804872d29fee12948308cd5bf6b22471.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 Module 19: Security l l l The Security Problem(安全问题) Authentication(授权) Program Threats(来自程序的威胁) System Threats(来自系统的威胁) Threat Monitoring(威胁的监控) Encryption(加密) 1 3/18/2018
Module 19: Security l l l The Security Problem(安全问题) Authentication(授权) Program Threats(来自程序的威胁) System Threats(来自系统的威胁) Threat Monitoring(威胁的监控) Encryption(加密) 1 3/18/2018
 安全 l l 保护是个内部问题,应该以一种怎样的方式,提供对存储 在计算机系统中的程序和数据的受控访问 安全:除了需要一个适当的保护系统外,还需考虑系统运 行的外部环境。 第十八章讨论了操作系统能够提供的机制,它们使用户得 以保护属于他们的资源,只有在用户遵守资源的使用和访 问规则时,这些机制才能很好地发挥作用。 必须有这样一些机制,它们能够将出现安全缺口的情况控 制在一个极小的概率范围内。 2 3/18/2018
安全 l l 保护是个内部问题,应该以一种怎样的方式,提供对存储 在计算机系统中的程序和数据的受控访问 安全:除了需要一个适当的保护系统外,还需考虑系统运 行的外部环境。 第十八章讨论了操作系统能够提供的机制,它们使用户得 以保护属于他们的资源,只有在用户遵守资源的使用和访 问规则时,这些机制才能很好地发挥作用。 必须有这样一些机制,它们能够将出现安全缺口的情况控 制在一个极小的概率范围内。 2 3/18/2018
 The Security Problem 安全问题 l l Security must consider external environment of the system, and protect it from: (安全必须考虑系统的外环境,以下方面防护:) n unauthorized access. (未授权访问) n malicious modification or destruction(恶意的修改和破坏) n accidental introduction of inconsistency. (意外的引入和不一致) Easier to protect against accidental than malicious misuse. (防止意 外的误用比防止恶意的误用更加容易) 3 3/18/2018
The Security Problem 安全问题 l l Security must consider external environment of the system, and protect it from: (安全必须考虑系统的外环境,以下方面防护:) n unauthorized access. (未授权访问) n malicious modification or destruction(恶意的修改和破坏) n accidental introduction of inconsistency. (意外的引入和不一致) Easier to protect against accidental than malicious misuse. (防止意 外的误用比防止恶意的误用更加容易) 3 3/18/2018
 The Security Problem l 恶意破坏的形式: n 末经授权的读数据操作 n 末经授权的修改数据操作 n 末经授权的数据破坏 n 阻止系统的正常使用 要保护系统,必须在 4个层次上采取安全机制: l 物理 n 人:减少授权用户授予入侵者访问权限的机会 n 网络:中途截取数据等 n 操作系统:防止自身意外 本章将在操作系统层次上讲授安全。 l n 4 3/18/2018
The Security Problem l 恶意破坏的形式: n 末经授权的读数据操作 n 末经授权的修改数据操作 n 末经授权的数据破坏 n 阻止系统的正常使用 要保护系统,必须在 4个层次上采取安全机制: l 物理 n 人:减少授权用户授予入侵者访问权限的机会 n 网络:中途截取数据等 n 操作系统:防止自身意外 本章将在操作系统层次上讲授安全。 l n 4 3/18/2018
 用户验证 l l l 用户持有的物品 用户的信息(用户鉴别、密码) 特征属性(指纹等) 5 3/18/2018
用户验证 l l l 用户持有的物品 用户的信息(用户鉴别、密码) 特征属性(指纹等) 5 3/18/2018
 Authentication l l User identity most often established through passwords, can be considered a special case of either keys or capabilities. (用户 身份通常使用密码确立,可以认为密码就是某种权限或者 钥匙) Passwords must be kept secret. (密码必须保持秘密的状态) n Frequent change of passwords. (经常更换密码) n Use of “non-guessable” passwords. (使用难猜的密码) n Log all invalid access attempts. (记录所有非法访问企图) 6 3/18/2018
Authentication l l User identity most often established through passwords, can be considered a special case of either keys or capabilities. (用户 身份通常使用密码确立,可以认为密码就是某种权限或者 钥匙) Passwords must be kept secret. (密码必须保持秘密的状态) n Frequent change of passwords. (经常更换密码) n Use of “non-guessable” passwords. (使用难猜的密码) n Log all invalid access attempts. (记录所有非法访问企图) 6 3/18/2018
 密码 l l 密码脆弱的一面 猜中 监听、泄露 被一授权用户非法传递给一个未授权用户 7 3/18/2018
密码 l l 密码脆弱的一面 猜中 监听、泄露 被一授权用户非法传递给一个未授权用户 7 3/18/2018
 Program Threats程序的威胁 l l Trojan Horse(特洛伊木马,一个误用自身的代码段) n Code segment that misuses its environment. (代码段滥用环境) n Exploits mechanisms for allowing programs written by users to be executed by other users. (利用机制使得某个用户写的程序可以被其 他用户运行) Trap Door(后门) n Specific user identifier or password that circumvents normal security procedures. (特殊的用户标识符或者密码可以绕过通常的安全检查) n Could be included in a compiler. (有可能包含在编译器中) 8 3/18/2018
Program Threats程序的威胁 l l Trojan Horse(特洛伊木马,一个误用自身的代码段) n Code segment that misuses its environment. (代码段滥用环境) n Exploits mechanisms for allowing programs written by users to be executed by other users. (利用机制使得某个用户写的程序可以被其 他用户运行) Trap Door(后门) n Specific user identifier or password that circumvents normal security procedures. (特殊的用户标识符或者密码可以绕过通常的安全检查) n Could be included in a compiler. (有可能包含在编译器中) 8 3/18/2018
 System Threats l l Worms – use spawn mechanism; standalone program Internet worm n Exploited UNIX networking features (remote access) and bugs in finger and sendmail programs. n Grappling hook program uploaded main worm program. Viruses – fragment of code embedded in a legitimate program. n Mainly effect microcomputer systems. n Downloading viral programs from public bulletin boards or exchanging floppy disks containing an infection. n Safe computing. Denial of Service n Overload the targeted computer preventing it from doing any sueful work. 9 3/18/2018
System Threats l l Worms – use spawn mechanism; standalone program Internet worm n Exploited UNIX networking features (remote access) and bugs in finger and sendmail programs. n Grappling hook program uploaded main worm program. Viruses – fragment of code embedded in a legitimate program. n Mainly effect microcomputer systems. n Downloading viral programs from public bulletin boards or exchanging floppy disks containing an infection. n Safe computing. Denial of Service n Overload the targeted computer preventing it from doing any sueful work. 9 3/18/2018
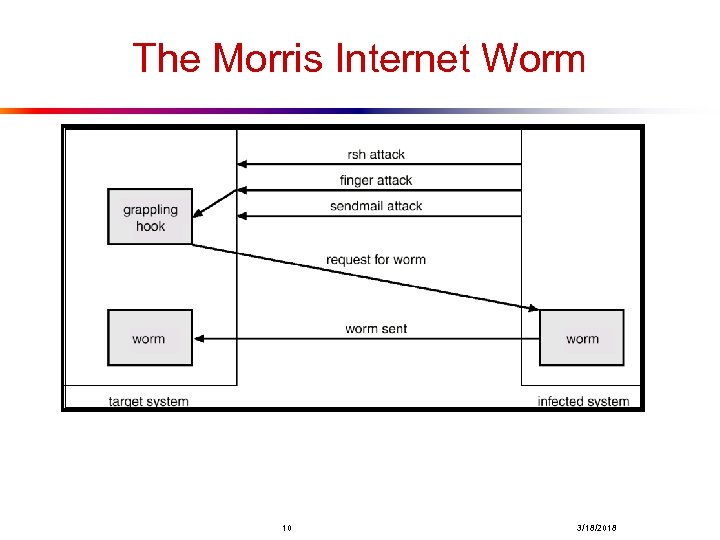 The Morris Internet Worm 10 3/18/2018
The Morris Internet Worm 10 3/18/2018
 Threat Monitoring l l l Check for suspicious patterns of activity – i. e. , several incorrect password attempts may signal password guessing. Audit log – records the time, user, and type of all accesses to an object; useful for recovery from a violation and developing better security measures. Scan the system periodically for security holes; done when the computer is relatively unused. 11 3/18/2018
Threat Monitoring l l l Check for suspicious patterns of activity – i. e. , several incorrect password attempts may signal password guessing. Audit log – records the time, user, and type of all accesses to an object; useful for recovery from a violation and developing better security measures. Scan the system periodically for security holes; done when the computer is relatively unused. 11 3/18/2018
 Threat Monitoring (Cont. ) l Check for: n Short or easy-to-guess passwords n Unauthorized set-uid programs n Unauthorized programs in system directories n Unexpected long-running processes n Improper directory protections n Improper protections on system data files n Dangerous entries in the program search path (Trojan horse) n Changes to system programs: monitor checksum values 12 3/18/2018
Threat Monitoring (Cont. ) l Check for: n Short or easy-to-guess passwords n Unauthorized set-uid programs n Unauthorized programs in system directories n Unexpected long-running processes n Improper directory protections n Improper protections on system data files n Dangerous entries in the program search path (Trojan horse) n Changes to system programs: monitor checksum values 12 3/18/2018
 Fire. Wall l A firewall is placed between trusted and untrusted hosts. l The firewall limits network access between these two security domains. 13 3/18/2018
Fire. Wall l A firewall is placed between trusted and untrusted hosts. l The firewall limits network access between these two security domains. 13 3/18/2018
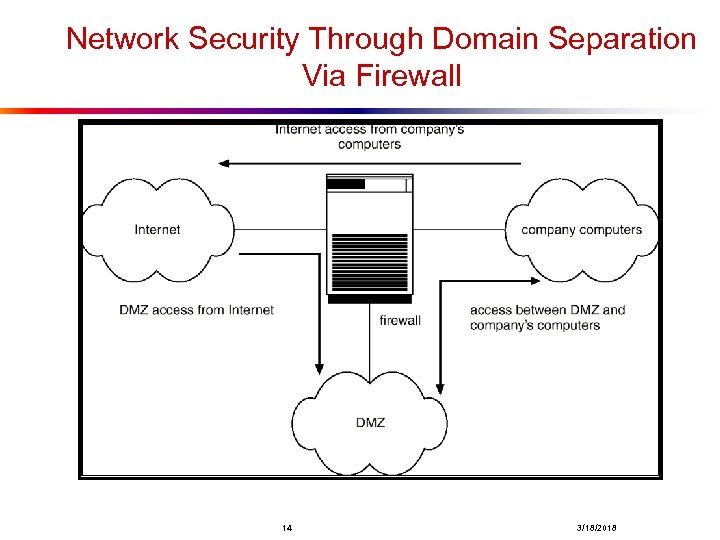 Network Security Through Domain Separation Via Firewall 14 3/18/2018
Network Security Through Domain Separation Via Firewall 14 3/18/2018
 Intrusion Detection l Detect attempts to intrude into computer systems. l Detection methods: n Auditing and logging. n Tripwire (UNIX software that checks if certain files and directories have been altered – I. e. password files) l System call monitoring 15 3/18/2018
Intrusion Detection l Detect attempts to intrude into computer systems. l Detection methods: n Auditing and logging. n Tripwire (UNIX software that checks if certain files and directories have been altered – I. e. password files) l System call monitoring 15 3/18/2018
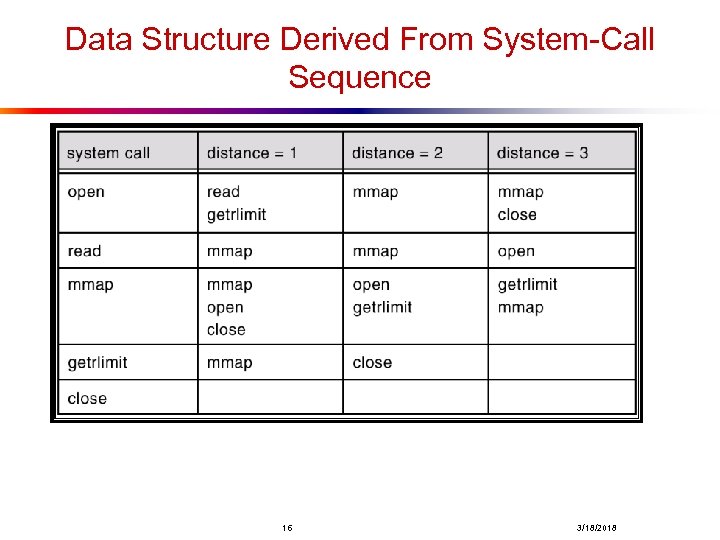 Data Structure Derived From System-Call Sequence 16 3/18/2018
Data Structure Derived From System-Call Sequence 16 3/18/2018
 Encryption l l l Encrypt clear text into cipher text. Properties of good encryption technique: n Relatively simple for authorized users to incrypt and decrypt data. n Encryption scheme depends not on the secrecy of the algorithm but on a parameter of the algorithm called the encryption key. n Extremely difficult for an intruder to determine the encryption key. Data Encryption Standard substitutes characters and rearranges their order on the basis of an encryption key provided to authorized users via a secure mechanism. Scheme only as secure as the mechanism. 17 3/18/2018
Encryption l l l Encrypt clear text into cipher text. Properties of good encryption technique: n Relatively simple for authorized users to incrypt and decrypt data. n Encryption scheme depends not on the secrecy of the algorithm but on a parameter of the algorithm called the encryption key. n Extremely difficult for an intruder to determine the encryption key. Data Encryption Standard substitutes characters and rearranges their order on the basis of an encryption key provided to authorized users via a secure mechanism. Scheme only as secure as the mechanism. 17 3/18/2018
 Encryption (Cont. ) l l Public-key encryption based on each user having two keys: n public key – published key used to encrypt data. n private key – key known only to individual user used to decrypt data. Must be an encryption scheme that can be made public without making it easy to figure out the decryption scheme. n Efficient algorithm for testing whether or not a number is prime. n No efficient algorithm is know for finding the prime factors of a number. 18 3/18/2018
Encryption (Cont. ) l l Public-key encryption based on each user having two keys: n public key – published key used to encrypt data. n private key – key known only to individual user used to decrypt data. Must be an encryption scheme that can be made public without making it easy to figure out the decryption scheme. n Efficient algorithm for testing whether or not a number is prime. n No efficient algorithm is know for finding the prime factors of a number. 18 3/18/2018
 Encryption Example - SSL l SSL – Secure Socket Layer l Cryptographic protocol that limits two computers to only exchange messages with each other. l Used between web servers and browsers for secure communication (credit card numbers) l The server is verified with a certificate. l Communication between each computers uses symmetric key cryptography. 19 3/18/2018
Encryption Example - SSL l SSL – Secure Socket Layer l Cryptographic protocol that limits two computers to only exchange messages with each other. l Used between web servers and browsers for secure communication (credit card numbers) l The server is verified with a certificate. l Communication between each computers uses symmetric key cryptography. 19 3/18/2018
 Computer Security Classifications l l l U. S. Department of Defense outlines four divisions of computer security: A, B, C, and D. D – Minimal security. C – Provides discretionary protection through auditing. Divided into C 1 and C 2. C 1 identifies cooperating users with the same level of protection. C 2 allows user-level access control. B – All the properties of C, however each object may have unique sensitivity labels. Divided into B 1, B 2, and B 3. A – Uses formal design and verification techniques to ensure security. 20 3/18/2018
Computer Security Classifications l l l U. S. Department of Defense outlines four divisions of computer security: A, B, C, and D. D – Minimal security. C – Provides discretionary protection through auditing. Divided into C 1 and C 2. C 1 identifies cooperating users with the same level of protection. C 2 allows user-level access control. B – All the properties of C, however each object may have unique sensitivity labels. Divided into B 1, B 2, and B 3. A – Uses formal design and verification techniques to ensure security. 20 3/18/2018
 Windows NT Example l Configurable security allows policies ranging from D to C 2. l Security is based on user accounts where each user has a security ID. l Uses a subject model to ensure access security. A subject tracks and manages permissions for each program that a user runs. l Each object in Windows NT has a security attribute defined by a security descriptor. For example, a file has a security descriptor that indicates the access permissions for all users. 21 3/18/2018
Windows NT Example l Configurable security allows policies ranging from D to C 2. l Security is based on user accounts where each user has a security ID. l Uses a subject model to ensure access security. A subject tracks and manages permissions for each program that a user runs. l Each object in Windows NT has a security attribute defined by a security descriptor. For example, a file has a security descriptor that indicates the access permissions for all users. 21 3/18/2018


