 Modern Genetics
Modern Genetics
 Watson and Crick • Watson and Crick – developed the model of DNA – It forms a double helix
Watson and Crick • Watson and Crick – developed the model of DNA – It forms a double helix
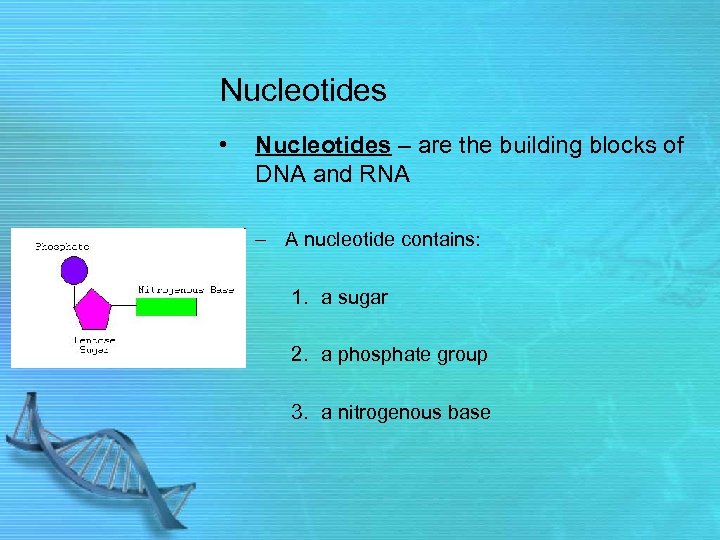 Nucleotides • Nucleotides – are the building blocks of DNA and RNA – A nucleotide contains: 1. a sugar 2. a phosphate group 3. a nitrogenous base
Nucleotides • Nucleotides – are the building blocks of DNA and RNA – A nucleotide contains: 1. a sugar 2. a phosphate group 3. a nitrogenous base
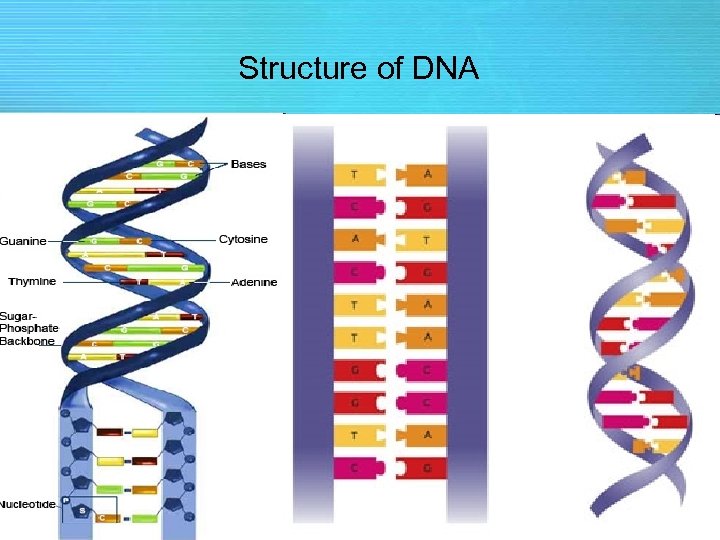 Structure of DNA
Structure of DNA
 DNA • DNA – stands for deoxyribonucleic acid – DNA is double-stranded and made of nucleotides – The sugar in DNA is deoxyribose – The nitrogenous bases in DNA are: 1. Adenine (A) 2. Guanine (G) 3. Cytosine (C) 4. Thymine (T)
DNA • DNA – stands for deoxyribonucleic acid – DNA is double-stranded and made of nucleotides – The sugar in DNA is deoxyribose – The nitrogenous bases in DNA are: 1. Adenine (A) 2. Guanine (G) 3. Cytosine (C) 4. Thymine (T)
 RNA • RNA – stands for ribonucleic acid – RNA is single-stranded and made of nucleotides – The sugar in RNA is ribose – The nitrogenous bases in RNA are: 1. Adenine (A) 2. Guanine (G) 3. Cytosine (C) 4. Uracil (U)
RNA • RNA – stands for ribonucleic acid – RNA is single-stranded and made of nucleotides – The sugar in RNA is ribose – The nitrogenous bases in RNA are: 1. Adenine (A) 2. Guanine (G) 3. Cytosine (C) 4. Uracil (U)
 Base Pairing • In DNA: Cytosine pairs with Guanine - C-G Adenine pairs with Thymine - A-T • In RNA: Cytosine pairs with Guanine - C-G Adenine pairs with Uracil - A-U
Base Pairing • In DNA: Cytosine pairs with Guanine - C-G Adenine pairs with Thymine - A-T • In RNA: Cytosine pairs with Guanine - C-G Adenine pairs with Uracil - A-U
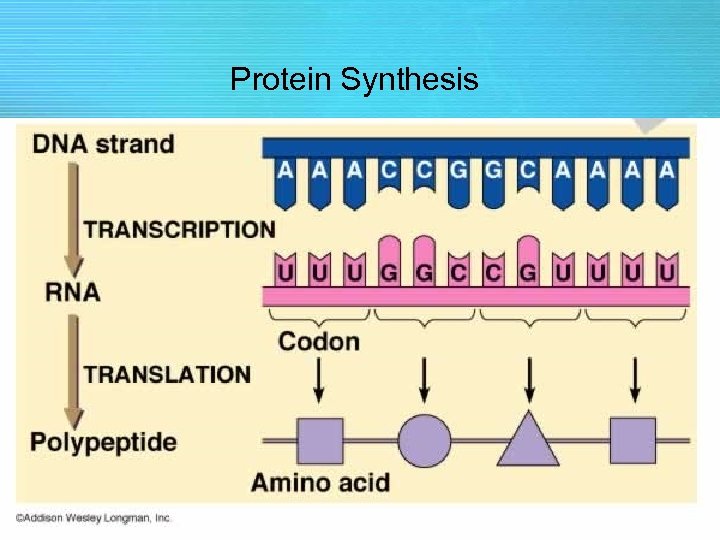
 Transcription • Transcription – is the process of copying the genetic code from a double-stranded DNA molecule into a single-stranded messenger RNA (m. RNA) molecule – This m. RNA molecule then leaves the nucleus and goes to the ribosome where protein synthesis (translation) occurs
Transcription • Transcription – is the process of copying the genetic code from a double-stranded DNA molecule into a single-stranded messenger RNA (m. RNA) molecule – This m. RNA molecule then leaves the nucleus and goes to the ribosome where protein synthesis (translation) occurs
 Translation • Translation – is the process of creating a protein by linking together specific amino acids using the genetic code Important concept: • The DNA in the nucleus of your cells is used to make proteins.
Translation • Translation – is the process of creating a protein by linking together specific amino acids using the genetic code Important concept: • The DNA in the nucleus of your cells is used to make proteins.
 Protein Synthesis
Protein Synthesis
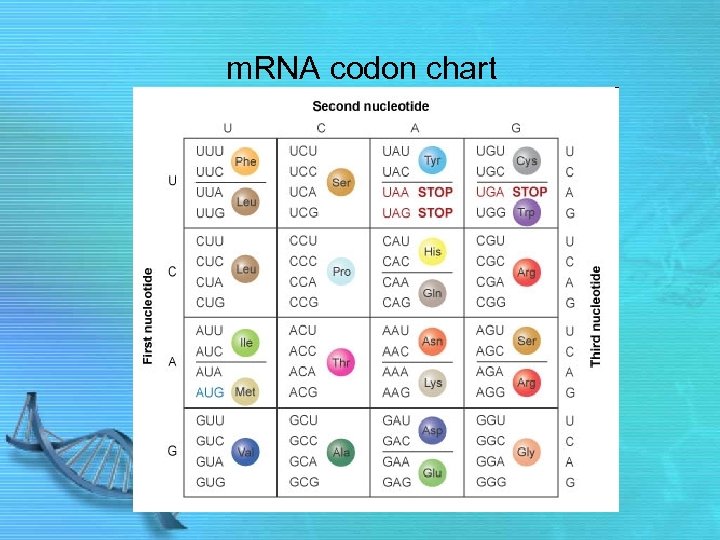 m. RNA codon chart
m. RNA codon chart