b21b9fcb41a0c93489675705107bcfdf.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17

Mojo in Kildare Presentation 1 st September 2016

Format 1. Local Context 2. LCDC role in relation to Mojo 3. Roll out of Mojo to date 4. Assessment of the programme in Kildare 5. Next steps
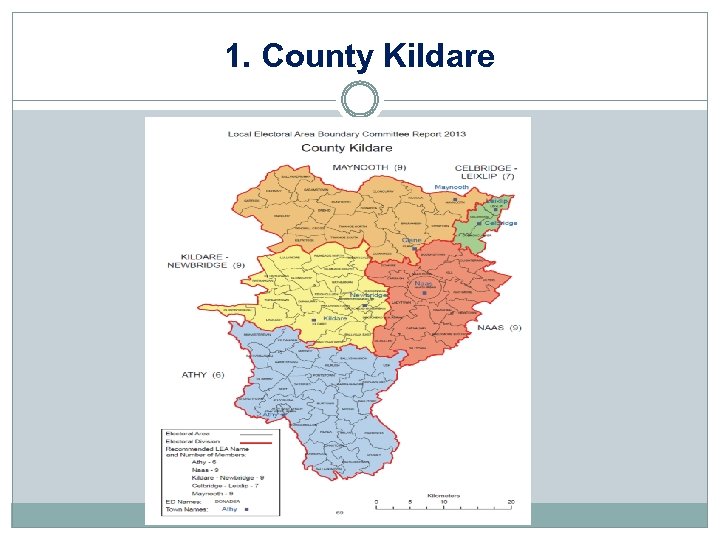
1. County Kildare

1. Urban- Ireland

1. Kildare

1. Kildare

1. Some Facts About Kildare 2011 - Total Population of Kildare 210, 212 Over 20 years, the population has grown by 71. 5% Kildare is the fifth most populated local authority in the state Over 60% of the population live in 10 largest towns No town in Kildare with a population of 25, 000 or more Kildare is a commuting county- almost 40% of residents work outside the county
1. Facts continued Kildare has the highest rate of young people (0 -24) in the country – 77, 832 It has amongst the lowest levels of services across all indices- Gardai, GP, mental health, classroom size, family resource centres…………. Only Dublin and Cork have higher numbers of people in receipt of rent supplement (4, 135) Growth No service Challenge ? ?

1. Why Mojo in Kildare? Community concerns regarding deaths by suicide In 2013, Kildare had the fourth highest number of deaths by suicide nationally One young person per week, under 17 presented to hospital as a result of self harm However, Dublin SW/Kildare/W Wicklow HSE mental health budget is the lowest per head of population € 63. 80 per head compared to € 199. 20 Kildare Integrated Services Programme (ISP) collaborative programme identified needs- men in particular Aware of success of Mojo in South Dublin, NOSP pilot

2. LCDC Role Proactive, experienced LCDC – 19 members LCDC, through Chief Officer, wrote to NOSP requesting that Kildare be considered as a pilot site Host organisation, member of LCDC Initial scoping, benefitted from LCDC connections Ultimately led to engagement and participation on Advisory Steering Group In addition LCDC agenda item

2. LCDC Role Reporting highlights success/challenges- created awareness of demand. North Kildare- focus Financial contributions of agencies- € 50 k to expand from initial pilot LECP- included as an action Chief Officer LCDC, HSE Chief Officer and Suicide Resource Officer met on behalf of LCDC to discuss Mojo inclusion in county wide suicide prevention plan LCDC enables ease of access to elected representatives, state agencies, voluntary sector organisations and local communities
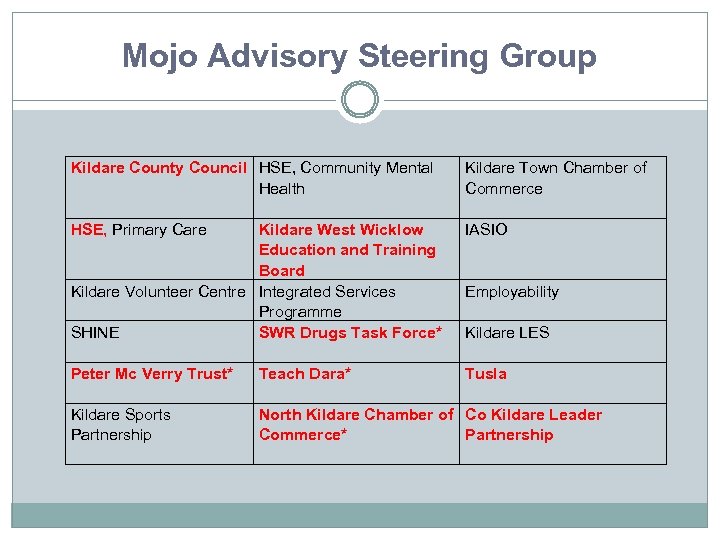
Mojo Advisory Steering Group Kildare County Council HSE, Community Mental Health HSE, Primary Care Kildare West Wicklow Education and Training Board Kildare Volunteer Centre Integrated Services Programme SHINE SWR Drugs Task Force* Peter Mc Verry Trust* Teach Dara* Kildare Sports North Kildare Chamber of Partnership Commerce* Kildare Town Chamber of Commerce IASIO Employability Kildare LES Tusla Co Kildare Leader Partnership

3. Mojo Outcomes to date Since September 2015 87 men engaged in Mojo and mini Mojo (4 week programme developed to respond to demand) since September 2014 The initial target was 28 men! Three Mojo and three mini Mojo have been run Over 80% retention rate Over 75% progression rate Hard to reach, vulnerable group Men continue to meet in locally post the programme Demand very high e. g. Celbridge 46 referrals for one programme

3. What Mojo means? Quotes “They actually genuinely care about you and genuinely want to know ‘how are you’. They can nearly sense when something might be wrong and can sense when something might not be ok’- Participant “I have more confidence to ask and find out directly. I wasn’t afraid or embarrassed about using the wrong words. That was the bit about self help advocacy an having the confidence to ask”-Participant “I spoke to the guy in the library for a half an hour about an access course in Maynooth-normally I’d grab the info and run”-Participant “Some more isolated men find it really hard to take that first step. What has been striking about mojo is the men's engagement, its really solid and that is striking. They are not being paid to attend. They don’t have to attend. ”- Agency

4. What Mojo has done for Kildare 1. Impact on men- themselves, their families, their 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. communities Agency co-operation, buy in, understanding Practical role for LCDC- increases understanding of men in distress, their needs/concerns Put mental health on broader agenda- LECP, HSE plans, political Highlights service deficits, gaps and needs in Kildare Informs national learning

Next Steps- challenges Sustainability- resourcing Responding to demand Maintaining high quality Retaining agency commitment Increase in budget available to mental health and support services generally
Thank You
b21b9fcb41a0c93489675705107bcfdf.ppt