Lexicology_intro.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 MODERN ENGLISH LEXICOLOGY Lexicology as a Science 1
MODERN ENGLISH LEXICOLOGY Lexicology as a Science 1
 Course of Modern English Lexicology as a science Ш Methods and procedures of lexicological analysis Ш lexicography Ш Word-structure Ш Word-formation Ш Semasiology Ш Word-Groups and set-expressions Ш Etymology Ш Vocabulary replenishment Ш Variants and dialects of the English language Ш 2
Course of Modern English Lexicology as a science Ш Methods and procedures of lexicological analysis Ш lexicography Ш Word-structure Ш Word-formation Ш Semasiology Ш Word-Groups and set-expressions Ш Etymology Ш Vocabulary replenishment Ш Variants and dialects of the English language Ш 2
 Lexicology = lexis + logos Gr. lexis – word, phrase Gr. logos – learning some field of knowledge Lexicology = the science of the word 3
Lexicology = lexis + logos Gr. lexis – word, phrase Gr. logos – learning some field of knowledge Lexicology = the science of the word 3
 Lexicology deals with vocabulary of the language properties of the word 4
Lexicology deals with vocabulary of the language properties of the word 4
 Vocabulary – the system of all the words and word equivalents that the language possesses. 5
Vocabulary – the system of all the words and word equivalents that the language possesses. 5
 Properties of the word l l l Origin Structure Meaning Connections in the vocabulary system – synonyms, antonyms, homonyms, etc. Combinability Usage (functional styles and registers, regional varieties, etc. ) 6
Properties of the word l l l Origin Structure Meaning Connections in the vocabulary system – synonyms, antonyms, homonyms, etc. Combinability Usage (functional styles and registers, regional varieties, etc. ) 6
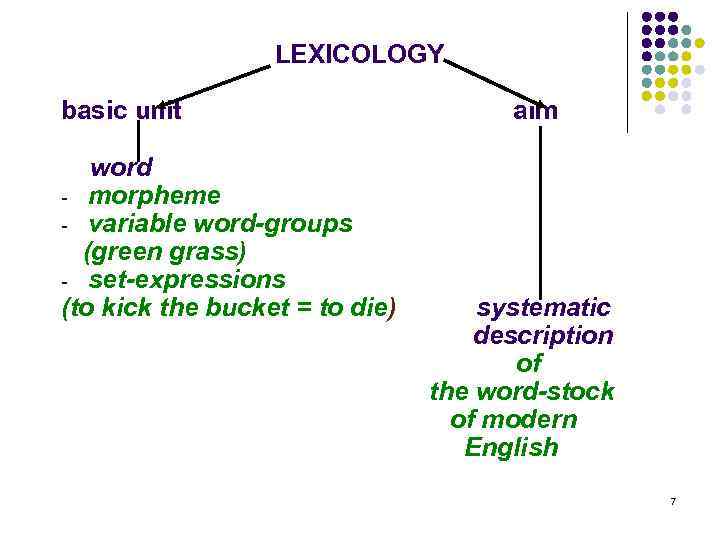 LEXICOLOGY basic unit word - morpheme - variable word-groups (green grass) - set-expressions (to kick the bucket = to die) aim systematic description of the word-stock of modern English 7
LEXICOLOGY basic unit word - morpheme - variable word-groups (green grass) - set-expressions (to kick the bucket = to die) aim systematic description of the word-stock of modern English 7
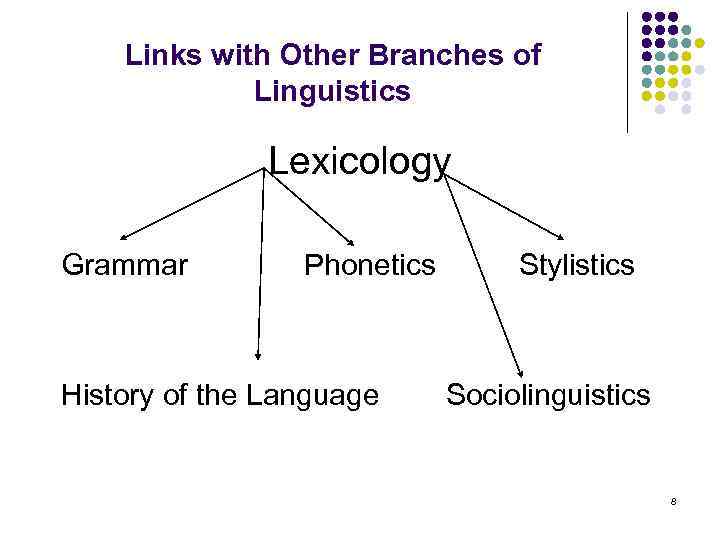 Links with Other Branches of Linguistics Lexicology Grammar Phonetics History of the Language Stylistics Sociolinguistics 8
Links with Other Branches of Linguistics Lexicology Grammar Phonetics History of the Language Stylistics Sociolinguistics 8
 Types of Lexicology 9
Types of Lexicology 9
 General Lexicology Deals with linguistic phenomena and properties common to all languages. 10
General Lexicology Deals with linguistic phenomena and properties common to all languages. 10
 Special Lexicology Studies vocabulary of a particular language (Russian, German, French, etc. ). 11
Special Lexicology Studies vocabulary of a particular language (Russian, German, French, etc. ). 11
 Contrastive Lexicology Describes vocabularies of different languages in comparison. 12
Contrastive Lexicology Describes vocabularies of different languages in comparison. 12
 Historical Lexicology or Etymology Studies the origin of words, their change and development, the linguistic and extra linguistic forces modifying their structure, meaning and usage. 13
Historical Lexicology or Etymology Studies the origin of words, their change and development, the linguistic and extra linguistic forces modifying their structure, meaning and usage. 13
 Descriptive Lexicology Deals with the morphological and semantic structures of the words at a given stage of the vocabulary development. 14
Descriptive Lexicology Deals with the morphological and semantic structures of the words at a given stage of the vocabulary development. 14
 Approaches to Language Study 15
Approaches to Language Study 15
 Synchronic Approach Gr. syn – “together, with” + Gr. chronos – “time” 16
Synchronic Approach Gr. syn – “together, with” + Gr. chronos – “time” 16
 Diachronic Approach Gr. dia - “through” + Gr. chronos – “time” 17
Diachronic Approach Gr. dia - “through” + Gr. chronos – “time” 17
 Procedures of Lexicological Analysis 18
Procedures of Lexicological Analysis 18
 Contrastive Analysis Compares the structure of a native & a target language on the phonetic, grammatical, lexical levels with the aim of finding common and contrastive features. 19
Contrastive Analysis Compares the structure of a native & a target language on the phonetic, grammatical, lexical levels with the aim of finding common and contrastive features. 19
 For example: English “foot” Russian “стопа”, “нога”. 20
For example: English “foot” Russian “стопа”, “нога”. 20
 Statistical Analysis Represents facts of the language using numbers. 21
Statistical Analysis Represents facts of the language using numbers. 21
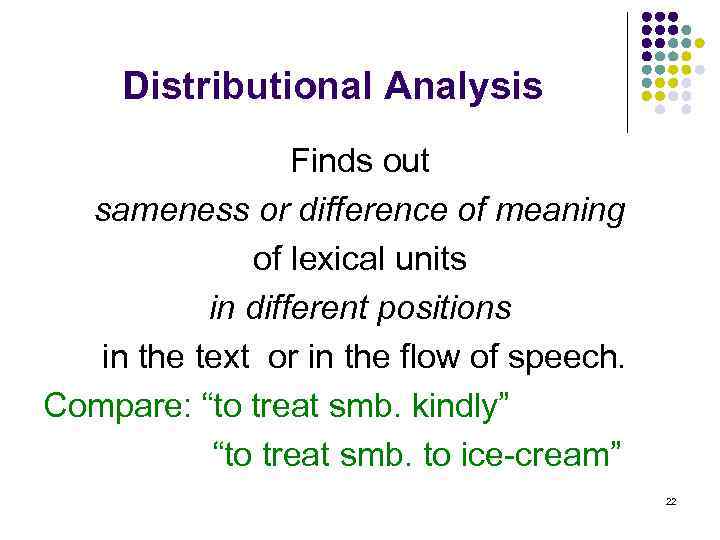 Distributional Analysis Finds out sameness or difference of meaning of lexical units in different positions in the text or in the flow of speech. Compare: “to treat smb. kindly” “to treat smb. to ice-cream” 22
Distributional Analysis Finds out sameness or difference of meaning of lexical units in different positions in the text or in the flow of speech. Compare: “to treat smb. kindly” “to treat smb. to ice-cream” 22
 Transformational Analysis Reorganizes practically identical structures in order to discover difference or sameness of their meaning. 23
Transformational Analysis Reorganizes practically identical structures in order to discover difference or sameness of their meaning. 23
 Pattern “possessive pronoun” + ”noun” his car he has a car – the meaning of possession his failure he failed - the meaning of action his arrest he was arrested - the meaning of passive action his kindness he is kind - the meaning of quality 24
Pattern “possessive pronoun” + ”noun” his car he has a car – the meaning of possession his failure he failed - the meaning of action his arrest he was arrested - the meaning of passive action his kindness he is kind - the meaning of quality 24
 Componential Analysis Helps to find out different semantic components which influence collocability of words. For example: during the day but not during the stairs, down the stairs but not down the day. 25
Componential Analysis Helps to find out different semantic components which influence collocability of words. For example: during the day but not during the stairs, down the stairs but not down the day. 25
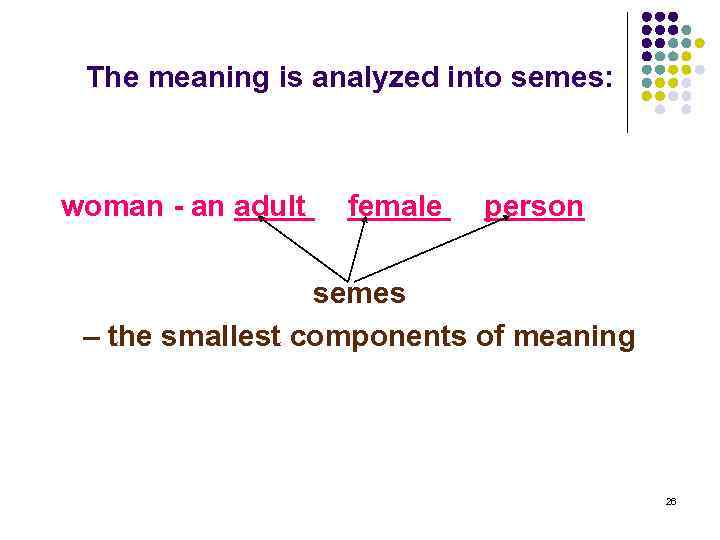 The meaning is analyzed into semes: woman - an adult female person semes – the smallest components of meaning 26
The meaning is analyzed into semes: woman - an adult female person semes – the smallest components of meaning 26
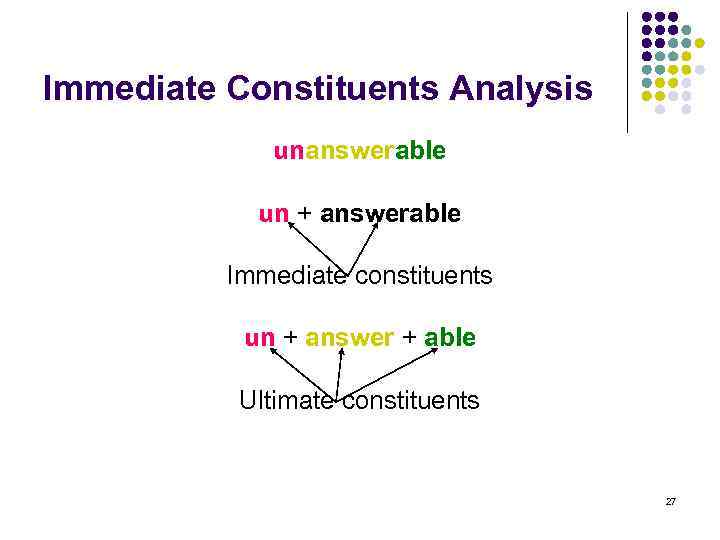 Immediate Constituents Analysis unanswerable un + answerable Immediate constituents un + answer + able Ultimate constituents 27
Immediate Constituents Analysis unanswerable un + answerable Immediate constituents un + answer + able Ultimate constituents 27


