9cd9f2511f5969f9cc0fc4b00360e4e8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30

Modeling Virtualized Environments in Simalytic® Models by Computing Missing Service Demand Parameters CMG 2009 Paper 9103, December 11, 2009 Dr. Tim R. Norton Simalytic Solutions, LLC 719 -635 -5825 email: tim. norton@simalytic. com http: //www. simalytic. com © 2009 Simalytic Solutions, LLC
OR Using Virtual Data to Model Virtual Systems © 2009 Simalytic Solutions, LLC

Agenda u Introduction £ Capacity Planning and Virtualization u The Problem £ Missing Measurements in Virtualization Guests u. A £ Proposed Solution Computing Missing Service Demand Parameters u Conclusion Simalytic® is a registered trademark and registered service mark of Simalytic Solutions, LLC. Simalytic Modeling. TM and Simalytic Function. TM are trademarks of Simalytic Solutions, LLC. All other trademarked names and terms are the property of their respective owners. © 2009 Simalytic Solutions, LLC Modeling Virtualized Environments by Computing Missing Service Demand Parameters CMG 2009 - Paper 9103, December 11, 2009 3

Introduction u Capacity £ Capacity is Measured by Business Performance Objectives n £ Planning Making decisions about resource requirements What do we have to buy and when do we have to buy it to make sure that the business applications perform at the level required to insure the business succeeds? © 2009 Simalytic Solutions, LLC Modeling Virtualized Environments by Computing Missing Service Demand Parameters CMG 2009 - Paper 9103, December 11, 2009 4
Introduction u Capacity £ Two key aspects: n Demand for available resources l n What do we have to buy Effective completion of business work l £ Planning When to buy it? Requires some predictive technique n Usually some form of model l l Simple: trend or other statistical techniques Advanced: simulation or queuing network © 2009 Simalytic Solutions, LLC Modeling Virtualized Environments by Computing Missing Service Demand Parameters CMG 2009 - Paper 9103, December 11, 2009 5
Introduction u Virtualization £ Increasing parallelization within the host system Increase productive business-related work n Increase the usage of resources n £ Virtualized environment control program n Hypervisor l n Usually implies a hardware implementation VMM (Virtual Machine Monitor) l VMM often implies a software implementation t Will use VMM for all virtualization control programs © 2009 Simalytic Solutions, LLC Modeling Virtualized Environments by Computing Missing Service Demand Parameters CMG 2009 - Paper 9103, December 11, 2009 6
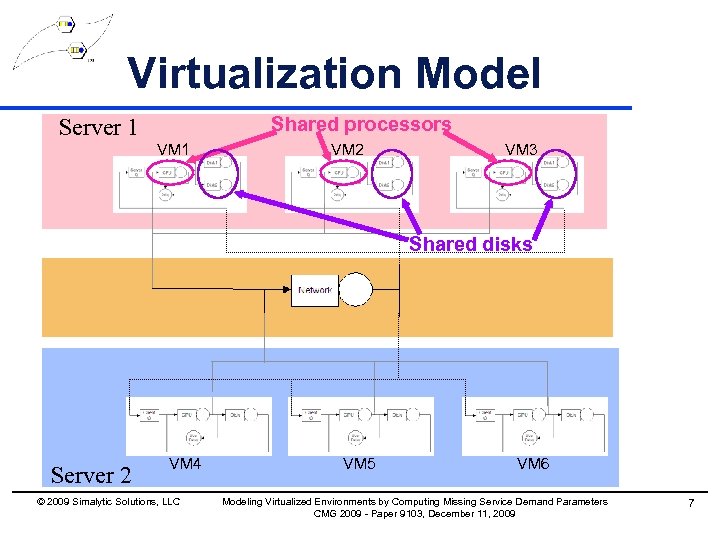
Virtualization Model Shared processors Server 1 VM 2 VM 3 Shared disks Server 2 VM 4 © 2009 Simalytic Solutions, LLC VM 5 VM 6 Modeling Virtualized Environments by Computing Missing Service Demand Parameters CMG 2009 - Paper 9103, December 11, 2009 7
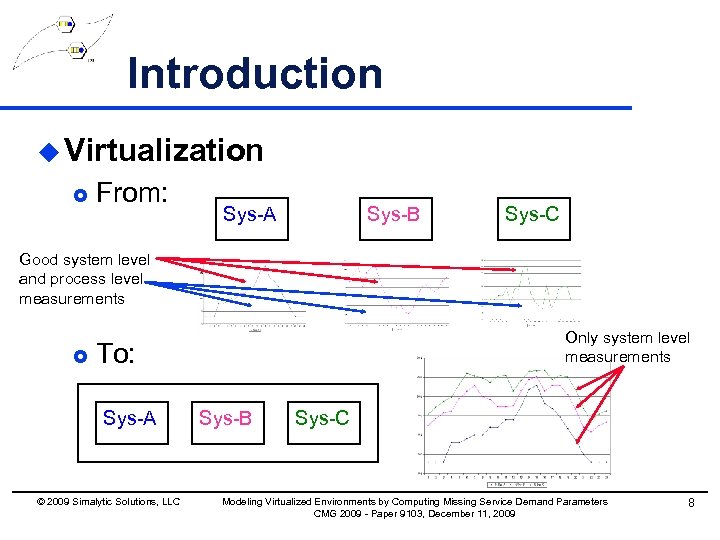
Introduction u Virtualization £ From: Sys-A Sys-B Sys-C Good system level and process level measurements £ Only system level measurements To: Sys-A © 2009 Simalytic Solutions, LLC Sys-B Sys-C Modeling Virtualized Environments by Computing Missing Service Demand Parameters CMG 2009 - Paper 9103, December 11, 2009 8
The Problem u Measurements in Virtualization Environments £ Guest Operating Systems n Most not Virtualization aware l £ Hypervisor n Accurately measures Guest VM active time l £ Incorrect accounting for time when guest VM not active t Rate based measurements incorrect t Count based measurements valid Cannot measure processes within the Guest O/S Affects measurements needed for models VM System Level Service Times good n Process Level Service Times incorrect n © 2009 Simalytic Solutions, LLC Modeling Virtualized Environments by Computing Missing Service Demand Parameters CMG 2009 - Paper 9103, December 11, 2009 9
Capacity Models u What £ Virtualization does to Models Reduces accuracy – Measurement issues: System clock n Accounting for dispatch time of other VMs n Interrupts – delays and re-driven to VM n VM vs. process priority n Delays – where are they accounted for n Virtualization overhead n l n £ VMM (Virtual Machine Monitor) and VM context switch Interference from other VMs Complicates Workload Characterization n Shared resources © 2009 Simalytic Solutions, LLC Modeling Virtualized Environments by Computing Missing Service Demand Parameters CMG 2009 - Paper 9103, December 11, 2009 10

Where’s the Data u. If £ It’s Not There… It’s missing! It’s Wrong… It’s missing! You Can’t Trust It… It’s missing! © 2009 Simalytic Solutions, LLC Modeling Virtualized Environments by Computing Missing Service Demand Parameters CMG 2009 - Paper 9103, December 11, 2009 11
A Proposed Solution u Use £ VM utilization n £ from the VMM (Virtual Machine Monitor) Transaction arrivals n £ known good measurements from application measurements Transaction response times n u Use from application measurements a Simalytic Model Builds relationships n Iterative design n Leverages existing tools n © 2009 Simalytic Solutions, LLC Modeling Virtualized Environments by Computing Missing Service Demand Parameters CMG 2009 - Paper 9103, December 11, 2009 12
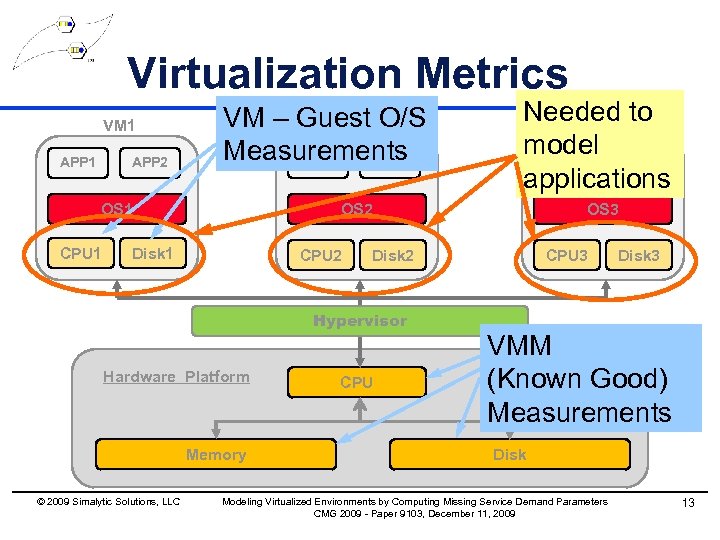
Virtualization Metrics VM 1 APP 2 VM – Guest O/S VM 2 Measurements APP 3 APP 4 OS 1 CPU 1 OS 2 Disk 1 CPU 2 Hardware Platform Memory OS 3 Disk 2 Hypervisor © 2009 Simalytic Solutions, LLC Needed to VM 3 model APP 6 APP 5 applications CPU 3 Disk 3 VMM (Known Good) Measurements Disk Modeling Virtualized Environments by Computing Missing Service Demand Parameters CMG 2009 - Paper 9103, December 11, 2009 13
Model Requirements u Application £ Count of transactions over many intervals u Application £ Response Times Always needed for validation of model results n Now needed for Solver calculations u Service £ Transaction Arrivals Demand Menascé technique to compute class service demand from total service demand n VMM measurements used to compute VM level measurements that guest O/S cannot provide © 2009 Simalytic Solutions, LLC Modeling Virtualized Environments by Computing Missing Service Demand Parameters CMG 2009 - Paper 9103, December 11, 2009 14
Implementation Approach u Collect Measurement Data Application – counts and response times £ VMM resource usage £ u Compute £ Service Demand by Application Validate against measured response times u Build Model of Overall Virtualization Environment £ Using a Simalytic Model to express the relationships between applications © 2009 Simalytic Solutions, LLC Modeling Virtualized Environments by Computing Missing Service Demand Parameters CMG 2009 - Paper 9103, December 11, 2009 15
Implementation u Measurements £ Collect measurements n From the applications l l n From the VMM l £ Actual response times Actual transaction counts Total utilization for each resource (CPU, disks, etc. ) Multiple intervals n Measurements are needed for many intervals l Variety is important! – but avoid problem areas like low utilization effect t Low to high counts for each application t Low to high resource utilization © 2009 Simalytic Solutions, LLC Modeling Virtualized Environments by Computing Missing Service Demand Parameters CMG 2009 - Paper 9103, December 11, 2009 16
Implementation u Compute £ Use collected measurements to construct multiple Open Multiclass QN formulae n £ Service Demand Each uses the transaction response time and count for each class (application) along with the total service demand for each resource (CPU, disks, etc. ) for one measurement interval. Solve the non-linear constraint problem Computing Missing Service Demand Parameters for Performance Models. Danny Menascé, CMG 2008. n Can be done with Microsoft Excel Solver n © 2009 Simalytic Solutions, LLC Modeling Virtualized Environments by Computing Missing Service Demand Parameters CMG 2009 - Paper 9103, December 11, 2009 17
Implementation u Model £ Measurement data provides historical view n Many intervals available l £ But at lower than expected future traffic volume Model results provide future view n Answer the classic questions: l l £ Beyond What was Measured When does response time become unacceptable? What resource saturates first? The following example takes this approach Measure system and applications at lower volumes n Predict behavior at higher volumes n l Different than example in the paper © 2009 Simalytic Solutions, LLC Modeling Virtualized Environments by Computing Missing Service Demand Parameters CMG 2009 - Paper 9103, December 11, 2009 18
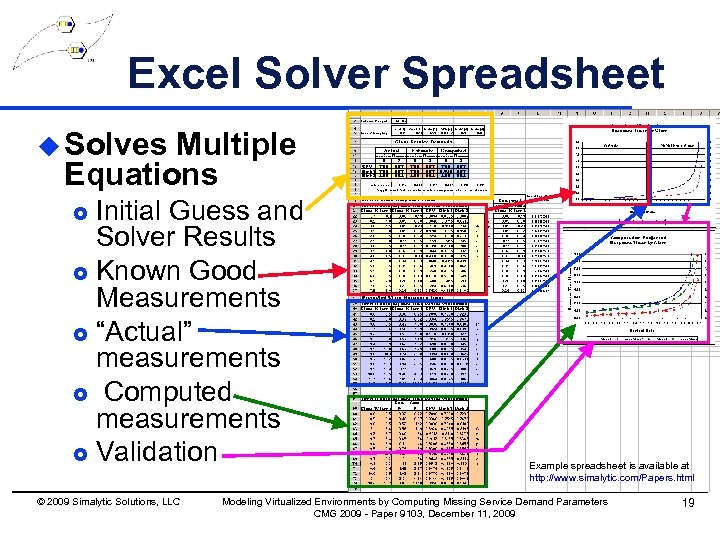
Excel Solver Spreadsheet u Solves Multiple Equations Initial Guess and Solver Results £ Known Good Measurements £ “Actual” measurements £ Computed measurements £ Validation £ © 2009 Simalytic Solutions, LLC Example spreadsheet is available at http: //www. simalytic. com/Papers. html Modeling Virtualized Environments by Computing Missing Service Demand Parameters CMG 2009 - Paper 9103, December 11, 2009 19
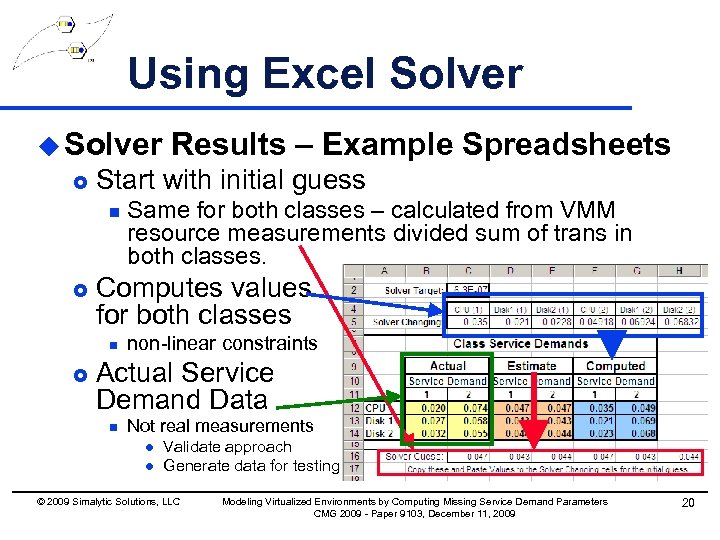
Using Excel Solver u Solver £ Start with initial guess n £ Same for both classes – calculated from VMM resource measurements divided sum of trans in both classes. Computes values for both classes n £ Results – Example Spreadsheets non-linear constraints Actual Service Demand Data n Not real measurements l l Validate approach Generate data for testing © 2009 Simalytic Solutions, LLC Modeling Virtualized Environments by Computing Missing Service Demand Parameters CMG 2009 - Paper 9103, December 11, 2009 20
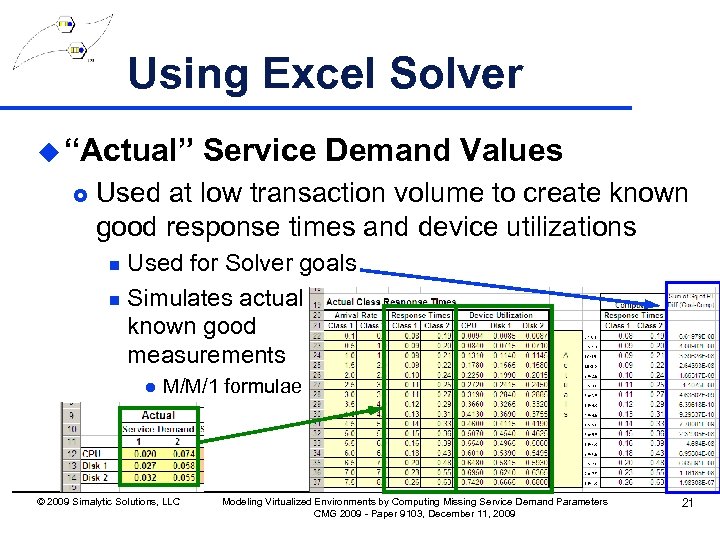
Using Excel Solver u “Actual” £ Service Demand Values Used at low transaction volume to create known good response times and device utilizations Used for Solver goals n Simulates actual known good measurements n l M/M/1 formulae © 2009 Simalytic Solutions, LLC Modeling Virtualized Environments by Computing Missing Service Demand Parameters CMG 2009 - Paper 9103, December 11, 2009 21
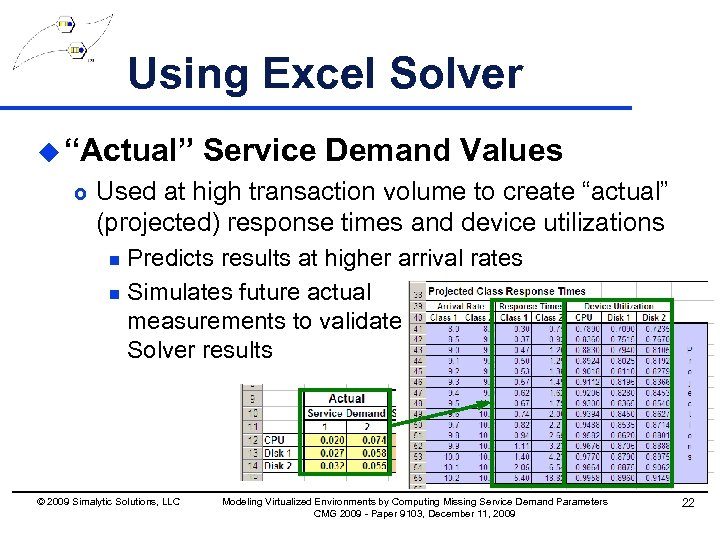
Using Excel Solver u “Actual” £ Service Demand Values Used at high transaction volume to create “actual” (projected) response times and device utilizations Predicts results at higher arrival rates n Simulates future actual measurements to validate Solver results n © 2009 Simalytic Solutions, LLC Modeling Virtualized Environments by Computing Missing Service Demand Parameters CMG 2009 - Paper 9103, December 11, 2009 22
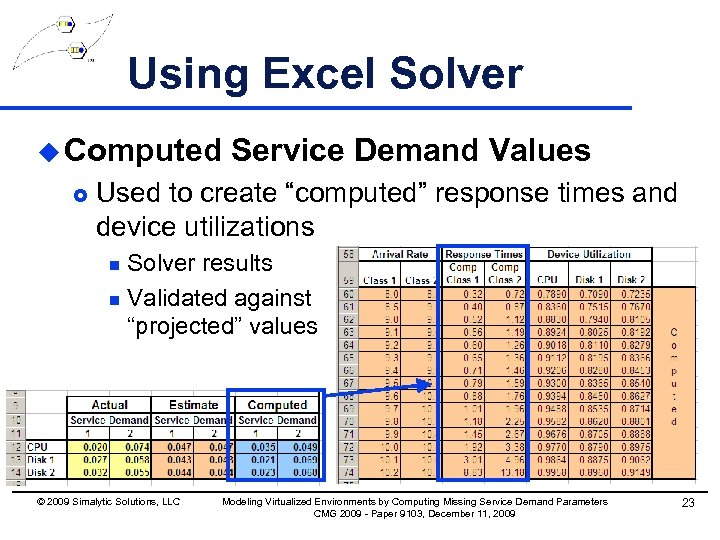
Using Excel Solver u Computed £ Service Demand Values Used to create “computed” response times and device utilizations Solver results n Validated against “projected” values n © 2009 Simalytic Solutions, LLC Modeling Virtualized Environments by Computing Missing Service Demand Parameters CMG 2009 - Paper 9103, December 11, 2009 23
Using Excel Solver u Solver Answer Report £ Shows details behind solution © 2009 Simalytic Solutions, LLC Modeling Virtualized Environments by Computing Missing Service Demand Parameters CMG 2009 - Paper 9103, December 11, 2009 24
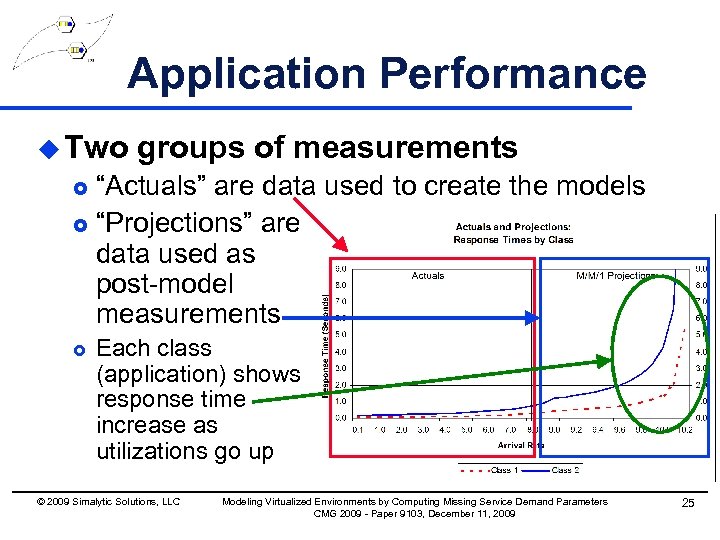
Application Performance u Two groups of measurements “Actuals” are data used to create the models £ “Projections” are data used as post-model measurements £ £ Each class (application) shows response time increase as utilizations go up © 2009 Simalytic Solutions, LLC Modeling Virtualized Environments by Computing Missing Service Demand Parameters CMG 2009 - Paper 9103, December 11, 2009 25
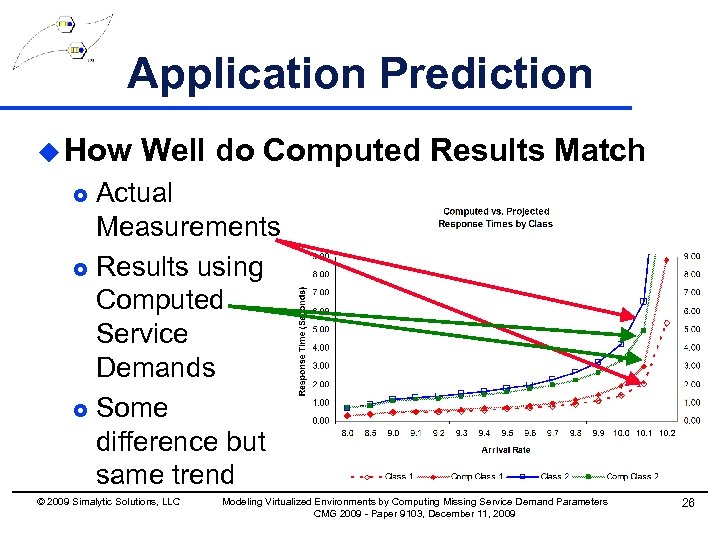
Application Prediction u How Well do Computed Results Match Actual Measurements £ Results using Computed Service Demands £ Some difference but same trend £ © 2009 Simalytic Solutions, LLC Modeling Virtualized Environments by Computing Missing Service Demand Parameters CMG 2009 - Paper 9103, December 11, 2009 26
Usage u How Can Computed Service Demands be Used? £ Stand-alone models n Same as measured service demands l £ Adjustments may be needed for VMM overhead and other interference – similar to other model calibrations Simalytic Models n Enhanced Simalytic Function for multi-tier models l Dynamic calculations to t simulate complex usage patterns t account for effects of spikes in other workloads © 2009 Simalytic Solutions, LLC Modeling Virtualized Environments by Computing Missing Service Demand Parameters CMG 2009 - Paper 9103, December 11, 2009 27
Conclusion u Future £ Work Explore criteria around measurement collection How many intervals needed for minimal effectiveness n What improves accuracy n £ Incorporate solver into modeling tool n Possibly as enhanced Simalytic Function © 2009 Simalytic Solutions, LLC Modeling Virtualized Environments by Computing Missing Service Demand Parameters CMG 2009 - Paper 9103, December 11, 2009 28
Conclusion u Valid £ Approach Works with synthetic test data n Some differences l n £ But trends usable for planning Refinement needed n £ between projected and computed results account for VMM overhead Model virtual systems with virtual data © 2009 Simalytic Solutions, LLC Modeling Virtualized Environments by Computing Missing Service Demand Parameters CMG 2009 - Paper 9103, December 11, 2009 29

Missing Data Doesn’t Stop a Real Modeler! Presentation and spreadsheet will be available at: http: //www. simalytic. com/Papers. html © 2009 Simalytic Solutions, LLC Modeling Virtualized Environments by Computing Missing Service Demand Parameters CMG 2009 - Paper 9103, December 11, 2009 30
9cd9f2511f5969f9cc0fc4b00360e4e8.ppt