dff74029b84ed0a32feb158cecfffec9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 Monetary Policy: Regulating Money Supply
Monetary Policy: Regulating Money Supply
 2 Types of Monetary Policy • LOOSE Monetary Policy (increasing the money supply) • TIGHT Monetary policy (decreasing the money supply)
2 Types of Monetary Policy • LOOSE Monetary Policy (increasing the money supply) • TIGHT Monetary policy (decreasing the money supply)
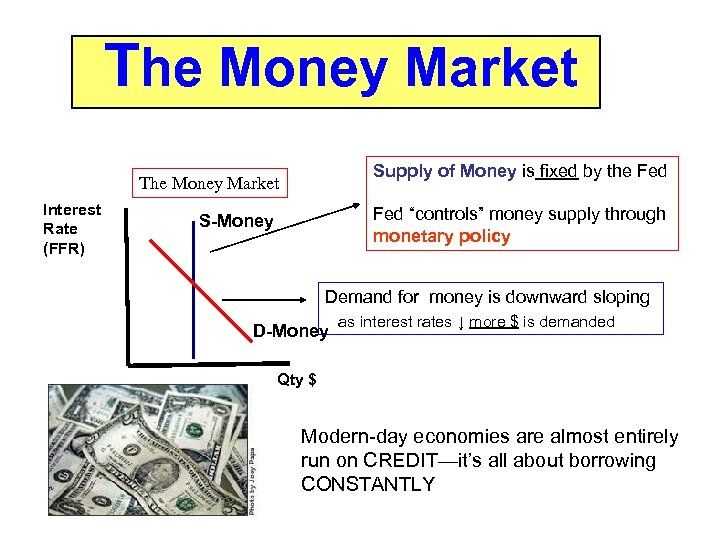 The Money Market Supply of Money is fixed by the Fed The Money Market Interest Rate (FFR) Fed “controls” money supply through monetary policy S-Money Demand for money is downward sloping D-Money as interest rates ↓ more $ is demanded Qty $ Modern-day economies are almost entirely run on CREDIT—it’s all about borrowing CONSTANTLY
The Money Market Supply of Money is fixed by the Fed The Money Market Interest Rate (FFR) Fed “controls” money supply through monetary policy S-Money Demand for money is downward sloping D-Money as interest rates ↓ more $ is demanded Qty $ Modern-day economies are almost entirely run on CREDIT—it’s all about borrowing CONSTANTLY
 Federal Reserve Structure Discount Rate=Interest rate that the Fed lends money directly to District Banks (rarely used) Meets. Federal Reserve to 8 times a year vote on Monetary Federal Open Board of Policy Market Committee= Governors (7 members) Ben Bernanke Chairman 7 Governors + 5 District Bank Presidents—meets 8 times per year Federal Funds Rate = Interest rate that the 12 District banks charge Each other on overnight loans SF Fed Building—Market Street 12 District Federal Reserve Banks Boston San Francisco New York Atlanta Chicago Dallas, etc. Member Banks All national banks Some state banks
Federal Reserve Structure Discount Rate=Interest rate that the Fed lends money directly to District Banks (rarely used) Meets. Federal Reserve to 8 times a year vote on Monetary Federal Open Board of Policy Market Committee= Governors (7 members) Ben Bernanke Chairman 7 Governors + 5 District Bank Presidents—meets 8 times per year Federal Funds Rate = Interest rate that the 12 District banks charge Each other on overnight loans SF Fed Building—Market Street 12 District Federal Reserve Banks Boston San Francisco New York Atlanta Chicago Dallas, etc. Member Banks All national banks Some state banks
 Two Tools of Monetary Policy 1. Discount Rate Changes • Changing the interest rate at which District Banks borrow directly from the Fed
Two Tools of Monetary Policy 1. Discount Rate Changes • Changing the interest rate at which District Banks borrow directly from the Fed
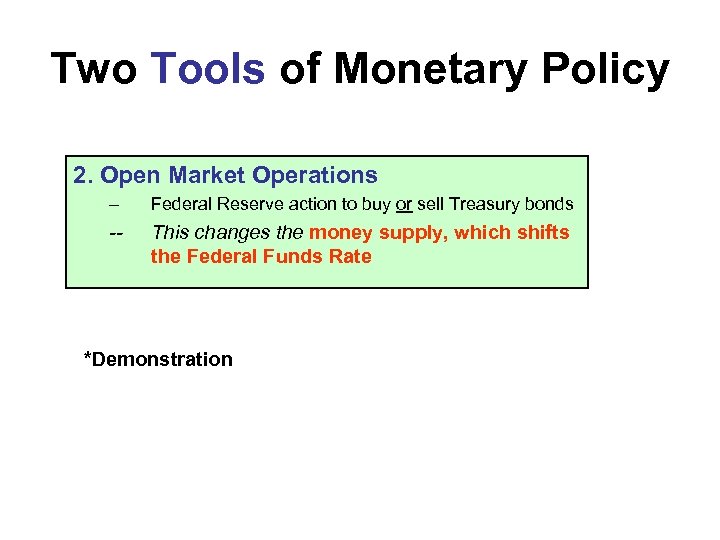 Two Tools of Monetary Policy 2. Open Market Operations – Federal Reserve action to buy or sell Treasury bonds -- This changes the money supply, which shifts the Federal Funds Rate *Demonstration
Two Tools of Monetary Policy 2. Open Market Operations – Federal Reserve action to buy or sell Treasury bonds -- This changes the money supply, which shifts the Federal Funds Rate *Demonstration
 7
7
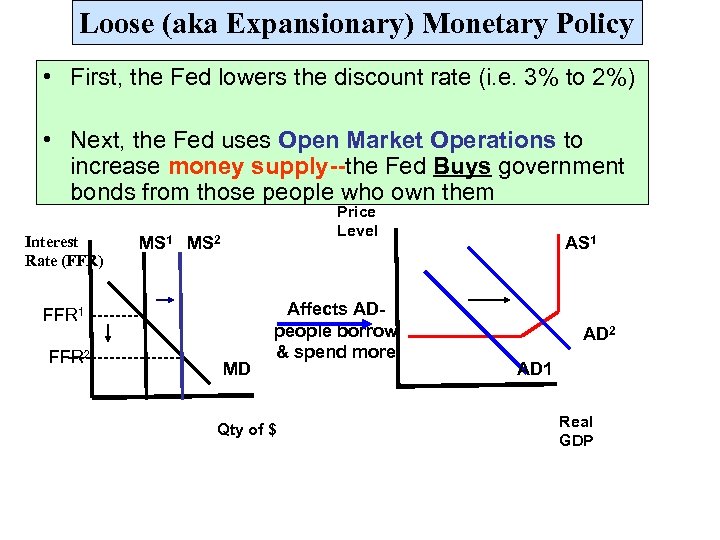 Loose (aka Expansionary) Monetary Policy • First, the Fed lowers the discount rate (i. e. 3% to 2%) • Next, the Fed uses Open Market Operations to increase money supply--the Fed Buys government bonds from those people who own them Interest Rate (FFR) Price Level MS 1 MS 2 FFR 1 ----FFR 2 ---------- MD Affects ADpeople borrow & spend more Qty of $ AS 1 AD 2 AD 1 Real GDP
Loose (aka Expansionary) Monetary Policy • First, the Fed lowers the discount rate (i. e. 3% to 2%) • Next, the Fed uses Open Market Operations to increase money supply--the Fed Buys government bonds from those people who own them Interest Rate (FFR) Price Level MS 1 MS 2 FFR 1 ----FFR 2 ---------- MD Affects ADpeople borrow & spend more Qty of $ AS 1 AD 2 AD 1 Real GDP
 Important Fact: Time Lag FYI: Both Fiscal Policy (6 -12 months) and Monetary Policy (12 -24 months) have a time lag Translation: they do not have immediate effect
Important Fact: Time Lag FYI: Both Fiscal Policy (6 -12 months) and Monetary Policy (12 -24 months) have a time lag Translation: they do not have immediate effect
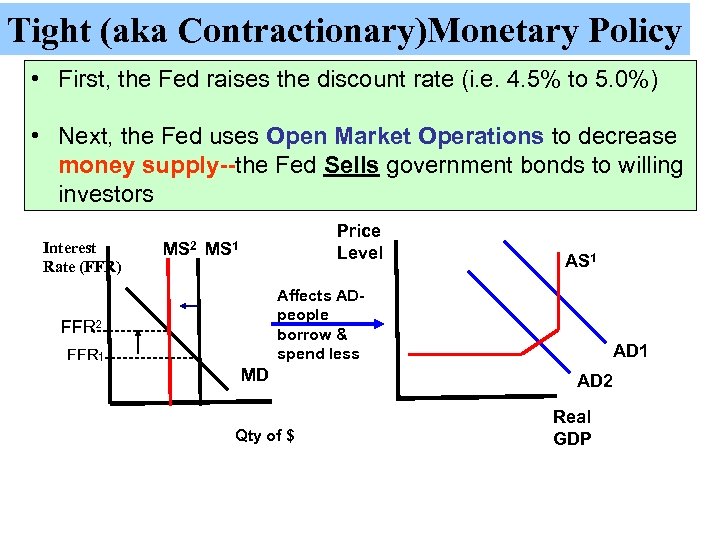 Tight (aka Contractionary)Monetary Policy • First, the Fed raises the discount rate (i. e. 4. 5% to 5. 0%) • Next, the Fed uses Open Market Operations to decrease money supply--the Fed Sells government bonds to willing investors Interest Rate (FFR) MS 2 Price Level MS 1 Affects ADpeople borrow & spend less FFR 2 ------FFR 1 -------- AS 1 MD Qty of $ AD 1 AD 2 Real GDP
Tight (aka Contractionary)Monetary Policy • First, the Fed raises the discount rate (i. e. 4. 5% to 5. 0%) • Next, the Fed uses Open Market Operations to decrease money supply--the Fed Sells government bonds to willing investors Interest Rate (FFR) MS 2 Price Level MS 1 Affects ADpeople borrow & spend less FFR 2 ------FFR 1 -------- AS 1 MD Qty of $ AD 1 AD 2 Real GDP
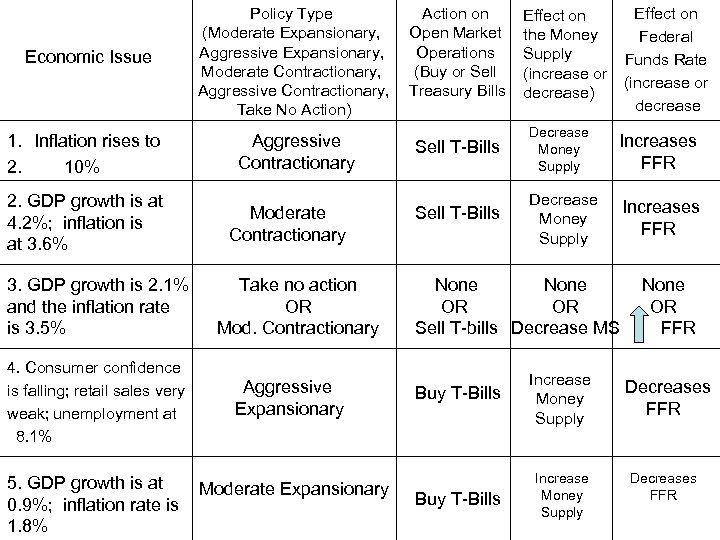 Economic Issue 1. Inflation rises to 2. 10% 2. GDP growth is at 4. 2%; inflation is at 3. 6% 3. GDP growth is 2. 1% and the inflation rate is 3. 5% 4. Consumer confidence is falling; retail sales very weak; unemployment at 8. 1% 5. GDP growth is at 0. 9%; inflation rate is 1. 8% Policy Type (Moderate Expansionary, Aggressive Expansionary, Moderate Contractionary, Aggressive Contractionary, Take No Action) Aggressive Contractionary Moderate Contractionary Take no action OR Mod. Contractionary Aggressive Expansionary Moderate Expansionary Action on Open Market Operations (Buy or Sell Treasury Bills Effect on Federal Funds Rate (increase or decrease Effect on the Money Supply (increase or decrease) Sell T-Bills Decrease Money Supply Increases FFR None OR OR Sell T-bills Decrease MS Buy T-Bills Increase Money Supply None OR FFR Decreases FFR
Economic Issue 1. Inflation rises to 2. 10% 2. GDP growth is at 4. 2%; inflation is at 3. 6% 3. GDP growth is 2. 1% and the inflation rate is 3. 5% 4. Consumer confidence is falling; retail sales very weak; unemployment at 8. 1% 5. GDP growth is at 0. 9%; inflation rate is 1. 8% Policy Type (Moderate Expansionary, Aggressive Expansionary, Moderate Contractionary, Aggressive Contractionary, Take No Action) Aggressive Contractionary Moderate Contractionary Take no action OR Mod. Contractionary Aggressive Expansionary Moderate Expansionary Action on Open Market Operations (Buy or Sell Treasury Bills Effect on Federal Funds Rate (increase or decrease Effect on the Money Supply (increase or decrease) Sell T-Bills Decrease Money Supply Increases FFR None OR OR Sell T-bills Decrease MS Buy T-Bills Increase Money Supply None OR FFR Decreases FFR
 News Clips http: //video. msn. com/video. aspx? mkt=en-us&vid=2 d 392 a 8 b-ac 77 -4 e 73 -8999 c 31 db 8966 b 68 ***(4: 29) good clip when Fed was considered cutting FFR from 1. 5% http: //video. msn. com/video. aspx? mkt=en-us&vid=5 dc 4 a 263 -0085 -4 db 0 -aecb-81 f 39870 a 9 (roundtable on FFR increase to 4. 75%) (7: 40) http: //video. google. com/videosearch? q=federal%20 funds%20 rate %20 suze%20 orman&rls=com. microsoft: *&oe=UTF-8&start. Index=&start Page=1&um=1&ie=UTF-8&sa=N&hl=en&tab=wv# (Suze Orman on FFR) (4: 32) http: //www. asterpix. com/v/8654211/fed-cuts-interest-rates/ ***(first 45 seconds of 2 minute clip)
News Clips http: //video. msn. com/video. aspx? mkt=en-us&vid=2 d 392 a 8 b-ac 77 -4 e 73 -8999 c 31 db 8966 b 68 ***(4: 29) good clip when Fed was considered cutting FFR from 1. 5% http: //video. msn. com/video. aspx? mkt=en-us&vid=5 dc 4 a 263 -0085 -4 db 0 -aecb-81 f 39870 a 9 (roundtable on FFR increase to 4. 75%) (7: 40) http: //video. google. com/videosearch? q=federal%20 funds%20 rate %20 suze%20 orman&rls=com. microsoft: *&oe=UTF-8&start. Index=&start Page=1&um=1&ie=UTF-8&sa=N&hl=en&tab=wv# (Suze Orman on FFR) (4: 32) http: //www. asterpix. com/v/8654211/fed-cuts-interest-rates/ ***(first 45 seconds of 2 minute clip)
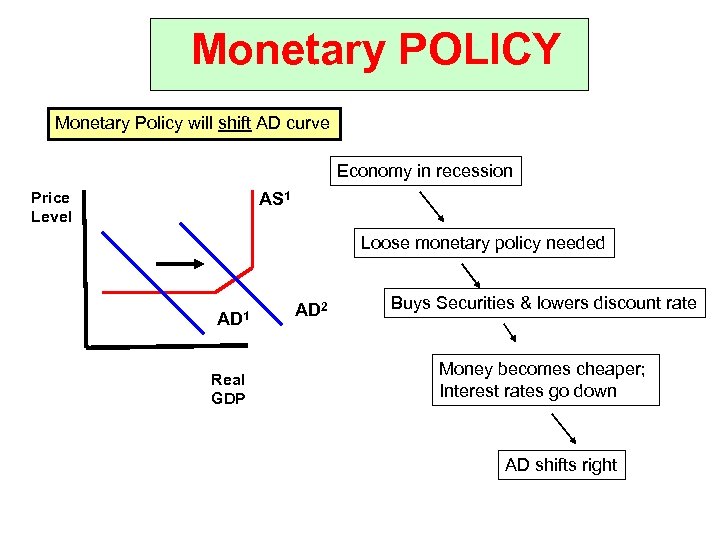 Monetary POLICY Monetary Policy will shift AD curve Economy in recession Price Level AS 1 Loose monetary policy needed AD 1 Real GDP AD 2 Buys Securities & lowers discount rate Money becomes cheaper; Interest rates go down AD shifts right
Monetary POLICY Monetary Policy will shift AD curve Economy in recession Price Level AS 1 Loose monetary policy needed AD 1 Real GDP AD 2 Buys Securities & lowers discount rate Money becomes cheaper; Interest rates go down AD shifts right
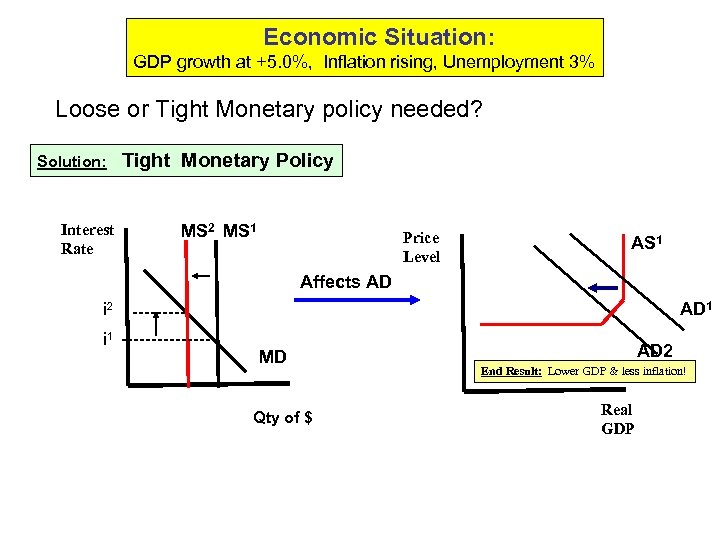 Economic Situation: GDP growth at +5. 0%, Inflation rising, Unemployment 3% Loose or Tight Monetary policy needed? Solution: Interest Rate Tight Monetary Policy MS 2 MS 1 Price Level AS 1 Affects AD i 2 AD 1 ----- i 1 -------- MD Qty of $ AD 2 End Result: Lower GDP & less inflation! Real GDP
Economic Situation: GDP growth at +5. 0%, Inflation rising, Unemployment 3% Loose or Tight Monetary policy needed? Solution: Interest Rate Tight Monetary Policy MS 2 MS 1 Price Level AS 1 Affects AD i 2 AD 1 ----- i 1 -------- MD Qty of $ AD 2 End Result: Lower GDP & less inflation! Real GDP
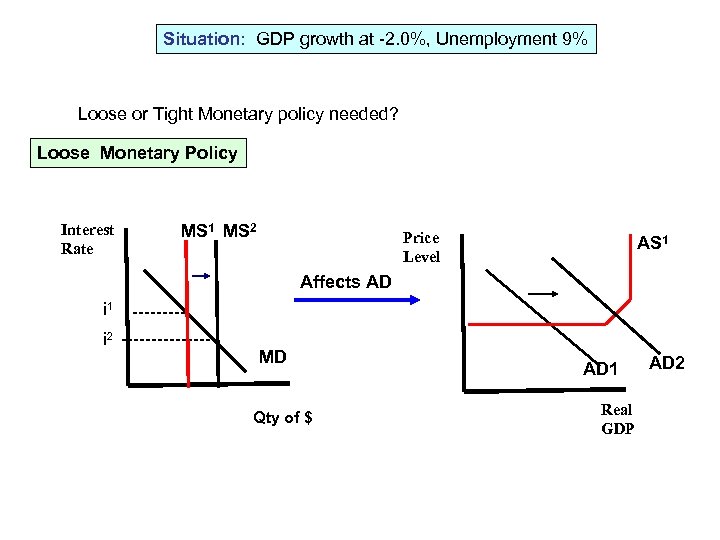 Situation: GDP growth at -2. 0%, Unemployment 9% Loose or Tight Monetary policy needed? Loose Monetary Policy Interest Rate MS 1 MS 2 Price Level AS 1 Affects AD i 1 ----- i 2 -------- MD Qty of $ AD 1 Real GDP AD 2
Situation: GDP growth at -2. 0%, Unemployment 9% Loose or Tight Monetary policy needed? Loose Monetary Policy Interest Rate MS 1 MS 2 Price Level AS 1 Affects AD i 1 ----- i 2 -------- MD Qty of $ AD 1 Real GDP AD 2
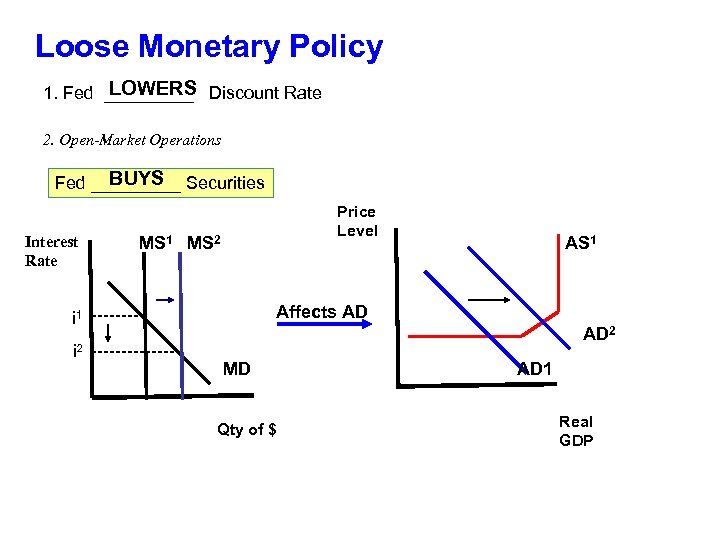 Loose Monetary Policy LOWERS 1. Fed _____ Discount Rate 2. Open-Market Operations BUYS Fed _____ Securities Interest Rate Price Level MS 1 MS 2 Affects AD i 1 ----i 2 -------- AS 1 AD 2 MD Qty of $ AD 1 Real GDP
Loose Monetary Policy LOWERS 1. Fed _____ Discount Rate 2. Open-Market Operations BUYS Fed _____ Securities Interest Rate Price Level MS 1 MS 2 Affects AD i 1 ----i 2 -------- AS 1 AD 2 MD Qty of $ AD 1 Real GDP
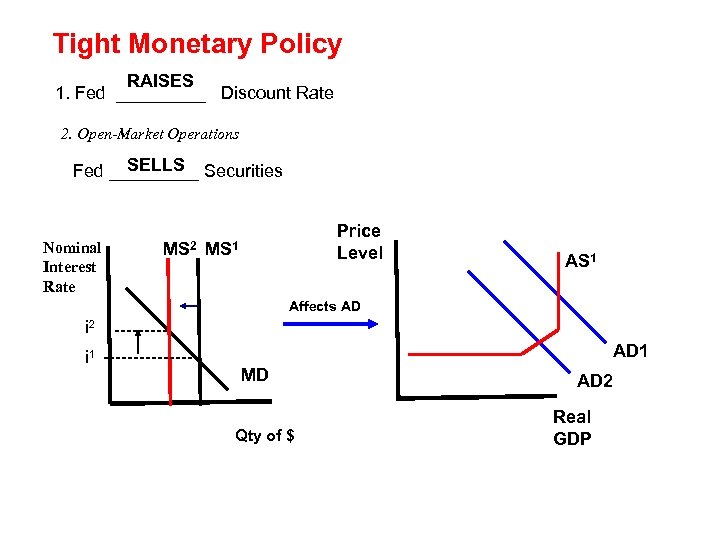 Tight Monetary Policy RAISES 1. Fed _____ Discount Rate 2. Open-Market Operations SELLS Fed _____ Securities Nominal Interest Rate MS 2 Price Level MS 1 Affects AD i 2 ----- i 1 -------- AD 1 MD Qty of $ AD 2 Real GDP
Tight Monetary Policy RAISES 1. Fed _____ Discount Rate 2. Open-Market Operations SELLS Fed _____ Securities Nominal Interest Rate MS 2 Price Level MS 1 Affects AD i 2 ----- i 1 -------- AD 1 MD Qty of $ AD 2 Real GDP


