d109ca32ce6d711a00db9e6af07d41b6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
 Modes of Video Production & Delivery for Learning & Teaching Wayne Britcliffe E-Learning Development Team University of York
Modes of Video Production & Delivery for Learning & Teaching Wayne Britcliffe E-Learning Development Team University of York
 Models of video use (non-exhaustive) Chemistry Environment 40 200 Biology Central Ed 1 st Yrs 24 Studies All 130 Experiment st Yrs/2000 Multiple Chemistry 120 technique All 1 Pro+ 80 Dev 10 Org Language 50 Health Sci 20 25 Virtual Ed Studies Field Trip Student Presentation Critique Naturally spoken language Video driven case study Information Assessment Support Demonstration (Learning & Student developed video Teaching Support) Virtual Field Trip Academic Integrity + Lib + IT Student ‘Welcome’ Sites
Models of video use (non-exhaustive) Chemistry Environment 40 200 Biology Central Ed 1 st Yrs 24 Studies All 130 Experiment st Yrs/2000 Multiple Chemistry 120 technique All 1 Pro+ 80 Dev 10 Org Language 50 Health Sci 20 25 Virtual Ed Studies Field Trip Student Presentation Critique Naturally spoken language Video driven case study Information Assessment Support Demonstration (Learning & Student developed video Teaching Support) Virtual Field Trip Academic Integrity + Lib + IT Student ‘Welcome’ Sites
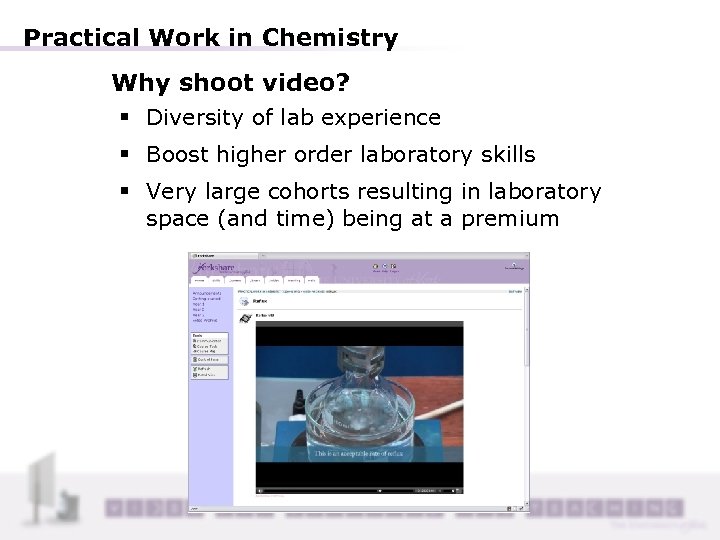 Practical Work in Chemistry Why shoot video? § Diversity of lab experience § Boost higher order laboratory skills § Very large cohorts resulting in laboratory space (and time) being at a premium
Practical Work in Chemistry Why shoot video? § Diversity of lab experience § Boost higher order laboratory skills § Very large cohorts resulting in laboratory space (and time) being at a premium
 Practical Work in Chemistry - Feedback § General feedback from staff – Easy to upload/integrate – Streaming off campus vital (Chemistry) – Support & guidance required for processing video (Chemistry) § From students (Chemistry) “Very good to show to carry out a procedure which you may not have done before. Also, they were good to remind you even if you had performed the procedure before. They were not too long either so were easy to watch. ” “It enables us to see how to do things much more effectively than written instructions and some lab demos. ” “Think they are excellent, hope they are a permanent feature on the VLE. ”
Practical Work in Chemistry - Feedback § General feedback from staff – Easy to upload/integrate – Streaming off campus vital (Chemistry) – Support & guidance required for processing video (Chemistry) § From students (Chemistry) “Very good to show to carry out a procedure which you may not have done before. Also, they were good to remind you even if you had performed the procedure before. They were not too long either so were easy to watch. ” “It enables us to see how to do things much more effectively than written instructions and some lab demos. ” “Think they are excellent, hope they are a permanent feature on the VLE. ”
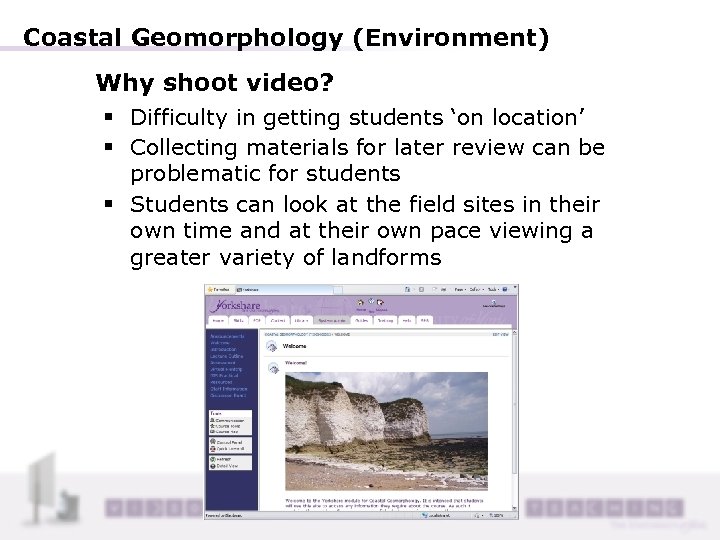 Coastal Geomorphology (Environment) Why shoot video? § Difficulty in getting students ‘on location’ § Collecting materials for later review can be problematic for students § Students can look at the field sites in their own time and at their own pace viewing a greater variety of landforms
Coastal Geomorphology (Environment) Why shoot video? § Difficulty in getting students ‘on location’ § Collecting materials for later review can be problematic for students § Students can look at the field sites in their own time and at their own pace viewing a greater variety of landforms
 Coastal Geomorphology - Feedback § General feedback from staff – Pleased that it was well-received – Initially time consuming editing film – Scope for this sort of work huge § From students (anecdotal via staff) – Students enjoyed the virtual fieldtrip and felt it was an excellent resource – Students felt commentary of the film clips would enhance learning experience
Coastal Geomorphology - Feedback § General feedback from staff – Pleased that it was well-received – Initially time consuming editing film – Scope for this sort of work huge § From students (anecdotal via staff) – Students enjoyed the virtual fieldtrip and felt it was an excellent resource – Students felt commentary of the film clips would enhance learning experience
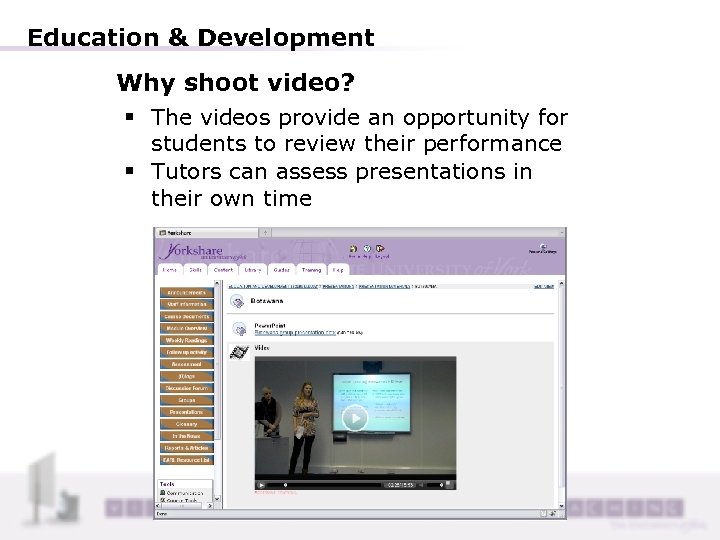 Education & Development Why shoot video? § The videos provide an opportunity for students to review their performance § Tutors can assess presentations in their own time
Education & Development Why shoot video? § The videos provide an opportunity for students to review their performance § Tutors can assess presentations in their own time
 Student Presentation - Feedback § General feedback from staff – There is a real potential to exploit simple technologies to provideo feedback to students either as a group or individually § From students (Chemistry)
Student Presentation - Feedback § General feedback from staff – There is a real potential to exploit simple technologies to provideo feedback to students either as a group or individually § From students (Chemistry)
 International Student Transition Why shoot video? § Initial reason for video development was partly to address the possible swine-flu epidemic § Reaching over 2000 international students face-to-face is difficult
International Student Transition Why shoot video? § Initial reason for video development was partly to address the possible swine-flu epidemic § Reaching over 2000 international students face-to-face is difficult
 Student Transition & Academic Skills - Feedback § General feedback from staff – Key messages much more easily remembered – Became much more knowledgeable about University student support generally – Network of people known radically improved and bonds made during shooting “The process of creating and collaborating on the video gave me detailed knowledge of the support services and opportunities available here at York, it also build lasting links with various departments and student networks. ” "Students generally react very warmly to video and it seems to stick in their memories, especially when it is made at York with York academic staff and students. " "Personally I found it a steep learning curve to create compelling video but very effective at conveying difficult and problematic concepts, for example 'collusion'. "
Student Transition & Academic Skills - Feedback § General feedback from staff – Key messages much more easily remembered – Became much more knowledgeable about University student support generally – Network of people known radically improved and bonds made during shooting “The process of creating and collaborating on the video gave me detailed knowledge of the support services and opportunities available here at York, it also build lasting links with various departments and student networks. ” "Students generally react very warmly to video and it seems to stick in their memories, especially when it is made at York with York academic staff and students. " "Personally I found it a steep learning curve to create compelling video but very effective at conveying difficult and problematic concepts, for example 'collusion'. "
 Student Transition & Academic Skills - Feedback § Feedback from students “The videos were a good stimulus. ” "The videos take a long time to buffer and download. ” “Video downloads take too long and the information in “The videos as it grabs them could be presented in your attention. ” other ways. ” “The videos convey a lot of information in an easy to understand format. ”
Student Transition & Academic Skills - Feedback § Feedback from students “The videos were a good stimulus. ” "The videos take a long time to buffer and download. ” “Video downloads take too long and the information in “The videos as it grabs them could be presented in your attention. ” other ways. ” “The videos convey a lot of information in an easy to understand format. ”
 Summary: why we need to support video use § There as many uses for video as a learning and teaching resource as there are staff wanting to use video § Where video has been integrated student responses have been very positive – Survey and focus group feedback § Staff feedback suggests a strong need for central support of video development/use – Survey and focus group feedback § Student feedback suggests a need to support infrastructure appropriate to the delivery of such audio visual resources
Summary: why we need to support video use § There as many uses for video as a learning and teaching resource as there are staff wanting to use video § Where video has been integrated student responses have been very positive – Survey and focus group feedback § Staff feedback suggests a strong need for central support of video development/use – Survey and focus group feedback § Student feedback suggests a need to support infrastructure appropriate to the delivery of such audio visual resources
 Key Support Considerations § Staff won’t necessarily have audio/video development skills or appropriate software/hardware § Audio/video will need to be ‘consumed’ both on and off campus § Audio/video resources may need to be secure (as reasonably possible) § Staff won’t necessarily have the skills to readily make audio/video available to students in as accessible a way as possible
Key Support Considerations § Staff won’t necessarily have audio/video development skills or appropriate software/hardware § Audio/video will need to be ‘consumed’ both on and off campus § Audio/video resources may need to be secure (as reasonably possible) § Staff won’t necessarily have the skills to readily make audio/video available to students in as accessible a way as possible
 Supporting video Infrastructure § Streaming service fully established – Was trialled and piloted before implementation – Building Block integration with institutional VLE § Secured funding to buy 20 Kodak zi 8 HD cameras – Including lapel microphones, tripods and reflectors § Lecture capture trials completed Training and support § Development of a blended workshop focussed around ‘talking-head’ footage and basic editing skills – Input from video professional § Funded cameras placed with AV for loan handling § Creation of custom ‘Win. FF’ download – File conversion for editing and streaming § Suite of guides and online resources developed
Supporting video Infrastructure § Streaming service fully established – Was trialled and piloted before implementation – Building Block integration with institutional VLE § Secured funding to buy 20 Kodak zi 8 HD cameras – Including lapel microphones, tripods and reflectors § Lecture capture trials completed Training and support § Development of a blended workshop focussed around ‘talking-head’ footage and basic editing skills – Input from video professional § Funded cameras placed with AV for loan handling § Creation of custom ‘Win. FF’ download – File conversion for editing and streaming § Suite of guides and online resources developed
 Moving forward § Staff Issues: – – – Audio/video editing/export Hardware use/choice Digitisation DVD Extraction Copyright/licensing How to best support § Future Development: – – Student video uploads Back-end video processing More flexible embedding of video Automatic bandwidth selection
Moving forward § Staff Issues: – – – Audio/video editing/export Hardware use/choice Digitisation DVD Extraction Copyright/licensing How to best support § Future Development: – – Student video uploads Back-end video processing More flexible embedding of video Automatic bandwidth selection
 Questions http: //vlesupport. york. ac. uk Yorkshare Headquarters Support Site
Questions http: //vlesupport. york. ac. uk Yorkshare Headquarters Support Site
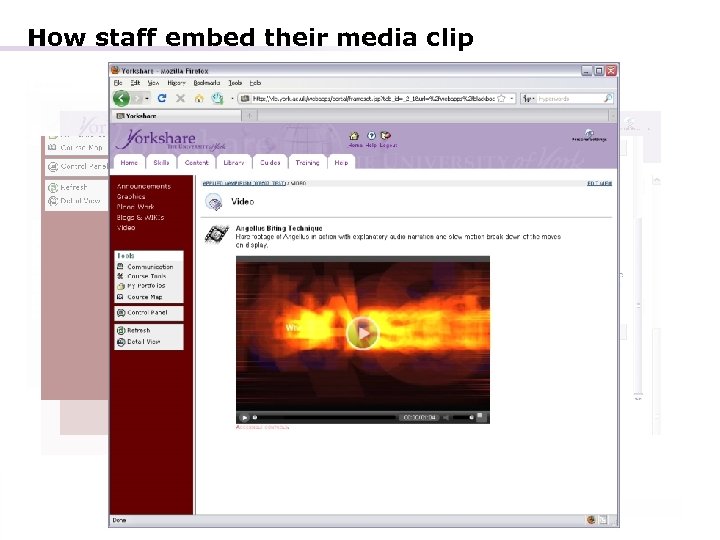 How staff embed their media clip
How staff embed their media clip
 Why establish video support? § A clear increasing demand from staff wanting to deliver audio/video resources in support of their teaching activities § A number of departments have a particular need for audio/video delivery: – – – Music Film, Theatre and Television Health Sciences Language and Linguistics Hull York Medical School § A central push towards developing student induction/transition resources and student skills materials that draw heavily on video clips
Why establish video support? § A clear increasing demand from staff wanting to deliver audio/video resources in support of their teaching activities § A number of departments have a particular need for audio/video delivery: – – – Music Film, Theatre and Television Health Sciences Language and Linguistics Hull York Medical School § A central push towards developing student induction/transition resources and student skills materials that draw heavily on video clips
 Models of video use (non-exhaustive) § Experiment technique (Chemistry & Biology) § Virtual field trip (Environment) § Student presentation critique (Educational Studies, Chemistry, Pro Org Dev) § Information for students transitioning to the York HE environment (inc. Int’nl Student specific materials) § Student developed teaching resources (Educational Studies) § Language and Linguistics (natural spoken language and linguistic usage)
Models of video use (non-exhaustive) § Experiment technique (Chemistry & Biology) § Virtual field trip (Environment) § Student presentation critique (Educational Studies, Chemistry, Pro Org Dev) § Information for students transitioning to the York HE environment (inc. Int’nl Student specific materials) § Student developed teaching resources (Educational Studies) § Language and Linguistics (natural spoken language and linguistic usage)


