Презентация Щербаковой TEMPUS.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 48
 Module Foreign Language Teaching Methodology
Module Foreign Language Teaching Methodology
 Summary of the Unit • Teaching Language Skills. Teaching Receptive Skills (Reading and Listening) • Teaching Language Skills. Teaching Productive Skills (Speaking and Writing) • Teaching Language Skills. Teaching integrated skills.
Summary of the Unit • Teaching Language Skills. Teaching Receptive Skills (Reading and Listening) • Teaching Language Skills. Teaching Productive Skills (Speaking and Writing) • Teaching Language Skills. Teaching integrated skills.
 Learning outcomes Learners will be able to: • gain competence in teaching reading and listening skills; • gain competence in teaching speaking and writing skills; • gain insight into language skills and will be able to incorporate all of the skills during the lesson.
Learning outcomes Learners will be able to: • gain competence in teaching reading and listening skills; • gain competence in teaching speaking and writing skills; • gain insight into language skills and will be able to incorporate all of the skills during the lesson.
 Content of the lessons
Content of the lessons
 Lesson 1. Teaching Receptive Skills (reading and listening) Spark 1 Challenge Problem • What is the difference between spoken and written language? • What is reading? • What is the purpose for reading and listening? • What is the process of reading and listening from psycholinguistic point of view?
Lesson 1. Teaching Receptive Skills (reading and listening) Spark 1 Challenge Problem • What is the difference between spoken and written language? • What is reading? • What is the purpose for reading and listening? • What is the process of reading and listening from psycholinguistic point of view?
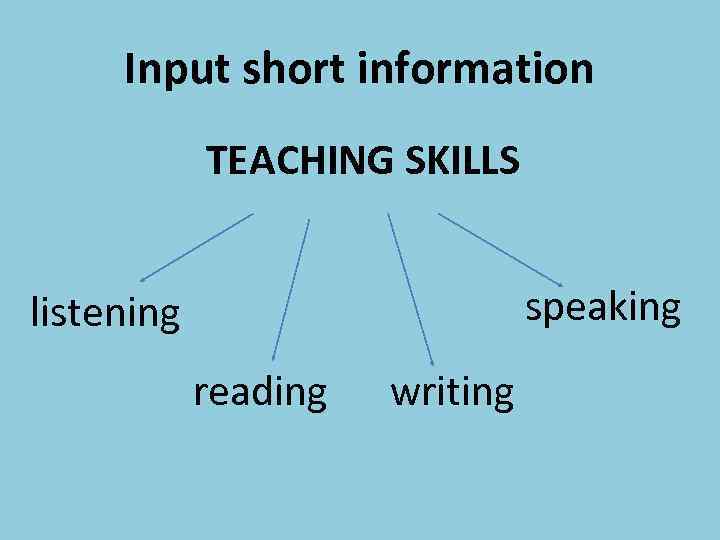 Input short information TEACHING SKILLS speaking listening reading writing
Input short information TEACHING SKILLS speaking listening reading writing
 The four basic skills are related to each other by two parameters: • the mode of communication: oral or written • the direction of communication: receiving or producing the message
The four basic skills are related to each other by two parameters: • the mode of communication: oral or written • the direction of communication: receiving or producing the message
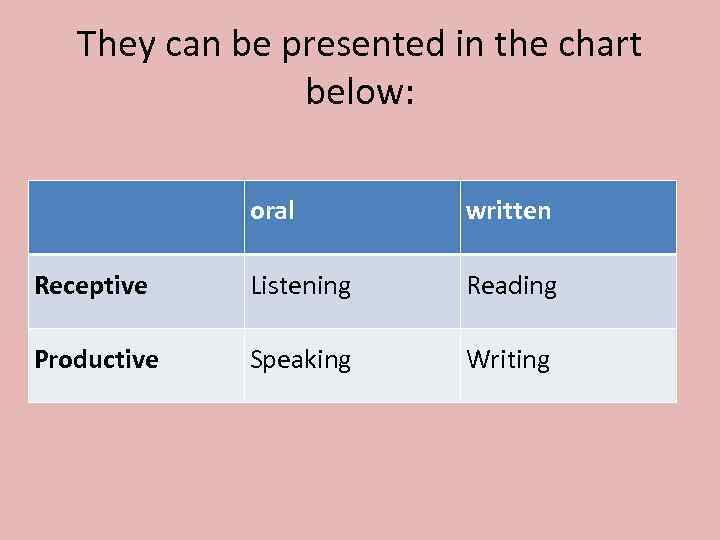 They can be presented in the chart below: oral written Receptive Listening Reading Productive Speaking Writing
They can be presented in the chart below: oral written Receptive Listening Reading Productive Speaking Writing
 Teaching reading Reading strategies: Before reading: Plan for the reading task • Set a purpose or decide in advance what to read for • Decide if more linguistic or background knowledge is needed • Determine whether to enter the text from the top down (attend to the overall meaning) or from the bottom up (focus on the words and phrases) During and after reading: Monitor comprehension • Verify predictions and check for inaccurate guesses • Decide what is and is not important to understand • Reread to check comprehension • Ask for help After reading: Evaluate comprehension and strategy use • Evaluate comprehension in a particular task or area • Evaluate overall progress in reading and in particular types of reading tasks • Decide if the strategies used were appropriate for the purpose and for the task • Modify strategies if necessary
Teaching reading Reading strategies: Before reading: Plan for the reading task • Set a purpose or decide in advance what to read for • Decide if more linguistic or background knowledge is needed • Determine whether to enter the text from the top down (attend to the overall meaning) or from the bottom up (focus on the words and phrases) During and after reading: Monitor comprehension • Verify predictions and check for inaccurate guesses • Decide what is and is not important to understand • Reread to check comprehension • Ask for help After reading: Evaluate comprehension and strategy use • Evaluate comprehension in a particular task or area • Evaluate overall progress in reading and in particular types of reading tasks • Decide if the strategies used were appropriate for the purpose and for the task • Modify strategies if necessary
 Teaching Listening strategies: Before listening: Plan for the listening task • Set a purpose or decide in advance what to listen for • Decide if more linguistic or background knowledge is needed • Determine whether to enter the text from the top down (attend to the overall meaning) or from the bottom up (focus on the words and phrases) During and after listening: Monitor comprehension • Verify predictions and check for inaccurate guesses • Decide what is and is not important to understand • Listen/view again to check comprehension • Ask for help After listening: Evaluate comprehension and strategy use • Evaluate comprehension in a particular task or area • Evaluate overall progress in listening and in particular types of listening tasks • Decide if the strategies used were appropriate for the purpose and for the task • Modify strategies if necessary
Teaching Listening strategies: Before listening: Plan for the listening task • Set a purpose or decide in advance what to listen for • Decide if more linguistic or background knowledge is needed • Determine whether to enter the text from the top down (attend to the overall meaning) or from the bottom up (focus on the words and phrases) During and after listening: Monitor comprehension • Verify predictions and check for inaccurate guesses • Decide what is and is not important to understand • Listen/view again to check comprehension • Ask for help After listening: Evaluate comprehension and strategy use • Evaluate comprehension in a particular task or area • Evaluate overall progress in listening and in particular types of listening tasks • Decide if the strategies used were appropriate for the purpose and for the task • Modify strategies if necessary
 Steps for reading and listening • • Predict and guess Indentify the topic Give general idea Specify the information Present the information in detail Analyze the text Interpret the text Give a synopsis of the text
Steps for reading and listening • • Predict and guess Indentify the topic Give general idea Specify the information Present the information in detail Analyze the text Interpret the text Give a synopsis of the text
 Lesson 2. Teaching Productive Language Skills (speaking and writing) Spark 2 Challenge Problem • What is the difference between spoken and written language? • What are the aspects of language acquisition? • What areas of knowledge does speaking involve? • What specific knowledge should you have to be good at writing?
Lesson 2. Teaching Productive Language Skills (speaking and writing) Spark 2 Challenge Problem • What is the difference between spoken and written language? • What are the aspects of language acquisition? • What areas of knowledge does speaking involve? • What specific knowledge should you have to be good at writing?
 Discussion 2 • What are the reasons of people’s communication? • What is the difference between accuracy and fluency in language acquisition? • What are psycholinguistic peculiarities within speaking and writing process? • What competences are obtained to accurate and fluent in speaking and writing? • What is the best way to encourage students to speaking and writing?
Discussion 2 • What are the reasons of people’s communication? • What is the difference between accuracy and fluency in language acquisition? • What are psycholinguistic peculiarities within speaking and writing process? • What competences are obtained to accurate and fluent in speaking and writing? • What is the best way to encourage students to speaking and writing?
 Teaching Productive Skills The difference between accuracy and fluency activities: • Accuracy activities are concentrated on producing correct language from cultural, lexical and grammatical view points. Such activities are usually controlled to ensure accurate reproduction of any language. • Fluency activities are concentrated on allowing the student to experiment and be creative with the language. We are less concerned with accuracy and more concerned with the effectiveness and flow of communication.
Teaching Productive Skills The difference between accuracy and fluency activities: • Accuracy activities are concentrated on producing correct language from cultural, lexical and grammatical view points. Such activities are usually controlled to ensure accurate reproduction of any language. • Fluency activities are concentrated on allowing the student to experiment and be creative with the language. We are less concerned with accuracy and more concerned with the effectiveness and flow of communication.
 SPEAKING Speaking involves three areas of knowledge: • Mechanics (pronunciation, grammar, and vocabulary): Using the right words in the right order with the correct pronunciation • Functions (transaction and interaction): Knowing when clarity of message is essential (transaction/information exchange) and when precise understanding is not required (interaction/relationship building) • Social and cultural rules and norms (turn-taking, rate of speech, length of pauses between speakers, relative roles of participants): Understanding how to take into account who is speaking to whom, in what circumstances, about what, and for what reason.
SPEAKING Speaking involves three areas of knowledge: • Mechanics (pronunciation, grammar, and vocabulary): Using the right words in the right order with the correct pronunciation • Functions (transaction and interaction): Knowing when clarity of message is essential (transaction/information exchange) and when precise understanding is not required (interaction/relationship building) • Social and cultural rules and norms (turn-taking, rate of speech, length of pauses between speakers, relative roles of participants): Understanding how to take into account who is speaking to whom, in what circumstances, about what, and for what reason.
 Steps for Speaking • • • Extend the vocabulary Develop structural accuracy Develop phonological accuracy Turn-taking Develop style Practise
Steps for Speaking • • • Extend the vocabulary Develop structural accuracy Develop phonological accuracy Turn-taking Develop style Practise
 Strategies for Developing Speaking Skills • • • using minimal responses, recognizing scripts, using language to talk about language, turn-taking, pragmatics/social skills activities
Strategies for Developing Speaking Skills • • • using minimal responses, recognizing scripts, using language to talk about language, turn-taking, pragmatics/social skills activities
 Activities To Promote Speaking • Structured Output Activities information gap and jigsaw activities • Communicative Output Activities role plays and discussions
Activities To Promote Speaking • Structured Output Activities information gap and jigsaw activities • Communicative Output Activities role plays and discussions
 WRITING Steps for Writing • Developing vocabulary • Developing structural accuracy • Developing orthographic accuracy • Writing • Revision
WRITING Steps for Writing • Developing vocabulary • Developing structural accuracy • Developing orthographic accuracy • Writing • Revision
 Writing strategies • • Pre-writing Drafting Dictation Revising/editing
Writing strategies • • Pre-writing Drafting Dictation Revising/editing
 Lesson 3. Teaching integrated skills Spark 3 Challenge Problem • What is the difference between receptive and productive skills? • What is integration? • What are the reasons for using integrated-skill techniques at the English lesson?
Lesson 3. Teaching integrated skills Spark 3 Challenge Problem • What is the difference between receptive and productive skills? • What is integration? • What are the reasons for using integrated-skill techniques at the English lesson?
 Discussion 3 • What skills do we incorporate while planning to present a new teaching item (sound, vocabulary word, etc. )?
Discussion 3 • What skills do we incorporate while planning to present a new teaching item (sound, vocabulary word, etc. )?
 Complex nature of Integrated skills The integration of skills can be defined as the combination of two or more skills within a communicative task paying attention to the following reasons: • continuity • realism • appropriateness • variety • recycling • confidence
Complex nature of Integrated skills The integration of skills can be defined as the combination of two or more skills within a communicative task paying attention to the following reasons: • continuity • realism • appropriateness • variety • recycling • confidence
 Useful integration of two skills • • • - Listening and speaking - Listening and reading - Reading and writing - Speaking and writing - Listening and writing.
Useful integration of two skills • • • - Listening and speaking - Listening and reading - Reading and writing - Speaking and writing - Listening and writing.
 Models for integration of language aspects • - Speaking → Reading →Writing →Speaking ( →Writing) • - Listening → Writing → Speaking → Writing • - Reading → Writing → Listening →Speaking (→ Writing) • - Listening →Speaking → Reading → Writing
Models for integration of language aspects • - Speaking → Reading →Writing →Speaking ( →Writing) • - Listening → Writing → Speaking → Writing • - Reading → Writing → Listening →Speaking (→ Writing) • - Listening →Speaking → Reading → Writing
 Teaching stages • • Eliciting ideas Highlighting lexis and its meaning Predicting Ordering jumbled paragraphs Listening Reading comprehension Acting out the story/Speaking.
Teaching stages • • Eliciting ideas Highlighting lexis and its meaning Predicting Ordering jumbled paragraphs Listening Reading comprehension Acting out the story/Speaking.
 Face-to-face exercises
Face-to-face exercises
 Matching Study the given information. Match words in the first column to their meanings in the second column: skimming productive skills are sometimes known as passive skills skanning a type of rapid reading technique, receptive skills a type of speed-reading technique are also known as active skills.
Matching Study the given information. Match words in the first column to their meanings in the second column: skimming productive skills are sometimes known as passive skills skanning a type of rapid reading technique, receptive skills a type of speed-reading technique are also known as active skills.
 Compare different kinds of speaking activities. Define the purpose of each of them. - Discussions Role Play Simulations Brainstorming Storytelling Interviews Story Completion Reporting Playing Cards Picture Narrating Picture Describing Find the Difference - Divide them into 2 groups: structured output activities communicative output activity
Compare different kinds of speaking activities. Define the purpose of each of them. - Discussions Role Play Simulations Brainstorming Storytelling Interviews Story Completion Reporting Playing Cards Picture Narrating Picture Describing Find the Difference - Divide them into 2 groups: structured output activities communicative output activity
 Discussion 1 Watch the video presentation of Reading course made by Janet Swaffar, a Professor of Germanic Studies at the University of Texas. Make a list of problems which students will encounter during the course. Discuss them in groups.
Discussion 1 Watch the video presentation of Reading course made by Janet Swaffar, a Professor of Germanic Studies at the University of Texas. Make a list of problems which students will encounter during the course. Discuss them in groups.
 Discussion 2 Watch the video “How to Teach Writing: The Writing Process”. Write down the five stages of writing proposed by Jamie Edward. What helpful tips are mentioned in this video? Discuss them in groups.
Discussion 2 Watch the video “How to Teach Writing: The Writing Process”. Write down the five stages of writing proposed by Jamie Edward. What helpful tips are mentioned in this video? Discuss them in groups.
 Discussion 3 • Watch the slide presentation “Integrating the four skills” made by Professor Brown, (the University of Texas. Make a list of the five methods proposed to integrate language skills in the ESL/EFL classroom. Discuss them in groups.
Discussion 3 • Watch the slide presentation “Integrating the four skills” made by Professor Brown, (the University of Texas. Make a list of the five methods proposed to integrate language skills in the ESL/EFL classroom. Discuss them in groups.
 Case-study 1 • What is Jigsaw Activity?
Case-study 1 • What is Jigsaw Activity?
 Case-study 2 What are the discursive and cognitive aspects of the development of writing skills? Read the article “Interactive Writing in the EFL Class: A Repertoire of Tasks”. Summarize with words that represent the ideas of the author added with your own reflections about the problem.
Case-study 2 What are the discursive and cognitive aspects of the development of writing skills? Read the article “Interactive Writing in the EFL Class: A Repertoire of Tasks”. Summarize with words that represent the ideas of the author added with your own reflections about the problem.
 Case-study 3 • Read the article “Integrating Receptive Skills and Productive Skills into a Reading Lesson”. Summarize with words that represent the ideas of the author added with your own reflections about the topics covered in the unit.
Case-study 3 • Read the article “Integrating Receptive Skills and Productive Skills into a Reading Lesson”. Summarize with words that represent the ideas of the author added with your own reflections about the topics covered in the unit.
 On-line exercises
On-line exercises

 Group work • Read the article “Advantages and Disadvantages of Using computers in ESL reading” and discuss the “pros” and “cons” of using computers in ESL reading.
Group work • Read the article “Advantages and Disadvantages of Using computers in ESL reading” and discuss the “pros” and “cons” of using computers in ESL reading.
 Films about teaching situations • Watch the video about the reading comprehension skills and be ready to report how to improve reading.
Films about teaching situations • Watch the video about the reading comprehension skills and be ready to report how to improve reading.
 Project work Study different EFL/ESL games to practice reading skills and introduce one of them in class.
Project work Study different EFL/ESL games to practice reading skills and introduce one of them in class.
 Read the article “ 7 billion: Are you typical? (Integrating video with all four skills)” and take the quiz on line
Read the article “ 7 billion: Are you typical? (Integrating video with all four skills)” and take the quiz on line
 References • English as a Second Language. Integrate Ireland Language and Training. Dublin. 2004 • http: //www. videojug. com/film/how-to-teach-listening • https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=VBsl. JMq 4 LAg • http: //coerll. utexas. edu/methods/modules/reading/ • http: //www. teachingenglish. org. uk/think/knowledge-wiki/receptive-skills • http: //www. teachingenglish. org. uk/try/lesson-plans/a-content-languageintegrated-learning-lesson accessed on 5 December 2008. • Integrating Receptive Skills and Productive Skills into a Reading Lesson Harits Masduqi. TEFL Lecture Series. June 12, 2009 • Harmer Jeremy. The practice of English language teaching. Longman. 2009. • Christine Nuttall “Teaching reading skills in a foreign language”. Mac. Millan Heinemann. Oxford. 1999.
References • English as a Second Language. Integrate Ireland Language and Training. Dublin. 2004 • http: //www. videojug. com/film/how-to-teach-listening • https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=VBsl. JMq 4 LAg • http: //coerll. utexas. edu/methods/modules/reading/ • http: //www. teachingenglish. org. uk/think/knowledge-wiki/receptive-skills • http: //www. teachingenglish. org. uk/try/lesson-plans/a-content-languageintegrated-learning-lesson accessed on 5 December 2008. • Integrating Receptive Skills and Productive Skills into a Reading Lesson Harits Masduqi. TEFL Lecture Series. June 12, 2009 • Harmer Jeremy. The practice of English language teaching. Longman. 2009. • Christine Nuttall “Teaching reading skills in a foreign language”. Mac. Millan Heinemann. Oxford. 1999.
 THANK YOU FOR ATTENTION!
THANK YOU FOR ATTENTION!


