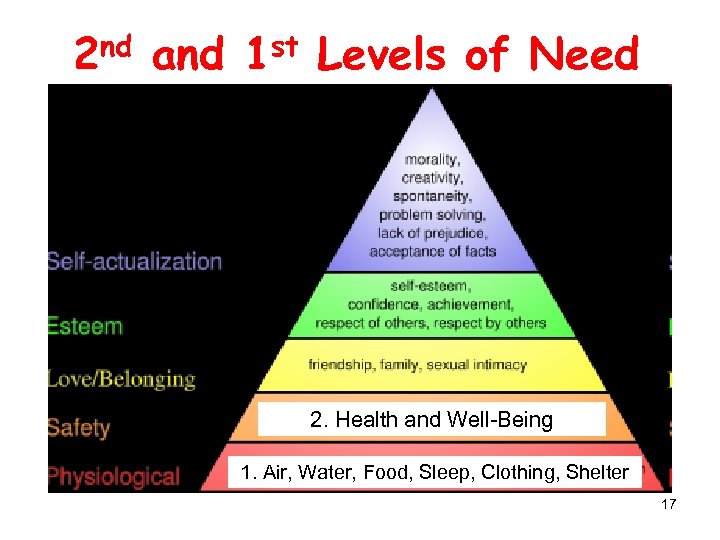 2 nd and 1 st Levels of Need 2. Health and Well-Being 1. Air, Water, Food, Sleep, Clothing, Shelter 17
2 nd and 1 st Levels of Need 2. Health and Well-Being 1. Air, Water, Food, Sleep, Clothing, Shelter 17
 Affordability Key to Overcoming Unmet Health and Human Services Needs 18
Affordability Key to Overcoming Unmet Health and Human Services Needs 18
 Affordability Trends (2 nd and 1 st Level Items) • Healthcare Affordability: (2 nd level) – Health and Well-Being • Basic Needs Affordability: (1 st level) – Food – Clothing – Shelter 19
Affordability Trends (2 nd and 1 st Level Items) • Healthcare Affordability: (2 nd level) – Health and Well-Being • Basic Needs Affordability: (1 st level) – Food – Clothing – Shelter 19
 Notes: 20
Notes: 20
 21
21
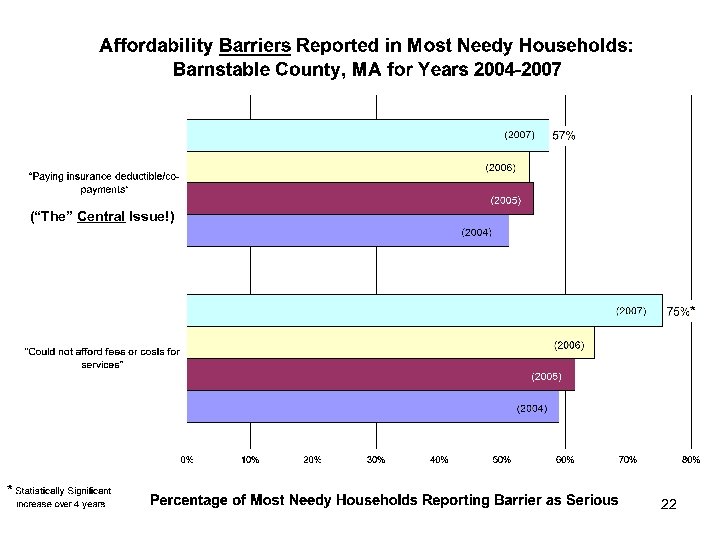 (“The” Central Issue!) 22
(“The” Central Issue!) 22
 “The” Central Issue • “Paying insurance deductible/co-payment” – Strongly related to key affordability problems – Correlated with “Could not afford fees or costs for services” (combined with it? ) – 58% of Most Needy households report this as a barrier to accessing needed services – Statistical analysis (correlation) confirms strong links to affordability of nutritious food, dental care, and leisure time/recreation. 23
“The” Central Issue • “Paying insurance deductible/co-payment” – Strongly related to key affordability problems – Correlated with “Could not afford fees or costs for services” (combined with it? ) – 58% of Most Needy households report this as a barrier to accessing needed services – Statistical analysis (correlation) confirms strong links to affordability of nutritious food, dental care, and leisure time/recreation. 23
 Trade-Offs ** Affordability ** 24
Trade-Offs ** Affordability ** 24
 Historical Trade-Offs (Time Period: 2004 -2007) • Historically Inter-Related Affordability Cluster: – – – – “Not able to afford nutritious food” “Not always having enough money for food” “Not being able to afford recreational activities” “Not having enough money to pay for housing” “Paying for a mental health counselor” “Paying for or getting dental [insurance] care” “Could not afford fees or costs for services” “Paying insurance deductible/co-payments” 25
Historical Trade-Offs (Time Period: 2004 -2007) • Historically Inter-Related Affordability Cluster: – – – – “Not able to afford nutritious food” “Not always having enough money for food” “Not being able to afford recreational activities” “Not having enough money to pay for housing” “Paying for a mental health counselor” “Paying for or getting dental [insurance] care” “Could not afford fees or costs for services” “Paying insurance deductible/co-payments” 25
 Today’s Trade-Offs (Latest 3 -Years: 2006 -2007 -2008) • Current Affordability Cluster: – – – “Not able to afford nutritious food” “Not being able to afford recreational activities” “Paying for or getting dental [insurance] care” “Could not afford fees or costs for services” “Paying insurance deductible/co-payments” 26
Today’s Trade-Offs (Latest 3 -Years: 2006 -2007 -2008) • Current Affordability Cluster: – – – “Not able to afford nutritious food” “Not being able to afford recreational activities” “Paying for or getting dental [insurance] care” “Could not afford fees or costs for services” “Paying insurance deductible/co-payments” 26
 Trade-Offs Shown By Survey Cost of Living Responses (Most Needy Households in 2008) • To Afford Food: Trading Off – – – Telephone service Clothing store items (all) Rent or lease payments Car/truck insurance Transit services • To Afford Nutritious Food: Trading Off – Telephone service – Out-of-home fun activities – Clothing store items – In-home fun activities – Transit services 27
Trade-Offs Shown By Survey Cost of Living Responses (Most Needy Households in 2008) • To Afford Food: Trading Off – – – Telephone service Clothing store items (all) Rent or lease payments Car/truck insurance Transit services • To Afford Nutritious Food: Trading Off – Telephone service – Out-of-home fun activities – Clothing store items – In-home fun activities – Transit services 27
 Trade-Offs (continued) • To Afford Housing: • To Afford Medical/Dental Care: Trading Off – Telephone service – Electric service – Clothing store items (school cloths) – Telephone service – Clothing store items (casual cloths) 28
Trade-Offs (continued) • To Afford Housing: • To Afford Medical/Dental Care: Trading Off – Telephone service – Electric service – Clothing store items (school cloths) – Telephone service – Clothing store items (casual cloths) 28
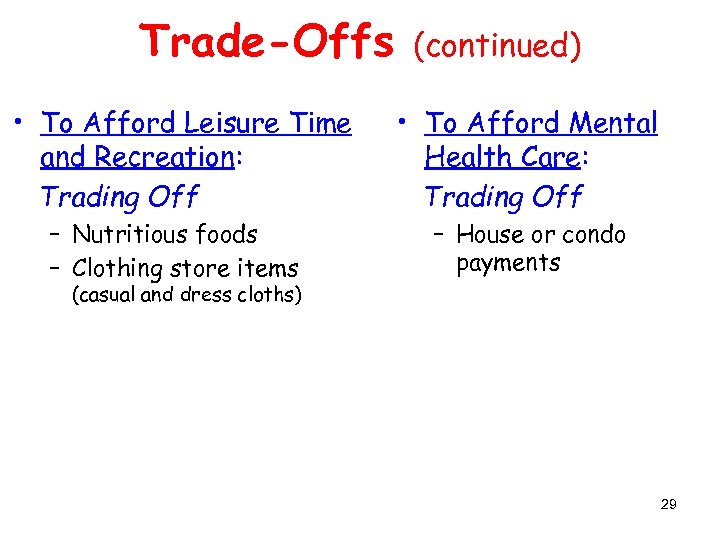 Trade-Offs • To Afford Leisure Time and Recreation: Trading Off – Nutritious foods – Clothing store items (continued) • To Afford Mental Health Care: Trading Off – House or condo payments (casual and dress cloths) 29
Trade-Offs • To Afford Leisure Time and Recreation: Trading Off – Nutritious foods – Clothing store items (continued) • To Afford Mental Health Care: Trading Off – House or condo payments (casual and dress cloths) 29
 Trends in Unmet Need Among Our Most Needy Households (2004 – 2007) 30
Trends in Unmet Need Among Our Most Needy Households (2004 – 2007) 30
 Definitions • Prevalence: – How widespread is the problem/barrier? • Proportion of households reporting a problem • Seriousness: – How detrimental is the problem/barrier? • Degree of seriousness on a “scale” (moderate, very serious, so serious did not get needed help) 31
Definitions • Prevalence: – How widespread is the problem/barrier? • Proportion of households reporting a problem • Seriousness: – How detrimental is the problem/barrier? • Degree of seriousness on a “scale” (moderate, very serious, so serious did not get needed help) 31
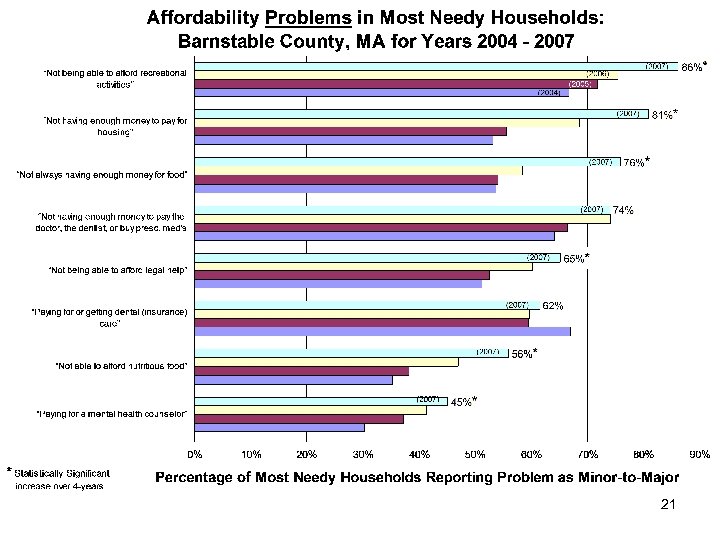
 Food/Nutrition (Changes 2004 – 2007) • Prevalence: – “Not always having enough money for food” [+41%] – “Not able to afford nutritious food” [+58%] • Seriousness: – “Not always having enough money for food” [+50%] – “Not able to afford nutritious food” [+73%] 32
Food/Nutrition (Changes 2004 – 2007) • Prevalence: – “Not always having enough money for food” [+41%] – “Not able to afford nutritious food” [+58%] • Seriousness: – “Not always having enough money for food” [+50%] – “Not able to afford nutritious food” [+73%] 32
 Housing (Changes 2004 – 2007) • Prevalence: – “Not having enough money to pay for housing” [+52%] • Seriousness: – “Not having enough money to pay for housing” [+66%] – Overcrowding: “Not enough room in your house for all of the people who live there” [+43%] 33
Housing (Changes 2004 – 2007) • Prevalence: – “Not having enough money to pay for housing” [+52%] • Seriousness: – “Not having enough money to pay for housing” [+66%] – Overcrowding: “Not enough room in your house for all of the people who live there” [+43%] 33
 Leisure Time/Recreation (Changes 2004 – 2007) • Prevalence: – “Not being able to afford recreational activities” [+29%] • Seriousness: – “Not being able to afford recreational activities” [+40%] 34
Leisure Time/Recreation (Changes 2004 – 2007) • Prevalence: – “Not being able to afford recreational activities” [+29%] • Seriousness: – “Not being able to afford recreational activities” [+40%] 34
 Medical/Dental (Changes 2004 – 2007) • Prevalence: – Do any of the household insurances “provide for dental care? ” [+39%] – “Is any adult (age 18+) in Fair-to-Poor health” [+64%] • Seriousness: – “Paying for or getting dental (insurance) care” [-10%] – “Not having enough money to pay the doctor, dentist, or to buy prescription medications” [+21%] 35
Medical/Dental (Changes 2004 – 2007) • Prevalence: – Do any of the household insurances “provide for dental care? ” [+39%] – “Is any adult (age 18+) in Fair-to-Poor health” [+64%] • Seriousness: – “Paying for or getting dental (insurance) care” [-10%] – “Not having enough money to pay the doctor, dentist, or to buy prescription medications” [+21%] 35
 Mental Health (Changes 2004 – 2007) • Prevalence: – “Paying for a mental health counselor” [+49%] • Seriousness: – “Paying for a mental health counselor” [+56%] – “Having a lot of anxiety or stress in the household” [+19%] 36
Mental Health (Changes 2004 – 2007) • Prevalence: – “Paying for a mental health counselor” [+49%] • Seriousness: – “Paying for a mental health counselor” [+56%] – “Having a lot of anxiety or stress in the household” [+19%] 36
 Overweight/Obesity (Changes 2004 – 2007) • Prevalence: – “Seriously overweight person(s) in household” [+1, 749%] • Seriousness: – “Seriously overweight person(s) in household” [+3, 600%] 37
Overweight/Obesity (Changes 2004 – 2007) • Prevalence: – “Seriously overweight person(s) in household” [+1, 749%] • Seriousness: – “Seriously overweight person(s) in household” [+3, 600%] 37
 Childcare (Changes 2004 – 2007) • Prevalence: – Average number of “children (age 17 or younger) living in your household? ” [-22%] • Seriousness: – “Not being able to find or afford afterschool child care” [+39%] 38
Childcare (Changes 2004 – 2007) • Prevalence: – Average number of “children (age 17 or younger) living in your household? ” [-22%] • Seriousness: – “Not being able to find or afford afterschool child care” [+39%] 38
 Legal Assistance (Changes 2004 – 2007) • Prevalence: – “Not being able to afford legal help” [+27%] • Seriousness: – “Not being able to afford legal help” [+37%] – “Immigration or Visa dispute” [+37%] 39
Legal Assistance (Changes 2004 – 2007) • Prevalence: – “Not being able to afford legal help” [+27%] • Seriousness: – “Not being able to afford legal help” [+37%] – “Immigration or Visa dispute” [+37%] 39
![Transportation (Changes 2004 – 2007) • Prevalence: – “Lack of transportation” [+76%] • Seriousness: Transportation (Changes 2004 – 2007) • Prevalence: – “Lack of transportation” [+76%] • Seriousness:](https://present5.com/presentation/73dbfb659bbae395b4f0ccaab4549cdd/image-40.jpg) Transportation (Changes 2004 – 2007) • Prevalence: – “Lack of transportation” [+76%] • Seriousness: – “Lack of transportation” [+79%] 40
Transportation (Changes 2004 – 2007) • Prevalence: – “Lack of transportation” [+76%] • Seriousness: – “Lack of transportation” [+79%] 40
![Discrimination (Changes 2004 – 2007) • Prevalence: – “Feelings of discrimination” [+47%] • Seriousness: Discrimination (Changes 2004 – 2007) • Prevalence: – “Feelings of discrimination” [+47%] • Seriousness:](https://present5.com/presentation/73dbfb659bbae395b4f0ccaab4549cdd/image-41.jpg) Discrimination (Changes 2004 – 2007) • Prevalence: – “Feelings of discrimination” [+47%] • Seriousness: – “Feelings of discrimination” [+69%] – “Discrimination (due to race, age, language, sexual identity/orientation, etc. )” [+142%] 41
Discrimination (Changes 2004 – 2007) • Prevalence: – “Feelings of discrimination” [+47%] • Seriousness: – “Feelings of discrimination” [+69%] – “Discrimination (due to race, age, language, sexual identity/orientation, etc. )” [+142%] 41
 Work/Employment (Changes 2004 – 2007) • Prevalence: – “All adults (age 18+) in your household are employed” [-31%] • Seriousness: – “Unable to take time away from work to go to services” [+17%] 42
Work/Employment (Changes 2004 – 2007) • Prevalence: – “All adults (age 18+) in your household are employed” [-31%] • Seriousness: – “Unable to take time away from work to go to services” [+17%] 42
 Comment on 2008 Most Needy • Due to a much broader-based demographic profile of the 2008 Most Needy households: – Household incomes are higher than usual: • Fewer affordability issues – Education levels are higher – Fewer children and child-related issues: • Fewer problems getting after-school child care – Fewer housing issues and less overcrowding – Fewer employed household members: • Fewer work-related access issues • Fewer leisure time/recreation issues • Fewer job training/skills upgrade issues • More retiree households – More households have a working vehicle: • Fewer transportation issues – Fewer feelings of discrimination – Fewer system capacity complaints ("not accepting new clients”) 43
Comment on 2008 Most Needy • Due to a much broader-based demographic profile of the 2008 Most Needy households: – Household incomes are higher than usual: • Fewer affordability issues – Education levels are higher – Fewer children and child-related issues: • Fewer problems getting after-school child care – Fewer housing issues and less overcrowding – Fewer employed household members: • Fewer work-related access issues • Fewer leisure time/recreation issues • Fewer job training/skills upgrade issues • More retiree households – More households have a working vehicle: • Fewer transportation issues – Fewer feelings of discrimination – Fewer system capacity complaints ("not accepting new clients”) 43
 Q & A • • What surprised you? What made you happy? What made you sad? What is most positive? What is most negative? What additional info do you need? What should be next? . . . 44
Q & A • • What surprised you? What made you happy? What made you sad? What is most positive? What is most negative? What additional info do you need? What should be next? . . . 44
 Notes: 45
Notes: 45
 The “Most Needy” 46
The “Most Needy” 46
 Who Are “Most Needy” • Compared to Overall Cape Cod Sample: – Problems and Service Barriers: • 2. 5 x to 3 x Times More Households Report Problems/Barriers also, • 2. 5 x to 3 x Times More Seriousness Reported 47
Who Are “Most Needy” • Compared to Overall Cape Cod Sample: – Problems and Service Barriers: • 2. 5 x to 3 x Times More Households Report Problems/Barriers also, • 2. 5 x to 3 x Times More Seriousness Reported 47
 Historically “Most Needy” Cape Cod Households (Four Well-Defined Population “Groups”) 48
Historically “Most Needy” Cape Cod Households (Four Well-Defined Population “Groups”) 48
 Group #5: ALL Retired THEN Group #4: NOT All Retired 80% Working, Middle-Class Families/Individuals— ”Doing OK, in General” Group #3: Undefined Most Years “Most Needy” Group #2 20% “Most Needy” Group #1 49
Group #5: ALL Retired THEN Group #4: NOT All Retired 80% Working, Middle-Class Families/Individuals— ”Doing OK, in General” Group #3: Undefined Most Years “Most Needy” Group #2 20% “Most Needy” Group #1 49
 What Happened? Where Were These New Arrivals Last Year? 50
What Happened? Where Were These New Arrivals Last Year? 50
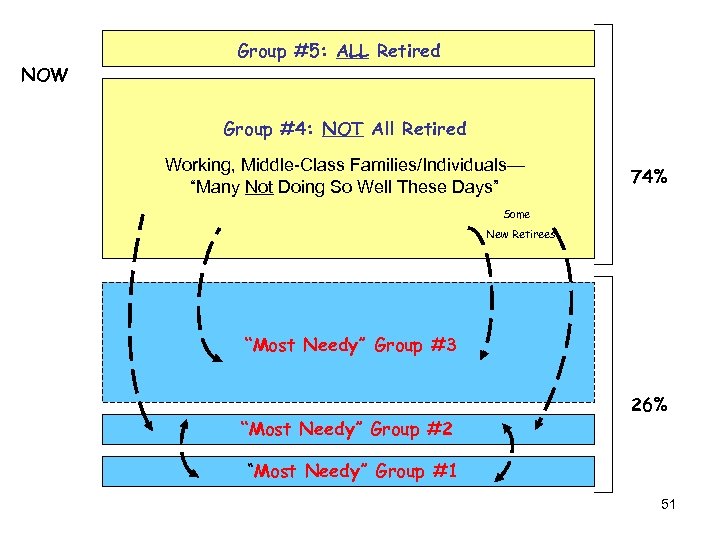 NOW Group #5: ALL Retired Group #4: NOT All Retired Working, Middle-Class Families/Individuals— “Many Not Doing So Well These Days” 74% Some New Retirees “Most Needy” Group #3 “Most Needy” Group #2 26% “Most Needy” Group #1 51
NOW Group #5: ALL Retired Group #4: NOT All Retired Working, Middle-Class Families/Individuals— “Many Not Doing So Well These Days” 74% Some New Retirees “Most Needy” Group #3 “Most Needy” Group #2 26% “Most Needy” Group #1 51


