e5de4ff26b0836f31c8b5a373fde2ea7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35
 Module 3: Policies & practice of mitigation & adaptation: Relevance to health
Module 3: Policies & practice of mitigation & adaptation: Relevance to health
 Key messages in Module 3 • Two climate change responses – mitigation & adaptation • Many mitigation & adaptation activities are relevant to the health sector • If emissions are reduced (mitigation), health of the population is improved (cobenefits/win-win) 2
Key messages in Module 3 • Two climate change responses – mitigation & adaptation • Many mitigation & adaptation activities are relevant to the health sector • If emissions are reduced (mitigation), health of the population is improved (cobenefits/win-win) 2
 Key messages in Module 3 • The health sector plays an important role in adaptation - requires multi-sectoral collaboration • Strong need for health sector to influence mitigation activities in other sectors 3
Key messages in Module 3 • The health sector plays an important role in adaptation - requires multi-sectoral collaboration • Strong need for health sector to influence mitigation activities in other sectors 3
 1 Module 3 outline 3 2 Basics of Options & co- Mitigation & adaptation & benefits of adaptation as mitigation risk mngmnt 4
1 Module 3 outline 3 2 Basics of Options & co- Mitigation & adaptation & benefits of adaptation as mitigation risk mngmnt 4
 1 BASICS OF ADAPTATION & 5
1 BASICS OF ADAPTATION & 5
 Really. Important. Science. Announcement. 6
Really. Important. Science. Announcement. 6
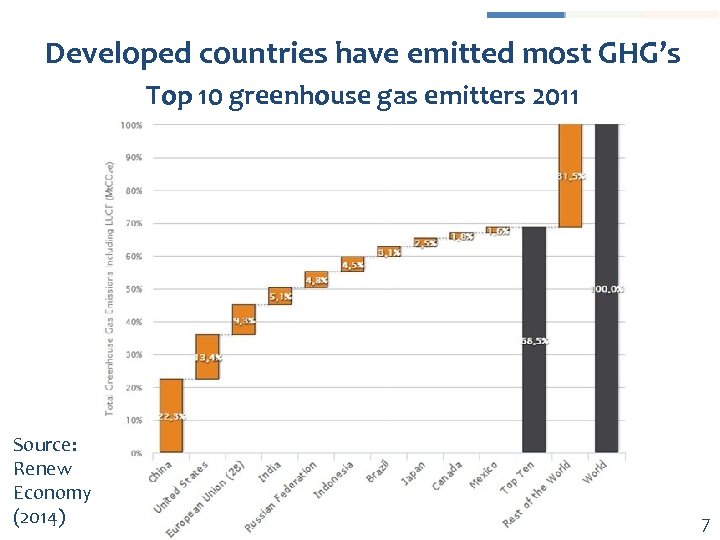 Developed countries have emitted most GHG’s Top 10 greenhouse gas emitters 2011 Source: Renew Economy (2014) 7
Developed countries have emitted most GHG’s Top 10 greenhouse gas emitters 2011 Source: Renew Economy (2014) 7
 Overview of health & climate change – Adaptation examples 8
Overview of health & climate change – Adaptation examples 8
 Why is mitigation necessary?
Why is mitigation necessary?
 Reminder: Mitigation 10
Reminder: Mitigation 10
 Urgent action is needed 11
Urgent action is needed 11
 2 OPTIONS & CO-BENEFITS OF MITIGATION 12
2 OPTIONS & CO-BENEFITS OF MITIGATION 12
 Mitigation options Renewable energy Reducing waste, methane recovery Active transport Energy efficient buildings, lighting & appliances Industry energy efficiency, heat & power recovery Best practice agriculture to increase soil carbon storage • Land restoration • Forestry & forest protection • • • 13
Mitigation options Renewable energy Reducing waste, methane recovery Active transport Energy efficient buildings, lighting & appliances Industry energy efficiency, heat & power recovery Best practice agriculture to increase soil carbon storage • Land restoration • Forestry & forest protection • • • 13
 Renewable energy Source: Climate Commission (2012) 14
Renewable energy Source: Climate Commission (2012) 14
 Reduce waste
Reduce waste
 Reduce food waste
Reduce food waste
 Use & promote active transport
Use & promote active transport
 Summary: Mitigation options Renewable energy Reducing waste, methane recovery Active transport Energy efficient buildings, lighting & appliances Industry energy efficiency, heat & power recovery Best practice agriculture to increase soil carbon storage • Land restoration • Forestry & forest protection • • • 18
Summary: Mitigation options Renewable energy Reducing waste, methane recovery Active transport Energy efficient buildings, lighting & appliances Industry energy efficiency, heat & power recovery Best practice agriculture to increase soil carbon storage • Land restoration • Forestry & forest protection • • • 18
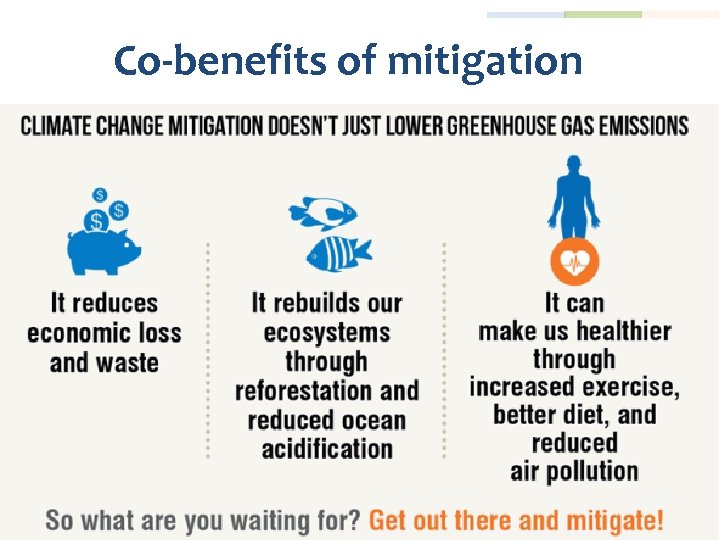 Co-benefits of mitigation
Co-benefits of mitigation
 3 Mitigation & adaptation as risk management 20
3 Mitigation & adaptation as risk management 20
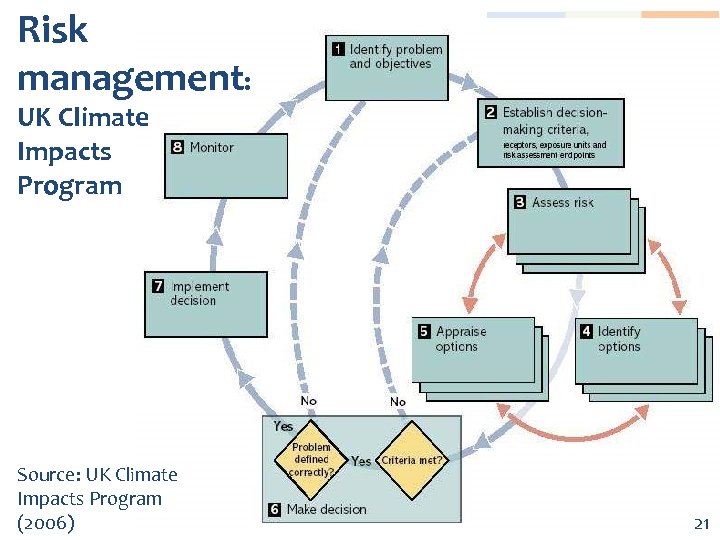 Risk management: UK Climate Impacts Program Source: UK Climate Impacts Program (2006) 21
Risk management: UK Climate Impacts Program Source: UK Climate Impacts Program (2006) 21
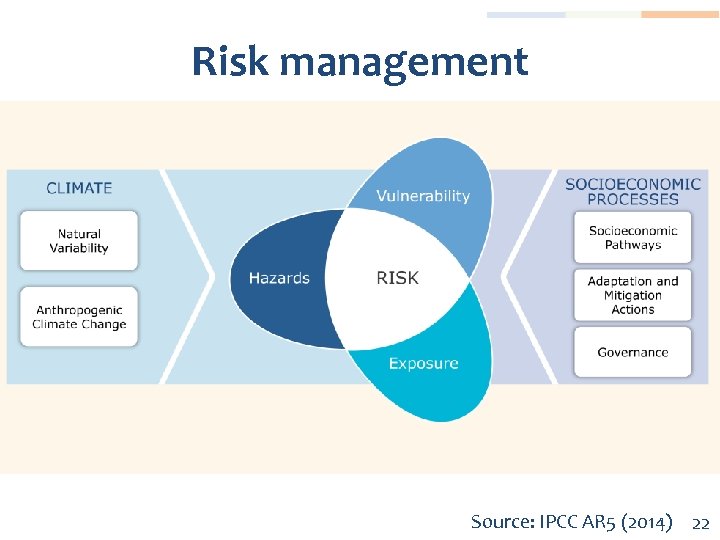 Risk management Source: IPCC AR 5 (2014) 22
Risk management Source: IPCC AR 5 (2014) 22
 Public health responses to the risks of climate change • Reduce exposures – Legislative policies – Alterations in built environment – Alterations in natural environment • Prevent onset of adverse outcomes – Early warning systems – Surveillance & monitoring – Vector control programs – Public education & outreach 23
Public health responses to the risks of climate change • Reduce exposures – Legislative policies – Alterations in built environment – Alterations in natural environment • Prevent onset of adverse outcomes – Early warning systems – Surveillance & monitoring – Vector control programs – Public education & outreach 23
 Public health responses to the risks of climate change • Response / treatment – Medical training & awareness – Treatment – Emergency response Residual climate change-related health impacts 24
Public health responses to the risks of climate change • Response / treatment – Medical training & awareness – Treatment – Emergency response Residual climate change-related health impacts 24
 Adaptation Actions taken by individuals, institutions, & governments • Anticipatory (actions taken in advance of climate change effects) • Reactive (taken in response to experienced climate change effects) The severity of impacts will depend on the capacity to adapt & its effective deployment 25
Adaptation Actions taken by individuals, institutions, & governments • Anticipatory (actions taken in advance of climate change effects) • Reactive (taken in response to experienced climate change effects) The severity of impacts will depend on the capacity to adapt & its effective deployment 25
 Questions for designing adaptation policies & measures • Adaptation to what? • What is currently being done to reduce the burden of disease? – How effective are these policies & measures? – Are additional interventions needed? • What are the projections for the outcome? – Who is vulnerable? 26
Questions for designing adaptation policies & measures • Adaptation to what? • What is currently being done to reduce the burden of disease? – How effective are these policies & measures? – Are additional interventions needed? • What are the projections for the outcome? – Who is vulnerable? 26
 Questions for designing adaptation policies & measures • Who adapts? How does adaptation occur? • When should interventions be implemented? • How good or likely is the adaptation? • Apply win/win or no-regrets strategies 27
Questions for designing adaptation policies & measures • Who adapts? How does adaptation occur? • When should interventions be implemented? • How good or likely is the adaptation? • Apply win/win or no-regrets strategies 27
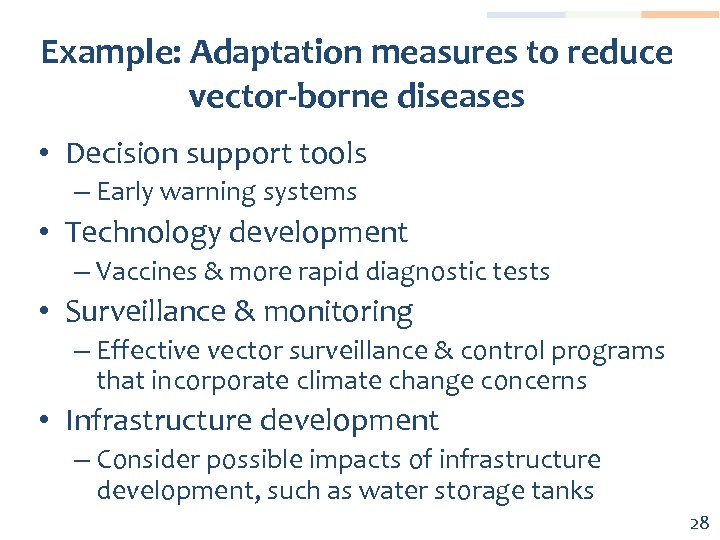 Example: Adaptation measures to reduce vector-borne diseases • Decision support tools – Early warning systems • Technology development – Vaccines & more rapid diagnostic tests • Surveillance & monitoring – Effective vector surveillance & control programs that incorporate climate change concerns • Infrastructure development – Consider possible impacts of infrastructure development, such as water storage tanks 28
Example: Adaptation measures to reduce vector-borne diseases • Decision support tools – Early warning systems • Technology development – Vaccines & more rapid diagnostic tests • Surveillance & monitoring – Effective vector surveillance & control programs that incorporate climate change concerns • Infrastructure development – Consider possible impacts of infrastructure development, such as water storage tanks 28
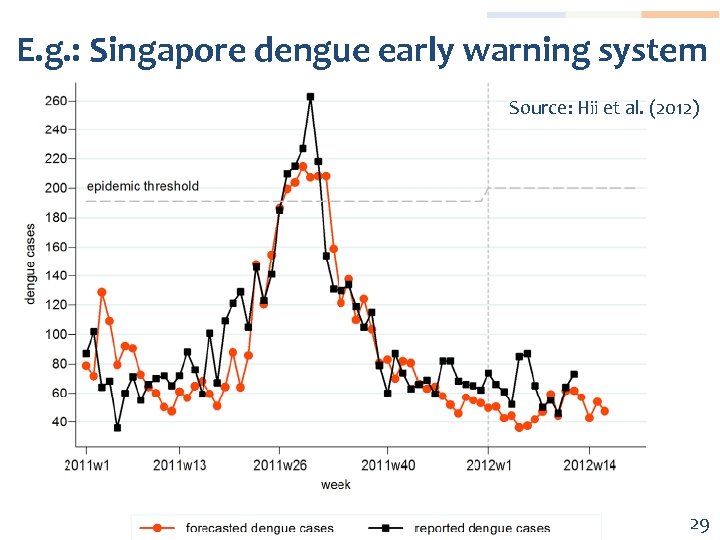 E. g. : Singapore dengue early warning system Source: Hii et al. (2012) 29
E. g. : Singapore dengue early warning system Source: Hii et al. (2012) 29
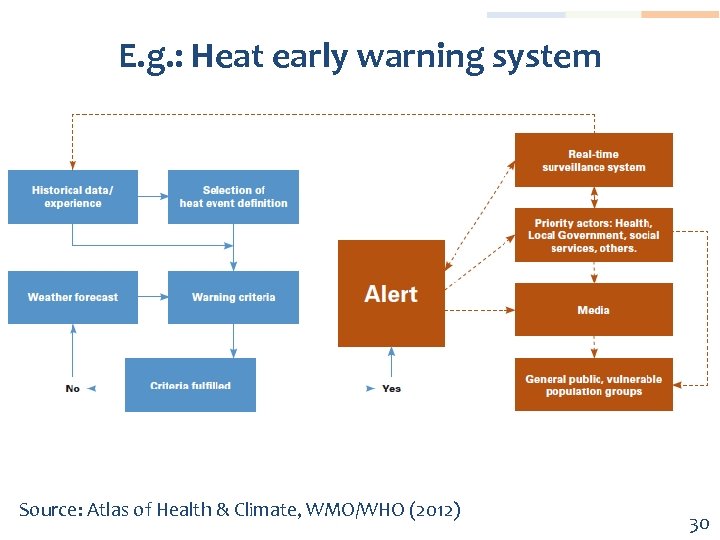 E. g. : Heat early warning system Source: Atlas of Health & Climate, WMO/WHO (2012) 30
E. g. : Heat early warning system Source: Atlas of Health & Climate, WMO/WHO (2012) 30
 What we covered in Module 3 1 3 2 Basics of Options & co- Mitigation & adaptation & benefits of adaptation as mitigation risk mngmnt 31
What we covered in Module 3 1 3 2 Basics of Options & co- Mitigation & adaptation & benefits of adaptation as mitigation risk mngmnt 31
 Learning from Module 3 • Two climate change responses – mitigation & adaptation • Many mitigation & adaptation activities are relevant to the health sector • Strong need for health sector to influence mitigation activities in other sectors 32
Learning from Module 3 • Two climate change responses – mitigation & adaptation • Many mitigation & adaptation activities are relevant to the health sector • Strong need for health sector to influence mitigation activities in other sectors 32
 Learning from Module 3 • If emissions are reduced (mitigation), health of the population is improved (cobenefits/win-win) • Health sector plays an important role in adaptation - requires multi-sectoral collaboration 33
Learning from Module 3 • If emissions are reduced (mitigation), health of the population is improved (cobenefits/win-win) • Health sector plays an important role in adaptation - requires multi-sectoral collaboration 33
 What action will you take in your work, given what you learnt in Module 3?
What action will you take in your work, given what you learnt in Module 3?
 Coming up next… Module 14: UNFCCC & international IPCC negotiations 35
Coming up next… Module 14: UNFCCC & international IPCC negotiations 35


