 MODERN STRATEGIC ANALYSIS: structures of growing company Dr. Prof. Aleksandr Kozlov 08/11/201
MODERN STRATEGIC ANALYSIS: structures of growing company Dr. Prof. Aleksandr Kozlov 08/11/201
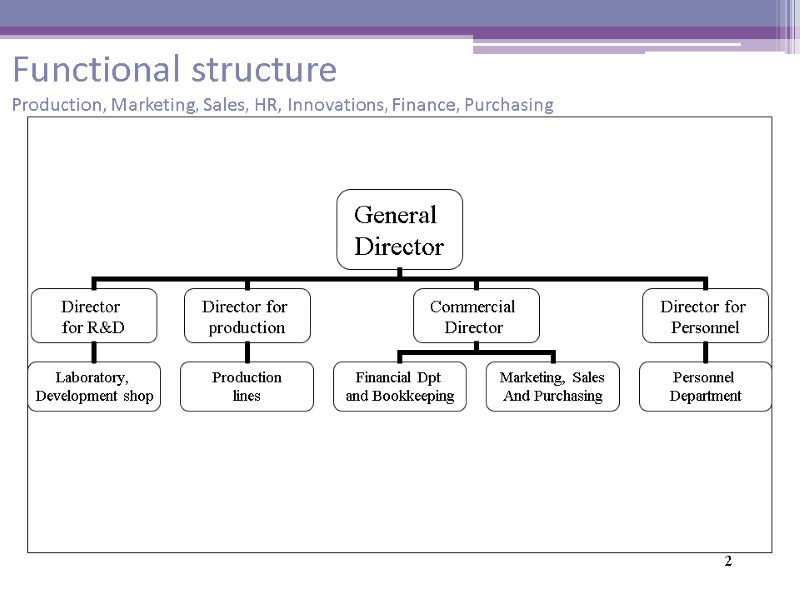 2 Functional structure Production, Marketing, Sales, HR, Innovations, Finance, Purchasing
2 Functional structure Production, Marketing, Sales, HR, Innovations, Finance, Purchasing
 Functional structure Advantages Simple, evident Centralised control Clear spheres of responsibility High level of professionalism of functional specialists High level of efficiency in functional departments 3
Functional structure Advantages Simple, evident Centralised control Clear spheres of responsibility High level of professionalism of functional specialists High level of efficiency in functional departments 3
 4 Functional structure Disadvantages Long time decision making process Lack of systematic vision for functional managers Functional myopia Contradictory interests of functional departments and possible conflicts between them
4 Functional structure Disadvantages Long time decision making process Lack of systematic vision for functional managers Functional myopia Contradictory interests of functional departments and possible conflicts between them
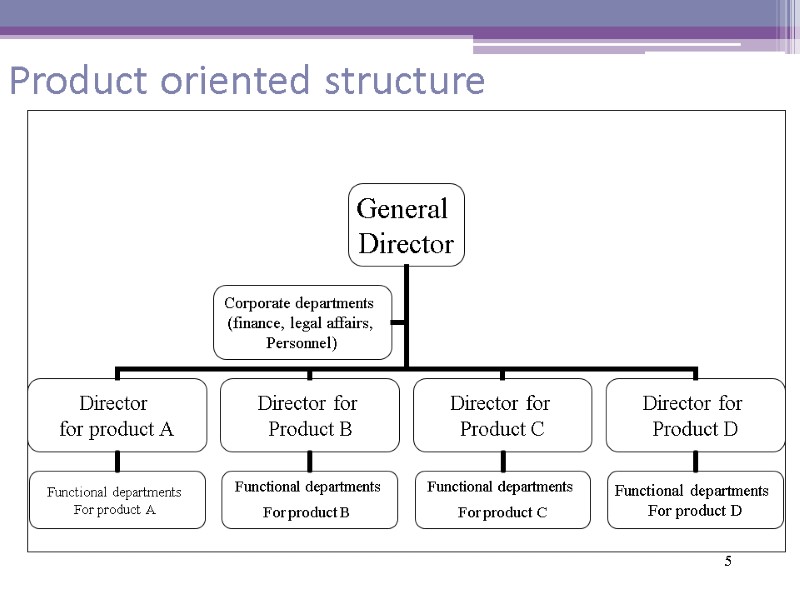 5 Product oriented structure
5 Product oriented structure
 6 Product oriented structure Advantages Gives chance to make focus on the particular product, taking into accounts specifics of it’s sales Allows to investigate market details for every product Allows to build a team of professionals in sales of every product Increases responsibility of managers in specific product sales Allows to calculate precise profitability of every product
6 Product oriented structure Advantages Gives chance to make focus on the particular product, taking into accounts specifics of it’s sales Allows to investigate market details for every product Allows to build a team of professionals in sales of every product Increases responsibility of managers in specific product sales Allows to calculate precise profitability of every product
 Product oriented structure Disadvantages Managers of product groups are demonstrating a “product egoism” Doubling of management functions Barriers in coordination between different product groups 7
Product oriented structure Disadvantages Managers of product groups are demonstrating a “product egoism” Doubling of management functions Barriers in coordination between different product groups 7
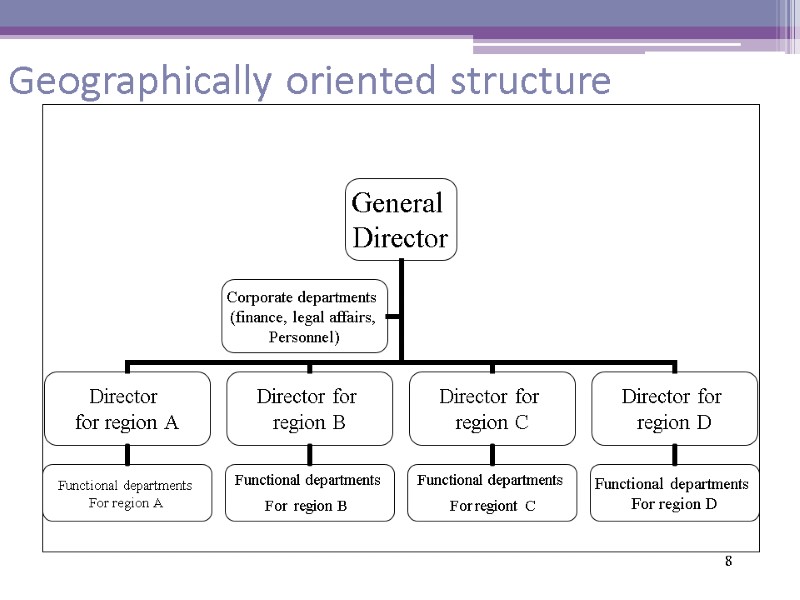 8 Geographically oriented structure
8 Geographically oriented structure
 Geographically oriented structure Advantages Allows to take into account peculiarities of every geographical market Delegation of responsibility to lower level of hierarchy Barriers in coordination between different product groups Regional branches are the good school for managers preparing them to successful carrier 9
Geographically oriented structure Advantages Allows to take into account peculiarities of every geographical market Delegation of responsibility to lower level of hierarchy Barriers in coordination between different product groups Regional branches are the good school for managers preparing them to successful carrier 9
 Geographically oriented structure Disadvantages Difficult to keep one nad individed corporate image Doubling of management functions Makes the structure more complicated since geographical departments have to be built 10
Geographically oriented structure Disadvantages Difficult to keep one nad individed corporate image Doubling of management functions Makes the structure more complicated since geographical departments have to be built 10
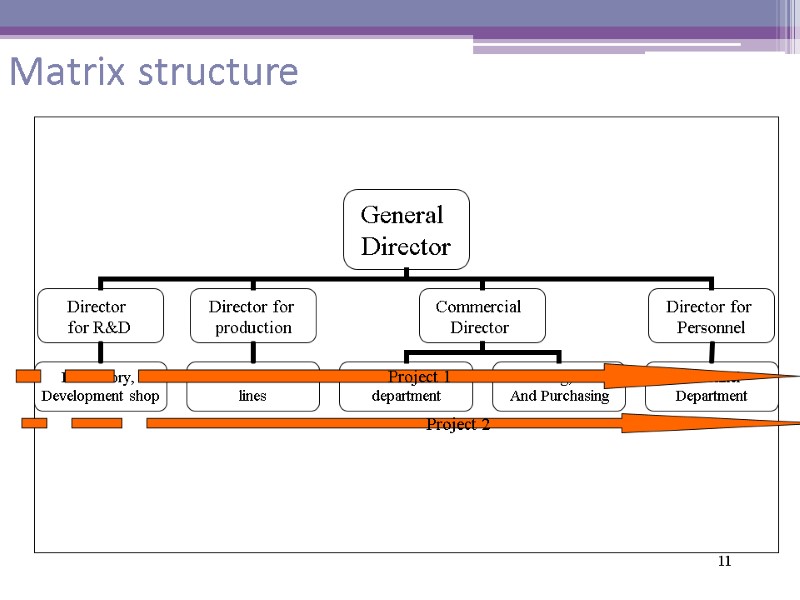 11 Matrix structure Project 1 Project 2
11 Matrix structure Project 1 Project 2
 Matrix structure Advantage Gives flexibility in decision making for big companies Problems Difficult to run because of two lines of responsibility (linear and project) Depends on ability of staff involved into a project to work in teams 12
Matrix structure Advantage Gives flexibility in decision making for big companies Problems Difficult to run because of two lines of responsibility (linear and project) Depends on ability of staff involved into a project to work in teams 12
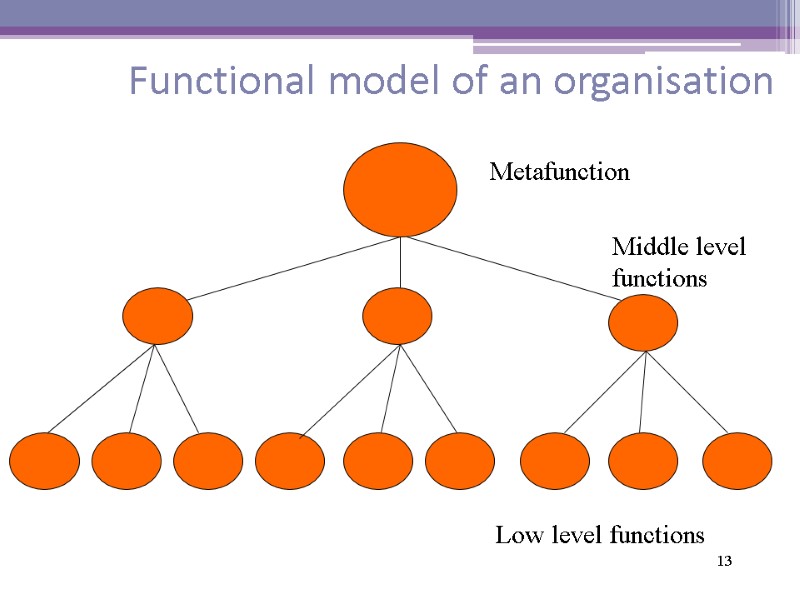 13 Functional model of an organisation Metafunction Middle level functions Low level functions
13 Functional model of an organisation Metafunction Middle level functions Low level functions
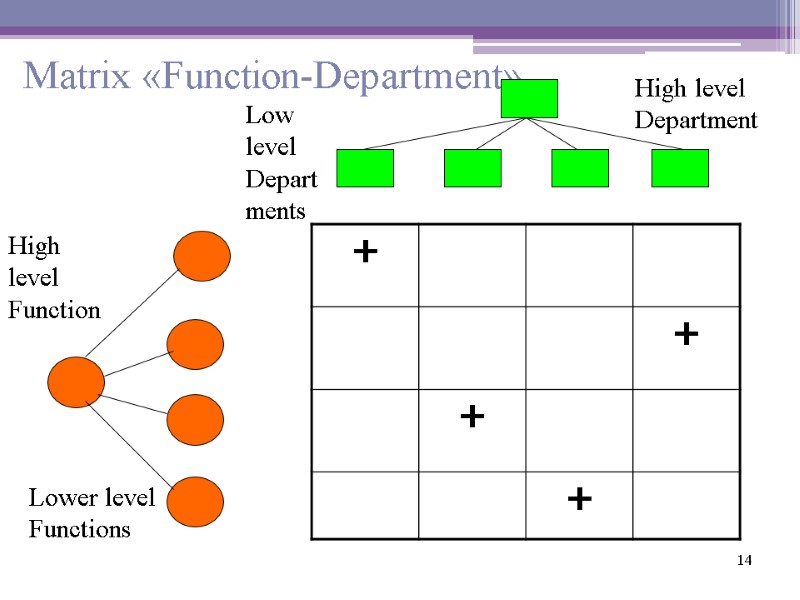 14 Matrix «Function-Department» High level Function Lower level Functions High level Department Low level Departments
14 Matrix «Function-Department» High level Function Lower level Functions High level Department Low level Departments
 Flexible organisational structures Flexibility is defined as the ability of the company proactively, reactively or inherently to implement changes in its components and its relationships with environment 15
Flexible organisational structures Flexibility is defined as the ability of the company proactively, reactively or inherently to implement changes in its components and its relationships with environment 15
 Flexible organisational structures Ad Hoc Structures Ad hoc team is to be created to handle a temporary project. Ad hoc teams are flexible because they enable companies to handle special projects quickly and then dissolve the team after the work is completed. 16
Flexible organisational structures Ad Hoc Structures Ad hoc team is to be created to handle a temporary project. Ad hoc teams are flexible because they enable companies to handle special projects quickly and then dissolve the team after the work is completed. 16
 Flexible organisational structures Network A network organizational structure consists of multiple organizations that work together to produce goods or provide services. It is more complicated and complex than any other structure Managers in network structures spend most of their time coordinating and controlling external relations I.E. While business giants risk becoming too clumsy to proact, act and react efficiently, the new network organizations contract out any business function from “mother” company 17
Flexible organisational structures Network A network organizational structure consists of multiple organizations that work together to produce goods or provide services. It is more complicated and complex than any other structure Managers in network structures spend most of their time coordinating and controlling external relations I.E. While business giants risk becoming too clumsy to proact, act and react efficiently, the new network organizations contract out any business function from “mother” company 17
 Flexible organisational structures Virtual A special form of boundaryless organization, existing within a network of alliances, using the Internet The virtual organization is not physically existing as such 18
Flexible organisational structures Virtual A special form of boundaryless organization, existing within a network of alliances, using the Internet The virtual organization is not physically existing as such 18





































