18c1eb93315f23cb68d0048fa3a8f116.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 54
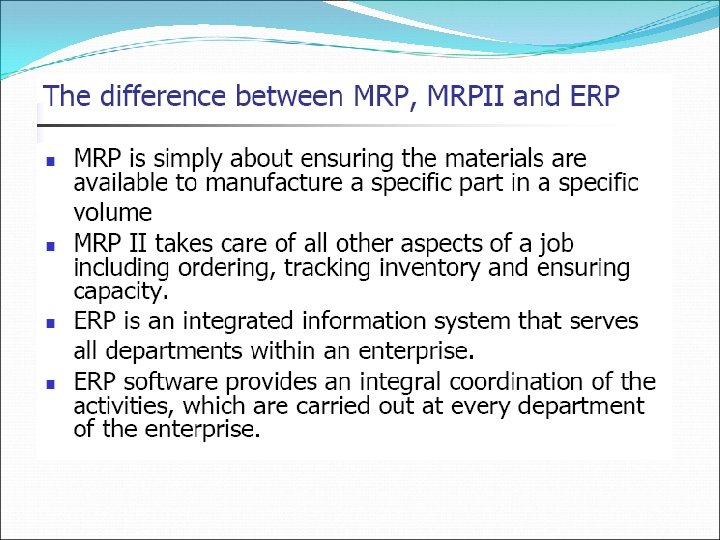
 Module VIII MRP II and its interaction with Business Information Systems
Module VIII MRP II and its interaction with Business Information Systems
 What does a company’s strategy consist of ? Company strategies concern, • How to grow the business • How to satisfy customers • How to out compete rivals • How to respond to changing in market conditions • How to manage each functional piece of the business and develop needed organizational capabilities • How to achieve strategic and financial objectives
What does a company’s strategy consist of ? Company strategies concern, • How to grow the business • How to satisfy customers • How to out compete rivals • How to respond to changing in market conditions • How to manage each functional piece of the business and develop needed organizational capabilities • How to achieve strategic and financial objectives
 Introduction Manufacturing Organizations are complex `Systems' where the interactions between the various functions Sales, Distribution, Manufacturing, Materials, Finance, Human Resources, Maintenance have to be managed towards a common purpose of delivering the customers maximum value at the optimum price. However, since most of these organizations have a `Functional Structure', each function/department works towards their own goals and objectives, rather than the organizational goals. These are the issues addressed by `Enterprise Resource Planning' software solutions providing a common, consistent system to capture data organization wide, with minimum redundancy.
Introduction Manufacturing Organizations are complex `Systems' where the interactions between the various functions Sales, Distribution, Manufacturing, Materials, Finance, Human Resources, Maintenance have to be managed towards a common purpose of delivering the customers maximum value at the optimum price. However, since most of these organizations have a `Functional Structure', each function/department works towards their own goals and objectives, rather than the organizational goals. These are the issues addressed by `Enterprise Resource Planning' software solutions providing a common, consistent system to capture data organization wide, with minimum redundancy.
 What is ERP? ERP integrates the information across functions, and provides a set of tools for planning and monitoring the various functions and processes and ensuring progress towards a common purpose A business management system that integrates all facets of the business, including planning, manufacturing, sales, and marketing. ERP helps business managers to implement ERP in business activities such as inventory control, order tracking, customer service, finance and human resources
What is ERP? ERP integrates the information across functions, and provides a set of tools for planning and monitoring the various functions and processes and ensuring progress towards a common purpose A business management system that integrates all facets of the business, including planning, manufacturing, sales, and marketing. ERP helps business managers to implement ERP in business activities such as inventory control, order tracking, customer service, finance and human resources


 MRP – the predecessor to and backbone of MRP II And ERP a joint effort between J. I. Case, a manufacturer of tractors and other construction machinery, in partnership with IBM. Initial MRP solutions were big, clumsy and expensive. (1960 -1970)
MRP – the predecessor to and backbone of MRP II And ERP a joint effort between J. I. Case, a manufacturer of tractors and other construction machinery, in partnership with IBM. Initial MRP solutions were big, clumsy and expensive. (1960 -1970)
 Trends objective Demand management Reports Inventory Transaction (Sales forecasting) Inventory level Strategic management & Business plan Master production plan Resource requirement planning Resource req. scheduling MRP : MRPII Elements -BOM -Lead Time -Lot sizing -Planned purchase report -Performance reports Capacity req. Buy Planning(CRP) Realistic Factory coordination Realistic Supplier
Trends objective Demand management Reports Inventory Transaction (Sales forecasting) Inventory level Strategic management & Business plan Master production plan Resource requirement planning Resource req. scheduling MRP : MRPII Elements -BOM -Lead Time -Lot sizing -Planned purchase report -Performance reports Capacity req. Buy Planning(CRP) Realistic Factory coordination Realistic Supplier
 In 1972 five engineers in Mannheim, Germany, started up SAP (Systemanalyse und Programmentwicklung). The purpose of the company was to produce and market standard software for integrated business solutions.
In 1972 five engineers in Mannheim, Germany, started up SAP (Systemanalyse und Programmentwicklung). The purpose of the company was to produce and market standard software for integrated business solutions.
 The term Enterprise resource planning (ERP) was coined in the early 1990 s by the Gartner Group (Wylie, 1990). Their definition of ERP included criteria for evaluating the extent that software was actually integrated both across and within the various functional
The term Enterprise resource planning (ERP) was coined in the early 1990 s by the Gartner Group (Wylie, 1990). Their definition of ERP included criteria for evaluating the extent that software was actually integrated both across and within the various functional
 A typical Example
A typical Example
 Data Flow Diagram to support Part product approval process
Data Flow Diagram to support Part product approval process
 How WIP could be improved by implementation of ERP (Work in Process ) Without using of any integrated system using of integrated system
How WIP could be improved by implementation of ERP (Work in Process ) Without using of any integrated system using of integrated system
 Some Questions What are the major types of systems in a business? What role do they play? How do information systems support the major business functions? Why should managers pay attention to business processes?
Some Questions What are the major types of systems in a business? What role do they play? How do information systems support the major business functions? Why should managers pay attention to business processes?
 Major Types of Systems • Executive Support Systems (ESS) • Decision Support Systems (DSS) • Management Information Systems (MIS) • Knowledge Work Systems (KWS) • Office Systems • Transaction Processing Systems (TPS)
Major Types of Systems • Executive Support Systems (ESS) • Decision Support Systems (DSS) • Management Information Systems (MIS) • Knowledge Work Systems (KWS) • Office Systems • Transaction Processing Systems (TPS)

 Transaction Processing Systems (TPS): • Basic business systems that serve the operational level • A computerized system that performs and records the daily routine transactions necessary to the conduct of the business
Transaction Processing Systems (TPS): • Basic business systems that serve the operational level • A computerized system that performs and records the daily routine transactions necessary to the conduct of the business
 Types of TPS Systems
Types of TPS Systems
 Payroll TPS
Payroll TPS
 Executive Support System (ESS): Strategic level Inputs: Aggregate data Processing: Interactive Outputs: Projections Users: Senior managers Example: 5 -year operating plan
Executive Support System (ESS): Strategic level Inputs: Aggregate data Processing: Interactive Outputs: Projections Users: Senior managers Example: 5 -year operating plan
 Management Information System (MIS): Management level Inputs: High volume data Processing: Simple models Outputs: Summary reports Users: Middle managers Example: Annual budgeting
Management Information System (MIS): Management level Inputs: High volume data Processing: Simple models Outputs: Summary reports Users: Middle managers Example: Annual budgeting
 Decision Support System (DSS): Management level Inputs: Low volume data Processing: Interactive Outputs: Decision analysis Users: Professionals, staff Example: Contract cost analysis
Decision Support System (DSS): Management level Inputs: Low volume data Processing: Interactive Outputs: Decision analysis Users: Professionals, staff Example: Contract cost analysis
 Knowledge Work Systems (KWS): Knowledge level Inputs: Design specs Processing: Modeling Outputs: Designs, graphics Users: Technical staff and professionals Example: Engineering work station
Knowledge Work Systems (KWS): Knowledge level Inputs: Design specs Processing: Modeling Outputs: Designs, graphics Users: Technical staff and professionals Example: Engineering work station
 Decision Support System (DSS)
Decision Support System (DSS)
 Decision Support System (DSS)
Decision Support System (DSS)
 Relation Between 5 systems
Relation Between 5 systems
 (MIS) With out any Integrated system (ESS) (KWS) (TPS)
(MIS) With out any Integrated system (ESS) (KWS) (TPS)
 Using Integrated system
Using Integrated system
 ERP elements Enterprise resources planning software Supply Best Practice : Chain management Comparing your process with similar processes In higher companies 6 level of sys. (ESS, MIS, TPS, …) +MRPII
ERP elements Enterprise resources planning software Supply Best Practice : Chain management Comparing your process with similar processes In higher companies 6 level of sys. (ESS, MIS, TPS, …) +MRPII
 ERP Software Companies & Marketshares Software Market Share SAP 15. 6 Peoplesoft 4. 9 Oracle 4. 8 Baan 3. 0 CA 3. 0 JDE 2. 2 SSA 2. 1 GEAC 2. 0 IBM 1. 8 JBA 1. 7 Others 59. 0
ERP Software Companies & Marketshares Software Market Share SAP 15. 6 Peoplesoft 4. 9 Oracle 4. 8 Baan 3. 0 CA 3. 0 JDE 2. 2 SSA 2. 1 GEAC 2. 0 IBM 1. 8 JBA 1. 7 Others 59. 0
 TABLE 1. 2 Business Functions Potentially Supported by ERP source : T. H. Davenport, ” Putting the Enterprise into the Enterprise System. ” Harvard Business Review, July-August 1998. Financial Human Resources Operations and Logistics Sales and Marketing Accounts receivable and payable Time accounting Inventory management Order management Asset accounting Payroll Materials Requirement Planning (MRP) Pricing Cash forecasting Personnel planning Plant maintenance Sales management Cost accounting Travel expenses Production planning Sales planning Executive information systems Project management Financial consolidation Purchasing General ledger Quality management Profitability analysis Shipping Standard costing Vendor evaluation
TABLE 1. 2 Business Functions Potentially Supported by ERP source : T. H. Davenport, ” Putting the Enterprise into the Enterprise System. ” Harvard Business Review, July-August 1998. Financial Human Resources Operations and Logistics Sales and Marketing Accounts receivable and payable Time accounting Inventory management Order management Asset accounting Payroll Materials Requirement Planning (MRP) Pricing Cash forecasting Personnel planning Plant maintenance Sales management Cost accounting Travel expenses Production planning Sales planning Executive information systems Project management Financial consolidation Purchasing General ledger Quality management Profitability analysis Shipping Standard costing Vendor evaluation
 Modules Offered by Leading Vendors Functional Description SAP Records sales orders and scheduled deliveries , customer information SD( Sales and Distribution) Marketing Sales Supply Chain Supply chain management Order management Purchasing and raw materials inventory, work- in-process. customer information MM (Materials Management Procurement Supplier Relationship Management Inventory Management Procurement Production Planning and scheduling actual production PP (production planning ) Manufacturing Product inspections , material certifications , quality control QM (quality Management) Preventive maintenance, resource management PM (plant Maintenance) Service Enterprise Service Automation Recruiting, hiring training , payroll , benefits HR (Human Resources Human Capital Management Oracle People Soft JD Eswards Manufacturing Management Enterprise Performance Management Technical Foundation Workforce Management
Modules Offered by Leading Vendors Functional Description SAP Records sales orders and scheduled deliveries , customer information SD( Sales and Distribution) Marketing Sales Supply Chain Supply chain management Order management Purchasing and raw materials inventory, work- in-process. customer information MM (Materials Management Procurement Supplier Relationship Management Inventory Management Procurement Production Planning and scheduling actual production PP (production planning ) Manufacturing Product inspections , material certifications , quality control QM (quality Management) Preventive maintenance, resource management PM (plant Maintenance) Service Enterprise Service Automation Recruiting, hiring training , payroll , benefits HR (Human Resources Human Capital Management Oracle People Soft JD Eswards Manufacturing Management Enterprise Performance Management Technical Foundation Workforce Management
 Reasons for Implementing ERP-Rating 1(Not Important) to 5(very Important) Reason United States Sweden Replace legacy systems 4. 06 4. 11 Simplify and standardize systems 3. 85 3. 67 Improve interactions with suppliers & customers 3. 55 3. 16 Gain strategic advantage 3. 46 3. 18 Link to global activities 3. 17 2. 85 Pressure to keep up with competitors 2. 99 2. 48 Ease of upgrading systems 2. 91 2. 96 Restructure organization 2. 58 2. 70
Reasons for Implementing ERP-Rating 1(Not Important) to 5(very Important) Reason United States Sweden Replace legacy systems 4. 06 4. 11 Simplify and standardize systems 3. 85 3. 67 Improve interactions with suppliers & customers 3. 55 3. 16 Gain strategic advantage 3. 46 3. 18 Link to global activities 3. 17 2. 85 Pressure to keep up with competitors 2. 99 2. 48 Ease of upgrading systems 2. 91 2. 96 Restructure organization 2. 58 2. 70
 Modules Offered by Leading Vendors Functional Description SAP Oracle People Soft JD Eswards Internal management, cost analysis by cost center CO (Controlling) Fixed-asset purchase and depreciation AM (Asset Management) Asset Management Enterprise Asset Management R&D , construction, marketing projects PS (Asset Management) Projects Project Management Contracts Subcontract Management Real Estate Management Automate system, task – flow analysis, Prompt actions WF (Workflow) Best practices IS (Industry Solutions) Time and Expense Management
Modules Offered by Leading Vendors Functional Description SAP Oracle People Soft JD Eswards Internal management, cost analysis by cost center CO (Controlling) Fixed-asset purchase and depreciation AM (Asset Management) Asset Management Enterprise Asset Management R&D , construction, marketing projects PS (Asset Management) Projects Project Management Contracts Subcontract Management Real Estate Management Automate system, task – flow analysis, Prompt actions WF (Workflow) Best practices IS (Industry Solutions) Time and Expense Management
 Relative ERP Module Use Module Midwestern ERP Users Swedish ERP Users 91. 5% 87. 3% Materials management 89. 2 91. 8 Production planning 88. 5 90. 5 Order entry 87. 7 92. 4 Purchasing 86. 9 93. 0 Financial control 81. 5 82. 3 Distribution/logistics 75. 4 84. 8 Asset management 57. 7 63. 3 Quality management 44. 6 47. 5 Personnel/human resources 44. 6 57. 6 Maintenance 40. 8 44. 3 R&D management 30. 8 34. 2 Financial and Accounting
Relative ERP Module Use Module Midwestern ERP Users Swedish ERP Users 91. 5% 87. 3% Materials management 89. 2 91. 8 Production planning 88. 5 90. 5 Order entry 87. 7 92. 4 Purchasing 86. 9 93. 0 Financial control 81. 5 82. 3 Distribution/logistics 75. 4 84. 8 Asset management 57. 7 63. 3 Quality management 44. 6 47. 5 Personnel/human resources 44. 6 57. 6 Maintenance 40. 8 44. 3 R&D management 30. 8 34. 2 Financial and Accounting
 Advantages and Disadvantages of Alternative ERP Development Methods Method Advantages Disadvantages Develop in-house Best fit with organizational needs Most difficult to develop Most expensive Slowest In-house system With vendor supplements Gain commercial advantages Combined with organizational fit Difficult to develop Expensive slow Best-of-breed Customized vendor system Theoretically while keeping Retain flexibility while keeping Vendor expertise Difficult to link modules Slower Usually more expensive Selected vendor modules Less risk If expand, long run time and cost higher Relatively fast Least expensive Full vendor system Fast Less expensive Efficient Inflexible Application device provider Least risk Least cost Fastest Least subject to vendor change At the mercy of ASP provider No control Subject to price increases
Advantages and Disadvantages of Alternative ERP Development Methods Method Advantages Disadvantages Develop in-house Best fit with organizational needs Most difficult to develop Most expensive Slowest In-house system With vendor supplements Gain commercial advantages Combined with organizational fit Difficult to develop Expensive slow Best-of-breed Customized vendor system Theoretically while keeping Retain flexibility while keeping Vendor expertise Difficult to link modules Slower Usually more expensive Selected vendor modules Less risk If expand, long run time and cost higher Relatively fast Least expensive Full vendor system Fast Less expensive Efficient Inflexible Application device provider Least risk Least cost Fastest Least subject to vendor change At the mercy of ASP provider No control Subject to price increases
 Expected ERP Project Installation Time Requirements Installation Time United States Sweden 12 months or less 34% 38% 13 to 24 months 45 49 25 to 36 months 11 8 35 to 48 months 6 4 Over 48 months 2 1
Expected ERP Project Installation Time Requirements Installation Time United States Sweden 12 months or less 34% 38% 13 to 24 months 45 49 25 to 36 months 11 8 35 to 48 months 6 4 Over 48 months 2 1
 ERP Estimated Installation Project Cost Installation Cost United States Sweden Less than $5 million 42% 48% $5 million to $25 million 33 35 $26 million to $50 million 10 18 7 7 7 (in prior category) $51 million to $100 million Over $100 million
ERP Estimated Installation Project Cost Installation Cost United States Sweden Less than $5 million 42% 48% $5 million to $25 million 33 35 $26 million to $50 million 10 18 7 7 7 (in prior category) $51 million to $100 million Over $100 million
 ERP Installation Project Cost Proportions Installation Cost Proportion Project Installation Cost Proportion in United States Cost Proportion in Sweden Software 30% 24% Consulting 24 30 Hardware 18 19 Implementation team 14 12 Training 11 14 Other 3 1
ERP Installation Project Cost Proportions Installation Cost Proportion Project Installation Cost Proportion in United States Cost Proportion in Sweden Software 30% 24% Consulting 24 30 Hardware 18 19 Implementation team 14 12 Training 11 14 Other 3 1

 A supply chain is characterized by the flow of materials and information both within and between business entities including suppliers, manufacturers and customers. The ultimate goal of supply chain management is to meet customer’s demand more efficiently. For a manufacturing company, it is to make the right product, for the right customer, in the right amount, at the right time.
A supply chain is characterized by the flow of materials and information both within and between business entities including suppliers, manufacturers and customers. The ultimate goal of supply chain management is to meet customer’s demand more efficiently. For a manufacturing company, it is to make the right product, for the right customer, in the right amount, at the right time.


 ERP System Options and Selection Methods Enterprise resource planning systems are very large IS/IT projects. The cost range is enormous, depending upon the size of the firm implementing the system , as well as on how many modules are used.
ERP System Options and Selection Methods Enterprise resource planning systems are very large IS/IT projects. The cost range is enormous, depending upon the size of the firm implementing the system , as well as on how many modules are used.



 ERP Implementation And Maintenance ERP Systems Are Adopted In The Hopes That They Will Improve The Performance Of An Organization On A Number Of Key Performance Indicators , Such As Profitability , Efficiency , And Accuracy In Information System Data And Reports. ERP Vendors Typically Promise Gains Of 10 To 15 Percent In Revenue , Customer Satisfaction , And Other Measures Of Value. The Effort Required To Build These Systems Is Significant. Meta Group found that the average ERP implementation takes 23 months with total Ownership cost of $15 million.
ERP Implementation And Maintenance ERP Systems Are Adopted In The Hopes That They Will Improve The Performance Of An Organization On A Number Of Key Performance Indicators , Such As Profitability , Efficiency , And Accuracy In Information System Data And Reports. ERP Vendors Typically Promise Gains Of 10 To 15 Percent In Revenue , Customer Satisfaction , And Other Measures Of Value. The Effort Required To Build These Systems Is Significant. Meta Group found that the average ERP implementation takes 23 months with total Ownership cost of $15 million.
 Business Intelligence Systems And ERP Enterprise Resource Planning Systems Offer Powerful Tools To Better Measure And Control Organizational Operations. Many Organizations Have Found That This Valuable Tool Can Be Enhanced To Provide Even Greater Value Though The Addition Of Powerful Business Intelligence Systems. Business Intelligence In This Context Is Supported By Sorting Data (Data Warehouse And Related Systems) And Conducting Studies Using This Data To Solve Business Problems ( One Means To Do This Though Data Mining ). One Of The Most Popular Forms Of Data Mining In ERP Systems Is Support Of Customer Relationship Management (CRM). Data Warehouses Are One Of The Most Popular Extensions To ERP Systems , With Over Two-Thirds Of U. S. Manufacturers Adopting Or Planning Such Systems ( And Slightly Less Than Two – Thirds of Swedish Manufacturers doing the same ). There Has Been Tremendous Progress In Computer Storage Of Data. Many Applications Are Being Found For This new capacity. one major user of massive storage capacity is ERP systems, witch have large storage requirements due to their comprehensive nature.
Business Intelligence Systems And ERP Enterprise Resource Planning Systems Offer Powerful Tools To Better Measure And Control Organizational Operations. Many Organizations Have Found That This Valuable Tool Can Be Enhanced To Provide Even Greater Value Though The Addition Of Powerful Business Intelligence Systems. Business Intelligence In This Context Is Supported By Sorting Data (Data Warehouse And Related Systems) And Conducting Studies Using This Data To Solve Business Problems ( One Means To Do This Though Data Mining ). One Of The Most Popular Forms Of Data Mining In ERP Systems Is Support Of Customer Relationship Management (CRM). Data Warehouses Are One Of The Most Popular Extensions To ERP Systems , With Over Two-Thirds Of U. S. Manufacturers Adopting Or Planning Such Systems ( And Slightly Less Than Two – Thirds of Swedish Manufacturers doing the same ). There Has Been Tremendous Progress In Computer Storage Of Data. Many Applications Are Being Found For This new capacity. one major user of massive storage capacity is ERP systems, witch have large storage requirements due to their comprehensive nature.
 Data Mining Overview Refers To The Analysis Of The Large Quantities Of Data Stored In Computers. For Example , Grocery Stores Have Large Amounts Of Data Generated By Purchases. Bar Coding Has Made Grocery Checkout Very Convenient. Grocery Stores And Other Retail Stores Are Able To Quickly Process Purchases , And Use Computers To Accurately Determine Product Prices. These Same Computers Help The Stores With Inventory Management By Instantaneously Determining The Quantity Of Items Of Each Product On Hand. Stores Can Also Apply Computer Technology To Contact Their Vendors So That They Do Not Run Out Of Items. Computers Allow The Store’s Accounting System To More Accurately Measure Costs And Determine The Profit That Store Stockholders Are Concerned About. All Of This Information Is Available Based Upon The Bar Coding Information Attached To Each Product. The Benefits Of Bar Coding Encompass For More Than Faster Checkout Service. The Entire Business Management Process Can Use The Information Generated.
Data Mining Overview Refers To The Analysis Of The Large Quantities Of Data Stored In Computers. For Example , Grocery Stores Have Large Amounts Of Data Generated By Purchases. Bar Coding Has Made Grocery Checkout Very Convenient. Grocery Stores And Other Retail Stores Are Able To Quickly Process Purchases , And Use Computers To Accurately Determine Product Prices. These Same Computers Help The Stores With Inventory Management By Instantaneously Determining The Quantity Of Items Of Each Product On Hand. Stores Can Also Apply Computer Technology To Contact Their Vendors So That They Do Not Run Out Of Items. Computers Allow The Store’s Accounting System To More Accurately Measure Costs And Determine The Profit That Store Stockholders Are Concerned About. All Of This Information Is Available Based Upon The Bar Coding Information Attached To Each Product. The Benefits Of Bar Coding Encompass For More Than Faster Checkout Service. The Entire Business Management Process Can Use The Information Generated.
 ERP And Supply Chains Supply Chain Are Collections Of Organizations That Work Together To Provide Raw Materials That Are Converted Into Products And Delivered To Retail Outlets Where Customers Can Obtain Them. In The Past , Monopolies Would Sometimes Seek Vertical Integration So That They Could Control The Entire Supply Chain ( Standard Oil Went A Long Way Toward Total Vertical Integration ; Steel Companies Also Attained At Lest Something Approaching It ). The Dutch East India Companies Are An Early Example Of A Global Supply Chain. Military Logistics Systems Are The Epitome Of Supply Chain Is Control And Efficiency. Today‘S Companies Gain Efficiency Through A Higher Degree Of Specialization. This Appears In Various Forms , Including Outsourcing. The Idea Behind Outsourcing Is That There Are Specialists Throughout The Supply Chain Who Can Do A Better Job Of The Specific Function They Perform.
ERP And Supply Chains Supply Chain Are Collections Of Organizations That Work Together To Provide Raw Materials That Are Converted Into Products And Delivered To Retail Outlets Where Customers Can Obtain Them. In The Past , Monopolies Would Sometimes Seek Vertical Integration So That They Could Control The Entire Supply Chain ( Standard Oil Went A Long Way Toward Total Vertical Integration ; Steel Companies Also Attained At Lest Something Approaching It ). The Dutch East India Companies Are An Early Example Of A Global Supply Chain. Military Logistics Systems Are The Epitome Of Supply Chain Is Control And Efficiency. Today‘S Companies Gain Efficiency Through A Higher Degree Of Specialization. This Appears In Various Forms , Including Outsourcing. The Idea Behind Outsourcing Is That There Are Specialists Throughout The Supply Chain Who Can Do A Better Job Of The Specific Function They Perform.
 I n c r I e n D a c e s D r c e e I e r d c n I a e r c n s a e r c e s a e r d e s a e d e s a d e s d e d
I n c r I e n D a c e s D r c e e I e r d c n I a e r c n s a e r c e s a e r d e s a e d e s a d e s d e d
 Conclusion • The growing information needs of an enterprise make it imperative to improve or replace old systems. • Especially under the present business environment, where the globalization has been initiated, full convertibility is coined. • Infrastructure Projects are nearing completion, and it is expected that the whole business system will undergo a major shift. • Implementation of ERP solutions is one of the largest drivers of growth in the consultancy business. • The introduction of such a large and complex software like ERP, enables an organization to integrate their manufacturing, finance and marketing operations at all levels, is in itself a challenge, since it calls for technical and functional skills and a change in user mindsets.
Conclusion • The growing information needs of an enterprise make it imperative to improve or replace old systems. • Especially under the present business environment, where the globalization has been initiated, full convertibility is coined. • Infrastructure Projects are nearing completion, and it is expected that the whole business system will undergo a major shift. • Implementation of ERP solutions is one of the largest drivers of growth in the consultancy business. • The introduction of such a large and complex software like ERP, enables an organization to integrate their manufacturing, finance and marketing operations at all levels, is in itself a challenge, since it calls for technical and functional skills and a change in user mindsets.


