lecture 4-2016.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
Modern view at asphaltenes • The basic idea about the PDS dispersed phase - resins, asphaltenes, carbenes and carboids • Separating crude oil (SARA) • Definition onset • The various models of a structure asphaltenes : packing (onion), continental (or island) and fractal 14/09/16 lecture 4 1
![Component analysis • Paraffines [alkanes]: n-/izostructure • Naphthenes: [cycloalkanes] • Aromatic hydrocarbons [arenes] Component analysis • Paraffines [alkanes]: n-/izostructure • Naphthenes: [cycloalkanes] • Aromatic hydrocarbons [arenes]](https://present5.com/presentation/3/-127881896_437896411.pdf-img/-127881896_437896411.pdf-2.jpg)
Component analysis • Paraffines [alkanes]: n-/izostructure • Naphthenes: [cycloalkanes] • Aromatic hydrocarbons [arenes] • Hydrocarbons of mixed structure: in Diesel fraction and above • Non-hydrocarbon oil components: S, N, O • Mineral components: H 2 O, salts • Macromolecular components 14/09/16 lecture 4 2

High-molecular oil components • Wax: – С 18 -С 35 (300 -450 а. е. ) • Cerezines: – С 36 -С 55 (500 -700 а. е. ) • Resins-asphaltenic substances (RAS): – Resines: < 1000 а. е. – Asphaltenes: > 1000 а. е. 14/09/16 lecture 4 3

RAS classification • Resins: • M <1000 • soluble in alkanes • condensed systems related with aliphatic chains • Asphaltenes: Ø M > 1000 Ø ≈ 1 D and above Ø insoluble in alkanes Ø soluble in benzene, CS 2, CCl 4, etc. Ø tend to associations, define the structure of oil disperse systems 14/09/16 lecture 4 4

14/09/16 lecture 4 5
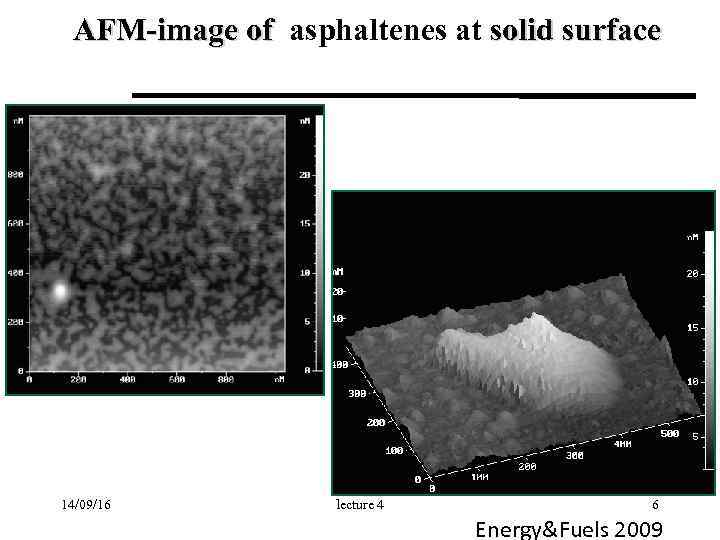

АFМ-image of asphaltenes at solid surface 14/09/16 lecture 4 6 Energy&Fuels 2009
14/09/16 lecture 4 7
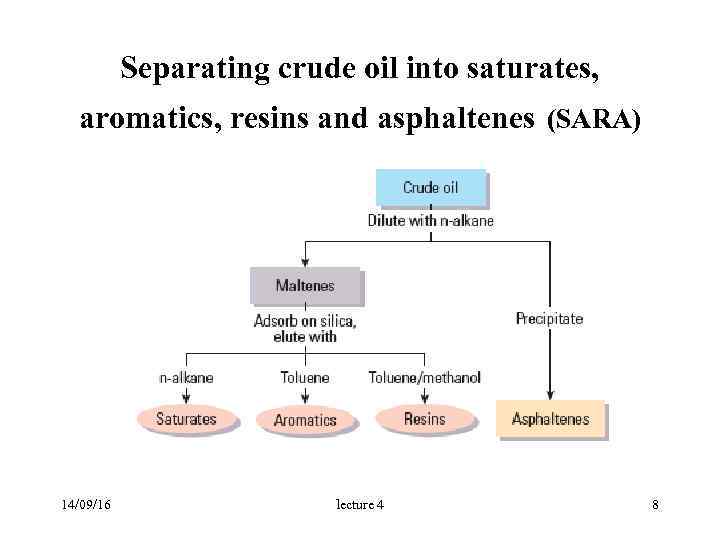
Separating crude oil into saturates, aromatics, resins and asphaltenes (SARA) 14/09/16 lecture 4 8
14/09/16 lecture 4 9
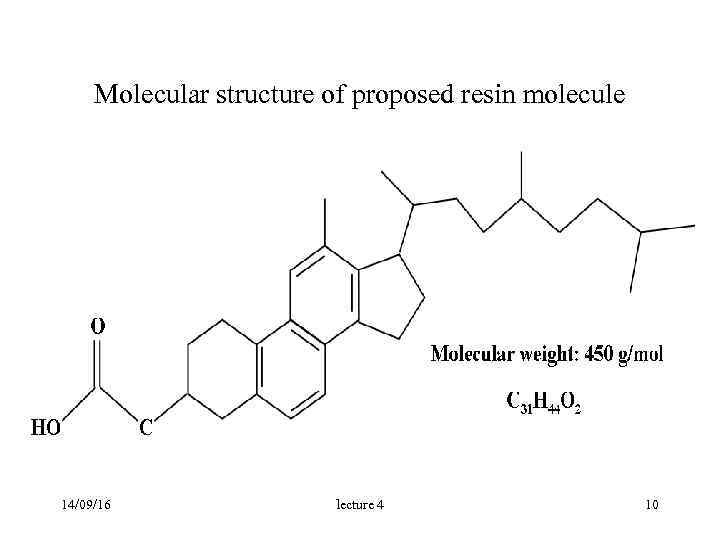
Molecular structure of proposed resin molecule 14/09/16 lecture 4 10
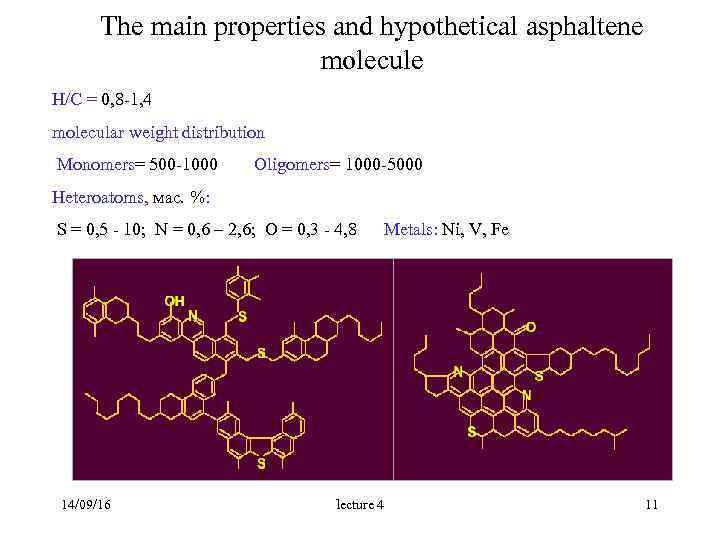
The main properties and hypothetical asphaltene molecule H/C = 0, 8 -1, 4 molecular weight distribution Monomers= 500 -1000 Oligomers= 1000 -5000 Heteroatoms, мас. %: S = 0, 5 - 10; N = 0, 6 – 2, 6; O = 0, 3 - 4, 8 Metals: Ni, V, Fe 14/09/16 lecture 4 11
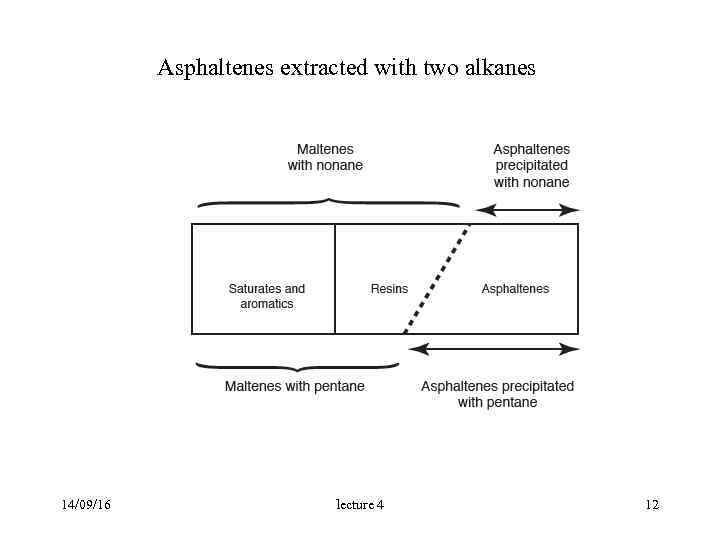
Asphaltenes extracted with two alkanes 14/09/16 lecture 4 12
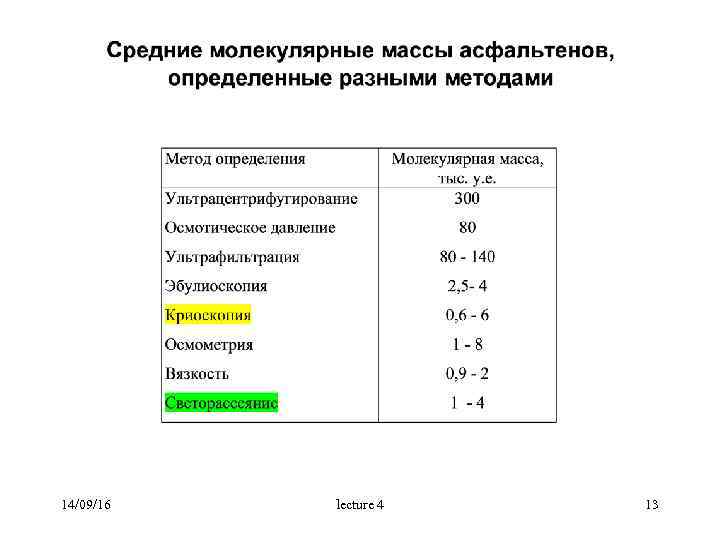
14/09/16 lecture 4 13
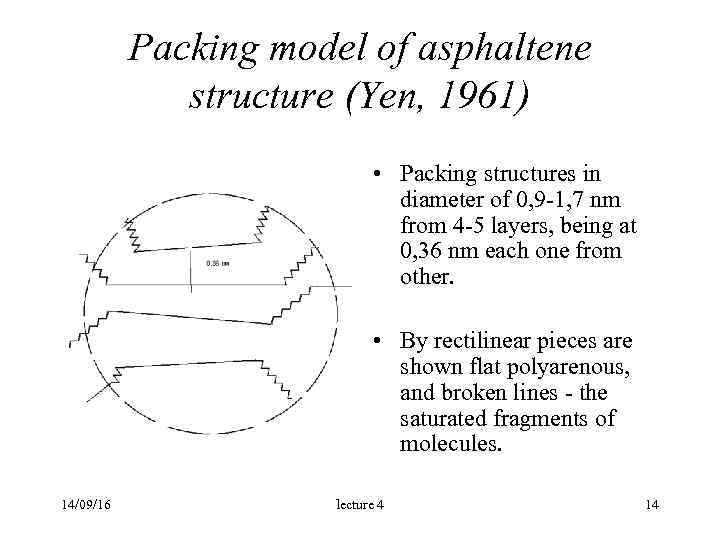
Packing model of asphaltene structure (Yen, 1961) • Packing structures in diameter of 0, 9 -1, 7 nm from 4 -5 layers, being at 0, 36 nm each one from other. • By rectilinear pieces are shown flat polyarenous, and broken lines - the saturated fragments of molecules. 14/09/16 lecture 4 14
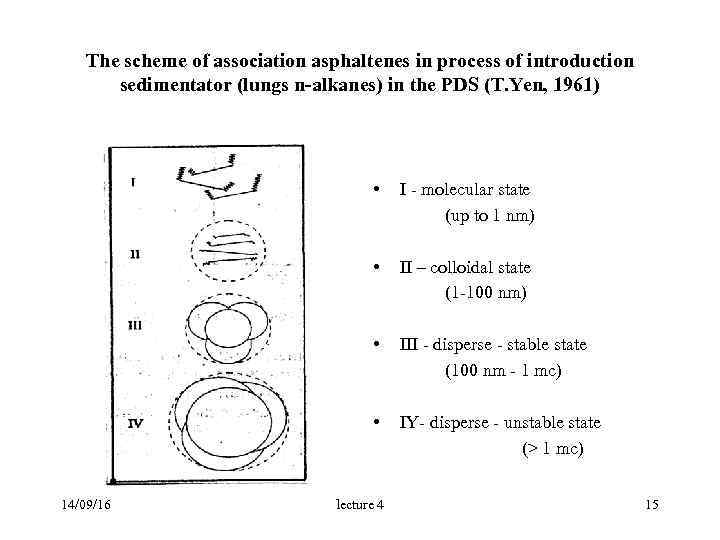
The scheme of association asphaltenes in process of introduction sedimentator (lungs n-alkanes) in the PDS (T. Yen, 1961) • I - molecular state (up to 1 nm) • II – colloidal state (1 -100 nm) • III - disperse - stable state (100 nm - 1 mc) • IY- disperse - unstable state (> 1 mc) 14/09/16 lecture 4 15

Organization level of ashaltens (1) • Monomers • Yen elementary particles (9 ÷ 17 Å) • Oligomers (25 ÷ 50 Å) • Polymers (> 150 Å) • + Aggregation processes, including the processes of gel / glass 14/09/16 lecture 4 16
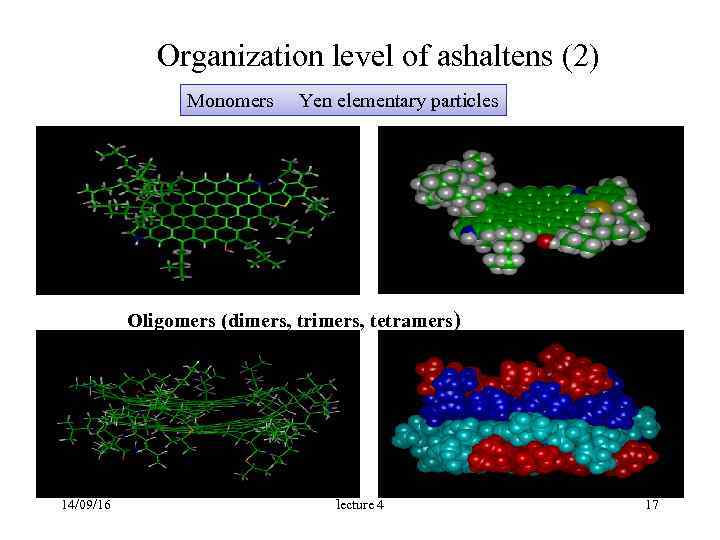
Organization level of ashaltens (2) Monomers Yen elementary particles Oligomers (dimers, trimers, tetramers) 14/09/16 lecture 4 17
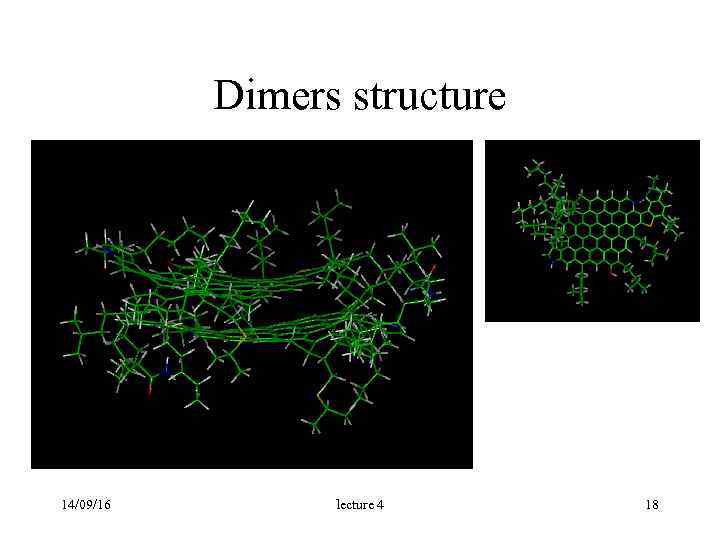
Dimers structure 14/09/16 lecture 4 18
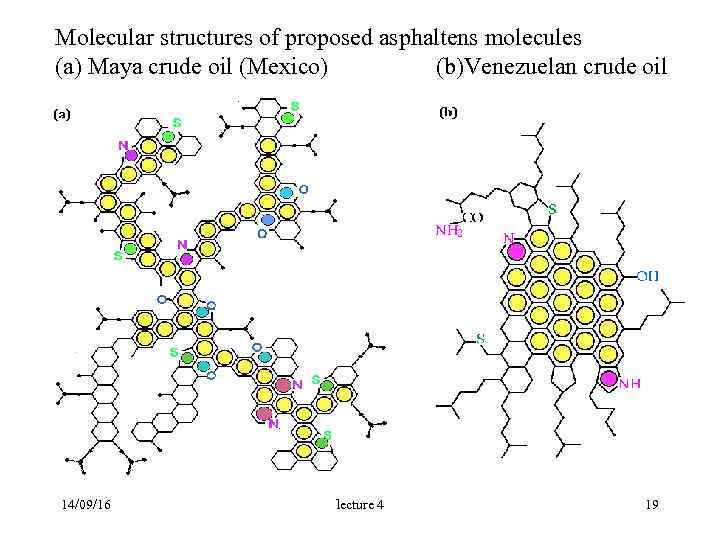
Molecular structures of proposed asphaltens molecules (a) Maya crude oil (Mexico) (b)Venezuelan crude oil 14/09/16 lecture 4 19
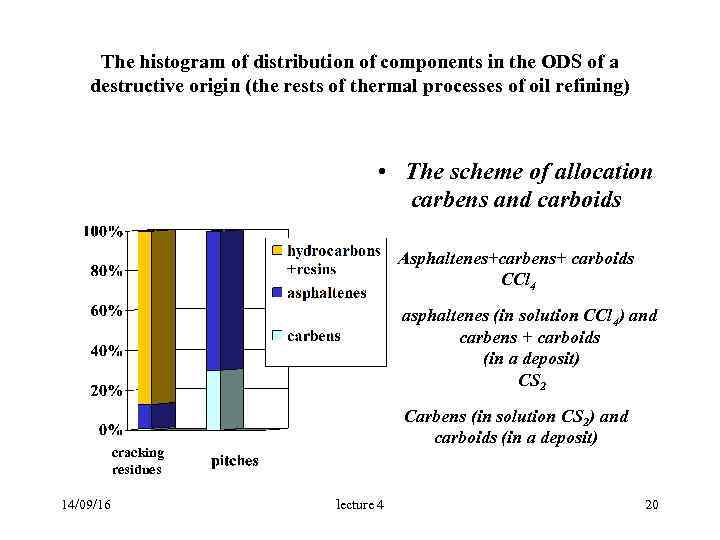
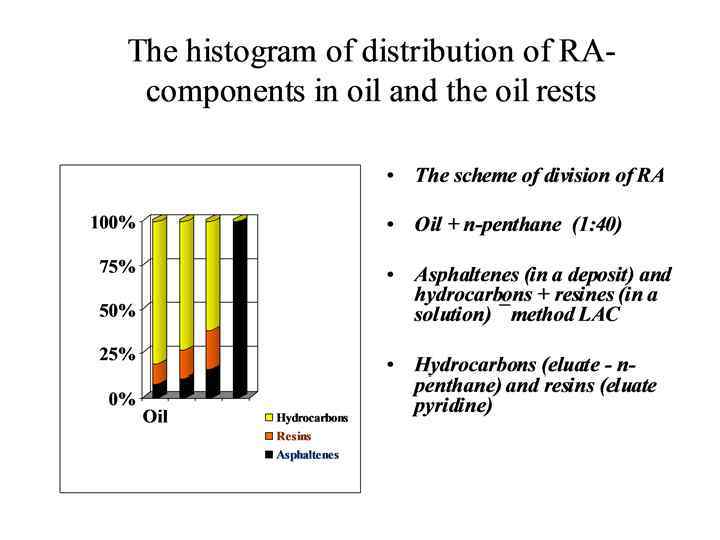
The histogram of distribution of components in the ODS of a destructive origin (the rests of thermal processes of oil refining) • The scheme of allocation carbens and carboids Asphaltenes+carbens+ carboids CCl 4 asphaltenes (in solution CCl 4) and carbens + carboids (in a deposit) CS 2 Carbens (in solution CS 2) and carboids (in a deposit) cracking residues 14/09/16 lecture 4 20
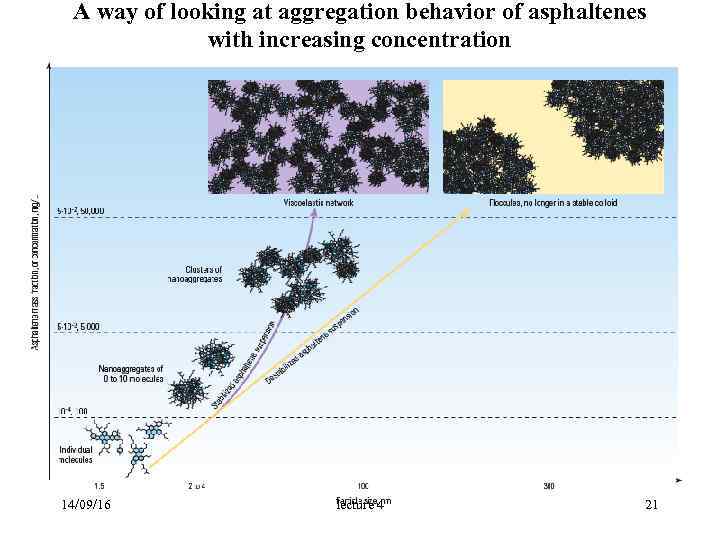
A way of looking at aggregation behavior of asphaltenes with increasing concentration 14/09/16 lecture 4 21
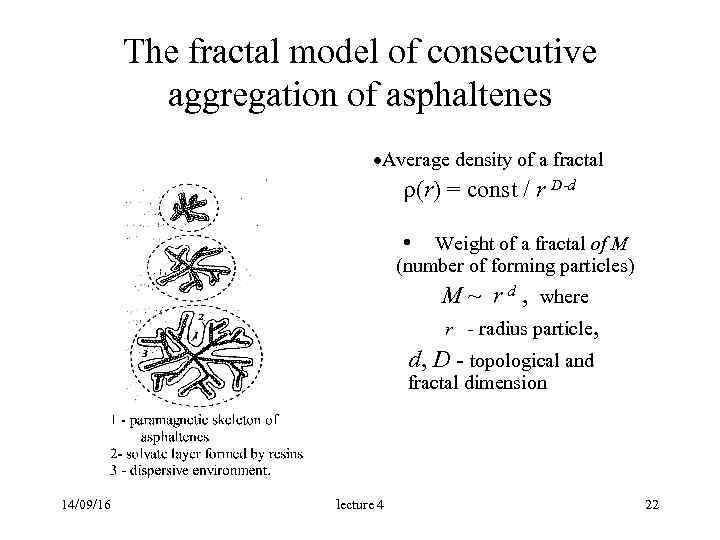
The fractal model of consecutive aggregation of asphaltenes ·Average density of a fractal (r) = const / r D-d • Weight of a fractal of M (number of forming particles) М ~ r d , where r - radius particle, d, D - topological and fractal dimension 14/09/16 lecture 4 22
lecture 4-2016.ppt