 MODULE 3: MARKETING
MODULE 3: MARKETING
 Unit 3. 1 – The Role of Marketing Content l Definition and nature of marketing. l Marketing Objectives l Marketing in non-profit organisations. l Ethics of marketing
Unit 3. 1 – The Role of Marketing Content l Definition and nature of marketing. l Marketing Objectives l Marketing in non-profit organisations. l Ethics of marketing
 Learning Outcomes l Define marketing and describe its relationship with other activities. l Understand the goals that an organisation is trying to achieve through its marketing, for example, market share and corporate image. l Describe the distinction between marketing goods and services. l Describe how non-profit organisations may need to market their products. l Explain the ethical issues involve in marketing.
Learning Outcomes l Define marketing and describe its relationship with other activities. l Understand the goals that an organisation is trying to achieve through its marketing, for example, market share and corporate image. l Describe the distinction between marketing goods and services. l Describe how non-profit organisations may need to market their products. l Explain the ethical issues involve in marketing.
 Reading Focus l Bruce L Jewell, An Integrated Approach to Business Studies, Units 14, 18, pp. 195202, 233 -239
Reading Focus l Bruce L Jewell, An Integrated Approach to Business Studies, Units 14, 18, pp. 195202, 233 -239
 CONTEXT The two most famous brands in the world are Mc. Donald's and Coca – Cola. The names of these brands conjure up a variety of images – it might be the unique ‘M’ shape which greets you when ever you visit a Mc. Donald's, or perhaps a Big Mac and medium fries. With the name Coca- Cola, you might think of energetic , youthful advertising, or the taste of the drink, or even the colour red! Both Mc. Donalds and Coca-Cola make simple products – one is a variant of beef burger, the other is a fizzy drink, yet both these brands are worth billions of dollars. More complicated, technological products can have comparatively little value because of the amount of money which has been invested in the marketing process over the lifetime of the products. Both Mc. Donald’s and Coca-Cola have placed enormous emphasis on marketing: spending money on building the image and popularity of the products in the eyes of the customer.
CONTEXT The two most famous brands in the world are Mc. Donald's and Coca – Cola. The names of these brands conjure up a variety of images – it might be the unique ‘M’ shape which greets you when ever you visit a Mc. Donald's, or perhaps a Big Mac and medium fries. With the name Coca- Cola, you might think of energetic , youthful advertising, or the taste of the drink, or even the colour red! Both Mc. Donalds and Coca-Cola make simple products – one is a variant of beef burger, the other is a fizzy drink, yet both these brands are worth billions of dollars. More complicated, technological products can have comparatively little value because of the amount of money which has been invested in the marketing process over the lifetime of the products. Both Mc. Donald’s and Coca-Cola have placed enormous emphasis on marketing: spending money on building the image and popularity of the products in the eyes of the customer.
 What is Marketing? Case A Marketing Classic: Coke are it! Issues arising from the case l l What kind of products were sold by Mr. Pemberton and by Mr. Candler? What do you believe has made Coke one of the America’s all time favorite product? Do you feel Coca-Cola’s advertising is effective in the current “battle of colas”? What do you think influenced the price of coca-cola company?
What is Marketing? Case A Marketing Classic: Coke are it! Issues arising from the case l l What kind of products were sold by Mr. Pemberton and by Mr. Candler? What do you believe has made Coke one of the America’s all time favorite product? Do you feel Coca-Cola’s advertising is effective in the current “battle of colas”? What do you think influenced the price of coca-cola company?
 Important thing to keep in mind No amount of promotion, no level of price cuts and not even one of the best brand names in the business can save a product which does not satisfy consumer wants or demand. A business should determine the extent of future demand changes by means of researching customer needs and competitors’ plans. FOCUS OF MARKETING
Important thing to keep in mind No amount of promotion, no level of price cuts and not even one of the best brand names in the business can save a product which does not satisfy consumer wants or demand. A business should determine the extent of future demand changes by means of researching customer needs and competitors’ plans. FOCUS OF MARKETING
 Definition of Marketing is the process of researching into identifying consumers needs and employing appropriate price, product, place and promotion strategies in order to satisfy these needs profitably (Peter Stimpson, 2002). (4 P’s) Marketing is a management process involved in identifying, anticipating and satisfying consumer requirements profitably (Hall, Jones, and Raffo, 2003) Market orientation
Definition of Marketing is the process of researching into identifying consumers needs and employing appropriate price, product, place and promotion strategies in order to satisfy these needs profitably (Peter Stimpson, 2002). (4 P’s) Marketing is a management process involved in identifying, anticipating and satisfying consumer requirements profitably (Hall, Jones, and Raffo, 2003) Market orientation
 The marketing department must work towards satisfying all of the following issues l Products which the customer demands. l Pricing which the customer can afford. l Distribution to a place where the customer will purchase the product. l Promotion to persuade the customer to purchase in a competitive market. Collectively, these are known as the four Ps – Product, Place, Price and Promotion.
The marketing department must work towards satisfying all of the following issues l Products which the customer demands. l Pricing which the customer can afford. l Distribution to a place where the customer will purchase the product. l Promotion to persuade the customer to purchase in a competitive market. Collectively, these are known as the four Ps – Product, Place, Price and Promotion.
 Features of the definitions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Customers are of vital importance. Marketing is a process. Its does not have a start or an end but is ongoing all the time. Marketing involves building relationships with customers. Marketing is a business philosophy. It’s a way of thinking about how to satisfy customers needs. Marketing affect all aspects of the business. Marketing is not just about selling. Marketing and advertising are not the same. Marketing must satisfy consumer wants profitably.
Features of the definitions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Customers are of vital importance. Marketing is a process. Its does not have a start or an end but is ongoing all the time. Marketing involves building relationships with customers. Marketing is a business philosophy. It’s a way of thinking about how to satisfy customers needs. Marketing affect all aspects of the business. Marketing is not just about selling. Marketing and advertising are not the same. Marketing must satisfy consumer wants profitably.
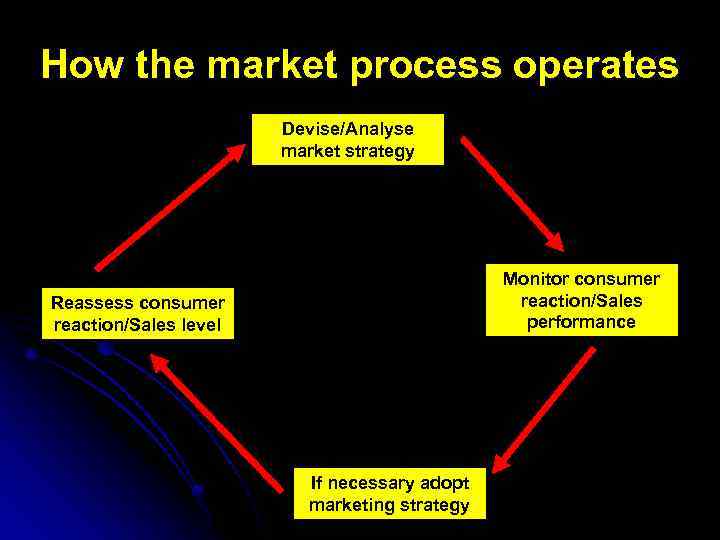 How the market process operates Devise/Analyse market strategy Monitor consumer reaction/Sales performance Reassess consumer reaction/Sales level If necessary adopt marketing strategy
How the market process operates Devise/Analyse market strategy Monitor consumer reaction/Sales performance Reassess consumer reaction/Sales level If necessary adopt marketing strategy
 The rise in the importance of marketing and its effects on business Economic Growth l Changes in Fashion l Technology l Competition l
The rise in the importance of marketing and its effects on business Economic Growth l Changes in Fashion l Technology l Competition l
 From Product to Market Orientation Before marketing was used to develop a competitive advantage, producers used to develop products that they thought would sell profitably, then use hard hitting advertising, and a determined sales force to generate sales. Unfortunately, this took no account of customer demand. The result was a hit-and-hope effect which meant that many companies were left with large levels of unsold stock. This approach is known as Product Orientation where the firm focused everything on the product, hoping it would fit in with customer expectation. Hard Sell Product Invented Customer Product Orientation A number of industries today are still said to be product oriented, for example, those firms which have to produce a final product which matches a technical specification.
From Product to Market Orientation Before marketing was used to develop a competitive advantage, producers used to develop products that they thought would sell profitably, then use hard hitting advertising, and a determined sales force to generate sales. Unfortunately, this took no account of customer demand. The result was a hit-and-hope effect which meant that many companies were left with large levels of unsold stock. This approach is known as Product Orientation where the firm focused everything on the product, hoping it would fit in with customer expectation. Hard Sell Product Invented Customer Product Orientation A number of industries today are still said to be product oriented, for example, those firms which have to produce a final product which matches a technical specification.
 Features of the Product Oriented Business l The business focuses on the production process and the product itself. l The Product Oriented Business invents and develop products in the belief that they will find consumers to purchase them. l Product oriented businesses concentrate their efforts on efficiently producing high quality goods. They recon that if the product is of high enough quality then it will be purchased by consumers who value this feature over market fashion.
Features of the Product Oriented Business l The business focuses on the production process and the product itself. l The Product Oriented Business invents and develop products in the belief that they will find consumers to purchase them. l Product oriented businesses concentrate their efforts on efficiently producing high quality goods. They recon that if the product is of high enough quality then it will be purchased by consumers who value this feature over market fashion.
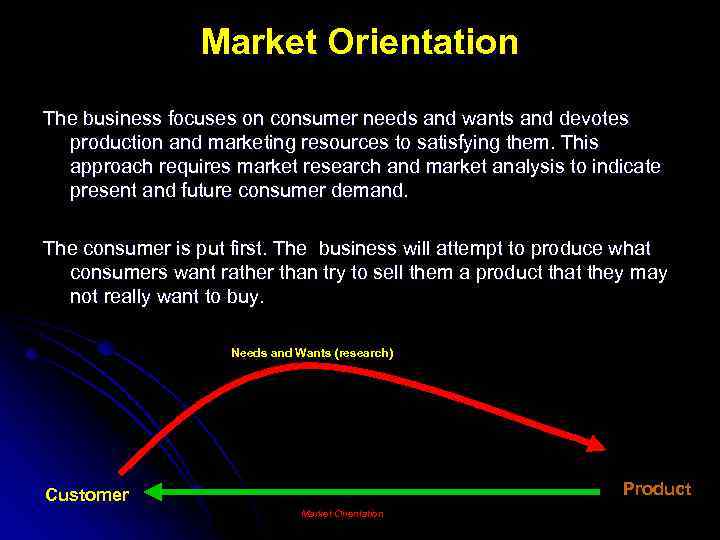 Market Orientation The business focuses on consumer needs and wants and devotes production and marketing resources to satisfying them. This approach requires market research and market analysis to indicate present and future consumer demand. The consumer is put first. The business will attempt to produce what consumers want rather than try to sell them a product that they may not really want to buy. Needs and Wants (research) Product Customer Market Orientation
Market Orientation The business focuses on consumer needs and wants and devotes production and marketing resources to satisfying them. This approach requires market research and market analysis to indicate present and future consumer demand. The consumer is put first. The business will attempt to produce what consumers want rather than try to sell them a product that they may not really want to buy. Needs and Wants (research) Product Customer Market Orientation
 Advantages of Market Oriented Businesses l It can respond more quickly to the changes in the market because of its use of market information. l It will be in a stronger position to meet the challenges of new competition entering the market. l It will be more able to anticipate market changes. l It will be more confident that the launch of a new product will be successful. Question: To what extent do you believe that the internet is a result of product or market orientation?
Advantages of Market Oriented Businesses l It can respond more quickly to the changes in the market because of its use of market information. l It will be in a stronger position to meet the challenges of new competition entering the market. l It will be more able to anticipate market changes. l It will be more confident that the launch of a new product will be successful. Question: To what extent do you believe that the internet is a result of product or market orientation?
 What are the effects of Market Orientation Approach? l Consultation with customers. l Products are designed according to wishes of consumers. l Products are produced in quantities that customers want to buy. l Products are distributed according to the buying habits and delivery requirement of the consumer. l Prices of the products are set at a level that customers are prepared to pay.
What are the effects of Market Orientation Approach? l Consultation with customers. l Products are designed according to wishes of consumers. l Products are produced in quantities that customers want to buy. l Products are distributed according to the buying habits and delivery requirement of the consumer. l Prices of the products are set at a level that customers are prepared to pay.
 Influences on Product and Market Orientation The nature of the product l Policy decisions l The views of those in control l The nature and size of the market. l The degree of competition l
Influences on Product and Market Orientation The nature of the product l Policy decisions l The views of those in control l The nature and size of the market. l The degree of competition l
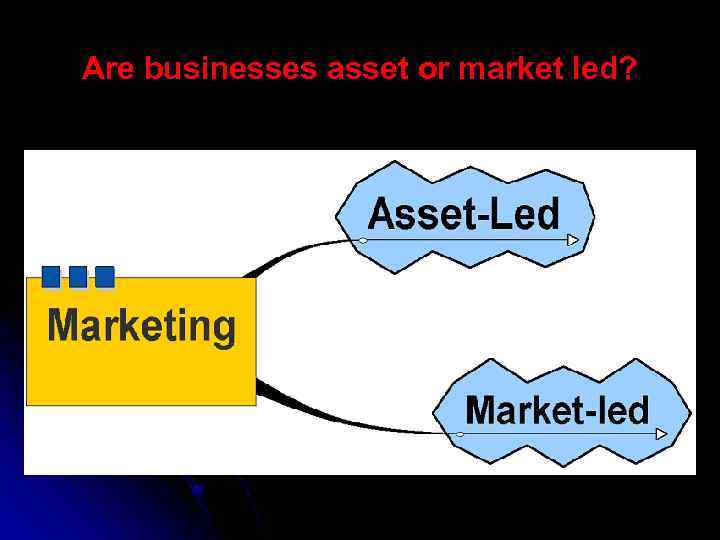 Are businesses asset or market led?
Are businesses asset or market led?
 Features of Asset Led Marketing core-competence of a business in developing new products and services. Those assets may be human, physical or intangible assets.
Features of Asset Led Marketing core-competence of a business in developing new products and services. Those assets may be human, physical or intangible assets.
 Strengths of the Business l Physical Assets l l Intangible Assets l l Distribution Manufacturing base Global reach Brand name Image Personnel Core Competence – what the business sees itself as being ‘good at’
Strengths of the Business l Physical Assets l l Intangible Assets l l Distribution Manufacturing base Global reach Brand name Image Personnel Core Competence – what the business sees itself as being ‘good at’
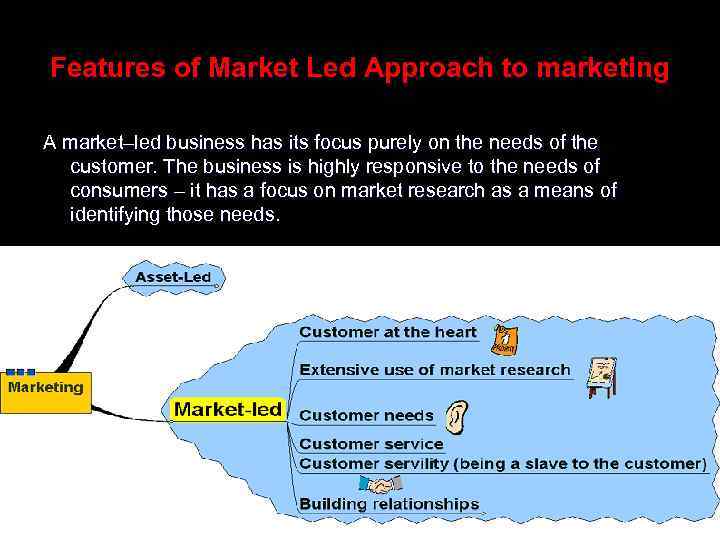 Features of Market Led Approach to marketing A market–led business has its focus purely on the needs of the customer. The business is highly responsive to the needs of consumers – it has a focus on market research as a means of identifying those needs.
Features of Market Led Approach to marketing A market–led business has its focus purely on the needs of the customer. The business is highly responsive to the needs of consumers – it has a focus on market research as a means of identifying those needs.
 Principles of a Market-Led approach to marketing l The customer is king! l Customer service is paramount. l Needs of consumers uppermost in new product development. l Customer servility. l Do not contemplate the cost of doing something to meet customer needs, contemplate the cost of not doing it!
Principles of a Market-Led approach to marketing l The customer is king! l Customer service is paramount. l Needs of consumers uppermost in new product development. l Customer servility. l Do not contemplate the cost of doing something to meet customer needs, contemplate the cost of not doing it!
 Marketing is about building relationships l Importance of building relationships to meet customers needs and expectations. l Suppliers – good relationship with suppliers means that goods are available when the consumer needs them and that the business is able to respond flexibly to change. l Customers – knowing who your customers are, what their needs are and how the market is changing.
Marketing is about building relationships l Importance of building relationships to meet customers needs and expectations. l Suppliers – good relationship with suppliers means that goods are available when the consumer needs them and that the business is able to respond flexibly to change. l Customers – knowing who your customers are, what their needs are and how the market is changing.
 The Requirements of a Successful Marketing Program l Establishing marketing objectives. l Carrying out effective market research and identifying target groups. l Analyzing the markets the firm operates in or plans to enter. l Designing and developing the product. l Testing consumer reaction to product, price and packaging. l Deciding on the most appropriate price. l Establishing a suitable promotion strategy and promotion budget. l Putting in place an effective distribution system. l Continually assessing product sales against target-adjusted marketing variables if sales fail to meet budgeted levels.
The Requirements of a Successful Marketing Program l Establishing marketing objectives. l Carrying out effective market research and identifying target groups. l Analyzing the markets the firm operates in or plans to enter. l Designing and developing the product. l Testing consumer reaction to product, price and packaging. l Deciding on the most appropriate price. l Establishing a suitable promotion strategy and promotion budget. l Putting in place an effective distribution system. l Continually assessing product sales against target-adjusted marketing variables if sales fail to meet budgeted levels.
 Questions l l l l What is meant by the term marketing? Why is marketing described as a process? How can marketing techniques be employed by a nonprofit making organisation? What factors have made marketing so important in today’s business environment? Why might product orientation still be important today? What are the min advantages of a market oriented approach? Why might a market oriented approach be unsuccessful?
Questions l l l l What is meant by the term marketing? Why is marketing described as a process? How can marketing techniques be employed by a nonprofit making organisation? What factors have made marketing so important in today’s business environment? Why might product orientation still be important today? What are the min advantages of a market oriented approach? Why might a market oriented approach be unsuccessful?
 Marketing Objectives Context Objectives are what we attempt or wish to achieve. Marketing objectives are marketing targets, for products and markets, set by a business for future time period. These objectives must: l l l Fit with the over all aims and mission of the business. Be determined by senior , management. Be realistic, motivating, achievable, measurable and clearly communicated to all in the organisation. Failure to link these objectives with the overall aims of the business can lead to different departments pulling in different directions.
Marketing Objectives Context Objectives are what we attempt or wish to achieve. Marketing objectives are marketing targets, for products and markets, set by a business for future time period. These objectives must: l l l Fit with the over all aims and mission of the business. Be determined by senior , management. Be realistic, motivating, achievable, measurable and clearly communicated to all in the organisation. Failure to link these objectives with the overall aims of the business can lead to different departments pulling in different directions.
 Setting Marketing Objectives The marketing objectives a business sets should be SMART in the same way as the overall objectives of the business. They should be: Specific stating exactly what is trying to be achieved, able to be measured to decide if they have been achieved, what usually involves setting targets, agreed by everyone involved, realistic and able to be achieved within constraints of the business and time specific stating exactly when they should be achieved.
Setting Marketing Objectives The marketing objectives a business sets should be SMART in the same way as the overall objectives of the business. They should be: Specific stating exactly what is trying to be achieved, able to be measured to decide if they have been achieved, what usually involves setting targets, agreed by everyone involved, realistic and able to be achieved within constraints of the business and time specific stating exactly when they should be achieved.
 Why are marketing objectives important? l They provide a sense of direction for the marketing department. l Progress can be assessed. l They can be broken down into limited short term targets and also divided between different products and geographical regions of the firm. l They will impact on other department of the business. l The objective will be used as a starting point for the business marketing strategy.
Why are marketing objectives important? l They provide a sense of direction for the marketing department. l Progress can be assessed. l They can be broken down into limited short term targets and also divided between different products and geographical regions of the firm. l They will impact on other department of the business. l The objective will be used as a starting point for the business marketing strategy.
 What does marketing objectives involve? Marketing objectives Will involve/determine some or all of the following: l l l Market Penetration New Product Development Branding Diversification SWOT Analysis Product Portfolio – Product Life Cycle, Boston Matrix
What does marketing objectives involve? Marketing objectives Will involve/determine some or all of the following: l l l Market Penetration New Product Development Branding Diversification SWOT Analysis Product Portfolio – Product Life Cycle, Boston Matrix
 What are some goals an organisation seek to achieve through its marketing? l Growth : Through increase sales, revenue, profit and market share. l Maintaining sales and Market Share: A business may attempt to prevent losses and declining sales, and maintain market share, through its marketing. l Product Differentiation: A business may seek to differentiate its products from those of its competitors by changing the Marketing Mix. l Product Introduction and Innovation: The marketing objective of a business might be to launch a new product on the market. l Consumer Knowledge and Satisfaction: Consumer need to know what products are available from the business. They also need to be happy about the products they buy. Businesses which have satisfied customers are more likely to gain brand loyalty. Other Goals include l l l Corporate image Market Development Market Penetration
What are some goals an organisation seek to achieve through its marketing? l Growth : Through increase sales, revenue, profit and market share. l Maintaining sales and Market Share: A business may attempt to prevent losses and declining sales, and maintain market share, through its marketing. l Product Differentiation: A business may seek to differentiate its products from those of its competitors by changing the Marketing Mix. l Product Introduction and Innovation: The marketing objective of a business might be to launch a new product on the market. l Consumer Knowledge and Satisfaction: Consumer need to know what products are available from the business. They also need to be happy about the products they buy. Businesses which have satisfied customers are more likely to gain brand loyalty. Other Goals include l l l Corporate image Market Development Market Penetration
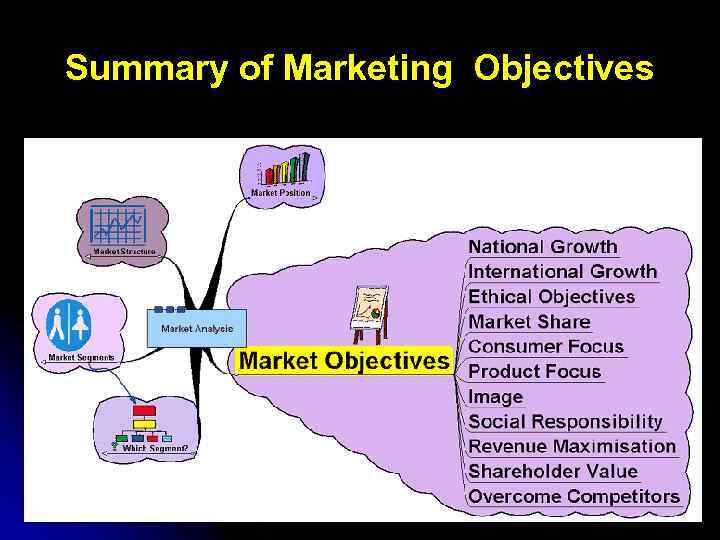 Summary of Marketing Objectives
Summary of Marketing Objectives
 Constraints on marketing objectives There a number of constraints that could affect the marketing objectives set by a business. They could be internal and external. Internal: External l Finance Political Factors l Organisation The Economy l The product Social Factors l Price Technology l Place Environmental Factors
Constraints on marketing objectives There a number of constraints that could affect the marketing objectives set by a business. They could be internal and external. Internal: External l Finance Political Factors l Organisation The Economy l The product Social Factors l Price Technology l Place Environmental Factors
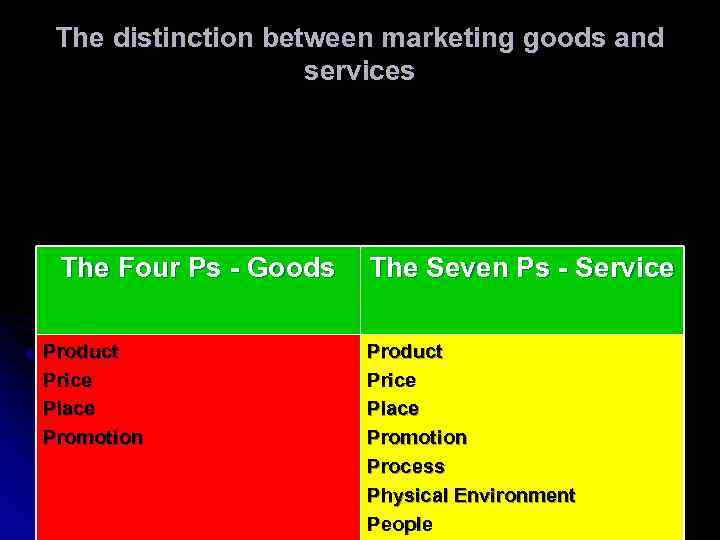 The distinction between marketing goods and services The Four Ps - Goods Product Price Place Promotion The Seven Ps - Service Product Price Place Promotion Process Physical Environment People
The distinction between marketing goods and services The Four Ps - Goods Product Price Place Promotion The Seven Ps - Service Product Price Place Promotion Process Physical Environment People
 Marketing in Non-profit organizations
Marketing in Non-profit organizations
 Group Research and Presentation Discuss the ethical issues involve in marketing and their impact on the organization's need to satisfy its customers profitably. You may refer to specific local or international rules and regulations which dictates the level of ethical considerations businesses must have when they decide to market a product.
Group Research and Presentation Discuss the ethical issues involve in marketing and their impact on the organization's need to satisfy its customers profitably. You may refer to specific local or international rules and regulations which dictates the level of ethical considerations businesses must have when they decide to market a product.
 BIBLIOGRAPHY l Barratt Michael, Mottershead Andy, AS and A Level Business Studies, Pearson Education Ltd, 2000. l Hall Dave, Jones Rob, Raffo Carlo, Business Studies, 3 rd Edition, Causeway Press Ltd, 2004. l Jewell Bruce, AS and A Level Business Studies, 4 th Edition, Pearson Education Ltd, 2000 l Stimpson Peter, AS and A Level Business Studies, Cambridge University Press, 2000. www. bized. ac. uk l
BIBLIOGRAPHY l Barratt Michael, Mottershead Andy, AS and A Level Business Studies, Pearson Education Ltd, 2000. l Hall Dave, Jones Rob, Raffo Carlo, Business Studies, 3 rd Edition, Causeway Press Ltd, 2004. l Jewell Bruce, AS and A Level Business Studies, 4 th Edition, Pearson Education Ltd, 2000 l Stimpson Peter, AS and A Level Business Studies, Cambridge University Press, 2000. www. bized. ac. uk l
 Marketing ethics is the study of right and wrong with respect to marketing policies, practices, and systems. Marketing ethics comprises principles and standards that guide appropriate performance in organizations. Nowadays, most ethicists believe that Relationship Marketing is a reasonable practice leading to positive relationships between buyers and sellers. This allows buyers and sellers to work together.
Marketing ethics is the study of right and wrong with respect to marketing policies, practices, and systems. Marketing ethics comprises principles and standards that guide appropriate performance in organizations. Nowadays, most ethicists believe that Relationship Marketing is a reasonable practice leading to positive relationships between buyers and sellers. This allows buyers and sellers to work together.
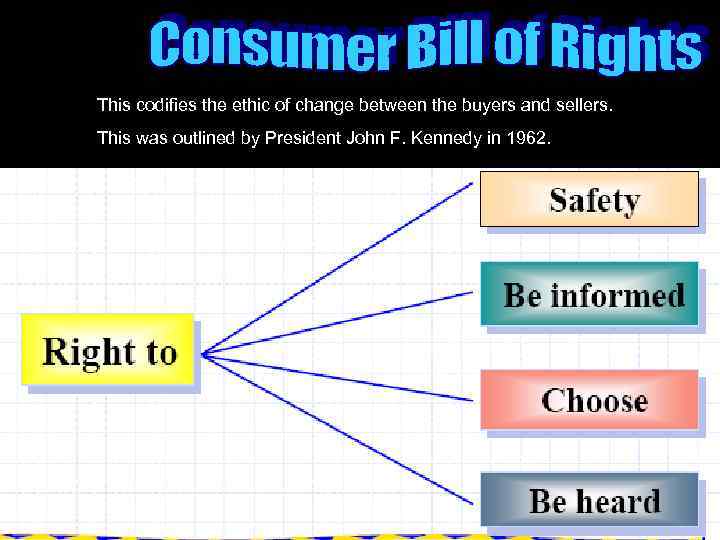 This codifies the ethic of change between the buyers and sellers. This was outlined by President John F. Kennedy in 1962.
This codifies the ethic of change between the buyers and sellers. This was outlined by President John F. Kennedy in 1962.
 Responsibility of the marketer Marketers must accept responsibility for the consequences of their activities and make every effort to ensure that their decisions, recommendations, and actions function to identify, serve, and satisfy all relevant publics: customers, organizations and society. Honesty and fairness Marketers shall maintain and advance the integrity, honor and dignity. Rights & duties in the marketing exchange process Participants should be able to expect that products and services are safe and fit for intended uses; not deceptive. Organizational relationships Marketers should be aware of how their behavior influences the behavior of others in organizational relationships. They should not demand, encourage, or apply coercion to encourage unethical behavior in their relationships with others.
Responsibility of the marketer Marketers must accept responsibility for the consequences of their activities and make every effort to ensure that their decisions, recommendations, and actions function to identify, serve, and satisfy all relevant publics: customers, organizations and society. Honesty and fairness Marketers shall maintain and advance the integrity, honor and dignity. Rights & duties in the marketing exchange process Participants should be able to expect that products and services are safe and fit for intended uses; not deceptive. Organizational relationships Marketers should be aware of how their behavior influences the behavior of others in organizational relationships. They should not demand, encourage, or apply coercion to encourage unethical behavior in their relationships with others.
 Marketers must be aware of ethical standards and acceptable behavior. This awareness means that marketers must recognize the viewpoints of three key players: v The Company v The Industry v The Society 1. Since these three groups almost always have different needs and wants, ethical conflicts are likely to arise 2. It could also arise when personal values conflict with the organization ; Both can also be called a conflict of interest. This brings challenge to the business.
Marketers must be aware of ethical standards and acceptable behavior. This awareness means that marketers must recognize the viewpoints of three key players: v The Company v The Industry v The Society 1. Since these three groups almost always have different needs and wants, ethical conflicts are likely to arise 2. It could also arise when personal values conflict with the organization ; Both can also be called a conflict of interest. This brings challenge to the business.
 An example of the first type of conflict is the tobacco industry. Cigarettes have for many decades been a beneficial business. So, cigarette and tobacco marketing have been good for companies and good for the tobacco industry. Many thousands of people around the world are employed in the tobacco industry. So, the world economy has been somewhat dependent on cigarettes and tobacco. However, cigarettes are harmful to society. There is documented proof that cigarette smoking is harmful to health. This is an ethical conflict for cigarette marketers.
An example of the first type of conflict is the tobacco industry. Cigarettes have for many decades been a beneficial business. So, cigarette and tobacco marketing have been good for companies and good for the tobacco industry. Many thousands of people around the world are employed in the tobacco industry. So, the world economy has been somewhat dependent on cigarettes and tobacco. However, cigarettes are harmful to society. There is documented proof that cigarette smoking is harmful to health. This is an ethical conflict for cigarette marketers.
 An example of the second type of conflict, when one’s personal values conflict with the organization’s, occurs when a leader in the company seeks personal gain (usually financial profit) from false advertising. "Cures" for fatal diseases are one type of product that falls into this category of ethical conflict: In their greed to make a profit, a marketer convinces those who may be dying from an incurable disease to buy a product that may not be a cure, but which a desperately ill person (or members of his or her family) may choose to purchase in an effort to save the dying family member suffering. Promoting and marketing such products violates rules of marketing ethics.
An example of the second type of conflict, when one’s personal values conflict with the organization’s, occurs when a leader in the company seeks personal gain (usually financial profit) from false advertising. "Cures" for fatal diseases are one type of product that falls into this category of ethical conflict: In their greed to make a profit, a marketer convinces those who may be dying from an incurable disease to buy a product that may not be a cure, but which a desperately ill person (or members of his or her family) may choose to purchase in an effort to save the dying family member suffering. Promoting and marketing such products violates rules of marketing ethics.
 Standards for ethical marketing guide business in efforts to do the right thing. Such standards have four functions: v To help identify acceptable practices v Foster internal control v Avoid confusion v Facilitate a basis for discussion.
Standards for ethical marketing guide business in efforts to do the right thing. Such standards have four functions: v To help identify acceptable practices v Foster internal control v Avoid confusion v Facilitate a basis for discussion.
 BIBLIOGRAPHY: Ethical Issues: http: //pwebs. net/marketing/ethics/articles/internetethics. htm Business Ethics: http: //exchanges. state. gov/forum/journal/bus 10 background. htm Marketing Ethics & Marketing Strategy: http: //www. utdallas. edu/~tskim/Lecture%20 Note%202. pdf
BIBLIOGRAPHY: Ethical Issues: http: //pwebs. net/marketing/ethics/articles/internetethics. htm Business Ethics: http: //exchanges. state. gov/forum/journal/bus 10 background. htm Marketing Ethics & Marketing Strategy: http: //www. utdallas. edu/~tskim/Lecture%20 Note%202. pdf
 END OF UNIT
END OF UNIT


