c06b60ecfecc4a638bd9f5c788f016f2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28

Modelling DBA in a new Zebrafish Rps 19 deficient model and Developing an adult service and registry for DBA patients Dr Beth Payne MBCh. B Ph. D Consultant Haematologist UCLH Wellcome Trust Intermediate Clinical Fellow UK DBA Family Meeting 2016
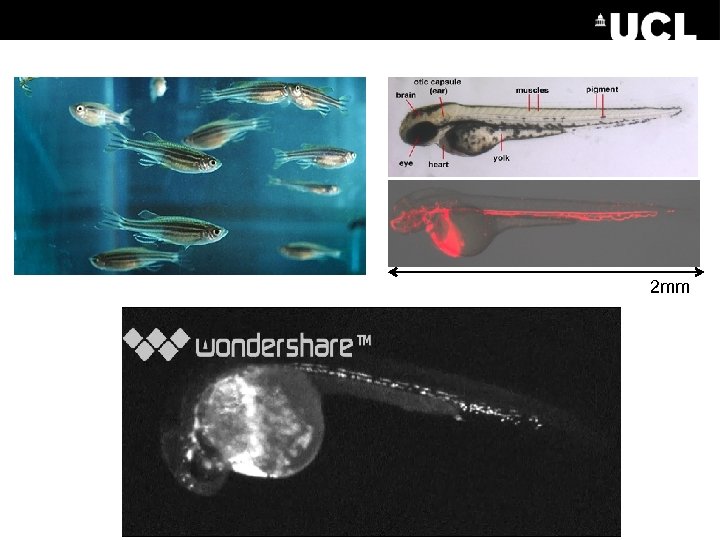
2 mm
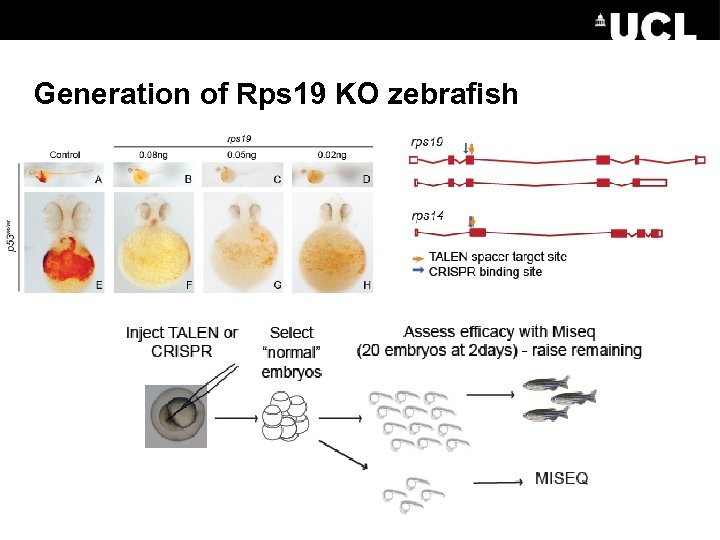
Generation of Rps 19 KO zebrafish
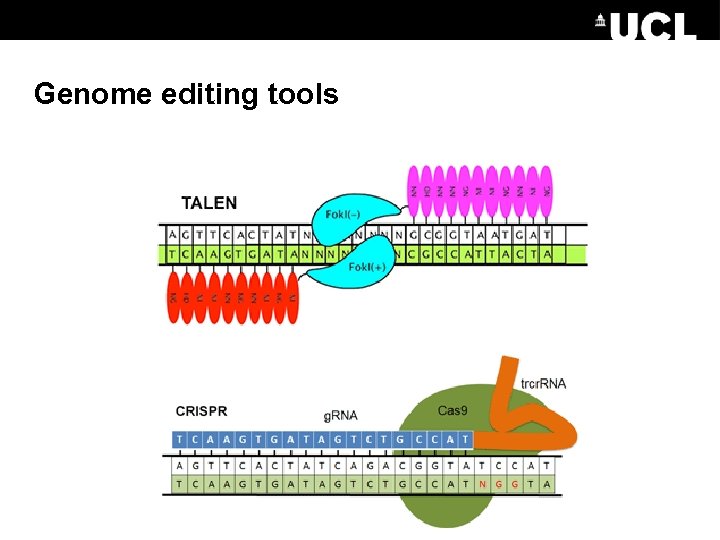
Genome editing tools
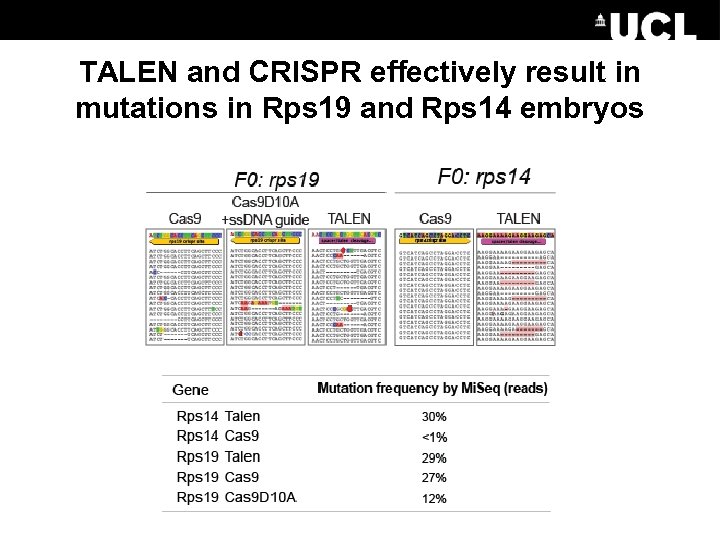
TALEN and CRISPR effectively result in mutations in Rps 19 and Rps 14 embryos
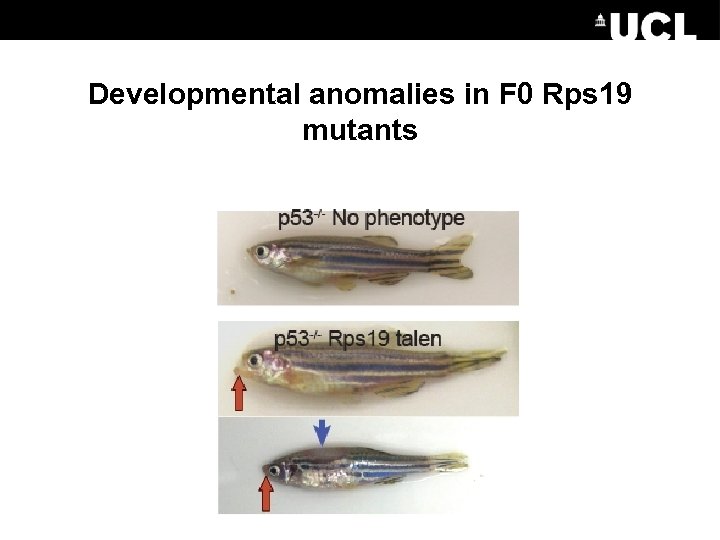
Developmental anomalies in F 0 Rps 19 mutants
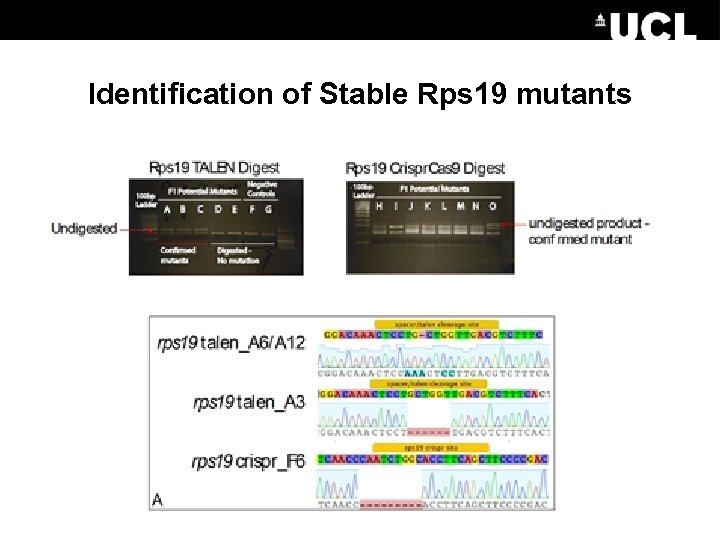
Identification of Stable Rps 19 mutants
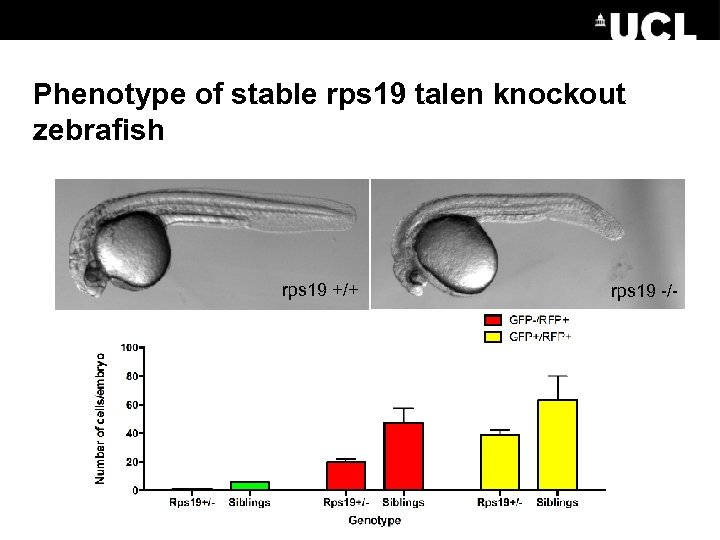
Phenotype of stable rps 19 talen knockout zebrafish rps 19 +/+ rps 19 -/-
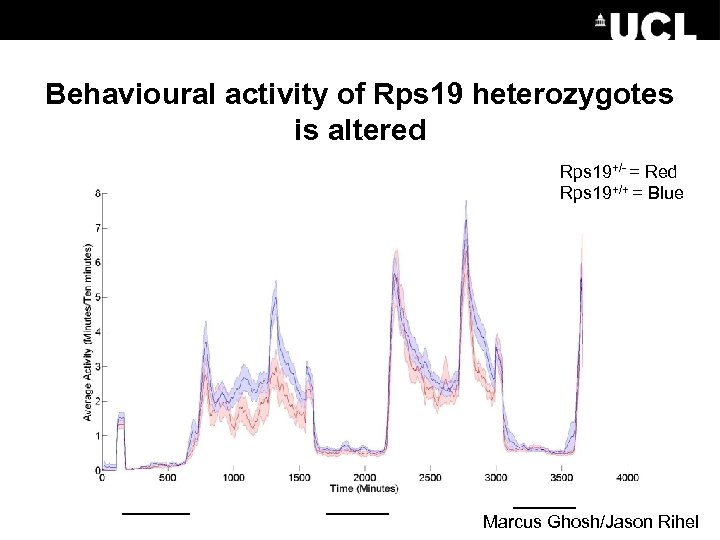
Behavioural activity of Rps 19 heterozygotes is altered Rps 19+/- = Red Rps 19+/+ = Blue Marcus Ghosh/Jason Rihel
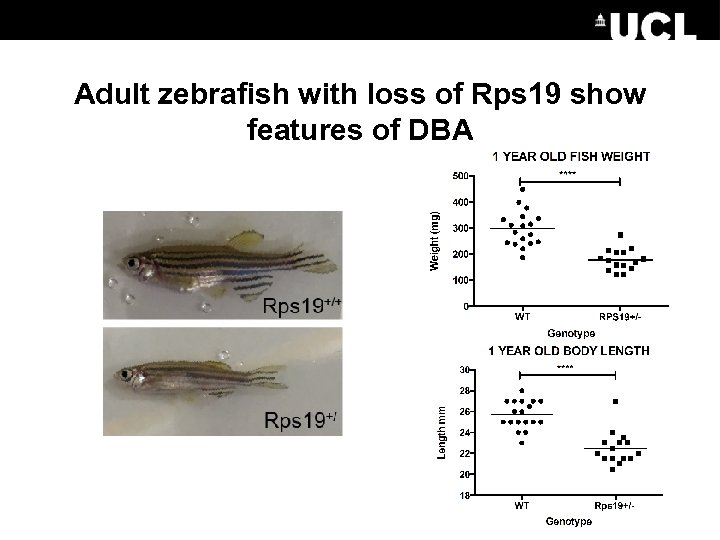
Adult zebrafish with loss of Rps 19 show features of DBA
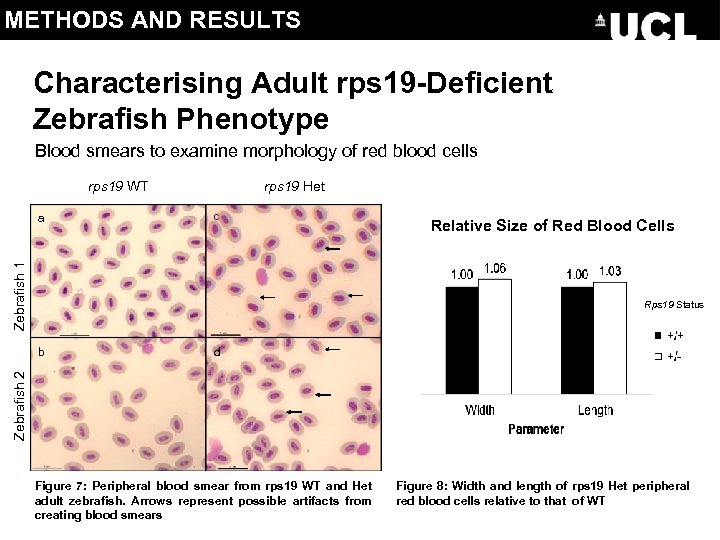
METHODS AND RESULTS Characterising Adult rps 19 -Deficient Zebrafish Phenotype Blood smears to examine morphology of red blood cells rps 19 WT c Zebrafish 1 a rps 19 Het Relative Size of Red Blood Cells Rps 19 Status d Zebrafish 2 b Figure 7: Peripheral blood smear from rps 19 WT and Het adult zebrafish. Arrows represent possible artifacts from creating blood smears Figure 8: Width and length of rps 19 Het peripheral red blood cells relative to that of WT
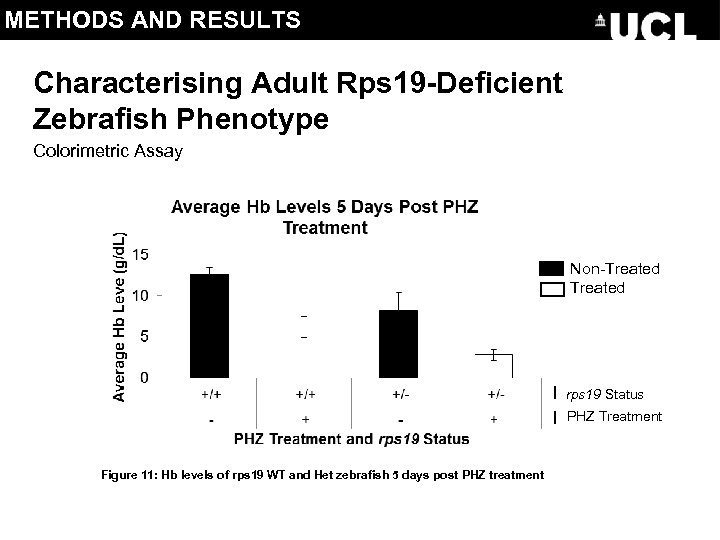
METHODS AND RESULTS Characterising Adult Rps 19 -Deficient Zebrafish Phenotype Colorimetric Assay Non-Treated rps 19 Status PHZ Treatment Figure 11: Hb levels of rps 19 WT and Het zebrafish 5 days post PHZ treatment
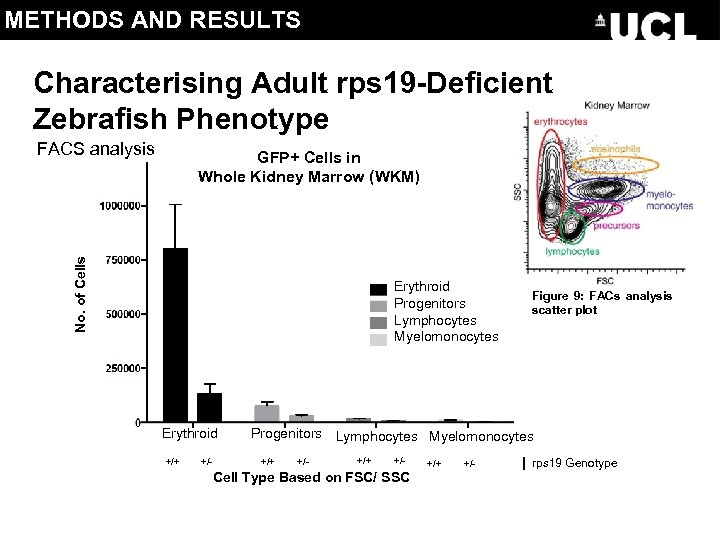
METHODS AND RESULTS Characterising Adult rps 19 -Deficient Zebrafish Phenotype FACS analysis No. of Cells GFP+ Cells in Whole Kidney Marrow (WKM) Erythroid Progenitors Lymphocytes Myelomonocytes Erythroid +/+ +/- Figure 9: FACs analysis scatter plot Progenitors Lymphocytes Myelomonocytes +/+ +/- Cell Type Based on FSC/ SSC +/+ +/- rps 19 Genotype
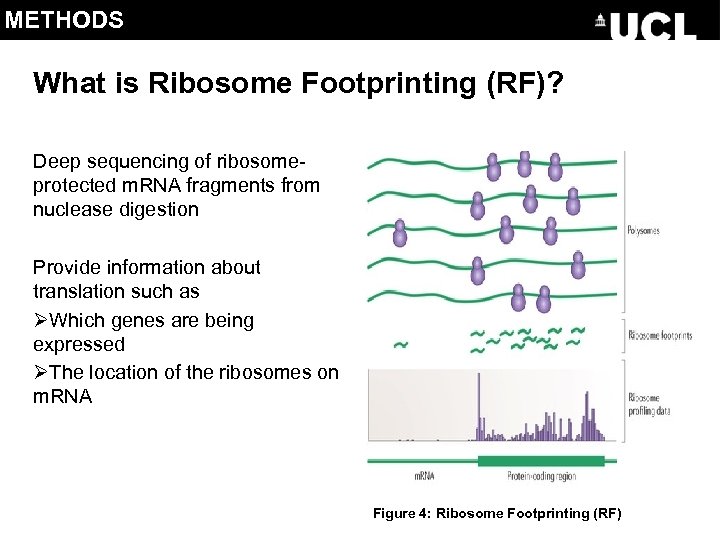
METHODS What is Ribosome Footprinting (RF)? Deep sequencing of ribosomeprotected m. RNA fragments from nuclease digestion Provide information about translation such as ØWhich genes are being expressed ØThe location of the ribosomes on m. RNA Figure 4: Ribosome Footprinting (RF)
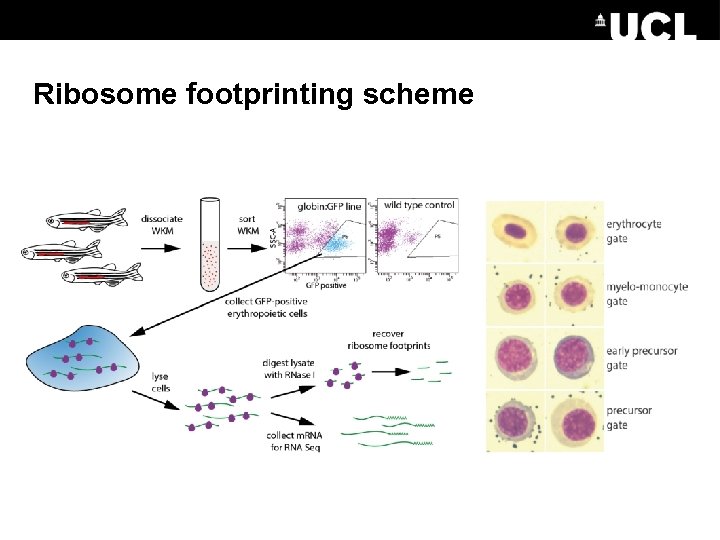
Ribosome footprinting scheme
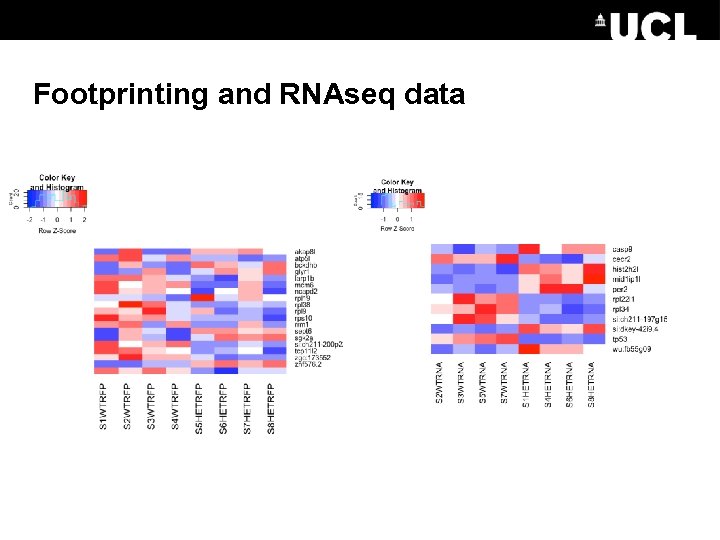
Footprinting and RNAseq data

Developing an adult service and registry for DBA patients

Formalize of a DBA registry • Goals of having a registry – Permit hospitals/clinicians around the UK to supply data to the database – Understand the breadth of clinical problems associated with DBA to facilitate better guidelines and management – Conduct basic and clinical research to determine novel treatments of DBA – Interface with European and US collaborators to create greater understanding of DBA patients worldwide

Haematology Team-UCLH • 4 consultants – – Dr Payne Prof John Porter Dr Perla Eleftheriou Dr Sara Trompeter (paeds/adolescents) • 2 CNS – Catherine Mk. Andawire (paeds/adolescents) – Bernadette Hylton

TYA (Teenage young adult) • UCLH offers specialist services for teenagers and young adults • Entire outpatient floor dedicated to patients aged 13 -24 • For inpatients there is a specialised ward for patients aged 18 -29 • Automated patient calling system that permit you to receive a text when the doctor is ready to see you

TYA unit

“One-stop” multi-disciplinary care • DBA patients (may) have complex multisystem problems • Clinic designed to facilitate seeing the necessary • Cardiology, Endocrinology, Andrology, Clinical Psychology, Fertility specialist, hepatology • Walk-in audiology testing • NGS (Oxford – 14 RP genes+GATA 1 /Imperial – All RP genes)

Biobanking • Pre-existing biobank at UCLH permits banking of children, adults and relatives of any surplus material from marrow or blood. • Additionally permits single 50 ml research only blood draw • Bone marrow samples biobanked at St Marys (Children and donors) no MTA for transfer of samples

Registry options • Option 1: – Use the UK National Haemoglobinopathy registry and modify the to contain the additional data needed for DBA • Option 2: – Bespoke DBA registry for UK DBA patient

Acknowledgements UCL Greg Pietka Greg Contento Catherine Hockings Jasmine Rowell Oscar Pena Laura Bruce Maria Virgiliio UCL fish facility UCLH Prof J Porter Dr S Trompeter Dr P Elftheriou
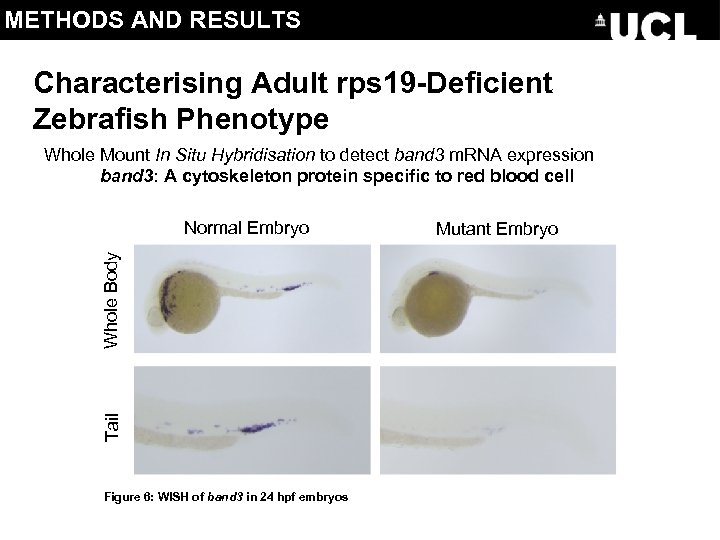
METHODS AND RESULTS Characterising Adult rps 19 -Deficient Zebrafish Phenotype Whole Mount In Situ Hybridisation to detect band 3 m. RNA expression band 3: A cytoskeleton protein specific to red blood cell Tail Whole Body Normal Embryo Figure 6: WISH of band 3 in 24 hpf embryos Mutant Embryo
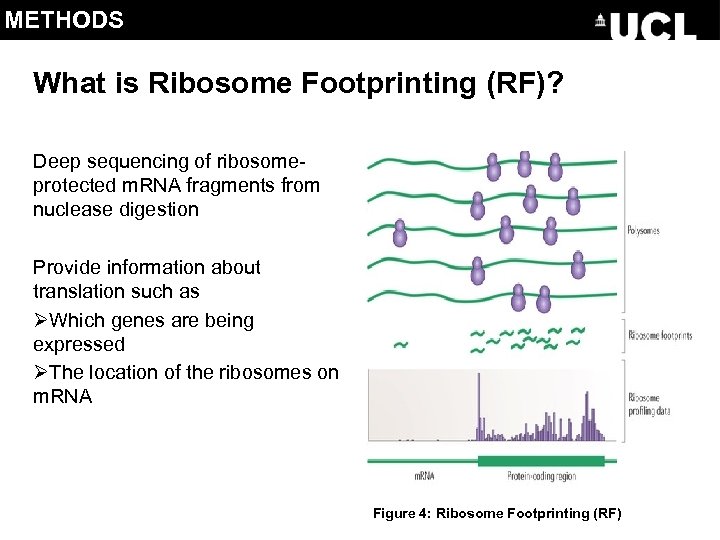
METHODS What is Ribosome Footprinting (RF)? Deep sequencing of ribosomeprotected m. RNA fragments from nuclease digestion Provide information about translation such as ØWhich genes are being expressed ØThe location of the ribosomes on m. RNA Figure 4: Ribosome Footprinting (RF)
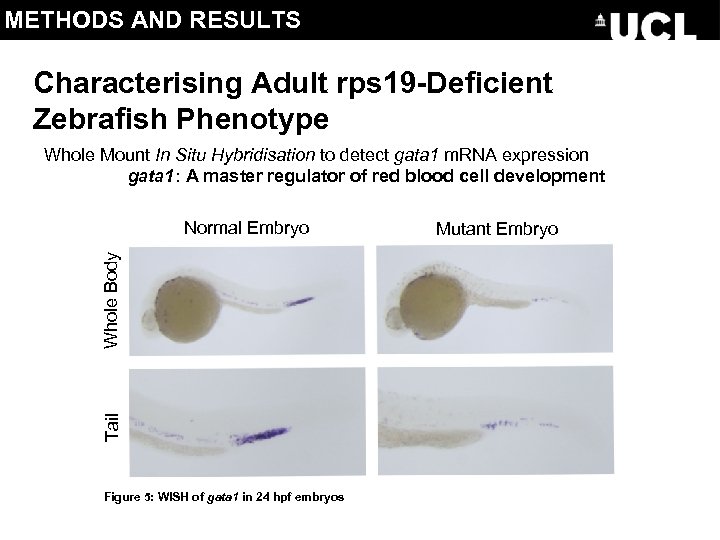
METHODS AND RESULTS Characterising Adult rps 19 -Deficient Zebrafish Phenotype Whole Mount In Situ Hybridisation to detect gata 1 m. RNA expression gata 1: A master regulator of red blood cell development Tail Whole Body Normal Embryo Figure 5: WISH of gata 1 in 24 hpf embryos Mutant Embryo
c06b60ecfecc4a638bd9f5c788f016f2.ppt