342171d03ee5bfcdd3d68a47ff5d14ec.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42

MOLECULAR BIOLOGY – Basic Genetics EXAMS – SAVE THE DATE! KMB 758 MCQ The exam format will be a multiple choice question (MCQ) test with 40 questions. There will be two possible exam dates. Please mark them in your diaries. Should you fail or are not satisfied with your grade you can have an aural retake exam with me.

Potential revision Class next time!! Alexander Bruce Ph. D. Aleksandar Mihajlovic M. Sc. USUAL TIME & PLACE 10 am in lecture theatre Giorgio Virnicchi M. Sc.
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY – Gene expression analysis MOLECULAR BIOLOGY TECHNIQUES III. analysis of gene expression
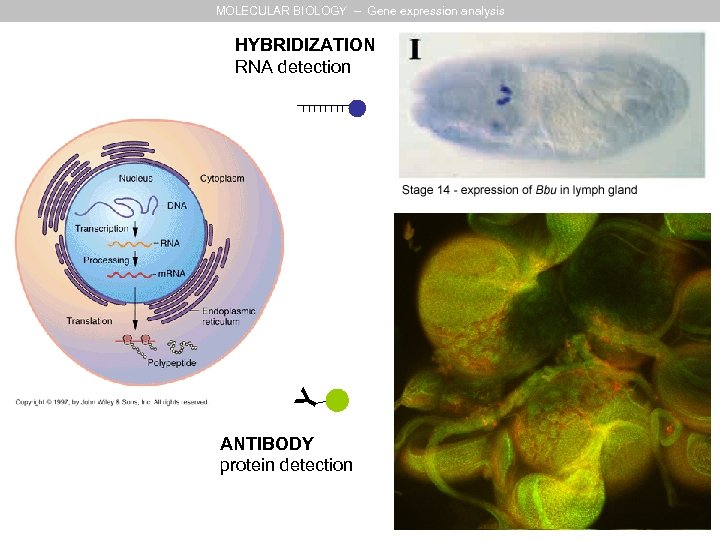
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY – Gene expression analysis Y HYBRIDIZATION RNA detection ANTIBODY protein detection
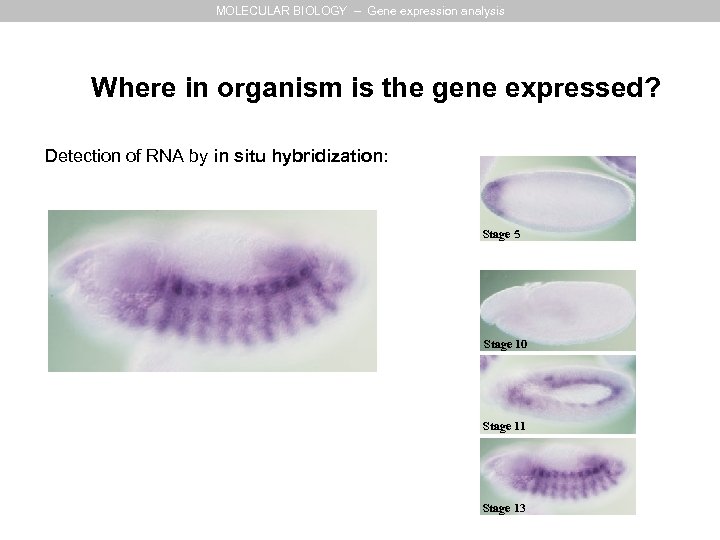
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY – Gene expression analysis Where in organism is the gene expressed? Detection of RNA by in situ hybridization: Stage 5 Stage 10 Stage 11 Stage 13
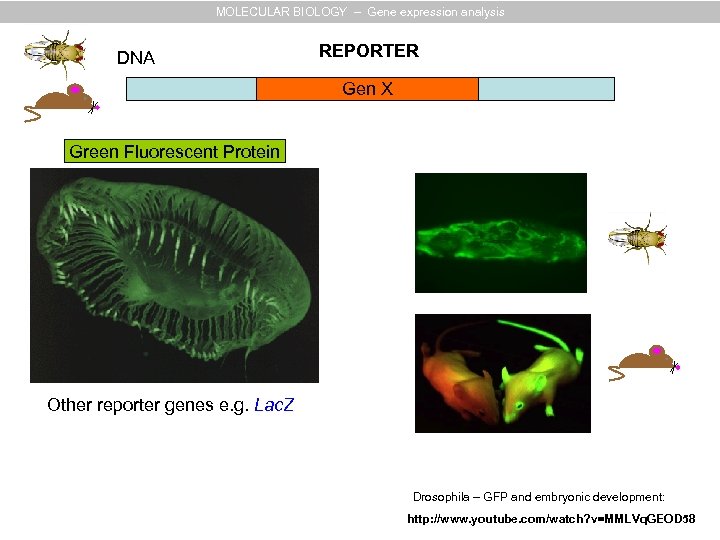
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY – Gene expression analysis DNA REPORTER Gen X Green Fluorescent Protein Other reporter genes e. g. Lac. Z Drosophila – GFP and embryonic development: http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=MMLVq. GEOD 58
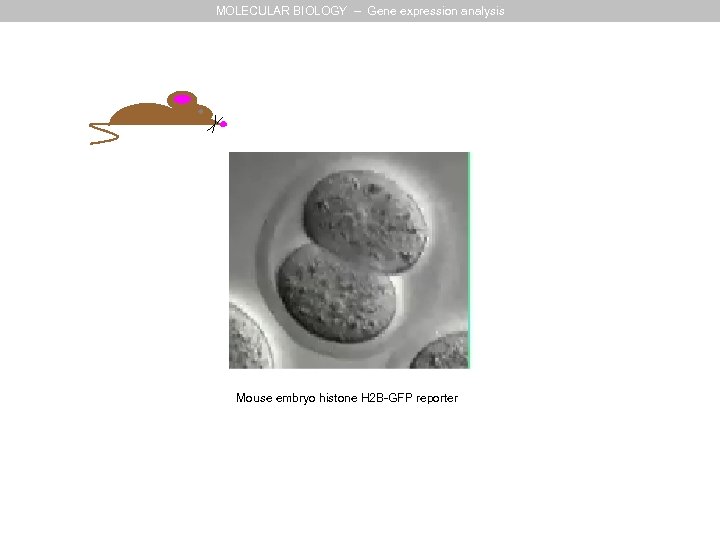
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY – Gene expression analysis Mouse embryo histone H 2 B-GFP reporter
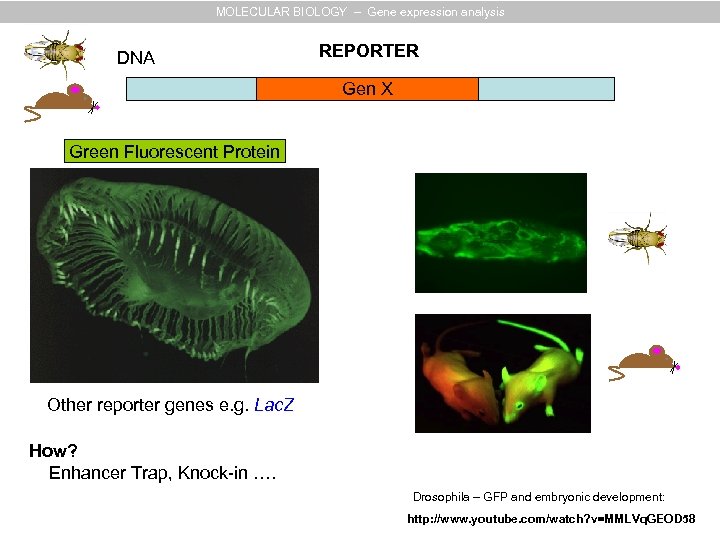
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY – Gene expression analysis DNA REPORTER Gen X Green Fluorescent Protein Other reporter genes e. g. Lac. Z How? Enhancer Trap, Knock-in …. Drosophila – GFP and embryonic development: http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=MMLVq. GEOD 58
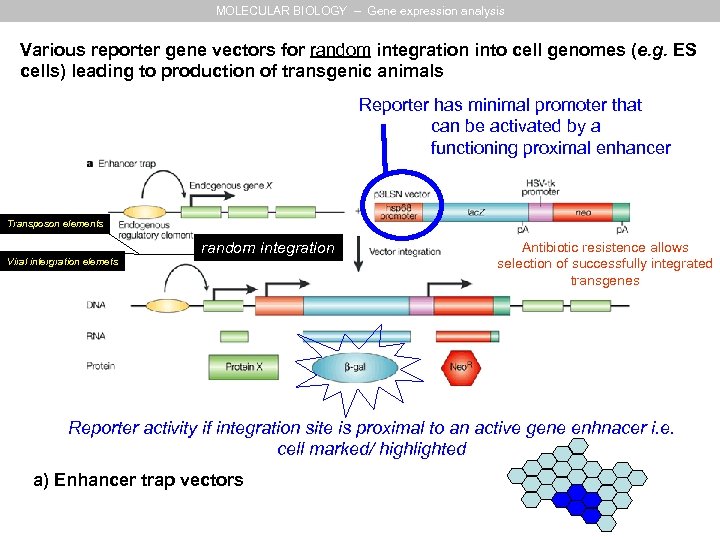
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY – Gene expression analysis Various reporter gene vectors for random integration into cell genomes (e. g. ES cells) leading to production of transgenic animals Reporter has minimal promoter that can be activated by a functioning proximal enhancer Transposon elements Viral intergration elemets random integration Antibiotic resistence allows selection of successfully integrated transgenes Reporter activity if integration site is proximal to an active gene enhnacer i. e. cell marked/ highlighted a) Enhancer trap vectors
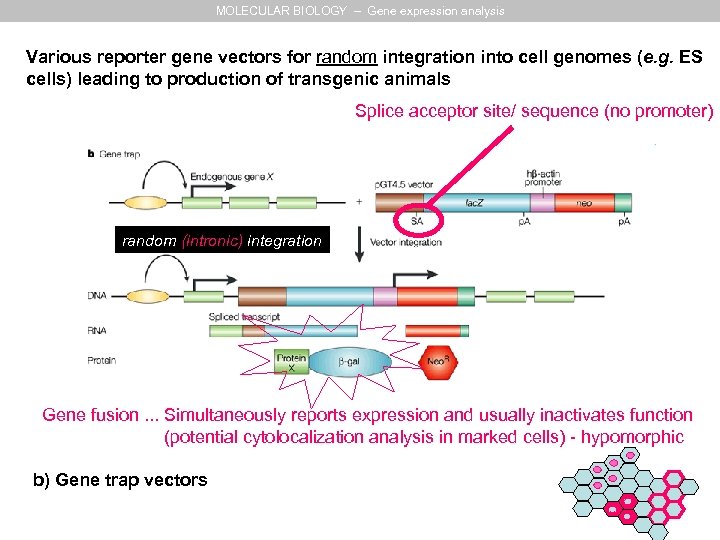
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY – Gene expression analysis Various reporter gene vectors for random integration into cell genomes (e. g. ES cells) leading to production of transgenic animals Splice acceptor site/ sequence (no promoter) random (intronic) integration Gene fusion. . . Simultaneously reports expression and usually inactivates function (potential cytolocalization analysis in marked cells) - hypomorphic b) Gene trap vectors
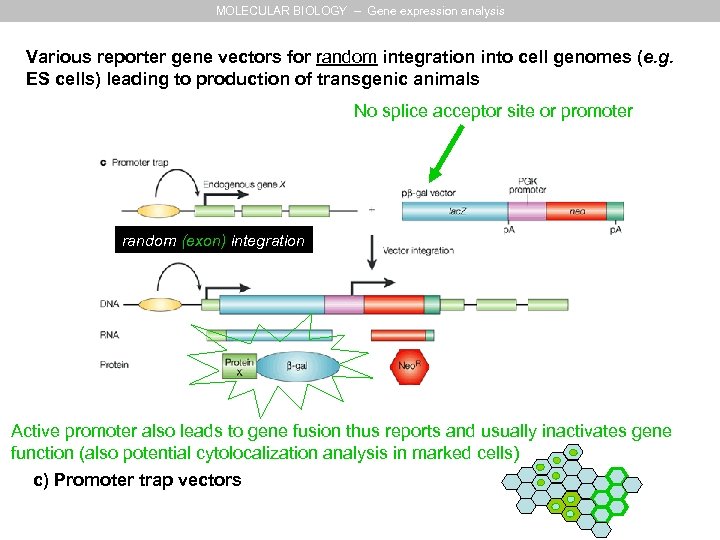
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY – Gene expression analysis Various reporter gene vectors for random integration into cell genomes (e. g. ES cells) leading to production of transgenic animals No splice acceptor site or promoter random (exon) integration Active promoter also leads to gene fusion thus reports and usually inactivates gene function (also potential cytolocalization analysis in marked cells) c) Promoter trap vectors
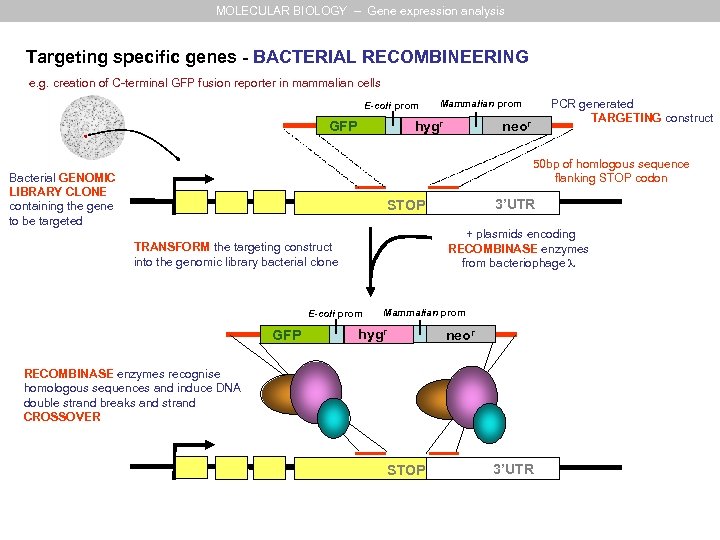
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY – Gene expression analysis Targeting specific genes - BACTERIAL RECOMBINEERING e. g. creation of C-terminal GFP fusion reporter in mammalian cells E-coli prom hygr GFP PCR generated TARGETING construct Mammalian prom neor 50 bp of homlogous sequence flanking STOP codon Bacterial GENOMIC LIBRARY CLONE containing the gene to be targeted 3’UTR STOP + plasmids encoding RECOMBINASE enzymes from bacteriophage TRANSFORM the targeting construct into the genomic library bacterial clone E-coli prom GFP Mammalian prom hygr neor RECOMBINASE enzymes recognise homologous sequences and induce DNA double strand breaks and strand CROSSOVER STOP 3’UTR
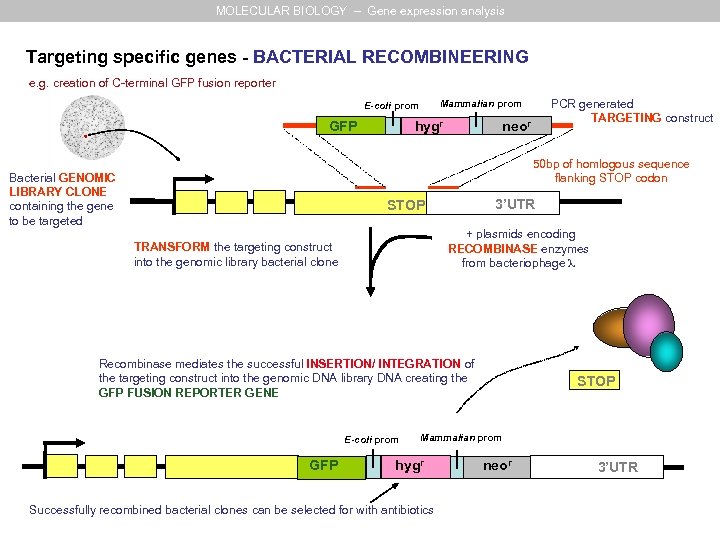
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY – Gene expression analysis Targeting specific genes - BACTERIAL RECOMBINEERING e. g. creation of C-terminal GFP fusion reporter hygr GFP PCR generated TARGETING construct Mammalian prom E-coli prom neor 50 bp of homlogous sequence flanking STOP codon Bacterial GENOMIC LIBRARY CLONE containing the gene to be targeted 3’UTR STOP + plasmids encoding RECOMBINASE enzymes from bacteriophage TRANSFORM the targeting construct into the genomic library bacterial clone Recombinase mediates the successful INSERTION/ INTEGRATION of the targeting construct into the genomic DNA library DNA creating the GFP FUSION REPORTER GENE E-coli prom GFP STOP Mammalian prom hygr Successfully recombined bacterial clones can be selected for with antibiotics neor 3’UTR
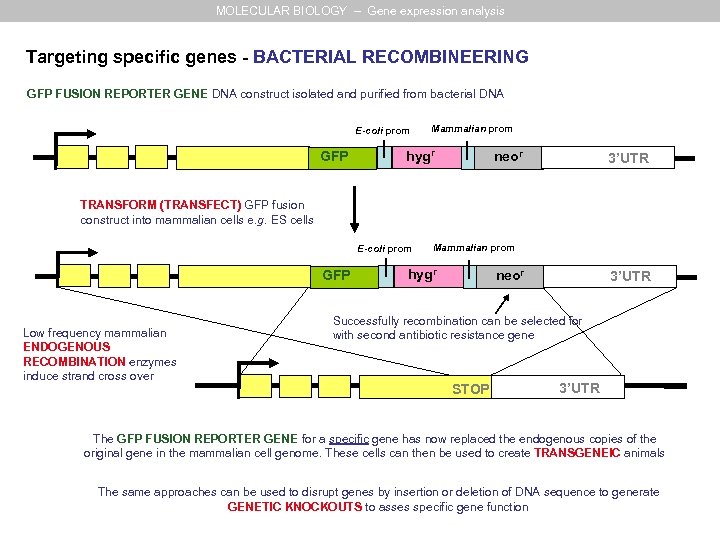
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY – Gene expression analysis Targeting specific genes - BACTERIAL RECOMBINEERING GFP FUSION REPORTER GENE DNA construct isolated and purified from bacterial DNA E-coli prom GFP Mammalian prom hygr neor 3’UTR TRANSFORM (TRANSFECT) GFP fusion construct into mammalian cells e. g. ES cells E-coli prom GFP Low frequency mammalian ENDOGENOUS RECOMBINATION enzymes induce strand cross over Mammalian prom hygr neor 3’UTR Successfully recombination can be selected for with second antibiotic resistance gene STOP 3’UTR The GFP FUSION REPORTER GENE for a specific gene has now replaced the endogenous copies of the original gene in the mammalian cell genome. These cells can then be used to create TRANSGENEIC animals The same approaches can be used to disrupt genes by insertion or deletion of DNA sequence to generate GENETIC KNOCKOUTS to asses specific gene function
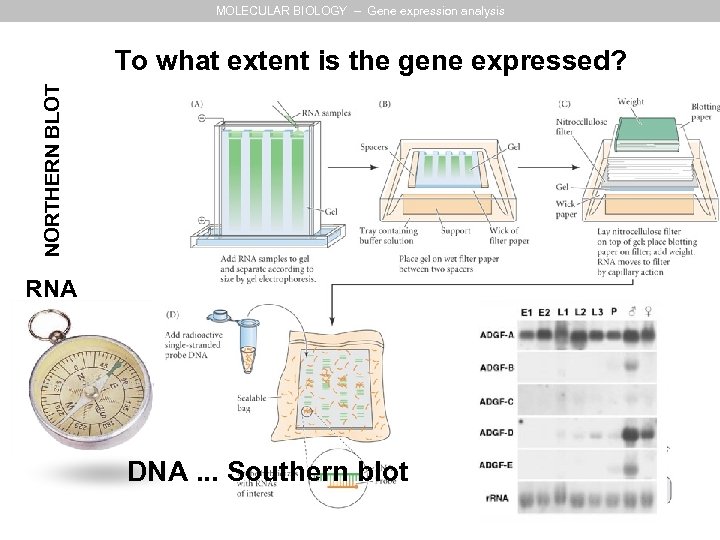
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY – Gene expression analysis NORTHERN BLOT To what extent is the gene expressed? RNA DNA. . . Southern blot
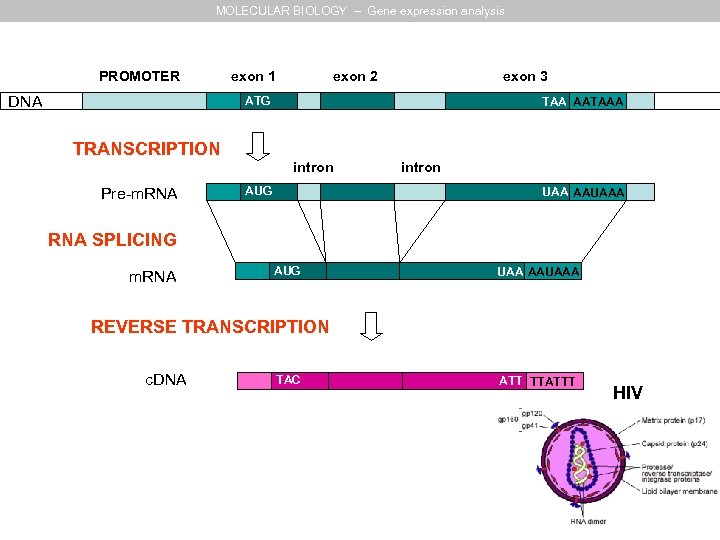
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY – Gene expression analysis PROMOTER DNA exon 1 exon 2 exon 3 ATG TAA AATAAA TRANSCRIPTION intron Pre-m. RNA AUG intron UAA AAUAAA RNA SPLICING m. RNA AUG UAA AAUAAA REVERSE TRANSCRIPTION c. DNA TAC ATT TTATTT HIV
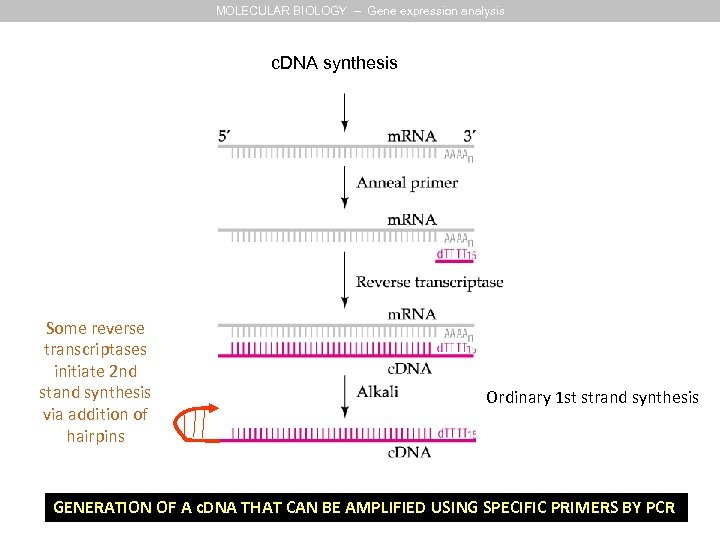
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY – Gene expression analysis c. DNA synthesis Some reverse transcriptases initiate 2 nd stand synthesis via addition of hairpins Ordinary 1 st strand synthesis GENERATION OF A c. DNA THAT CAN BE AMPLIFIED USING SPECIFIC PRIMERS BY PCR
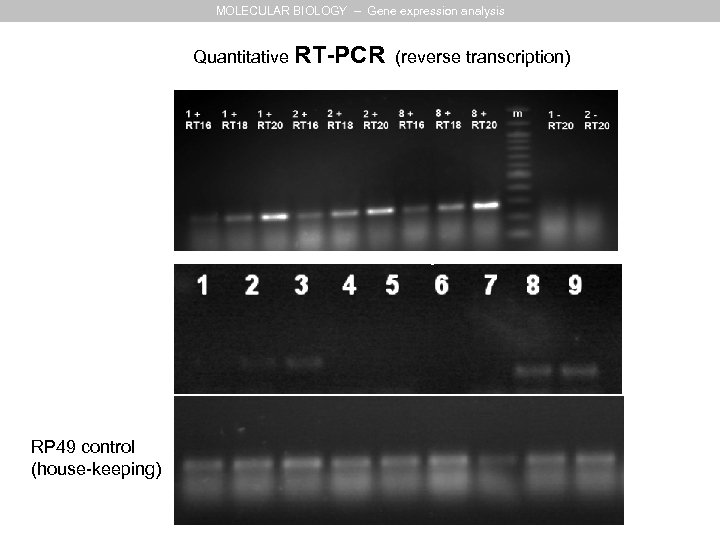
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY – Gene expression analysis Quantitative RT-PCR (reverse transcription) RP 49 control (house-keeping)
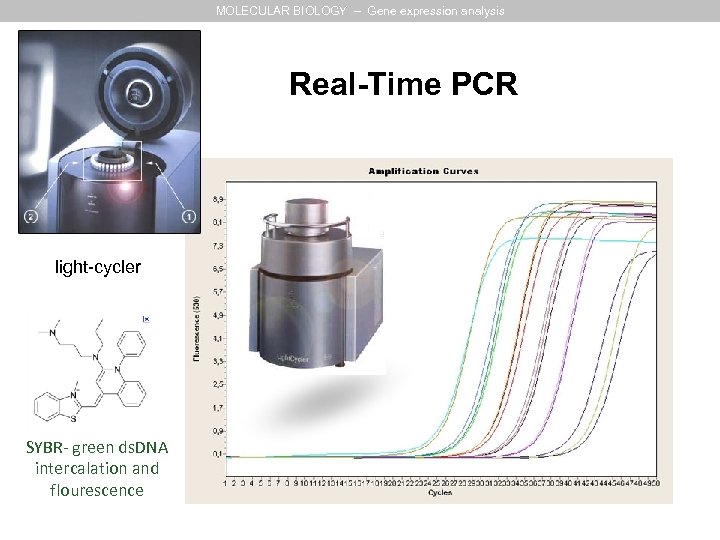
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY – Gene expression analysis Real-Time PCR light-cycler SYBR- green ds. DNA intercalation and flourescence
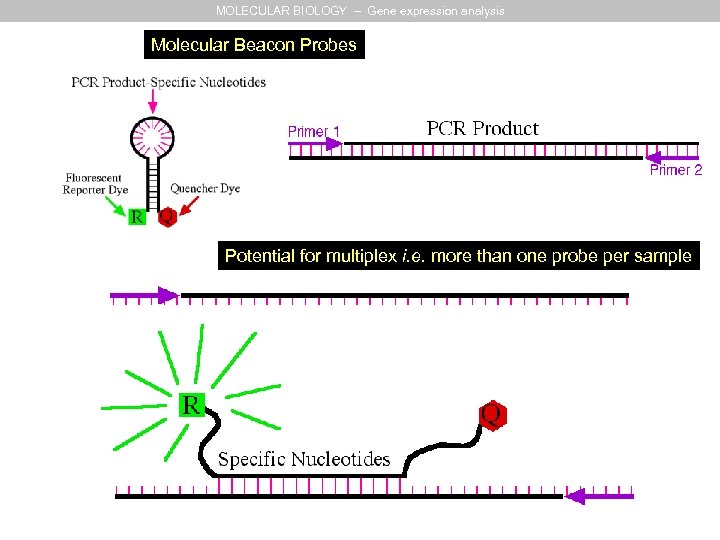
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY – Gene expression analysis Molecular Beacon Probes Potential for multiplex i. e. more than one probe per sample

MOLECULAR BIOLOGY – Gene expression analysis Norhern blot, RT-PCR to study one (couple) gene(s) at once. . . in genomic era?
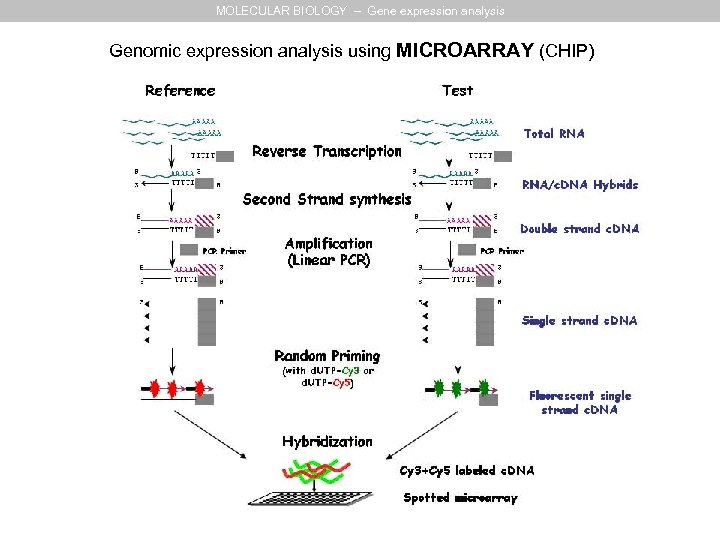
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY – Gene expression analysis Genomic expression analysis using MICROARRAY (CHIP)
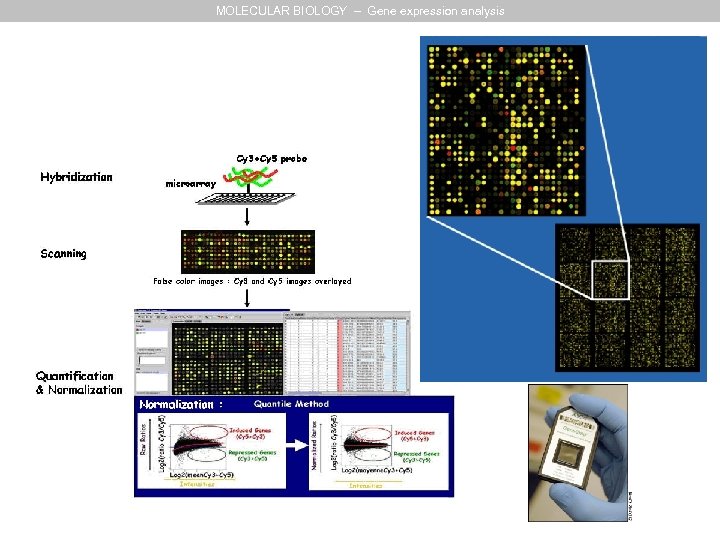
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY – Gene expression analysis
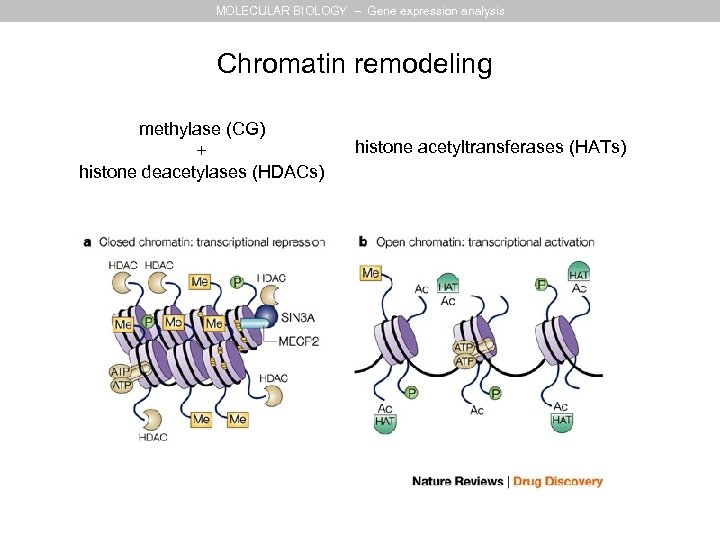
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY – Gene expression analysis Chromatin remodeling methylase (CG) + histone deacetylases (HDACs) histone acetyltransferases (HATs)
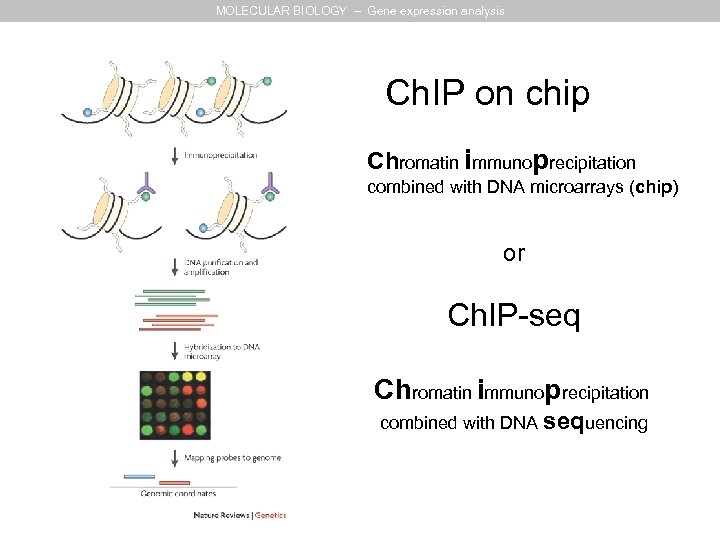
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY – Gene expression analysis Ch. IP on chip Chromatin immunoprecipitation combined with DNA microarrays (chip) or Ch. IP-seq Chromatin immunoprecipitation combined with DNA sequencing
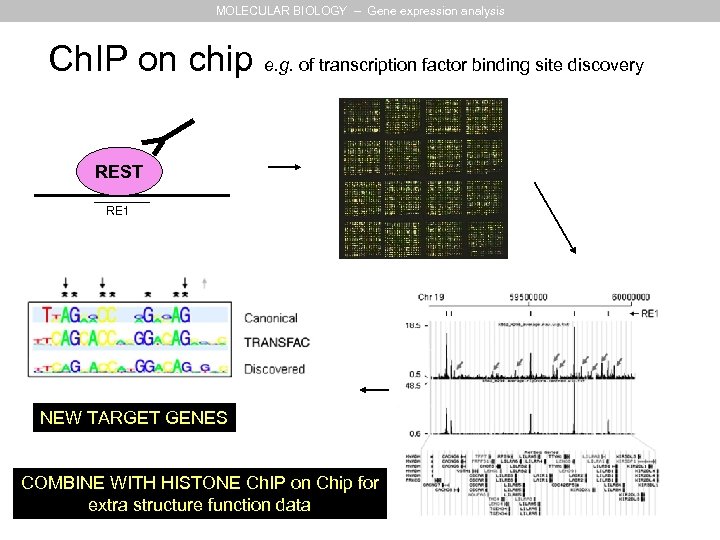
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY – Gene expression analysis Ch. IP on chip e. g. of transcription factor binding site discovery REST RE 1 NEW TARGET GENES COMBINE WITH HISTONE Ch. IP on Chip for extra structure function data
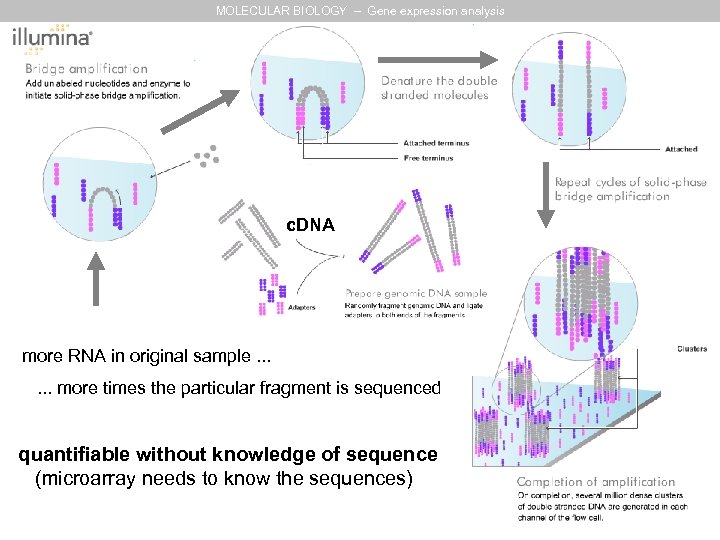
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY – Gene expression analysis c. DNA more RNA in original sample. . . more times the particular fragment is sequenced quantifiable without knowledge of sequence (microarray needs to know the sequences)
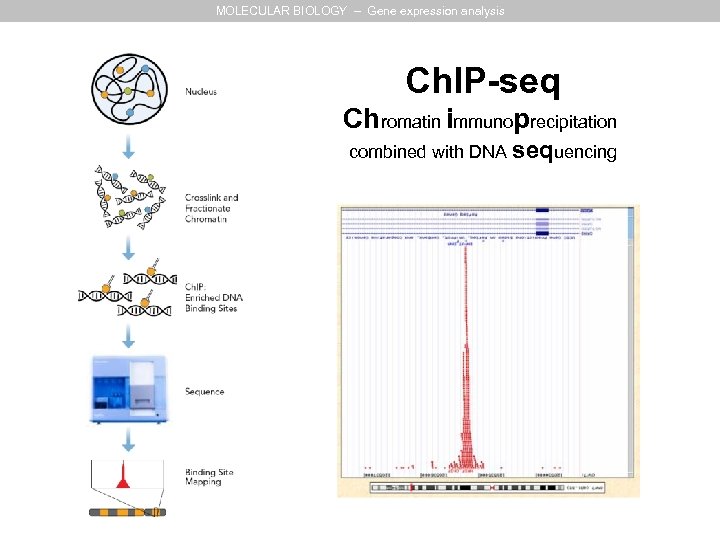
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY – Gene expression analysis Ch. IP-seq Chromatin immunoprecipitation combined with DNA sequencing
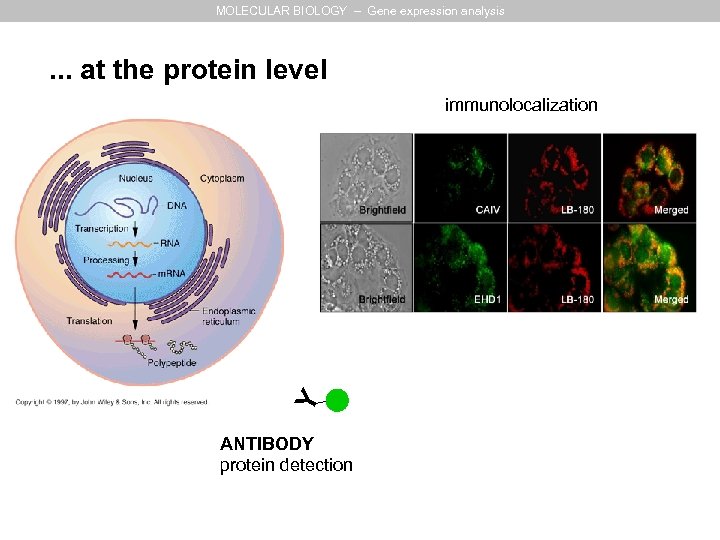
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY – Gene expression analysis . . . at the protein level Y immunolocalization ANTIBODY protein detection
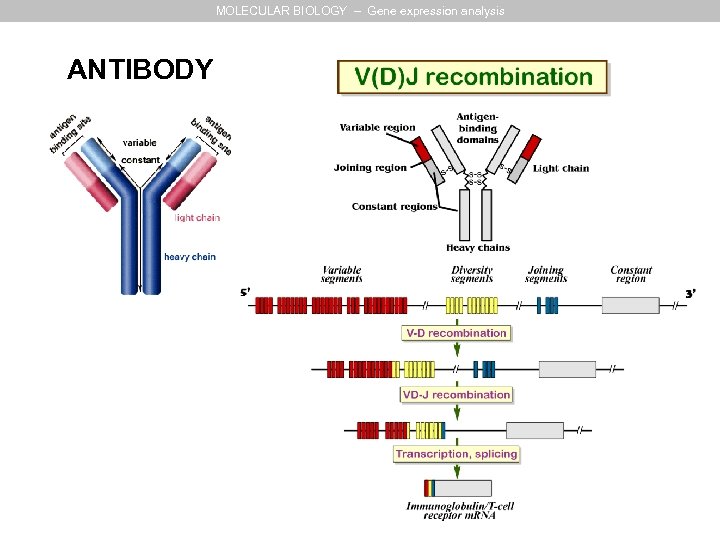
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY – Gene expression analysis ANTIBODY
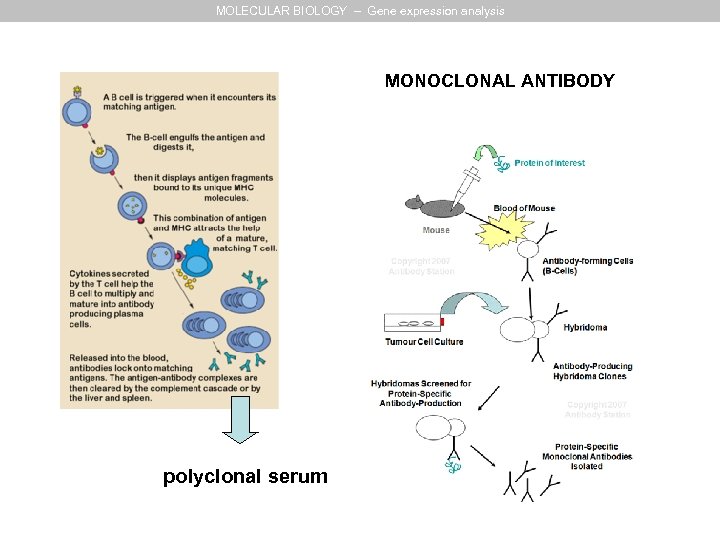
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY – Gene expression analysis MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY polyclonal serum
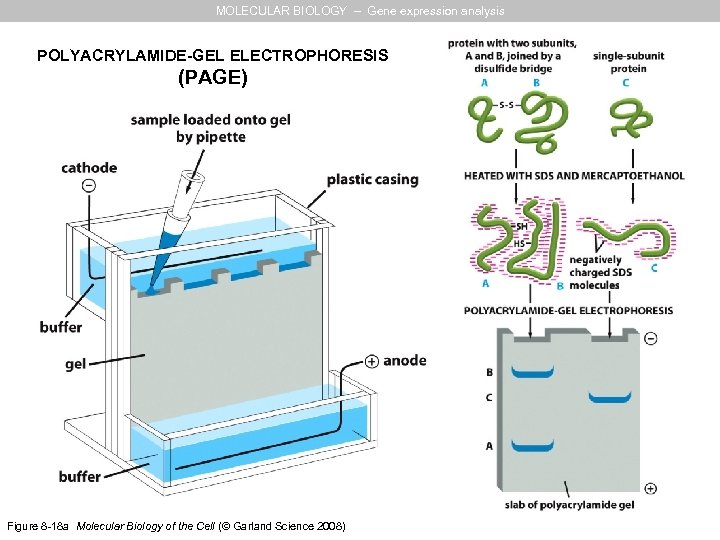
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY – Gene expression analysis POLYACRYLAMIDE-GEL ELECTROPHORESIS (PAGE) Figure 8 -18 a Molecular Biology of the Cell (© Garland Science 2008)
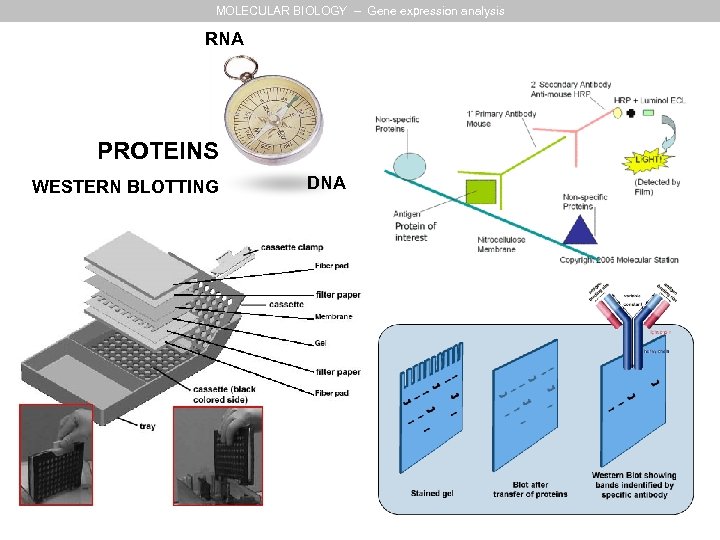
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY – Gene expression analysis RNA PROTEINS WESTERN BLOTTING DNA
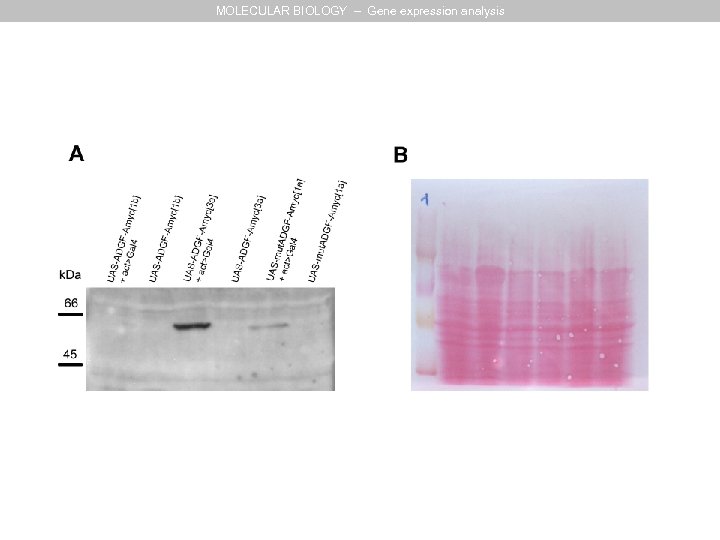
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY – Gene expression analysis
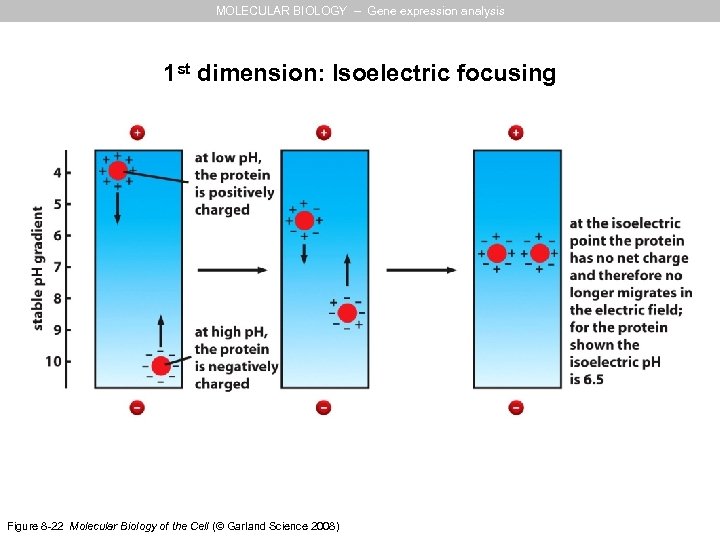
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY – Gene expression analysis 1 st dimension: Isoelectric focusing Figure 8 -22 Molecular Biology of the Cell (© Garland Science 2008)
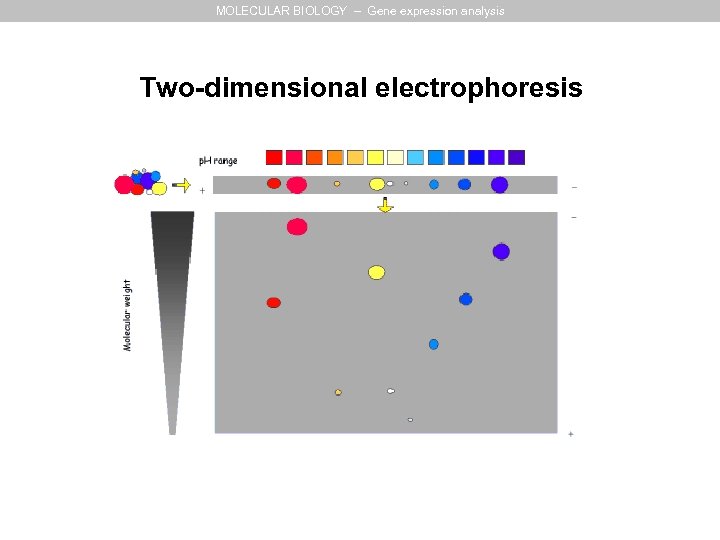
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY – Gene expression analysis Two-dimensional electrophoresis
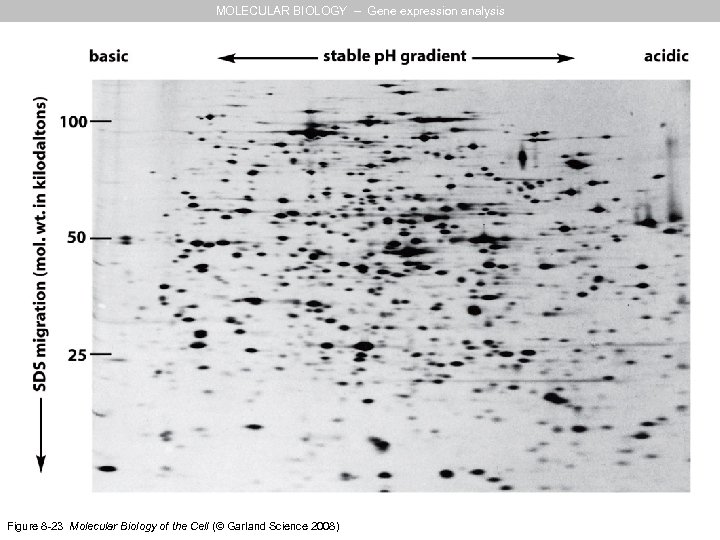
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY – Gene expression analysis Figure 8 -23 Molecular Biology of the Cell (© Garland Science 2008)

MOLECULAR BIOLOGY – Gene expression analysis PROTEOMICS What is the difference on B? identification by mass spectroscopy
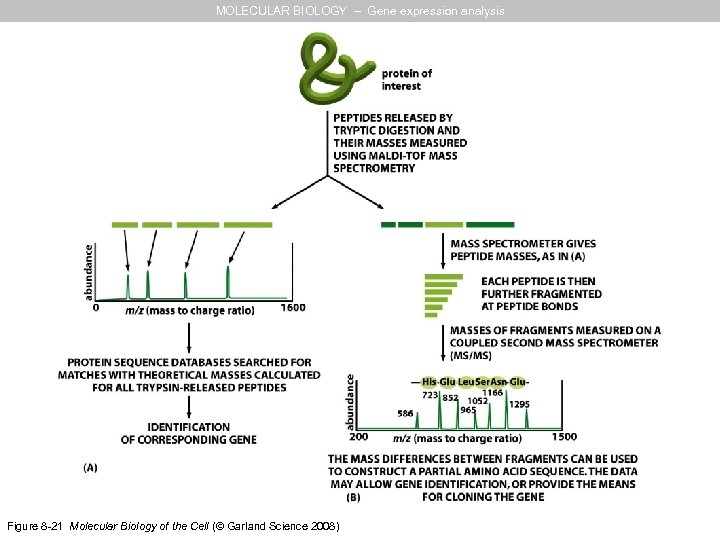
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY – Gene expression analysis Figure 8 -21 Molecular Biology of the Cell (© Garland Science 2008)
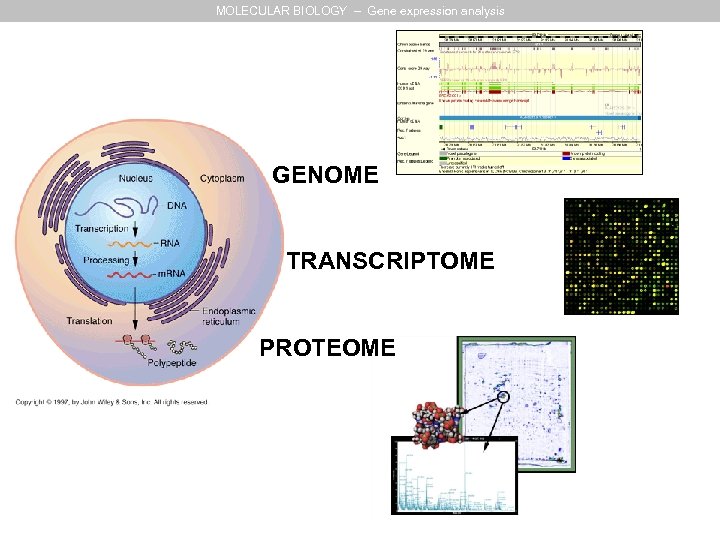
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY – Gene expression analysis GENOME TRANSCRIPTOME PROTEOME
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY – Gene expression analysis Good Luck E. . . AG P GE, A C GE, SA with molecular biology! RNA GE NO MI C S S OMIC SCRIPT TRAN PR OT EO MI CS PROTEINS RT-PCR Real-Time PCR Inverse PCR Nested PCR P FL R LP AF DNA

Potential revision Class next time!! Alexander Bruce Ph. D. Aleksandar Mihajlovic M. Sc. USUAL TIME & PLACE 10 am in lecture theatre Giorgio Virnicchi M. Sc.
342171d03ee5bfcdd3d68a47ff5d14ec.ppt