Lexicography.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 47

MODERN ENGLISH LEXICOLOGY Lexicography

Problems for Discussion Ú Lexicology and Lexicography Ú Types of Dictionaries Ú Encyclopaedic Dictionaries Ú Dictionaries of Language and Culture Ú Linguistic Dictionaries Ú Classification of Linguistic Dictionaries Ú Basic Problems of Dictionary Compiling

What questions can Lexicography answer? Lexicography Who compiles dictionaries? What is a dictionary? How are dictionaries compiled? What can we find in a dictionary? How to use it? What are dictionaries for and what are their types? Where do dictionaries come from?

Prominent Lexicographers Ú Webster, Noah (1758 -1843), American lexicographer, best known for his pioneering work An American Dictionary of the English Language and for his espousal of American usage of the language. Ú Johnson, Samuel (1709 -1784), English writer and lexicographer, wrote the Dictionary of the English Language, published in 1755.
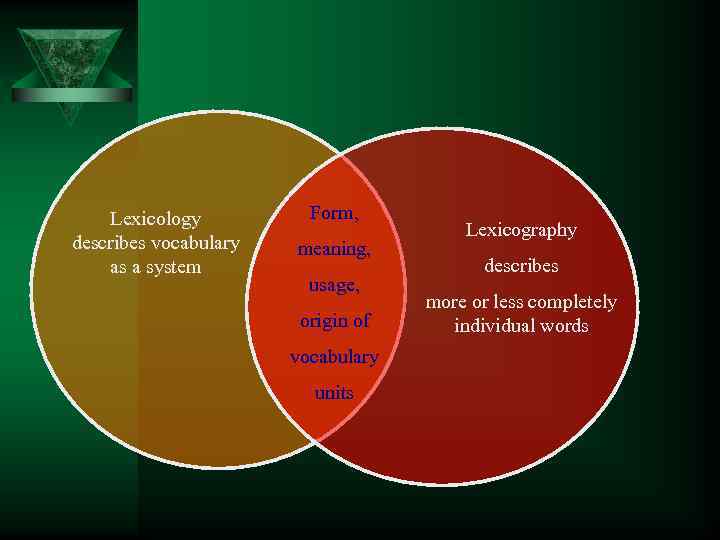
Lexicology describes vocabulary as a system Form, meaning, usage, origin of vocabulary units Lexicography describes more or less completely individual words

Types of Dictionaries DICTIONARY ENCYCLOPAEDIC OF LANGUAGE AND CULTURE LINGUISTIC

What do the types of dictionaries differ in? Ú In the choice of items included; Ú in the sort of information given about items included.

Encyclopaedic Dictionaries Greek enkyklios paideia - “comprehensive education” Encyclopedia or Encyclopaedia – collection of materials for instruction in all branches of knowledge, explaining systematically the contents and relations of the various arts and sciences.

How are words and notions explained in thing-books (encyclopaedias)? Cat, Domestic, small, mainly carnivorous animal, Felis catus, member of the family Felidae, popular as a household pet, and valuable for killing mice and rats. Like other members of the cat family, the domestic cat has retractile claws; keen hearing and smell; remarkable night vision; and a compact, muscular, and highly supple body. Cats possess excellent memory and exhibit considerable aptitude for learning by observation and experience. The natural life span of a domestic cat is about 15 years. Encarta Encyclopaedia
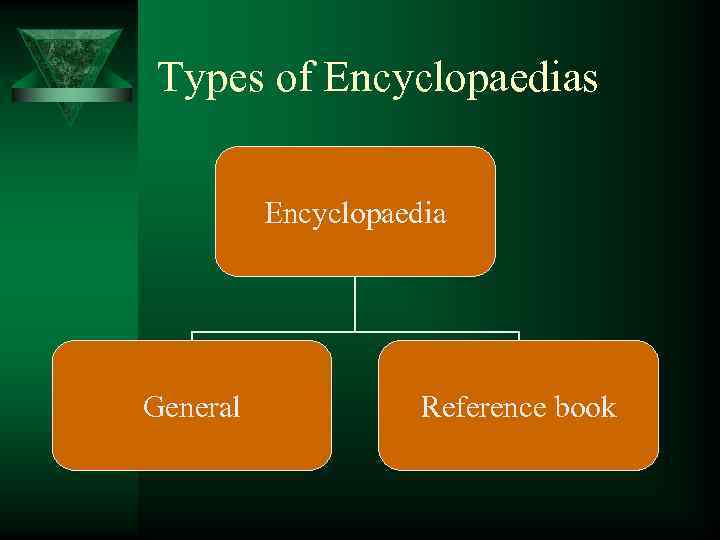
Types of Encyclopaedias Encyclopaedia General Reference book

Ú Ú Ú Ú General Encyclopaedias The Encyclopedia Americana, 30 volumes. The Columbia Encyclopedia, 1 volume The Collier's Encyclopedia, 24 volumes The Encyclopedia International, 20 volumes The Encyclopaedia Britannica, 30 volumes The Random House Encyclopedia, 2 volumes. The Academic American Encyclopedia, 21 volume. The Funk and Wagnalls New Encyclopedia, 29 volumes Reference Books ь The Oxford Companion to English Literature ь The Oxford Companion to Theatre ь Who’s Who dictionaries ь Cassell’s Encyclopaedia of World Literature

Dictionaries of Language and Culture Ú Longman Dictionary of English and Culture; Ú Collins Cobuild Dictionary of English and Culture; Ú Oxford Guide to British and American Language and Culture;

What is the entry like in a dictionary of language and culture? Guggenheim Museum, the [`gugənheim mju: `zi: əm] also the Gugenheim a museum in New York City that contains an important collection of modern art. It is named after the businessman who established it in 1939, Solomon R. Guggenheim, and is famous for its large circular building designed by Frank Lloyed Wright. In 1997 a new Guggenheim Museum was opened in Bilbao, Spain. Longman Dictionary of Language and Culture. Linguistic properties of the word: stress pattern, pronunciation. Encyclopaedic inclusion: information about the place.
![What information can be found in a linguistic dictionary? cat [kæt], noun [count] *** What information can be found in a linguistic dictionary? cat [kæt], noun [count] ***](https://present5.com/presentation/19869228_132342832/image-14.jpg)
What information can be found in a linguistic dictionary? cat [kæt], noun [count] *** an animal with soft fur, a long thin tail, and WHISKERS, that people keep as a pet or for catching mice. A young cat is called a kitten. A) a wild animal that looks like a big cat, for example a lion or TIGER: BIG CAT Macmillan Dictionary Linguistic properties of the word – pronunciation, grammar features, meaning, peculiarities of usage.

Types of Linguistic Dictionaries According to the nature of the word-list General Restricted

Most general dictionaries present the vocabulary as a whole and include: Ú the ordinary words of everyday life, such as bread, run and Ú Ú Ú Ú with; literary words, such as aggregation, despoil, incontrovertible; technical word, such as starboard, gene; words used on informal occasions, such as gap and wimp; old-fashioned words, such as aweary and avaunt; words or phrases form other languages, such as tofu from Japanese and barrio from Spanish; idioms, such as split hairs and under the thumb of; abbreviations, such as U. S. A. , Kans. ; important proper names, such as Buddha and Jupiter.

Special dictionaries cover only a certain part of the vocabulary Special dictionaries are divided depending on whether the words are chosen according to: Ú Ú Ú the sphere of human activity in which they are used (e. g. technical, medical dictionaries); the type of the units themselves (e. g. phraseological dictionaries); the relationships existing between them (e. g. dictionaries of synonyms).

Types of Linguistic Dictionaries According to the information they provide Explanatory Specialized

Specialized dictionaries concentrate on one of the distinctive features of the word: Ú on etymology (origin of the word) - etymological dictionaries; Ú on frequency – dictionaries of frequency; Ú on pronunciation – dictionaries of pronunciation; Ú etc.

Types of Linguistic Dictionaries According to the time axis Diachronic Synchronic

Types of Linguistic Dictionaries According to the language the information is provided in Monolingual Bilingual

Basic Problems of Dictionary-Compiling 1. The selection of lexical units for inclusion. 2. Setting of the entry. 3. The arrangement of entries. 4. Selection and arrangement of meanings. 5. Definition of meaning. 6. Illustrative examples. 7. Structure of the dictionary.

1. What should lexicographers take into account to decide which of the enormous number of words to include in a dictionary? Шthe type of the dictionary; Ш the prospective user (e. g. students or linguists? ); Шthe type of lexical units for inclusion; Шthe aim of the compilers; Шthe size of the dictionary;
![2. The information about words is given in the ENTRIES beautiful [`bju: təfl] adjective 2. The information about words is given in the ENTRIES beautiful [`bju: təfl] adjective](https://present5.com/presentation/19869228_132342832/image-24.jpg)
2. The information about words is given in the ENTRIES beautiful [`bju: təfl] adjective *** 1. a beautiful person is extremely attractive: Their mother was a very beautiful woman. 1. a. something that is beautiful is very pleasant to look at: That dress is really beautiful. 2. very pleasant: The weather has been beautiful this week. 3. done or made very well or with a lot of skill: The second goal was beautifully adverb: They were all beautifully dressed. Head-word Entry Run-on

2. 1. Which information to include in the entry? bear v borne [bɔ: n||bɔ: rn] 1 [T+obj + adv/prep] fml or lit to carry from one place to another; carry away; CONVVEY: The sound of music was borne on the wind. … 5 [T] usually fml to give birth to: a woman of childbearing age – see BORN 1 (USAGE) USAGE Compare abide, bear, endure, stand, tolerate. 1 Abide, bear, endure, stand are all used with “can” in questions and with negative words to express great dislike, but endure is usually used only about something really serious: I can’t abide/bear/stand black coffee. | I can’t endure talking to people who are racists. bear down phr v 1 [T] (bear sbdy. /sthg. – down) fml to defeat: borne down by poverty and deprivation. [bɔ: r], 1) Head-word 2) Part of speech 3) Pronunciation 4) Irregular form 5)Grammatical information 6) Style labels 7) Definition of the meaning 8) Example 9) Cross reference 10) Usage notes 11) Subentry

2. 2. Types of Labels Am. E American English appreciative Austr. E Australian English bibl Biblical Br. E British English Can. E Canadian English Car. E Caribbean English derogatory dialect euphemism fml formal Fr French German humorous Ind. E Indian English infml informal Ir. E Irish English It Italian Latin law legal literary medical

2. 2. Types of Labels (continued) nautical NEng. E Northern England English nonstandard NZE New Zealand English old-fashioned old use Pak. E Pakistani English poetical pompous rare SAfr. E South African English Scot. E Scottish English slang Sp Spanish taboo trademark technical

2. 3. What do usage notes do? explain the difference between words of roughly similar meaning; 2) explain difficult points of grammar and style; 3) explain important British and American differences; 4) explain the way some words and phrases can be used in conversation to suggest a meaning or attitude that could not be known simply through understanding the literal meanings of the words themselves. 1)

2. 4. What are the types of CROSS-REFERENCES? (1) opposites; (2) “compare” cross-references; (3) “see also” cross-references; (4) “see” cross-references.

3. What are the types of entry arrangement? Ú Alphabetical; Ú Cluster-type: - according to frequency index; - according to a common root in a word-family; - according to a synonymic dominant; according to a pivotal word. Ú Mixed type.

ÚAccording to a synonymic dominant: Look, Glance, Glimpse, Peep, Sight, редк. View один акт восприятия чего-л. глазами, взгляд, взор, быстрый взгляд, взгляд украдкой. Синонимы отличаются друг от друга по следующим смысловым признакам… Апресян Ю. Д. Англо-русский синонимический словарь

ÚWord-family: Dog dogcart dogcatcher dog-collar doggy dog-tired dog-trot dog-wood

ÚAccording to a pivotal word: Clear clear as a bell – very clear indeed; clear as crystal – very clear indeed; clear as day – very easy to see, understand; clear as mud – confusing, difficult to understand; in the clear – free from blame, suspicion; steer clear – to avoid deliberately; Collins Cobulld Dictionaey of Idioms

Arrangement of Meanings (1) historical order; (2) empirical or actual order; (3) logical order. Arrangement of meanings according to E. L. Thorndike: Ú literal uses come before figurative; Ú common meanings come before rare; Ú easily understandable uses come before difficult; Ú general meaning comes before special.

Definition of Meaning 1) encyclopedic definition; (2) descriptive definition; (3) with the help of synonymous words and expressions; (4) by means of cross-references.
![Encyclopaedic Definition Ono [`əunəu], Yoko [`jəukəu] (1933 - ) a Japanese artist and musician Encyclopaedic Definition Ono [`əunəu], Yoko [`jəukəu] (1933 - ) a Japanese artist and musician](https://present5.com/presentation/19869228_132342832/image-36.jpg)
Encyclopaedic Definition Ono [`əunəu], Yoko [`jəukəu] (1933 - ) a Japanese artist and musician who was married to John Lennon. She made several records with Lennon as part of their group the Plastic Ono Band, including the song Give Piece A Chance. Longman Dictionary of Language and Culture.
![Descriptive Definition Drum [`dr/m] noun ** [count] a musical instrument consisting of a tight Descriptive Definition Drum [`dr/m] noun ** [count] a musical instrument consisting of a tight](https://present5.com/presentation/19869228_132342832/image-37.jpg)
Descriptive Definition Drum [`dr/m] noun ** [count] a musical instrument consisting of a tight skin stretched over a round frame that you hit with your hands or a stick. Someone who plays a drum is a drummer. (c) Macmillan Publishers Ltd. 2003
![With the Help of Synonyms and Synonymous Expressions Stare [`steə] verb [intransitive] *** to With the Help of Synonyms and Synonymous Expressions Stare [`steə] verb [intransitive] *** to](https://present5.com/presentation/19869228_132342832/image-38.jpg)
With the Help of Synonyms and Synonymous Expressions Stare [`steə] verb [intransitive] *** to look at someone or something very directly for a long time: It's rude to stare. (c) Macmillan Publishers Ltd. 2003

By Means of Cross-references Brady, Ian – see Moors Murderes. Longman Dictionary of Language and Culture.

Illustrative Examples Ú the source of the citation; Ú length of the quotation; Ú the precision of the citation; Ú whether to indicate the author; Ú whether to indicate the work; Ú whether to indicate the page; Ú whether to indicate the date of publication.

Structure of the Dictionary Ú The guide; Ú the dictionary proper; Ú the supplementary material (tables, proper and geographical names, the lists of suffixes and prefexes, etc. )

How to characterize a dictionary? 1. Type of a dictionary a) according to the choice of items included and the sort of information given about them linguisticnon-linguistic (encyclopaedic: general or reference book)of language and culture; b) according to the nature of their word-list - generalrestricted (the subtype of a restricted dictionary is to be indicated);

c) according to the information provided explanatorytranslationspecialized (the type of a specialized dictionary is to be indicated); d) according to the time axis – synchronicdiachronic; e) according to the language of the information given about the items of a dictionary - unilingualbilingual;

2. The number of lexical units included 3. The principles of the selection of lexical units. 4. The structure of the dictionary. 5. The order of entry arrangement.

5. The information to be found in the entry: - accepted spelling and pronunciation; - grammatical characteristics of a word (e. g. part of speech, transitivity/intransitivity of verbs, irregular grammatical forms); - the system of subentries and run-ons; - the system of labels; - the system of usage notes; - other information not mentioned in the list (varies from dictionary to dictionary).

6. The ways of arranging the meanings (historicalempiricallogical). 7. The ways of defining the meanings (encyclopedicdescriptivewith the help of synonymous words and expressions by means of cross-reference). 8. The system of cross-references.

9. Illustrative materials (what material is quoted, the length of quotation and the precision of the citation, etc. ) and illustrations. 10. Supplementary material. 11. Aims of the dictionary. 12. Possible users of the dictionary.
Lexicography.ppt