15960aaaaa3bf68b9d72b4d8f49114e1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 Module D Waiting Line Models
Module D Waiting Line Models
 Elements of Waiting Line Analysis ü Queue ü A single waiting line ü Waiting line system consists of ü Arrivals ü Servers ü Waiting line structures
Elements of Waiting Line Analysis ü Queue ü A single waiting line ü Waiting line system consists of ü Arrivals ü Servers ü Waiting line structures
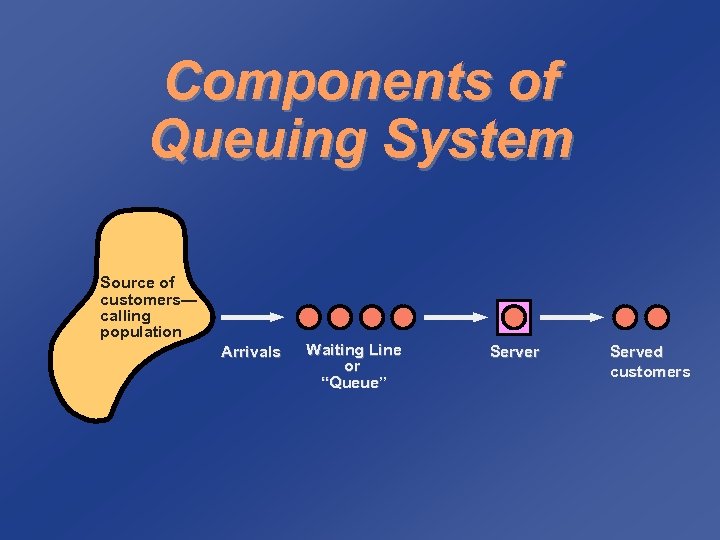 Components of Queuing System Source of customers— calling population Arrivals Waiting Line or “Queue” Server Served customers
Components of Queuing System Source of customers— calling population Arrivals Waiting Line or “Queue” Server Served customers
 Elements of a Waiting Line ü Calling population ü Source of customers ü Infinite - large enough that one more customer can always arrive to be served ü Finite - limited number of potential customers ü Arrival rate ( ) ü Frequency of customer arrivals at waiting line system ü Typically follows Poisson distribution
Elements of a Waiting Line ü Calling population ü Source of customers ü Infinite - large enough that one more customer can always arrive to be served ü Finite - limited number of potential customers ü Arrival rate ( ) ü Frequency of customer arrivals at waiting line system ü Typically follows Poisson distribution
 Elements of a Waiting Line ü Service time ü Often follows negative exponential distribution ü Average service rate = ü Arrival rate ( ) must be less than service rate or system never clears out
Elements of a Waiting Line ü Service time ü Often follows negative exponential distribution ü Average service rate = ü Arrival rate ( ) must be less than service rate or system never clears out
 Elements of a Waiting Line ü Queue discipline ü Order in which customers are served ü First come, first served is most common ü Length can be infinite or finite ü Infinite is most common ü Finite is limited by some physical structure (not covered)
Elements of a Waiting Line ü Queue discipline ü Order in which customers are served ü First come, first served is most common ü Length can be infinite or finite ü Infinite is most common ü Finite is limited by some physical structure (not covered)
 Basic Waiting Line Structures ü Channels are the number of parallel servers ü Phases denote number of sequential servers the customer must go through
Basic Waiting Line Structures ü Channels are the number of parallel servers ü Phases denote number of sequential servers the customer must go through
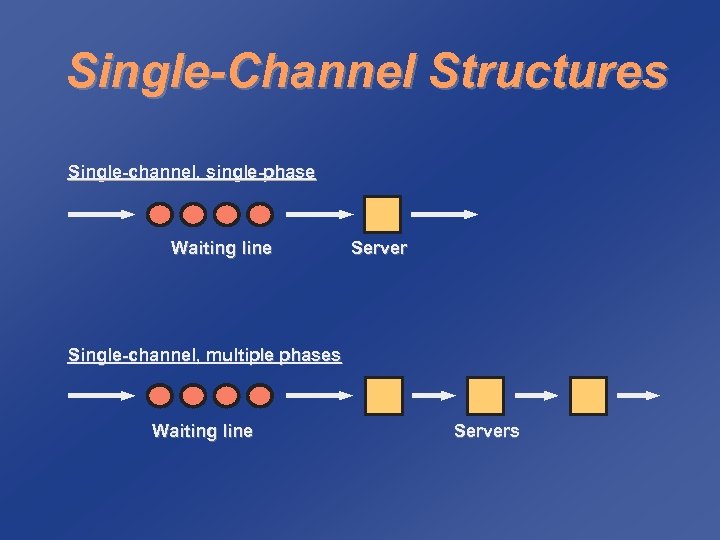 Single-Channel Structures Single-channel, single-phase Waiting line Server Single-channel, multiple phases Waiting line Servers
Single-Channel Structures Single-channel, single-phase Waiting line Server Single-channel, multiple phases Waiting line Servers
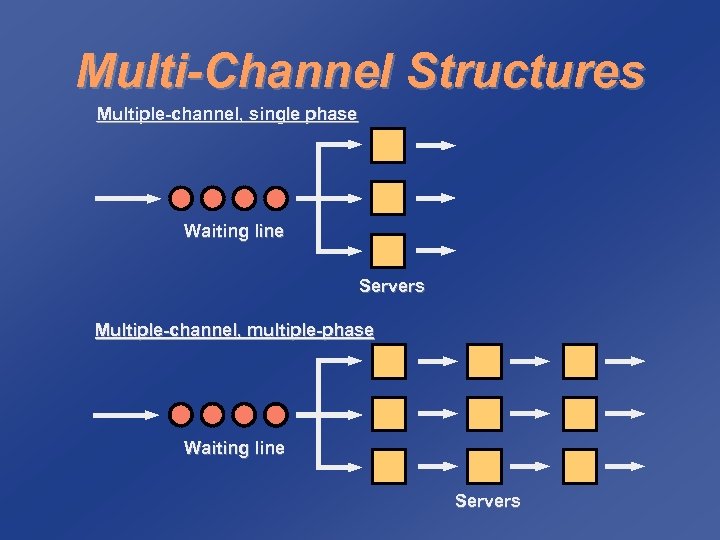 Multi-Channel Structures Multiple-channel, single phase Waiting line Servers Multiple-channel, multiple-phase Waiting line Servers
Multi-Channel Structures Multiple-channel, single phase Waiting line Servers Multiple-channel, multiple-phase Waiting line Servers
 Operating Characteristics ü Mathematics of queuing theory does not provide optimal or best solutions ü Operating characteristics are computed that describe system performance ü Steady state is constant, average value for performance characteristics that the system will reach after a long time
Operating Characteristics ü Mathematics of queuing theory does not provide optimal or best solutions ü Operating characteristics are computed that describe system performance ü Steady state is constant, average value for performance characteristics that the system will reach after a long time
 Operating Characteristics NOTATION OPERATING CHARACTERISTIC L Average number of customers in the system (waiting and being served) Lq Average number of customers in the waiting line W Average time a customer spends in the system (waiting and being served) Wq Average time a customer spends waiting in line
Operating Characteristics NOTATION OPERATING CHARACTERISTIC L Average number of customers in the system (waiting and being served) Lq Average number of customers in the waiting line W Average time a customer spends in the system (waiting and being served) Wq Average time a customer spends waiting in line
 Operating Characteristics NOTATION OPERATING CHARACTERISTIC P 0 Probability of no (zero) customers in the system Pn Probability of n customers in the system Utilization rate; the proportion of time the system is in use
Operating Characteristics NOTATION OPERATING CHARACTERISTIC P 0 Probability of no (zero) customers in the system Pn Probability of n customers in the system Utilization rate; the proportion of time the system is in use
 Single-Channel, Single. Phase Models ü All assume Poisson arrival rate ü Variations ü Exponential service times ü Constant service times ü Others are not considered
Single-Channel, Single. Phase Models ü All assume Poisson arrival rate ü Variations ü Exponential service times ü Constant service times ü Others are not considered
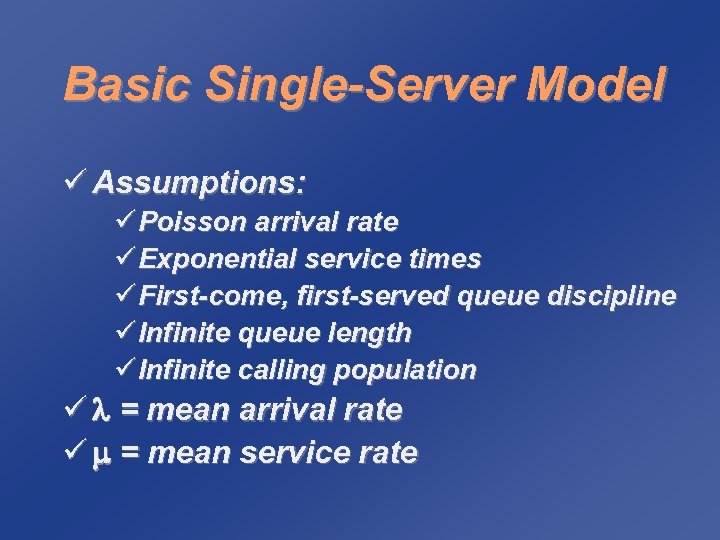 Basic Single-Server Model ü Assumptions: ü Poisson arrival rate ü Exponential service times ü First-come, first-served queue discipline ü Infinite queue length ü Infinite calling population ü = mean arrival rate ü = mean service rate
Basic Single-Server Model ü Assumptions: ü Poisson arrival rate ü Exponential service times ü First-come, first-served queue discipline ü Infinite queue length ü Infinite calling population ü = mean arrival rate ü = mean service rate
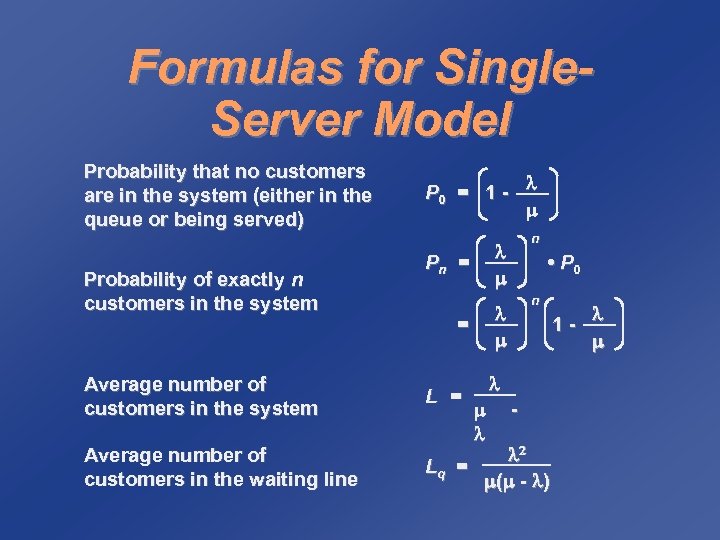 Formulas for Single. Server Model Probability that no customers are in the system (either in the queue or being served) Probability of exactly n customers in the system Average number of customers in the waiting line P 0 = 1 - Pn = = n • P 0 n Lq = ( - ) L = 1 -
Formulas for Single. Server Model Probability that no customers are in the system (either in the queue or being served) Probability of exactly n customers in the system Average number of customers in the waiting line P 0 = 1 - Pn = = n • P 0 n Lq = ( - ) L = 1 -
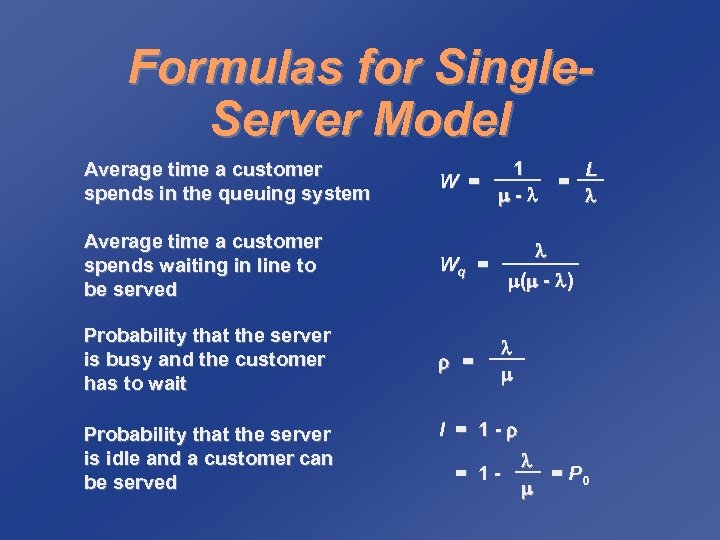 Formulas for Single. Server Model Average time a customer spends in the queuing system 1 L W = = - Average time a customer spends waiting in line to be served Wq = Probability that the server is busy and the customer has to wait Probability that the server is idle and a customer can be served = ( - ) I = 1 - = P 0
Formulas for Single. Server Model Average time a customer spends in the queuing system 1 L W = = - Average time a customer spends waiting in line to be served Wq = Probability that the server is busy and the customer has to wait Probability that the server is idle and a customer can be served = ( - ) I = 1 - = P 0
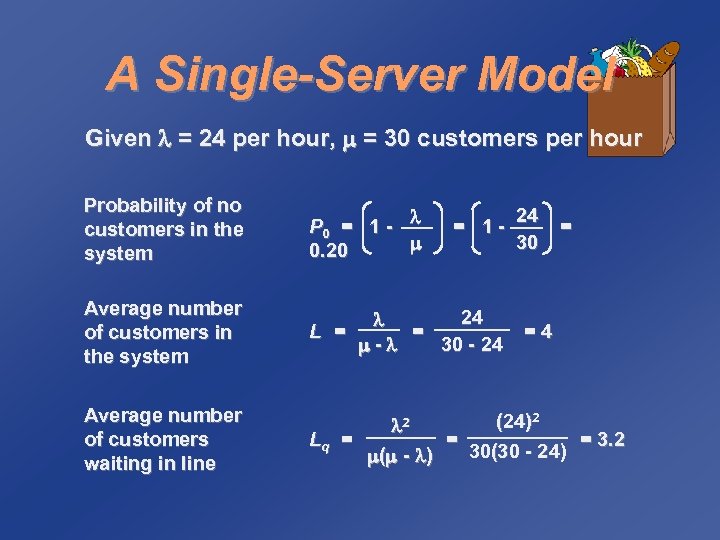 A Single-Server Model Given = 24 per hour, = 30 customers per hour Probability of no customers in the system P 0 = 1 - 0. 20 Average number of customers in the system L = Average number of customers waiting in line (24)2 2 Lq = = = 3. 2 30(30 - 24) ( - ) 24 = 130 24 = 30 - 24 - = =4
A Single-Server Model Given = 24 per hour, = 30 customers per hour Probability of no customers in the system P 0 = 1 - 0. 20 Average number of customers in the system L = Average number of customers waiting in line (24)2 2 Lq = = = 3. 2 30(30 - 24) ( - ) 24 = 130 24 = 30 - 24 - = =4
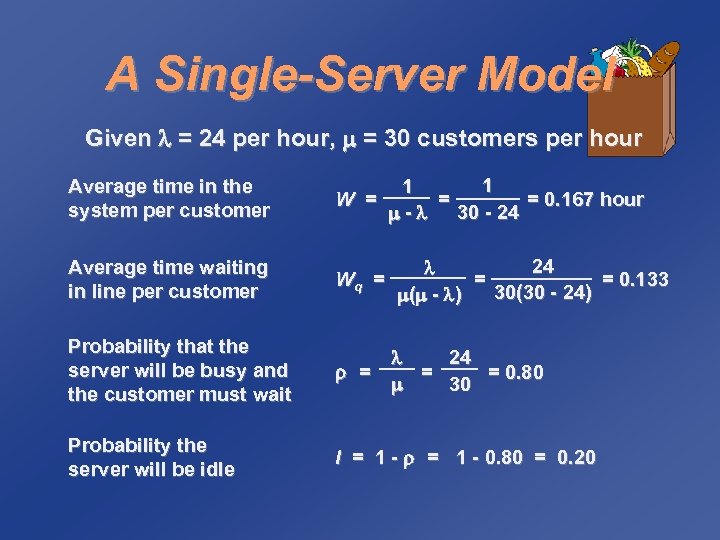 A Single-Server Model Given = 24 per hour, = 30 customers per hour 1 1 = = 0. 167 hour - 30 - 24 Average time in the system per customer W = Average time waiting in line per customer Wq = Probability that the server will be busy and the customer must wait = Probability the server will be idle I = 1 - 0. 80 = 0. 20 24 = = 0. 133 30(30 - 24) ( - ) 24 = = 0. 80 30
A Single-Server Model Given = 24 per hour, = 30 customers per hour 1 1 = = 0. 167 hour - 30 - 24 Average time in the system per customer W = Average time waiting in line per customer Wq = Probability that the server will be busy and the customer must wait = Probability the server will be idle I = 1 - 0. 80 = 0. 20 24 = = 0. 133 30(30 - 24) ( - ) 24 = = 0. 80 30
 Waiting Line Cost Analysis To improve customer services management wants to test two alternatives to reduce customer waiting time: 1. Another employee to pack up purchases 2. Another checkout counter
Waiting Line Cost Analysis To improve customer services management wants to test two alternatives to reduce customer waiting time: 1. Another employee to pack up purchases 2. Another checkout counter
 Waiting Line Cost Analysis ü Add extra employee to increase service rate from 30 to 40 customers per hour ü Extra employee costs $150/week ü Each one-minute reduction in customer waiting time avoids $75 in lost sales ü Waiting time with one employee = 8 minutes Wq = 0. 038 hours = 2. 25 minutes 8. 00 - 2. 25 = 5. 75 minutes reduction 5. 75 x $75/minute/week = $431. 25 per week New employee saves $431. 25 - $150. 00 = $281. 25/wk
Waiting Line Cost Analysis ü Add extra employee to increase service rate from 30 to 40 customers per hour ü Extra employee costs $150/week ü Each one-minute reduction in customer waiting time avoids $75 in lost sales ü Waiting time with one employee = 8 minutes Wq = 0. 038 hours = 2. 25 minutes 8. 00 - 2. 25 = 5. 75 minutes reduction 5. 75 x $75/minute/week = $431. 25 per week New employee saves $431. 25 - $150. 00 = $281. 25/wk
 Waiting Line Cost Analysis ü New counter costs $6000 plus $200 per week for checker ü Customers divide themselves between two checkout lines ü Arrival rate is reduced from = 24 to = 12 ü Service rate for each checker is = 30 Wq = 0. 022 hours = 1. 33 minutes 8. 00 - 1. 33 = 6. 67 minutes 6. 67 x $75/minute/week = $500. 00/wk - $200 = $300/wk Counter is paid off in 6000/300 = 20 weeks
Waiting Line Cost Analysis ü New counter costs $6000 plus $200 per week for checker ü Customers divide themselves between two checkout lines ü Arrival rate is reduced from = 24 to = 12 ü Service rate for each checker is = 30 Wq = 0. 022 hours = 1. 33 minutes 8. 00 - 1. 33 = 6. 67 minutes 6. 67 x $75/minute/week = $500. 00/wk - $200 = $300/wk Counter is paid off in 6000/300 = 20 weeks
 Waiting Line Cost Analysis ü Adding an employee results in savings and improved customer service ü Adding a new counter results in slightly greater savings and improved customer service, but only after the initial investment has been recovered ü A new counter results in more idle time for employees ü A new counter would take up potentially valuable floor space
Waiting Line Cost Analysis ü Adding an employee results in savings and improved customer service ü Adding a new counter results in slightly greater savings and improved customer service, but only after the initial investment has been recovered ü A new counter results in more idle time for employees ü A new counter would take up potentially valuable floor space
 Constant Service Times ü Constant service times occur with machinery and automated equipment ü Constant service times are a special case of the single-server model with general or undefined service times
Constant Service Times ü Constant service times occur with machinery and automated equipment ü Constant service times are a special case of the single-server model with general or undefined service times
 Operating Characteristics for Constant Service Times Probability that no customers are in system P 0 = 1 - Average number of customers in queue 2 Lq = 2 ( - ) Average number of customers in system L = Lq +
Operating Characteristics for Constant Service Times Probability that no customers are in system P 0 = 1 - Average number of customers in queue 2 Lq = 2 ( - ) Average number of customers in system L = Lq +
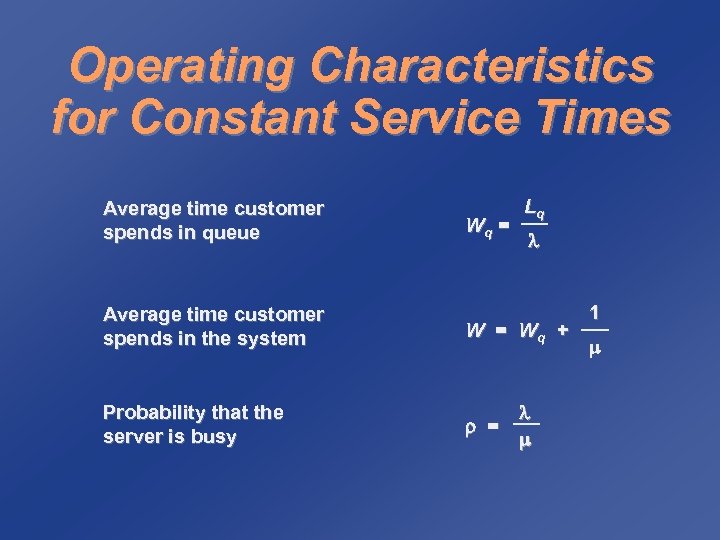 Operating Characteristics for Constant Service Times Average time customer spends in queue Lq Wq = Average time customer spends in the system W = Wq + Probability that the server is busy = 1
Operating Characteristics for Constant Service Times Average time customer spends in queue Lq Wq = Average time customer spends in the system W = Wq + Probability that the server is busy = 1
 Constant Service Times Automated car wash with service time = 4. 5 min Cars arrive at rate = 10/hour (Poisson) = 60/4. 5 = 13. 3/hour (10)2 2 Lq = = = 1. 14 cars waiting 2(13. 3)(13. 3 - 10) 2 ( - ) Wq = Lq = 1. 14/10 =. 114 hour or 6. 84 minutes
Constant Service Times Automated car wash with service time = 4. 5 min Cars arrive at rate = 10/hour (Poisson) = 60/4. 5 = 13. 3/hour (10)2 2 Lq = = = 1. 14 cars waiting 2(13. 3)(13. 3 - 10) 2 ( - ) Wq = Lq = 1. 14/10 =. 114 hour or 6. 84 minutes
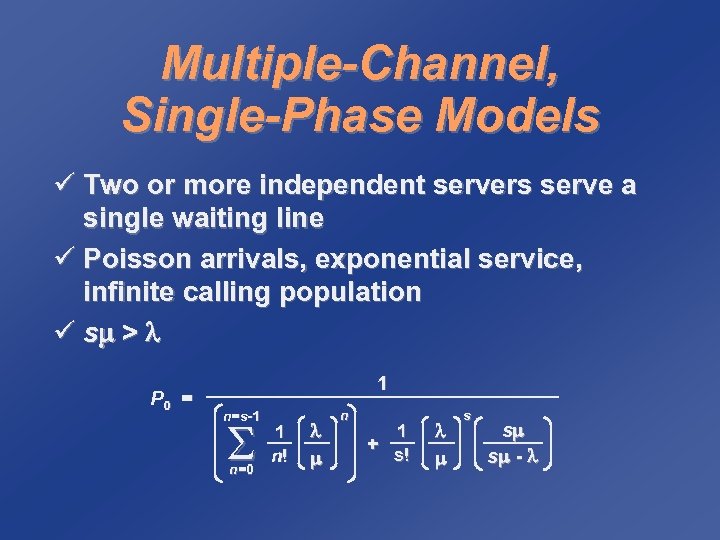 Multiple-Channel, Single-Phase Models ü Two or more independent servers serve a single waiting line ü Poisson arrivals, exponential service, infinite calling population ü s > P 0 = 1 n=s-1 n=0 1 n! n 1 + s! s s s -
Multiple-Channel, Single-Phase Models ü Two or more independent servers serve a single waiting line ü Poisson arrivals, exponential service, infinite calling population ü s > P 0 = 1 n=s-1 n=0 1 n! n 1 + s! s s s -
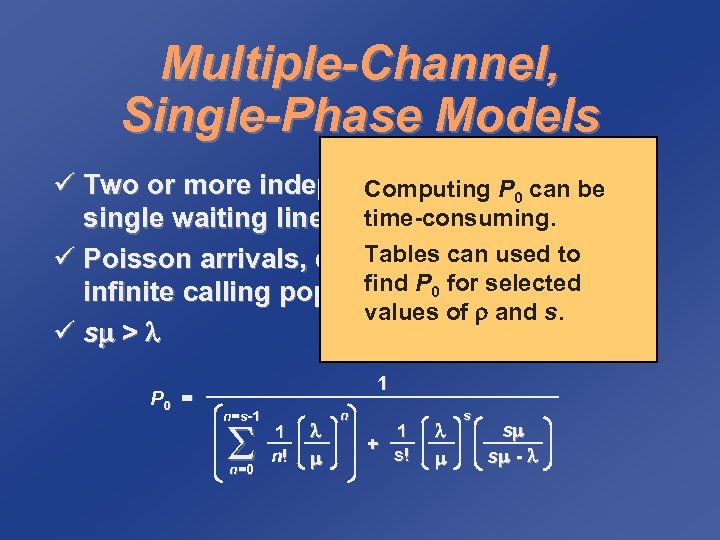 Multiple-Channel, Single-Phase Models ü Two or more independent serverscan be a Computing P 0 serve single waiting line time-consuming. Tables can used to ü Poisson arrivals, exponential service, find P infinite calling population 0 for selected values of and s. ü s > P 0 = 1 n=s-1 n=0 1 n! n 1 + s! s s s -
Multiple-Channel, Single-Phase Models ü Two or more independent serverscan be a Computing P 0 serve single waiting line time-consuming. Tables can used to ü Poisson arrivals, exponential service, find P infinite calling population 0 for selected values of and s. ü s > P 0 = 1 n=s-1 n=0 1 n! n 1 + s! s s s -
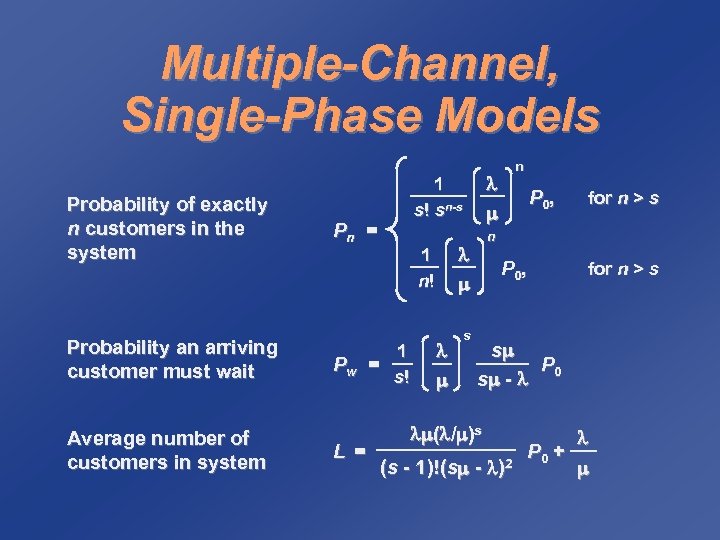 Multiple-Channel, Single-Phase Models Probability of exactly n customers in the system Probability an arriving customer must wait Average number of customers in system 1 s! s P 0 , for n > s n 1 n! Pw = L = 1 s! sn-s Pn = n P 0 , for n > s s P 0 s - ( / )s (s - 1)!(s - )2 P 0 +
Multiple-Channel, Single-Phase Models Probability of exactly n customers in the system Probability an arriving customer must wait Average number of customers in system 1 s! s P 0 , for n > s n 1 n! Pw = L = 1 s! sn-s Pn = n P 0 , for n > s s P 0 s - ( / )s (s - 1)!(s - )2 P 0 +
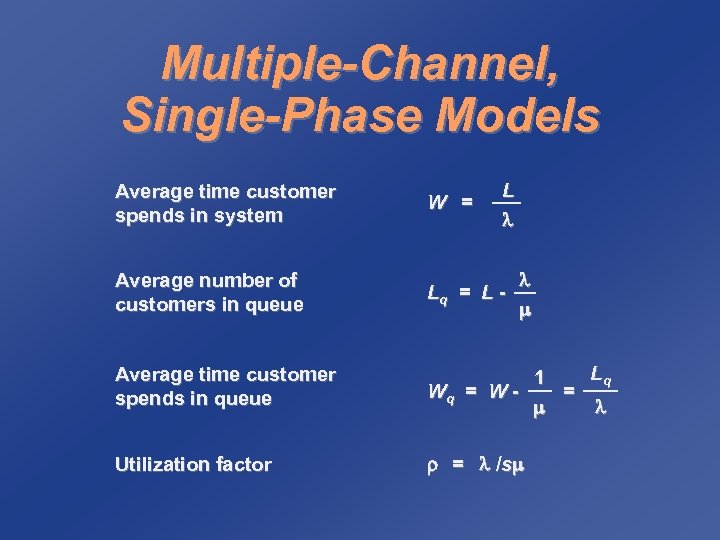 Multiple-Channel, Single-Phase Models L Average time customer spends in system W = Average number of customers in queue Lq = L - Average time customer spends in queue Lq 1 Wq = W = Utilization factor = /s
Multiple-Channel, Single-Phase Models L Average time customer spends in system W = Average number of customers in queue Lq = L - Average time customer spends in queue Lq 1 Wq = W = Utilization factor = /s


