e3a66b00178867c7ca1f4367f345aa15.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35
 Module 1: Introduction to Active Directory
Module 1: Introduction to Active Directory
 Overview u. Introduction to Active Directory u. Active Directory Logical Structure u. Role of DNS in Active Directory u. Active Directory Physical Structure u. Methods for Administering a Windows 2000 Network
Overview u. Introduction to Active Directory u. Active Directory Logical Structure u. Role of DNS in Active Directory u. Active Directory Physical Structure u. Methods for Administering a Windows 2000 Network
 Introduction to Active Directory u. What Is Active Directory? u. Active Directory Objects u. Active Directory Schema u. Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP)
Introduction to Active Directory u. What Is Active Directory? u. Active Directory Objects u. Active Directory Schema u. Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP)
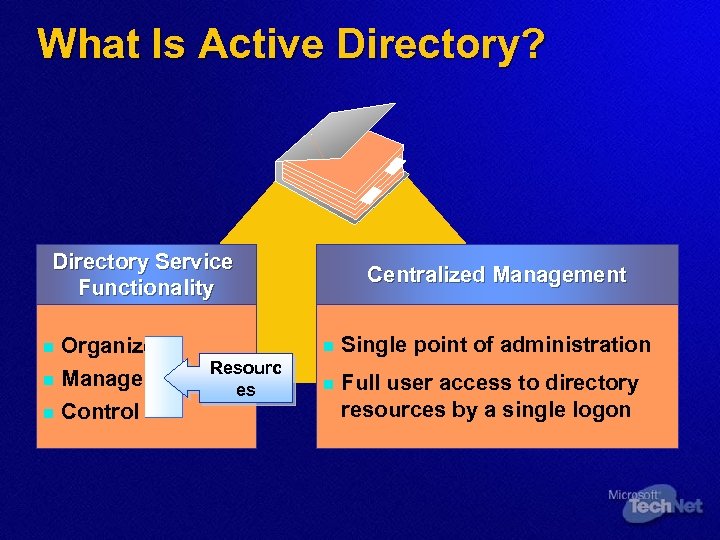 What Is Active Directory? Directory Service Functionality Organize n Manage n Control Centralized Management n n Resourc es Single point of administration n Full user access to directory resources by a single logon
What Is Active Directory? Directory Service Functionality Organize n Manage n Control Centralized Management n n Resourc es Single point of administration n Full user access to directory resources by a single logon
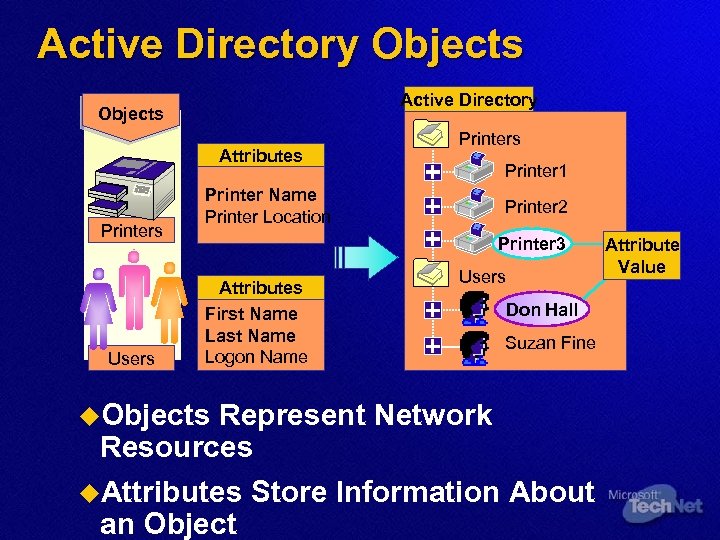 Active Directory Objects Attributes Printers Users Printer Name Printer Location Printers Printer 1 Printer 2 Printer 3 Attributes First Name Last Name Logon Name u. Objects Users Don Hall Suzan Fine Represent Network Resources u. Attributes Store Information About an Object Attribute Value
Active Directory Objects Attributes Printers Users Printer Name Printer Location Printers Printer 1 Printer 2 Printer 3 Attributes First Name Last Name Logon Name u. Objects Users Don Hall Suzan Fine Represent Network Resources u. Attributes Store Information About an Object Attribute Value
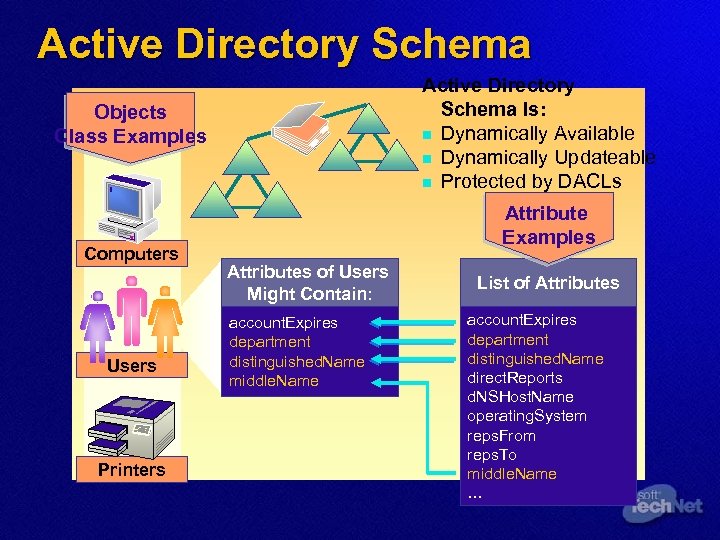 Active Directory Schema Is: n Dynamically Available n Dynamically Updateable n Protected by DACLs Objects Class Examples Computers Users Printers Attribute Examples Attributes of Users Might Contain: account. Expires department distinguished. Name middle. Name List of Attributes account. Expires department distinguished. Name direct. Reports d. NSHost. Name operating. System reps. From reps. To middle. Name …
Active Directory Schema Is: n Dynamically Available n Dynamically Updateable n Protected by DACLs Objects Class Examples Computers Users Printers Attribute Examples Attributes of Users Might Contain: account. Expires department distinguished. Name middle. Name List of Attributes account. Expires department distinguished. Name direct. Reports d. NSHost. Name operating. System reps. From reps. To middle. Name …
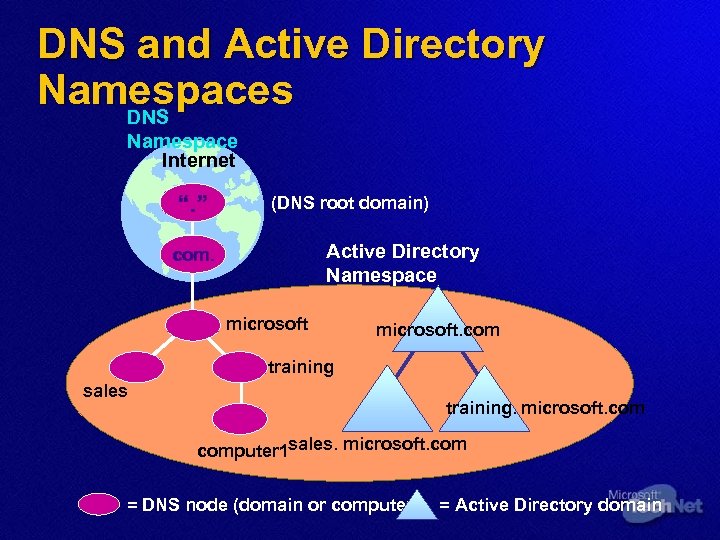 DNS and Active Directory Namespaces DNS Namespace Internet “. ” (DNS root domain) Active Directory Namespace com. microsoft. com training sales training. microsoft. computer 1 sales. microsoft. com = DNS node (domain or computer) = Active Directory domain
DNS and Active Directory Namespaces DNS Namespace Internet “. ” (DNS root domain) Active Directory Namespace com. microsoft. com training sales training. microsoft. computer 1 sales. microsoft. com = DNS node (domain or computer) = Active Directory domain
 Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) u. LDAP Provides a Way to Communicate with Active Directory by Specifying Unique Naming Paths for Each Object in the Directory u. LDAP Naming Paths Include: n Distinguished names CN=Suzan Fine, OU=Sales, DC=contoso, DC=msft Suzan Fine n Relative distinguished names
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) u. LDAP Provides a Way to Communicate with Active Directory by Specifying Unique Naming Paths for Each Object in the Directory u. LDAP Naming Paths Include: n Distinguished names CN=Suzan Fine, OU=Sales, DC=contoso, DC=msft Suzan Fine n Relative distinguished names
 Active Directory Logical Structure u. Domains u. Organizational Units u. Trees and Forests u. Global Catalog
Active Directory Logical Structure u. Domains u. Organizational Units u. Trees and Forests u. Global Catalog
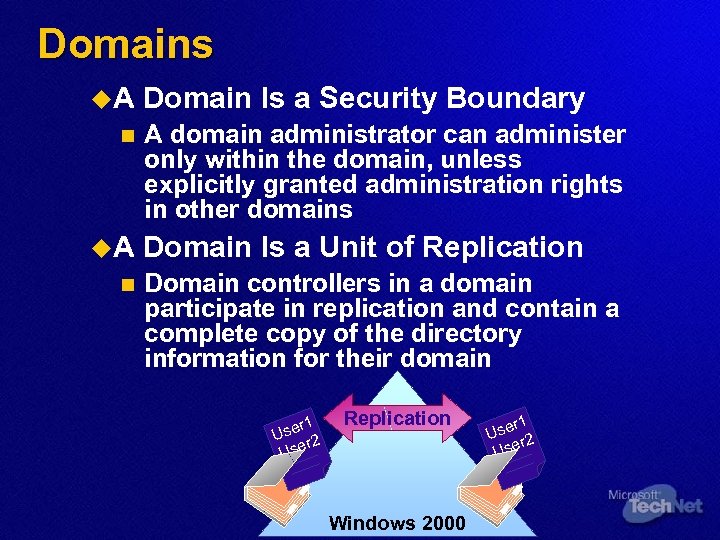 Domains u. A n Domain Is a Security Boundary A domain administrator can administer only within the domain, unless explicitly granted administration rights in other domains Domain Is a Unit of Replication Domain controllers in a domain participate in replication and contain a complete copy of the directory information for their domain r 1 Use r 2 Use Replication Windows 2000 r 1 Use r 2 Use
Domains u. A n Domain Is a Security Boundary A domain administrator can administer only within the domain, unless explicitly granted administration rights in other domains Domain Is a Unit of Replication Domain controllers in a domain participate in replication and contain a complete copy of the directory information for their domain r 1 Use r 2 Use Replication Windows 2000 r 1 Use r 2 Use
 Organizational Units Network Administrative Model Sales Organizational Structure Vancouver Users Computers u. Use Sales Repair OUs to Group Objects into a Logical Hierarchy That Best Suits the Needs of Your Organization u. Delegate Administrative Control over the Objects Within an OU by Assigning Specific Permissions to Users and Groups
Organizational Units Network Administrative Model Sales Organizational Structure Vancouver Users Computers u. Use Sales Repair OUs to Group Objects into a Logical Hierarchy That Best Suits the Needs of Your Organization u. Delegate Administrative Control over the Objects Within an OU by Assigning Specific Permissions to Users and Groups
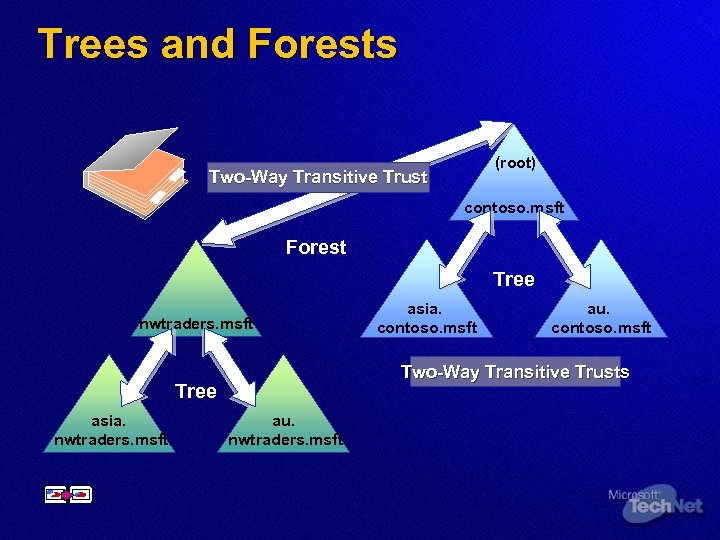 Trees and Forests (root) Two-Way Transitive Trust contoso. msft Forest Tree nwtraders. msft au. contoso. msft Two-Way Transitive Trusts Tree asia. nwtraders. msft asia. contoso. msft au. nwtraders. msft
Trees and Forests (root) Two-Way Transitive Trust contoso. msft Forest Tree nwtraders. msft au. contoso. msft Two-Way Transitive Trusts Tree asia. nwtraders. msft asia. contoso. msft au. nwtraders. msft
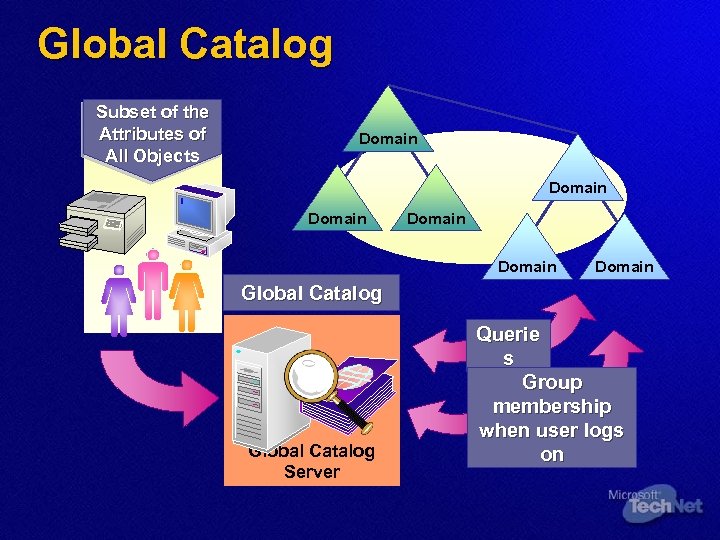 Global Catalog S u b s e t o f th e A ttr i b u te s o f A l l O b j e c ts Domain Domain Global Catalog Server Querie s Group membership when user logs on
Global Catalog S u b s e t o f th e A ttr i b u te s o f A l l O b j e c ts Domain Domain Global Catalog Server Querie s Group membership when user logs on
 Introduction to the Role of DNS in Active Directory u Name n n Resolution DNS translates computer names to IP addresses Computers use DNS to locate each other on the network u Naming n n Convention for Windows 2000 Domains Windows 2000 uses DNS naming standards for domain names DNS domains and Active Directory domains share a common hierarchical naming structure u Locating Directory n n the Physical Components of Active DNS identifies domain controllers by the services they provide Computers use DNS to locate domain controllers and global catalog servers
Introduction to the Role of DNS in Active Directory u Name n n Resolution DNS translates computer names to IP addresses Computers use DNS to locate each other on the network u Naming n n Convention for Windows 2000 Domains Windows 2000 uses DNS naming standards for domain names DNS domains and Active Directory domains share a common hierarchical naming structure u Locating Directory n n the Physical Components of Active DNS identifies domain controllers by the services they provide Computers use DNS to locate domain controllers and global catalog servers
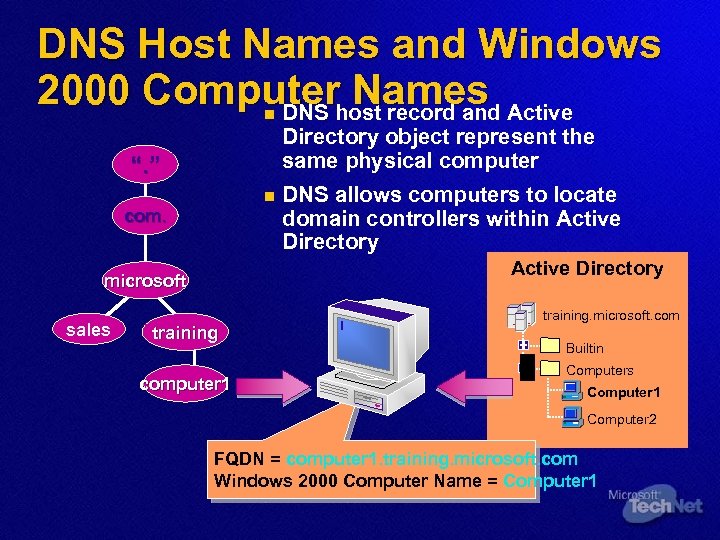 DNS Host Names and Windows 2000 Computerhost record and Active Names DNS n Directory object represent the same physical computer “. ” n com. Active Directory microsoft sales DNS allows computers to locate domain controllers within Active Directory training computer 1 training. microsoft. com Builtin Computers Computer 1 Computer 2 FQDN = computer 1. training. microsoft. com Windows 2000 Computer Name = Computer 1
DNS Host Names and Windows 2000 Computerhost record and Active Names DNS n Directory object represent the same physical computer “. ” n com. Active Directory microsoft sales DNS allows computers to locate domain controllers within Active Directory training computer 1 training. microsoft. com Builtin Computers Computer 1 Computer 2 FQDN = computer 1. training. microsoft. com Windows 2000 Computer Name = Computer 1
 DNS Requirements for Active Directory DNS Requirements to Support Active Directory Support for SRV records (mandatory) Support for the dynamic update protocol (recommended) Support for incremental zone transfers (recommended)
DNS Requirements for Active Directory DNS Requirements to Support Active Directory Support for SRV records (mandatory) Support for the dynamic update protocol (recommended) Support for incremental zone transfers (recommended)
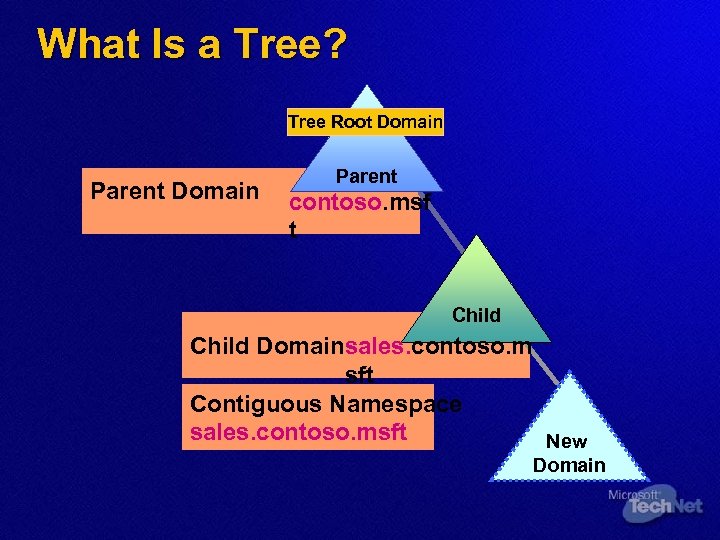 What Is a Tree? Tree Root Domain Parent contoso. msf t Child Domainsales. contoso. m sft Contiguous Namespace sales. contoso. msft New Domain
What Is a Tree? Tree Root Domain Parent contoso. msf t Child Domainsales. contoso. m sft Contiguous Namespace sales. contoso. msft New Domain
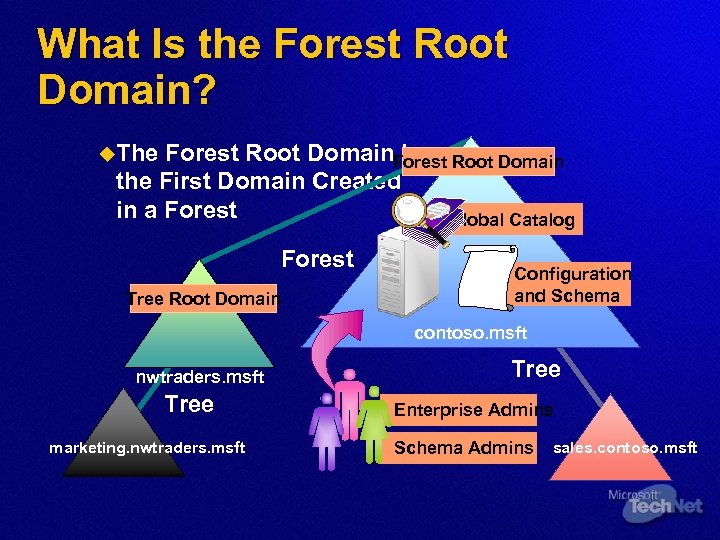 What Is the Forest Root Domain? u. The Forest Root Domain Is the First Domain Created in a Forest Global Catalog Forest Tree Root Domain Configuration and Schema contoso. msft nwtraders. msft Tree marketing. nwtraders. msft Tree Enterprise Admins Schema Admins sales. contoso. msft
What Is the Forest Root Domain? u. The Forest Root Domain Is the First Domain Created in a Forest Global Catalog Forest Tree Root Domain Configuration and Schema contoso. msft nwtraders. msft Tree marketing. nwtraders. msft Tree Enterprise Admins Schema Admins sales. contoso. msft
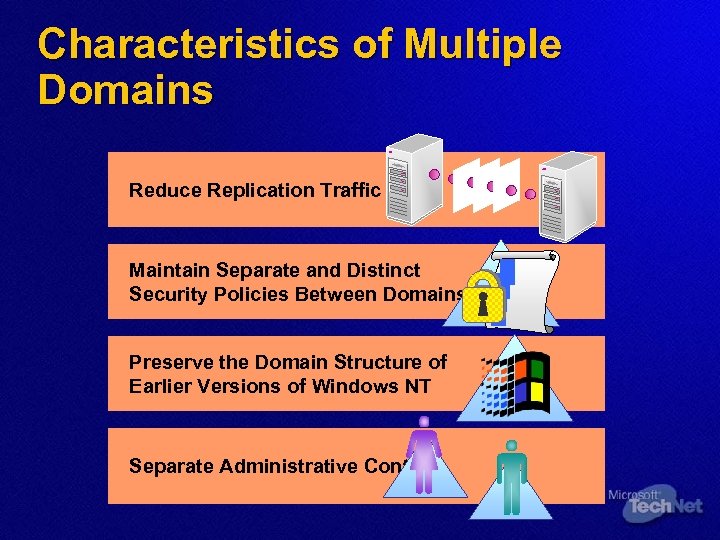 Characteristics of Multiple Domains Reduce Replication Traffic Maintain Separate and Distinct Security Policies Between Domains Preserve the Domain Structure of Earlier Versions of Windows NT Separate Administrative Control
Characteristics of Multiple Domains Reduce Replication Traffic Maintain Separate and Distinct Security Policies Between Domains Preserve the Domain Structure of Earlier Versions of Windows NT Separate Administrative Control
 Active Directory Physical Structure u. Domain u. Sites Controllers
Active Directory Physical Structure u. Domain u. Sites Controllers
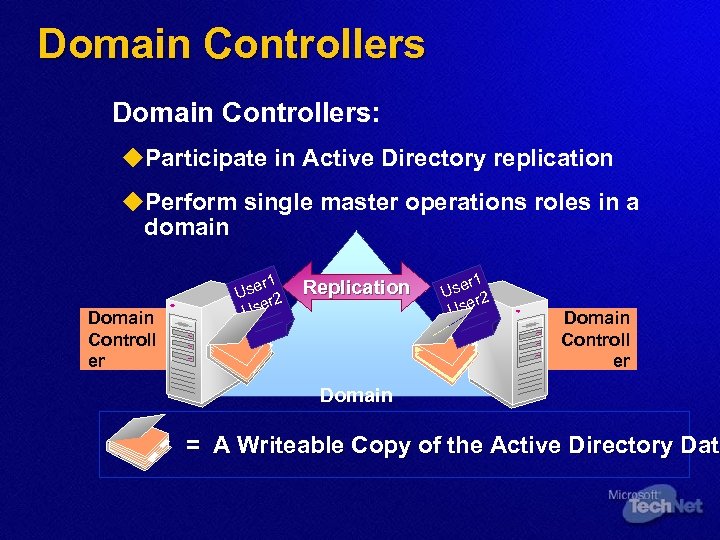 Domain Controllers: u. Participate in Active Directory replication u. Perform single master operations roles in a domain Domain Controll er r 1 Use r 2 Use Replication r 1 Use r 2 Use Domain Controll er Domain = A Writeable Copy of the Active Directory Data Dat
Domain Controllers: u. Participate in Active Directory replication u. Perform single master operations roles in a domain Domain Controll er r 1 Use r 2 Use Replication r 1 Use r 2 Use Domain Controll er Domain = A Writeable Copy of the Active Directory Data Dat
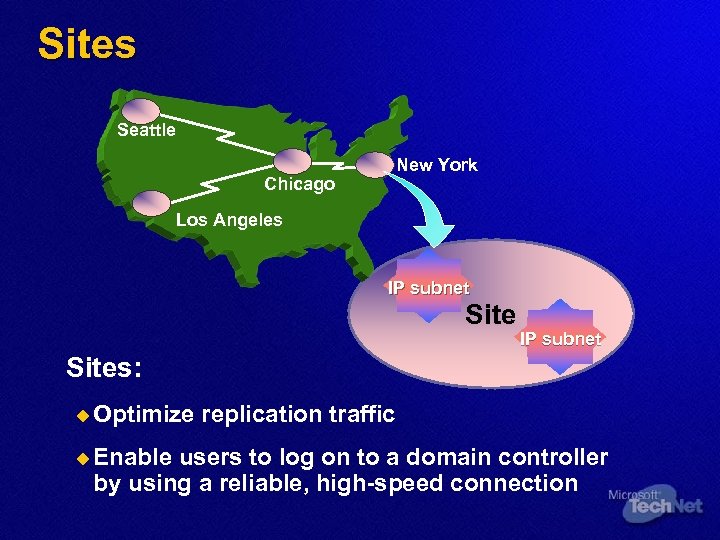 Sites Seattle New York Chicago Los Angeles IP subnet Sites: u Optimize u Enable replication traffic users to log on to a domain controller by using a reliable, high-speed connection
Sites Seattle New York Chicago Los Angeles IP subnet Sites: u Optimize u Enable replication traffic users to log on to a domain controller by using a reliable, high-speed connection
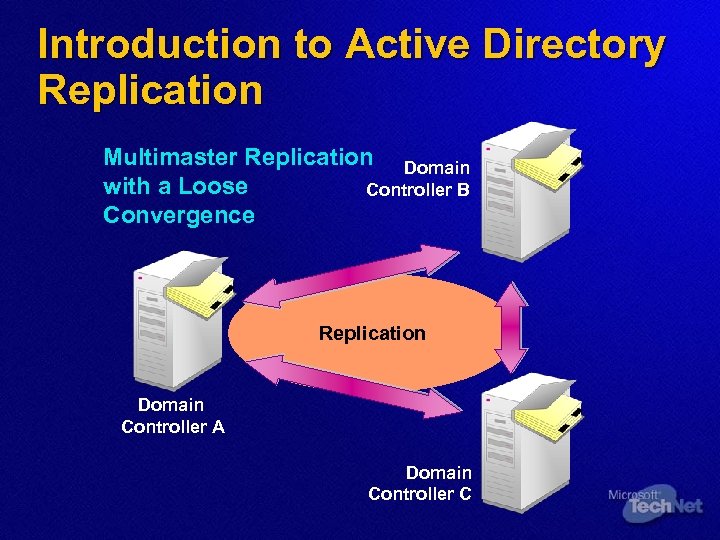 Introduction to Active Directory Replication Multimaster Replication Domain with a Loose Controller B Convergence Replication Domain Controller A Domain Controller C
Introduction to Active Directory Replication Multimaster Replication Domain with a Loose Controller B Convergence Replication Domain Controller A Domain Controller C
 Replication Components and Processes u. How Replication Works u. Replication Latency u. Resolving Replication Conflicts u. Optimizing Replication
Replication Components and Processes u. How Replication Works u. Replication Latency u. Resolving Replication Conflicts u. Optimizing Replication
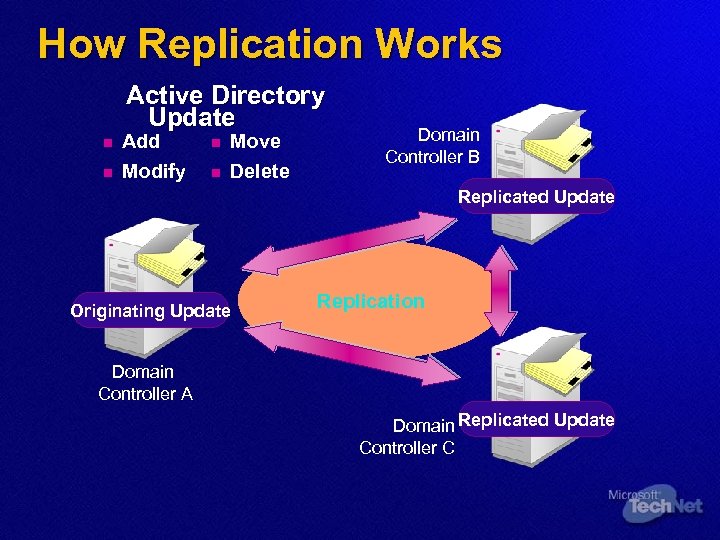 How Replication Works Active Directory Update n n Add Modify n n Move Delete Domain Controller B Replicated Update Originating Update Replication Domain Controller A Domain Replicated Update Controller C
How Replication Works Active Directory Update n n Add Modify n n Move Delete Domain Controller B Replicated Update Originating Update Replication Domain Controller A Domain Replicated Update Controller C
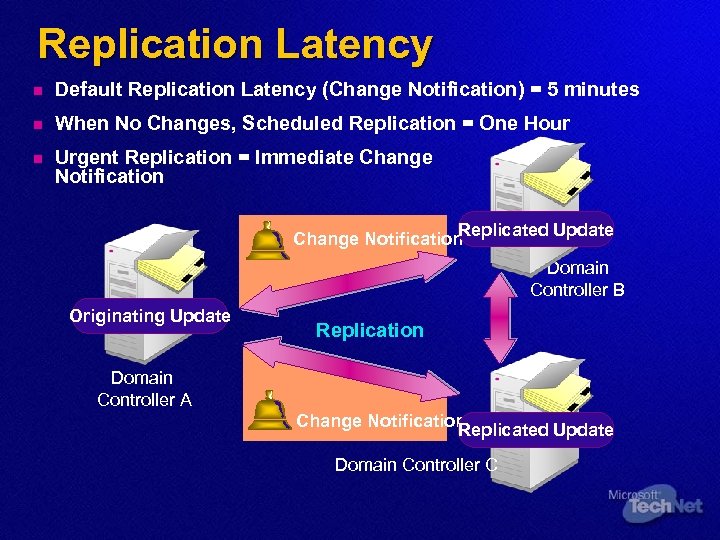 Replication Latency n Default Replication Latency (Change Notification) = 5 minutes n When No Changes, Scheduled Replication = One Hour n Urgent Replication = Immediate Change Notification Replicated Update Change Notification Domain Controller B Originating Update Replication Domain Controller A Change Notification Replicated Update Domain Controller C
Replication Latency n Default Replication Latency (Change Notification) = 5 minutes n When No Changes, Scheduled Replication = One Hour n Urgent Replication = Immediate Change Notification Replicated Update Change Notification Domain Controller B Originating Update Replication Domain Controller A Change Notification Replicated Update Domain Controller C
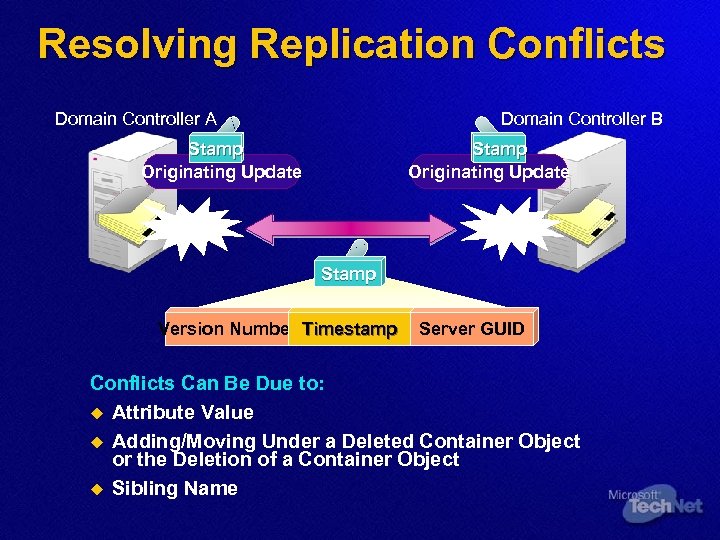 Resolving Replication Conflicts Domain Controller A Domain Controller B Stamp Originating Update Conflict Stamp Version Number Timestamp Server GUID Conflicts Can Be Due to: u Attribute Value u Adding/Moving Under a Deleted Container Object or the Deletion of a Container Object u Sibling Name
Resolving Replication Conflicts Domain Controller A Domain Controller B Stamp Originating Update Conflict Stamp Version Number Timestamp Server GUID Conflicts Can Be Due to: u Attribute Value u Adding/Moving Under a Deleted Container Object or the Deletion of a Container Object u Sibling Name
 Replication Topology u. Directory Partitions u. What Is Replication Topology? u. Global Catalog and Replication of Partitions
Replication Topology u. Directory Partitions u. What Is Replication Topology? u. Global Catalog and Replication of Partitions
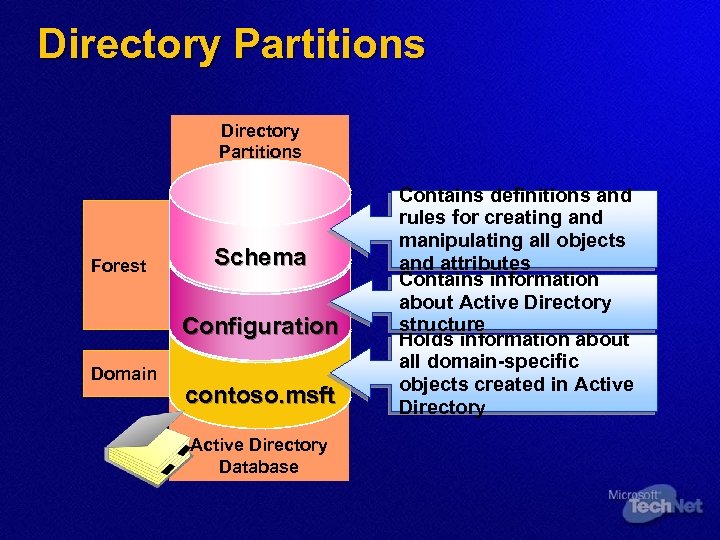 Directory Partitions Forest Schema Configuration Domain contoso. msft Active Directory Database Contains definitions and rules for creating and manipulating all objects and attributes Contains information about Active Directory structure Holds information about all domain-specific objects created in Active Directory
Directory Partitions Forest Schema Configuration Domain contoso. msft Active Directory Database Contains definitions and rules for creating and manipulating all objects and attributes Contains information about Active Directory structure Holds information about all domain-specific objects created in Active Directory
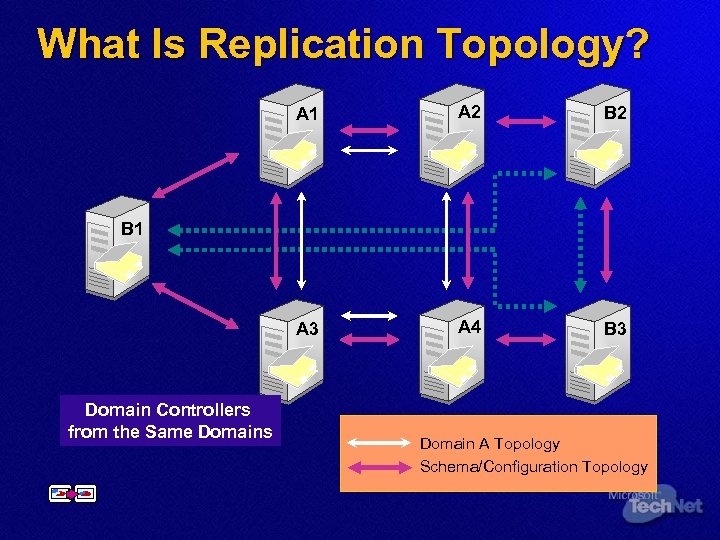 What Is Replication Topology? A 1 A 2 B 2 A 3 A 4 B 3 B 1 Domain Controllers from Different Domains from the Same Domains Domain A Topology Domain B Topology Schema/Configuration Topology
What Is Replication Topology? A 1 A 2 B 2 A 3 A 4 B 3 B 1 Domain Controllers from Different Domains from the Same Domains Domain A Topology Domain B Topology Schema/Configuration Topology
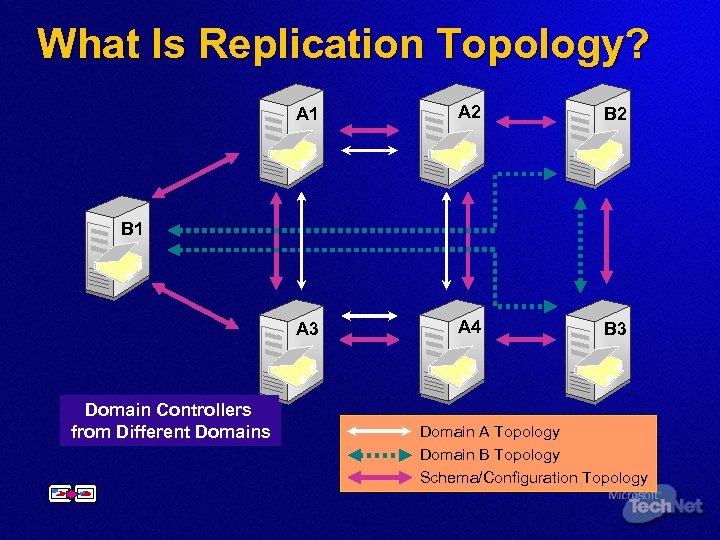 What Is Replication Topology? A 1 A 2 B 2 A 3 A 4 B 3 B 1 Domain Controllers from Different Domains from the Same Domains Domain A Topology Domain B Topology Schema/Configuration Topology
What Is Replication Topology? A 1 A 2 B 2 A 3 A 4 B 3 B 1 Domain Controllers from Different Domains from the Same Domains Domain A Topology Domain B Topology Schema/Configuration Topology
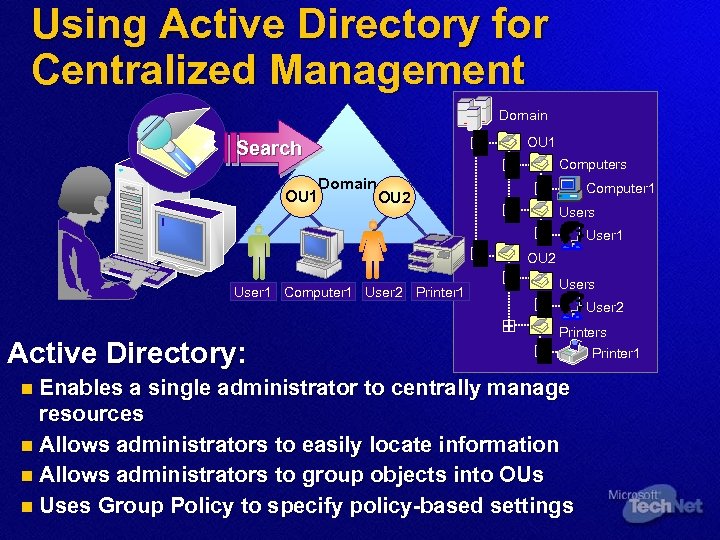 Using Active Directory for Centralized Management Domain OU 1 Search OU 1 Computers Domain Computer 1 OU 2 Users User 1 OU 2 User 1 Computer 1 User 2 Printer 1 Active Directory: Users User 2 Printers Printer 1 Enables a single administrator to centrally manage resources n Allows administrators to easily locate information n Allows administrators to group objects into OUs n Uses Group Policy to specify policy-based settings n
Using Active Directory for Centralized Management Domain OU 1 Search OU 1 Computers Domain Computer 1 OU 2 Users User 1 OU 2 User 1 Computer 1 User 2 Printer 1 Active Directory: Users User 2 Printers Printer 1 Enables a single administrator to centrally manage resources n Allows administrators to easily locate information n Allows administrators to group objects into OUs n Uses Group Policy to specify policy-based settings n
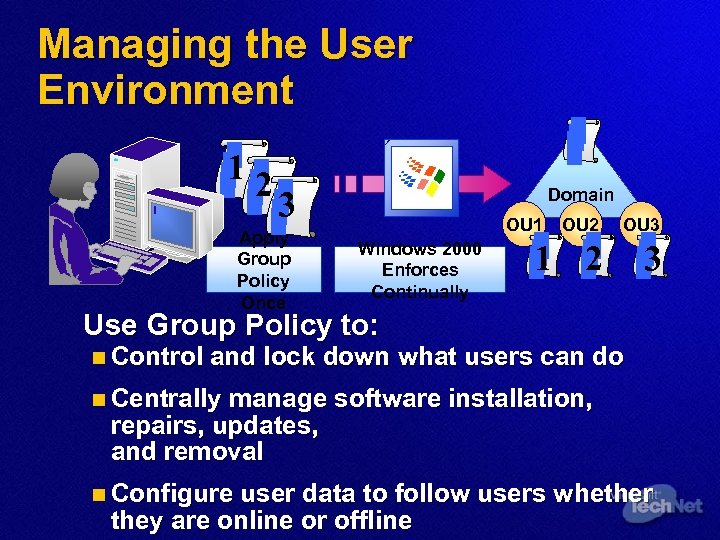 Managing the User Environment 12 3 Apply Group Policy Once Domain OU 1 Windows 2000 Enforces Continually OU 2 OU 3 1 2 3 Use Group Policy to: n Control and lock down what users can do n Centrally manage software installation, repairs, updates, and removal n Configure user data to follow users whether they are online or offline
Managing the User Environment 12 3 Apply Group Policy Once Domain OU 1 Windows 2000 Enforces Continually OU 2 OU 3 1 2 3 Use Group Policy to: n Control and lock down what users can do n Centrally manage software installation, repairs, updates, and removal n Configure user data to follow users whether they are online or offline
 Delegating Administrative Control Domain OU 1 Assign Permissions: l For specific OUs to other administrators l To modify specific attributes of an object in a single OU l To perform the same task in all OUs Customize Administrative Tools to: l Map to delegated administrative tasks l Simplify interface design Admin OU 2 Admin OU 3 Admin
Delegating Administrative Control Domain OU 1 Assign Permissions: l For specific OUs to other administrators l To modify specific attributes of an object in a single OU l To perform the same task in all OUs Customize Administrative Tools to: l Map to delegated administrative tasks l Simplify interface design Admin OU 2 Admin OU 3 Admin
 Review u. Introduction to Active Directory u. Active Directory Logical Structure u. Role of DNS in Active Directory u. Active Directory Physical Structure u. Methods for Administering a Windows 2000 Network
Review u. Introduction to Active Directory u. Active Directory Logical Structure u. Role of DNS in Active Directory u. Active Directory Physical Structure u. Methods for Administering a Windows 2000 Network


