 moderator Klyass Maria Zhestereva Elena Lysenko Anastasia
moderator Klyass Maria Zhestereva Elena Lysenko Anastasia
 q Meaning q Role functions q What to do q Techniques q Role limits
q Meaning q Role functions q What to do q Techniques q Role limits
 meaning ü To moderate ü Narrow goal: to broaden the partner’s vision of problem by using different tools ü More general goal: help to find the best way out for the problem
meaning ü To moderate ü Narrow goal: to broaden the partner’s vision of problem by using different tools ü More general goal: help to find the best way out for the problem
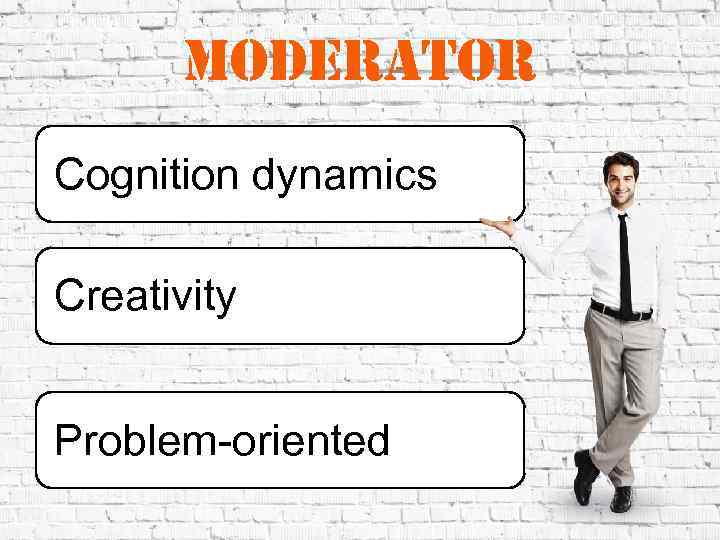 moderator Cognition dynamics Creativity Problem-oriented
moderator Cognition dynamics Creativity Problem-oriented
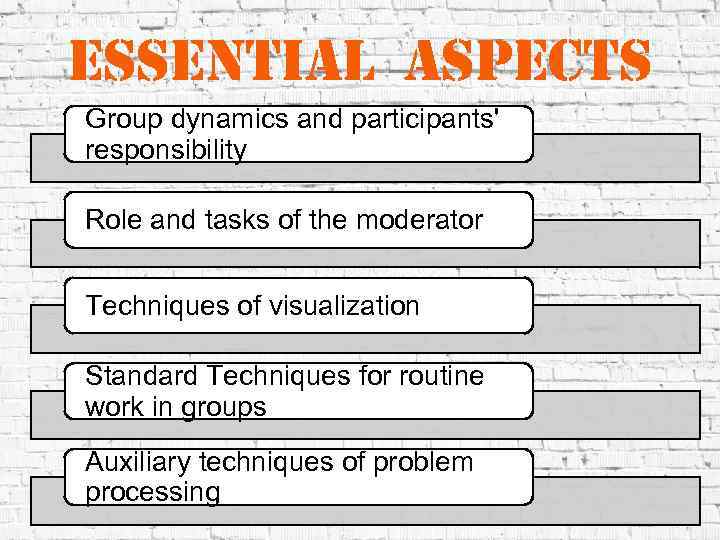 essential aspects Group dynamics and participants' responsibility Role and tasks of the moderator Techniques of visualization Standard Techniques for routine work in groups Auxiliary techniques of problem processing
essential aspects Group dynamics and participants' responsibility Role and tasks of the moderator Techniques of visualization Standard Techniques for routine work in groups Auxiliary techniques of problem processing
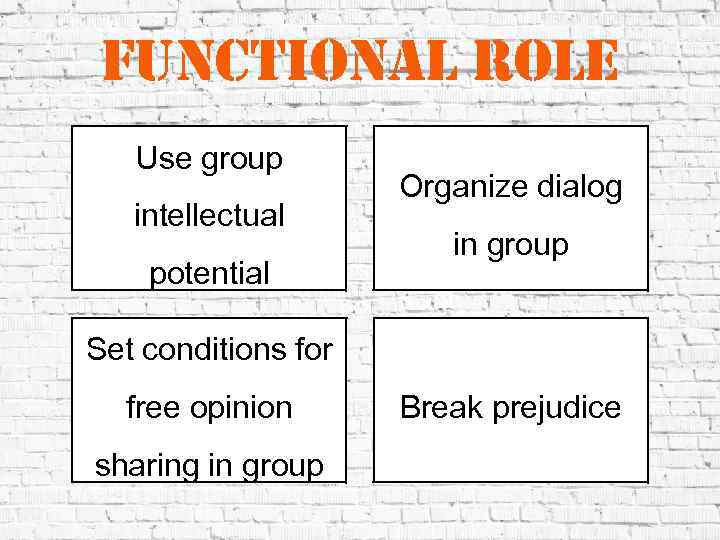 Functional role Use group intellectual potential Organize dialog in group Set conditions for free opinion sharing in group Break prejudice
Functional role Use group intellectual potential Organize dialog in group Set conditions for free opinion sharing in group Break prejudice
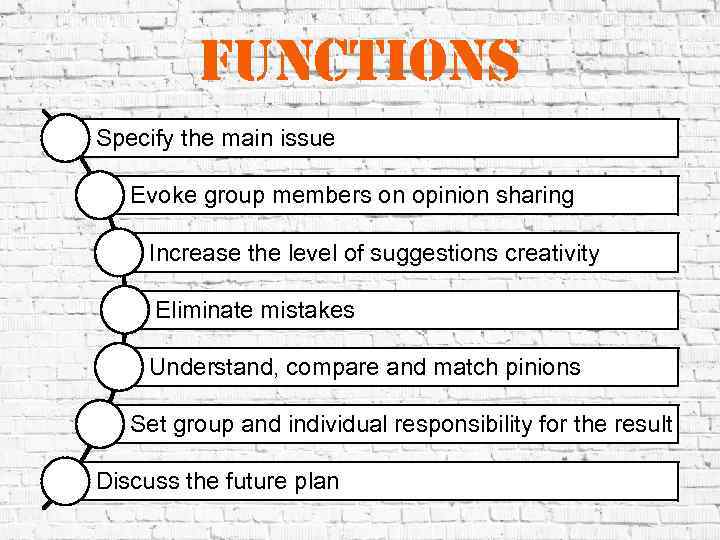 Functions Specify the main issue Evoke group members on opinion sharing Increase the level of suggestions creativity Eliminate mistakes Understand, compare and match pinions Set group and individual responsibility for the result Discuss the future plan
Functions Specify the main issue Evoke group members on opinion sharing Increase the level of suggestions creativity Eliminate mistakes Understand, compare and match pinions Set group and individual responsibility for the result Discuss the future plan
 what to do • Use questioning procedures problematization techniques • Use visualization • To be a good listener • To be a good communicator and
what to do • Use questioning procedures problematization techniques • Use visualization • To be a good listener • To be a good communicator and
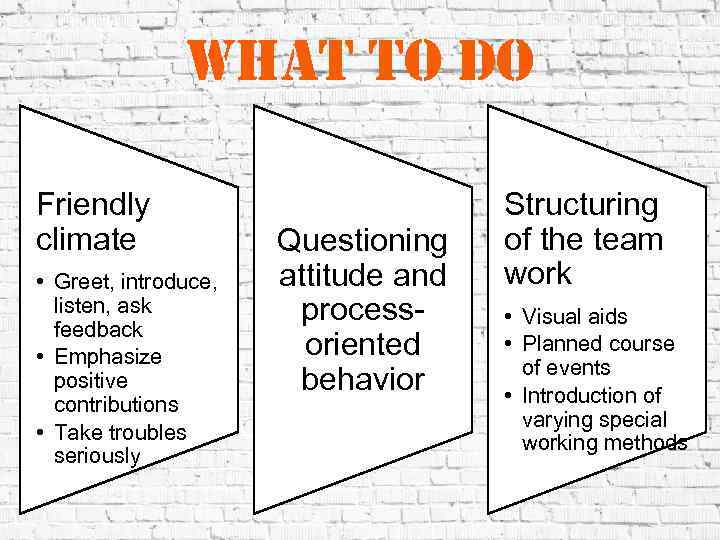 what to do Friendly climate • Greet, introduce, listen, ask feedback • Emphasize positive contributions • Take troubles seriously Questioning attitude and processoriented behavior Structuring of the team work • Visual aids • Planned course of events • Introduction of varying special working methods
what to do Friendly climate • Greet, introduce, listen, ask feedback • Emphasize positive contributions • Take troubles seriously Questioning attitude and processoriented behavior Structuring of the team work • Visual aids • Planned course of events • Introduction of varying special working methods
 Feedback Difficult situations Deal with criticism Transparency Elimination of burdens Self-assurance Time management cont’d
Feedback Difficult situations Deal with criticism Transparency Elimination of burdens Self-assurance Time management cont’d
 TECHNIQUES
TECHNIQUES
 routine work in group
routine work in group
 problem processing
problem processing
 role limits • Lack of clarity on the matters • Moderators need to take out the time and be motivated to find answers to the questions while preparing for the moderation sessions
role limits • Lack of clarity on the matters • Moderators need to take out the time and be motivated to find answers to the questions while preparing for the moderation sessions
 THANK YOU FOR ATTENTION!
THANK YOU FOR ATTENTION!