f10423b45cb4d74d5dc5edd00dd8f7ea.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 11
 Module Prototyping Sensor Requirements Phil Allport Representing the ATLAS Module Integration Working Group 2 nd July 2007 • ASIC and Hybrid Issues for the Sensor • Sensor Layout Proposal • Module Requirements
Module Prototyping Sensor Requirements Phil Allport Representing the ATLAS Module Integration Working Group 2 nd July 2007 • ASIC and Hybrid Issues for the Sensor • Sensor Layout Proposal • Module Requirements
 Recent Upgrade Meeting There was a recent meeting of the Module Integration Working Group on 1 st June http: //indico. cern. ch/conference. Display. py? conf. Id=16849
Recent Upgrade Meeting There was a recent meeting of the Module Integration Working Group on 1 st June http: //indico. cern. ch/conference. Display. py? conf. Id=16849
 ASIC and Hybrid Sensor Issues It is widely regarded as attractive to avoid fan-ins and 7. 5 mm still allows 2. 2 mm space for the FE capacitor between ASICs However, It is clear that some older machines would struggle to deliver the required bonding angle and there was concern that yields with modern machines may still be compromised. It was reported that LHCb had achieved a large number of bonds with similar constraints but the orientation of the bond pads had not been exactly as proposed here. There was also a discussion of the required placement accuracy but here it was felt there was less likelihood of problems. There is also urgent discussion on the location of bond pads within the sensor and a strong desire to be both able to prototype the narrowest feasible hybrid requiring bond pads about 31 mm apart and possibly a wide hybrid (with more comparable copper area to current hybrids for the power density) with bond pads 39 mm apart.
ASIC and Hybrid Sensor Issues It is widely regarded as attractive to avoid fan-ins and 7. 5 mm still allows 2. 2 mm space for the FE capacitor between ASICs However, It is clear that some older machines would struggle to deliver the required bonding angle and there was concern that yields with modern machines may still be compromised. It was reported that LHCb had achieved a large number of bonds with similar constraints but the orientation of the bond pads had not been exactly as proposed here. There was also a discussion of the required placement accuracy but here it was felt there was less likelihood of problems. There is also urgent discussion on the location of bond pads within the sensor and a strong desire to be both able to prototype the narrowest feasible hybrid requiring bond pads about 31 mm apart and possibly a wide hybrid (with more comparable copper area to current hybrids for the power density) with bond pads 39 mm apart.
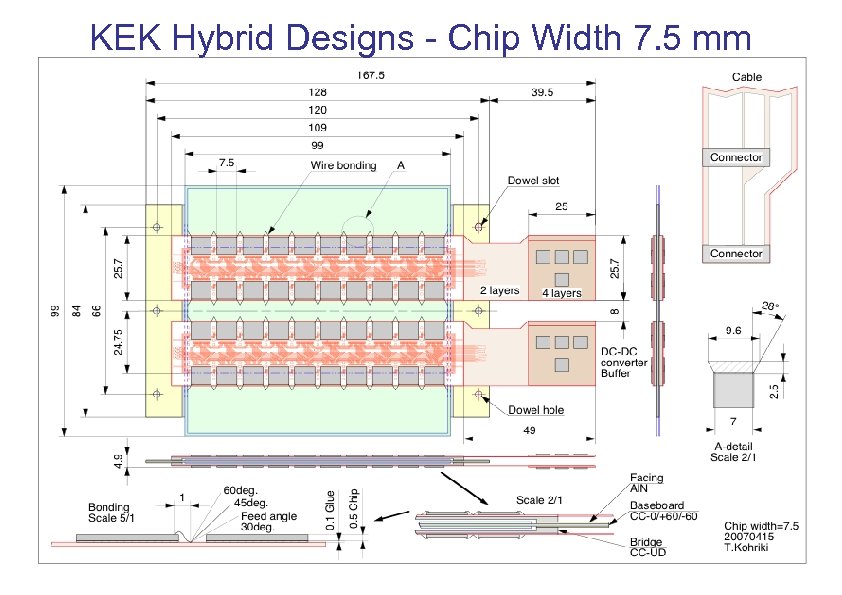 KEK Hybrid Designs - Chip Width 7. 5 mm
KEK Hybrid Designs - Chip Width 7. 5 mm
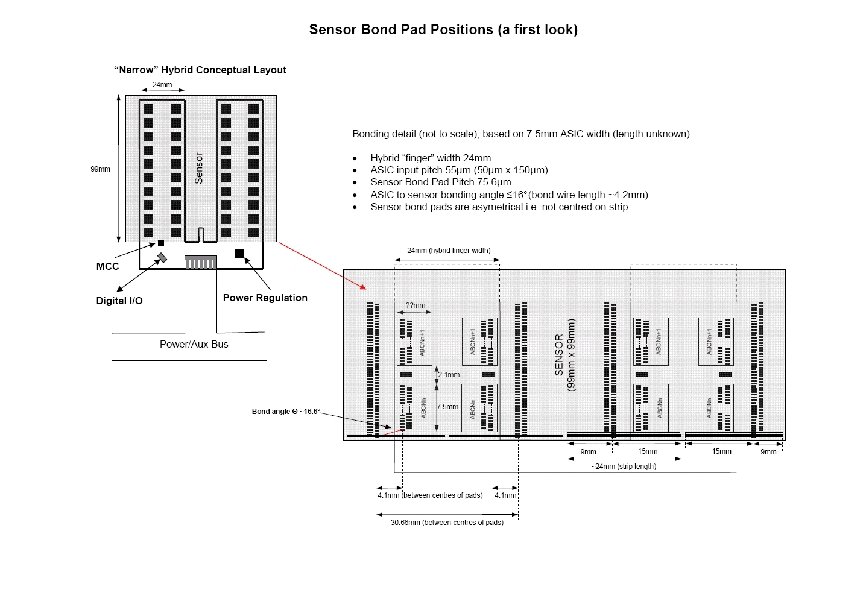
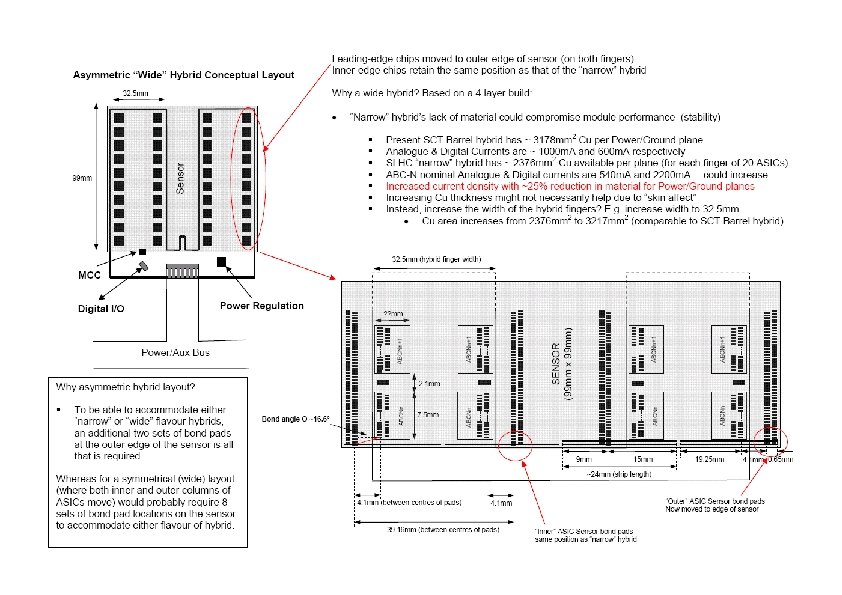
 Sensor Layout Discussions The sensor layout has been presented several times to the MIWG and discussed with Hamamatsu. The proposed mix of stereo and axial strips on the wafer would allow modules using rotated sensors back-to-back to offer stereo capability. It was agreed that bond pads could match well enough for the stereo section so as not to need changes to hybrid/module designs for that region The required schedule for the MIWG programme depends critically on when further orders might be placed. Assuming this order is the only one for the next 18 -24 months with HPK, it is both crucial to order the right number but also to be sure the designs are appropriate It might be possible to have a pre-order of ~10% wafers to check quality before releasing production for the remainder (I would like some with spray if possible) but this will impact on the schedule. (n. b. ABCn submission planned for end of 2007 so delivery of tested ASICs possibly only April 08 anyway)
Sensor Layout Discussions The sensor layout has been presented several times to the MIWG and discussed with Hamamatsu. The proposed mix of stereo and axial strips on the wafer would allow modules using rotated sensors back-to-back to offer stereo capability. It was agreed that bond pads could match well enough for the stereo section so as not to need changes to hybrid/module designs for that region The required schedule for the MIWG programme depends critically on when further orders might be placed. Assuming this order is the only one for the next 18 -24 months with HPK, it is both crucial to order the right number but also to be sure the designs are appropriate It might be possible to have a pre-order of ~10% wafers to check quality before releasing production for the remainder (I would like some with spray if possible) but this will impact on the schedule. (n. b. ABCn submission planned for end of 2007 so delivery of tested ASICs possibly only April 08 anyway)
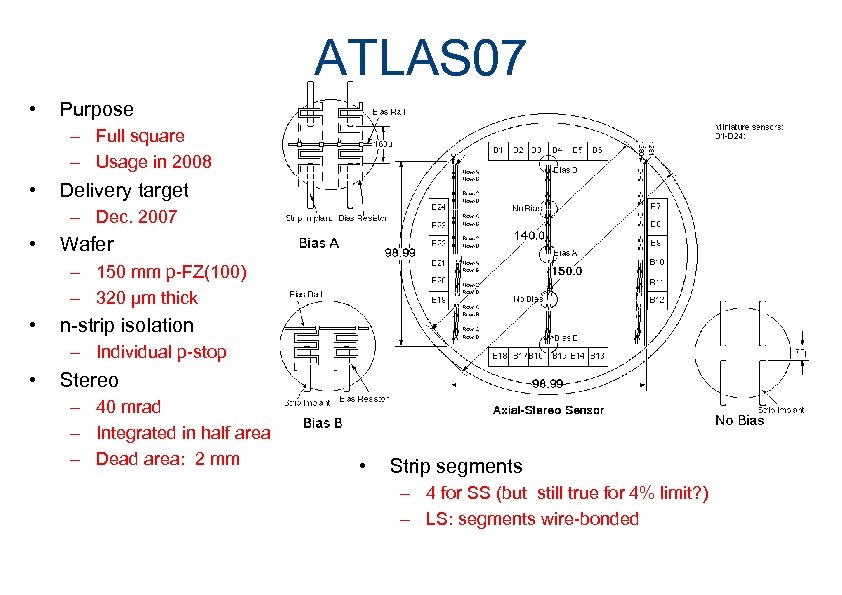 ATLAS 07 • Purpose – Full square – Usage in 2008 • Delivery target – Dec. 2007 • Wafer – 150 mm p-FZ(100) – 320 µm thick • n-strip isolation – Individual p-stop • Stereo – 40 mrad – Integrated in half area – Dead area: 2 mm • Strip segments – 4 for SS (but still true for 4% limit? ) – LS: segments wire-bonded
ATLAS 07 • Purpose – Full square – Usage in 2008 • Delivery target – Dec. 2007 • Wafer – 150 mm p-FZ(100) – 320 µm thick • n-strip isolation – Individual p-stop • Stereo – 40 mrad – Integrated in half area – Dead area: 2 mm • Strip segments – 4 for SS (but still true for 4% limit? ) – LS: segments wire-bonded
 Sensor Prototype Order • Proposal from David Lissauer • As part of the ATLAS tracker upgrade R&D we are planning to submit a common order for prototype sensors. The cost per sensor is contingent on the total number of sensors we will buy. • At present we are planning to put in a common order from ATLAS/CERN that will be managed by Markus Nordberg. To participate in the order you either have to join this common purchase and or give your order directly to Hamamatsu (via the local representative) • In case you join the common ATLAS purchase order – you will have to issue a TID to the ATLAS CERN team account designated by Markus.
Sensor Prototype Order • Proposal from David Lissauer • As part of the ATLAS tracker upgrade R&D we are planning to submit a common order for prototype sensors. The cost per sensor is contingent on the total number of sensors we will buy. • At present we are planning to put in a common order from ATLAS/CERN that will be managed by Markus Nordberg. To participate in the order you either have to join this common purchase and or give your order directly to Hamamatsu (via the local representative) • In case you join the common ATLAS purchase order – you will have to issue a TID to the ATLAS CERN team account designated by Markus.
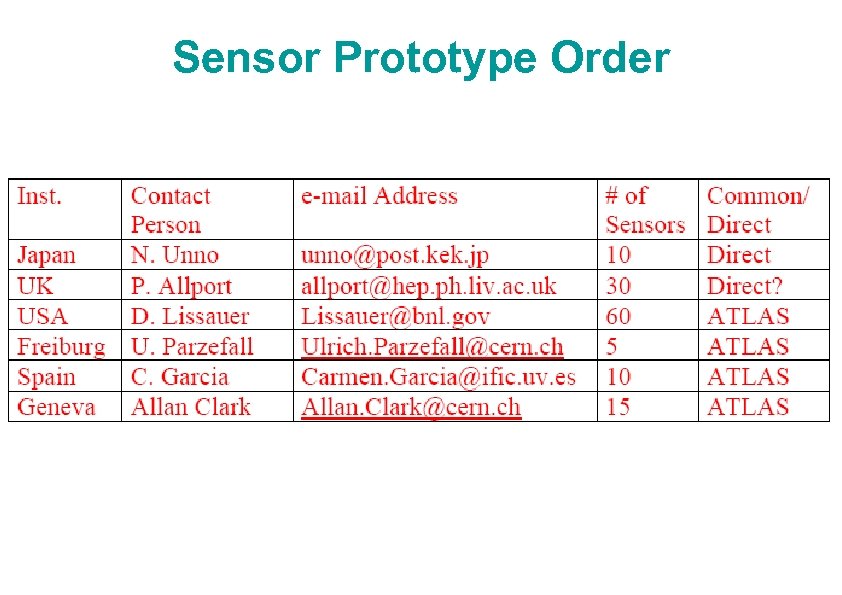 Sensor Prototype Order
Sensor Prototype Order
 Order Through CERN 1) We go the process called "Type B", i. e. , CERN will not do "tendering" but follow the selection of a company by an institute who has done the "proper/formal" selection (of the company). The institute should have received a price quotation/offer from the local distributor to which CERN will make a contract, and issues a letter of "proof of selection" to CERN together with the price quotation/offer and the "Transfer of Risk" from the institute. In summary, the institute should issue to CERN - Proof of Selection - Transfer of Risk (This is to clarify that any legal actions from the company is to be dealt with the institute and not CERN. ) - Price quotation/offer from the company (not including VAT. See (2)) 2) With the "proof of selection" from the institute, CERN will place an order for the institute and receive the product. Accordingly, - CERN will make a contract of procurement with the company - The company will issue an invoice to CERN upon delivery of the goods to CERN - CERN will pay to the company Therefore, - The price will include the dealer overhead, but not VAT as CERN is VAT exempted - There is no CERN overhead (as tendering process is not made) 3) ATLAS collects the money from the institutes who shares the procurement either by TID or invoicing and then move it to the account where the order is charged to. For this transfer, ATLAS needs - Individual financial pledges to the transfer 4) ATLAS will make an ATLAS agreement among the involved institutes regarding the TID transfers, with an associated document of the technical specification with the contact names of the specification, and how to share (any additional) costs or legal disputes
Order Through CERN 1) We go the process called "Type B", i. e. , CERN will not do "tendering" but follow the selection of a company by an institute who has done the "proper/formal" selection (of the company). The institute should have received a price quotation/offer from the local distributor to which CERN will make a contract, and issues a letter of "proof of selection" to CERN together with the price quotation/offer and the "Transfer of Risk" from the institute. In summary, the institute should issue to CERN - Proof of Selection - Transfer of Risk (This is to clarify that any legal actions from the company is to be dealt with the institute and not CERN. ) - Price quotation/offer from the company (not including VAT. See (2)) 2) With the "proof of selection" from the institute, CERN will place an order for the institute and receive the product. Accordingly, - CERN will make a contract of procurement with the company - The company will issue an invoice to CERN upon delivery of the goods to CERN - CERN will pay to the company Therefore, - The price will include the dealer overhead, but not VAT as CERN is VAT exempted - There is no CERN overhead (as tendering process is not made) 3) ATLAS collects the money from the institutes who shares the procurement either by TID or invoicing and then move it to the account where the order is charged to. For this transfer, ATLAS needs - Individual financial pledges to the transfer 4) ATLAS will make an ATLAS agreement among the involved institutes regarding the TID transfers, with an associated document of the technical specification with the contact names of the specification, and how to share (any additional) costs or legal disputes


