0f9148e92e204ff1c62a353b1373d42e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 71
 Module : Hospital Information Management Dr Kithsiri Edirisinghe MBBS , MSc, MD ( Medical Administration) Master Trainer Australia Crt. IV in TAE Cert. IVLP (USA)
Module : Hospital Information Management Dr Kithsiri Edirisinghe MBBS , MSc, MD ( Medical Administration) Master Trainer Australia Crt. IV in TAE Cert. IVLP (USA)
 Overview for the module ü Topic 01 : Management Information systems ü Topic 02 : Application of Information Systems in Hospitals ü Topic 03 : Hospitals ü Topic 04 : ü Topic 05 : MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001 2
Overview for the module ü Topic 01 : Management Information systems ü Topic 02 : Application of Information Systems in Hospitals ü Topic 03 : Hospitals ü Topic 04 : ü Topic 05 : MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001 2
 Topic 01 Management Information Systems Dr Kithsiri Edirisinghe
Topic 01 Management Information Systems Dr Kithsiri Edirisinghe
 Topic 01 w Introduction management Information systems (MIS) w Concept of information management and the definitions and the process involved. w Introduction to the hospital information system (HIS ) w Basic concepts and categories in information management in hospitals, information flow and the process chart in healthcare services setting w Description and the role of Medical record department and the responsibilities of the Medical Administrator in HIS. w Concept of Electronic Medical Records, current challenges and advantages.
Topic 01 w Introduction management Information systems (MIS) w Concept of information management and the definitions and the process involved. w Introduction to the hospital information system (HIS ) w Basic concepts and categories in information management in hospitals, information flow and the process chart in healthcare services setting w Description and the role of Medical record department and the responsibilities of the Medical Administrator in HIS. w Concept of Electronic Medical Records, current challenges and advantages.
 Management Information Systems What is MIS_. flv üRead -What is MIS w Introduction to Management Information Systems MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001 5
Management Information Systems What is MIS_. flv üRead -What is MIS w Introduction to Management Information Systems MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001 5
 Information Systems ü Why Do People Need Information? ü Individuals - Entertainment and enlightenment ü Businesses - Decision making, problem solving and control MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001 6
Information Systems ü Why Do People Need Information? ü Individuals - Entertainment and enlightenment ü Businesses - Decision making, problem solving and control MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001 6
 Information and Healthcare services ü Updates the level of knowledge ü Reduce uncertainty leading to avoid confusion and conflicts ü Aids in decision making. Improves representation of an entity ü Improves patient care output and put come leading efficiency and effectives of the health care services MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001 7
Information and Healthcare services ü Updates the level of knowledge ü Reduce uncertainty leading to avoid confusion and conflicts ü Aids in decision making. Improves representation of an entity ü Improves patient care output and put come leading efficiency and effectives of the health care services MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001 7
 Data, Information, and Systems ü Data vs. Information ü Data “given, ” or fact; a number, a statement, or a picture Represents something in the real world The raw materials in the production of information ü Information Data that have meaning within a context Data in relationships Data after manipulation MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001 8
Data, Information, and Systems ü Data vs. Information ü Data “given, ” or fact; a number, a statement, or a picture Represents something in the real world The raw materials in the production of information ü Information Data that have meaning within a context Data in relationships Data after manipulation MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001 8
 Data, Information, and Systems ü Intelligence Information is made more valuable Use experience and make judgment Facilitate faster and more realistic decision making Done by experts in the field MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001 9
Data, Information, and Systems ü Intelligence Information is made more valuable Use experience and make judgment Facilitate faster and more realistic decision making Done by experts in the field MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001 9
 Data, Information, and Systems ü Data Manipulation w Example: customer survey Reading through data collected from a customer survey with questions in various categories would be time-consuming and not very helpful. When manipulated, the surveys may provide useful information. MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001 10
Data, Information, and Systems ü Data Manipulation w Example: customer survey Reading through data collected from a customer survey with questions in various categories would be time-consuming and not very helpful. When manipulated, the surveys may provide useful information. MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001 10
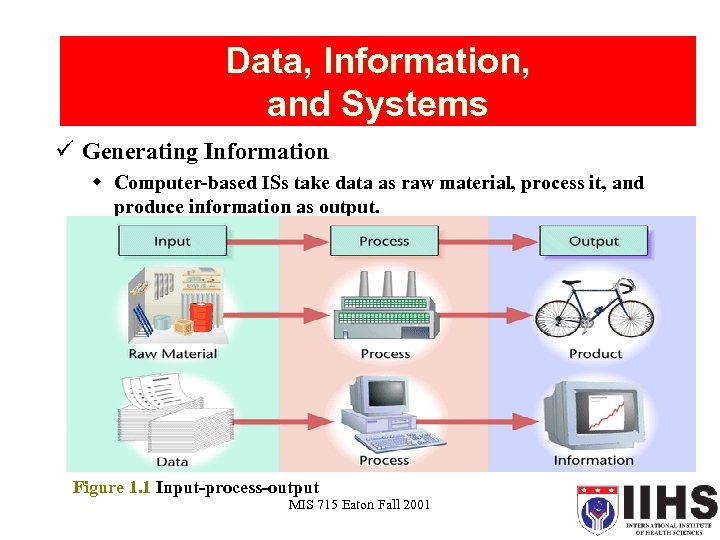 Data, Information, and Systems ü Generating Information w Computer-based ISs take data as raw material, process it, and produce information as output. Figure 1. 1 Input-process-output MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001 11
Data, Information, and Systems ü Generating Information w Computer-based ISs take data as raw material, process it, and produce information as output. Figure 1. 1 Input-process-output MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001 11
 Effective information ü Information in Context MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001 Figure 1. 2 Characteristics of useful information 12
Effective information ü Information in Context MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001 Figure 1. 2 Characteristics of useful information 12
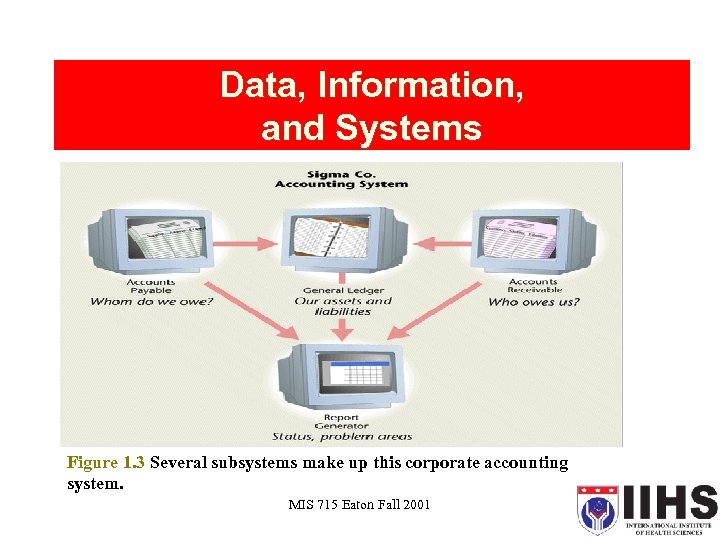 Data, Information, and Systems Figure 1. 3 Several subsystems make up this corporate accounting system. MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001 13
Data, Information, and Systems Figure 1. 3 Several subsystems make up this corporate accounting system. MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001 13
 Data, Information, and Systems ü What Is a System? ü System: A set of components that work together to achieve a common goal ü Subsystem: One part of a system where the products of more than one system are combined to reach an ultimate goal ü Closed system: Stand-alone system that has no contact with other systems ü Open system: System that interfaces with other systems MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001 14
Data, Information, and Systems ü What Is a System? ü System: A set of components that work together to achieve a common goal ü Subsystem: One part of a system where the products of more than one system are combined to reach an ultimate goal ü Closed system: Stand-alone system that has no contact with other systems ü Open system: System that interfaces with other systems MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001 14
 Data, Information, and Systems ü Information and Managers ü Systems thinking Creates a framework for problem solving and decision making. Keeps managers focused on overall goals and operations of business. MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001 15
Data, Information, and Systems ü Information and Managers ü Systems thinking Creates a framework for problem solving and decision making. Keeps managers focused on overall goals and operations of business. MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001 15
 Data, Information, and Systems Figure 1. 5 Qualities of humans and computers that contribute to synergy MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001 16
Data, Information, and Systems Figure 1. 5 Qualities of humans and computers that contribute to synergy MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001 16
 Data, Information, and Systems ü The Benefits of Human-Computer Synergy w Synergy When combined resources produce output that exceeds the sum of the outputs of the same resources employed separately w Allows human thought to be translated into efficient processing of large amounts of data MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001 17
Data, Information, and Systems ü The Benefits of Human-Computer Synergy w Synergy When combined resources produce output that exceeds the sum of the outputs of the same resources employed separately w Allows human thought to be translated into efficient processing of large amounts of data MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001 17
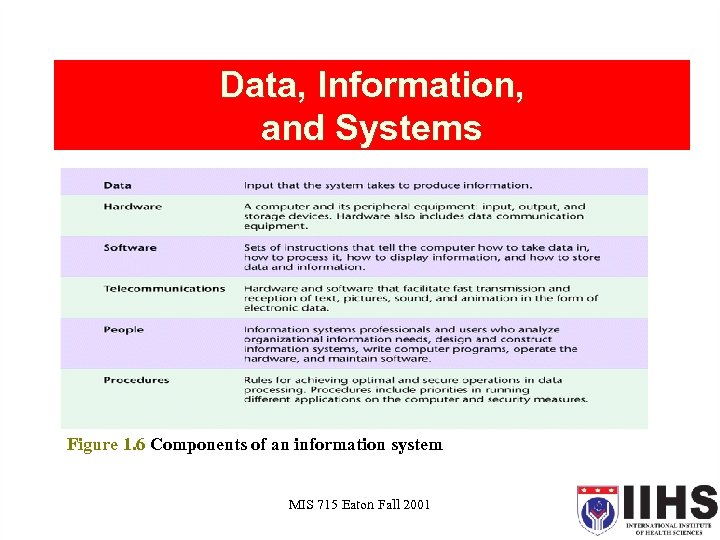 Data, Information, and Systems Figure 1. 6 Components of an information system MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001 18
Data, Information, and Systems Figure 1. 6 Components of an information system MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001 18
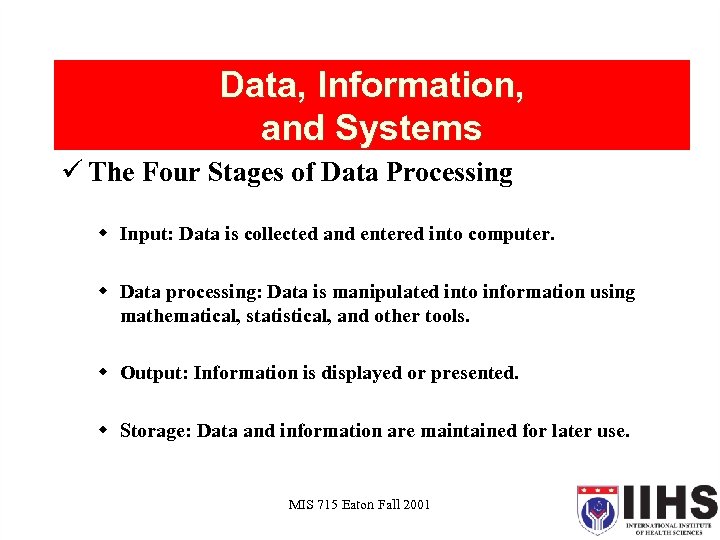 Data, Information, and Systems ü The Four Stages of Data Processing w Input: Data is collected and entered into computer. w Data processing: Data is manipulated into information using mathematical, statistical, and other tools. w Output: Information is displayed or presented. w Storage: Data and information are maintained for later use. MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001 19
Data, Information, and Systems ü The Four Stages of Data Processing w Input: Data is collected and entered into computer. w Data processing: Data is manipulated into information using mathematical, statistical, and other tools. w Output: Information is displayed or presented. w Storage: Data and information are maintained for later use. MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001 19
 Why Study IS? ü Information Systems Careers w Systems analyst, specialist in enterprise resource planning (ERP), database administrator, telecommunications specialist, consulting, etc. ü Knowledge Workers w Managers and non-managers w Employers seek computer-literate professionals who know how to use information technology. ü Computer Literacy Replacing Traditional Literacy w Key to full participation in western society MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001 20
Why Study IS? ü Information Systems Careers w Systems analyst, specialist in enterprise resource planning (ERP), database administrator, telecommunications specialist, consulting, etc. ü Knowledge Workers w Managers and non-managers w Employers seek computer-literate professionals who know how to use information technology. ü Computer Literacy Replacing Traditional Literacy w Key to full participation in western society MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001 20
 Ethical and Societal Issues The Not-So-Bright Side ü Consumer Privacy w Organizations collect (and sometimes sell) huge amounts of data on individuals. ü Employee Privacy w IT supports remote monitoring of employees, violating privacy and creating stress. MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001 21
Ethical and Societal Issues The Not-So-Bright Side ü Consumer Privacy w Organizations collect (and sometimes sell) huge amounts of data on individuals. ü Employee Privacy w IT supports remote monitoring of employees, violating privacy and creating stress. MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001 21
 Ethical and Societal Issues The Not-So-Bright Side ü Freedom of Speech w IT increases opportunities for pornography, hate speech, intellectual property crime, an d other intrusions; prevention may abridge free speech. ü IT Professionalism w No mandatory or enforced code of ethics for IT professionals--unlike other professions. ü Social Inequality w Less than 20% of the world’s population have ever used a PC; less than 3% have Internet access. MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001 22
Ethical and Societal Issues The Not-So-Bright Side ü Freedom of Speech w IT increases opportunities for pornography, hate speech, intellectual property crime, an d other intrusions; prevention may abridge free speech. ü IT Professionalism w No mandatory or enforced code of ethics for IT professionals--unlike other professions. ü Social Inequality w Less than 20% of the world’s population have ever used a PC; less than 3% have Internet access. MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001 22
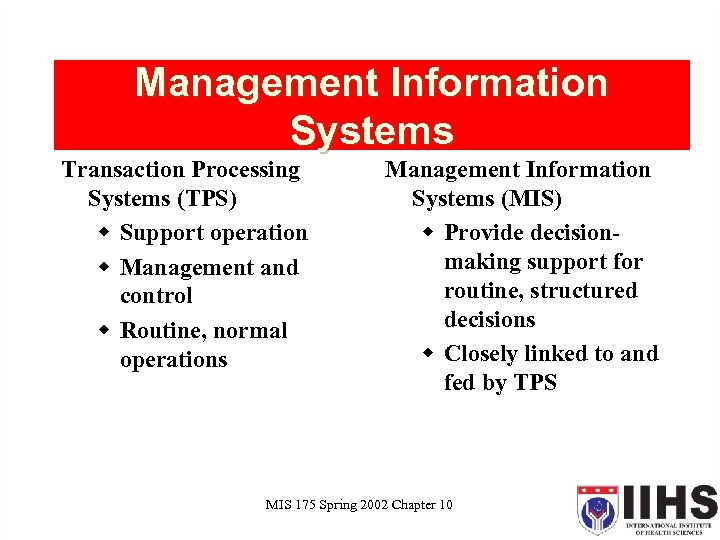 Management Information Systems Transaction Processing Systems (TPS) w Support operation w Management and control w Routine, normal operations Management Information Systems (MIS) w Provide decisionmaking support for routine, structured decisions w Closely linked to and fed by TPS MIS 175 Spring 2002 Chapter 10 23
Management Information Systems Transaction Processing Systems (TPS) w Support operation w Management and control w Routine, normal operations Management Information Systems (MIS) w Provide decisionmaking support for routine, structured decisions w Closely linked to and fed by TPS MIS 175 Spring 2002 Chapter 10 23
 Management Information Systems ü Terminology Confusion w MIS = the study of information technology in business settings w But, MIS is also term to refer to class of systems used to support operational and tactical decisionmaking MIS 175 Spring 2002 Chapter 10 24
Management Information Systems ü Terminology Confusion w MIS = the study of information technology in business settings w But, MIS is also term to refer to class of systems used to support operational and tactical decisionmaking MIS 175 Spring 2002 Chapter 10 24
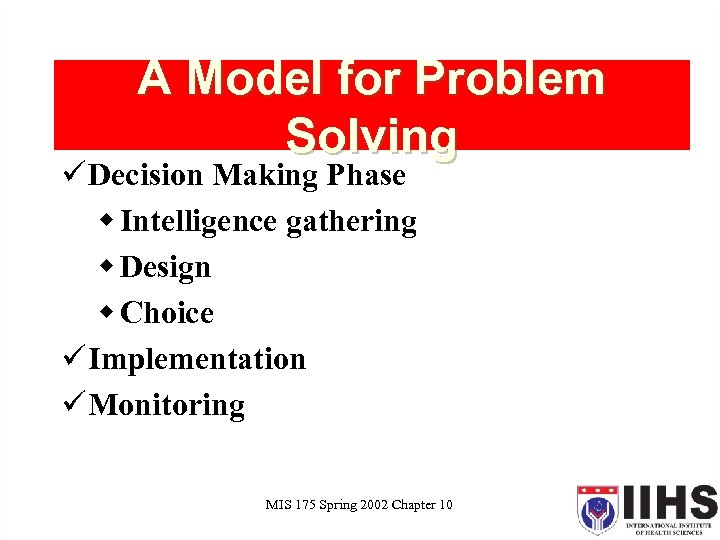 A Model for Problem Solving ü Decision Making Phase w Intelligence gathering w Design w Choice ü Implementation ü Monitoring MIS 175 Spring 2002 Chapter 10 25
A Model for Problem Solving ü Decision Making Phase w Intelligence gathering w Design w Choice ü Implementation ü Monitoring MIS 175 Spring 2002 Chapter 10 25
 Decision Making ü A step in problem solving ü Intelligence gathering w Definition of problem w Data gathered on scope w Constraints identified ü Design phase w Alternatives identified and assessed ü Choice w Selection of an alternative MIS 175 Spring 2002 Chapter 10 26
Decision Making ü A step in problem solving ü Intelligence gathering w Definition of problem w Data gathered on scope w Constraints identified ü Design phase w Alternatives identified and assessed ü Choice w Selection of an alternative MIS 175 Spring 2002 Chapter 10 26
 Structured vs. Unstructured Problems ü Structured problems lend themselves to programmed decisions w The implication is that a repeatable process can be employed and these can be automated ü Unstructured problems require unprogrammed decisions MIS 175 Spring 2002 Chapter 10 27
Structured vs. Unstructured Problems ü Structured problems lend themselves to programmed decisions w The implication is that a repeatable process can be employed and these can be automated ü Unstructured problems require unprogrammed decisions MIS 175 Spring 2002 Chapter 10 27
 Unstructured Problems ü Can be addressed (or partially addressed) with Decision Support Systems MIS 175 Spring 2002 Chapter 10 28
Unstructured Problems ü Can be addressed (or partially addressed) with Decision Support Systems MIS 175 Spring 2002 Chapter 10 28
 Structured Problems ü Can be addressed by an MIS ü Three decision models or techniques w Optimization Find the best solution w Satisficing Find a solution which meets certain criteria w Heuristics Rule-based solution generation MIS 175 Spring 2002 Chapter 10 29
Structured Problems ü Can be addressed by an MIS ü Three decision models or techniques w Optimization Find the best solution w Satisficing Find a solution which meets certain criteria w Heuristics Rule-based solution generation MIS 175 Spring 2002 Chapter 10 29
 Goals of an MIS ü Provide managers with information ü Regular, routine operations ü Control, organize and plan better MIS 175 Spring 2002 Chapter 10 30
Goals of an MIS ü Provide managers with information ü Regular, routine operations ü Control, organize and plan better MIS 175 Spring 2002 Chapter 10 30
 Typical Inputs and Outputs ü Inputs: Information from the TPS ü Outputs: hard and softcopy reports w Scheduled reports w On-demand reports w Key-indicator (business fundamentals) w Exception reports MIS 175 Spring 2002 Chapter 10 31
Typical Inputs and Outputs ü Inputs: Information from the TPS ü Outputs: hard and softcopy reports w Scheduled reports w On-demand reports w Key-indicator (business fundamentals) w Exception reports MIS 175 Spring 2002 Chapter 10 31
 Functional Perspectives of MIS ü Financial MIS w Will integrate information from multiple sources w Functions Costing P&L reporting Auditing Funds management MIS 175 Spring 2002 Chapter 10 32
Functional Perspectives of MIS ü Financial MIS w Will integrate information from multiple sources w Functions Costing P&L reporting Auditing Funds management MIS 175 Spring 2002 Chapter 10 32
 Functional Perspectives of MIS ü Manufacturing w Design and Engineering w Master Production Scheduling w Inventory Control w Materials Planning w Manufacturing and Process Control w Quality Control MIS 175 Spring 2002 Chapter 10 33
Functional Perspectives of MIS ü Manufacturing w Design and Engineering w Master Production Scheduling w Inventory Control w Materials Planning w Manufacturing and Process Control w Quality Control MIS 175 Spring 2002 Chapter 10 33
 Functional Perspectives of MIS ü Marketing w Market research Web-based market research w Pricing MIS 175 Spring 2002 Chapter 10 34
Functional Perspectives of MIS ü Marketing w Market research Web-based market research w Pricing MIS 175 Spring 2002 Chapter 10 34
 Functional Perspectives of MIS ü Transportation and Logistics w Route and schedule optimization ü Human Resources ü Accounting MIS 175 Spring 2002 Chapter 10 35
Functional Perspectives of MIS ü Transportation and Logistics w Route and schedule optimization ü Human Resources ü Accounting MIS 175 Spring 2002 Chapter 10 35
 Decision Support Systems ü Used for unstructured problems ü Characteristics w w w Data from multiple sources internal and external to organization Presentation flexibility Simulation and what-if capability Support for multiple decision approaches Statistical analysis MIS 175 Spring 2002 Chapter 10 36
Decision Support Systems ü Used for unstructured problems ü Characteristics w w w Data from multiple sources internal and external to organization Presentation flexibility Simulation and what-if capability Support for multiple decision approaches Statistical analysis MIS 175 Spring 2002 Chapter 10 36
 Components of a DSS ü Model management software w Provides a variety of solution models Financial, statistical, graphical, project management ü Dialogue Manager w Allows user interaction with DSS MIS 175 Spring 2002 Chapter 10 37
Components of a DSS ü Model management software w Provides a variety of solution models Financial, statistical, graphical, project management ü Dialogue Manager w Allows user interaction with DSS MIS 175 Spring 2002 Chapter 10 37
 Group Decision Making Systems ü Very interesting field ü How can information technology improve how decisions are made by groups? MIS 175 Spring 2002 Chapter 10 38
Group Decision Making Systems ü Very interesting field ü How can information technology improve how decisions are made by groups? MIS 175 Spring 2002 Chapter 10 38
 Group Decision Making Systems ü Applications w w w Where time is critical Where participants are geographically dispersed Where authority obstructs communication Military Business Government MIS 175 Spring 2002 Chapter 10 39
Group Decision Making Systems ü Applications w w w Where time is critical Where participants are geographically dispersed Where authority obstructs communication Military Business Government MIS 175 Spring 2002 Chapter 10 39
 Group Decision Making Systems ü Common characteristics w Meeting moderation/facilitation w Signed anonymous comments w Structured deliberations Presentation period Comment period Automated collation of comments “Voting” ü Face-to-face and remote MIS 175 Spring 2002 Chapter 10 40
Group Decision Making Systems ü Common characteristics w Meeting moderation/facilitation w Signed anonymous comments w Structured deliberations Presentation period Comment period Automated collation of comments “Voting” ü Face-to-face and remote MIS 175 Spring 2002 Chapter 10 40
 Executive Information Systems ü What information does a chief executive of board member require? MIS 175 Spring 2002 Chapter 10 41
Executive Information Systems ü What information does a chief executive of board member require? MIS 175 Spring 2002 Chapter 10 41
 Executive Information Systems ü High level with drill down ü Key business and industry data ü Structured and unstructured information w Structured: MTD orders w Unstructured: Industry newsfeed ü Graphical MIS 175 Spring 2002 Chapter 10 42
Executive Information Systems ü High level with drill down ü Key business and industry data ü Structured and unstructured information w Structured: MTD orders w Unstructured: Industry newsfeed ü Graphical MIS 175 Spring 2002 Chapter 10 42
 Activity 01 ü What are the benefits in MIS for healthcare services ? Make a mind map MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001 43
Activity 01 ü What are the benefits in MIS for healthcare services ? Make a mind map MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001 43
 Introduction to Process analysis Work flow process MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001
Introduction to Process analysis Work flow process MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001
 HM 01 3. 2 Systems Management in Hospitals
HM 01 3. 2 Systems Management in Hospitals
 Hospital Environment
Hospital Environment
 Organizational Environment • Organization can not function in isolation • Complex factors • Dynamic • Mainly 02 – Internal & external • Internal • External – – • Near Far
Organizational Environment • Organization can not function in isolation • Complex factors • Dynamic • Mainly 02 – Internal & external • Internal • External – – • Near Far
 Internal environment ü Staff , Resources, facilities ü Within the organization ü Controlled by the manager ü Influenced by the Near & Far environments
Internal environment ü Staff , Resources, facilities ü Within the organization ü Controlled by the manager ü Influenced by the Near & Far environments
 Near Environment ü Patients, suppliers, competitors, local politicians ü Interact with the organization ü Can not control internal environment ü Can influence both ways
Near Environment ü Patients, suppliers, competitors, local politicians ü Interact with the organization ü Can not control internal environment ü Can influence both ways
 Far Environment • Political • Economic • Social • Technology • Health related variables • Organization can not influence or control • Need to adopt / respond • Faster response – success
Far Environment • Political • Economic • Social • Technology • Health related variables • Organization can not influence or control • Need to adopt / respond • Faster response – success
 Boundaries ü In-house service environment ü Out sourced services
Boundaries ü In-house service environment ü Out sourced services
 Stake holders • Keen interest in the organization on – What it does – How it does • Employees , managers , directors, board members • Patients , customers • Suppliers • Competitors • Regulators • Trade unions • Partners
Stake holders • Keen interest in the organization on – What it does – How it does • Employees , managers , directors, board members • Patients , customers • Suppliers • Competitors • Regulators • Trade unions • Partners
 Hospital systems management & Introduction to Process Management
Hospital systems management & Introduction to Process Management
 What is Hospital ? “An institution that provides medical, surgical, or psychiatric care and treatment for the sick or the injured” Care = Concern Treatment = action, management, healing American Heritage® Dictionary
What is Hospital ? “An institution that provides medical, surgical, or psychiatric care and treatment for the sick or the injured” Care = Concern Treatment = action, management, healing American Heritage® Dictionary
 What is an Institute • Group • Club • Organization • Union • Business A complete unit – Ex: Human body , a hospital
What is an Institute • Group • Club • Organization • Union • Business A complete unit – Ex: Human body , a hospital
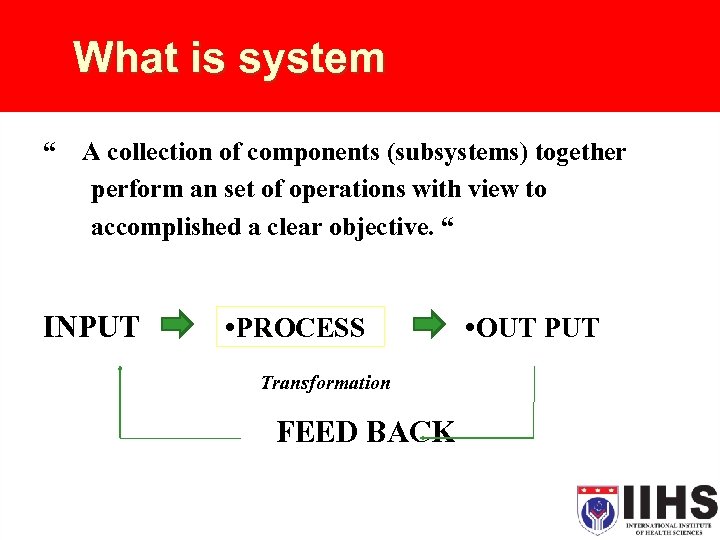 What is system “ A collection of components (subsystems) together perform an set of operations with view to accomplished a clear objective. “ INPUT PROCESS Transformation FEED BACK OUT PUT
What is system “ A collection of components (subsystems) together perform an set of operations with view to accomplished a clear objective. “ INPUT PROCESS Transformation FEED BACK OUT PUT
 Hospital as a system • Input – Sick patients /Resources • Process – Different service units transform the patient and the related components • Output – Well Managed patient/ Used resources
Hospital as a system • Input – Sick patients /Resources • Process – Different service units transform the patient and the related components • Output – Well Managed patient/ Used resources
 A Hospital • Self sustained entity • Open system • Dynamic • To sustain needs -clear input /out put • This is supported by Sub systems • Sub systems = services • Ambulance services – transport system / services • Engineering services - electrical • Supply Chain Mg. - supplies • Janitorial – waste management services / system • Protection – security system/ services Patient care – core service
A Hospital • Self sustained entity • Open system • Dynamic • To sustain needs -clear input /out put • This is supported by Sub systems • Sub systems = services • Ambulance services – transport system / services • Engineering services - electrical • Supply Chain Mg. - supplies • Janitorial – waste management services / system • Protection – security system/ services Patient care – core service
 A Hospital as a system • It is a part of a large healthcare system • Dynamic balance with wider social system • Boundaries are hazy • Open system interacts with the environment • Dynamic • Clear out put is difficult measure when compared with inputs
A Hospital as a system • It is a part of a large healthcare system • Dynamic balance with wider social system • Boundaries are hazy • Open system interacts with the environment • Dynamic • Clear out put is difficult measure when compared with inputs
 What is a Sub system • Unit = OPD unit • Has clear Input / Out put • Consist of Functional units – functional units
What is a Sub system • Unit = OPD unit • Has clear Input / Out put • Consist of Functional units – functional units
 Functional units & the process • Each unit has processes – main / core process - ON STAGE – supportive/ sub process - BACK STAGE • Human Cardio Vascular system • • • heart – core process – PUMP BLOOD tubes / blood components -TRANSPORT OPD – Patient care process – Consultation – SEE PATIENTS – Supportive process - Janitorial – back stage - CLEAN ROOMS
Functional units & the process • Each unit has processes – main / core process - ON STAGE – supportive/ sub process - BACK STAGE • Human Cardio Vascular system • • • heart – core process – PUMP BLOOD tubes / blood components -TRANSPORT OPD – Patient care process – Consultation – SEE PATIENTS – Supportive process - Janitorial – back stage - CLEAN ROOMS
 Process • Course of action • Core process • Support process • OPD – Patient care process – core – Facility process – supportive • Performed in functional units – Patient care process – Consultation unit – Facility process – Reception units
Process • Course of action • Core process • Support process • OPD – Patient care process – core – Facility process – supportive • Performed in functional units – Patient care process – Consultation unit – Facility process – Reception units
 The Process “A process is a set of logically related tasks performed to achieve a defined outcome” FUNCTIONS – ACTIVITIES – TASKS
The Process “A process is a set of logically related tasks performed to achieve a defined outcome” FUNCTIONS – ACTIVITIES – TASKS
 A. Functions • Functions • Well demarcated part of the process • Generally in different sub units • At OPD – Reception – Registration – Payment
A. Functions • Functions • Well demarcated part of the process • Generally in different sub units • At OPD – Reception – Registration – Payment
 B. Activities • Sub unit of Functions • At OPD • Functional unit – Reception • Activities – Greeting – Registering – Directing
B. Activities • Sub unit of Functions • At OPD • Functional unit – Reception • Activities – Greeting – Registering – Directing
 C. Tasks • Final sub unit • Very clear , simple out put • Greeting activity • Tasks – Presenting – Greeting – Introducing – Identifying
C. Tasks • Final sub unit • Very clear , simple out put • Greeting activity • Tasks – Presenting – Greeting – Introducing – Identifying
 SAMPLE PROCESS ANALYSIS ü . . DHADHA 01Module 01HM 01. 3. 11. 2. 3Process analysis selected units. xls
SAMPLE PROCESS ANALYSIS ü . . DHADHA 01Module 01HM 01. 3. 11. 2. 3Process analysis selected units. xls
 Why need to manage process in hospitals ü ü ü ü Faced with multiple pressures Increasing patient loads Increasing hospital operating costs Shortage of qualified healthcare staff Limited hospital facilities Reduction of the profit margin In hospitals there are substantial fixed costs due to facility and equipment investments from year to year. ü Cost. Time. Quality
Why need to manage process in hospitals ü ü ü ü Faced with multiple pressures Increasing patient loads Increasing hospital operating costs Shortage of qualified healthcare staff Limited hospital facilities Reduction of the profit margin In hospitals there are substantial fixed costs due to facility and equipment investments from year to year. ü Cost. Time. Quality
 Activity 02 ü List you daily work process in your unit ü Identify core process and support process ü Concentrate on the core process and list the functions , activities and tasks ü Organize it a flow chart format ü Identify the information flow in each function ü Identify delay in each areas ü Suggest a better method to save cost, time and improve quality MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001 69
Activity 02 ü List you daily work process in your unit ü Identify core process and support process ü Concentrate on the core process and list the functions , activities and tasks ü Organize it a flow chart format ü Identify the information flow in each function ü Identify delay in each areas ü Suggest a better method to save cost, time and improve quality MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001 69
 Flow chart symbols ü flow charts. xls MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001 70
Flow chart symbols ü flow charts. xls MIS 715 Eaton Fall 2001 70
 Thank you !
Thank you !


