10266A_15.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
 Module 15 Integrating Visual C# Code with Dynamic Languages and COM Components
Module 15 Integrating Visual C# Code with Dynamic Languages and COM Components
 Module Overview • Integrating Visual C# Code with Ruby and Python • Accessing COM Components from Visual C#
Module Overview • Integrating Visual C# Code with Ruby and Python • Accessing COM Components from Visual C#
 Lesson 1: Integrating Visual C# Code with Ruby and Python • What Is the Dynamic Language Runtime? • Using the dynamic Keyword • Instantiating a Dynamic Object • Invoking and Using a Dynamic Object • Demonstration: Calling Python Code from Visual C#
Lesson 1: Integrating Visual C# Code with Ruby and Python • What Is the Dynamic Language Runtime? • Using the dynamic Keyword • Instantiating a Dynamic Object • Invoking and Using a Dynamic Object • Demonstration: Calling Python Code from Visual C#
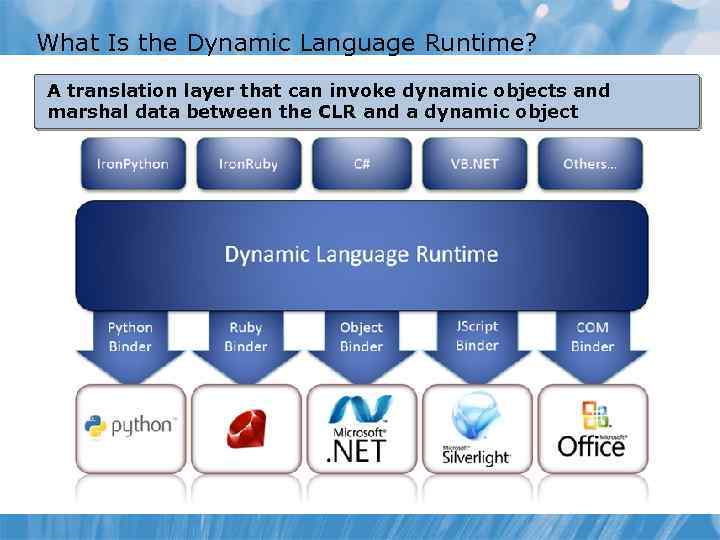 What Is the Dynamic Language Runtime? A translation layer that can invoke dynamic objects and marshal data between the CLR and a dynamic object
What Is the Dynamic Language Runtime? A translation layer that can invoke dynamic objects and marshal data between the CLR and a dynamic object
 Using the dynamic Keyword Specifies that the C# compiler should defer type checking until run time Syntactically similar to a type Semantically it defines an object dynamic. Object; Use dynamic to refer to dynamic objects whose type can only be determined at run time A dynamic variable can hold any type at any time dynamic var 1 = 99; . . . var 1 = “Hello”; Intelli. Sense is not available with dynamic variables Code will compile, but may result in run-time errors if methods, operators, and properties do not exist or are misspelled dynamic var 2 = var 1 * 5; // ? Will compile but may not run
Using the dynamic Keyword Specifies that the C# compiler should defer type checking until run time Syntactically similar to a type Semantically it defines an object dynamic. Object; Use dynamic to refer to dynamic objects whose type can only be determined at run time A dynamic variable can hold any type at any time dynamic var 1 = 99; . . . var 1 = “Hello”; Intelli. Sense is not available with dynamic variables Code will compile, but may result in run-time errors if methods, operators, and properties do not exist or are misspelled dynamic var 2 = var 1 * 5; // ? Will compile but may not run
 Instantiating a Dynamic Object You cannot use the C# new operator to instantiate a dynamic object The runtime for a dynamic object is responsible for creating the object A common technique is to provide a factory method for the dynamic object and call the factory method from Visual C# through the DLR [Python] class Customer: def __init__(self, id, name, telephone): . . . def Get. New. Customer(id, name, telephone): return Customer(id, name, telephone) To call the method, start the runtime for the dynamic object, and invoke the script that defines the object (details will vary) [Example – Iron. Python] dynamic python. Script = Python. Create. Runtime(). Use. File("Customer. py"); dynamic customer = python. Script. Get. New. Customer(99, "Fred", "111");
Instantiating a Dynamic Object You cannot use the C# new operator to instantiate a dynamic object The runtime for a dynamic object is responsible for creating the object A common technique is to provide a factory method for the dynamic object and call the factory method from Visual C# through the DLR [Python] class Customer: def __init__(self, id, name, telephone): . . . def Get. New. Customer(id, name, telephone): return Customer(id, name, telephone) To call the method, start the runtime for the dynamic object, and invoke the script that defines the object (details will vary) [Example – Iron. Python] dynamic python. Script = Python. Create. Runtime(). Use. File("Customer. py"); dynamic customer = python. Script. Get. New. Customer(99, "Fred", "111");
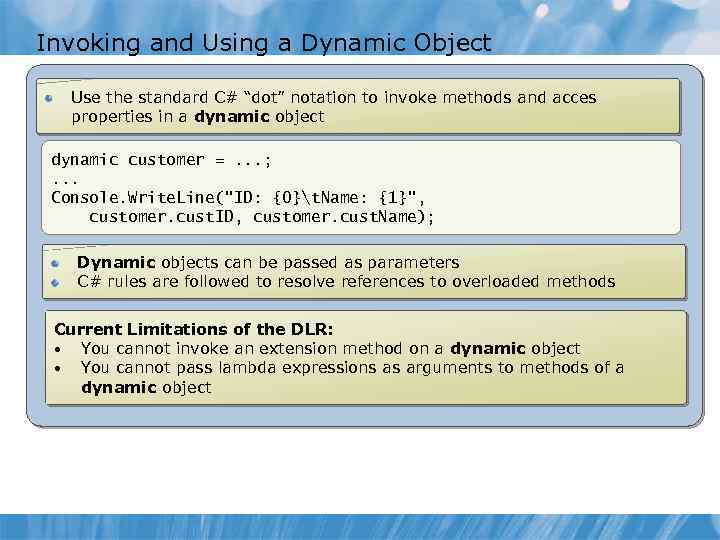 Invoking and Using a Dynamic Object Use the standard C# “dot” notation to invoke methods and acces properties in a dynamic object dynamic customer =. . . ; . . . Console. Write. Line("ID: {0}t. Name: {1}", customer. cust. ID, customer. cust. Name); Dynamic objects can be passed as parameters C# rules are followed to resolve references to overloaded methods Current Limitations of the DLR: • You cannot invoke an extension method on a dynamic object • You cannot pass lambda expressions as arguments to methods of a dynamic object
Invoking and Using a Dynamic Object Use the standard C# “dot” notation to invoke methods and acces properties in a dynamic object dynamic customer =. . . ; . . . Console. Write. Line("ID: {0}t. Name: {1}", customer. cust. ID, customer. cust. Name); Dynamic objects can be passed as parameters C# rules are followed to resolve references to overloaded methods Current Limitations of the DLR: • You cannot invoke an extension method on a dynamic object • You cannot pass lambda expressions as arguments to methods of a dynamic object
 Demonstration: Calling Python Code From Visual C# In this demonstration, you will see how to: • Reference a Python script from Visual C# • Create Python objects in Visual C# • Call Python methods from Visual C#
Demonstration: Calling Python Code From Visual C# In this demonstration, you will see how to: • Reference a Python script from Visual C# • Create Python objects in Visual C# • Call Python methods from Visual C#
 Lesson 2: Accessing COM Components from Visual C# • Interoperating with COM from a Visual C# Application • Creating a COM Interop Assembly • Instantiating a COM Component by Using a Runtime Callable Wrapper • Calling Methods on a COM Object • Deploying Without a Primary Interop Assembly
Lesson 2: Accessing COM Components from Visual C# • Interoperating with COM from a Visual C# Application • Creating a COM Interop Assembly • Instantiating a COM Component by Using a Runtime Callable Wrapper • Calling Methods on a COM Object • Deploying Without a Primary Interop Assembly
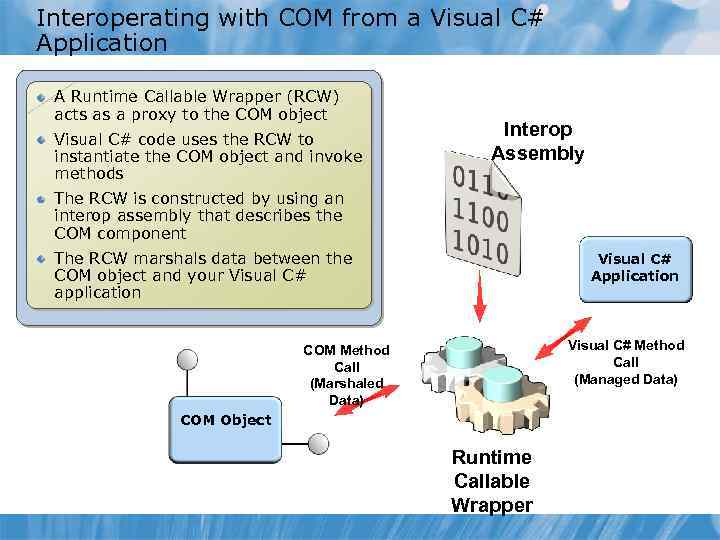 Interoperating with COM from a Visual C# Application A Runtime Callable Wrapper (RCW) acts as a proxy to the COM object Visual C# code uses the RCW to instantiate the COM object and invoke methods Interop Assembly The RCW is constructed by using an interop assembly that describes the COM component The RCW marshals data between the COM object and your Visual C# application Visual C# Application Visual C# Method Call (Managed Data) COM Method Call (Marshaled Data) COM Object Runtime Callable Wrapper
Interoperating with COM from a Visual C# Application A Runtime Callable Wrapper (RCW) acts as a proxy to the COM object Visual C# code uses the RCW to instantiate the COM object and invoke methods Interop Assembly The RCW is constructed by using an interop assembly that describes the COM component The RCW marshals data between the COM object and your Visual C# application Visual C# Application Visual C# Method Call (Managed Data) COM Method Call (Marshaled Data) COM Object Runtime Callable Wrapper
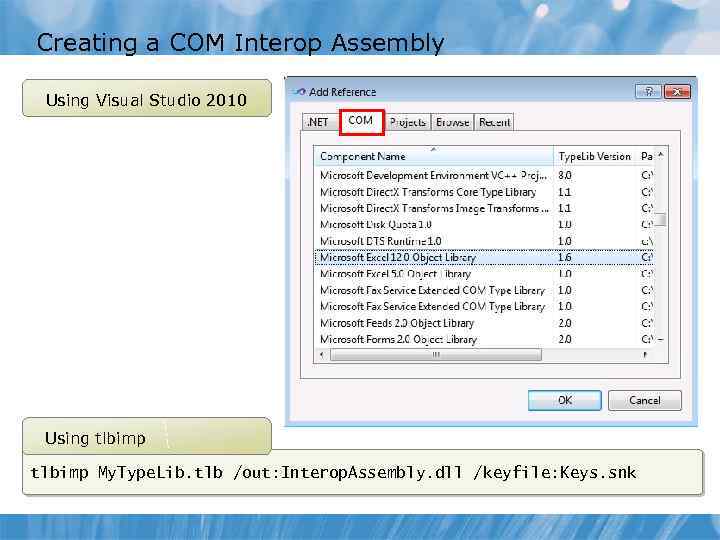 Creating a COM Interop Assembly Using Visual Studio 2010 Using tlbimp My. Type. Lib. tlb /out: Interop. Assembly. dll /keyfile: Keys. snk
Creating a COM Interop Assembly Using Visual Studio 2010 Using tlbimp My. Type. Lib. tlb /out: Interop. Assembly. dll /keyfile: Keys. snk
 Instantiating a COM Component by Using a Runtime Callable Wrapper The RCW provides access to COM coclasses that the COM component defines through managed wrappers around COM interfaces Instantiate COM objects by using the managed wrappers around the COM interfaces Some COM objects provide factory methods for creating related types defined by the object model implemented by the COM component Example: Office Excel // Use the Application interface to create an // instance of the Application. Class coclass Application excel. App = new Application(); // Use factory methods to instantiate related objects defined // by the Office Excel object model Workbook excel. WB = excel. App. Workbooks. Add(); // Factory method The syntax for instantiating COM objects is indistinguishable from that for creating managed C# objects.
Instantiating a COM Component by Using a Runtime Callable Wrapper The RCW provides access to COM coclasses that the COM component defines through managed wrappers around COM interfaces Instantiate COM objects by using the managed wrappers around the COM interfaces Some COM objects provide factory methods for creating related types defined by the object model implemented by the COM component Example: Office Excel // Use the Application interface to create an // instance of the Application. Class coclass Application excel. App = new Application(); // Use factory methods to instantiate related objects defined // by the Office Excel object model Workbook excel. WB = excel. App. Workbooks. Add(); // Factory method The syntax for instantiating COM objects is indistinguishable from that for creating managed C# objects.
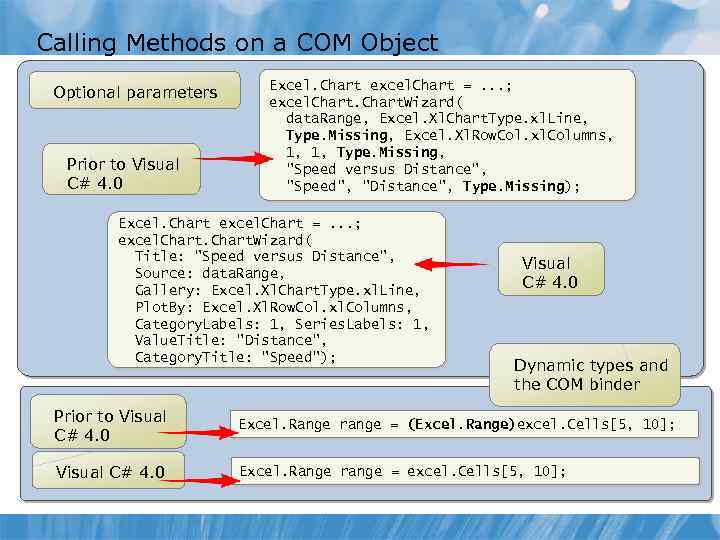 Calling Methods on a COM Object Optional parameters Prior to Visual C# 4. 0 Excel. Chart excel. Chart =. . . ; excel. Chart. Wizard( data. Range, Excel. Xl. Chart. Type. xl. Line, Type. Missing, Excel. Xl. Row. Col. xl. Columns, 1, 1, Type. Missing, "Speed versus Distance", "Speed", "Distance", Type. Missing); Excel. Chart excel. Chart =. . . ; excel. Chart. Wizard( Title: "Speed versus Distance", Source: data. Range, Gallery: Excel. Xl. Chart. Type. xl. Line, Plot. By: Excel. Xl. Row. Col. xl. Columns, Category. Labels: 1, Series. Labels: 1, Value. Title: "Distance", Category. Title: "Speed"); Visual C# 4. 0 Dynamic types and the COM binder Prior to Visual C# 4. 0 Excel. Range range = (Excel. Range)excel. Cells[5, 10]; Visual C# 4. 0 Excel. Range range = excel. Cells[5, 10];
Calling Methods on a COM Object Optional parameters Prior to Visual C# 4. 0 Excel. Chart excel. Chart =. . . ; excel. Chart. Wizard( data. Range, Excel. Xl. Chart. Type. xl. Line, Type. Missing, Excel. Xl. Row. Col. xl. Columns, 1, 1, Type. Missing, "Speed versus Distance", "Speed", "Distance", Type. Missing); Excel. Chart excel. Chart =. . . ; excel. Chart. Wizard( Title: "Speed versus Distance", Source: data. Range, Gallery: Excel. Xl. Chart. Type. xl. Line, Plot. By: Excel. Xl. Row. Col. xl. Columns, Category. Labels: 1, Series. Labels: 1, Value. Title: "Distance", Category. Title: "Speed"); Visual C# 4. 0 Dynamic types and the COM binder Prior to Visual C# 4. 0 Excel. Range range = (Excel. Range)excel. Cells[5, 10]; Visual C# 4. 0 Excel. Range range = excel. Cells[5, 10];
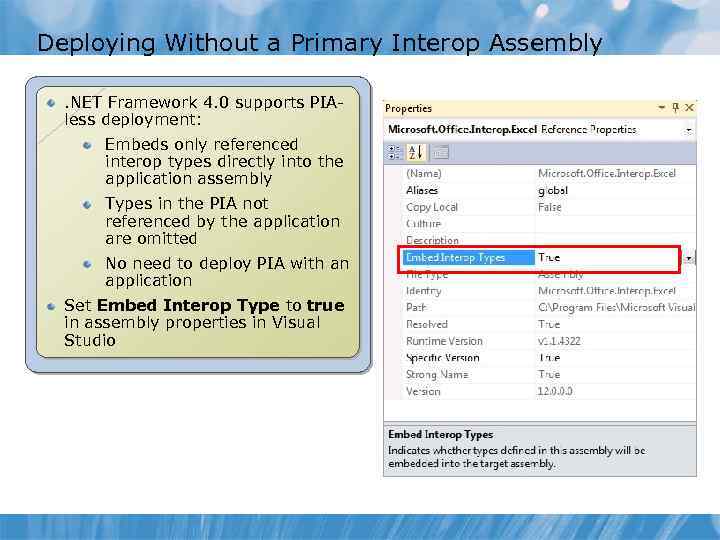 Deploying Without a Primary Interop Assembly. NET Framework 4. 0 supports PIAless deployment: Embeds only referenced interop types directly into the application assembly Types in the PIA not referenced by the application are omitted No need to deploy PIA with an application Set Embed Interop Type to true in assembly properties in Visual Studio
Deploying Without a Primary Interop Assembly. NET Framework 4. 0 supports PIAless deployment: Embeds only referenced interop types directly into the application assembly Types in the PIA not referenced by the application are omitted No need to deploy PIA with an application Set Embed Interop Type to true in assembly properties in Visual Studio
 Lab: Integrating Visual C# Code with Dynamic Languages and COM Components • Exercise 1: Integrating Code Written by Using a Dynamic Language into a Visual C# Application • Exercise 2: Using a COM Component from a Visual C# Application Logon information Virtual machine 10266 A-GEN-DEV User name Student Password Pa$$w 0 rd Estimated time: 60 minutes
Lab: Integrating Visual C# Code with Dynamic Languages and COM Components • Exercise 1: Integrating Code Written by Using a Dynamic Language into a Visual C# Application • Exercise 2: Using a COM Component from a Visual C# Application Logon information Virtual machine 10266 A-GEN-DEV User name Student Password Pa$$w 0 rd Estimated time: 60 minutes
 Lab Scenario
Lab Scenario
 Lab Review Questions • Which component is responsible for translating Visual C# method calls to a Python object into Python method calls? • Which component is responsible for translating values that a Python method returns into a format that a Visual C# application can use? • How did you create the interop assembly that your application used to interact with Office Excel?
Lab Review Questions • Which component is responsible for translating Visual C# method calls to a Python object into Python method calls? • Which component is responsible for translating values that a Python method returns into a format that a Visual C# application can use? • How did you create the interop assembly that your application used to interact with Office Excel?
 Module Review and Takeaways • Review Questions • Best Practices
Module Review and Takeaways • Review Questions • Best Practices
 Course Evaluation
Course Evaluation


