mod2_-2.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 22

Module 2: Identifying Hazard and Risk SMS BASICS FOR PUBLIC SERVICE AVIATION

HAZARD VS RISK HAZARD A condition that can impair missions by causing harm or damage. Can be dynamic with no indication of its mission significance. Risk A hazard for which we have already estimated the severity, probability, and exposure to determine its impact our mission.

Hazard Assessment ⨀ The “concept” is to identify and learn of all foreseeable hazards before the mission. Then have a plan to avoid or mitigate. ⨀ The entire organization must be a part of this concept. ⨀ Question: If we must do the mission then how do we prepare the unit and our crews for it? ⨀ Question: What are the risks and hazards associated with this mission or operational tasking?

Risk Assessment Risk must be linked to a specific hazard (There are many hazards) ⨀ ⨀ Hazard Reporting must be proactive ⨀ Hazard Detection Systems must include: ⧐ People ⧐ Technology ⧐ Outside sources ⧐ Known Precedents ⧐ Standardized reporting methods

Safety Hazard Assessment Plan ⨀ Organize ⧐ Identify and define hazard……is it a problem ? ⧐ Collect data on hazard ⨀ Assess Hazard and Risk ⧐ Preliminary Hazard List (PHL) ⧐ Preliminary Hazard Analysis (PHA) ⧐ Hazard mitigation steps ⧐ Analysis to Decision Makers ⨀ Manage Risk/Hazard ⧐ Evaluate constantly ⧐ Monitor and Measure ⧐ Modify mission or SOP ⧐ Maintain Proactive hazard awareness

Preliminary Hazard List (PHL) Identification Tools ⨀ “WHAT IF” POTENTIAL HAZARDS TO AN OPERATION ⧐ Purpose: To capture the input of operational personnel in a brainstorming-like environment. ⧐ Method: Choose an area (not the entire operation), get a group and generate as many “what ifs” as possible. Utilize unit expertise, outside resources, historical research etc. Who has done this mission? Find out and get in touch with them. ⨀ SCENARIO PROCESSING TOOL ⧐ Purpose: To use imagination and visualizations to capture unusual hazards or potential hazards outside normal ops. ⧐ Method: Using the operations analysis as a guide, visualize the flow of events.

Applications of PHL ⨀ Special Operations, Routes or Missions ⨀ Operations at new airports, ramps, hangars, etc. ⨀ New Aircraft or integration of mixed fleet ⨀ New cockpit instrumentations and technology ⨀ Crew Paring ⨀ Training of non-standard maneuvers ⨀ Use of different aircraft in training ⨀ Altering SOPs ⨀ Establishing new landing areas, ramps, etc. ⨀ Changes in watches and work schedules
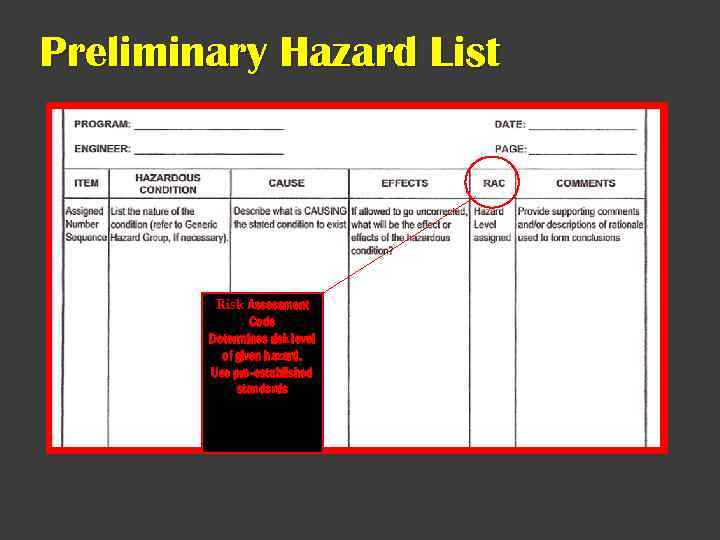
Preliminary Hazard List Risk Assessment Code Determines risk level of given hazard. Use pre-established standards
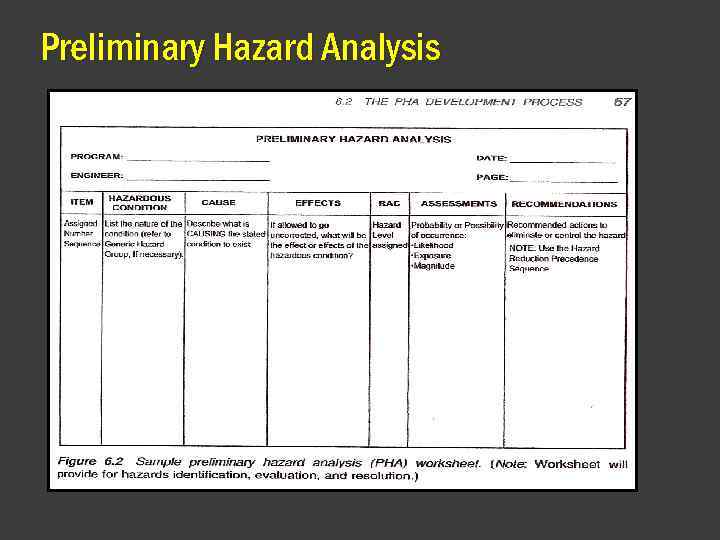
Preliminary Hazard Analysis

Primary Hazard Assessment (PHA) Levels ⨀ Unacceptable Example: Dangerous Parking Pad ⧐ Stop: Warn All ⨀ Undesirable ⧐ Restrict: Warn all ⨀ Acceptable with action ⧐ Alert Management and Crews ⧐ Detailed action plan of resolution ⨀ Acceptable with monitoring ⧐ Alert Management and crew ⧐ Establish SOP monitoring parameters ⨀ Acceptable ⧐ Risk profile monitoring-ongoing

System Safety Criteria MIL-STD-882 DOD/NASA ⨀ Levels of hazard and risk need to be standardized. Some safety analysis terms: ⧐ Hazard Severity ⧐ Hazard Probability ⧐ Risk Assessment Matrix ⧐ Risk vs. Cost Matrix

Hazard Mitigation Steps ⨀ Level 1: Design out or avoid hazard –modify the system. ⨀ Level 2: Physical guards barriers to prevent risk from occurring. ⨀ Level 3: Warning or alert when hazard will occur. ⨀ Level 4: Training changes ( recurrent +). ⨀ Level 5: Advisement (placards notices). ⨀ Level 6: Personal protection equipment.

Hazard Resolution Steps ⨀ Is the Hazard worth Resolving? ⨀ What is the likelihood of encountering it? ⨀ What is the cost of resolving it? ⨀ Resolution Steps 1. Engineer it out 2. Control Solution 3. Personneal Solution 4. Protective Equipment Solution

Hazard Resolution Step 1 1. Engineer it out : ⨀ This removes the hazard and risk completely ⧐Example: Tight or poorly designed parking ramp for helicopter ⧐Resolution: Remove it or redesign

Hazard Resolution Step 2 2. Control Solution : Close, guard or limit access. ⨀ Example: Tight or poorly designed parking ramp for helicopter. ⨀ Close the ramp area.

Hazard Resolution Step 3 3. Personnel Solution : Warn and guard about hazard ⨀ Example: Tight or poorly designed parking ramp for helicopter. ⨀ Post info and warn crews about non standard area, provide procedures.

Hazard Resolution Step 4 4. Personnel Protection Equip ⨀ Example: Tight or poorly designed parking ramp for helicopter. ⨀ Post flaggers or ground personnel near area with safety equipment for FOD and noise protection.
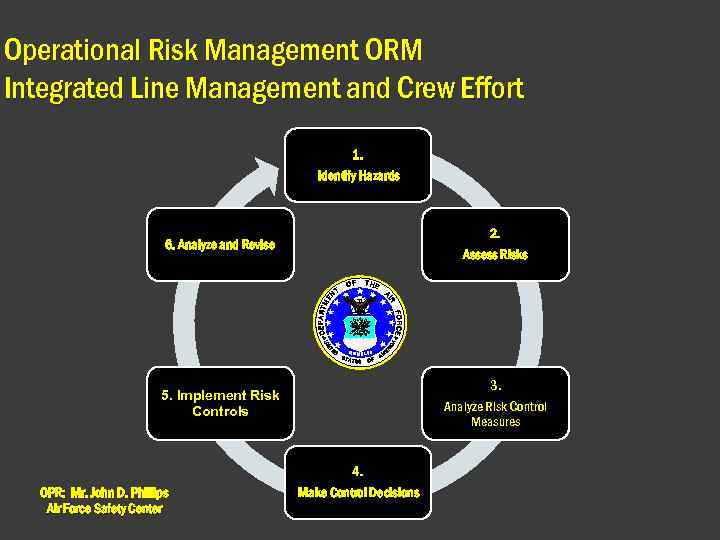
Operational Risk Management ORM Integrated Line Management and Crew Effort 1. Identify Hazards 2. Assess Risks 6. Analyze and Revise 3. 5. Implement Risk Controls OPR: Mr. John D. Phillips Air Force Safety Center Analyze Risk Control Measures 4. Make Control Decisions

Warning: Hazards can be unseen until they strike. ⨀ Maintain proactive effort to identify hazards in all aspects of the operation.
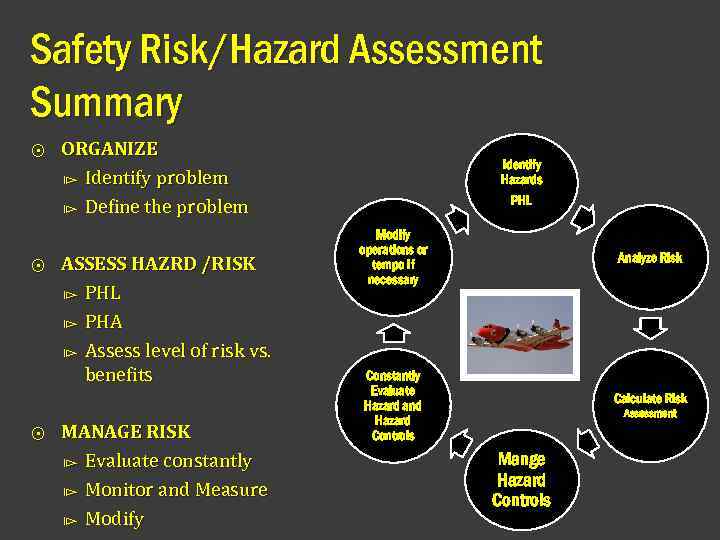
Safety Risk/Hazard Assessment Summary ⨀ ⨀ ⨀ ORGANIZE ⧐ Identify problem ⧐ Define the problem ASSESS HAZRD /RISK ⧐ PHL ⧐ PHA ⧐ Assess level of risk vs. benefits MANAGE RISK ⧐ Evaluate constantly ⧐ Monitor and Measure ⧐ Modify Identify Hazards PHL Modify operations or tempo if necessary Analyze Risk Constantly Evaluate Hazard and Hazard Controls Calculate Risk Assessment Mange Hazard Controls

Wrap Up and Key Points… ⨀ ⨀ ⨀ ⨀ ⨀ Maintain a proactive hazard detection and reporting system. Accurately define hazard and its magnitude. Utilize a Preliminary Hazard List(PHL) to list hazards about a mission or operation. Analyze cause and effect of hazard using Preliminary Hazard Analysis(PHA) Develop mitigation steps, if possible. Constantly monitor operations for developing hazards. Reporting actual or perceived hazards in any aspect of the unit or operation is a team effort. Develop hazard reporting forms and system in unit. Record and track all reported hazards. Communicate to all personnel.

End
mod2_-2.pptx