6392ec4042deb92234cde171a1a92661.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 113

MODULE 10 Electrical Standards

Hazard Brainstorming § Where are electrical hazards on oil and gas well sites? 2 © 2006 TEEX
Statistics § Electrocution: Among most frequent causes of occupational injury death in US § 295 fatalities/year; 4309 lost time § 1992 -2002: 9% decrease § Most frequent cause: Overhead power lines 3 © 2006 TEEX

Factors in Fatal Electrocutions § Safe work practices implemented and followed? § Adequate/required PPE provided and worn? § Lockout/tagout procedures implemented and followed? § OSHA, NEC, NESC compliance? § Worker and supervisor training adequate? § (from NIOSH) 4 © 2006 TEEX
Types of Electrical Injuries § Electrocution (death due to electrical shock) § Electrical shock § Burns (ugly pictures here) § Falls 5 © 2006 TEEX

Hazard Recognition § How can you sense electrical danger? § Cannot see, smell, taste, or hear danger § Can recognize unsafe conditions 6 © 2006 TEEX
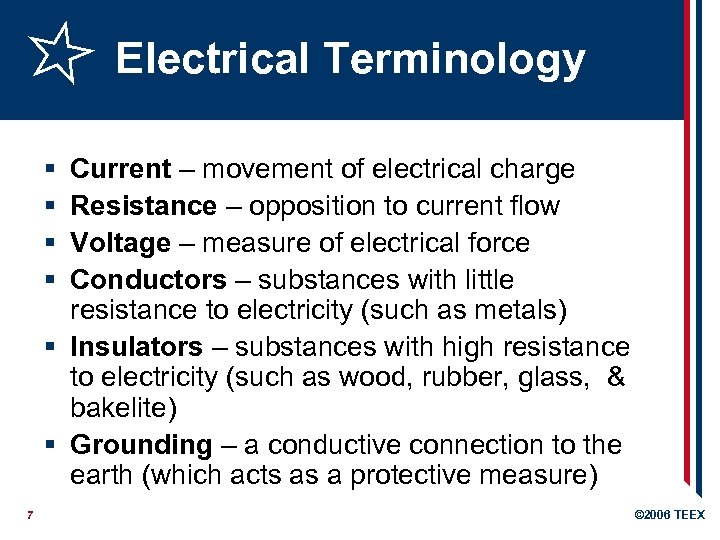
Electrical Terminology § § Current – movement of electrical charge Resistance – opposition to current flow Voltage – measure of electrical force Conductors – substances with little resistance to electricity (such as metals) § Insulators – substances with high resistance to electricity (such as wood, rubber, glass, & bakelite) § Grounding – a conductive connection to the earth (which acts as a protective measure) 7 © 2006 TEEX

Electrical Shock § Received when current passes through body § Severity depends on: § § Path of current through body Amount of current flowing through body Length of time body is in circuit Also: voltage, moisture, heart cycle, health § Low voltage is NOT low hazard! 8 © 2006 TEEX

Dangers of Electrical Shock § Currents >75 m. A* can cause ventricular fibrillation (rapid, ineffective heartbeat) § m. A = milliampere = 1/1, 000 of an ampere § Death within minutes unless a defibrillator is used § 75 m. A is not much current (a small power drill uses 30 times as much) 9 © 2006 TEEX
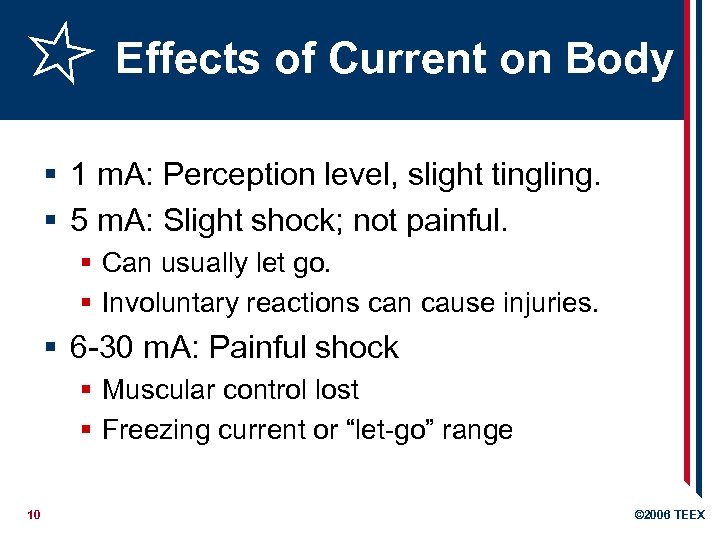
Effects of Current on Body § 1 m. A: Perception level, slight tingling. § 5 m. A: Slight shock; not painful. § Can usually let go. § Involuntary reactions can cause injuries. § 6 -30 m. A: Painful shock § Muscular control lost § Freezing current or “let-go” range 10 © 2006 TEEX
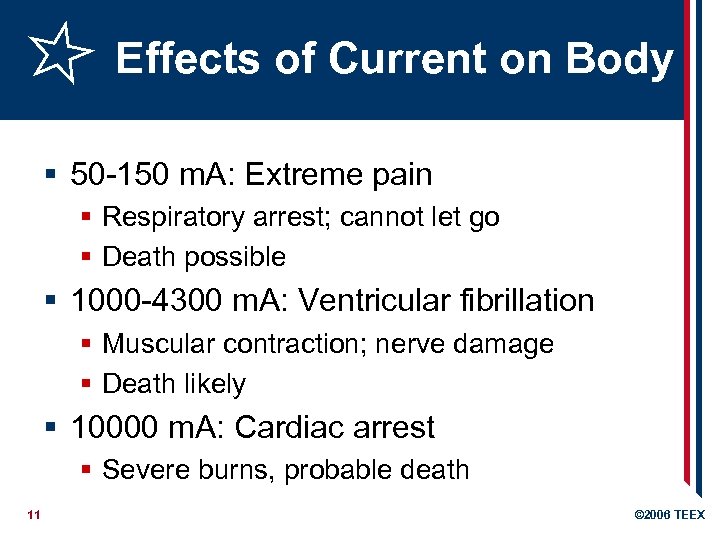
Effects of Current on Body § 50 -150 m. A: Extreme pain § Respiratory arrest; cannot let go § Death possible § 1000 -4300 m. A: Ventricular fibrillation § Muscular contraction; nerve damage § Death likely § 10000 m. A: Cardiac arrest § Severe burns, probable death 11 © 2006 TEEX

How Shock Happens § Connection between: § 2 wires of energized circuit § 1 wire of energized circuit and ground § Metallic part in contact with energized wire and ground 12 © 2006 TEEX
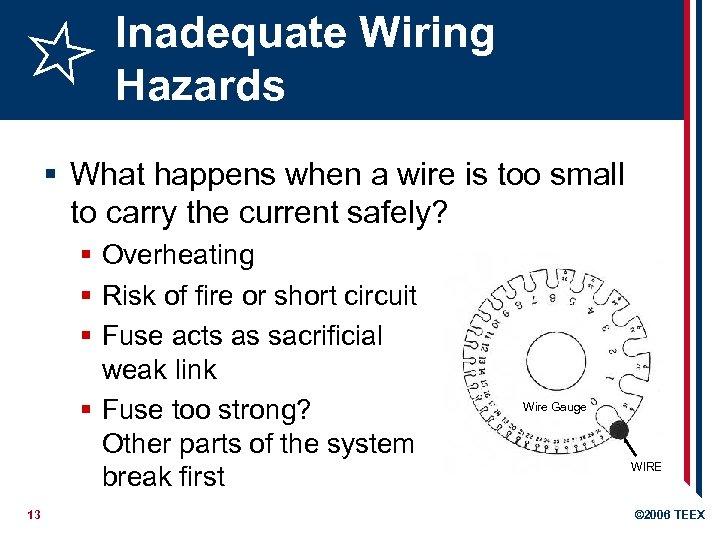
Inadequate Wiring Hazards § What happens when a wire is too small to carry the current safely? § Overheating § Risk of fire or short circuit § Fuse acts as sacrificial weak link § Fuse too strong? Other parts of the system break first 13 Wire Gauge WIRE © 2006 TEEX

29 CFR 1910 and 29 CFR 1926 § 1910 Subpart S = Electrical § Revised 2/14/2007; effective in 180 days § 1910 Subpart I = PPE § 1910. 137 Electrical Protective Devices § 1926 Subpart K = Electrical § Protect against recognized hazards 14 © 2006 TEEX

Other Standards § NFPA 70 E enacted to help meet CFR § Revised Subpart S based heavily on 2000 version § 2004 version now published § OSHA chose which provisions of 70 E to adopt 15 © 2006 TEEX

29 CFR 1910 Subpart S § Electrical standards for general industry § § 302 -308 and 399 updated: PM App. C § 5 main groups of standards: § § 16 Design safety standards § 302 -330 Safety-related work practices § 331 -360 Reserved: maintenance, special equipment Definitions: § 399 © 2006 TEEX

1910. 302 Electric utilization systems (PM Appendix C) § Applicability of regulations § By type of installation § By installation date 17 © 2006 TEEX

1903. 303 General

1910. 303 (a) Approval § Conductors and equipment acceptable only if approved § Note: If installation is made in accordance with NEC or ANSI/NFPA it will be deemed in compliance. § See definitions 19 © 2006 TEEX

1910. 303(b) Examination, installation, and use of equipment § Examination – shall be free of recognized hazards § Suitability (check listing/labeling) § Other factors listed in regulation § Installation and use – by instructions § Insulation integrity § Interrupting rating (fuses, breakers) 20 © 2006 TEEX

1910. 303(b) Examination, installation, and use of equipment § Circuit impedance… § Deteriorating agents – water, gases, excessive temperature, corrosives… § Mechanical execution of work § § 21 Close unused openings for protection Conductors racked for safe access Internal parts not contaminated No damaged parts © 2006 TEEX

1910. 303(b) Examination, installation, and use of equipment § Mounting and cooling § Firmly secured § Air circulation; clearance § Ventilation openings not obstructed 22 © 2006 TEEX
1910. 303(c) Electrical connections § General – dissimilar metals § Terminals – connections § Splices – correctly performed, insulated 23 © 2006 TEEX

1910. 303(d) Arcing parts § Some electrical equipment normally produces arcs, sparks, flames, molten metal § Keep isolated from combustible material 24 © 2006 TEEX

1910. 303(e) Marking § Manufacturer and ratings must be marked § Voltage, current, wattage, etc. § Durable markings in environment 25 © 2006 TEEX

1910. 303(f) Disconnecting means and circuits § Legibly marked to indicate purpose § Unless purpose is evident § Durable § Able to be locked open § Series combination rating = special marking 26 © 2006 TEEX
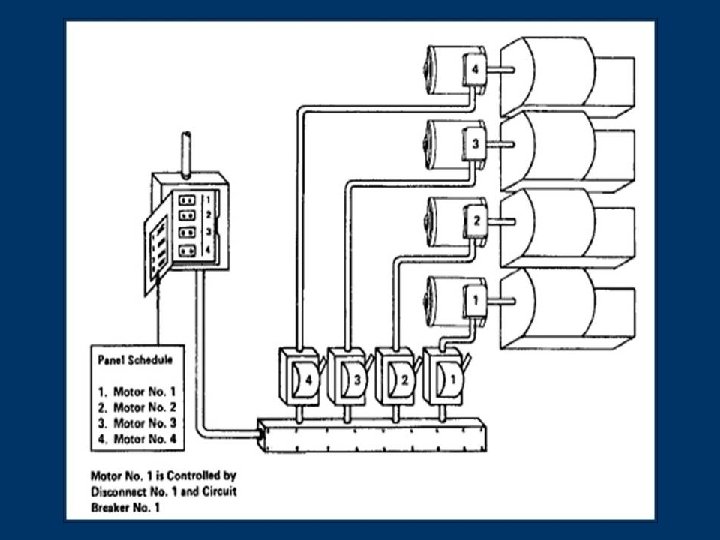
Example of properly labeled electric service: motors, disconnects and breakers FOR EXAMPLE… Subtitles & Transitions

1910. 303(g) 600 Volts, nominal, or less 1. Space about electric equipment § § § 28 Space, not used for storage Guarded when parts exposed Entrances Illumination Headroom Control boards in dedicated, protected space © 2006 TEEX

1910. 303(g) 600 Volts, nominal, or less 2. Guarding of live parts § § § 29 Live parts 50 volts protected from people Protection from damage Warning signs for unqualified persons © 2006 TEEX

1910. 303(h) Over 600 volts, nominal 2. 3. 4. 5. 30 Enclosure / access control Work space about equipment Entrance and access to work space Working space and guarding © 2006 TEEX

Wiring Design and Protection 1903. 304

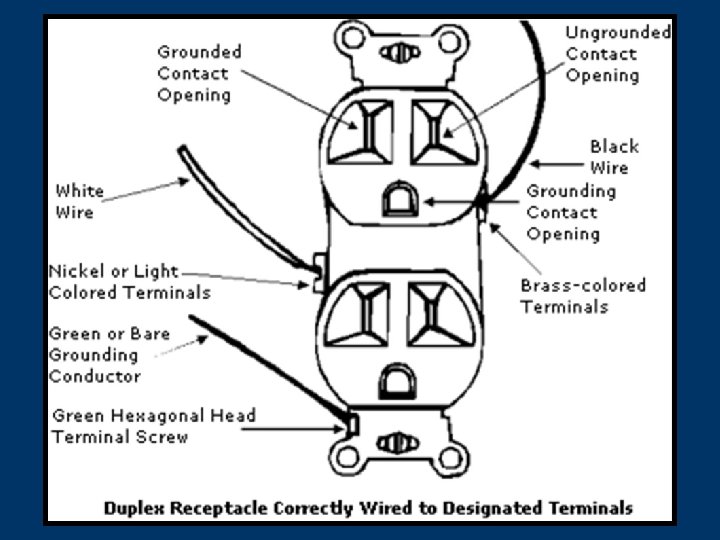
1910. 304(a) Use and identification of grounding conductors 1. Grounded & equipment grounding conductors identifiable & distinguishable § § Grounded = white or gray Equipment grounding = green, or green with yellow strips, or bare 2. Polarity may not be reversed 3. Grounding devices not used for other purposes 32 © 2006 TEEX
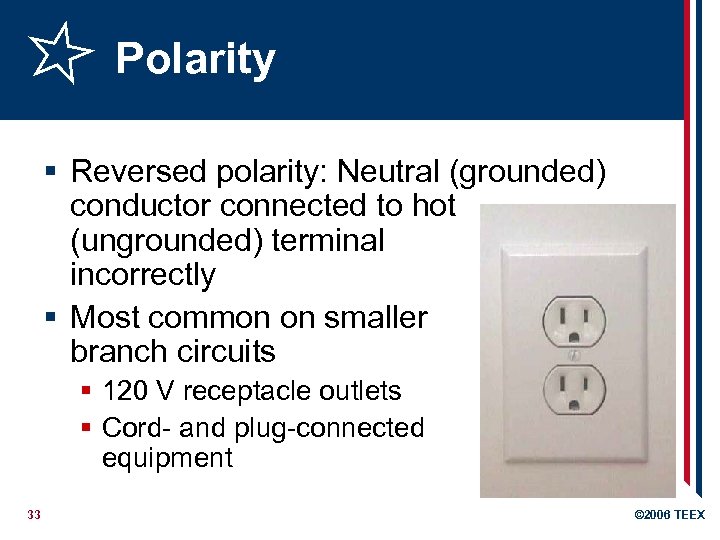
Polarity § Reversed polarity: Neutral (grounded) conductor connected to hot (ungrounded) terminal incorrectly § Most common on smaller branch circuits § 120 V receptacle outlets § Cord- and plug-connected equipment 33 © 2006 TEEX
Example of properly labeled electric service: motors, disconnects and breakers FOR EXAMPLE… Subtitles & Transitions
1910. 304(b) Branch circuits 1. Identification of multiwire branch circuits § § § 35 For >1 voltage system in a building ID phase and system Permanently posted at each panelboard © 2006 TEEX
1910. 304(b) Branch circuits 2. Receptacles and cord connectors i. Grounding type for 15 A & 20 A circuits § Receptacles only on circuits matching voltage and current rating ii. Grounding contacts grounded § § Except portable / vehicle-mounted generators Except replacement receptacles iii. Grounding contact connected to equipment grounding conductor 36 © 2006 TEEX
1910. 304(b) Branch circuits 2. Receptacles and cord connectors iv. Replacement of receptacles § § § Grounding-type where grounding means exists GFCI where required Options for lack of grounding means v. Plugs not interchangeable for different voltage, frequency, type of current 37 © 2006 TEEX
1910. 304(b) Branch circuits 3. Ground-fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) i. Bathroom or rooftops ii. Temporary wiring: § § 38 Including extension cords If unavailable for less-usual type of receptacle: assured equipment grounding conductor program. © 2006 TEEX
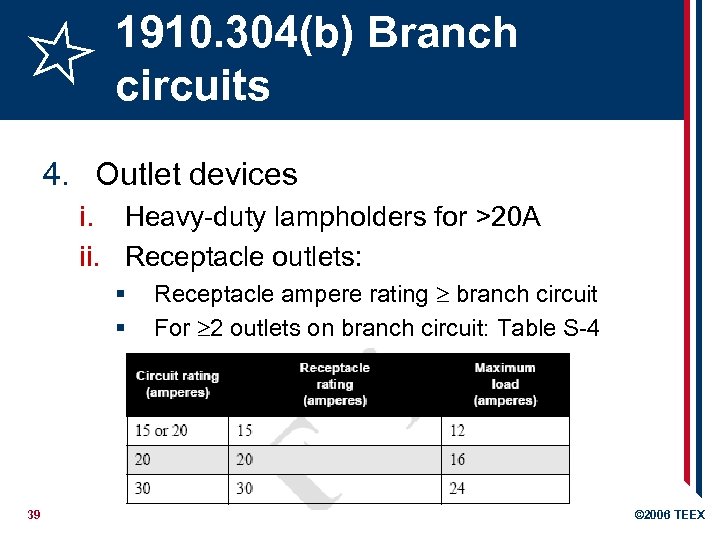
1910. 304(b) Branch circuits 4. Outlet devices i. Heavy-duty lampholders for >20 A ii. Receptacle outlets: § § 39 Receptacle ampere rating branch circuit For 2 outlets on branch circuit: Table S-4 © 2006 TEEX
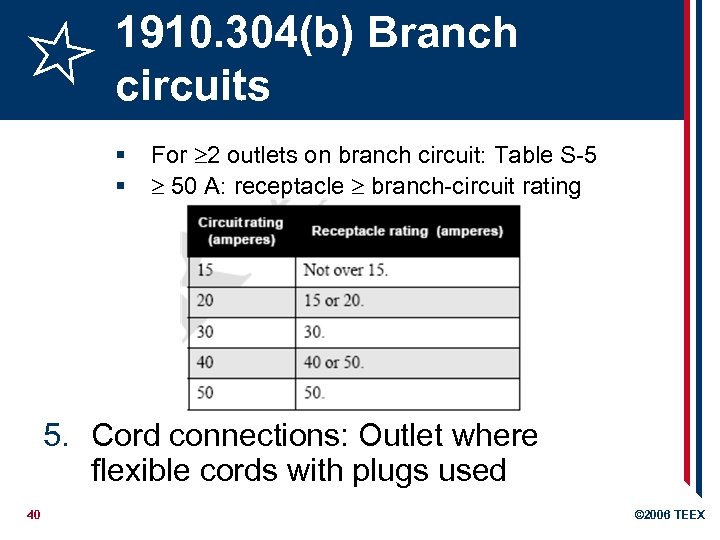
1910. 304(b) Branch circuits § § For 2 outlets on branch circuit: Table S-5 50 A: receptacle branch-circuit rating 5. Cord connections: Outlet where flexible cords with plugs used 40 © 2006 TEEX

1910. 304(c) Outside conductors, 600 volts, nominal, or less § Clearance 1. Power conductors on poles 2. Clearance of open conductors from ground: § § 41 10 feet – above sidewalk, grade, platform 12 feet – vehicular traffic 15 feet – truck traffic 18 feet – public streets, alleys, driveways © 2006 TEEX

1910. 304(c) Outside conductors, 600 volts, nominal, or less 3. Clearance from building openings § § No outer jacket: 3 foot clearance, except above window Not beneath or obstructing openings where materials may be moved 4. Above roofs: 8 ft above, 3 ft from edge § § 42 Pedestrians? Platform Exceptions for slope, attachment © 2006 TEEX

1910. 304(d) Location of outdoor lamps d. Location of outdoor lamps § Under energized equipment unless § § 43 Equipment can be locked out or Clearance/other safeguards adequate © 2006 TEEX

1910. 304(e) Services § Disconnecting means § § Services over 600 volts, nominal § 44 Main switch disconnects all, indicates on/off Accessible only to qualified; warning signs © 2006 TEEX

1910. 304(f) Overcurrent protection 1. 600 volts, nominal, or less i. Protect conductors and equipment iv. Overcurrent devices readily accessible § § To employees & building management Not exposed to damage or ignitable material v. Located/shielded to avoid injury/burns vi. On/off position clearly indicated vii. Vertical: up = on 45 2. Special rules for over 600 volts © 2006 TEEX

1910. 304(g) Grounding 1. Systems to be grounded i. 3 -wire DC: neutral conductor ii. 2 -wire DC, >50 V-300 V, with exceptions iii. AC <50 V in certain cases iv. AC 50 V-1000 V (unless exempt) under 4 conditions v. Exemptions for AC 50 V-1000 V 46 © 2006 TEEX

1910. 304(g) Grounding 2. Conductor to be grounded 3. Portable and vehicle-mounted generators: frame as grounding electrode 4. Grounding connections 5. Grounding path: permanent, continuous, effective 47 © 2006 TEEX

Grounding § One conductor of the circuit intentionally grounded to earth § Protects circuit from lightning or other high voltage contact § Stabilizes the voltage in the system so “expected voltage levels” are not exceeded under normal conditions 48 © 2006 TEEX

Grounding § Metal frames / enclosures of equipment grounded by permanent connection or bond § Equipment grounding conductor provides path for dangerous fault current to return to ground § If damage, corrosion, loosening, etc. impairs continuity, shock and burn hazards will develop 49 © 2006 TEEX

Grounding Path § Shall have capacity to conduct safely any likely fault current. § Fault currents may be many times normal currents; can melt points of poor conductivity § High temperatures = hazard; can destroy ground-fault path 50 © 2006 TEEX

1910. 304(g) Grounding 6. Supports, enclosures, equipment vi. Exposed non-current-carrying metal parts of cord- and plug-connected equipment 51 7. Nonelectrical equipment 8. Methods of grounding fixed equipment 9. Grounding of systems and circuits 1000 volts and over (high voltage) © 2006 TEEX
Ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCI’s) § GFCI overcurrent device like a fuse or circuit breaker § Designed to sense an imbalance in current flow over the normal path § Opens circuit if current in hot and grounded wires differ by 5 m. A 1 m. A § Must be installed correctly and tested 52 © 2006 TEEX

1903. 305 Wiring Methods, Components, and Equipment for General Use

1910. 305(a) Wiring methods § Not applicable to factory-assembled 1. General requirements i. Metal parts as grounding conductors: effectively bonded ii. Internal insulated grounding conductor for isolated enclosure iii. No wiring systems in ventilation ducts 54 © 2006 TEEX

1910. 305(a) Wiring methods 2. Temporary wiring § § § 55 Restricted uses Removed after project completion Requirements for feeders and branch circuits Grounding receptacles No bare conductors or earth returns Disconnecting switches © 2006 TEEX

1910. 305(a) Wiring methods 2. Temporary wiring, continued § Lamps protected from contact or breakage § Flexible cords protected from damage § Cables supported 56 © 2006 TEEX

1910. 305(b) Cabinets, boxes, and fittings 1. Conductors entering boxes, cabinets, or fittings § § Must be protected from abrasion Openings must be closed, with or without wires running through 2. Covers and canopies § § 57 Metal covers must be grounded >600 V: complete, secure, marked enclosure © 2006 TEEX

1910. 305(c) Switches § Gravity must not close switches § Warning if power may still be available while switch is closed § Faceplates where appropriate § Grounding 58 © 2006 TEEX

panelboards, and enclosures for damp locations § Switchboards and panelboards § Switchboards with exposed live parts: in dry places accessible only to qualified persons § Panelboards: in enclosures with no live parts on front § Switches dead when open § Enclosures for wet locations § Airspace, weatherproof 59 © 2006 TEEX

1910. 305(f) Conductors for general wiring § Insulated unless otherwise permitted § Approved type for use § Distinguishable by color or other means § Grounded § Ungrounded § Equipment grounding 60 © 2006 TEEX
1910. 305(g) Flexible cords and cables § In general much more easily damaged § Should not be used if recognized options can be used instead § Must be approved for conditions and location § Allowable purposes listed 61 © 2006 TEEX

1910. 305(g) Flexible cords and cables § May not be substituted for fixed wiring § May not be run through walls, ceilings, floors, doors, windows § May not be attached to buildings § May not be concealed in walls, ceilings, floors § May not be spliced, except hard service #14 § Strain relief needed on connections 62 © 2006 TEEX

Flexible cords: Acceptable? § Short cord as part of a tool? Yes. § Temporary use of extension cord for tool/appliance? Yes. § Obviously not temporary? No. § Extended over distance to avoid installing fixed outlet? No. 63 © 2006 TEEX

1910. 305(j) Equipment for general use 1. Lighting fixtures, lampholders, lamps, receptacles 2. Receptacles, cord connectors, and attachment plugs (caps) 3. Appliances 4. Motors 5. Transformers 6. Capacitors 7. Storage batteries 64 © 2006 TEEX

1903. 306 Specific Purpose Equipment and Installations

1910. 306 Specific purpose equipment and installations a. Electric signs and outline lighting b. Cranes and hoists d. Electric welders—disconnecting means g. Induction and dielectric 66 © 2006 TEEX

1903. 307 Hazardous (Classified) Locations

1910. 307 Hazardous (classified) locations § Classification based on flammable vapors, liquids, gases, combustible dusts or fibers § Each area considered individually § Classified by classes and divisions or zones § Documentation available for users, designers, installers, maintainers of electric equipment 68 © 2006 TEEX

1910. 307 Hazardous (classified) locations § Definitions of classes and divisions in 1910. 399, Definitions § Class I: flammable gases/vapors; explosive or ignitable mixtures § Class II: combustible dust § Class III: easily ignitable fibers or flyings; not likely to be in suspension § Division 1 & 2 for each; Zones 0 -2 for Class I 69 © 2006 TEEX

1910. 307(c) Electrical installations § Equipment must be one of these: § Intrinsically safe § Approved for hazardous (classified) location § Approved and marked for class and properties of material present § Safe for hazardous (classified) location § NFPA 70 referenced 70 © 2006 TEEX

Conduits and equipment d. Conduits: threaded, wrench-tight or bonding jumper e. Equipment in Division 2 locations: § § 71 Division 1 approved equipment = OK General-purpose equipment OK if demonstrably not a source of ignition © 2006 TEEX

1910. 307(f) Protection techniques § Explosionproof apparatus § Dust ignitionproof § Dust-tight § Purged and pressurized § Nonincendive circuit 72 § Nonincendive equipment Nonincendive component § Oil immersion § Hermetically sealed § Other protection techniques © 2006 TEEX

1910. 307(g) Class I, Zone 0, 1, and 2 locations § Zone = alternative to divisions for Class 1 § Classified by chemical properties and likelihood of combustible atmosphere § Proper installation of conduit & equipment to avoid sparks in flammable/combustible atmosphere § Protection techniques for certain zones 73 © 2006 TEEX

1910. 307(g) Class I, Zone 0, 1, and 2 locations § Special precaution: PE must classify areas and specify equipment § Listing and marking: § § Listed for Zone 0 = OK for Zone 1 -2 Listed for Zone 1 = OK for Zone 2 (For same gas or vapor) Marking requirements & exemption § More information in NFPA 70 74 © 2006 TEEX
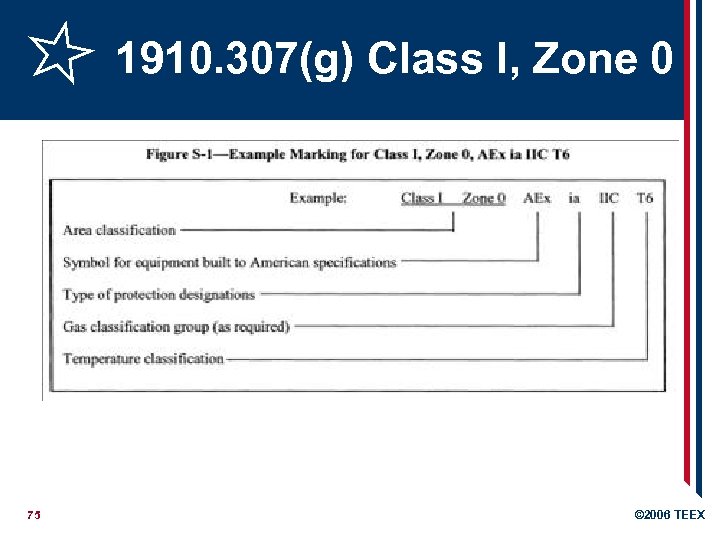
1910. 307(g) Class I, Zone 0 75 © 2006 TEEX

1910. 308 Special Systems

1910. 308 Special systems a. Systems over 600 volts, nominal b. Emergency power systems c. Remote control, signaling, and power-limited circuits d. Fire alarm systems e. Communications systems f. Solar photovoltaic systems g. Integrated electrical systems 77 © 2006 TEEX

1910. 399 Definitions

1904. 399 Definitions § New version supersedes older version in CFR book 79 © 2006 TEEX

1910 SUBPART S APPENDIX A References for Further Information

1910 Subpart S Appendix A § Nonmandatory references aid in understanding § Not a substitute for compliance with CFR § Appendices B and C removed 81 © 2006 TEEX

Safety-Related Work Practices 1910. 331 -1910. 335

1910. 331 Scope § Qualified persons (who have training in avoiding the electrical hazards) § Unqualified persons (with little or no such training) § Working on or near: § § 83 Premises wiring Wiring for connection to supply Other wiring Vehicles excluded © 2006 TEEX

1910. 332 Training a. Scope: employees with electric shock risk not reduced to safe level by installation requirements b. Training content: § § § Work practices for job assignments 1910. 331 -335 and others necessary Qualified vs. unqualified c. Classroom or on-the-job; risk based 84 © 2006 TEEX

Employees to be Trained § Electricians and welders § Any others if: § work they do or supervise § comes close enough to exposed parts of electric circuits 50 V § for hazard to exist 85 © 2006 TEEX

1910. 333 Selection and Use of Work Practices

1910. 333 (a)(1) Deenergized parts § Live parts deenergized before employee works on or near them: § Unless infeasible or causes greater hazard § <50 V not deenergized if no increased exposure to burns or arcs § Examples in CFR § If not deenergized, other work practices must protect employees 87 © 2006 TEEX

1910. 333(b) Working on or near exposed deenergized parts § If not locked out or tagged out, treated as energized § Lockout/tagout rules followed in order § 1910. 147 provisions may also be OK § Written copy of procedures available 88 © 2006 TEEX

1910. 333(b) Working on or near exposed deenergized parts § Lockout/tagout steps in section (2): ii. iv. v. 89 Deenergizing equipment Application of locks and tags Verification of deenergized condition Reenergizing equipment after work © 2006 TEEX

1910. 333(c) Working on or near exposed energized parts § Only qualified persons may work on energized electric circuit parts § For work near overhead lines: § Lines deenergized and grounded, or § Other protective measures provided 90 © 2006 TEEX

Working near overhead power lines § Unqualified person near energized lines § Person and longest conductive object not closer than 10 ft, + 4 in/10 k. V above 50 k. V § For elevated or ground work § Qualified person: § Closer approach only with insulation § Table S-5: distance varies by voltage § Equipment: same distance as unqualified 91 © 2006 TEEX

Working near overhead power lines § Equipment: same distance as unqualified, with exceptions: § § In transit, structure lowered: 4 ft +4 in/10 k. V Insulating barriers, not part of vehicle Aerial lift, insulated, with qualified person Ground employees may not contact equipment without protection or distance § Employees may not stand at grounding location when line contact possible 92 © 2006 TEEX

1910. 333(c) Working on or near exposed energized parts 4. Illumination must allow safe work – may not reach blindly in 5. Confined space work requires protective insulation & secured doors 6. Conductive materials: prevent contact with energized parts 7. Portable ladders: nonconductive siderails 93 © 2006 TEEX

1910. 333(c) Working on or near exposed energized parts 8. Conductive apparel not worn, or insulated 9. Housekeeping near live parts: § § Requires safeguards No conductive cleaning materials, including liquid solutions 10. Interlocks may only be defeated temporarily by qualified person 94 © 2006 TEEX

1910. 334 Use of Equipment

1910. 334(a) Portable electric equipment § Handled in a manner to not cause damage § Cords not used to raise/lower equipment § Cords not stapled or hung in ways that damage insulation 96 © 2006 TEEX

1910. 334(a) Portable electric equipment § Visual inspection required before use: § Portable cord / plug connected equipment § Extension cords § For external defects and evidence of internal damage § If not exposed to damage, only when relocated § Defect or damage: remove, do not use until repaired and tested § Plug and receptacle checked for compatibility 97 © 2006 TEEX

1910. 334(a) Portable electric equipment § Grounding type equipment: ground must be maintained § Conductive work locations (e. g. wet) require approved equipment and cords § Connecting plugs: § Never plug or unplug live equipment with wet hands § Protect hands from conductive path (water) § Locking connectors: properly secured 98 © 2006 TEEX
1910. 334(b) Electric power and lighting circuits § Never reenergize a blown fuse § Never reenergize a circuit breaker until it is safe (Overload or fault? ) § Never modify overcurrent protection beyond § 304 requirements 99 © 2006 TEEX

1910. 334(c) and (d) c. Test instruments and equipment § § § Only qualified persons may test electric circuits or equipment Test instruments must be visually inspected Must be rated for circuits & environment d. Occasional use of flammable and ignitable materials: Do not use equipment that could ignite them 100 © 2006 TEEX

1910. 335 Safeguards for Personnel Protection

1910. 335(a) Use of protective equipment § Personal protective equipment § § § Must be provided with & use equipment Maintained, inspected, and tested Insulating material protected Nonconductive head protection Eye or face protection for arcs, flashes, flying objects from explosions § Insulated tools or handling equipment § Shields, insulation for heating/arcing 102 © 2006 TEEX

1910. 335(b) Alerting techniques § Techniques to warn and protect employees: § Safety signs and tags § Barricades § Attendants 103 © 2006 TEEX

Relevant Standards Outside 29 CFR 1910 § 29 CFR 1926 Subpart K: construction § API RP 54 § Section 9. 14 Generators, Motors, and Lighting § Section 10: Drilling and Well Servicing Rig Electrical Systems § API RP 14 F for offshore wiring § API RP 500 and 505: area classification 104 © 2006 TEEX
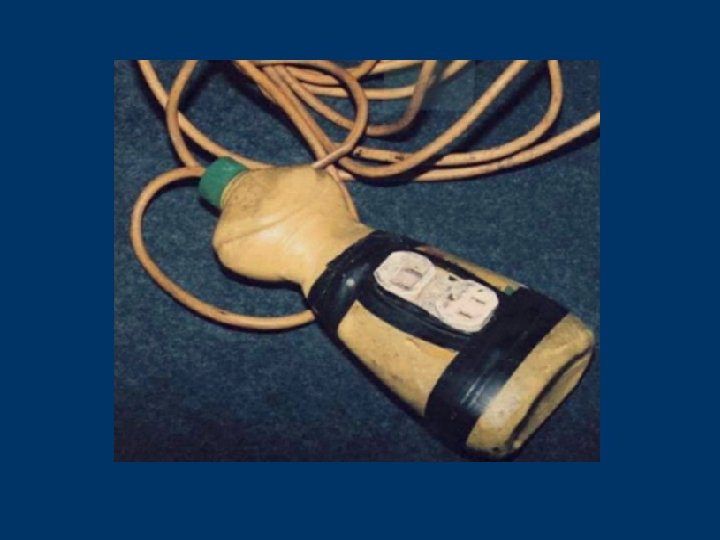
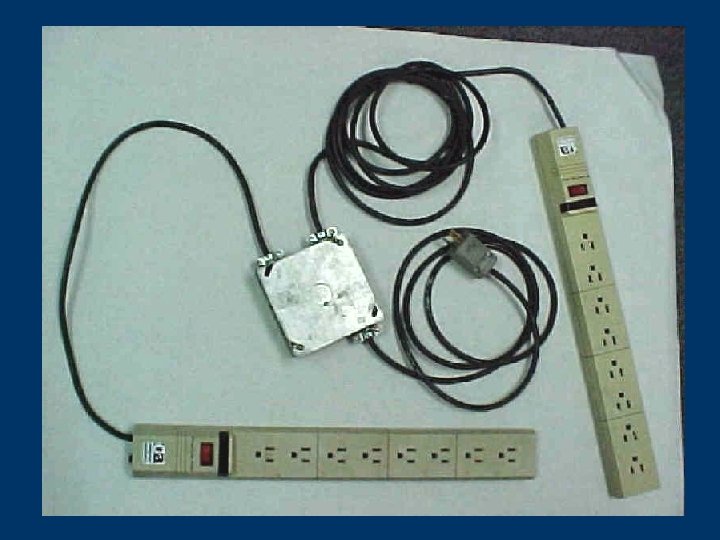
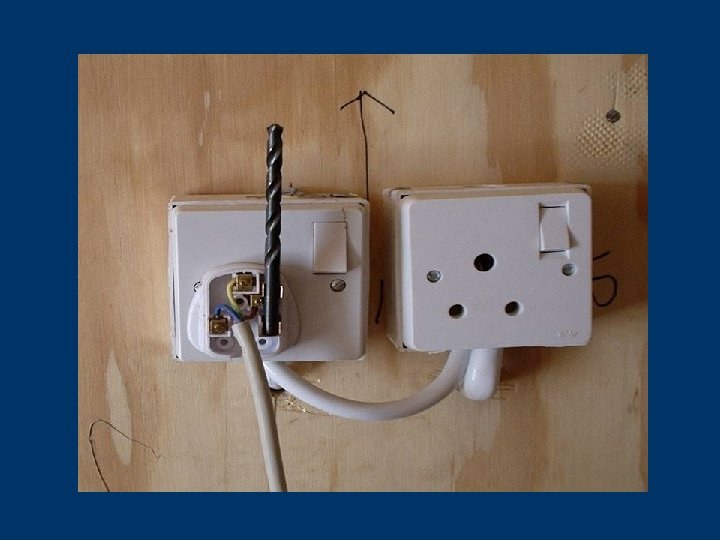
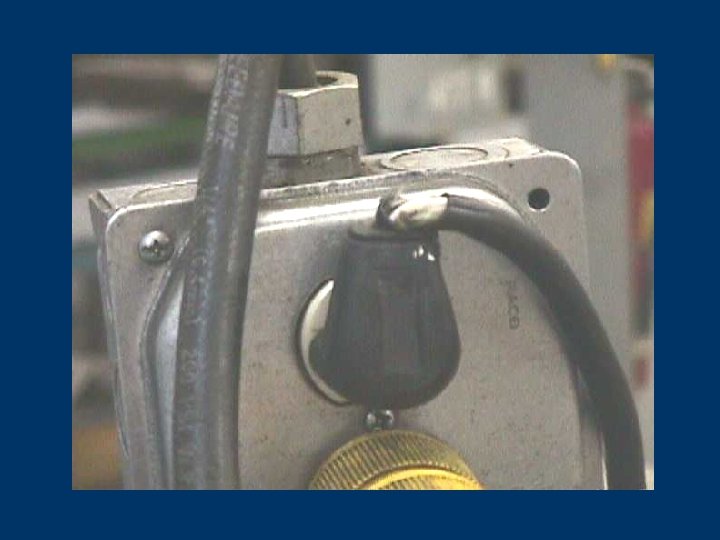
Clues that Electrical Hazards Exist § Tripped circuit breakers or blown fuses § Warm tools, wires, cords, connections, or junction boxes § GFCI that shuts off a circuit § Worn or frayed insulation around wire or connection 105 © 2006 TEEX
Example of properly labeled electric service: motors, disconnects and breakers FOR EXAMPLE… Subtitles & Transitions

Example of properly labeled electric service: motors, disconnects and breakers FOR EXAMPLE… Subtitles & Transitions

Example of properly labeled electric service: motors, disconnects and breakers FOR EXAMPLE… Subtitles & Transitions

Example of properly labeled electric service: motors, disconnects and breakers FOR EXAMPLE… Subtitles & Transitions

Example of properly labeled electric service: motors, disconnects and breakers FOR EXAMPLE… Subtitles & Transitions

Example of properly labeled electric service: motors, disconnects and breakers FOR EXAMPLE… Subtitles & Transitions

OSHA Resources § Pub 3075 Controlling Electrical Hazards § Small Business Handbook section § Inspection Procedures § Electrical Safety-Related Work Practices -Inspection Procedures and Interpretation Guidelines 112 © 2006 TEEX

Interpretations § Training requirements for employees who perform non-electrical work on electrical equipment § Qualifications for resetting circuits or replacing fuses; electrical enclosures must be approved § Use of compressed air above 30 p. s. i. for cleaning purposes; nonmetallicsheathed cable for temporary wiring 113 © 2006 TEEX
6392ec4042deb92234cde171a1a92661.ppt