Kozlov_SM_6_18_10_16_Intern_choice.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 MODERN STRATEGIC ANALYSIS Theme 2. Process of strategic management, internal analysis , strategy choice Dr. Prof. Aleksandr Kozlov 18/10/2016
MODERN STRATEGIC ANALYSIS Theme 2. Process of strategic management, internal analysis , strategy choice Dr. Prof. Aleksandr Kozlov 18/10/2016
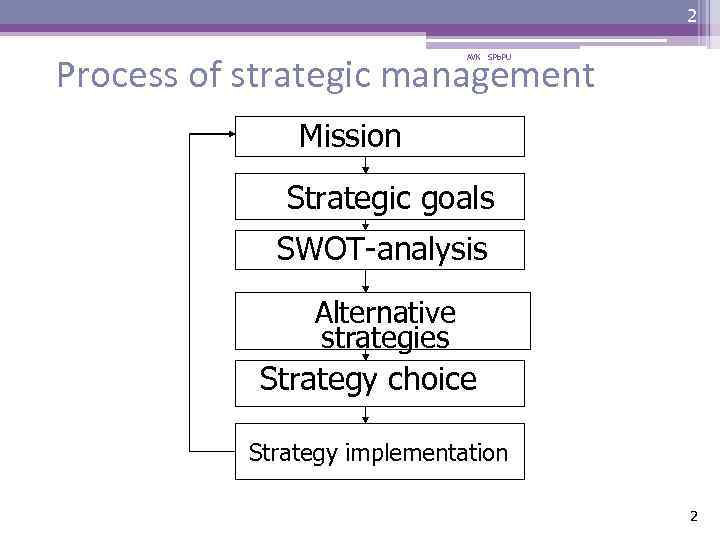 2 Process of strategic management AVK SPb. PU Mission Strategic goals SWOT-analysis Alternative strategies Strategy choice Strategy implementation 2
2 Process of strategic management AVK SPb. PU Mission Strategic goals SWOT-analysis Alternative strategies Strategy choice Strategy implementation 2
 3 Internal analysis • Production • Finance • Purchasing • Marketing • Sales • HRM • Management • Innovations AVK SPb. PU
3 Internal analysis • Production • Finance • Purchasing • Marketing • Sales • HRM • Management • Innovations AVK SPb. PU
 4 AVK SPb. PU Internal analysis criteria • Comparison with the past • Comparison with competitors • External evaluation (experts) • Official recognition • Public recognition
4 AVK SPb. PU Internal analysis criteria • Comparison with the past • Comparison with competitors • External evaluation (experts) • Official recognition • Public recognition
 5 Strengths • Advantages of proposition? • Capabilities? • Competitive advantages? • USP's (unique selling points)? • Resources, Assets, People? • Experience, knowledge, data? • Financial reserves, likely returns? • Marketing - reach, distribution, awareness? AVK SPb. PU • Cultural, attitudinal, behavioural? • Location and geographical? • Price, value, quality? • Accreditations, qualifications, certifications? • Processes, systems, IT, communications? • Innovative aspects?
5 Strengths • Advantages of proposition? • Capabilities? • Competitive advantages? • USP's (unique selling points)? • Resources, Assets, People? • Experience, knowledge, data? • Financial reserves, likely returns? • Marketing - reach, distribution, awareness? AVK SPb. PU • Cultural, attitudinal, behavioural? • Location and geographical? • Price, value, quality? • Accreditations, qualifications, certifications? • Processes, systems, IT, communications? • Innovative aspects?
 6 Weaknesses AVK SPb. PU • Effects on core activities, • Disadvantages of proposition? distraction? • Gaps in capabilities? • Reliability of data, plan • Lack of competitive strength? predictability? • Reputation, presence and • Morale, commitment, reach? leadership? • Financials? • Accreditations, etc? • Own known vulnerabilities? • Processes and systems, • Timescales, deadlines and etc? pressures? • Continuity, supply chain • Cashflow, start-up cash-drain? robustness?
6 Weaknesses AVK SPb. PU • Effects on core activities, • Disadvantages of proposition? distraction? • Gaps in capabilities? • Reliability of data, plan • Lack of competitive strength? predictability? • Reputation, presence and • Morale, commitment, reach? leadership? • Financials? • Accreditations, etc? • Own known vulnerabilities? • Processes and systems, • Timescales, deadlines and etc? pressures? • Continuity, supply chain • Cashflow, start-up cash-drain? robustness?
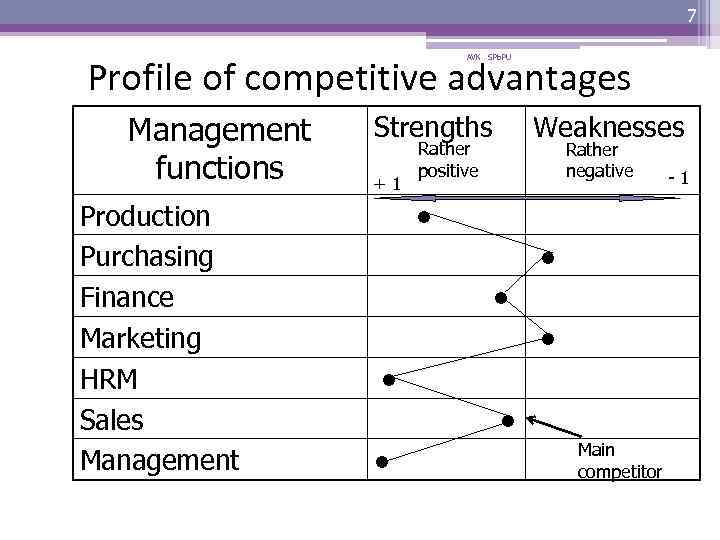 7 AVK SPb. PU Profile of competitive advantages Management functions Production Purchasing Finance Marketing HRM Sales Management Strengths +1 Weaknesses Rather positive Rather negative ● ● ● ● Main competitor -1
7 AVK SPb. PU Profile of competitive advantages Management functions Production Purchasing Finance Marketing HRM Sales Management Strengths +1 Weaknesses Rather positive Rather negative ● ● ● ● Main competitor -1
 8 AVK SPb. PU Modern tools of strategic analysis. Value chain • Value chain analysis ▫ a process where a firm identifies its priorities and support activities that add value to its final product and then analyze these activities to reduce costs or increase differentiation. • Value chain represents the internal activities a firm engages in when transforming inputs into outputs. ”
8 AVK SPb. PU Modern tools of strategic analysis. Value chain • Value chain analysis ▫ a process where a firm identifies its priorities and support activities that add value to its final product and then analyze these activities to reduce costs or increase differentiation. • Value chain represents the internal activities a firm engages in when transforming inputs into outputs. ”
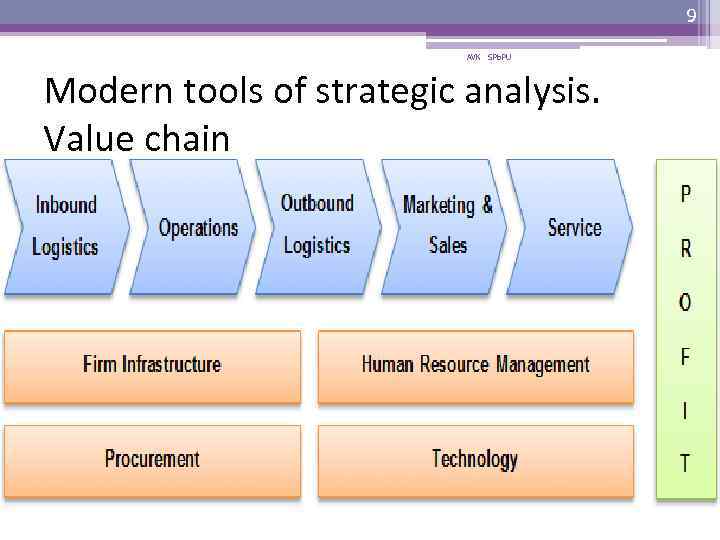 9 AVK SPb. PU Modern tools of strategic analysis. Value chain
9 AVK SPb. PU Modern tools of strategic analysis. Value chain
 10 AVK SPb. PU Business Strategy Choice • Choice about business positioning relative to competitors, creating strategic capabilities and competitive advantage
10 AVK SPb. PU Business Strategy Choice • Choice about business positioning relative to competitors, creating strategic capabilities and competitive advantage
 11 AVK SPb. PU Competitive advantage principles VRIN • Value, • Rarity, • Inimitability and • Non-substitutability From: Jay Barney: ‘Firm resources and sustained competitive advantage’, Journal of Management, vol. 17 (1991), no. 1, pp. 99– 120.
11 AVK SPb. PU Competitive advantage principles VRIN • Value, • Rarity, • Inimitability and • Non-substitutability From: Jay Barney: ‘Firm resources and sustained competitive advantage’, Journal of Management, vol. 17 (1991), no. 1, pp. 99– 120.
 12 AVK SPb. PU VRIN: Value Strategic capabilities are of value when they: • take advantage of opportunities and neutralise threats, • provide value to customers • provide potential competitive advantage at a cost that allows an organisation to realise acceptable levels of return
12 AVK SPb. PU VRIN: Value Strategic capabilities are of value when they: • take advantage of opportunities and neutralise threats, • provide value to customers • provide potential competitive advantage at a cost that allows an organisation to realise acceptable levels of return
 13 VRIN: Rarity AVK SPb. PU • Rare capabilities are those possessed uniquely by one organisation or by a few others only. (E. g. a company may have patented products, have supremely talented people or a powerful brand. ) • Rarity could be temporary. (Eg: Patents expire, key individuals can leave or brands can be de-valued by adverse publicity. )
13 VRIN: Rarity AVK SPb. PU • Rare capabilities are those possessed uniquely by one organisation or by a few others only. (E. g. a company may have patented products, have supremely talented people or a powerful brand. ) • Rarity could be temporary. (Eg: Patents expire, key individuals can leave or brands can be de-valued by adverse publicity. )
 14 VRIN: Inimitability AVK SPb. PU Inimitable capabilities are those that competitors find difficult to imitate or obtain. • Competitive advantage can be built on unique resources (a key individual or IT system) but these may not be sustainable (key people leave or others acquire the same systems). • Sustainable advantage is more often found in competences (the way resources are managed, developed and deployed) and the way competences are linked together and integrated
14 VRIN: Inimitability AVK SPb. PU Inimitable capabilities are those that competitors find difficult to imitate or obtain. • Competitive advantage can be built on unique resources (a key individual or IT system) but these may not be sustainable (key people leave or others acquire the same systems). • Sustainable advantage is more often found in competences (the way resources are managed, developed and deployed) and the way competences are linked together and integrated
 15 AVK SPb. PU VRIN: Non-substitutability Competitive advantage may not be sustainable if there is a threat of substitution. • Product or service substitution from a different industry/market. For example, postal services partly substituted by e-mail. • Competence substitution. For example, a skill substituted by expert systems or IT solutions
15 AVK SPb. PU VRIN: Non-substitutability Competitive advantage may not be sustainable if there is a threat of substitution. • Product or service substitution from a different industry/market. For example, postal services partly substituted by e-mail. • Competence substitution. For example, a skill substituted by expert systems or IT solutions
 16 Alternative strategies • Growth • Diversification ▫ Conglomerated ▫ Concentric • Focus • Integration ▫ Vertical ▫ Horizontal • Withdrawal AVK SPb. PU
16 Alternative strategies • Growth • Diversification ▫ Conglomerated ▫ Concentric • Focus • Integration ▫ Vertical ▫ Horizontal • Withdrawal AVK SPb. PU
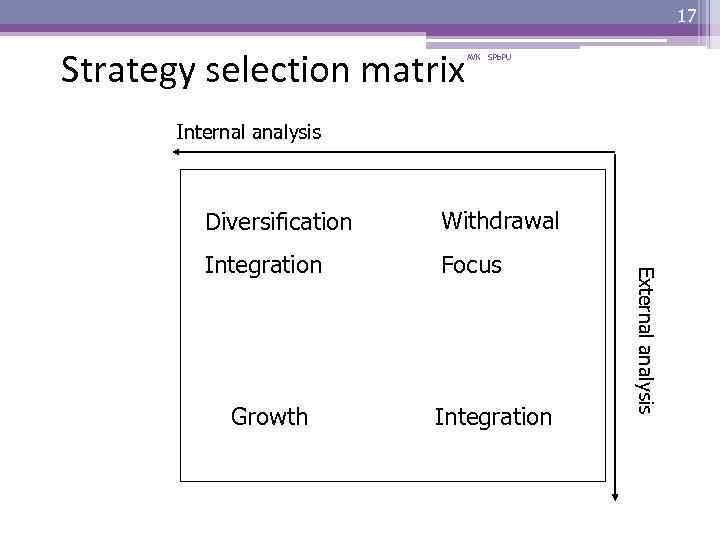 17 Strategy selection matrix AVK SPb. PU Internal analysis Withdrawal Integration Focus Growth Integration External analysis Diversification
17 Strategy selection matrix AVK SPb. PU Internal analysis Withdrawal Integration Focus Growth Integration External analysis Diversification


