6a9385708adaeba83aa04ec809e9fe55.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 174
 Module 1 Welcome KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 1 REV BASIC, 1/02
Module 1 Welcome KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 1 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Overview • Introductions • Administrative • Course Objectives • Course Schedule • Style of Course • Course Materials KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 2 REV BASIC, 1/02
Overview • Introductions • Administrative • Course Objectives • Course Schedule • Style of Course • Course Materials KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 2 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Administrative • Breaks • Sign-In Sheet KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 3 REV BASIC, 1/02
Administrative • Breaks • Sign-In Sheet KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 3 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Targeted Audience • Mix of project personnel with variable levels of experience in KSC development projects • Prerequisites: • Project management or systems engineering experience (at least one year) • Assumptions: • Prior knowledge of risk or risk management is not required KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 4 REV BASIC, 1/02
Targeted Audience • Mix of project personnel with variable levels of experience in KSC development projects • Prerequisites: • Project management or systems engineering experience (at least one year) • Assumptions: • Prior knowledge of risk or risk management is not required KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 4 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Course Objectives • Understand the concepts and principles of Continuous Risk Management and how to apply them • Develop basic risk management skills for each component of Continuous Risk Management • Be aware of key methods and tools • Understand how CRM could be tailored to a project • Be able to differentiate between Risks and Problems KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 5 REV BASIC, 1/02
Course Objectives • Understand the concepts and principles of Continuous Risk Management and how to apply them • Develop basic risk management skills for each component of Continuous Risk Management • Be aware of key methods and tools • Understand how CRM could be tailored to a project • Be able to differentiate between Risks and Problems KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 5 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Module 2 Introduction KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 6 REV BASIC, 1/02
Module 2 Introduction KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 6 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Overview • Agency Risk Management (RM) Requirements • Risk Definitions • RM/Project Management Relationship • Risk Management Benefits • Continuous Risk Management (CRM) Process • CRM Process Application • Risk Management Planning/Documentation • Who Performs Continuous Risk Management? KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 7 REV BASIC, 1/02
Overview • Agency Risk Management (RM) Requirements • Risk Definitions • RM/Project Management Relationship • Risk Management Benefits • Continuous Risk Management (CRM) Process • CRM Process Application • Risk Management Planning/Documentation • Who Performs Continuous Risk Management? KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 7 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Agency Risk Management Requirements • Risk Management Documentation • NPD 7120. 4, Program/Project Management, describes the management systems for program/project formulation, implementation, and evaluation • NPG 7120. 5, NASA Program and Project Management Processes and Requirements, dictates basic risk management requirements • NPG 8000. 4, Risk Management Procedures and Guidelines, provides additional information for applying risk management to programs and projects as required by NPG 7120. 5 • Procurement Notice (PN) 97 -58, Risk Management KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 8 REV BASIC, 1/02
Agency Risk Management Requirements • Risk Management Documentation • NPD 7120. 4, Program/Project Management, describes the management systems for program/project formulation, implementation, and evaluation • NPG 7120. 5, NASA Program and Project Management Processes and Requirements, dictates basic risk management requirements • NPG 8000. 4, Risk Management Procedures and Guidelines, provides additional information for applying risk management to programs and projects as required by NPG 7120. 5 • Procurement Notice (PN) 97 -58, Risk Management KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 8 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Agency Risk Management Requirements • Fundamental Risk Management Requirements • Program and project decisions shall be made on the basis of an orderly risk management effort • Risk management includes identification, assessment, mitigation, and disposition of risk throughout the project formulation, approval, implementation, and disposal phases • Project/Program Manager (PM) has the overall responsibility for the implementation of risk management, ensuring an integrated, coherent risk management approach throughout the project KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 9 REV BASIC, 1/02
Agency Risk Management Requirements • Fundamental Risk Management Requirements • Program and project decisions shall be made on the basis of an orderly risk management effort • Risk management includes identification, assessment, mitigation, and disposition of risk throughout the project formulation, approval, implementation, and disposal phases • Project/Program Manager (PM) has the overall responsibility for the implementation of risk management, ensuring an integrated, coherent risk management approach throughout the project KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 9 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Agency Risk Management Requirements • Fundamental Risk Management Requirements • Risk management planning will be developed during the project/program formulation phase, included in project/program plans, and executed during the implementation phase • Programs and projects will develop and maintain prioritized risk lists • Programs and projects must develop and clearly communicate “success criteria” to all levels of the program and project to define the scope of the effort and to guide risk decisions KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 10 REV BASIC, 1/02
Agency Risk Management Requirements • Fundamental Risk Management Requirements • Risk management planning will be developed during the project/program formulation phase, included in project/program plans, and executed during the implementation phase • Programs and projects will develop and maintain prioritized risk lists • Programs and projects must develop and clearly communicate “success criteria” to all levels of the program and project to define the scope of the effort and to guide risk decisions KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 10 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Agency Risk Management Requirements • Fundamental Risk Management Requirements • Programs and projects must define, within the constraints imposed upon them (e. g. , budget, schedule), what level of risk (i. e. , “acceptable risk”) is reasonable for the program/ project to accept while still achieving mission success • Primary risks (i. e. , risks having high probability and high impact/severity) must be classified, with acceptance rationale documented and concurred with by the Governing Program Management Council (GPMC) KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 11 REV BASIC, 1/02
Agency Risk Management Requirements • Fundamental Risk Management Requirements • Programs and projects must define, within the constraints imposed upon them (e. g. , budget, schedule), what level of risk (i. e. , “acceptable risk”) is reasonable for the program/ project to accept while still achieving mission success • Primary risks (i. e. , risks having high probability and high impact/severity) must be classified, with acceptance rationale documented and concurred with by the Governing Program Management Council (GPMC) KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 11 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Risk Definitions • Risk is the combination of the probability (qualitative or quantitative) that a program or project will experience an undesired event (cost overrun, schedule slip, safety mishap, security compromise) and the consequences (impact) of the undesired event, were it to occur. • NPG 8000. 4 KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 12 REV BASIC, 1/02
Risk Definitions • Risk is the combination of the probability (qualitative or quantitative) that a program or project will experience an undesired event (cost overrun, schedule slip, safety mishap, security compromise) and the consequences (impact) of the undesired event, were it to occur. • NPG 8000. 4 KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 12 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Risk Definitions Risk involves the probability that Risk involves the impact of an undesired event will occur. the event should it occur. Qualitative or Quantitative Risk Exposure = Probability x Impact KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 13 REV BASIC, 1/02
Risk Definitions Risk involves the probability that Risk involves the impact of an undesired event will occur. the event should it occur. Qualitative or Quantitative Risk Exposure = Probability x Impact KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 13 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Some Perspectives on Risk • Risk will always be present in programs and projects • Not all risk can be avoided • Management and stakeholders must be active participants in the mission risk acceptance process • Risks are different from problems KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 14 REV BASIC, 1/02
Some Perspectives on Risk • Risk will always be present in programs and projects • Not all risk can be avoided • Management and stakeholders must be active participants in the mission risk acceptance process • Risks are different from problems KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 14 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Goal of Risk Management • Achieving Mission Success • Provide program/project managers principles and practices for decision making • Search out, identify, and manage risk • Keep safety paramount • Deliver a quality product on time and within cost KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 15 REV BASIC, 1/02
Goal of Risk Management • Achieving Mission Success • Provide program/project managers principles and practices for decision making • Search out, identify, and manage risk • Keep safety paramount • Deliver a quality product on time and within cost KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 15 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Success Criteria Emphasis • Program/project teams must develop clear “Success Criteria” during the formulation phase • Success criteria must be clearly communicated to all levels of the program and project to define scope of the effort and to guide risk decisions • Success criteria need to be developed at system, subsystem, and component level to define trade space and support risk decisions • Success criteria will continue to evolve throughout the life cycle of the project KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 16 REV BASIC, 1/02
Success Criteria Emphasis • Program/project teams must develop clear “Success Criteria” during the formulation phase • Success criteria must be clearly communicated to all levels of the program and project to define scope of the effort and to guide risk decisions • Success criteria need to be developed at system, subsystem, and component level to define trade space and support risk decisions • Success criteria will continue to evolve throughout the life cycle of the project KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 16 REV BASIC, 1/02
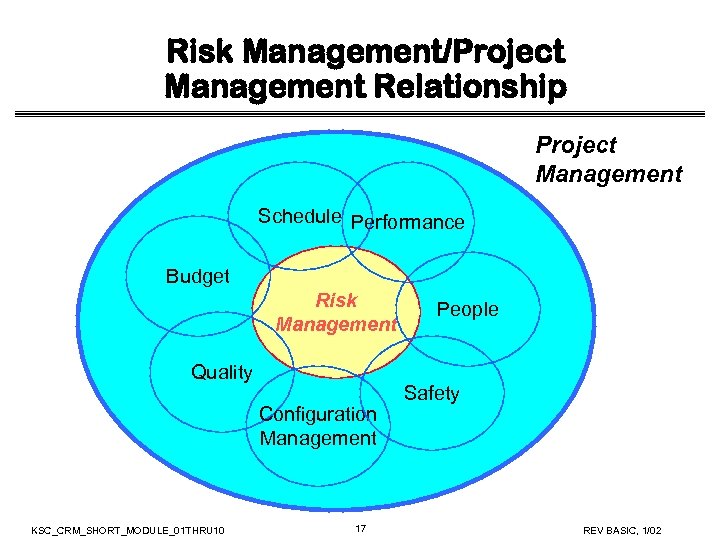 Risk Management/Project Management Relationship Project Management Schedule Performance Budget Risk Management Quality Configuration Management KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 17 People Safety REV BASIC, 1/02
Risk Management/Project Management Relationship Project Management Schedule Performance Budget Risk Management Quality Configuration Management KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 17 People Safety REV BASIC, 1/02
 Risk Management Benefits • Early identification of potential risks • Facilitates setting priorities • Increases chance of project success • Enables more efficient use of resources • Promote teamwork by involving personnel in all levels of the project • Information for tradeoffs is based on priorities and quantified assessments • Identify hidden risks KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 18 REV BASIC, 1/02
Risk Management Benefits • Early identification of potential risks • Facilitates setting priorities • Increases chance of project success • Enables more efficient use of resources • Promote teamwork by involving personnel in all levels of the project • Information for tradeoffs is based on priorities and quantified assessments • Identify hidden risks KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 18 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Everybody Wants to Understand Risk Dilbert Scott Adams KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 19 REV BASIC, 1/02
Everybody Wants to Understand Risk Dilbert Scott Adams KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 19 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Continuous Risk Management Process • Continuous Risk Management (CRM) is a structured, formalized management practice with processes, methods, and tools for managing risks in a project • It provides a disciplined environment for proactive decision making to: • • Assessment (continual) of what could go wrong (risks) Determination of which risks are most important to deal with Implementation of mitigation strategies to deal with those risks Assured, measured effectiveness of the implemented mitigation strategies KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 20 REV BASIC, 1/02
Continuous Risk Management Process • Continuous Risk Management (CRM) is a structured, formalized management practice with processes, methods, and tools for managing risks in a project • It provides a disciplined environment for proactive decision making to: • • Assessment (continual) of what could go wrong (risks) Determination of which risks are most important to deal with Implementation of mitigation strategies to deal with those risks Assured, measured effectiveness of the implemented mitigation strategies KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 20 REV BASIC, 1/02
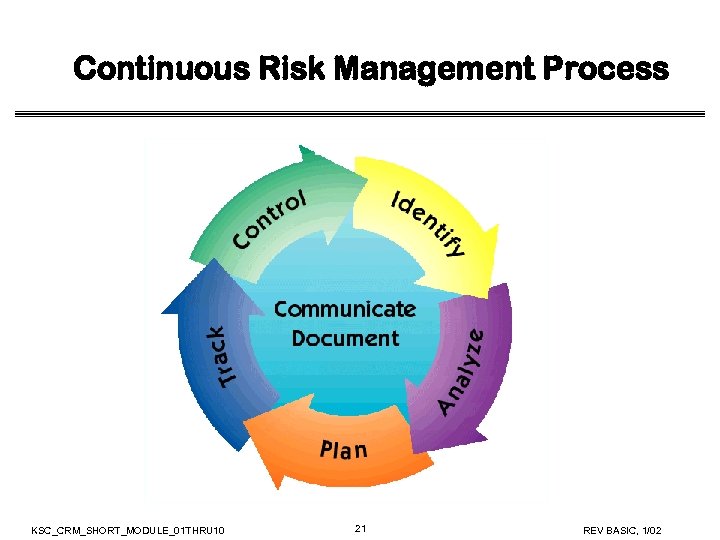 Continuous Risk Management Process KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 21 REV BASIC, 1/02
Continuous Risk Management Process KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 21 REV BASIC, 1/02
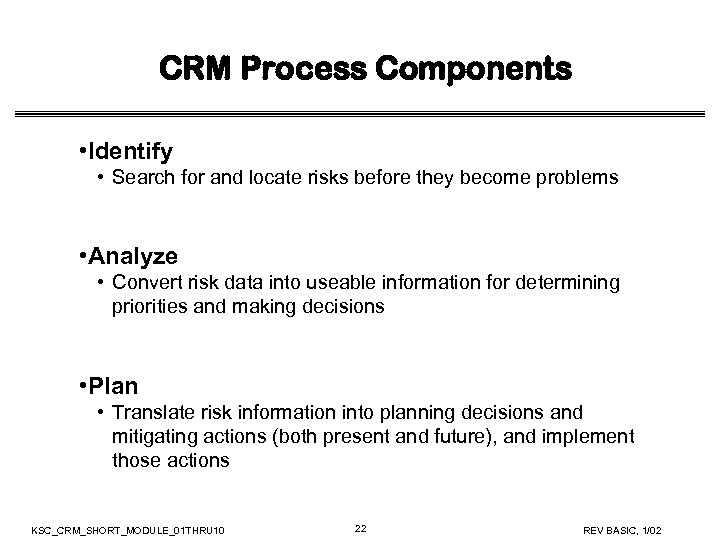 CRM Process Components • Identify • Search for and locate risks before they become problems • Analyze • Convert risk data into useable information for determining priorities and making decisions • Plan • Translate risk information into planning decisions and mitigating actions (both present and future), and implement those actions KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 22 REV BASIC, 1/02
CRM Process Components • Identify • Search for and locate risks before they become problems • Analyze • Convert risk data into useable information for determining priorities and making decisions • Plan • Translate risk information into planning decisions and mitigating actions (both present and future), and implement those actions KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 22 REV BASIC, 1/02
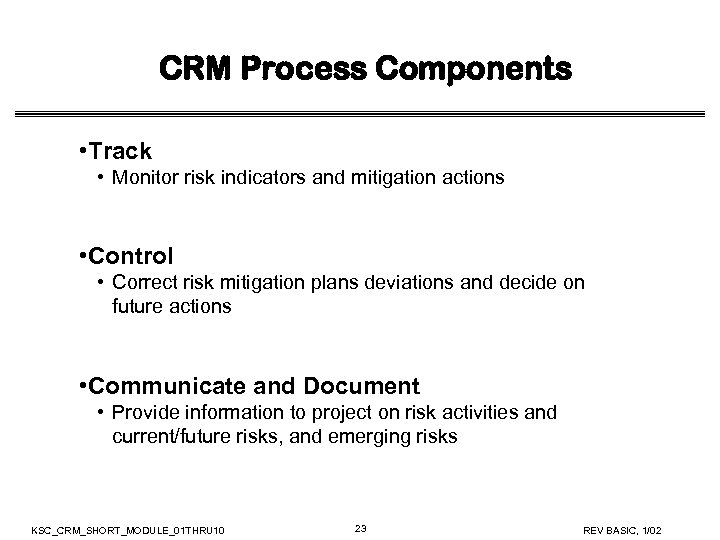 CRM Process Components • Track • Monitor risk indicators and mitigation actions • Control • Correct risk mitigation plans deviations and decide on future actions • Communicate and Document • Provide information to project on risk activities and current/future risks, and emerging risks KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 23 REV BASIC, 1/02
CRM Process Components • Track • Monitor risk indicators and mitigation actions • Control • Correct risk mitigation plans deviations and decide on future actions • Communicate and Document • Provide information to project on risk activities and current/future risks, and emerging risks KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 23 REV BASIC, 1/02
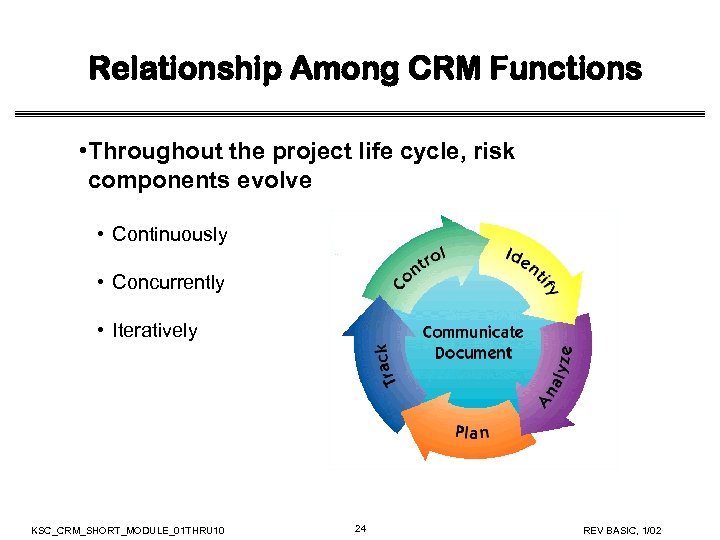 Relationship Among CRM Functions • Throughout the project life cycle, risk components evolve • Continuously • Concurrently • Iteratively KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 24 REV BASIC, 1/02
Relationship Among CRM Functions • Throughout the project life cycle, risk components evolve • Continuously • Concurrently • Iteratively KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 24 REV BASIC, 1/02
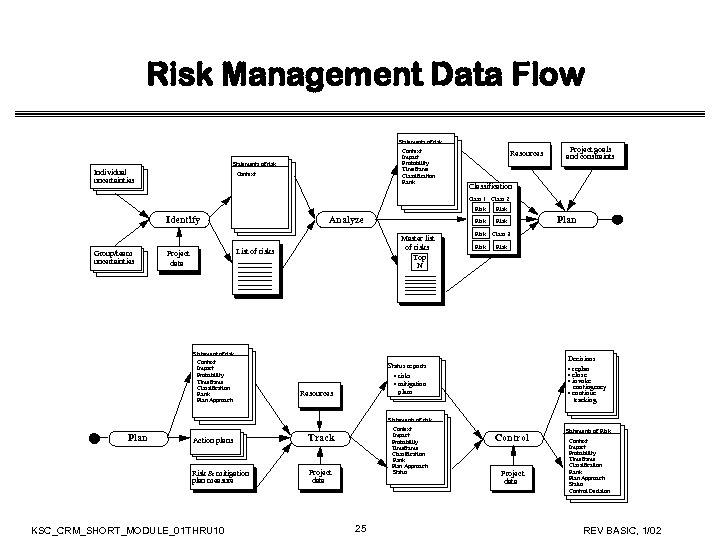 Risk Management Data Flow Statements of risk Context Impact Probability Timeframe Classification Rank Statements of risk Individual uncertainties Context Resources Project goals and constraints Classification Class 1 Class 2 Risk Identify Group/team uncertainties Analyze Master list of risks Top N List of risks Project data Statement of risk Context Impact Probability Timeframe Classification Rank Plan Approach Risk Risk Decisions • replan • close • invoke contingency • continue tracking Status reports • risks • mitigation plans Resources Plan Class 3 Statements of risk Plan Action plans Risk & mitigation plan measure Context Impact Probability Timeframe Classification Rank Plan Approach Status Track Project data KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 25 Control Project data Statements of Risk Context Impact Probability Timeframe Classification Rank Plan Approach Status Control Decision REV BASIC, 1/02
Risk Management Data Flow Statements of risk Context Impact Probability Timeframe Classification Rank Statements of risk Individual uncertainties Context Resources Project goals and constraints Classification Class 1 Class 2 Risk Identify Group/team uncertainties Analyze Master list of risks Top N List of risks Project data Statement of risk Context Impact Probability Timeframe Classification Rank Plan Approach Risk Risk Decisions • replan • close • invoke contingency • continue tracking Status reports • risks • mitigation plans Resources Plan Class 3 Statements of risk Plan Action plans Risk & mitigation plan measure Context Impact Probability Timeframe Classification Rank Plan Approach Status Track Project data KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 25 Control Project data Statements of Risk Context Impact Probability Timeframe Classification Rank Plan Approach Status Control Decision REV BASIC, 1/02
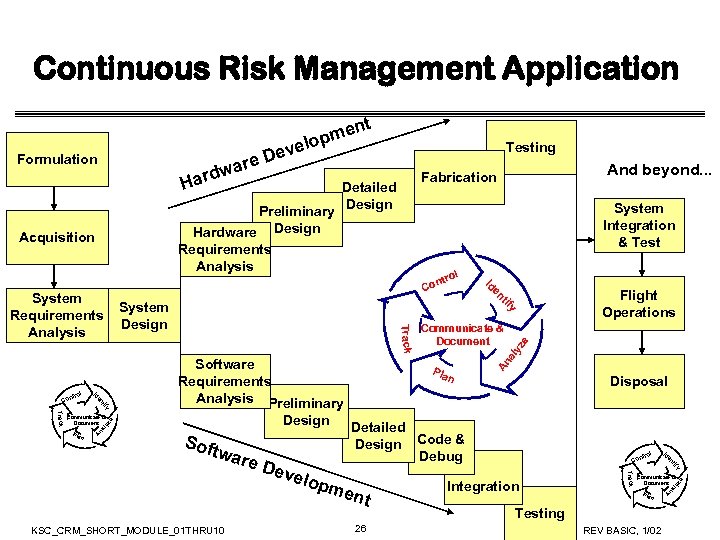 Continuous Risk Management Application t en opm el Dev re Requirements Analysis Detailed Design Code & Debug t 26 Integration y tif pme n ol ntr Co en KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 velo Disposal Track e De n Id Soft war Pla Communicate & Document e Design Communicate & Document Flight Operations al Software Requirements Analysis Preliminary e al yz An y n tif Pla en Track Communicate & Document Track y tif en C System Design Id ont rol nt Co Id System Requirements Analysis rol System Integration & Test yz e Acquisition Detailed Design al yz Preliminary Hardware Design And beyond. . . Fabrication Pla n Testing REV BASIC, 1/02 An a ardw H Testing An Formulation
Continuous Risk Management Application t en opm el Dev re Requirements Analysis Detailed Design Code & Debug t 26 Integration y tif pme n ol ntr Co en KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 velo Disposal Track e De n Id Soft war Pla Communicate & Document e Design Communicate & Document Flight Operations al Software Requirements Analysis Preliminary e al yz An y n tif Pla en Track Communicate & Document Track y tif en C System Design Id ont rol nt Co Id System Requirements Analysis rol System Integration & Test yz e Acquisition Detailed Design al yz Preliminary Hardware Design And beyond. . . Fabrication Pla n Testing REV BASIC, 1/02 An a ardw H Testing An Formulation
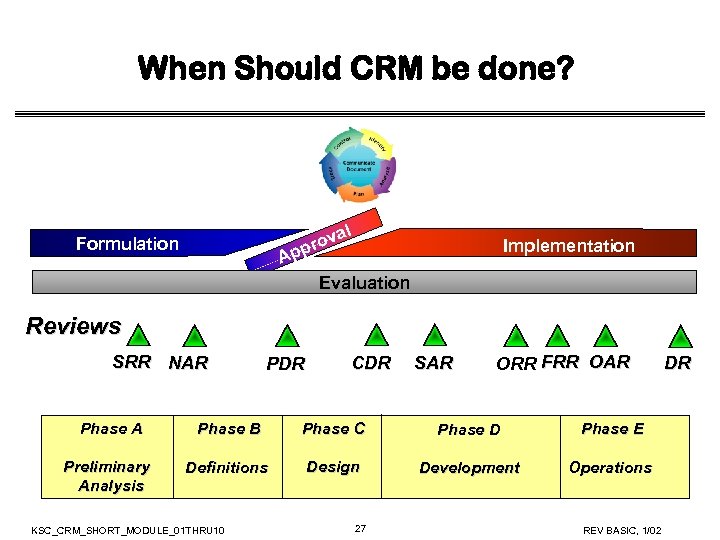 When Should CRM be done? Formulation A al rov pp Implementation Evaluation Reviews SRR NAR PDR CDR SAR ORR FRR OAR Phase A Phase B Phase C Phase D Phase E Preliminary Analysis Definitions Design Development Operations KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 27 REV BASIC, 1/02 DR
When Should CRM be done? Formulation A al rov pp Implementation Evaluation Reviews SRR NAR PDR CDR SAR ORR FRR OAR Phase A Phase B Phase C Phase D Phase E Preliminary Analysis Definitions Design Development Operations KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 27 REV BASIC, 1/02 DR
 RM Planning/Documentation • Risk Management planning early in the project life cycle (i. e. , formulation) is required per NPG 7120. 5 (Section 4. 3. 2 a); NPG 8000. 4 • Options • Stand-Alone Risk Management Plan (Medium-to-Large Projects) • Risk Management Section in Project Plan (Smaller Projects) KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 28 REV BASIC, 1/02
RM Planning/Documentation • Risk Management planning early in the project life cycle (i. e. , formulation) is required per NPG 7120. 5 (Section 4. 3. 2 a); NPG 8000. 4 • Options • Stand-Alone Risk Management Plan (Medium-to-Large Projects) • Risk Management Section in Project Plan (Smaller Projects) KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 28 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Risk Management Plan Details • Purpose • Documents the risk management practice (processes, methods, and tools) to be used for a specific project • Contents • • • Introduction/Overview Project organization, roles, responsibilities Practice details (e. g. , how risks are identified) Risk management milestones (e. g. , quarterly risk list reviews) Risk information documentation (e. g. , database) De-scope options • Available Information • SE&T/YA-B, conjunction with SH&IA/QA-C, has established risk management and project plan templates, and can offer consulting and guidance during plan development KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 29 REV BASIC, 1/02
Risk Management Plan Details • Purpose • Documents the risk management practice (processes, methods, and tools) to be used for a specific project • Contents • • • Introduction/Overview Project organization, roles, responsibilities Practice details (e. g. , how risks are identified) Risk management milestones (e. g. , quarterly risk list reviews) Risk information documentation (e. g. , database) De-scope options • Available Information • SE&T/YA-B, conjunction with SH&IA/QA-C, has established risk management and project plan templates, and can offer consulting and guidance during plan development KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 29 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Relationship to Everyday Practice Learning Continuous Risk Management is similar to incorporating any new habit into your daily life. KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 30 REV BASIC, 1/02
Relationship to Everyday Practice Learning Continuous Risk Management is similar to incorporating any new habit into your daily life. KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 30 REV BASIC, 1/02
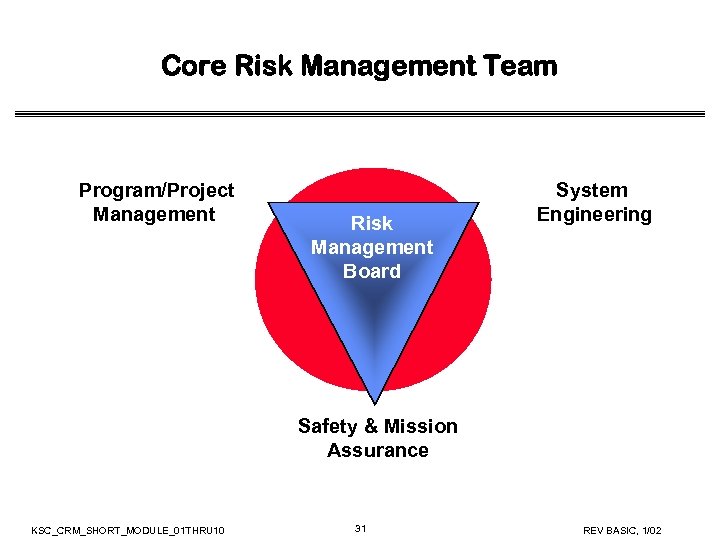 Core Risk Management Team Program/Project Management Risk Management Board System Engineering Safety & Mission Assurance KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 31 REV BASIC, 1/02
Core Risk Management Team Program/Project Management Risk Management Board System Engineering Safety & Mission Assurance KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 31 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Who Performs Continuous Risk Management? • Everyone! KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 32 REV BASIC, 1/02
Who Performs Continuous Risk Management? • Everyone! KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 32 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Module 3 Identify tif en Id C ol r ont y Pla An al yz e Track Communicate & Document n KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 33 REV BASIC, 1/02
Module 3 Identify tif en Id C ol r ont y Pla An al yz e Track Communicate & Document n KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 33 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Overview • Identification activities • Capturing statements of risk • Capturing the context of a risk • Identification methods and tools • • • Brainstorming Questionnaires and checklists Personal knowledge/experience RM/S&MA analysis tools (FMEA, FTA, PRA) Lessons Learned KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 34 REV BASIC, 1/02
Overview • Identification activities • Capturing statements of risk • Capturing the context of a risk • Identification methods and tools • • • Brainstorming Questionnaires and checklists Personal knowledge/experience RM/S&MA analysis tools (FMEA, FTA, PRA) Lessons Learned KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 34 REV BASIC, 1/02
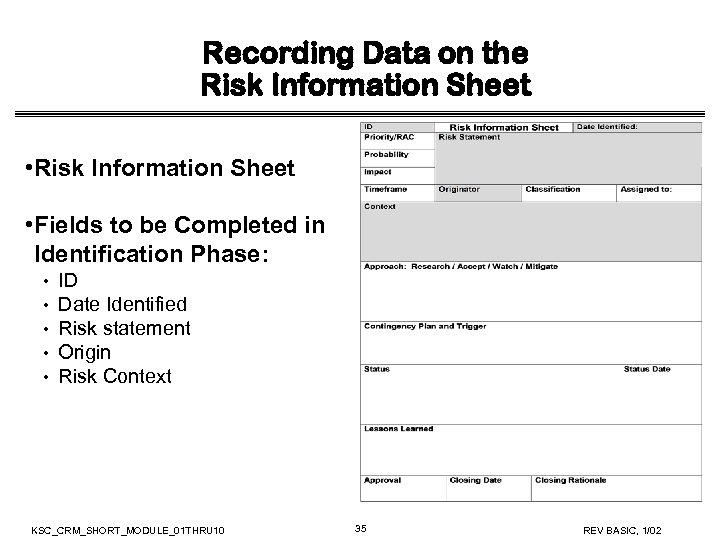 Recording Data on the Risk Information Sheet • Fields to be Completed in Identification Phase: • • • ID Date Identified Risk statement Origin Risk Context KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 35 REV BASIC, 1/02
Recording Data on the Risk Information Sheet • Fields to be Completed in Identification Phase: • • • ID Date Identified Risk statement Origin Risk Context KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 35 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Capturing Statements of Risk • Purpose: • Arrive at a concise description of risk, which can be understood by everyone and acted upon • Description: • Involves considering and recording the condition that is causing concern for a potential loss to the project, followed by a brief description of the potential consequences of this condition KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 36 REV BASIC, 1/02
Capturing Statements of Risk • Purpose: • Arrive at a concise description of risk, which can be understood by everyone and acted upon • Description: • Involves considering and recording the condition that is causing concern for a potential loss to the project, followed by a brief description of the potential consequences of this condition KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 36 REV BASIC, 1/02
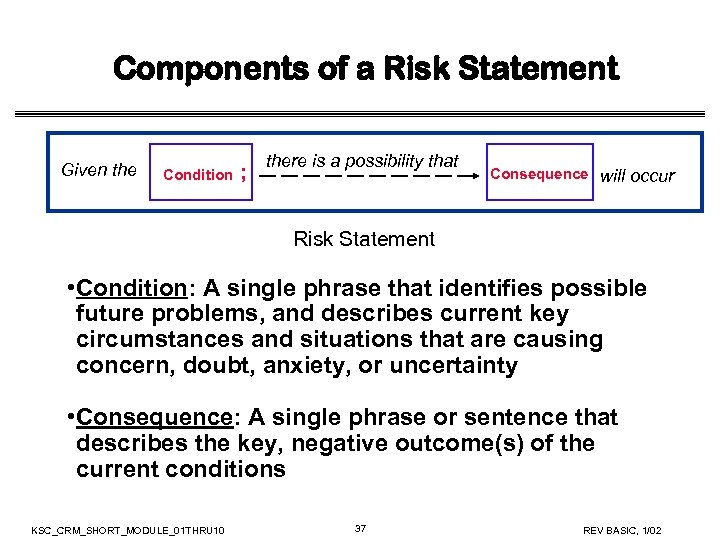 Components of a Risk Statement Given the Condition ; there is a possibility that Consequence will occur Risk Statement • Condition: A single phrase that identifies possible future problems, and describes current key circumstances and situations that are causing concern, doubt, anxiety, or uncertainty • Consequence: A single phrase or sentence that describes the key, negative outcome(s) of the current conditions KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 37 REV BASIC, 1/02
Components of a Risk Statement Given the Condition ; there is a possibility that Consequence will occur Risk Statement • Condition: A single phrase that identifies possible future problems, and describes current key circumstances and situations that are causing concern, doubt, anxiety, or uncertainty • Consequence: A single phrase or sentence that describes the key, negative outcome(s) of the current conditions KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 37 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Elements of a Good Risk Statement • Consider these questions when looking at a risk statement: • • • Is it clear and concise? Will most project members understand it? Is there a clear condition or source of concern? If a consequence is provided, is it clear? Is there only ONE condition, followed by one (or more) consequence? KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 38 REV BASIC, 1/02
Elements of a Good Risk Statement • Consider these questions when looking at a risk statement: • • • Is it clear and concise? Will most project members understand it? Is there a clear condition or source of concern? If a consequence is provided, is it clear? Is there only ONE condition, followed by one (or more) consequence? KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 38 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Example Risk Statements Good or bad risk statements? 1. Object Oriented Development (OOD)! 2. The staff will need time and training to learn object oriented development. 3. This is the first time that the software staff will use OOD; the staff may have a lower than expected productivity rate and schedules may slip because of the associated learning curve. KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 39 REV BASIC, 1/02
Example Risk Statements Good or bad risk statements? 1. Object Oriented Development (OOD)! 2. The staff will need time and training to learn object oriented development. 3. This is the first time that the software staff will use OOD; the staff may have a lower than expected productivity rate and schedules may slip because of the associated learning curve. KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 39 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Capturing the Context of a Risk • Purpose: • Provide enough additional information about the risk to ensure that the original intent of the risk can be understood by other personnel, particularly after time has passed • Description: • Capture additional information regarding the circumstances, events, and interrelationships not described in the statement of risk KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 40 REV BASIC, 1/02
Capturing the Context of a Risk • Purpose: • Provide enough additional information about the risk to ensure that the original intent of the risk can be understood by other personnel, particularly after time has passed • Description: • Capture additional information regarding the circumstances, events, and interrelationships not described in the statement of risk KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 40 REV BASIC, 1/02
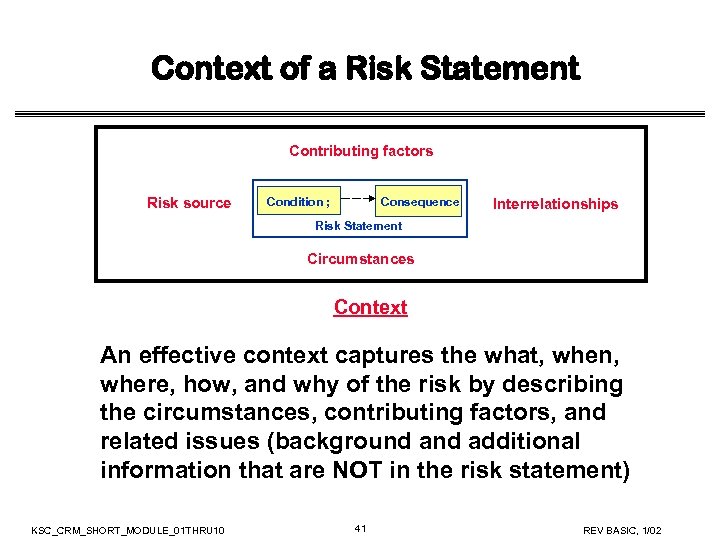 Context of a Risk Statement Contributing factors Risk source Condition ; Consequence Interrelationships Risk Statement Circumstances Context An effective context captures the what, when, where, how, and why of the risk by describing the circumstances, contributing factors, and related issues (background additional information that are NOT in the risk statement) KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 41 REV BASIC, 1/02
Context of a Risk Statement Contributing factors Risk source Condition ; Consequence Interrelationships Risk Statement Circumstances Context An effective context captures the what, when, where, how, and why of the risk by describing the circumstances, contributing factors, and related issues (background additional information that are NOT in the risk statement) KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 41 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Elements of Good Context • Consider these questions when looking at the context • Can you identify which risk statement this context is associated with? • Is it clear what the source or cause of the risk is? • Is it clear what the impact might be? • Would you know who to assign the risk to for mitigation? Would they (the person responsible for risk mitigation) know what to do? • Would you be able to tell if the risk has gone away? KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 42 REV BASIC, 1/02
Elements of Good Context • Consider these questions when looking at the context • Can you identify which risk statement this context is associated with? • Is it clear what the source or cause of the risk is? • Is it clear what the impact might be? • Would you know who to assign the risk to for mitigation? Would they (the person responsible for risk mitigation) know what to do? • Would you be able to tell if the risk has gone away? KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 42 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Example Context (#1) Risk Statement: • This is the first time that the software staff will use Object Oriented Development (OOD); the staff may have a lower-than-expected productivity rate and schedules may slip because of the associated learning curve. Risk context • It’s a typical NASA project – new concepts without training. • Is this an example of good or bad context? KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 43 REV BASIC, 1/02
Example Context (#1) Risk Statement: • This is the first time that the software staff will use Object Oriented Development (OOD); the staff may have a lower-than-expected productivity rate and schedules may slip because of the associated learning curve. Risk context • It’s a typical NASA project – new concepts without training. • Is this an example of good or bad context? KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 43 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Example Context (#2) Risk Statement • This is the first time that the software staff will use OOD; the staff may have a lower than expected productivity rate and schedules may slip because of the associated learning curve. Risk Context: • Object oriented development is a very different approach that requires special training. There will be a learning curve until the staff is up to speed. The time and resources must be built in for this or the schedule and budget will overrun. KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 44 REV BASIC, 1/02
Example Context (#2) Risk Statement • This is the first time that the software staff will use OOD; the staff may have a lower than expected productivity rate and schedules may slip because of the associated learning curve. Risk Context: • Object oriented development is a very different approach that requires special training. There will be a learning curve until the staff is up to speed. The time and resources must be built in for this or the schedule and budget will overrun. KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 44 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Risks are Not Problems (1) • Risk: • A future event • A potential problem • Has a level of uncertainty (>0% and <100% chance of occurrence) • Problem • Is happening now • Must be dealt with immediately • No uncertainty (it’s occurring now) KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 45 REV BASIC, 1/02
Risks are Not Problems (1) • Risk: • A future event • A potential problem • Has a level of uncertainty (>0% and <100% chance of occurrence) • Problem • Is happening now • Must be dealt with immediately • No uncertainty (it’s occurring now) KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 45 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Risks are Not Problems (2) • Risks are anticipated problems • Example: Delivery of Class S parts on schedule is questionable • A Problem is a Risk that has occurred • Example: Class S parts have not been delivered • Problems may create new risks • Change in design, increased testing • Schedule slip, screening cost KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 46 REV BASIC, 1/02
Risks are Not Problems (2) • Risks are anticipated problems • Example: Delivery of Class S parts on schedule is questionable • A Problem is a Risk that has occurred • Example: Class S parts have not been delivered • Problems may create new risks • Change in design, increased testing • Schedule slip, screening cost KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 46 REV BASIC, 1/02
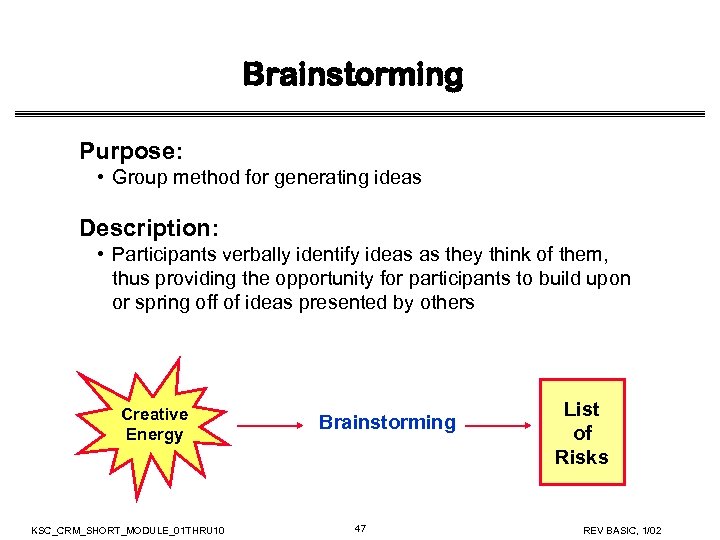 Brainstorming Purpose: • Group method for generating ideas Description: • Participants verbally identify ideas as they think of them, thus providing the opportunity for participants to build upon or spring off of ideas presented by others Creative Energy KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 Brainstorming 47 List of Risks REV BASIC, 1/02
Brainstorming Purpose: • Group method for generating ideas Description: • Participants verbally identify ideas as they think of them, thus providing the opportunity for participants to build upon or spring off of ideas presented by others Creative Energy KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 Brainstorming 47 List of Risks REV BASIC, 1/02
 Risk Statement Identification Tools -Taxonomy-Based Questionnaire (TBQ) • Taxonomy – The classification of something in an ordered system that indicates natural relationships; division into ordered groups or categories • TBQs are questionnaires organized according to the taxonomy of a particular body of knowledge • TBQs provide a structured approach for identifying risks associated with a project • CRM Guidebook (pp. 471 -493) KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 48 REV BASIC, 1/02
Risk Statement Identification Tools -Taxonomy-Based Questionnaire (TBQ) • Taxonomy – The classification of something in an ordered system that indicates natural relationships; division into ordered groups or categories • TBQs are questionnaires organized according to the taxonomy of a particular body of knowledge • TBQs provide a structured approach for identifying risks associated with a project • CRM Guidebook (pp. 471 -493) KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 48 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Additional Risk Identification Methods • Failure Modes and Effects Analysis • Fault Tree Analysis • Probabilistic Risk Assessment (PRA) • Lessons Learned (http: //llis. nasa. gov) • Various Other Checklists KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 49 REV BASIC, 1/02
Additional Risk Identification Methods • Failure Modes and Effects Analysis • Fault Tree Analysis • Probabilistic Risk Assessment (PRA) • Lessons Learned (http: //llis. nasa. gov) • Various Other Checklists KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 49 REV BASIC, 1/02
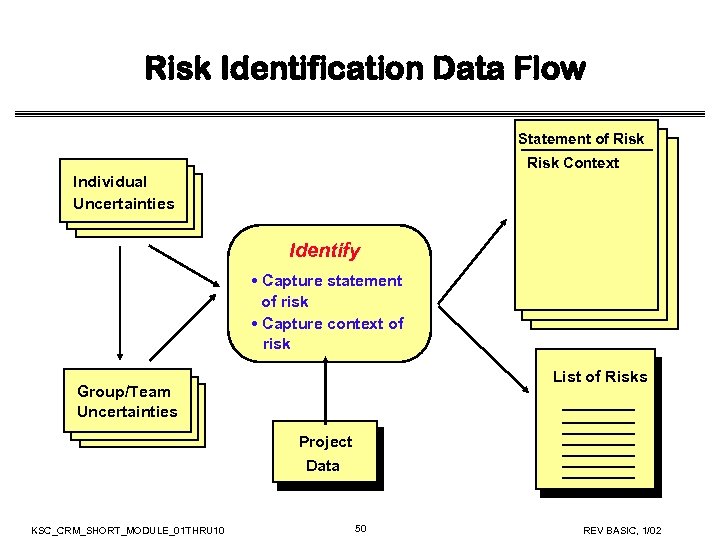 Risk Identification Data Flow Statement of Risk Context Individual Uncertainties Identify • Capture statement of risk • Capture context of risk List of Risks Group/Team Uncertainties Project Data KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 50 REV BASIC, 1/02
Risk Identification Data Flow Statement of Risk Context Individual Uncertainties Identify • Capture statement of risk • Capture context of risk List of Risks Group/Team Uncertainties Project Data KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 50 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Risk Information Sheet (After the Identification Phase) • Risk Information Sheet (RIS) after the CRM Identify phase KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 51 REV BASIC, 1/02
Risk Information Sheet (After the Identification Phase) • Risk Information Sheet (RIS) after the CRM Identify phase KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 51 REV BASIC, 1/02
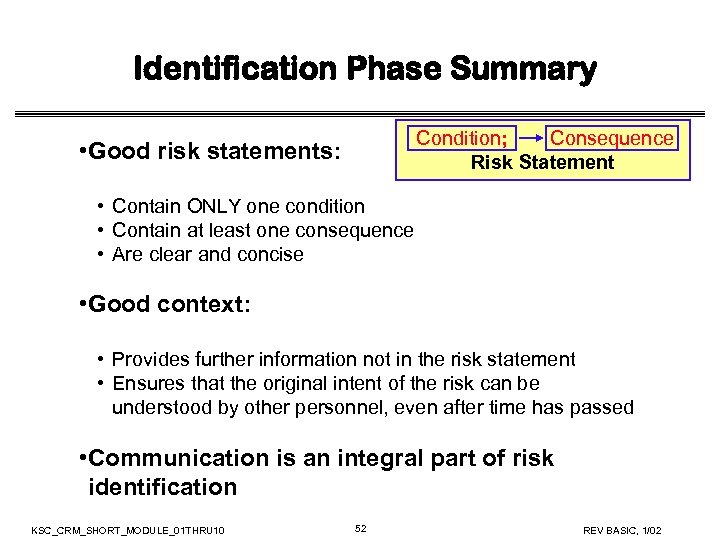 Identification Phase Summary Condition; Consequence Risk Statement • Good risk statements: • Contain ONLY one condition • Contain at least one consequence • Are clear and concise • Good context: • Provides further information not in the risk statement • Ensures that the original intent of the risk can be understood by other personnel, even after time has passed • Communication is an integral part of risk identification KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 52 REV BASIC, 1/02
Identification Phase Summary Condition; Consequence Risk Statement • Good risk statements: • Contain ONLY one condition • Contain at least one consequence • Are clear and concise • Good context: • Provides further information not in the risk statement • Ensures that the original intent of the risk can be understood by other personnel, even after time has passed • Communication is an integral part of risk identification KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 52 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Module 4 Analyze y tif en Id C ol r ont Pla An al yz e Track Communicate & Document n KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 53 REV BASIC, 1/02
Module 4 Analyze y tif en Id C ol r ont Pla An al yz e Track Communicate & Document n KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 53 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Overview • Analysis activities • Evaluating attributes of risk • Classifying risks • Prioritizing risks KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 54 REV BASIC, 1/02
Overview • Analysis activities • Evaluating attributes of risk • Classifying risks • Prioritizing risks KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 54 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Recording Data on the Risk Information Sheet • Fields to be Completed in Analysis Phase: • • • Priority Probability Impact Timeframe Class KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 55 REV BASIC, 1/02
Recording Data on the Risk Information Sheet • Fields to be Completed in Analysis Phase: • • • Priority Probability Impact Timeframe Class KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 55 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Evaluating Attributes of Risk • Purpose • To gain a better understanding of the risk by determining the expected impact, probability, and timeframe of the risk • Description • Involves establishing values for: • Impact: the loss or effect on the project if the risk occurs • Probability: the likelihood the risk will occur • Timeframe: the period when you must take action to mitigate the risk (NOT: when the risk will occur) KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 56 REV BASIC, 1/02
Evaluating Attributes of Risk • Purpose • To gain a better understanding of the risk by determining the expected impact, probability, and timeframe of the risk • Description • Involves establishing values for: • Impact: the loss or effect on the project if the risk occurs • Probability: the likelihood the risk will occur • Timeframe: the period when you must take action to mitigate the risk (NOT: when the risk will occur) KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 56 REV BASIC, 1/02
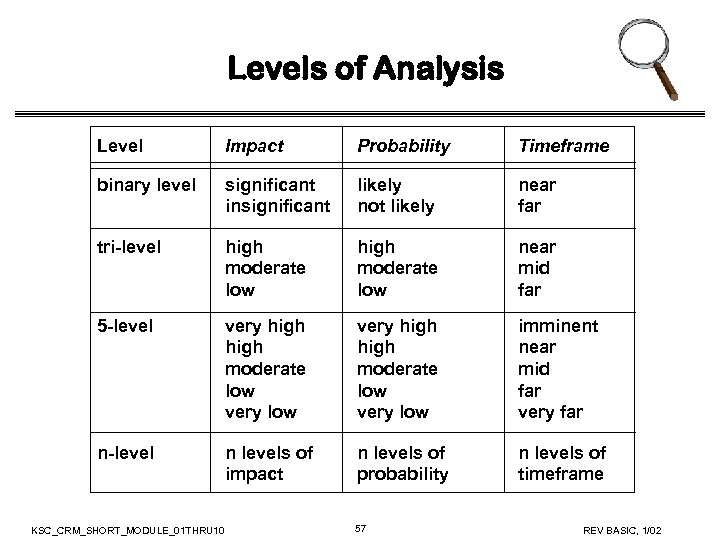 Levels of Analysis Level Impact Probability Timeframe binary level significant insignificant likely not likely near far tri-level high moderate low near mid far 5 -level very high moderate low very low imminent near mid far very far n-level n levels of impact n levels of probability n levels of timeframe KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 57 REV BASIC, 1/02
Levels of Analysis Level Impact Probability Timeframe binary level significant insignificant likely not likely near far tri-level high moderate low near mid far 5 -level very high moderate low very low imminent near mid far very far n-level n levels of impact n levels of probability n levels of timeframe KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 57 REV BASIC, 1/02
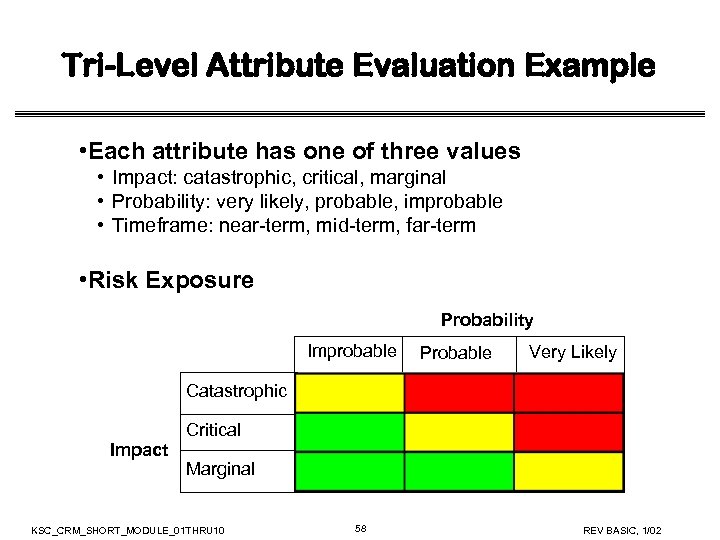 Tri-Level Attribute Evaluation Example • Each attribute has one of three values • Impact: catastrophic, critical, marginal • Probability: very likely, probable, improbable • Timeframe: near-term, mid-term, far-term • Risk Exposure Probability Improbable Probable Very Likely Catastrophic Critical Impact Marginal KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 58 REV BASIC, 1/02
Tri-Level Attribute Evaluation Example • Each attribute has one of three values • Impact: catastrophic, critical, marginal • Probability: very likely, probable, improbable • Timeframe: near-term, mid-term, far-term • Risk Exposure Probability Improbable Probable Very Likely Catastrophic Critical Impact Marginal KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 58 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Example: Probability Definitions • A risk is very likely if there is a >70% probability that it will occur • A risk is probable if there is a 30 -70% probability that it will occur • A risk is improbable if there is a <30% probability that it will occur KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 59 REV BASIC, 1/02
Example: Probability Definitions • A risk is very likely if there is a >70% probability that it will occur • A risk is probable if there is a 30 -70% probability that it will occur • A risk is improbable if there is a <30% probability that it will occur KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 59 REV BASIC, 1/02
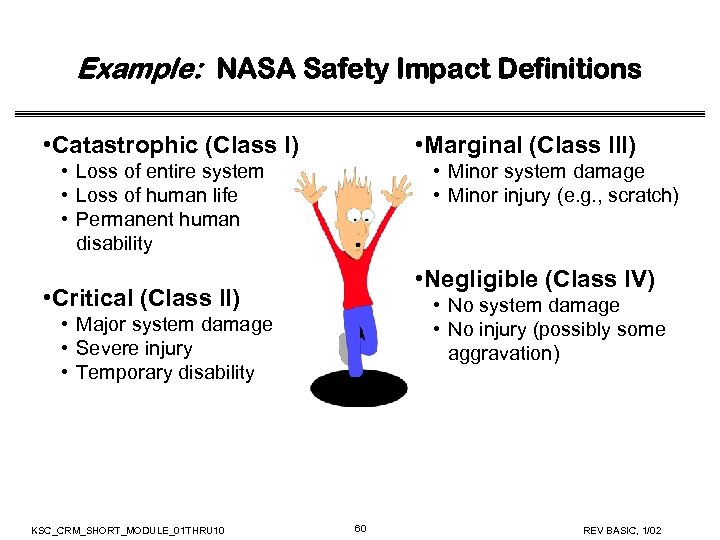 Example: NASA Safety Impact Definitions • Catastrophic (Class I) • Marginal (Class III) • Loss of entire system • Loss of human life • Permanent human disability • Minor system damage • Minor injury (e. g. , scratch) • Negligible (Class IV) • Critical (Class II) • No system damage • No injury (possibly some aggravation) • Major system damage • Severe injury • Temporary disability KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 60 REV BASIC, 1/02
Example: NASA Safety Impact Definitions • Catastrophic (Class I) • Marginal (Class III) • Loss of entire system • Loss of human life • Permanent human disability • Minor system damage • Minor injury (e. g. , scratch) • Negligible (Class IV) • Critical (Class II) • No system damage • No injury (possibly some aggravation) • Major system damage • Severe injury • Temporary disability KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 60 REV BASIC, 1/02
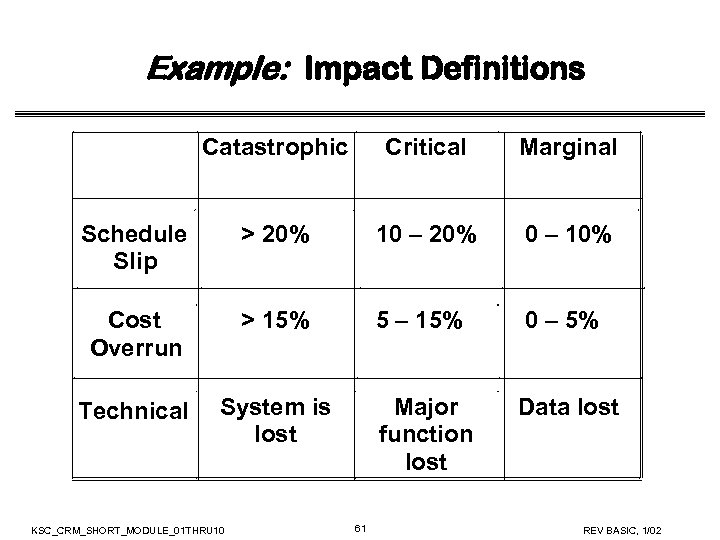 Example: Impact Definitions Catastrophic Critical Marginal Schedule Slip > 20% 10 – 20% 0 – 10% Cost Overrun > 15% 5 – 15% 0 – 5% Technical System is lost Major function lost Data lost KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 61 REV BASIC, 1/02
Example: Impact Definitions Catastrophic Critical Marginal Schedule Slip > 20% 10 – 20% 0 – 10% Cost Overrun > 15% 5 – 15% 0 – 5% Technical System is lost Major function lost Data lost KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 61 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Example: Timeframe Definitions • A risk has a near-term timeframe if the project must take mitigation action in the next 90 days • A risk has a mid-term timeframe if the project must take mitigation action in the next 90 -180 days • A risk has a far-term timeframe if the project does not need to take mitigation action within the next 180 days KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 62 REV BASIC, 1/02
Example: Timeframe Definitions • A risk has a near-term timeframe if the project must take mitigation action in the next 90 days • A risk has a mid-term timeframe if the project must take mitigation action in the next 90 -180 days • A risk has a far-term timeframe if the project does not need to take mitigation action within the next 180 days KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 62 REV BASIC, 1/02
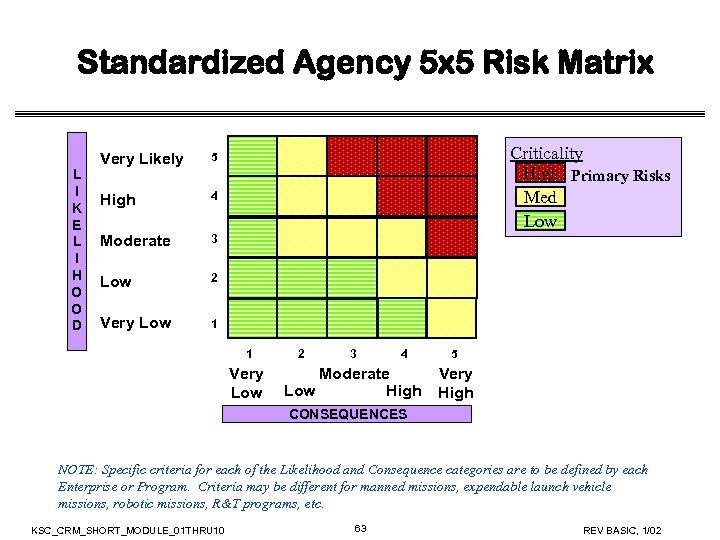 Standardized Agency 5 x 5 Risk Matrix L I K E L I H O O D Very Likely High 4 Moderate 3 Low 2 Very Low Criticality High Primary Risks Med Low 5 1 1 Very Low 2 3 4 Moderate Low High 5 Very High CONSEQUENCES NOTE: Specific criteria for each of the Likelihood and Consequence categories are to be defined by each Enterprise or Program. Criteria may be different for manned missions, expendable launch vehicle missions, robotic missions, R&T programs, etc. KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 63 REV BASIC, 1/02
Standardized Agency 5 x 5 Risk Matrix L I K E L I H O O D Very Likely High 4 Moderate 3 Low 2 Very Low Criticality High Primary Risks Med Low 5 1 1 Very Low 2 3 4 Moderate Low High 5 Very High CONSEQUENCES NOTE: Specific criteria for each of the Likelihood and Consequence categories are to be defined by each Enterprise or Program. Criteria may be different for manned missions, expendable launch vehicle missions, robotic missions, R&T programs, etc. KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 63 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Definition of a Primary Risk • NPG 8000. 4 defined a Primary Risk as those undesirable events (risks) having both high probability and high impact/severity • Characterization of a Primary Risk as “Acceptable” shall be supported by rationale, with concurrence of the Governing Program Management Council (GPMC), that all reasonable mitigation options (within cost, schedule, and technical constraints) have been instituted KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 64 REV BASIC, 1/02
Definition of a Primary Risk • NPG 8000. 4 defined a Primary Risk as those undesirable events (risks) having both high probability and high impact/severity • Characterization of a Primary Risk as “Acceptable” shall be supported by rationale, with concurrence of the Governing Program Management Council (GPMC), that all reasonable mitigation options (within cost, schedule, and technical constraints) have been instituted KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 64 REV BASIC, 1/02
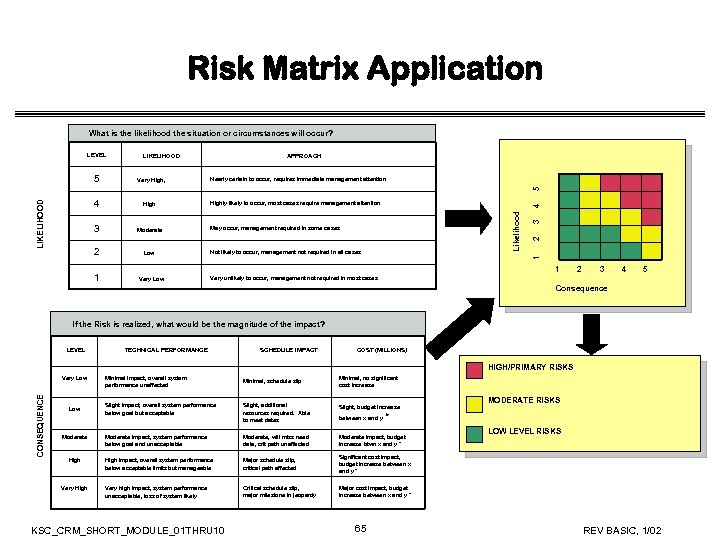 Risk Matrix Application What is the likelihood the situation or circumstances will occur? LEVEL Very High, Nearly certain to occur, requires immediate management attention 5 5 APPROACH LIKELIHOOD 1 4 Not likely to occur, management not required in all cases 3 Low 2 2 May occur, management required in some cases 1 Moderate Highly likely to occur, most cases require management attention Likelihood High 3 LIKELIHOOD 4 1 Very Low 2 3 4 5 Very unlikely to occur, management not required in most cases Consequence If the Risk is realized, what would be the magnitude of the impact? LEVEL TECHNICAL PERFORMANCE SCHEDULE IMPACT COST (MILLIONS) HIGH/PRIMARY RISKS CONSEQUENCE Very Low Moderate High Very High Minimal impact, overall system performance unaffected Minimal, schedule slip Minimal, no significant cost increase Slight impact, overall system performance below goal but acceptable Slight, additional resources required. Able to meet dates Slight, budget increase Moderate impact, system performance below goal and unacceptable Moderate, will miss need date, crit path unaffected Moderate impact, budget increase btwn x and y * High impact, overall system performance below acceptable limits but manageable Major schedule slip, critical path affected Significant cost impact, budget increase between x and y * Very high impact, system performance unacceptable, loss of system likely Critical schedule slip, major milestone in jeopardy MODERATE RISKS Major cost impact, budget increase between x and y * KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 between x and y 65 * LOW LEVEL RISKS REV BASIC, 1/02
Risk Matrix Application What is the likelihood the situation or circumstances will occur? LEVEL Very High, Nearly certain to occur, requires immediate management attention 5 5 APPROACH LIKELIHOOD 1 4 Not likely to occur, management not required in all cases 3 Low 2 2 May occur, management required in some cases 1 Moderate Highly likely to occur, most cases require management attention Likelihood High 3 LIKELIHOOD 4 1 Very Low 2 3 4 5 Very unlikely to occur, management not required in most cases Consequence If the Risk is realized, what would be the magnitude of the impact? LEVEL TECHNICAL PERFORMANCE SCHEDULE IMPACT COST (MILLIONS) HIGH/PRIMARY RISKS CONSEQUENCE Very Low Moderate High Very High Minimal impact, overall system performance unaffected Minimal, schedule slip Minimal, no significant cost increase Slight impact, overall system performance below goal but acceptable Slight, additional resources required. Able to meet dates Slight, budget increase Moderate impact, system performance below goal and unacceptable Moderate, will miss need date, crit path unaffected Moderate impact, budget increase btwn x and y * High impact, overall system performance below acceptable limits but manageable Major schedule slip, critical path affected Significant cost impact, budget increase between x and y * Very high impact, system performance unacceptable, loss of system likely Critical schedule slip, major milestone in jeopardy MODERATE RISKS Major cost impact, budget increase between x and y * KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 between x and y 65 * LOW LEVEL RISKS REV BASIC, 1/02
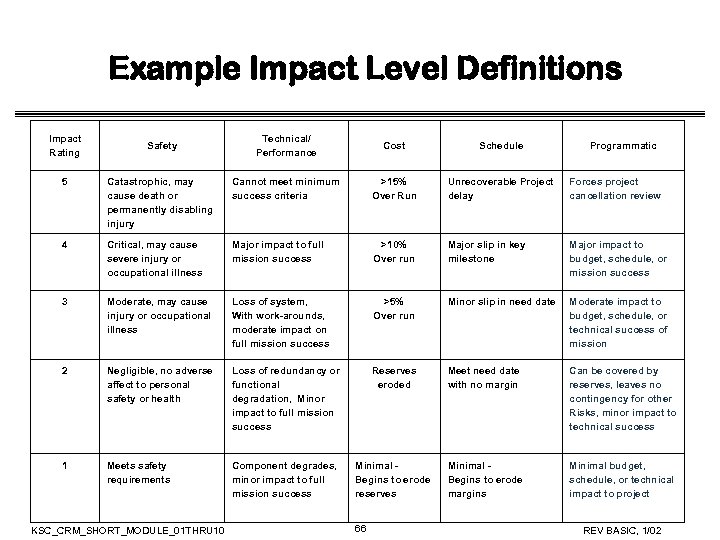 Example Impact Level Definitions Impact Rating Safety Technical/ Performance Cost Schedule Programmatic 5 Catastrophic, may cause death or permanently disabling injury Cannot meet minimum success criteria >15% Over Run Unrecoverable Project delay Forces project cancellation review 4 Critical, may cause severe injury or occupational illness Major impact to full mission success >10% Over run Major slip in key milestone Major impact to budget, schedule, or mission success 3 Moderate, may cause injury or occupational illness Loss of system, With work-arounds, moderate impact on full mission success >5% Over run Minor slip in need date Moderate impact to budget, schedule, or technical success of mission 2 Negligible, no adverse affect to personal safety or health Loss of redundancy or functional degradation, Minor impact to full mission success Reserves eroded Meet need date with no margin Can be covered by reserves, leaves no contingency for other Risks, minor impact to technical success 1 Meets safety requirements Component degrades, minor impact to full mission success Minimal Begins to erode reserves Minimal Begins to erode margins Minimal budget, schedule, or technical impact to project KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 66 REV BASIC, 1/02
Example Impact Level Definitions Impact Rating Safety Technical/ Performance Cost Schedule Programmatic 5 Catastrophic, may cause death or permanently disabling injury Cannot meet minimum success criteria >15% Over Run Unrecoverable Project delay Forces project cancellation review 4 Critical, may cause severe injury or occupational illness Major impact to full mission success >10% Over run Major slip in key milestone Major impact to budget, schedule, or mission success 3 Moderate, may cause injury or occupational illness Loss of system, With work-arounds, moderate impact on full mission success >5% Over run Minor slip in need date Moderate impact to budget, schedule, or technical success of mission 2 Negligible, no adverse affect to personal safety or health Loss of redundancy or functional degradation, Minor impact to full mission success Reserves eroded Meet need date with no margin Can be covered by reserves, leaves no contingency for other Risks, minor impact to technical success 1 Meets safety requirements Component degrades, minor impact to full mission success Minimal Begins to erode reserves Minimal Begins to erode margins Minimal budget, schedule, or technical impact to project KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 66 REV BASIC, 1/02
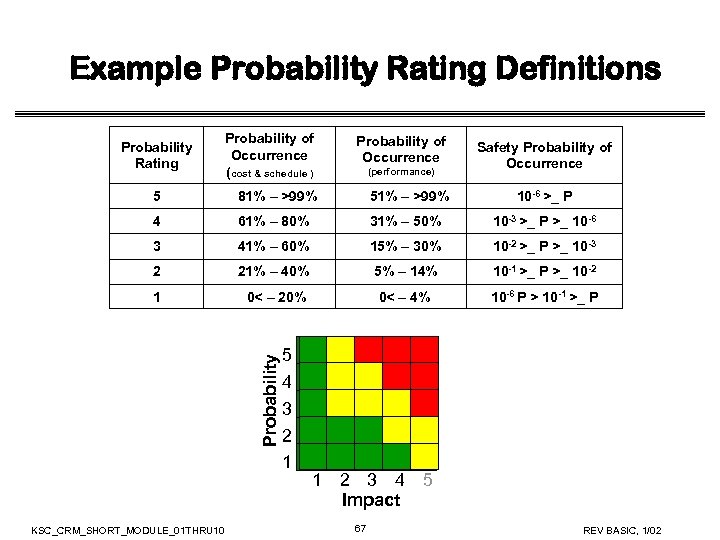 Example Probability Rating Definitions Probability of Occurrence (cost & schedule ) Probability of Occurrence 5 81% – >99% 51% – >99% 10 -6 >_ P 4 61% – 80% 31% – 50% 10 -3 >_ P >_ 10 -6 3 41% – 60% 15% – 30% 10 -2 >_ P >_ 10 -3 2 21% – 40% 5% – 14% 10 -1 >_ P >_ 10 -2 1 0< – 20% 0< – 4% 10 -6 P > 10 -1 >_ P Probability Rating KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 5 4 3 2 1 (performance) Safety Probability of Occurrence 1 2 3 4 5 Impact 67 REV BASIC, 1/02
Example Probability Rating Definitions Probability of Occurrence (cost & schedule ) Probability of Occurrence 5 81% – >99% 51% – >99% 10 -6 >_ P 4 61% – 80% 31% – 50% 10 -3 >_ P >_ 10 -6 3 41% – 60% 15% – 30% 10 -2 >_ P >_ 10 -3 2 21% – 40% 5% – 14% 10 -1 >_ P >_ 10 -2 1 0< – 20% 0< – 4% 10 -6 P > 10 -1 >_ P Probability Rating KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 5 4 3 2 1 (performance) Safety Probability of Occurrence 1 2 3 4 5 Impact 67 REV BASIC, 1/02
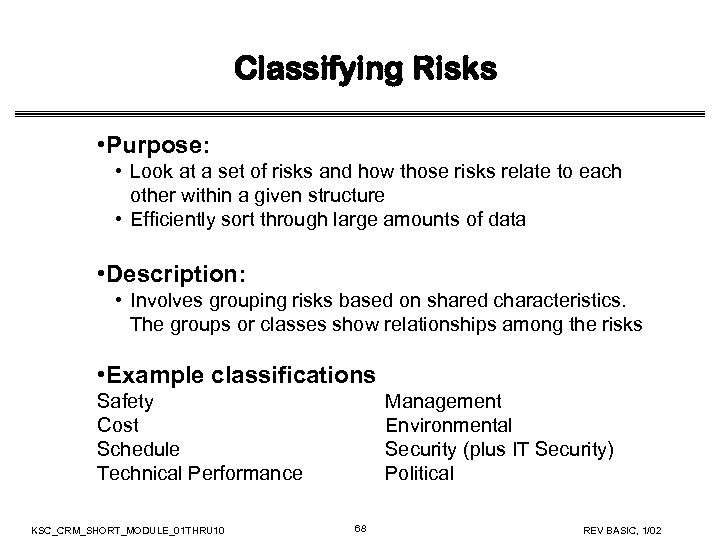 Classifying Risks • Purpose: • Look at a set of risks and how those risks relate to each other within a given structure • Efficiently sort through large amounts of data • Description: • Involves grouping risks based on shared characteristics. The groups or classes show relationships among the risks • Example classifications Safety Cost Schedule Technical Performance KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 Management Environmental Security (plus IT Security) Political 68 REV BASIC, 1/02
Classifying Risks • Purpose: • Look at a set of risks and how those risks relate to each other within a given structure • Efficiently sort through large amounts of data • Description: • Involves grouping risks based on shared characteristics. The groups or classes show relationships among the risks • Example classifications Safety Cost Schedule Technical Performance KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 Management Environmental Security (plus IT Security) Political 68 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Prioritizing Risks Master list of risks Top N • Purpose: • Sort through a large amount of risks and determine which are most important • Separate out which risks should be dealt with first (the vital few risks) when allocating resources • Description: • Involves partitioning risks or groups of risks based on the Pareto “vital few” sense and ranking risks or sets of risks based upon a criterion or set of criteria • Prioritization should utilize the project’s “success criteria” • Prioritization should yield the project’s “Primary Risks” KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 69 REV BASIC, 1/02
Prioritizing Risks Master list of risks Top N • Purpose: • Sort through a large amount of risks and determine which are most important • Separate out which risks should be dealt with first (the vital few risks) when allocating resources • Description: • Involves partitioning risks or groups of risks based on the Pareto “vital few” sense and ranking risks or sets of risks based upon a criterion or set of criteria • Prioritization should utilize the project’s “success criteria” • Prioritization should yield the project’s “Primary Risks” KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 69 REV BASIC, 1/02
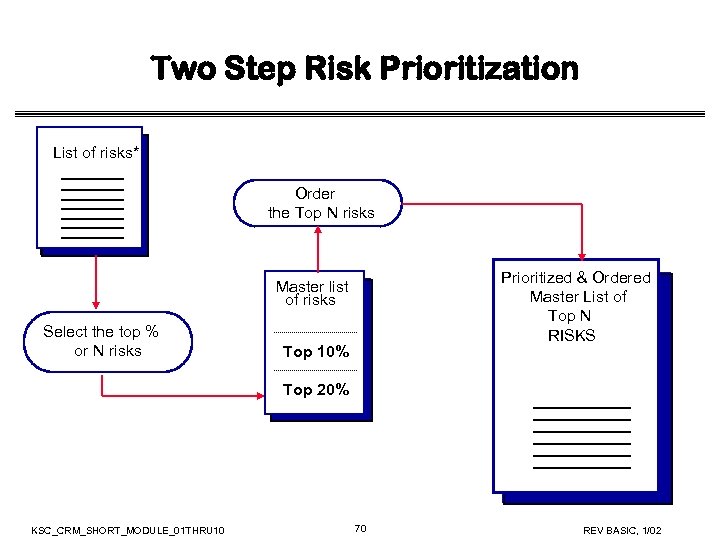 Two Step Risk Prioritization List of risks* Order the Top N risks Prioritized & Ordered Master List of Top N RISKS Master list of risks Select the top % or N risks Top 10% Top 20% KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 70 REV BASIC, 1/02
Two Step Risk Prioritization List of risks* Order the Top N risks Prioritized & Ordered Master List of Top N RISKS Master list of risks Select the top % or N risks Top 10% Top 20% KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 70 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Risk Prioritization Using Multivoting • Multivoting is a technique for prioritizing a subset of items from a larger set (usually one-third of the items on a list) • Each evaluator in a group gets a certain number of votes (e. g. , 3) to use for risk prioritization • Each evaluator then assigns a number between “ 1” and “ 3” (i. e. , the number of votes they have) to the risks they feel are most important (e. g. , a “ 3” is a higher priority risk than a “ 1”) • Totals for each risk are tallied – highest priority risks are those with the most points KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 71 REV BASIC, 1/02
Risk Prioritization Using Multivoting • Multivoting is a technique for prioritizing a subset of items from a larger set (usually one-third of the items on a list) • Each evaluator in a group gets a certain number of votes (e. g. , 3) to use for risk prioritization • Each evaluator then assigns a number between “ 1” and “ 3” (i. e. , the number of votes they have) to the risks they feel are most important (e. g. , a “ 3” is a higher priority risk than a “ 1”) • Totals for each risk are tallied – highest priority risks are those with the most points KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 71 REV BASIC, 1/02
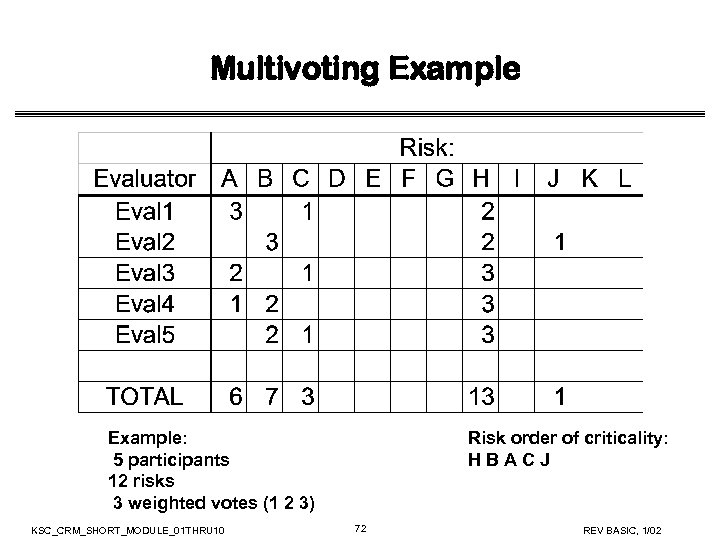 Multivoting Example: 5 participants 12 risks 3 weighted votes (1 2 3) KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 Risk order of criticality: HBACJ 72 REV BASIC, 1/02
Multivoting Example: 5 participants 12 risks 3 weighted votes (1 2 3) KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 Risk order of criticality: HBACJ 72 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Risk Prioritization Using a Risk Assessment Code (RAC) • The use of Risk Assessment Code (RAC) is an additional, qualitative method for prioritizing risks • The RAC is a tool used to express comparative risks in all categories by evaluating both the potential severity of a condition and the probability of its occurrence • RACs can be utilized to determine a project’s “Primary Risks” (i. e. , those risks with both a high probability and a high impact) [e. g. , those risks with a RAC of 1 or 2] • RACs can be assigned in a tailored manner to meet the needs or complexity of a program or project KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 73 REV BASIC, 1/02
Risk Prioritization Using a Risk Assessment Code (RAC) • The use of Risk Assessment Code (RAC) is an additional, qualitative method for prioritizing risks • The RAC is a tool used to express comparative risks in all categories by evaluating both the potential severity of a condition and the probability of its occurrence • RACs can be utilized to determine a project’s “Primary Risks” (i. e. , those risks with both a high probability and a high impact) [e. g. , those risks with a RAC of 1 or 2] • RACs can be assigned in a tailored manner to meet the needs or complexity of a program or project KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 73 REV BASIC, 1/02
![Risk Assessment Code (RAC) [Project Example] Likelihood Estimate Impact/Severity High risk Medium Low • Risk Assessment Code (RAC) [Project Example] Likelihood Estimate Impact/Severity High risk Medium Low •](https://present5.com/presentation/6a9385708adaeba83aa04ec809e9fe55/image-74.jpg) Risk Assessment Code (RAC) [Project Example] Likelihood Estimate Impact/Severity High risk Medium Low • RACs are assigned a number based on the risk exposure (product of probability times impact), with each attribute level having a score from 1 to 5 in this risk matrix • For this example, the RED (High Risk) risks having a value of 15 -25 would be classified as Primary Risks KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 74 REV BASIC, 1/02
Risk Assessment Code (RAC) [Project Example] Likelihood Estimate Impact/Severity High risk Medium Low • RACs are assigned a number based on the risk exposure (product of probability times impact), with each attribute level having a score from 1 to 5 in this risk matrix • For this example, the RED (High Risk) risks having a value of 15 -25 would be classified as Primary Risks KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 74 REV BASIC, 1/02
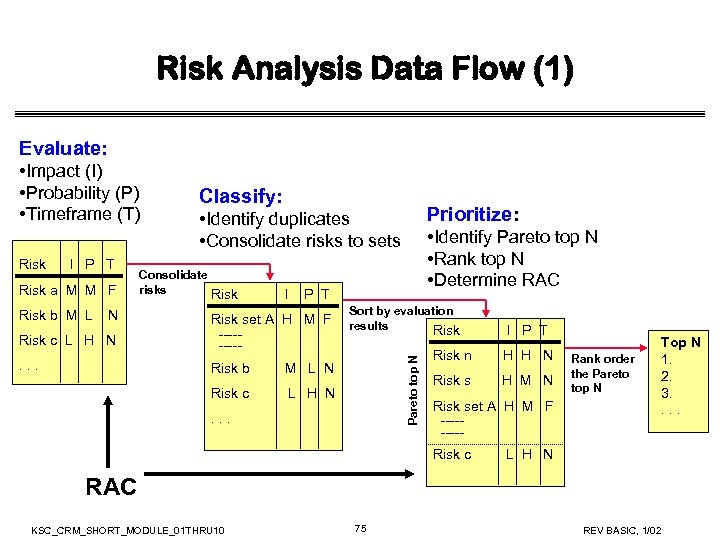 Risk Analysis Data Flow (1) Evaluate: • Impact (I) • Probability (P) • Timeframe (T) Risk I P T Risk a M M F Risk b M L N Classify: Prioritize: • Identify duplicates • Consolidate risks to sets • Identify Pareto top N • Rank top N • Determine RAC Consolidate risks Risk I P T . . . Sort by evaluation results Risk I P T Risk b M L N Pareto top N Risk c L H N Risk set A H M F ----Risk c L H N. . . Risk n H H N Risk s H M N Risk set A H M F ----- Rank order the Pareto top N Top N 1. 2. 3. . Risk c L H N RAC KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 75 REV BASIC, 1/02
Risk Analysis Data Flow (1) Evaluate: • Impact (I) • Probability (P) • Timeframe (T) Risk I P T Risk a M M F Risk b M L N Classify: Prioritize: • Identify duplicates • Consolidate risks to sets • Identify Pareto top N • Rank top N • Determine RAC Consolidate risks Risk I P T . . . Sort by evaluation results Risk I P T Risk b M L N Pareto top N Risk c L H N Risk set A H M F ----Risk c L H N. . . Risk n H H N Risk s H M N Risk set A H M F ----- Rank order the Pareto top N Top N 1. 2. 3. . Risk c L H N RAC KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 75 REV BASIC, 1/02
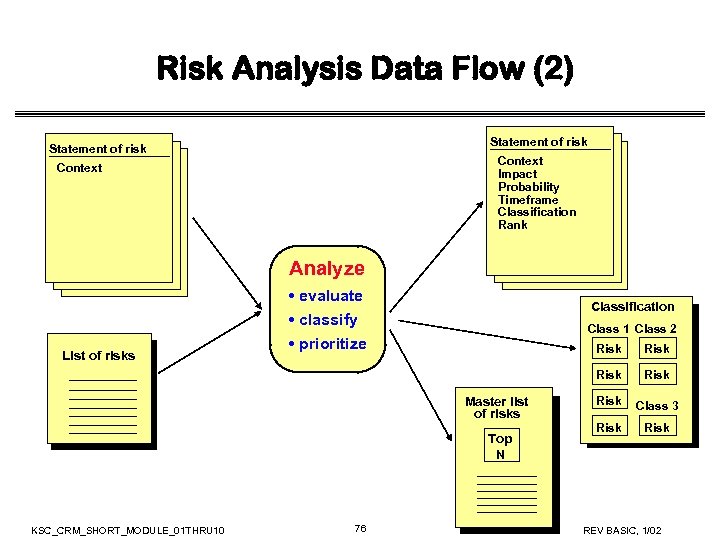 Risk Analysis Data Flow (2) Statement of risk Context Impact Probability Timeframe Classification Rank Context Analyze • evaluate • classify • prioritize Classification Class 1 Class 2 Risk Master list of risks Top N KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 76 Risk List of risks Risk Class 3 Risk REV BASIC, 1/02
Risk Analysis Data Flow (2) Statement of risk Context Impact Probability Timeframe Classification Rank Context Analyze • evaluate • classify • prioritize Classification Class 1 Class 2 Risk Master list of risks Top N KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 76 Risk List of risks Risk Class 3 Risk REV BASIC, 1/02
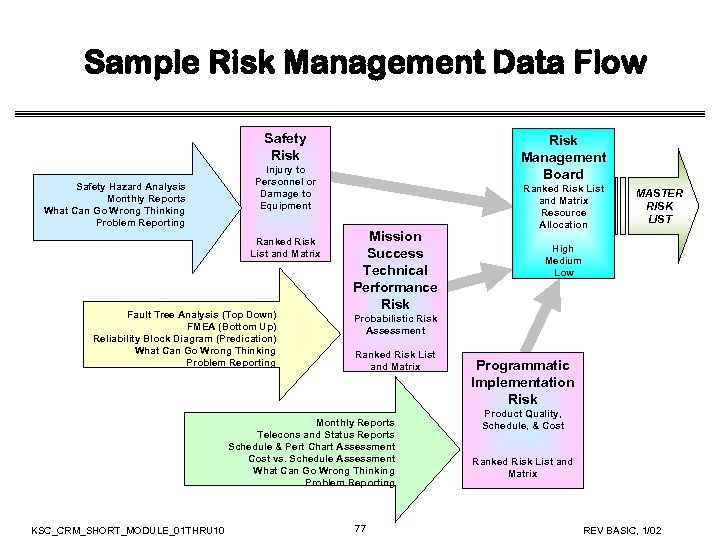 Sample Risk Management Data Flow Safety Risk Safety Hazard Analysis Monthly Reports What Can Go Wrong Thinking Problem Reporting Risk Management Board Injury to Personnel or Damage to Equipment Ranked Risk List and Matrix Fault Tree Analysis (Top Down) FMEA (Bottom Up) Reliability Block Diagram (Predication) What Can Go Wrong Thinking Problem Reporting Mission Success Technical Performance Risk MASTER RISK LIST High Medium Low Probabilistic Risk Assessment Ranked Risk List and Matrix Monthly Reports Telecons and Status Reports Schedule & Pert Chart Assessment Cost vs. Schedule Assessment What Can Go Wrong Thinking Problem Reporting KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 Ranked Risk List and Matrix Resource Allocation 77 Programmatic Implementation Risk Product Quality, Schedule, & Cost Ranked Risk List and Matrix REV BASIC, 1/02
Sample Risk Management Data Flow Safety Risk Safety Hazard Analysis Monthly Reports What Can Go Wrong Thinking Problem Reporting Risk Management Board Injury to Personnel or Damage to Equipment Ranked Risk List and Matrix Fault Tree Analysis (Top Down) FMEA (Bottom Up) Reliability Block Diagram (Predication) What Can Go Wrong Thinking Problem Reporting Mission Success Technical Performance Risk MASTER RISK LIST High Medium Low Probabilistic Risk Assessment Ranked Risk List and Matrix Monthly Reports Telecons and Status Reports Schedule & Pert Chart Assessment Cost vs. Schedule Assessment What Can Go Wrong Thinking Problem Reporting KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 Ranked Risk List and Matrix Resource Allocation 77 Programmatic Implementation Risk Product Quality, Schedule, & Cost Ranked Risk List and Matrix REV BASIC, 1/02
 Risk Information Sheet after Analyze Phase • Risk Information Sheet (RIS) after the CRM Analyze phase KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 78 REV BASIC, 1/02
Risk Information Sheet after Analyze Phase • Risk Information Sheet (RIS) after the CRM Analyze phase KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 78 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Analyze Phase Summary (1) • Evaluate risks at a level that is sufficient to determine the relative importance • Select attribute definitions (e. g. , catastrophic impact, RAC 1) that make sense for your project – document these in the project Risk Management Plan • Classify risks to help the project understand the risks • Group related risks into sets to help build more cost-effective mitigation plans KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 79 REV BASIC, 1/02
Analyze Phase Summary (1) • Evaluate risks at a level that is sufficient to determine the relative importance • Select attribute definitions (e. g. , catastrophic impact, RAC 1) that make sense for your project – document these in the project Risk Management Plan • Classify risks to help the project understand the risks • Group related risks into sets to help build more cost-effective mitigation plans KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 79 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Analyze Phase Summary (2) • Prioritize to determine which risks should be dealt with first when allocating resources • Prioritize the risks based on the criteria for what is most important to the project • Communication is central to • • • Defining project evaluation definitions Evaluating risks Selecting a project classification scheme Classifying risks Defining prioritization criteria Identifying and prioritizing the Top N risks KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 80 REV BASIC, 1/02
Analyze Phase Summary (2) • Prioritize to determine which risks should be dealt with first when allocating resources • Prioritize the risks based on the criteria for what is most important to the project • Communication is central to • • • Defining project evaluation definitions Evaluating risks Selecting a project classification scheme Classifying risks Defining prioritization criteria Identifying and prioritizing the Top N risks KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 80 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Module 5 Plan y tif en Id C ol r ont Pla An al yz e Track Communicate & Document n KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 81 REV BASIC, 1/02
Module 5 Plan y tif en Id C ol r ont Pla An al yz e Track Communicate & Document n KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 81 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Overview • Risk Planning activities • Assigning responsibility • Determining risk mitigation approach • Defining scope and actions • Mitigating a set of related risks KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 82 REV BASIC, 1/02
Overview • Risk Planning activities • Assigning responsibility • Determining risk mitigation approach • Defining scope and actions • Mitigating a set of related risks KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 82 REV BASIC, 1/02
 What Is Risk Planning? • Risk planning is the function of deciding what, if anything, should be done with a risk • Risk planning answers the questions: • • Who does planning? Is it my risk? (responsibility) What can I do? (approach) How much and what should I do? (scope and actions) KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 83 REV BASIC, 1/02
What Is Risk Planning? • Risk planning is the function of deciding what, if anything, should be done with a risk • Risk planning answers the questions: • • Who does planning? Is it my risk? (responsibility) What can I do? (approach) How much and what should I do? (scope and actions) KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 83 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Recording Data on the Risk Information Sheet • Fields to be Completed in Risk Planning Function: • • • Assigned to Mitigation Strategy Contingency Plan and Trigger KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 84 REV BASIC, 1/02
Recording Data on the Risk Information Sheet • Fields to be Completed in Risk Planning Function: • • • Assigned to Mitigation Strategy Contingency Plan and Trigger KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 84 REV BASIC, 1/02
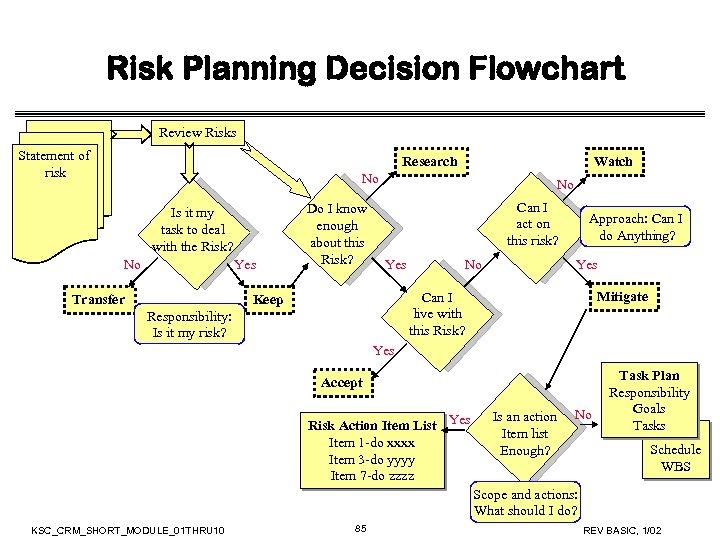 Risk Planning Decision Flowchart Review Risks Statement of risk Research Watch No Is it my task to deal with the Risk? No Yes Transfer Do I know enough about this Risk? No Can I act on this risk? Yes No Approach: Can I do Anything? Yes Mitigate Can I live with this Risk? Keep Responsibility: Is it my risk? Yes Accept Risk Action Item List Yes Item 1 -do xxxx Item 3 -do yyyy Item 7 -do zzzz Is an action Item list Enough? No Task Plan Responsibility Goals Tasks Schedule WBS Scope and actions: What should I do? KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 85 REV BASIC, 1/02
Risk Planning Decision Flowchart Review Risks Statement of risk Research Watch No Is it my task to deal with the Risk? No Yes Transfer Do I know enough about this Risk? No Can I act on this risk? Yes No Approach: Can I do Anything? Yes Mitigate Can I live with this Risk? Keep Responsibility: Is it my risk? Yes Accept Risk Action Item List Yes Item 1 -do xxxx Item 3 -do yyyy Item 7 -do zzzz Is an action Item list Enough? No Task Plan Responsibility Goals Tasks Schedule WBS Scope and actions: What should I do? KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 85 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Project Considerations Regarding Risk Planning • What are the risk attributes? • Is it a Primary Risk? • What is currently important to the project, management, customer, or user? • Are there critical milestones the project is currently is facing? • What limits or constraints do the project, organization, or manager have? • What resources are available for mitigation? • How does the risk fit into the overall project issues and concerns? When is the best time to address or mitigate a risk? KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 86 REV BASIC, 1/02
Project Considerations Regarding Risk Planning • What are the risk attributes? • Is it a Primary Risk? • What is currently important to the project, management, customer, or user? • Are there critical milestones the project is currently is facing? • What limits or constraints do the project, organization, or manager have? • What resources are available for mitigation? • How does the risk fit into the overall project issues and concerns? When is the best time to address or mitigate a risk? KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 86 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Assigning Responsibility for Risk Planning • Purpose: • Ensure that no risks are ignored • Make effective use of expertise and knowledge within the project when planning for risk mitigation • Ensure that risks are being managed by those with the appropriate abilities, knowledge, and authority to commit resources for mitigation • Description: • Involves reviewing the risk(s) and determining who is best able to deal with the risk(s) KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 87 REV BASIC, 1/02
Assigning Responsibility for Risk Planning • Purpose: • Ensure that no risks are ignored • Make effective use of expertise and knowledge within the project when planning for risk mitigation • Ensure that risks are being managed by those with the appropriate abilities, knowledge, and authority to commit resources for mitigation • Description: • Involves reviewing the risk(s) and determining who is best able to deal with the risk(s) KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 87 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Determining Risk Planning Approach • Purpose: • Ensure you know enough to make an informed decision • Pick an appropriate approach for effective management of the risk(s) • Establish measurable mitigation goals that provide a target for evaluating success and direction during the development of action plans • Description: • Involves reviewing the risk(s) and determining the best approach to take KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 88 REV BASIC, 1/02
Determining Risk Planning Approach • Purpose: • Ensure you know enough to make an informed decision • Pick an appropriate approach for effective management of the risk(s) • Establish measurable mitigation goals that provide a target for evaluating success and direction during the development of action plans • Description: • Involves reviewing the risk(s) and determining the best approach to take KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 88 REV BASIC, 1/02
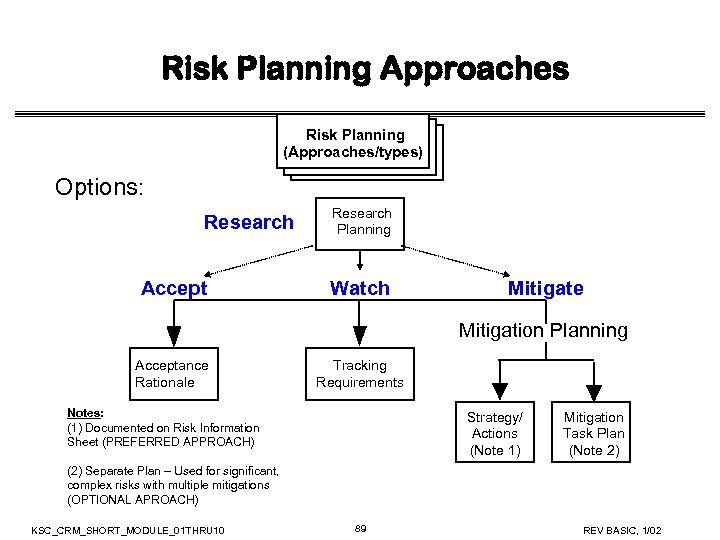 Risk Planning Approaches Risk Planning (Approaches/types) Options: Research Accept Research Planning Watch Mitigate Mitigation Planning Acceptance Rationale Tracking Requirements Notes: (1) Documented on Risk Information Sheet (PREFERRED APPROACH) Strategy/ Actions (Note 1) Mitigation Task Plan (Note 2) (2) Separate Plan – Used for significant, complex risks with multiple mitigations (OPTIONAL APROACH) KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 89 REV BASIC, 1/02
Risk Planning Approaches Risk Planning (Approaches/types) Options: Research Accept Research Planning Watch Mitigate Mitigation Planning Acceptance Rationale Tracking Requirements Notes: (1) Documented on Risk Information Sheet (PREFERRED APPROACH) Strategy/ Actions (Note 1) Mitigation Task Plan (Note 2) (2) Separate Plan – Used for significant, complex risks with multiple mitigations (OPTIONAL APROACH) KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 89 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Contingency Planning • Not all risk mitigation strategies can or should be carried out immediately, for example: • There may not be sufficient funding at this time • Other circumstance (available personnel) may not be right • Risk may be low probability, catastrophic impact with an expensive mitigation strategy • Current strategy might not be working • May need to develop a contingency risk mitigation strategy (to be used as Plan B if Plan A fails) • Contingency risk mitigation strategy plans are held in reserve until specific trigger conditions are true or certain events occur • Watch for the conditions and events! KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 90 REV BASIC, 1/02
Contingency Planning • Not all risk mitigation strategies can or should be carried out immediately, for example: • There may not be sufficient funding at this time • Other circumstance (available personnel) may not be right • Risk may be low probability, catastrophic impact with an expensive mitigation strategy • Current strategy might not be working • May need to develop a contingency risk mitigation strategy (to be used as Plan B if Plan A fails) • Contingency risk mitigation strategy plans are held in reserve until specific trigger conditions are true or certain events occur • Watch for the conditions and events! KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 90 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Defining Scope and Actions for Risk Mitigation Strategies • Purpose: • Take a balanced approach in developing effective actions to mitigate risks • Description: • Involves reviewing the risk(s) and determining the appropriate level of mitigation to take and the goal of the mitigation KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 91 REV BASIC, 1/02
Defining Scope and Actions for Risk Mitigation Strategies • Purpose: • Take a balanced approach in developing effective actions to mitigate risks • Description: • Involves reviewing the risk(s) and determining the appropriate level of mitigation to take and the goal of the mitigation KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 91 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Determining Risk Mitigation Goals and Success Measures • There is a need to set realistic, measurable (or verifiable) goals for mitigating individual risks: • Avoid changes to scheduled milestones • Eliminate change requests unsupported by funding to implement the change • Define mitigation success criteria – it is important to know when you’ve succeeded or failed in mitigating risks • All current change requests implemented by DD/MM/YY, with no change to scheduled milestones KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 92 REV BASIC, 1/02
Determining Risk Mitigation Goals and Success Measures • There is a need to set realistic, measurable (or verifiable) goals for mitigating individual risks: • Avoid changes to scheduled milestones • Eliminate change requests unsupported by funding to implement the change • Define mitigation success criteria – it is important to know when you’ve succeeded or failed in mitigating risks • All current change requests implemented by DD/MM/YY, with no change to scheduled milestones KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 92 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Discussion -- Risk Mitigation Goals and Success Measures Risk 7 • Science requirements have substantial TBDs; late completion of TBDs likely, with reduction in adequate testing time, possible science application software failure, incorrect science data being captured, hardware damage if incorrect safety limits were provided, extensive rework and substantial cost overruns, mission failure if problems not found before system is in operation • What risk mitigation goals and success measures would you look for? KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 93 REV BASIC, 1/02
Discussion -- Risk Mitigation Goals and Success Measures Risk 7 • Science requirements have substantial TBDs; late completion of TBDs likely, with reduction in adequate testing time, possible science application software failure, incorrect science data being captured, hardware damage if incorrect safety limits were provided, extensive rework and substantial cost overruns, mission failure if problems not found before system is in operation • What risk mitigation goals and success measures would you look for? KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 93 REV BASIC, 1/02
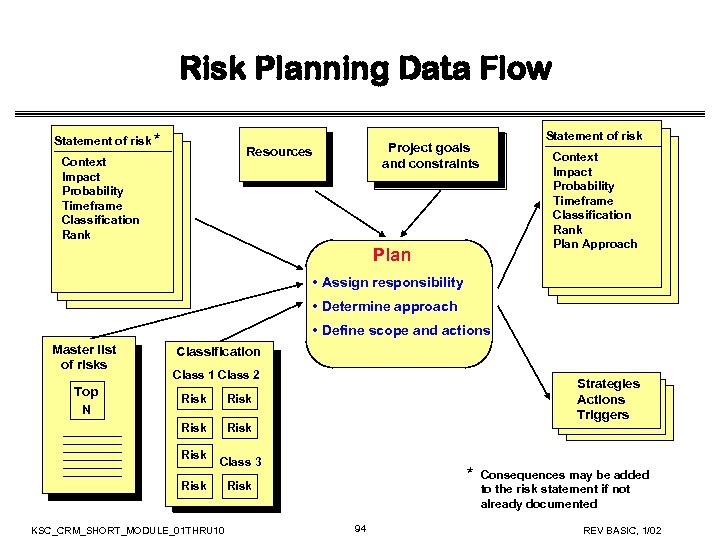 Risk Planning Data Flow Statement of risk * Resources Context Impact Probability Timeframe Classification Rank Statement of risk Project goals and constraints Context Impact Probability Timeframe Classification Rank Plan Approach Plan • Assign responsibility • Determine approach • Define scope and actions Master list of risks Top N Classification Class 1 Class 2 Risk Strategies Actions Triggers Risk Class 3 Risk KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 * Risk 94 Consequences may be added to the risk statement if not already documented REV BASIC, 1/02
Risk Planning Data Flow Statement of risk * Resources Context Impact Probability Timeframe Classification Rank Statement of risk Project goals and constraints Context Impact Probability Timeframe Classification Rank Plan Approach Plan • Assign responsibility • Determine approach • Define scope and actions Master list of risks Top N Classification Class 1 Class 2 Risk Strategies Actions Triggers Risk Class 3 Risk KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 * Risk 94 Consequences may be added to the risk statement if not already documented REV BASIC, 1/02
 Risk Information Sheet (After the Risk Planning Phase) • Risk Information Sheet (RIS) after the CRM Risk Planning phase KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 95 REV BASIC, 1/02
Risk Information Sheet (After the Risk Planning Phase) • Risk Information Sheet (RIS) after the CRM Risk Planning phase KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 95 REV BASIC, 1/02
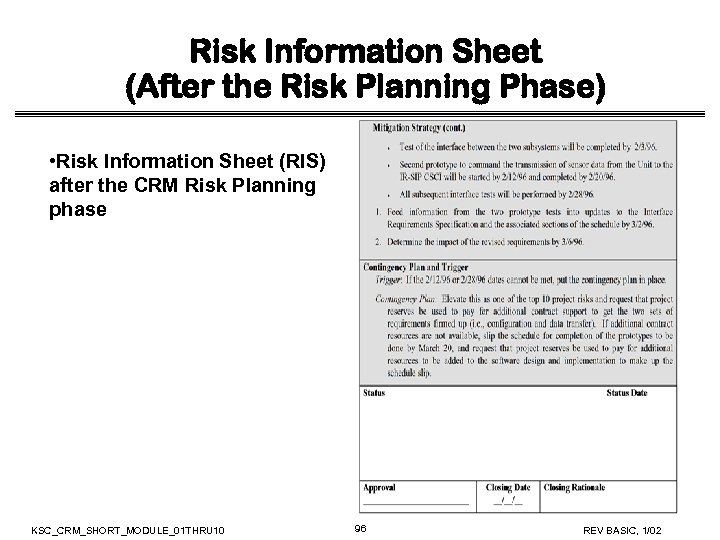 Risk Information Sheet (After the Risk Planning Phase) • Risk Information Sheet (RIS) after the CRM Risk Planning phase KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 96 REV BASIC, 1/02
Risk Information Sheet (After the Risk Planning Phase) • Risk Information Sheet (RIS) after the CRM Risk Planning phase KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 96 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Risk Planning Phase Summary (1) • The result of risk planning is a documented decision about what should be done with each risk • The risk planning approach, as well as the mitigation strategy-related details are documented on the Risk Information Sheet. The risk planning approaches and their related risk planning documentation are: • • Research (Research Planning) Accept (Acceptance Rationale) Watch (Tracking Requirements) Mitigate (Mitigation Strategy, Actions, Completion Dates, Triggers, Contingency Strategies) KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 97 REV BASIC, 1/02
Risk Planning Phase Summary (1) • The result of risk planning is a documented decision about what should be done with each risk • The risk planning approach, as well as the mitigation strategy-related details are documented on the Risk Information Sheet. The risk planning approaches and their related risk planning documentation are: • • Research (Research Planning) Accept (Acceptance Rationale) Watch (Tracking Requirements) Mitigate (Mitigation Strategy, Actions, Completion Dates, Triggers, Contingency Strategies) KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 97 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Risk Planning Phase Summary (2) • Mitigate unacceptable risks to the project • You can’t mitigate all risks – but you need to understand which risks you are taking • Watch the risks that you can’t currently mitigate and don’t want to accept • Unassigned tasks tend to fall through the cracks • Don’t over plan – documentation of mitigation strategy actions on the Risk Information Sheet is sufficient for almost all identified project risks KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 98 REV BASIC, 1/02
Risk Planning Phase Summary (2) • Mitigate unacceptable risks to the project • You can’t mitigate all risks – but you need to understand which risks you are taking • Watch the risks that you can’t currently mitigate and don’t want to accept • Unassigned tasks tend to fall through the cracks • Don’t over plan – documentation of mitigation strategy actions on the Risk Information Sheet is sufficient for almost all identified project risks KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 98 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Module 6 Track y tif en Id C ol r ont Pla An al yz e Track Communicate & Document n KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 99 REV BASIC, 1/02
Module 6 Track y tif en Id C ol r ont Pla An al yz e Track Communicate & Document n KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 99 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Overview • Tracking activities • Acquiring Data • Compiling and Evaluating Data • Reporting Status (planning, risks) KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 100 REV BASIC, 1/02
Overview • Tracking activities • Acquiring Data • Compiling and Evaluating Data • Reporting Status (planning, risks) KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 100 REV BASIC, 1/02
 What do We Mean by Tracking? • Tracking • A process for watched and mitigated risks where related data are acquired, compiled, analyzed, and reported • Risks can be tracked individually or in sets KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 101 REV BASIC, 1/02
What do We Mean by Tracking? • Tracking • A process for watched and mitigated risks where related data are acquired, compiled, analyzed, and reported • Risks can be tracked individually or in sets KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 101 REV BASIC, 1/02
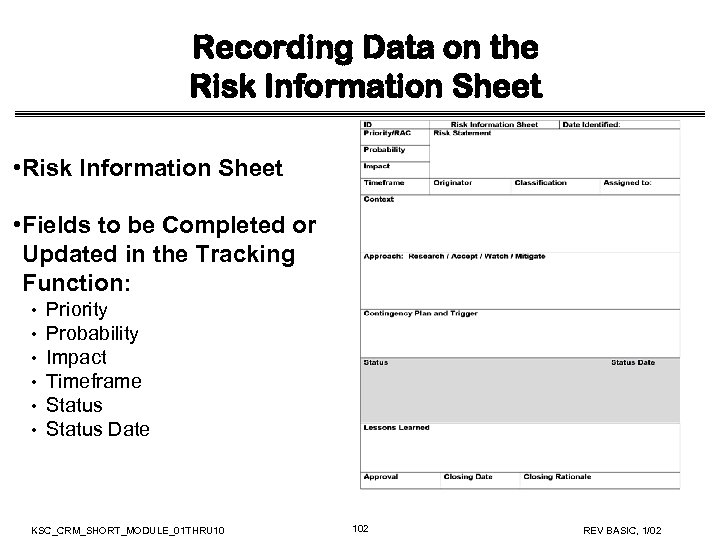 Recording Data on the Risk Information Sheet • Fields to be Completed or Updated in the Tracking Function: • • • Priority Probability Impact Timeframe Status Date KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 102 REV BASIC, 1/02
Recording Data on the Risk Information Sheet • Fields to be Completed or Updated in the Tracking Function: • • • Priority Probability Impact Timeframe Status Date KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 102 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Tracking Risks and Mitigation Strategies • Tracking risk mitigation strategies will indicate • Whether the mitigation strategy is being executed correctly • If risk mitigation is on schedule (including action items) • Tracking individual risk attributes will indicate • Mitigation strategy effectiveness • Is the impact/probability reduced? KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 103 REV BASIC, 1/02
Tracking Risks and Mitigation Strategies • Tracking risk mitigation strategies will indicate • Whether the mitigation strategy is being executed correctly • If risk mitigation is on schedule (including action items) • Tracking individual risk attributes will indicate • Mitigation strategy effectiveness • Is the impact/probability reduced? KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 103 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Risk Metrics • Risk Metrics are used to: • Measure attributes of a risk - Impact, probability, and timeframe - Other risk- or project-specific attributes • Provide meaningful information to enable more informed control decisions • Assess the impact or success of a mitigation strategy • Identify new risks (if indicated by the risk metrics) KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 104 REV BASIC, 1/02
Risk Metrics • Risk Metrics are used to: • Measure attributes of a risk - Impact, probability, and timeframe - Other risk- or project-specific attributes • Provide meaningful information to enable more informed control decisions • Assess the impact or success of a mitigation strategy • Identify new risks (if indicated by the risk metrics) KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 104 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Acquiring Data • Purpose • To collect tracking data for a given risk • Description • A process that includes all of the steps associated with collecting information about and updating the values of risk measures and status indicators for watched and mitigated risks KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 105 REV BASIC, 1/02
Acquiring Data • Purpose • To collect tracking data for a given risk • Description • A process that includes all of the steps associated with collecting information about and updating the values of risk measures and status indicators for watched and mitigated risks KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 105 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Considerations When Acquiring Data • Status information is only as good as its accuracy and timeliness • Stale data are more dangerous to decision makers than no data at all • When a group of indicators is required, all of the data must be acquired from the same time period • Collect just the data needed to track the project’s risks. Collect only what you need and use what you collect KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 106 REV BASIC, 1/02
Considerations When Acquiring Data • Status information is only as good as its accuracy and timeliness • Stale data are more dangerous to decision makers than no data at all • When a group of indicators is required, all of the data must be acquired from the same time period • Collect just the data needed to track the project’s risks. Collect only what you need and use what you collect KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 106 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Data Acquisition (Metrics Examples) • Requirements • Ambiguity = Weak Phrases and/or Optional Language • Measure of Completeness = TBD + TBA + TBR • Design and Implementation • Structure/Architecture = Complexity and Size • Testing • Problem Reporting Tracking = Open, Closed, Severity • Defect Density • Process • Schedule = Effort, Completion Rates • Budget KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 107 REV BASIC, 1/02
Data Acquisition (Metrics Examples) • Requirements • Ambiguity = Weak Phrases and/or Optional Language • Measure of Completeness = TBD + TBA + TBR • Design and Implementation • Structure/Architecture = Complexity and Size • Testing • Problem Reporting Tracking = Open, Closed, Severity • Defect Density • Process • Schedule = Effort, Completion Rates • Budget KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 107 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Compiling and Evaluating Data • Purpose • Organize and understand the relevant tracking data for a given risk • Description • A process in which data for a given risk is combined, calculated, organized, and interpreted for the tracking of a risk and its associated mitigation strategy KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 108 REV BASIC, 1/02
Compiling and Evaluating Data • Purpose • Organize and understand the relevant tracking data for a given risk • Description • A process in which data for a given risk is combined, calculated, organized, and interpreted for the tracking of a risk and its associated mitigation strategy KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 108 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Triggers/Thresholds • A value of an indicator that specifies the level at which an action, such as implementing a contingency plan, may need to be taken • Triggers and thresholds are generally used to • Provide early warning of an impending critical event • Indicate the need to implement a contingency plan to preempt a problem • Request immediate attention for a risk • Triggers and thresholds are effective if • They do not trip unnecessarily • They are easy to calculate and report KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 109 REV BASIC, 1/02
Triggers/Thresholds • A value of an indicator that specifies the level at which an action, such as implementing a contingency plan, may need to be taken • Triggers and thresholds are generally used to • Provide early warning of an impending critical event • Indicate the need to implement a contingency plan to preempt a problem • Request immediate attention for a risk • Triggers and thresholds are effective if • They do not trip unnecessarily • They are easy to calculate and report KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 109 REV BASIC, 1/02
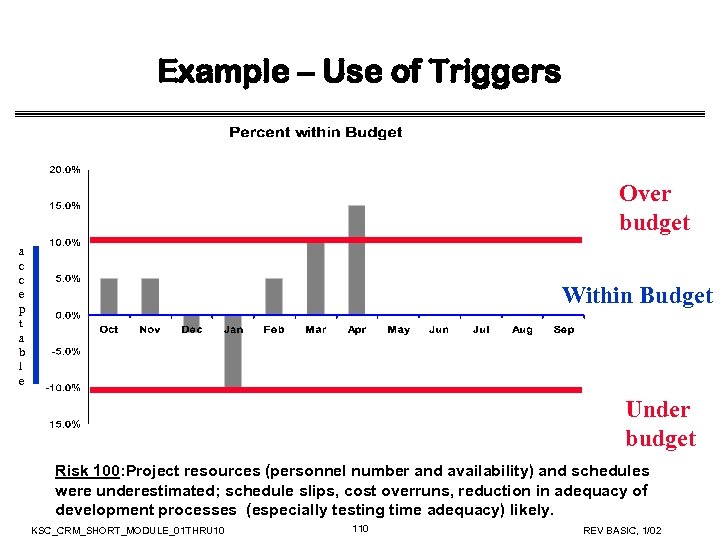 Example – Use of Triggers Over budget a c c e p t a b l e Within Budget Under budget Risk 100: Project resources (personnel number and availability) and schedules were underestimated; schedule slips, cost overruns, reduction in adequacy of development processes (especially testing time adequacy) likely. KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 110 REV BASIC, 1/02
Example – Use of Triggers Over budget a c c e p t a b l e Within Budget Under budget Risk 100: Project resources (personnel number and availability) and schedules were underestimated; schedule slips, cost overruns, reduction in adequacy of development processes (especially testing time adequacy) likely. KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 110 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Process (Metrics Example) • Risk # 6: Project software schedule and resources were underestimated; schedule slips, reduction in adequate testing time • Data to be collected • Effort per activity • Trigger • Exceeds expected percentages KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 111 REV BASIC, 1/02
Process (Metrics Example) • Risk # 6: Project software schedule and resources were underestimated; schedule slips, reduction in adequate testing time • Data to be collected • Effort per activity • Trigger • Exceeds expected percentages KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 111 REV BASIC, 1/02
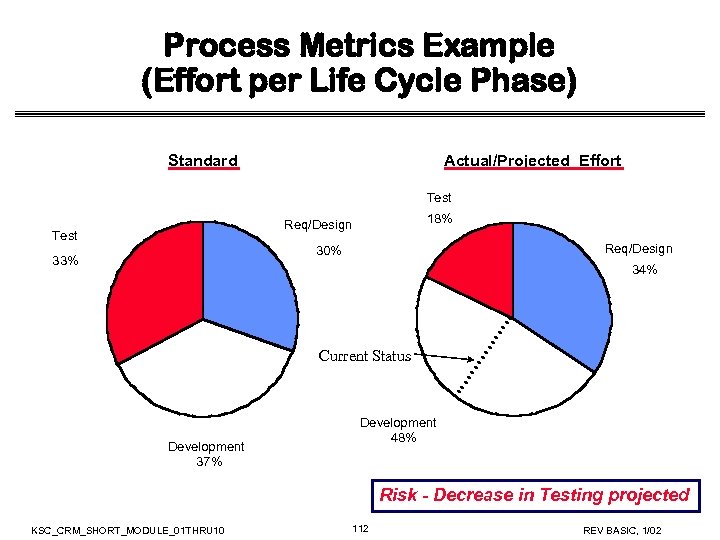 Process Metrics Example (Effort per Life Cycle Phase) Standard Actual/Projected Effort Test 18% Req/Design Test Req/Design 30% 33% 34% Current Status Development 37% Development 48% Risk - Decrease in Testing projected KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 112 REV BASIC, 1/02
Process Metrics Example (Effort per Life Cycle Phase) Standard Actual/Projected Effort Test 18% Req/Design Test Req/Design 30% 33% 34% Current Status Development 37% Development 48% Risk - Decrease in Testing projected KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 112 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Reporting Data • Purpose • Communicate risk status reports to support effective decision making (inputs for the “Control” function) • Description • A process in which status information about risks and mitigation strategies is communicated to decision makers and team members KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 113 REV BASIC, 1/02
Reporting Data • Purpose • Communicate risk status reports to support effective decision making (inputs for the “Control” function) • Description • A process in which status information about risks and mitigation strategies is communicated to decision makers and team members KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 113 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Reporting Considerations • What information needs to be reported? • What presentation formats best present the analyzed data? • Does the information and the format of the report provide the basis needed by decision makers? KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 114 REV BASIC, 1/02
Reporting Considerations • What information needs to be reported? • What presentation formats best present the analyzed data? • Does the information and the format of the report provide the basis needed by decision makers? KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 114 REV BASIC, 1/02
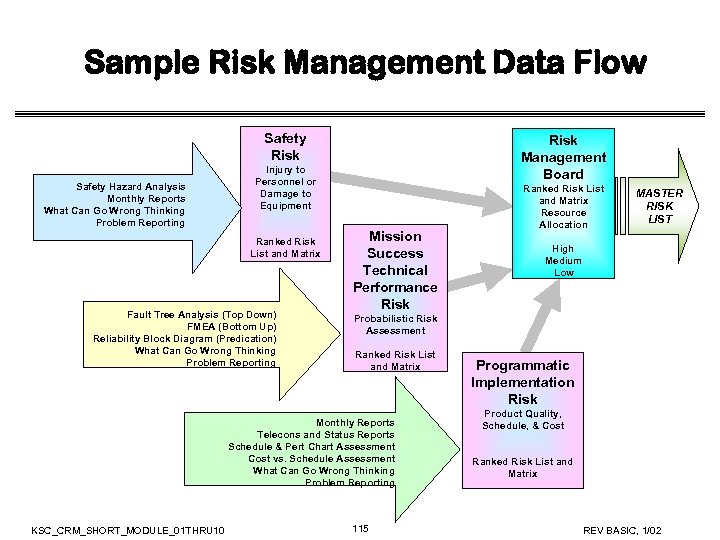 Sample Risk Management Data Flow Safety Risk Safety Hazard Analysis Monthly Reports What Can Go Wrong Thinking Problem Reporting Risk Management Board Injury to Personnel or Damage to Equipment Ranked Risk List and Matrix Fault Tree Analysis (Top Down) FMEA (Bottom Up) Reliability Block Diagram (Predication) What Can Go Wrong Thinking Problem Reporting Mission Success Technical Performance Risk MASTER RISK LIST High Medium Low Probabilistic Risk Assessment Ranked Risk List and Matrix Monthly Reports Telecons and Status Reports Schedule & Pert Chart Assessment Cost vs. Schedule Assessment What Can Go Wrong Thinking Problem Reporting KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 Ranked Risk List and Matrix Resource Allocation 115 Programmatic Implementation Risk Product Quality, Schedule, & Cost Ranked Risk List and Matrix REV BASIC, 1/02
Sample Risk Management Data Flow Safety Risk Safety Hazard Analysis Monthly Reports What Can Go Wrong Thinking Problem Reporting Risk Management Board Injury to Personnel or Damage to Equipment Ranked Risk List and Matrix Fault Tree Analysis (Top Down) FMEA (Bottom Up) Reliability Block Diagram (Predication) What Can Go Wrong Thinking Problem Reporting Mission Success Technical Performance Risk MASTER RISK LIST High Medium Low Probabilistic Risk Assessment Ranked Risk List and Matrix Monthly Reports Telecons and Status Reports Schedule & Pert Chart Assessment Cost vs. Schedule Assessment What Can Go Wrong Thinking Problem Reporting KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 Ranked Risk List and Matrix Resource Allocation 115 Programmatic Implementation Risk Product Quality, Schedule, & Cost Ranked Risk List and Matrix REV BASIC, 1/02
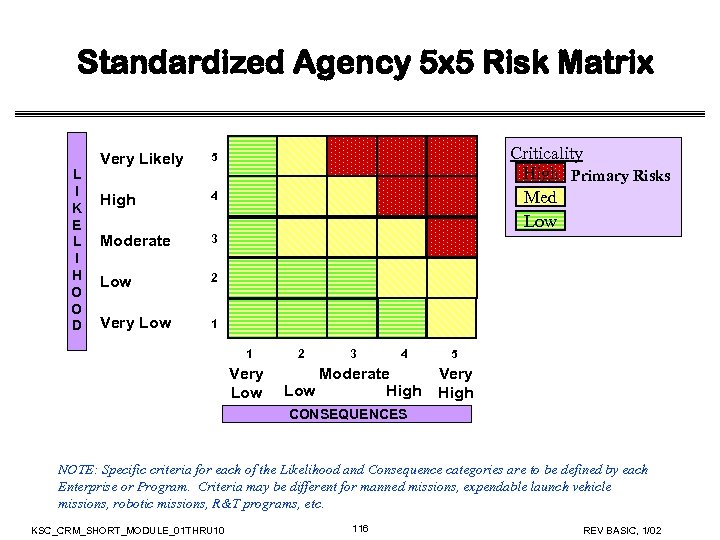 Standardized Agency 5 x 5 Risk Matrix L I K E L I H O O D Very Likely High 4 Moderate 3 Low 2 Very Low Criticality High Primary Risks Med Low 5 1 1 Very Low 2 3 4 Moderate Low High 5 Very High CONSEQUENCES NOTE: Specific criteria for each of the Likelihood and Consequence categories are to be defined by each Enterprise or Program. Criteria may be different for manned missions, expendable launch vehicle missions, robotic missions, R&T programs, etc. KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 116 REV BASIC, 1/02
Standardized Agency 5 x 5 Risk Matrix L I K E L I H O O D Very Likely High 4 Moderate 3 Low 2 Very Low Criticality High Primary Risks Med Low 5 1 1 Very Low 2 3 4 Moderate Low High 5 Very High CONSEQUENCES NOTE: Specific criteria for each of the Likelihood and Consequence categories are to be defined by each Enterprise or Program. Criteria may be different for manned missions, expendable launch vehicle missions, robotic missions, R&T programs, etc. KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 116 REV BASIC, 1/02
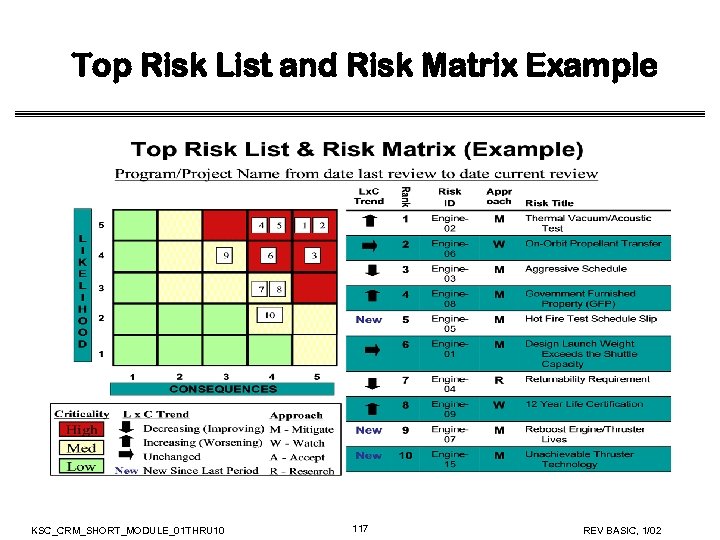 Top Risk List and Risk Matrix Example KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 117 REV BASIC, 1/02
Top Risk List and Risk Matrix Example KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 117 REV BASIC, 1/02
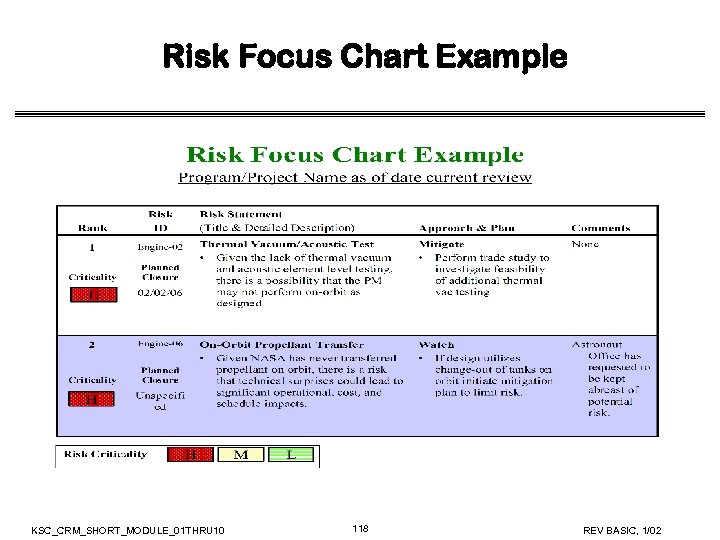 Risk Focus Chart Example KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 118 REV BASIC, 1/02
Risk Focus Chart Example KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 118 REV BASIC, 1/02
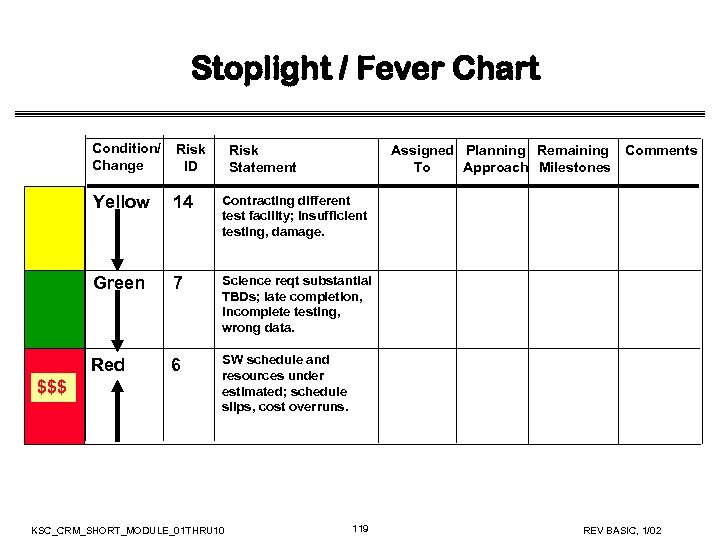 Stoplight / Fever Chart Condition/ Change Yellow 14 Contracting different test facility; insufficient testing, damage. Green 7 Science reqt substantial TBDs; late completion, incomplete testing, wrong data. Red $$$ Risk ID 6 SW schedule and resources under estimated; schedule slips, cost overruns. Risk Statement KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 Assigned Planning Remaining Comments To Approach Milestones 119 REV BASIC, 1/02
Stoplight / Fever Chart Condition/ Change Yellow 14 Contracting different test facility; insufficient testing, damage. Green 7 Science reqt substantial TBDs; late completion, incomplete testing, wrong data. Red $$$ Risk ID 6 SW schedule and resources under estimated; schedule slips, cost overruns. Risk Statement KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 Assigned Planning Remaining Comments To Approach Milestones 119 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Reporting Schedule • Reports are generally delivered as part of routine project management activities: • Weekly status meetings • Monthly project meetings • The frequency of reporting depends on: • The reporting requirements for each risk or risk set • The manner in which the report will be used • Exception reporting may be necessary KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 120 REV BASIC, 1/02
Reporting Schedule • Reports are generally delivered as part of routine project management activities: • Weekly status meetings • Monthly project meetings • The frequency of reporting depends on: • The reporting requirements for each risk or risk set • The manner in which the report will be used • Exception reporting may be necessary KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 120 REV BASIC, 1/02
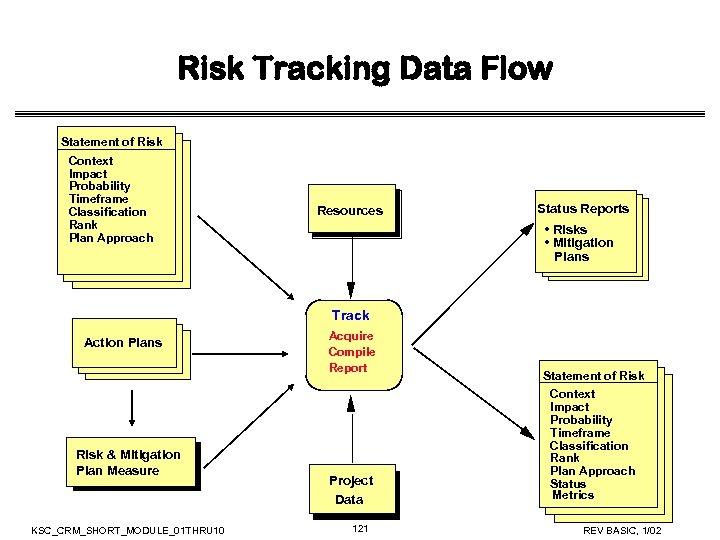 Risk Tracking Data Flow Statement of Risk Context Impact Probability Timeframe Classification Rank Plan Approach Resources Status Reports • Risks • Mitigation Plans Track Action Plans Risk & Mitigation Plan Measure KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 Acquire Compile Report Project Data 121 Statement of Risk Context Impact Probability Timeframe Classification Rank Plan Approach Status Metrics REV BASIC, 1/02
Risk Tracking Data Flow Statement of Risk Context Impact Probability Timeframe Classification Rank Plan Approach Resources Status Reports • Risks • Mitigation Plans Track Action Plans Risk & Mitigation Plan Measure KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 Acquire Compile Report Project Data 121 Statement of Risk Context Impact Probability Timeframe Classification Rank Plan Approach Status Metrics REV BASIC, 1/02
 Tracking Phase Summary • Tracking reports communicate information required for effective control decisions • Tracking information and reports can include quantitative indicator data as well as more subjective information (e. g. , recommendations) • Tracking information is not limited to formal reporting mechanisms • Informal reporting of risk-related information by all project personnel can aid decision making • Risk tracking should be integrated with standard management practices – risk management should be tailored for a project KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 122 REV BASIC, 1/02
Tracking Phase Summary • Tracking reports communicate information required for effective control decisions • Tracking information and reports can include quantitative indicator data as well as more subjective information (e. g. , recommendations) • Tracking information is not limited to formal reporting mechanisms • Informal reporting of risk-related information by all project personnel can aid decision making • Risk tracking should be integrated with standard management practices – risk management should be tailored for a project KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 122 REV BASIC, 1/02
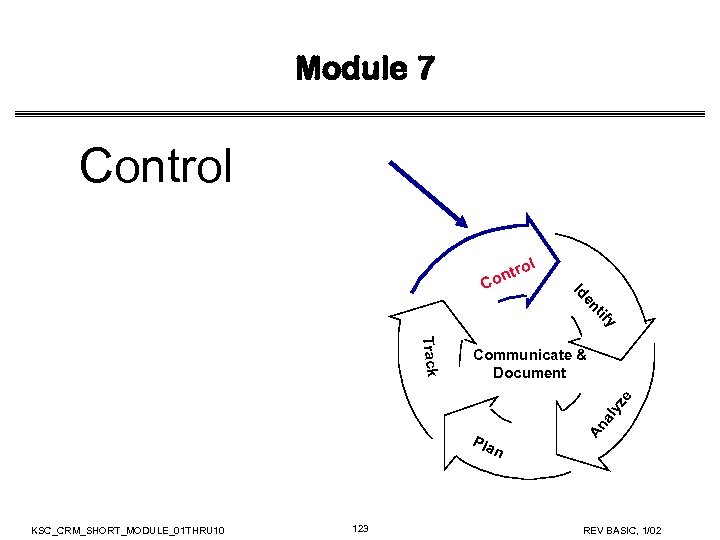 Module 7 Control ol r ont y tif en Id C Pla An al yz e Track Communicate & Document n KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 123 REV BASIC, 1/02
Module 7 Control ol r ont y tif en Id C Pla An al yz e Track Communicate & Document n KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 123 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Control Overview • Control activities • Evaluate tracking results • Decide on course of action • Execute control actions KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 124 REV BASIC, 1/02
Control Overview • Control activities • Evaluate tracking results • Decide on course of action • Execute control actions KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 124 REV BASIC, 1/02
 What is Control? • Control • A process in which decisions are made based on the data presented in the tracking reports • Risks can be controlled individually or in sets KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 125 REV BASIC, 1/02
What is Control? • Control • A process in which decisions are made based on the data presented in the tracking reports • Risks can be controlled individually or in sets KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 125 REV BASIC, 1/02
 What Is Effective Control? • Monitoring the quality of risk mitigation execution • Assessing the effectiveness of mitigation strategies • Assessing significant changes in risks and trends • Determining appropriate responses • Executing the plan of attack • Communicating the above information KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 126 REV BASIC, 1/02
What Is Effective Control? • Monitoring the quality of risk mitigation execution • Assessing the effectiveness of mitigation strategies • Assessing significant changes in risks and trends • Determining appropriate responses • Executing the plan of attack • Communicating the above information KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 126 REV BASIC, 1/02
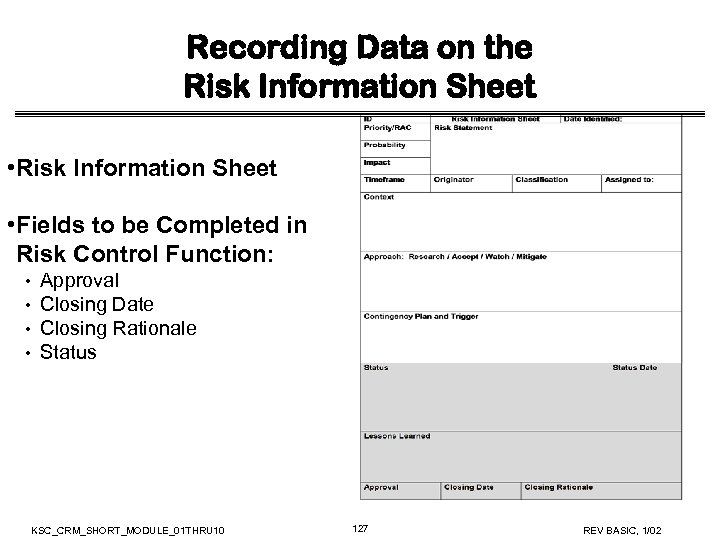 Recording Data on the Risk Information Sheet • Fields to be Completed in Risk Control Function: • • Approval Closing Date Closing Rationale Status KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 127 REV BASIC, 1/02
Recording Data on the Risk Information Sheet • Fields to be Completed in Risk Control Function: • • Approval Closing Date Closing Rationale Status KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 127 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Evaluate Tracking Results • Purpose • Allows decision makers to identify significant changes in risks, to assess the effectiveness of mitigation strategies, and to accurately determine the best courses of action • Description • Uses tracking data to reassess project risks for trends, deviations, and anomalies KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 128 REV BASIC, 1/02
Evaluate Tracking Results • Purpose • Allows decision makers to identify significant changes in risks, to assess the effectiveness of mitigation strategies, and to accurately determine the best courses of action • Description • Uses tracking data to reassess project risks for trends, deviations, and anomalies KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 128 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Metric Trend Analysis • The Risk Management Plan can document which project metrics to track • Trend and data analysis of project metrics can be used to identify new risks • Trends can be observed through the evaluation of successive reports • Persistent lateness in taking action • Oscillating priority values • Significant changes in the number of high impact risks or risks of a particular type KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 129 REV BASIC, 1/02
Metric Trend Analysis • The Risk Management Plan can document which project metrics to track • Trend and data analysis of project metrics can be used to identify new risks • Trends can be observed through the evaluation of successive reports • Persistent lateness in taking action • Oscillating priority values • Significant changes in the number of high impact risks or risks of a particular type KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 129 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Trending Metrics Example • Given concerns about unstable or incomplete requirements, which metrics might be useful in controlling this risk area? • Risk #7 – Science requirements have substantial TBDs; late completion of TBDs likely, with reduction in adequate testing time, possible science application software failure, incorrect science data being captured, hardware damage if incorrect safety limits were provided, extensive rework and substantial cost overruns, mission failure if problems not found before system is operational • What data would you collect? What trends would you expect to see evolve? KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 130 REV BASIC, 1/02
Trending Metrics Example • Given concerns about unstable or incomplete requirements, which metrics might be useful in controlling this risk area? • Risk #7 – Science requirements have substantial TBDs; late completion of TBDs likely, with reduction in adequate testing time, possible science application software failure, incorrect science data being captured, hardware damage if incorrect safety limits were provided, extensive rework and substantial cost overruns, mission failure if problems not found before system is operational • What data would you collect? What trends would you expect to see evolve? KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 130 REV BASIC, 1/02
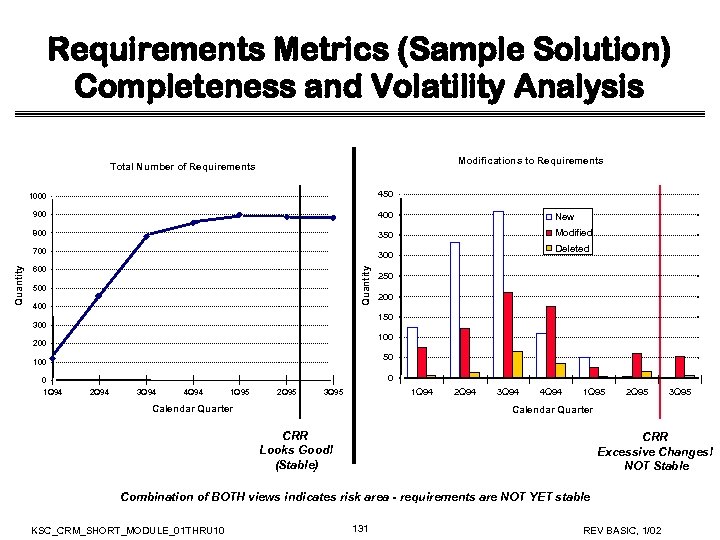 Requirements Metrics (Sample Solution) Completeness and Volatility Analysis Modifications to Requirements Total Number of Requirements 450 900 400 New 800 350 Modified 700 300 600 Quantity 1000 500 400 250 200 150 300 100 200 50 100 0 1 Q 94 Deleted 0 2 Q 94 3 Q 94 4 Q 94 1 Q 95 2 Q 95 1 Q 94 3 Q 95 Calendar Quarter 2 Q 94 3 Q 94 4 Q 94 1 Q 95 2 Q 95 Calendar Quarter CRR Looks Good! (Stable) CRR Excessive Changes! NOT Stable Combination of BOTH views indicates risk area - requirements are NOT YET stable KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 3 Q 95 131 REV BASIC, 1/02
Requirements Metrics (Sample Solution) Completeness and Volatility Analysis Modifications to Requirements Total Number of Requirements 450 900 400 New 800 350 Modified 700 300 600 Quantity 1000 500 400 250 200 150 300 100 200 50 100 0 1 Q 94 Deleted 0 2 Q 94 3 Q 94 4 Q 94 1 Q 95 2 Q 95 1 Q 94 3 Q 95 Calendar Quarter 2 Q 94 3 Q 94 4 Q 94 1 Q 95 2 Q 95 Calendar Quarter CRR Looks Good! (Stable) CRR Excessive Changes! NOT Stable Combination of BOTH views indicates risk area - requirements are NOT YET stable KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 3 Q 95 131 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Decide on Course of Action • Purpose • Ensure that project risks continue to be managed effectively • Description • Uses tracking data to determine how to proceed with project risks - Close the risk - Continue tracking and executing the current mitigation strategies - Re-plan risk mitigation - Invoke an alternate mitigation strategy (e. g. , use a contingency plan) KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 132 REV BASIC, 1/02
Decide on Course of Action • Purpose • Ensure that project risks continue to be managed effectively • Description • Uses tracking data to determine how to proceed with project risks - Close the risk - Continue tracking and executing the current mitigation strategies - Re-plan risk mitigation - Invoke an alternate mitigation strategy (e. g. , use a contingency plan) KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 132 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Execute Control Actions • Purpose • Implement both the decision made about a risk and mitigation strategy as well as to ensure that all decisions are appropriately documented for future reference and historical record maintenance • Ensure approval and resources are allocated • Description • The process where control decisions are implemented KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 133 REV BASIC, 1/02
Execute Control Actions • Purpose • Implement both the decision made about a risk and mitigation strategy as well as to ensure that all decisions are appropriately documented for future reference and historical record maintenance • Ensure approval and resources are allocated • Description • The process where control decisions are implemented KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 133 REV BASIC, 1/02
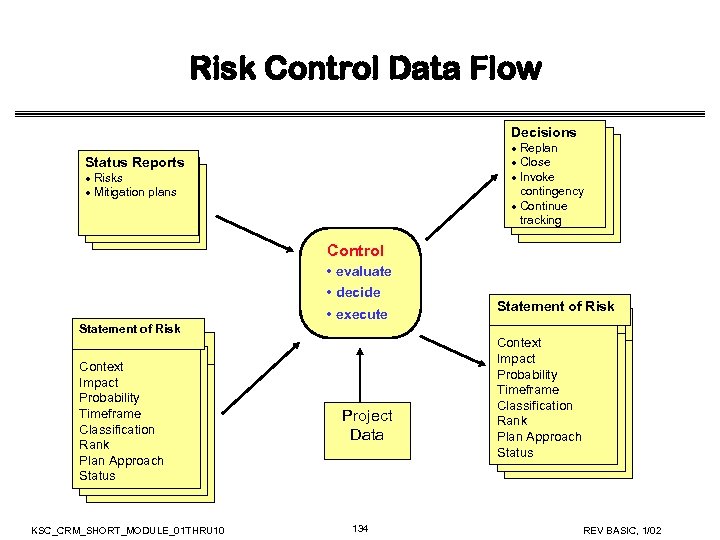 Risk Control Data Flow Decisions · Replan · Close · Invoke contingency · Continue tracking Status Reports · Risks · Mitigation plans Control • evaluate • decide • execute Statement of Risk Context Impact Probability Timeframe Classification Rank Plan Approach Status KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 Project Data 134 Statement of Risk Context Impact Probability Timeframe Classification Rank Plan Approach Status REV BASIC, 1/02
Risk Control Data Flow Decisions · Replan · Close · Invoke contingency · Continue tracking Status Reports · Risks · Mitigation plans Control • evaluate • decide • execute Statement of Risk Context Impact Probability Timeframe Classification Rank Plan Approach Status KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 Project Data 134 Statement of Risk Context Impact Probability Timeframe Classification Rank Plan Approach Status REV BASIC, 1/02
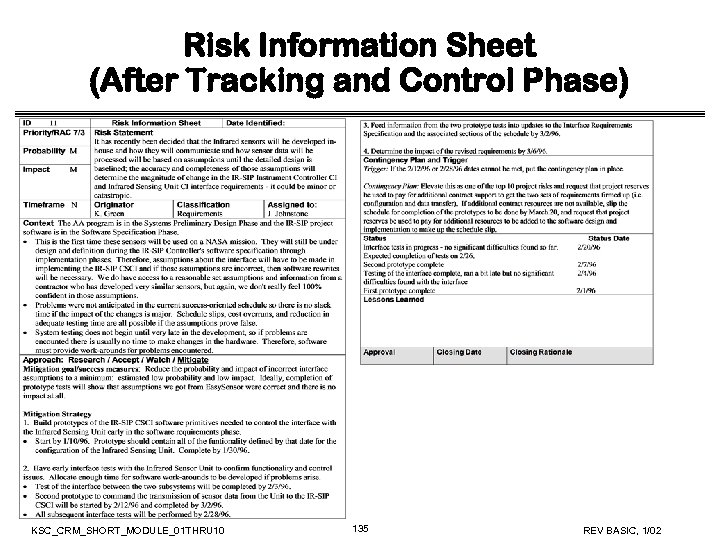 Risk Information Sheet (After Tracking and Control Phase) KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 135 REV BASIC, 1/02
Risk Information Sheet (After Tracking and Control Phase) KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 135 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Risk Control Phase Summary • Control Decisions are based on current information as well as experience, and are required to respond to changing conditions in watched and mitigated risks • Risk tracking and control should be integrated with standard project management practices – risk management should be tailored for a project KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 136 REV BASIC, 1/02
Risk Control Phase Summary • Control Decisions are based on current information as well as experience, and are required to respond to changing conditions in watched and mitigated risks • Risk tracking and control should be integrated with standard project management practices – risk management should be tailored for a project KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 136 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Module 8 Communicate & Document y tif en Id C ol r ont Pla An al yz e Track Communicate Document n KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 137 REV BASIC, 1/02
Module 8 Communicate & Document y tif en Id C ol r ont Pla An al yz e Track Communicate Document n KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 137 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Overview • What is communication? • Relationship to other CRM Process functions • Enablers to communication • Barriers to communication • Documentation of risks KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 138 REV BASIC, 1/02
Overview • What is communication? • Relationship to other CRM Process functions • Enablers to communication • Barriers to communication • Documentation of risks KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 138 REV BASIC, 1/02
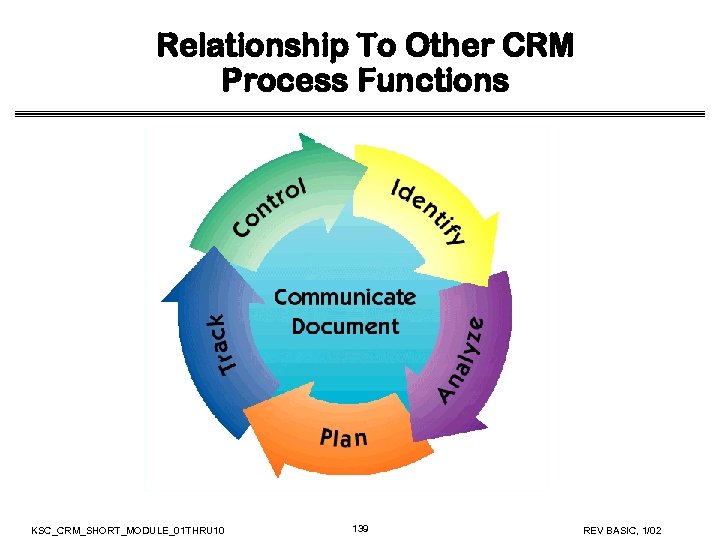 Relationship To Other CRM Process Functions KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 139 REV BASIC, 1/02
Relationship To Other CRM Process Functions KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 139 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Why Communicate Risks? • Makes risks, plans, actions, concerns, exchanges, forecast, and progress known • Ensures the visibility of risk information • To enable all project members to participate in defining and managing risks • Ensures understanding of risks and mitigation plans • Establishes an effective, ongoing dialog between the manager and the project team • Ensures appropriate attention is focused on issues and concerns KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 140 REV BASIC, 1/02
Why Communicate Risks? • Makes risks, plans, actions, concerns, exchanges, forecast, and progress known • Ensures the visibility of risk information • To enable all project members to participate in defining and managing risks • Ensures understanding of risks and mitigation plans • Establishes an effective, ongoing dialog between the manager and the project team • Ensures appropriate attention is focused on issues and concerns KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 140 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Why Document Risks? • In order to track and collect risk information internally and externally • Risks have a life cycle and eventually all risks go away • Probability or impact goes to zero • Risk becomes a problem • Documenting the life cycle of risks • Helps you learn what worked and didn’t work • Should help you avoid similar difficulties • Provides the opportunity to help other projects learn from your experience (Input to Lessons Learned Database) KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 141 REV BASIC, 1/02
Why Document Risks? • In order to track and collect risk information internally and externally • Risks have a life cycle and eventually all risks go away • Probability or impact goes to zero • Risk becomes a problem • Documenting the life cycle of risks • Helps you learn what worked and didn’t work • Should help you avoid similar difficulties • Provides the opportunity to help other projects learn from your experience (Input to Lessons Learned Database) KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 141 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Risk Documentation Types • Risk Management Plan (*NPG 7120. 5 B, NPG 8000. 4) • Risk Implementation Plan • Risk Information Sheets (*) • Prioritized Risk List (*NPG 7120. 5 B) • Risk Profile • Risk Analysis Reports • Risk Mitigation Status Reports • Risk Databases (*) • Spreadsheet Risk Tracking Logs (*) Recommended for KSC risk management activities KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 142 REV BASIC, 1/02
Risk Documentation Types • Risk Management Plan (*NPG 7120. 5 B, NPG 8000. 4) • Risk Implementation Plan • Risk Information Sheets (*) • Prioritized Risk List (*NPG 7120. 5 B) • Risk Profile • Risk Analysis Reports • Risk Mitigation Status Reports • Risk Databases (*) • Spreadsheet Risk Tracking Logs (*) Recommended for KSC risk management activities KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 142 REV BASIC, 1/02
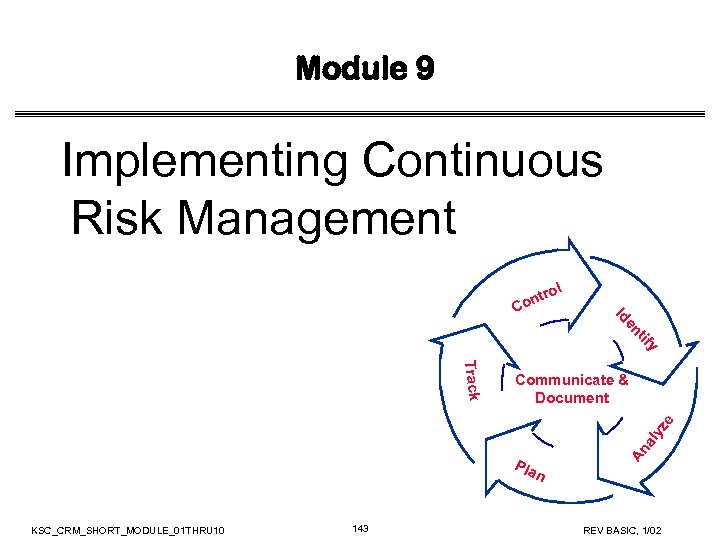 Module 9 Implementing Continuous Risk Management ol y tif en Id r ont C Pla n KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 143 An al yz e Track Communicate & Document REV BASIC, 1/02
Module 9 Implementing Continuous Risk Management ol y tif en Id r ont C Pla n KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 143 An al yz e Track Communicate & Document REV BASIC, 1/02
 Overview • Frequently asked CRM implementation questions • • • When do I start? Who’s involved? What do I need? What should I choose? What actions should I take? • Hints and Tips • Things to watch out for KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 144 REV BASIC, 1/02
Overview • Frequently asked CRM implementation questions • • • When do I start? Who’s involved? What do I need? What should I choose? What actions should I take? • Hints and Tips • Things to watch out for KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 144 REV BASIC, 1/02
 When do I Start CRM? Opportunity Actions Pre-contract activity Include risk management provisions in the solicitation and statement of work. Major project milestones (e. g. , contract award) Prepare for a major project decision point, and the need to increase knowledge about risks for improved strategic planning. Major project review Prepare for standard reviews, such as design reviews, functional tests. Best time to start is at the beginning! KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 145 REV BASIC, 1/02
When do I Start CRM? Opportunity Actions Pre-contract activity Include risk management provisions in the solicitation and statement of work. Major project milestones (e. g. , contract award) Prepare for a major project decision point, and the need to increase knowledge about risks for improved strategic planning. Major project review Prepare for standard reviews, such as design reviews, functional tests. Best time to start is at the beginning! KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 145 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Who’s Involved? (1) Role/Description Responsibilities and Tasks Sponsor (e. g. , senior mgr. , VP, division chief) • Provide visible support and encouragement • Reward effective management of risks Project manager (responsible for ultimate success of project) • Provide resources and funding • Reward effective management of risks • Monitor progress Champion (advocates new technology or process within the project) Change agents (plan and implement changes in organizations and projects KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 • Publicize and promote CRM • Coordinate changes and improvements on the project • Assist with recommendations of plans • Evaluate existing and new tools 146 REV BASIC, 1/02
Who’s Involved? (1) Role/Description Responsibilities and Tasks Sponsor (e. g. , senior mgr. , VP, division chief) • Provide visible support and encouragement • Reward effective management of risks Project manager (responsible for ultimate success of project) • Provide resources and funding • Reward effective management of risks • Monitor progress Champion (advocates new technology or process within the project) Change agents (plan and implement changes in organizations and projects KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 • Publicize and promote CRM • Coordinate changes and improvements on the project • Assist with recommendations of plans • Evaluate existing and new tools 146 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Who’s Involved? (2) Role/Description Responsibilities and Tasks Facilitators (trained in meeting skills, conflict resolution, tools, etc. , - act individually or as a team) • Conduct training sessions • Provide CRM expertise • Provide consulting during evaluation of progress Technical managers (e. g. , team or functional leads, such as software/hardware manager, test mgr. , etc. ) • Encourage and support use of CRM within their teams • Report risk information to project manager • Evaluate progress within their teams Project personnel (e. g. , software or hardware engineers, testers, etc. ) • Add CRM activities to day-to-day operations • Maintain open communication about risks KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 147 REV BASIC, 1/02
Who’s Involved? (2) Role/Description Responsibilities and Tasks Facilitators (trained in meeting skills, conflict resolution, tools, etc. , - act individually or as a team) • Conduct training sessions • Provide CRM expertise • Provide consulting during evaluation of progress Technical managers (e. g. , team or functional leads, such as software/hardware manager, test mgr. , etc. ) • Encourage and support use of CRM within their teams • Report risk information to project manager • Evaluate progress within their teams Project personnel (e. g. , software or hardware engineers, testers, etc. ) • Add CRM activities to day-to-day operations • Maintain open communication about risks KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 147 REV BASIC, 1/02
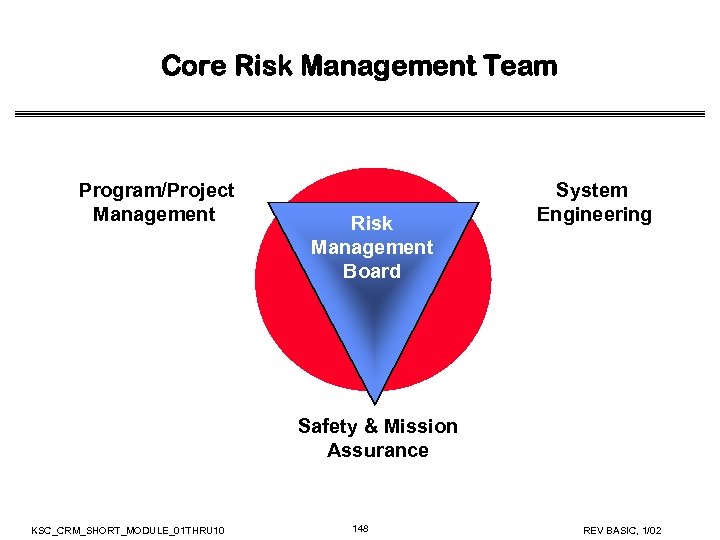 Core Risk Management Team Program/Project Management Risk Management Board System Engineering Safety & Mission Assurance KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 148 REV BASIC, 1/02
Core Risk Management Team Program/Project Management Risk Management Board System Engineering Safety & Mission Assurance KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 148 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Core RM Team Key Responsibilities (1) • Reviews current and previous risk issues to validate, classify and group risks at the project level • Determines risk attributes (probability, impact, and timeframe) and reprioritizes risks as needed • Determines if addition information is needed (trade-studies or research) • Implements mitigation options (contingency plans, descope plans). Determines who is involved and assigns risk owner. Reassigns risks when necessary • Adjusts action planning (mitigation plans, mitigation time frames, etc) KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 149 REV BASIC, 1/02
Core RM Team Key Responsibilities (1) • Reviews current and previous risk issues to validate, classify and group risks at the project level • Determines risk attributes (probability, impact, and timeframe) and reprioritizes risks as needed • Determines if addition information is needed (trade-studies or research) • Implements mitigation options (contingency plans, descope plans). Determines who is involved and assigns risk owner. Reassigns risks when necessary • Adjusts action planning (mitigation plans, mitigation time frames, etc) KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 149 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Core RM Team Key Responsibilities (2) • Tracks, communicates and controls risks • Makes control decision recommendations (analyze, decide, execute) to PM for all risks • Makes recommendations to PM regarding CRM policy and the communication of risks • Makes recommendations to PM regarding risk closure and/or acceptance • Make recommendations to PM concerning allocations of resources to mitigate risks KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 150 REV BASIC, 1/02
Core RM Team Key Responsibilities (2) • Tracks, communicates and controls risks • Makes control decision recommendations (analyze, decide, execute) to PM for all risks • Makes recommendations to PM regarding CRM policy and the communication of risks • Makes recommendations to PM regarding risk closure and/or acceptance • Make recommendations to PM concerning allocations of resources to mitigate risks KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 150 REV BASIC, 1/02
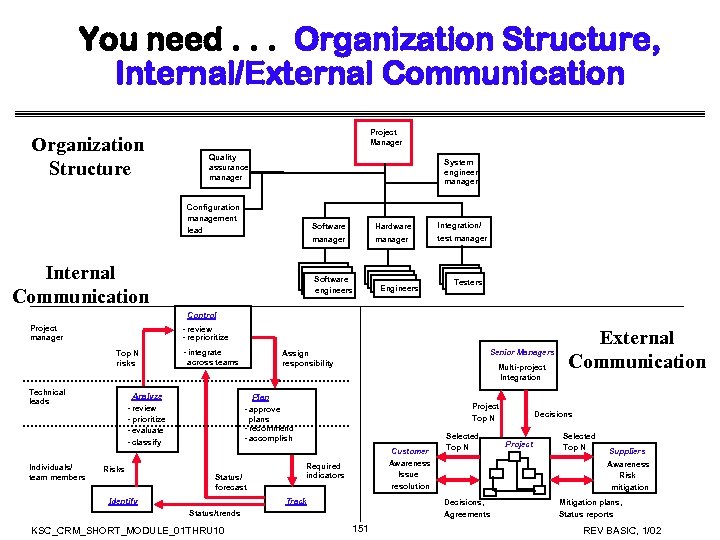 You need. . . Organization Structure, Internal/External Communication Organization Structure Project Manager Quality assurance manager System engineer manager Configuration management lead Software Integration/ manager Internal Communication Hardware manager test manager Software engineers Engineers Testers Control Project manager - review - reprioritize Top N risks Technical leads Individuals/ team members - integrate across teams Analyze - review - prioritize - evaluate - classify Risks Senior Managers Assign responsibility Multi-project Integration Plan - approve plans - recommend - accomplish Status/ forecast Identify Project Top N Customer Awareness Issue resolution Required indicators Track 151 Decisions Project Selected Top N Suppliers Awareness Risk mitigation Decisions, Agreements Status/trends KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 Selected Top N External Communication Mitigation plans, Status reports REV BASIC, 1/02
You need. . . Organization Structure, Internal/External Communication Organization Structure Project Manager Quality assurance manager System engineer manager Configuration management lead Software Integration/ manager Internal Communication Hardware manager test manager Software engineers Engineers Testers Control Project manager - review - reprioritize Top N risks Technical leads Individuals/ team members - integrate across teams Analyze - review - prioritize - evaluate - classify Risks Senior Managers Assign responsibility Multi-project Integration Plan - approve plans - recommend - accomplish Status/ forecast Identify Project Top N Customer Awareness Issue resolution Required indicators Track 151 Decisions Project Selected Top N Suppliers Awareness Risk mitigation Decisions, Agreements Status/trends KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 Selected Top N External Communication Mitigation plans, Status reports REV BASIC, 1/02
 Risk Management Planning Documentation Options • Risk Management Plan • Guides project personnel through the tailored process, methods, and tools for managing their project risks • Recommended and preferred risk management planning documentation approach for KSC projects • Risk Management Implementation Plan • Guides project personnel (in the pre-formulation phase) regarding how they intend to bring risk management into the project’s infrastructure and processes • Utilized primarily for extremely large programs/projects, where there is a need to establish sponsorship, resources, and infrastructure for the overall risk management approach • Development of a Risk Management Implementation Plan is not envisioned for KSC projects (Refer to Tab L [Module 11] for an example plan) KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 152 REV BASIC, 1/02
Risk Management Planning Documentation Options • Risk Management Plan • Guides project personnel through the tailored process, methods, and tools for managing their project risks • Recommended and preferred risk management planning documentation approach for KSC projects • Risk Management Implementation Plan • Guides project personnel (in the pre-formulation phase) regarding how they intend to bring risk management into the project’s infrastructure and processes • Utilized primarily for extremely large programs/projects, where there is a need to establish sponsorship, resources, and infrastructure for the overall risk management approach • Development of a Risk Management Implementation Plan is not envisioned for KSC projects (Refer to Tab L [Module 11] for an example plan) KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 152 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Risk Management Plan Elements (NPG 8000. 4, Section 2. 7. 4) • Introduction/Overview of Risk Management process • Project Organization and Responsibilities • Risk Management activities and practices in detail • Budget, resources, and milestones for risk management activities and risk mitigation • Procedure for documenting risks • Assumptions • Technical Considerations • Constraints • De-Scope Options KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 153 Overvi ew Budget Goals Proced ures nes ilesto M REV BASIC, 1/02
Risk Management Plan Elements (NPG 8000. 4, Section 2. 7. 4) • Introduction/Overview of Risk Management process • Project Organization and Responsibilities • Risk Management activities and practices in detail • Budget, resources, and milestones for risk management activities and risk mitigation • Procedure for documenting risks • Assumptions • Technical Considerations • Constraints • De-Scope Options KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 153 Overvi ew Budget Goals Proced ures nes ilesto M REV BASIC, 1/02
 Sample Risk Management Plan • KSC’s Advanced Technology Development Center (ATDC) Risk Management Plan can serve as an example for your project to use • Take a few minutes to read the ATDC Risk Management Plan (After Module 11) Risk Management Plan KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 154 REV BASIC, 1/02
Sample Risk Management Plan • KSC’s Advanced Technology Development Center (ATDC) Risk Management Plan can serve as an example for your project to use • Take a few minutes to read the ATDC Risk Management Plan (After Module 11) Risk Management Plan KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 154 REV BASIC, 1/02
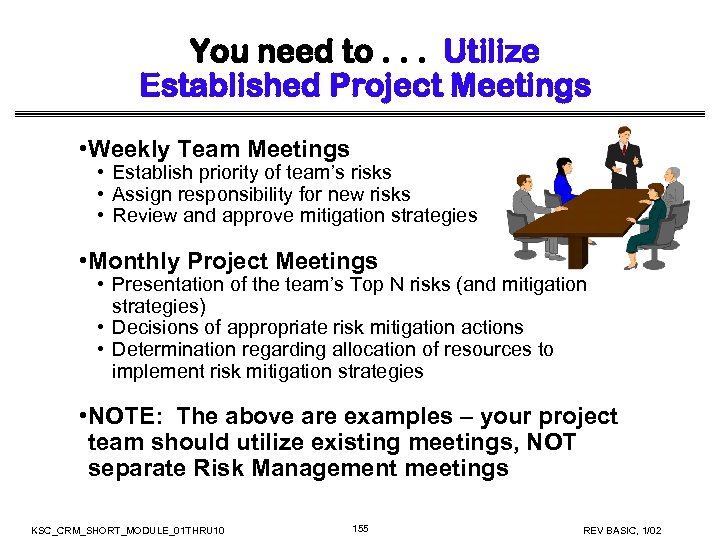 You need to. . . Utilize Established Project Meetings • Weekly Team Meetings • Establish priority of team’s risks • Assign responsibility for new risks • Review and approve mitigation strategies • Monthly Project Meetings • Presentation of the team’s Top N risks (and mitigation strategies) • Decisions of appropriate risk mitigation actions • Determination regarding allocation of resources to implement risk mitigation strategies • NOTE: The above are examples – your project team should utilize existing meetings, NOT separate Risk Management meetings KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 155 REV BASIC, 1/02
You need to. . . Utilize Established Project Meetings • Weekly Team Meetings • Establish priority of team’s risks • Assign responsibility for new risks • Review and approve mitigation strategies • Monthly Project Meetings • Presentation of the team’s Top N risks (and mitigation strategies) • Decisions of appropriate risk mitigation actions • Determination regarding allocation of resources to implement risk mitigation strategies • NOTE: The above are examples – your project team should utilize existing meetings, NOT separate Risk Management meetings KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 155 REV BASIC, 1/02
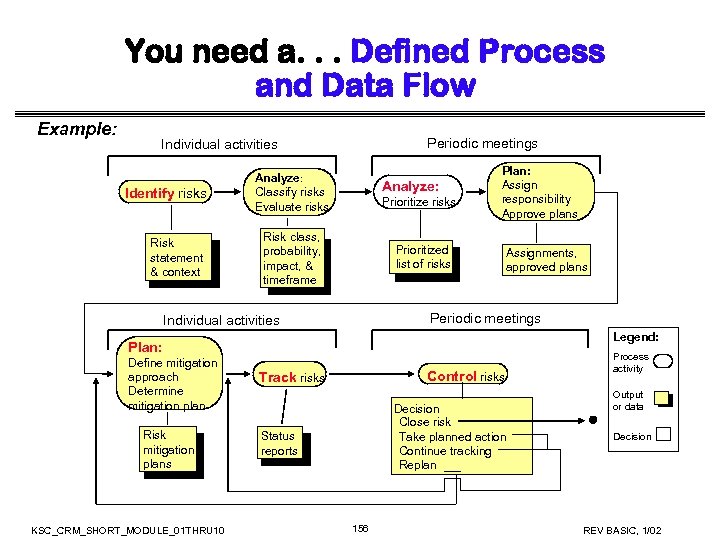 You need a. . . Defined Process and Data Flow Example: Periodic meetings Individual activities Identify risks Risk statement & context Analyze: Classify risks Evaluate risks Analyze: Prioritize risks Risk class, probability, impact, & timeframe Plan: Assign responsibility Approve plans Prioritized list of risks Assignments, approved plans Periodic meetings Individual activities Legend: Plan: Define mitigation approach Determine mitigation plan Risk mitigation plans KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 Control risks Track risks Decision Close risk Take planned action Continue tracking Replan Status reports 156 Process activity Output or data Decision REV BASIC, 1/02
You need a. . . Defined Process and Data Flow Example: Periodic meetings Individual activities Identify risks Risk statement & context Analyze: Classify risks Evaluate risks Analyze: Prioritize risks Risk class, probability, impact, & timeframe Plan: Assign responsibility Approve plans Prioritized list of risks Assignments, approved plans Periodic meetings Individual activities Legend: Plan: Define mitigation approach Determine mitigation plan Risk mitigation plans KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 Control risks Track risks Decision Close risk Take planned action Continue tracking Replan Status reports 156 Process activity Output or data Decision REV BASIC, 1/02
 You must choose your. . . Methods and Tools Control • Cause and Effect Analysis • Closing a Risk • Cost-Benefit Analysis • List Reduction • Mitigation Status Report • Multivoting • PERT Chart • Problem-Solving Planning • Risk Information Sheet • Spreadsheet Risk Tracking • Stoplight Chart • Project Metrics Risk Management Plan A Risk Management Plan documents how risks will be managed on a project: the process, activities, milestones, and responsibilities associated with risk management. It is a subset of the project plan and is written before the project begins. Track Co ol ntr ify t en Id al yz e Communicate Document Pla An Track • Bar Graph • Mitigation Status Report • Risk Information Sheet • Spreadsheet Risk Tracking • Stoplight Chart • Time Correlation Chart • Time Graph • Project Metrics • Statistical Process • Action Item Plan Control (SPC) • Baseline List • Planning Decision Planning • Planning Flowchart • Problem-Solving Worksheet - Affinity Planning - Grouping - Cause and Effect Brainstormi - Cost-Benefit Analysis ng - Gantt Analysis - Goal-Question. Charts - Interrelationship Measure - List Digraph - Reduction - PERT Multivotin - Work Breakdown Chart g • Risk Information Structure KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 Sheet Identify • Baseline Identification and Analysis • Brainstorming • Periodic Risk Reporting • Project Profile Questions • Risk Information Sheet • Short TBQ • Taxonomy-Based Questionnaire • TBQ Interviews (TBQ) • Voluntary Reporting • Project Metrics • Failure Modes & Effect Analysis (FMEA) • Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) n Analyze • Affinity Grouping • Baseline Identification and Analysis • Binary Attribute Evaluation • Comparison Risk Ranking • Multivoting • Pareto Top N • Potential Top N • Taxonomy Classification • Risk Information Sheet • Top 5 • Tri-level Attribute Evaluation • FMEA • FTA 157 REV BASIC, 1/02
You must choose your. . . Methods and Tools Control • Cause and Effect Analysis • Closing a Risk • Cost-Benefit Analysis • List Reduction • Mitigation Status Report • Multivoting • PERT Chart • Problem-Solving Planning • Risk Information Sheet • Spreadsheet Risk Tracking • Stoplight Chart • Project Metrics Risk Management Plan A Risk Management Plan documents how risks will be managed on a project: the process, activities, milestones, and responsibilities associated with risk management. It is a subset of the project plan and is written before the project begins. Track Co ol ntr ify t en Id al yz e Communicate Document Pla An Track • Bar Graph • Mitigation Status Report • Risk Information Sheet • Spreadsheet Risk Tracking • Stoplight Chart • Time Correlation Chart • Time Graph • Project Metrics • Statistical Process • Action Item Plan Control (SPC) • Baseline List • Planning Decision Planning • Planning Flowchart • Problem-Solving Worksheet - Affinity Planning - Grouping - Cause and Effect Brainstormi - Cost-Benefit Analysis ng - Gantt Analysis - Goal-Question. Charts - Interrelationship Measure - List Digraph - Reduction - PERT Multivotin - Work Breakdown Chart g • Risk Information Structure KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 Sheet Identify • Baseline Identification and Analysis • Brainstorming • Periodic Risk Reporting • Project Profile Questions • Risk Information Sheet • Short TBQ • Taxonomy-Based Questionnaire • TBQ Interviews (TBQ) • Voluntary Reporting • Project Metrics • Failure Modes & Effect Analysis (FMEA) • Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) n Analyze • Affinity Grouping • Baseline Identification and Analysis • Binary Attribute Evaluation • Comparison Risk Ranking • Multivoting • Pareto Top N • Potential Top N • Taxonomy Classification • Risk Information Sheet • Top 5 • Tri-level Attribute Evaluation • FMEA • FTA 157 REV BASIC, 1/02
 You should carefully. . . Adapt CRM to Your Project • Purpose: • Make maximum use of existing, effective project management processes and methods while integrating a set of proactive risk management activities • Document the tailored processes, methods, and tools in a risk management plan • Define a schedule for transitioning specific methods, tools, and activities into the project • Description: • Tailors risk management processes, methods, and tools for use on the project KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 158 REV BASIC, 1/02
You should carefully. . . Adapt CRM to Your Project • Purpose: • Make maximum use of existing, effective project management processes and methods while integrating a set of proactive risk management activities • Document the tailored processes, methods, and tools in a risk management plan • Define a schedule for transitioning specific methods, tools, and activities into the project • Description: • Tailors risk management processes, methods, and tools for use on the project KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 158 REV BASIC, 1/02
 You should choose a. . . Risk Database • A database is the simplest means to retain and keep risk information current • Data entry forms and reports can be used as the risk information sheet, spreadsheet, and other templates • A risk database enables documentation of lessons learned, trend analysis, and pattern analysis to support identifying common risks (and solutions) across projects KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 159 REV BASIC, 1/02
You should choose a. . . Risk Database • A database is the simplest means to retain and keep risk information current • Data entry forms and reports can be used as the risk information sheet, spreadsheet, and other templates • A risk database enables documentation of lessons learned, trend analysis, and pattern analysis to support identifying common risks (and solutions) across projects KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 159 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Sample Risk Tracking Database (NASA GRC RM Database Tool) • Developed at NASA Glenn Research Center (GRC) to help capture and track project risks • Based on experience and the Continuous Risk Management Guidebook • Contains most of the items found on the Risk Information Sheet (RIS) • Further information available from website http: //smo. gsfc. nasa. gov/riskman/relatedlinks. html • Database can be downloaded from the Internet if you have Access 97 or greater KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 160 REV BASIC, 1/02
Sample Risk Tracking Database (NASA GRC RM Database Tool) • Developed at NASA Glenn Research Center (GRC) to help capture and track project risks • Based on experience and the Continuous Risk Management Guidebook • Contains most of the items found on the Risk Information Sheet (RIS) • Further information available from website http: //smo. gsfc. nasa. gov/riskman/relatedlinks. html • Database can be downloaded from the Internet if you have Access 97 or greater KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 160 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Sample Risk Tracking Database (NASA GRC RM Database Tool) KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 161 REV BASIC, 1/02
Sample Risk Tracking Database (NASA GRC RM Database Tool) KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 161 REV BASIC, 1/02
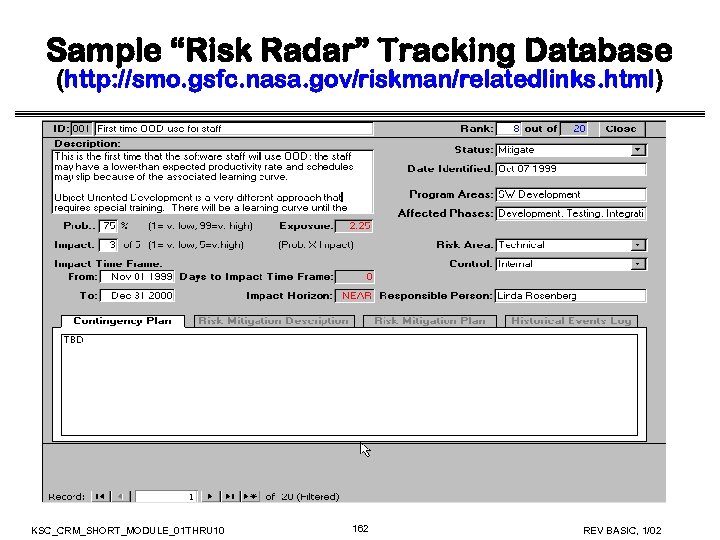 Sample “Risk Radar” Tracking Database (http: //smo. gsfc. nasa. gov/riskman/relatedlinks. html) KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 162 REV BASIC, 1/02
Sample “Risk Radar” Tracking Database (http: //smo. gsfc. nasa. gov/riskman/relatedlinks. html) KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 162 REV BASIC, 1/02
 CRM Implementation Tips and Hints • Start simple; learn to “think risk” • Never throw out or ignore any risk information; scan it once in a while for applicability • Always ask for feedback on how things are going and what is working • Use outside facilitators until you’re comfortable with the CRM process KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 163 REV BASIC, 1/02
CRM Implementation Tips and Hints • Start simple; learn to “think risk” • Never throw out or ignore any risk information; scan it once in a while for applicability • Always ask for feedback on how things are going and what is working • Use outside facilitators until you’re comfortable with the CRM process KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 163 REV BASIC, 1/02
 CRM Implementation Summary • Adapt Risk Management to your specific project’s complexity and needs • Document your risk management practice and rationale in a Risk Management Plan • Your CRM practice will evolve and improve as you gain experience and learn from others’ experiences • Capture Lessons Learned KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 164 Risk Management Plan REV BASIC, 1/02
CRM Implementation Summary • Adapt Risk Management to your specific project’s complexity and needs • Document your risk management practice and rationale in a Risk Management Plan • Your CRM practice will evolve and improve as you gain experience and learn from others’ experiences • Capture Lessons Learned KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 164 Risk Management Plan REV BASIC, 1/02
 Module 10 Course Summary ol y tif en Id ntr Co Pla An al yz e Track Communicate & Document n KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 165 REV BASIC, 1/02
Module 10 Course Summary ol y tif en Id ntr Co Pla An al yz e Track Communicate & Document n KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 165 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Review of CRM Short Course Objectives • Understand the concepts and principles of Continuous Risk Management and how to apply them • Develop basic risk management skills for each function of Continuous Risk Management • Become aware of key methods and tools • Understand how CRM could be tailored to a project • Be able to differentiate between Risks and Problems KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 166 REV BASIC, 1/02
Review of CRM Short Course Objectives • Understand the concepts and principles of Continuous Risk Management and how to apply them • Develop basic risk management skills for each function of Continuous Risk Management • Become aware of key methods and tools • Understand how CRM could be tailored to a project • Be able to differentiate between Risks and Problems KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 166 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Risk Definitions • Risk is the combination of the probability (qualitative or quantitative) that a program or project will experience an undesired event (cost overrun, schedule slip, safety mishap, security compromise) and the consequences (impact) of the undesired event, were it to occur. • NPG 8000. 4 KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 167 REV BASIC, 1/02
Risk Definitions • Risk is the combination of the probability (qualitative or quantitative) that a program or project will experience an undesired event (cost overrun, schedule slip, safety mishap, security compromise) and the consequences (impact) of the undesired event, were it to occur. • NPG 8000. 4 KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 167 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Risk Definitions Risk involves the probability that Risk involves the impact of an undesired event will occur. the event should it occur. Qualitative or Quantitative Risk Exposure = Probability x Impact KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 168 REV BASIC, 1/02
Risk Definitions Risk involves the probability that Risk involves the impact of an undesired event will occur. the event should it occur. Qualitative or Quantitative Risk Exposure = Probability x Impact KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 168 REV BASIC, 1/02
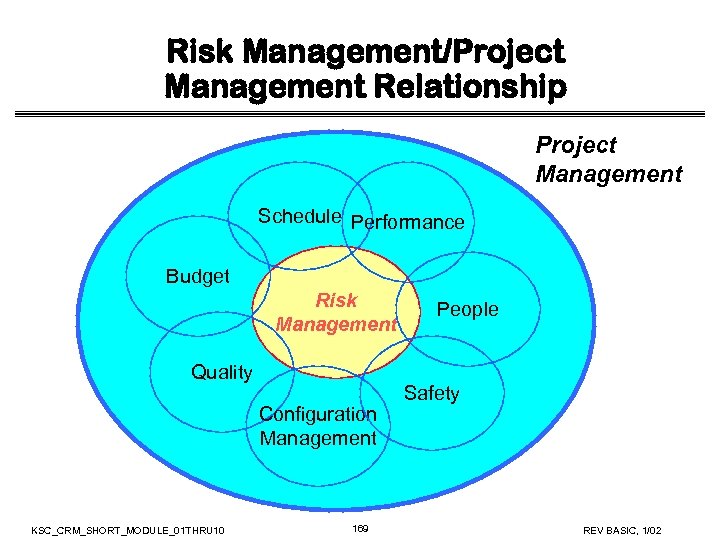 Risk Management/Project Management Relationship Project Management Schedule Performance Budget Risk Management Quality Configuration Management KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 169 People Safety REV BASIC, 1/02
Risk Management/Project Management Relationship Project Management Schedule Performance Budget Risk Management Quality Configuration Management KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 169 People Safety REV BASIC, 1/02
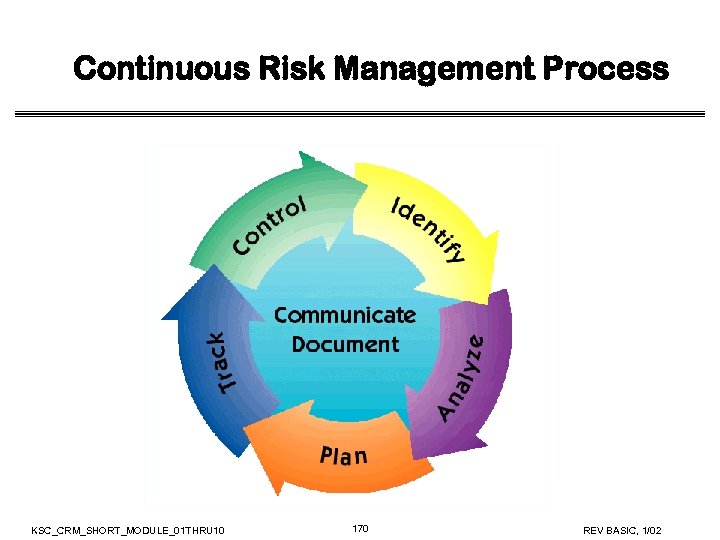 Continuous Risk Management Process KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 170 REV BASIC, 1/02
Continuous Risk Management Process KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 170 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Risk Management Planning • A Risk Management Plan (NPG 7120. 5 B, Section 4. 3. 2 a) describes how the project will perform its tailored risk management process, methods, and tools • • Introduction Risk Management practice overview Project organization, roles, and responsibilities Risk Management practice details Risk management resources and milestones Risk information documentation De-Scope Options KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 171 REV BASIC, 1/02
Risk Management Planning • A Risk Management Plan (NPG 7120. 5 B, Section 4. 3. 2 a) describes how the project will perform its tailored risk management process, methods, and tools • • Introduction Risk Management practice overview Project organization, roles, and responsibilities Risk Management practice details Risk management resources and milestones Risk information documentation De-Scope Options KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 171 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Risk Management Implementation • Begin risk management effort as early as possible in the Project’s life cycle • Adapt risk management to your specific project’s complexity and needs • Establish a baseline set of risks before project start to identify major risks to be avoided • Document your risk management practice and rationale in a Risk Management plan • Identify and acquire any needed tools, training, and supporting infrastructure to support the project risk management effort KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 172 REV BASIC, 1/02
Risk Management Implementation • Begin risk management effort as early as possible in the Project’s life cycle • Adapt risk management to your specific project’s complexity and needs • Establish a baseline set of risks before project start to identify major risks to be avoided • Document your risk management practice and rationale in a Risk Management plan • Identify and acquire any needed tools, training, and supporting infrastructure to support the project risk management effort KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 172 REV BASIC, 1/02
 KSC Risk Management (RM) Resources • RM consulting is available from KSC Risk Analysis Manager (John Branard, QA-C, 867 -2268) • RM Policy/Requirements/Approach/Plans/Tools • RM Training (Full CRM Course, Risk Baselining Workshop) • Risk-Based Acquisition Management (R-BAM) • Project RM/S&MA consulting is available from the SE&T S&MA Project Assessment Office (Ron Gillett, YA-B, 867 -9135) • • • RM approach RM Plan development RM/S&MA analysis tool selection Risk tracking tools Project/Mission risk reporting techniques KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 173 REV BASIC, 1/02
KSC Risk Management (RM) Resources • RM consulting is available from KSC Risk Analysis Manager (John Branard, QA-C, 867 -2268) • RM Policy/Requirements/Approach/Plans/Tools • RM Training (Full CRM Course, Risk Baselining Workshop) • Risk-Based Acquisition Management (R-BAM) • Project RM/S&MA consulting is available from the SE&T S&MA Project Assessment Office (Ron Gillett, YA-B, 867 -9135) • • • RM approach RM Plan development RM/S&MA analysis tool selection Risk tracking tools Project/Mission risk reporting techniques KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 173 REV BASIC, 1/02
 Final questions? KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 174 REV BASIC, 1/02
Final questions? KSC_CRM_SHORT_MODULE_01 THRU 10 174 REV BASIC, 1/02


