 Monetary policy 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Open market operations Discount rate Reserve requirements Foreign exchange intervention Central Bank’s objectives Monetary expansion & restriction Targeting
Monetary policy 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Open market operations Discount rate Reserve requirements Foreign exchange intervention Central Bank’s objectives Monetary expansion & restriction Targeting
 Open-market operations Central Bank buys government securities using newly created money, or sells them to influence amount of money. Thus it can be increased (by buying securities) or decreased (by selling them).
Open-market operations Central Bank buys government securities using newly created money, or sells them to influence amount of money. Thus it can be increased (by buying securities) or decreased (by selling them).
 Discount rate is the rate at which central bank is ready to loan reserves to member banks. Thus CB can perform the role of last resort lender for commercial banks. Using the rate CB can influence rates in the money market, where commercial banks lend money to each other. When CB decreases the rate resources in MM become cheaper and vice versa.
Discount rate is the rate at which central bank is ready to loan reserves to member banks. Thus CB can perform the role of last resort lender for commercial banks. Using the rate CB can influence rates in the money market, where commercial banks lend money to each other. When CB decreases the rate resources in MM become cheaper and vice versa.
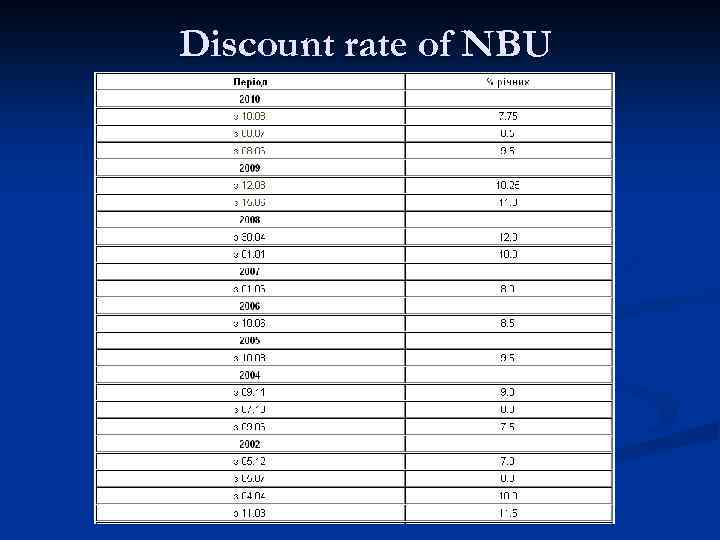 Discount rate of NBU
Discount rate of NBU
 Reserve requirements
Reserve requirements
 Reserve requirements Reserve Requirement is a fraction of bank’s liabilities, which is to be held according to Central Bank’s demand to maintain the stability of banking system. When CB decreases requirements amount of money increases and vice versa. This tool is considered rather blunt in comparison to open market operations.
Reserve requirements Reserve Requirement is a fraction of bank’s liabilities, which is to be held according to Central Bank’s demand to maintain the stability of banking system. When CB decreases requirements amount of money increases and vice versa. This tool is considered rather blunt in comparison to open market operations.
 Foreign exchange intervention Central bank get directly involved with the foreign exchange market by either buying or selling currency in an attempt to drive the exchange rate in a particular direction. There two types of foreign exchange interventions: sterilized and non-sterilized.
Foreign exchange intervention Central bank get directly involved with the foreign exchange market by either buying or selling currency in an attempt to drive the exchange rate in a particular direction. There two types of foreign exchange interventions: sterilized and non-sterilized.
 Sterilized foreign exchange interventions Buying foreign currency CB sells national currency and therefore increases it’s amount. To avoid it CB can issue deposit certificates, which will bind excess amount of money and prevent inflation. Non-sterilized foreign exchange interventions do not involve this type of transactions.
Sterilized foreign exchange interventions Buying foreign currency CB sells national currency and therefore increases it’s amount. To avoid it CB can issue deposit certificates, which will bind excess amount of money and prevent inflation. Non-sterilized foreign exchange interventions do not involve this type of transactions.
 Central Bank’s objectives Strategic – basic macroeconomic goals like high level of production development, low unemployment level, low inflation rate, etc. n Intermediate – indicators, which shows to the central bank whether it’s policy is effective. Because there is a time gap between usage of a tool and the result of this action. Example – M 3. n Tactic – depend on the CB’s decision only, like discount rate, reserve requirements, etc n
Central Bank’s objectives Strategic – basic macroeconomic goals like high level of production development, low unemployment level, low inflation rate, etc. n Intermediate – indicators, which shows to the central bank whether it’s policy is effective. Because there is a time gap between usage of a tool and the result of this action. Example – M 3. n Tactic – depend on the CB’s decision only, like discount rate, reserve requirements, etc n
 Monetary expansion (cheap money policy) means fast money supply increase due to which money are quickly becoming cheap, while inflation is showing high rates. This type of policy is used to boost effective demand and, thus, to stimulate economic development. As a rule this policy results in high-rate inflation. Because at the first stage of this policy use excess demand cause prices to grow, but increasing in production amount comes later.
Monetary expansion (cheap money policy) means fast money supply increase due to which money are quickly becoming cheap, while inflation is showing high rates. This type of policy is used to boost effective demand and, thus, to stimulate economic development. As a rule this policy results in high-rate inflation. Because at the first stage of this policy use excess demand cause prices to grow, but increasing in production amount comes later.
 Monetary restriction (expensive money policy) means sharp reduction of money supply in circulation, in most cases to slow down inflation. This objective can be reached by increase of discount rate, reserve requirements, decreasing refinancing amounts, selling government securities. But this policy also slows down economic development because of high price of money (expensive credits).
Monetary restriction (expensive money policy) means sharp reduction of money supply in circulation, in most cases to slow down inflation. This objective can be reached by increase of discount rate, reserve requirements, decreasing refinancing amounts, selling government securities. But this policy also slows down economic development because of high price of money (expensive credits).
 Targeting means that central bank chooses the main goal of its monetary policy and uses all it’s tools to reach it. Because CB has not so many tools to influence economy and that’s why it has to choose it’s objectives. There are inflation targeting (the most popular nowadays), exchange rate targeting, money amount targeting, etc.
Targeting means that central bank chooses the main goal of its monetary policy and uses all it’s tools to reach it. Because CB has not so many tools to influence economy and that’s why it has to choose it’s objectives. There are inflation targeting (the most popular nowadays), exchange rate targeting, money amount targeting, etc.
 Inflation targeting is an economic policy in which a central bank estimates and makes public a projected, or "target", inflation rate and then attempts to steer actual inflation towards the target through the use of interest rate changes and other monetary tools.
Inflation targeting is an economic policy in which a central bank estimates and makes public a projected, or "target", inflation rate and then attempts to steer actual inflation towards the target through the use of interest rate changes and other monetary tools.


