803ce6a338ab1c7eb34f029cba550e79.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 71
 Module 8 CRISIS MANAGEMENT AND PREVENTION Giovanni Marizza gianni. marizza@yahoo. it 13 May 2014, 15. 00 -19. 00
Module 8 CRISIS MANAGEMENT AND PREVENTION Giovanni Marizza gianni. marizza@yahoo. it 13 May 2014, 15. 00 -19. 00
 Summary: -Module Program, -Basic Definitions, -Tipology of crises, -Examples of crises
Summary: -Module Program, -Basic Definitions, -Tipology of crises, -Examples of crises
 Summary: -Module Program, -Basic Definitions, -Tipology of crises, -Examples of crises Aim: finding Lessons Learned
Summary: -Module Program, -Basic Definitions, -Tipology of crises, -Examples of crises Aim: finding Lessons Learned
 Summary: -Module Program, -Basic Definitions, -Tipology of crises, -Examples of crises For each crisis: Historical framework!
Summary: -Module Program, -Basic Definitions, -Tipology of crises, -Examples of crises For each crisis: Historical framework!
 Module Program: § § No visits No references Conceptual context: 13 May Prevention and management of natural disasters: 14 May § Management of human-made crises: 19, 20 21, 26 May § Assessment in proficiency: 3 June (individual work)
Module Program: § § No visits No references Conceptual context: 13 May Prevention and management of natural disasters: 14 May § Management of human-made crises: 19, 20 21, 26 May § Assessment in proficiency: 3 June (individual work)
 “Remember, gentlemen, next week no crises at all: my agenda is completely full of commitments” (Henry Kissinger)
“Remember, gentlemen, next week no crises at all: my agenda is completely full of commitments” (Henry Kissinger)
 Basic Definitions: § Crisis: passage from one situation to a different one (opposite of “routine”)
Basic Definitions: § Crisis: passage from one situation to a different one (opposite of “routine”)
 Basic Definitions: § Crisis: passage from one situation to a different one (opposite of “routine”) § Human crisis: any crisis affecting mankind
Basic Definitions: § Crisis: passage from one situation to a different one (opposite of “routine”) § Human crisis: any crisis affecting mankind
 § “Climate change is a silent human crisis” (Kofi Annan, President of Global Humanitarian Forum) § “This is not only a financial crisis; it's a human crisis as well” (Bob Zoellik, President of the World Bank)
§ “Climate change is a silent human crisis” (Kofi Annan, President of Global Humanitarian Forum) § “This is not only a financial crisis; it's a human crisis as well” (Bob Zoellik, President of the World Bank)
 Basic Definitions: § Crisis: passage from one situation to a different one (opposite of “routine”) § Human crisis: any crisis affecting mankind § Humanitarian crisis: large masses of poor people in danger
Basic Definitions: § Crisis: passage from one situation to a different one (opposite of “routine”) § Human crisis: any crisis affecting mankind § Humanitarian crisis: large masses of poor people in danger
 Examples of humanitarian crises: § Ireland, 1815 § Great Famine, Ireland (1845 -1849) mushroom – potatoes – 1 million victims –emigration – 2 million people in USA § Boat people, Vietnam (1975 -1979, 19881990) § Darfur, Sudan (last 10 years)
Examples of humanitarian crises: § Ireland, 1815 § Great Famine, Ireland (1845 -1849) mushroom – potatoes – 1 million victims –emigration – 2 million people in USA § Boat people, Vietnam (1975 -1979, 19881990) § Darfur, Sudan (last 10 years)
 differences: Crisis: short/medium/long, wide Emergency: short, local Pathology: extremely long / forever
differences: Crisis: short/medium/long, wide Emergency: short, local Pathology: extremely long / forever
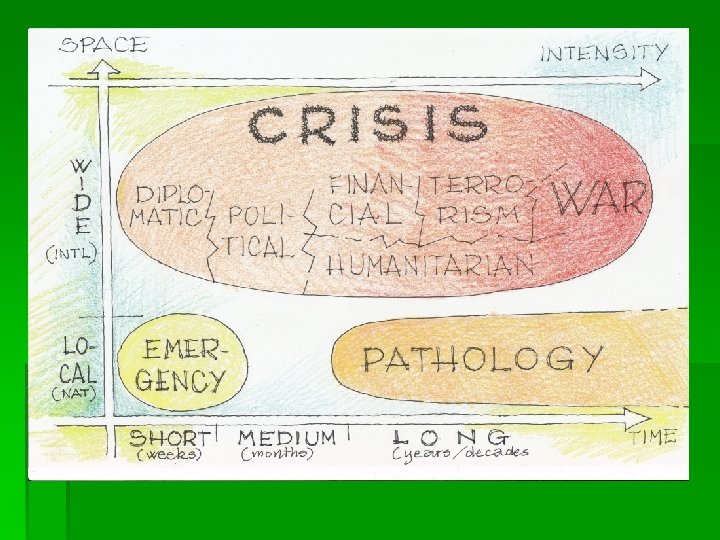
 Example of emergency Rifiuti a Napoli
Example of emergency Rifiuti a Napoli
 Example of crisis USA 1929
Example of crisis USA 1929
 Example of pathology (1) Traffico a roma
Example of pathology (1) Traffico a roma
 Example of pathology (1) Traffico a roma
Example of pathology (1) Traffico a roma
 Example of pathology (2) Palestinian Refugee Camps
Example of pathology (2) Palestinian Refugee Camps
 Basic Definitions: § Crisis: passage from one situation to a different one (opposite of “routine”) § Human crisis: any crisis affecting mankind § Normally: tension, crisis, stabilisation § Necessity of preventing, managing § In a crisis everything becomes great (joy, pain, efforts, fatigue, creativity, …) § Presence of opportunities
Basic Definitions: § Crisis: passage from one situation to a different one (opposite of “routine”) § Human crisis: any crisis affecting mankind § Normally: tension, crisis, stabilisation § Necessity of preventing, managing § In a crisis everything becomes great (joy, pain, efforts, fatigue, creativity, …) § Presence of opportunities
 CRISIS DANGER OPPORTUNITY
CRISIS DANGER OPPORTUNITY
 From Danger to Opportunity The best historical example: Jewish people § WW 1: “Jewish Brigade”, Balfour Declaration, creation of a “foyer” in Palestine § WW 2: shoah, creation of the Jewish State § Arab-Israeli wars: territorial gains
From Danger to Opportunity The best historical example: Jewish people § WW 1: “Jewish Brigade”, Balfour Declaration, creation of a “foyer” in Palestine § WW 2: shoah, creation of the Jewish State § Arab-Israeli wars: territorial gains
 Basic Definitions: § Crisis: passage from one situation to a different one (opposite of “routine”) § Human crisis: any crisis affecting mankind § Humanitarian crisis: large masses of poor peolpe in danger § Crisis prevention: doing something in order to avoid a crisis
Basic Definitions: § Crisis: passage from one situation to a different one (opposite of “routine”) § Human crisis: any crisis affecting mankind § Humanitarian crisis: large masses of poor peolpe in danger § Crisis prevention: doing something in order to avoid a crisis
 Basic Definitions: § Crisis: passage from one situation to a different one (opposite of “routine”) § Human crisis: any crisis affecting mankind § Humanitarian crisis: large masses of poor peolpe in danger § Crisis prevention: doing something in order to avoid a crisis § Crisis management: reducing negative consequences (“consequence management”)
Basic Definitions: § Crisis: passage from one situation to a different one (opposite of “routine”) § Human crisis: any crisis affecting mankind § Humanitarian crisis: large masses of poor peolpe in danger § Crisis prevention: doing something in order to avoid a crisis § Crisis management: reducing negative consequences (“consequence management”)
 Different kinds of Crises: § Politico-military: armed conflicts Particular aspect of Crisis Management: “Casus Belli” (inventing a reason for a war) [next 20 May]
Different kinds of Crises: § Politico-military: armed conflicts Particular aspect of Crisis Management: “Casus Belli” (inventing a reason for a war) [next 20 May]
 Different kinds of Crises: § Politico-military: armed conflicts local / world short / long occupation / liberation defensive / aggressive conventional / nuclear response / preventive independence / civil war …. .
Different kinds of Crises: § Politico-military: armed conflicts local / world short / long occupation / liberation defensive / aggressive conventional / nuclear response / preventive independence / civil war …. .
 Different kinds of Crises: § Politico-military: armed conflicts local / world short / long occupation / liberation defensive / aggressive conventional / nuclear response / preventive independence / civil war …. . Today: MOOTW, PK, PEnforcing, NBuilding, S&R, …
Different kinds of Crises: § Politico-military: armed conflicts local / world short / long occupation / liberation defensive / aggressive conventional / nuclear response / preventive independence / civil war …. . Today: MOOTW, PK, PEnforcing, NBuilding, S&R, …
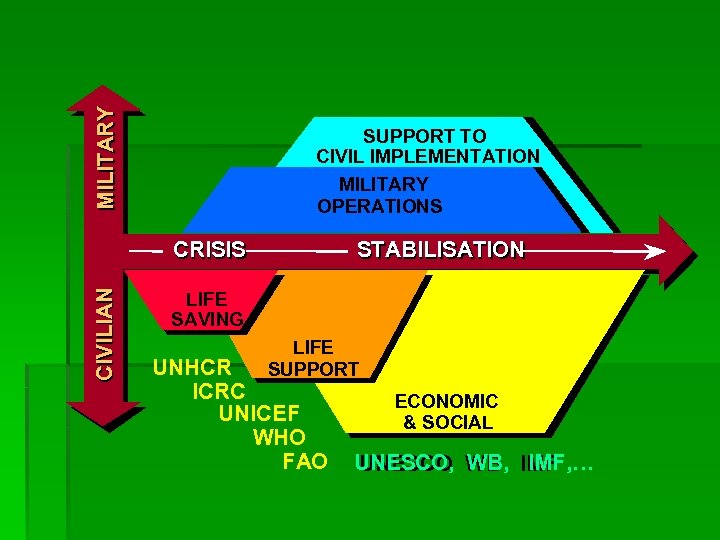 MILITARY SUPPORT TO CIVIL IMPLEMENTATION MILITARY OPERATIONS CIVILIAN CRISIS STABILISATION LIFE SAVING LIFE SUPPORT UNHCR ICRC UNICEF WHO FAO ECONOMIC & SOCIAL UNESCO, WB IMF UNESCO WB, IMF, …
MILITARY SUPPORT TO CIVIL IMPLEMENTATION MILITARY OPERATIONS CIVILIAN CRISIS STABILISATION LIFE SAVING LIFE SUPPORT UNHCR ICRC UNICEF WHO FAO ECONOMIC & SOCIAL UNESCO, WB IMF UNESCO WB, IMF, …
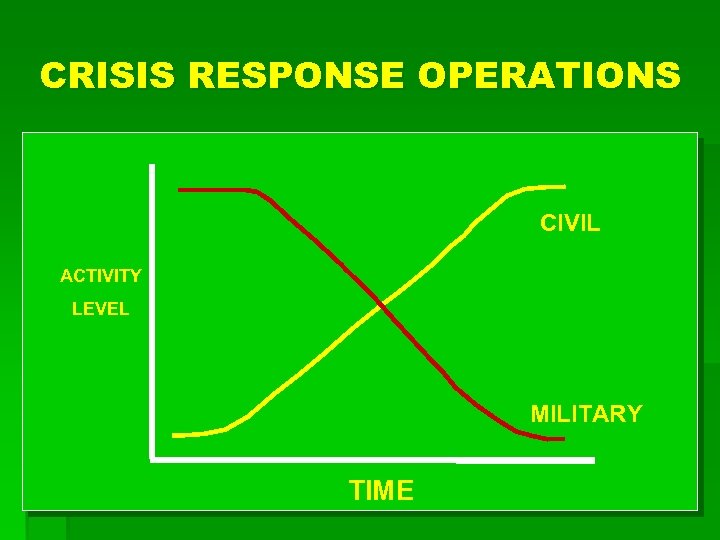 CRISIS RESPONSE OPERATIONS CIVIL ACTIVITY LEVEL MILITARY TIME
CRISIS RESPONSE OPERATIONS CIVIL ACTIVITY LEVEL MILITARY TIME
 Different kinds of Crises: § Politico-military: armed conflicts terrorist attacks
Different kinds of Crises: § Politico-military: armed conflicts terrorist attacks
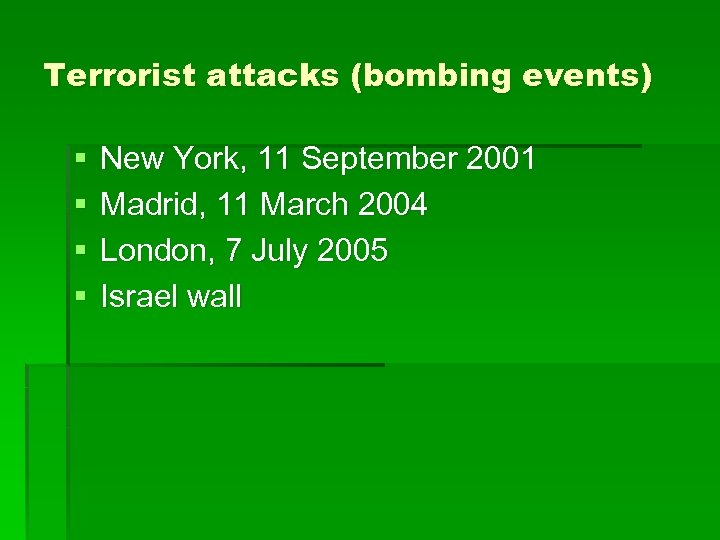 Terrorist attacks (bombing events) § § New York, 11 September 2001 Madrid, 11 March 2004 London, 7 July 2005 Israel wall
Terrorist attacks (bombing events) § § New York, 11 September 2001 Madrid, 11 March 2004 London, 7 July 2005 Israel wall
 New York, 11 September 2001 2. 974 victims + 24 missing + 19 Controversial Crisis Management: -GWOT -Afghanistan -Iraq 911 in Europe?
New York, 11 September 2001 2. 974 victims + 24 missing + 19 Controversial Crisis Management: -GWOT -Afghanistan -Iraq 911 in Europe?
 Madrid, 11 March 2004 191 victims 2. 057 wounded WRONG CRISIS MANAGEMENT
Madrid, 11 March 2004 191 victims 2. 057 wounded WRONG CRISIS MANAGEMENT
 Atocha: a wrong Crisis Management § 10 March 2004: electoral campaign, Mr Aznar is sure to be confirmed § 11 March, 07. 39: 4 explosions § 08. 43: field hospital established § 09. 48: Mo. I on the spot § 10. 43: mobile telephon net collapsed § 14. 00: “ETA is guilty” § 17. 28: MFA: letter to the Ambassadors: “ETA is responsible!” § 12 March: ETA? No: AQ! § 13 March: Mr. Zapatero wins, SP troops out of Iraq
Atocha: a wrong Crisis Management § 10 March 2004: electoral campaign, Mr Aznar is sure to be confirmed § 11 March, 07. 39: 4 explosions § 08. 43: field hospital established § 09. 48: Mo. I on the spot § 10. 43: mobile telephon net collapsed § 14. 00: “ETA is guilty” § 17. 28: MFA: letter to the Ambassadors: “ETA is responsible!” § 12 March: ETA? No: AQ! § 13 March: Mr. Zapatero wins, SP troops out of Iraq
 Lessons learned: § Be always ready to help (Field Hospitals, …) § Importance of mobile phone net § Terrorist attacks can influence internal, external policy, Geopolitics
Lessons learned: § Be always ready to help (Field Hospitals, …) § Importance of mobile phone net § Terrorist attacks can influence internal, external policy, Geopolitics
 Another example: § 2008: new electoral campaign. Zapatero: “I will win if the % will be more than 75%” § 7 March: ETA kills Matias Carrasco, PSOE § Carrasco’s daughter on TV: “The best way to honor my father: please vote!” § 9 March: % over 75%, Zapatero wins again § 2004, 2008 terrorists have influenced the results of the elections in SP.
Another example: § 2008: new electoral campaign. Zapatero: “I will win if the % will be more than 75%” § 7 March: ETA kills Matias Carrasco, PSOE § Carrasco’s daughter on TV: “The best way to honor my father: please vote!” § 9 March: % over 75%, Zapatero wins again § 2004, 2008 terrorists have influenced the results of the elections in SP.
 London, 7 July 2005 52 victims 700 wounded EXCELLENT CRISIS MANAGEMENT
London, 7 July 2005 52 victims 700 wounded EXCELLENT CRISIS MANAGEMENT
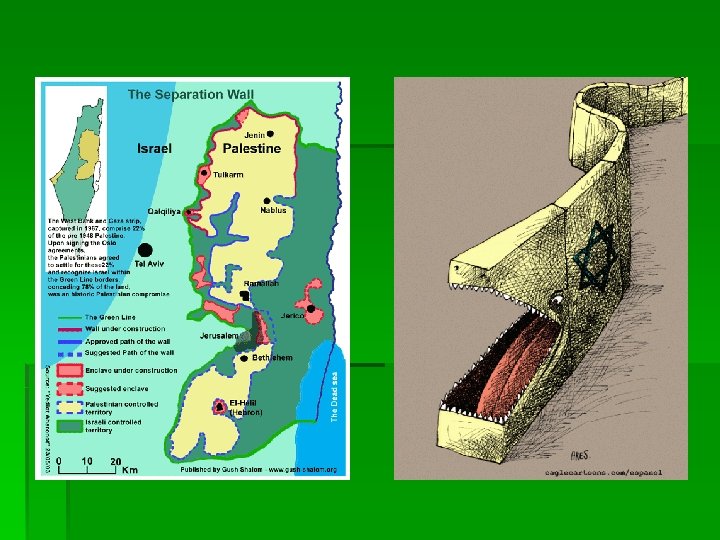
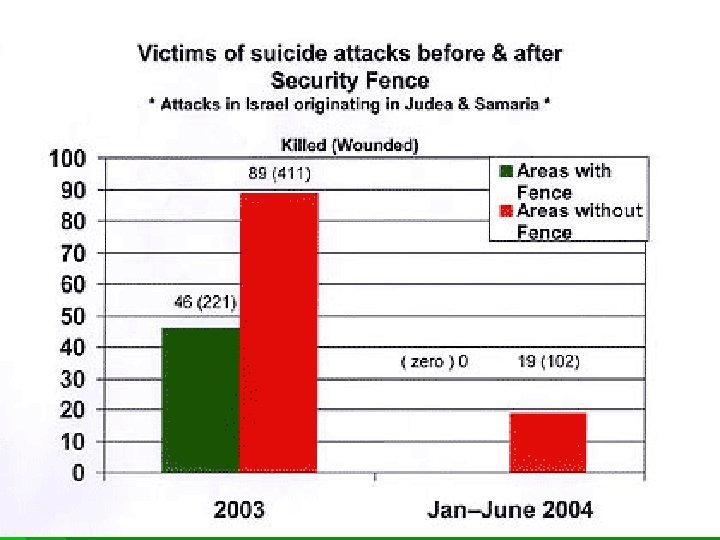
 Israel wall (apartheid wall, security wall, the Fence, …)
Israel wall (apartheid wall, security wall, the Fence, …)

 Terrorist attacks (hostage kidnapping events) § Munich, Olympic Games 1972 (Black September) § Entebbe airport, 1976 (Baader Meinhoff, PLO, …Barak*, Netanyahu) * Begin
Terrorist attacks (hostage kidnapping events) § Munich, Olympic Games 1972 (Black September) § Entebbe airport, 1976 (Baader Meinhoff, PLO, …Barak*, Netanyahu) * Begin
 http: //ukinitaly. fco. gov. uk/it/ “ 31 October 1946… a terroristic attack…”
http: //ukinitaly. fco. gov. uk/it/ “ 31 October 1946… a terroristic attack…”
 Terrorist attacks (hostage kidnapping events) § Munich, Olympic Games 1972 (Black September) § Entebbe airport, 1976 (Baader Meinhoff, PLO, …Barak, Netanyahu) § Tehran US embassy, 1979 -80 (disaster) § Budyonnovsk hospital, 1995 (2. 000 hostages, Chernomyrdin-Basayev) § Lima, JP embassy, 1997 (tupamaros) § Moscow, Dubrovka theater, 2002 (700, gas) § Beslan, school, 2004 (1. 200, NL: EU presidency asking explanations to the victims)
Terrorist attacks (hostage kidnapping events) § Munich, Olympic Games 1972 (Black September) § Entebbe airport, 1976 (Baader Meinhoff, PLO, …Barak, Netanyahu) § Tehran US embassy, 1979 -80 (disaster) § Budyonnovsk hospital, 1995 (2. 000 hostages, Chernomyrdin-Basayev) § Lima, JP embassy, 1997 (tupamaros) § Moscow, Dubrovka theater, 2002 (700, gas) § Beslan, school, 2004 (1. 200, NL: EU presidency asking explanations to the victims)
 …some lessons/considerations: § If GE Special Forces fail (Fuerstenfeldbruck), Mossad don’t § Worst case: US rescue attempt in Iran (C 130+helo+sandstorm… 444 days) § “Best” case: Dubrovka (60 Chechens, all killed, also 119 hostages out of 700) § Russian raids: always within 48 hrs
…some lessons/considerations: § If GE Special Forces fail (Fuerstenfeldbruck), Mossad don’t § Worst case: US rescue attempt in Iran (C 130+helo+sandstorm… 444 days) § “Best” case: Dubrovka (60 Chechens, all killed, also 119 hostages out of 700) § Russian raids: always within 48 hrs
 Different kinds of Crises: § Politico-military: armed conflicts terrorist attacks accidents
Different kinds of Crises: § Politico-military: armed conflicts terrorist attacks accidents
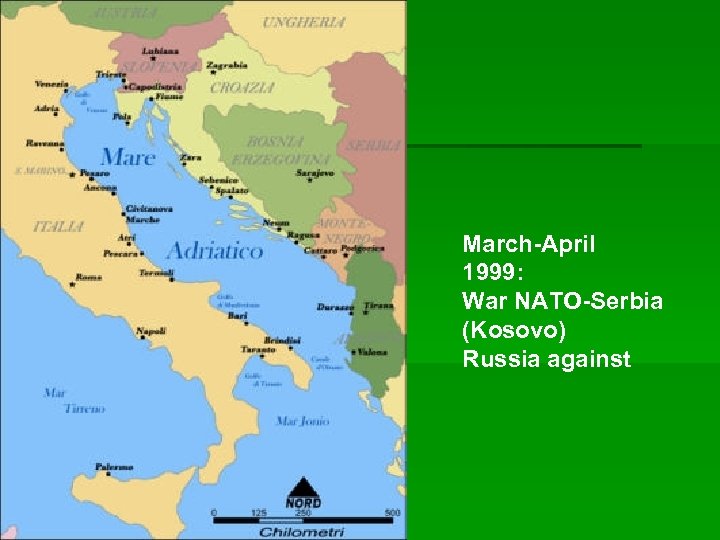 March-April 1999: War NATO-Serbia (Kosovo) Russia against
March-April 1999: War NATO-Serbia (Kosovo) Russia against
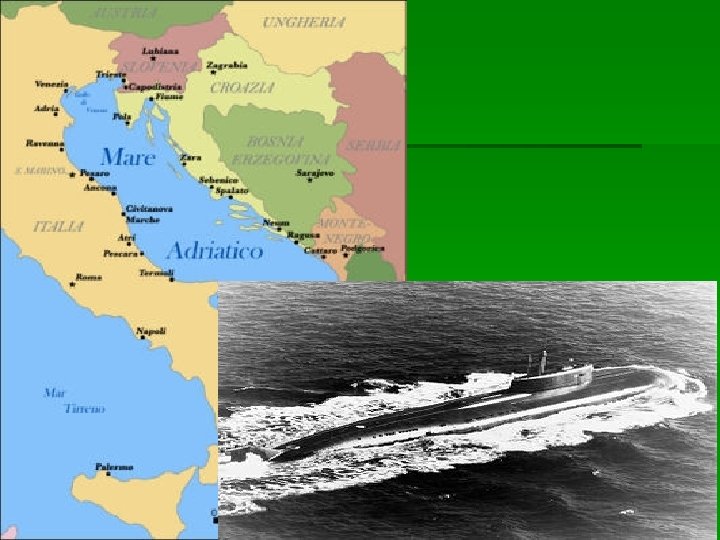
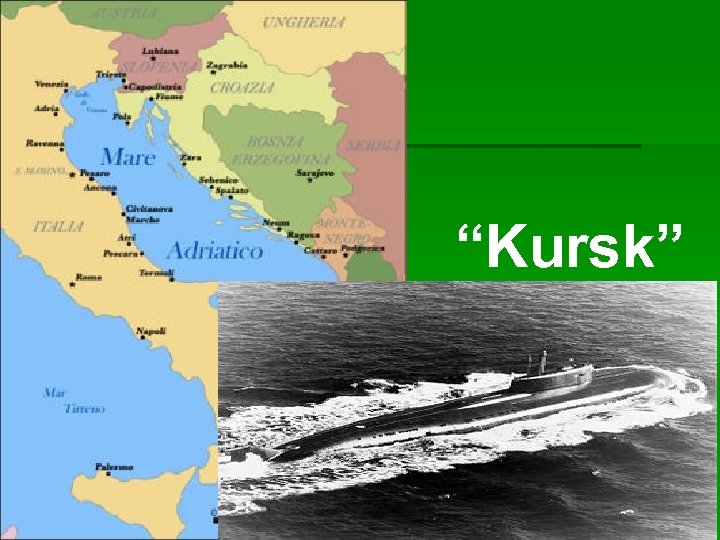 “Kursk”
“Kursk”
 § Aug 2000: Barents Sea § 12 August: Putin on the Black Sea § 11. 30: 2 explosions, end of radio contacts § 13 August: Kursk localized § 14 August: 1 st rescue attempt, failed
§ Aug 2000: Barents Sea § 12 August: Putin on the Black Sea § 11. 30: 2 explosions, end of radio contacts § 13 August: Kursk localized § 14 August: 1 st rescue attempt, failed
 15 August: Russian govt still silent (3 days after!) 16 August: Kremlin asking help (4 days after!), Norway ready to help 17 August: Putin (still at BS): “We don’t need foreign help, Russia has everything!” 18 August: Putin decides to stop his holidays (6 days after!)
15 August: Russian govt still silent (3 days after!) 16 August: Kremlin asking help (4 days after!), Norway ready to help 17 August: Putin (still at BS): “We don’t need foreign help, Russia has everything!” 18 August: Putin decides to stop his holidays (6 days after!)
 Different kinds of Crises: § Politico-military: armed conflicts terrorist attacks accidents § Politics: Political crisis
Different kinds of Crises: § Politico-military: armed conflicts terrorist attacks accidents § Politics: Political crisis
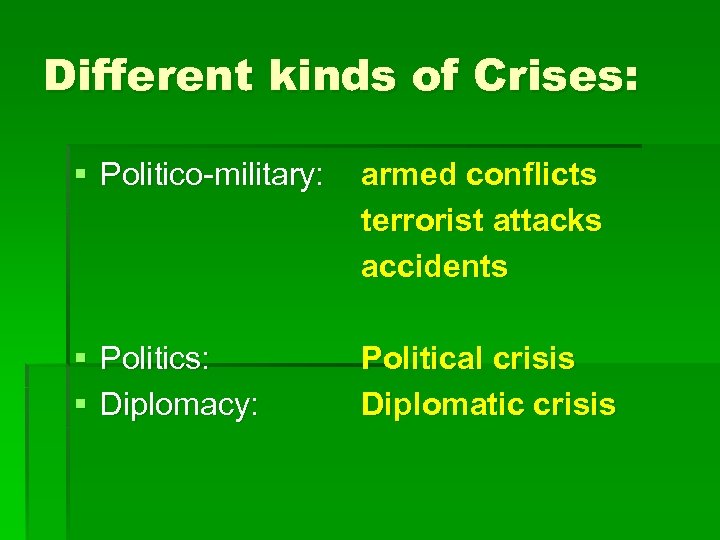 Different kinds of Crises: § Politico-military: armed conflicts terrorist attacks accidents § Politics: § Diplomacy: Political crisis Diplomatic crisis
Different kinds of Crises: § Politico-military: armed conflicts terrorist attacks accidents § Politics: § Diplomacy: Political crisis Diplomatic crisis
 2012 -14: diplomatic crisis Italy-India
2012 -14: diplomatic crisis Italy-India
 Different kinds of Crises: § Politico-military: § § § armed conflicts terrorist attacks accidents Politics: Political crisis Diplomacy: Diplomatic crisis Economic-financial: economic crisis (1929, 2008 -today, Greece 2010 -2012)
Different kinds of Crises: § Politico-military: § § § armed conflicts terrorist attacks accidents Politics: Political crisis Diplomacy: Diplomatic crisis Economic-financial: economic crisis (1929, 2008 -today, Greece 2010 -2012)
 Different kinds of Crises: § Politico-military: armed conflicts terrorist attacks accidents § Politics: Political crisis § Diplomacy: Diplomatic crisis § Economic-financial: economic crisis (1929, 2008 today, Greece 2010 -2012) § Social: humanitarian crisis (famine, diseases, migrations, …)
Different kinds of Crises: § Politico-military: armed conflicts terrorist attacks accidents § Politics: Political crisis § Diplomacy: Diplomatic crisis § Economic-financial: economic crisis (1929, 2008 today, Greece 2010 -2012) § Social: humanitarian crisis (famine, diseases, migrations, …)
 Examples of humanitarian crises: Darfur
Examples of humanitarian crises: Darfur
 Examples of humanitarian crises:
Examples of humanitarian crises:
 Examples of humanitarian crises:
Examples of humanitarian crises:
 Example of humanitarian crisis: Syria
Example of humanitarian crisis: Syria
 Crises are never stand-alone Crises have deep roots
Crises are never stand-alone Crises have deep roots
 Crises: never stand-alone
Crises: never stand-alone
 Crises have deep roots 31 May 2010: Freedom Flotilla
Crises have deep roots 31 May 2010: Freedom Flotilla
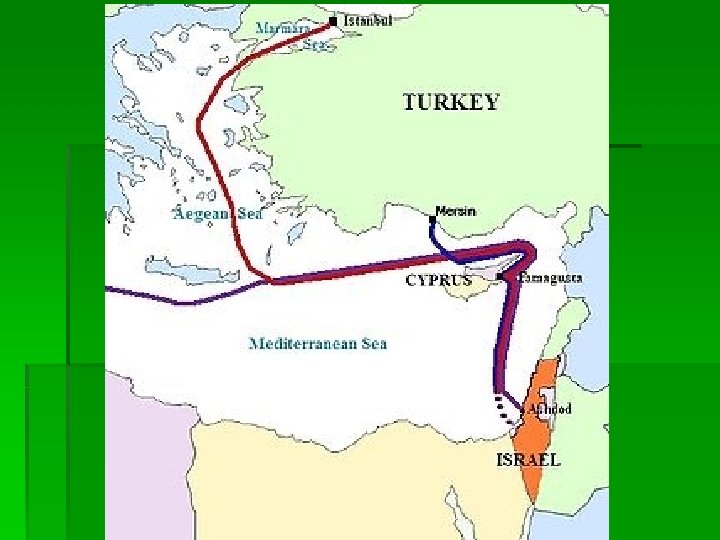
 Crises have deep roots 31 May 2010: Freedom Flotilla
Crises have deep roots 31 May 2010: Freedom Flotilla
 Crises have deep roots 1948: Israel, 1948 -today: Israeli-Arab wars, 2009: Gaza war, 2010: humanitarian situation in Gaza, 31 May 2010: Freedom Flotilla
Crises have deep roots 1948: Israel, 1948 -today: Israeli-Arab wars, 2009: Gaza war, 2010: humanitarian situation in Gaza, 31 May 2010: Freedom Flotilla
 Crises have deep roots 1914: Sarajevo: G. Princip kills F. Ferdinand, 1914 -1918: WW 1, 1919: Versailles Treaty, 1939 -1945: WW 2, Shoah, 1948: Israel, 1948 -today: Israeli-Arab wars, 2009: Gaza war, 2010: humanitarian situation in Gaza, 31 May 2010: Freedom Flotilla
Crises have deep roots 1914: Sarajevo: G. Princip kills F. Ferdinand, 1914 -1918: WW 1, 1919: Versailles Treaty, 1939 -1945: WW 2, Shoah, 1948: Israel, 1948 -today: Israeli-Arab wars, 2009: Gaza war, 2010: humanitarian situation in Gaza, 31 May 2010: Freedom Flotilla
 Different kinds of Crises: § Politico-military: armed conflicts terrorist attacks accidents § Politics: Political crisis § Diplomacy: Diplomatic crisis § Economic-financial: economic crisis (1929, 2008 today, Greece 2010 -2011) § Social: humanitarian crisis (famine, diseases, migrations, …) public disasters (natural, artificial or human-made)
Different kinds of Crises: § Politico-military: armed conflicts terrorist attacks accidents § Politics: Political crisis § Diplomacy: Diplomatic crisis § Economic-financial: economic crisis (1929, 2008 today, Greece 2010 -2011) § Social: humanitarian crisis (famine, diseases, migrations, …) public disasters (natural, artificial or human-made)
 Suggestions for the final thesis: § “Crisis Management: hostage kidnapping events. Comparison of several case studies”
Suggestions for the final thesis: § “Crisis Management: hostage kidnapping events. Comparison of several case studies”
 Module 8, assessment in proficiency (3 June): individual work -subject/format: already submitted by e. mail (29 April). doc format (not. docx, . pdf, …) -time: at any time before 2 June -3 June: brief presentation (verbally, no ppt required) -mark: max 30/30
Module 8, assessment in proficiency (3 June): individual work -subject/format: already submitted by e. mail (29 April). doc format (not. docx, . pdf, …) -time: at any time before 2 June -3 June: brief presentation (verbally, no ppt required) -mark: max 30/30
 individual work: Valentina Martin Andrea Yuri Rebecca Pajwak Sohiala Imre Nagy, 1956 Charles De Gaulle, 1958 -1962 John Kennedy, 1963 Alexander Dubcek, 1968 Margaret Thatcher, 1982 George W. Bush, 2001 Nicholas Sarkozy, 2011
individual work: Valentina Martin Andrea Yuri Rebecca Pajwak Sohiala Imre Nagy, 1956 Charles De Gaulle, 1958 -1962 John Kennedy, 1963 Alexander Dubcek, 1968 Margaret Thatcher, 1982 George W. Bush, 2001 Nicholas Sarkozy, 2011
 Module 8 CRISIS MANAGEMENT AND PREVENTION Giovanni Marizza Mail: gianni. marizza@yahoo. it Cell: 3339483814 Skype: Giaggia 2012 Facebook Whatsapp
Module 8 CRISIS MANAGEMENT AND PREVENTION Giovanni Marizza Mail: gianni. marizza@yahoo. it Cell: 3339483814 Skype: Giaggia 2012 Facebook Whatsapp


