b0a54f42caea54304aca16b7dc0ffc4a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28
 Modeling Tool for Stiff Heterogeneous Systems Yury Shornikov 1, Eugeny Novikov 2 Design Technological Institute of Digital Techniques SB RAS, Novosibirsk, Russia, shornikov@inbox. ru 1 Institute of Computational Modeling SB RAS, Krasnoyarsk, Russia, novikov@icm. krasn. ru 2
Modeling Tool for Stiff Heterogeneous Systems Yury Shornikov 1, Eugeny Novikov 2 Design Technological Institute of Digital Techniques SB RAS, Novosibirsk, Russia, shornikov@inbox. ru 1 Institute of Computational Modeling SB RAS, Krasnoyarsk, Russia, novikov@icm. krasn. ru 2
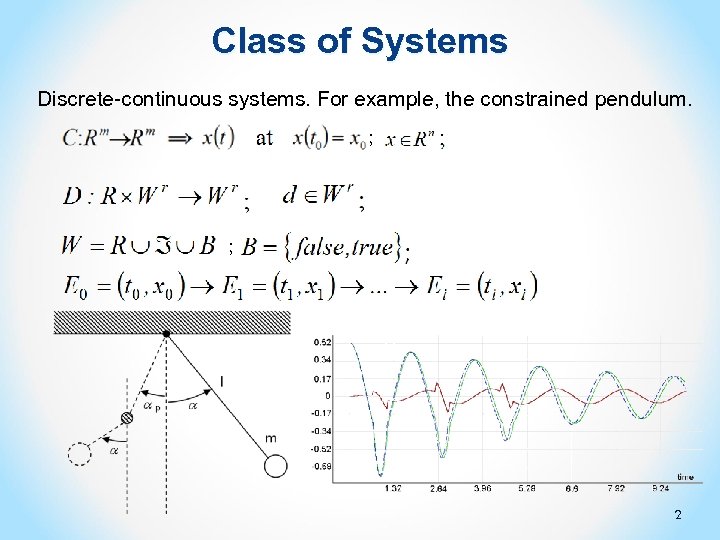 Class of Systems Discrete-continuous systems. For example, the constrained pendulum. ; ; 2
Class of Systems Discrete-continuous systems. For example, the constrained pendulum. ; ; 2
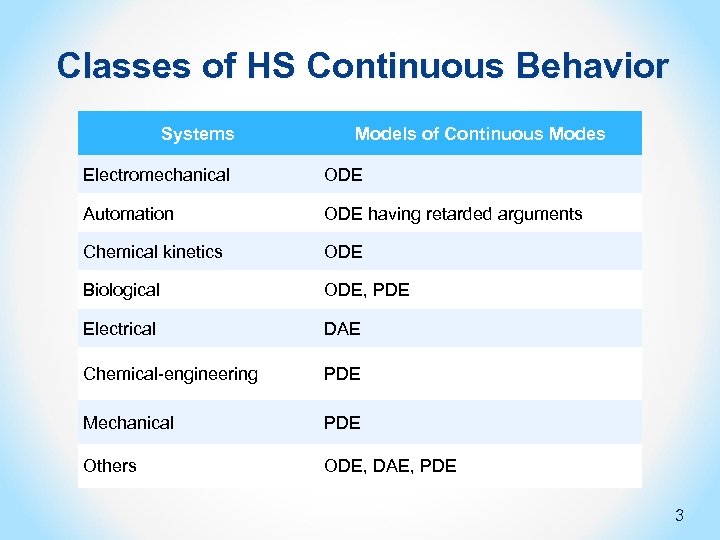 Classes of HS Continuous Behavior Systems Models of Continuous Modes Electromechanical ODE Automation ODE having retarded arguments Chemical kinetics ODE Biological ODE, PDE Electrical DAE Chemical-engineering PDE Mechanical PDE Others ODE, DAE, PDE 3
Classes of HS Continuous Behavior Systems Models of Continuous Modes Electromechanical ODE Automation ODE having retarded arguments Chemical kinetics ODE Biological ODE, PDE Electrical DAE Chemical-engineering PDE Mechanical PDE Others ODE, DAE, PDE 3
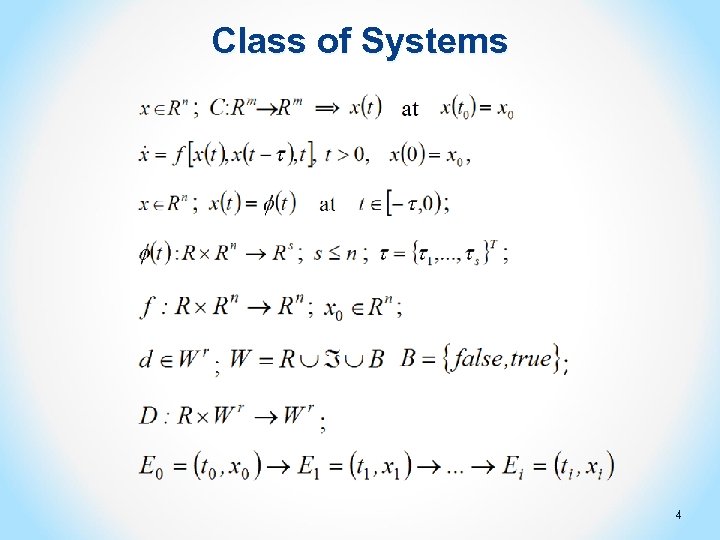 Class of Systems 4
Class of Systems 4
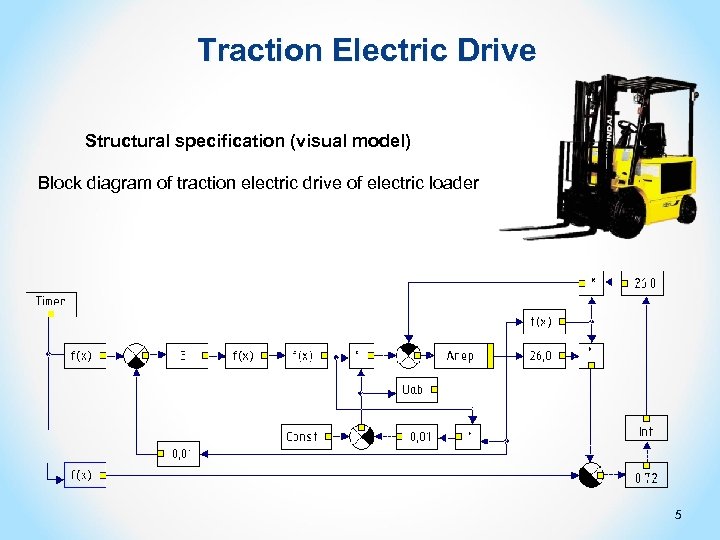 Traction Electric Drive Structural specification (visual model) Block diagram of traction electric drive of electric loader 5
Traction Electric Drive Structural specification (visual model) Block diagram of traction electric drive of electric loader 5
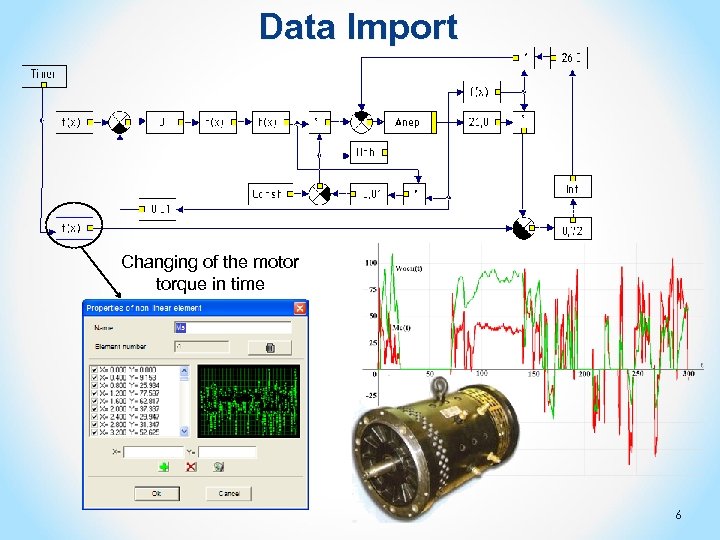 Data Import Changing of the motor torque in time 6
Data Import Changing of the motor torque in time 6
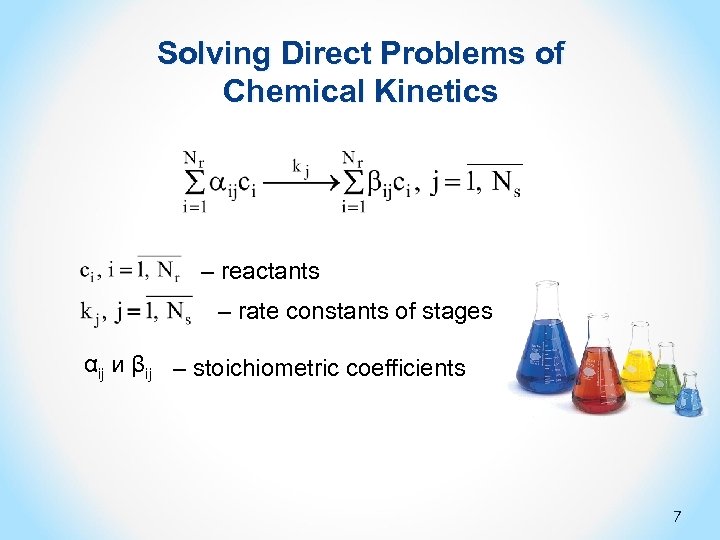 Solving Direct Problems of Chemical Kinetics – reactants – rate constants of stages αij и βij – stoichiometric coefficients 7
Solving Direct Problems of Chemical Kinetics – reactants – rate constants of stages αij и βij – stoichiometric coefficients 7
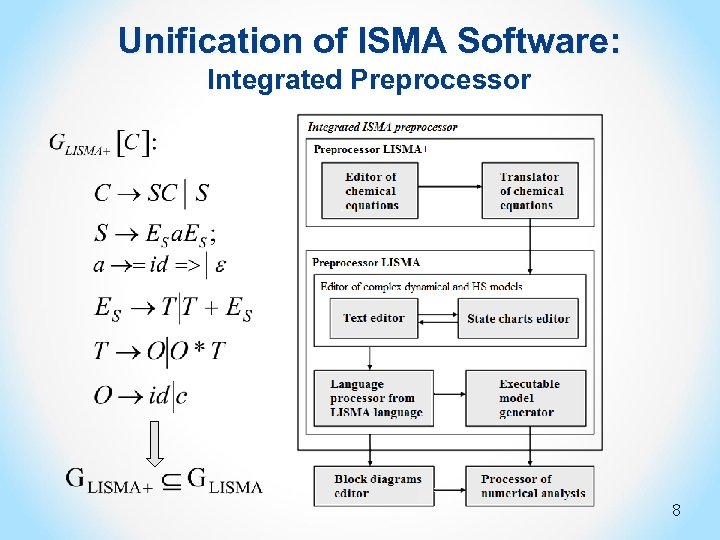 Unification of ISMA Software: Integrated Preprocessor 8
Unification of ISMA Software: Integrated Preprocessor 8
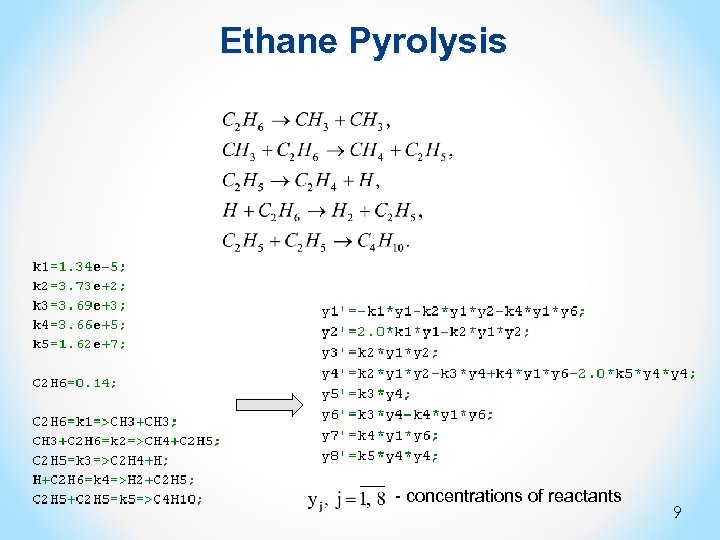 Ethane Pyrolysis - concentrations of reactants 9
Ethane Pyrolysis - concentrations of reactants 9
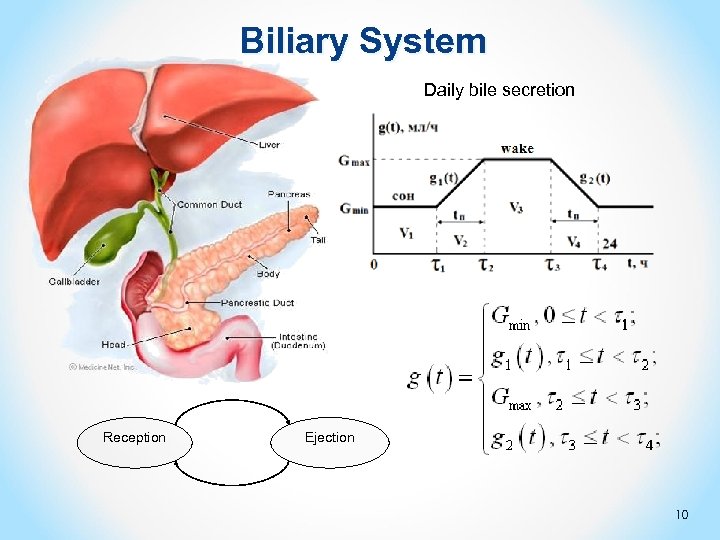 Biliary System Daily bile secretion Reception Ejection 10
Biliary System Daily bile secretion Reception Ejection 10
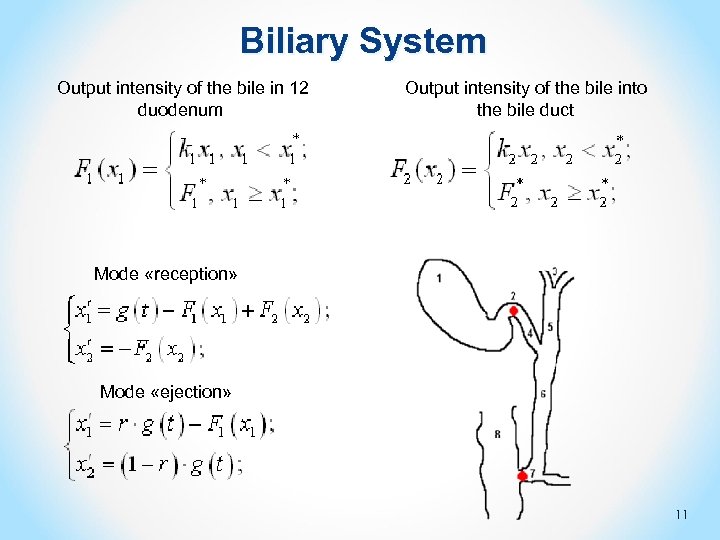 Biliary System Output intensity of the bile in 12 duodenum Output intensity of the bile into the bile duct Mode «reception» Mode «ejection» 11
Biliary System Output intensity of the bile in 12 duodenum Output intensity of the bile into the bile duct Mode «reception» Mode «ejection» 11
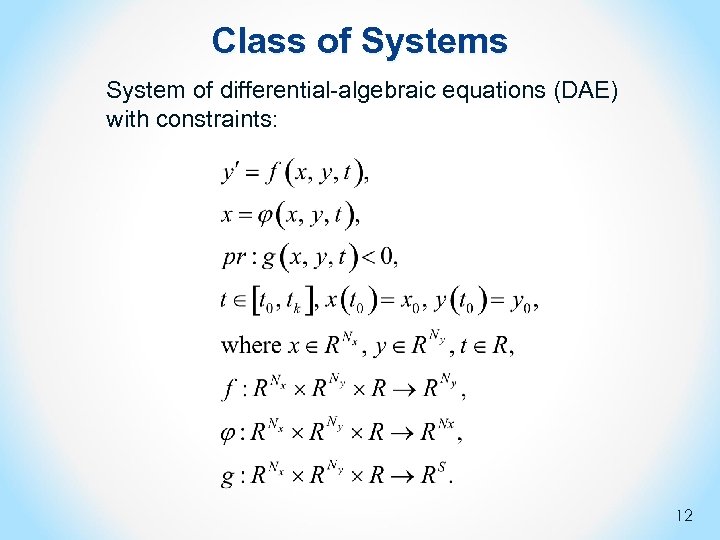 Class of Systems System of differential-algebraic equations (DAE) with constraints: 12
Class of Systems System of differential-algebraic equations (DAE) with constraints: 12
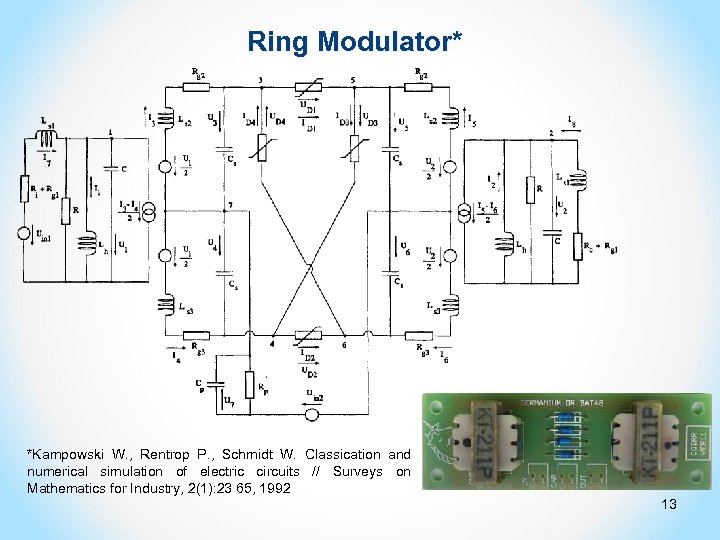 Ring Modulator* *Kampowski W. , Rentrop P. , Schmidt W. Classication and numerical simulation of electric circuits // Surveys on Mathematics for Industry, 2(1): 23 65, 1992 13
Ring Modulator* *Kampowski W. , Rentrop P. , Schmidt W. Classication and numerical simulation of electric circuits // Surveys on Mathematics for Industry, 2(1): 23 65, 1992 13
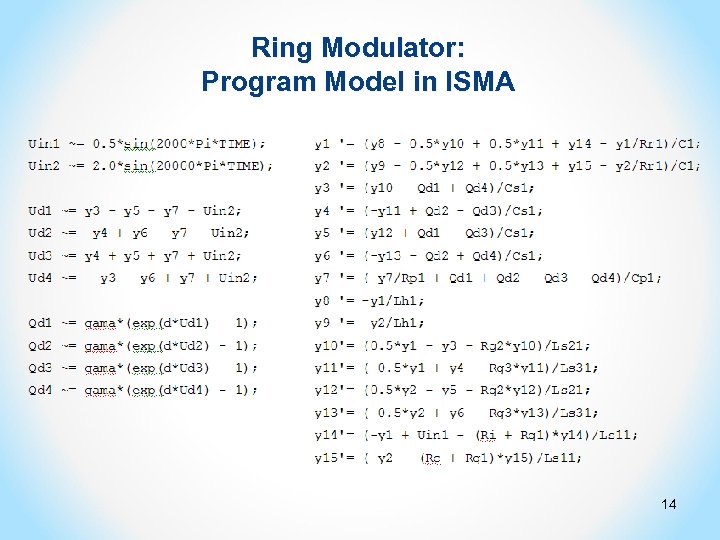 Ring Modulator: Program Model in ISMA 14
Ring Modulator: Program Model in ISMA 14
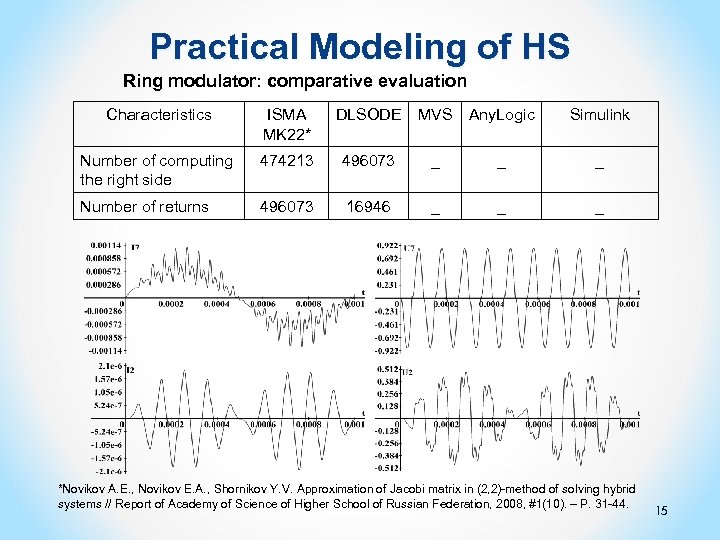 Practical Modeling of HS Ring modulator: comparative evaluation Characteristics ISMA MK 22* DLSODE MVS Any. Logic Simulink Number of computing the right side 474213 496073 _ _ _ Number of returns 496073 16946 _ _ _ *Novikov А. Е. , Novikov Е. А. , Shornikov Y. V. Approximation of Jacobi matrix in (2, 2)-method of solving hybrid systems // Report of Academy of Science of Higher School of Russian Federation, 2008, #1(10). – P. 31 -44. 15
Practical Modeling of HS Ring modulator: comparative evaluation Characteristics ISMA MK 22* DLSODE MVS Any. Logic Simulink Number of computing the right side 474213 496073 _ _ _ Number of returns 496073 16946 _ _ _ *Novikov А. Е. , Novikov Е. А. , Shornikov Y. V. Approximation of Jacobi matrix in (2, 2)-method of solving hybrid systems // Report of Academy of Science of Higher School of Russian Federation, 2008, #1(10). – P. 31 -44. 15
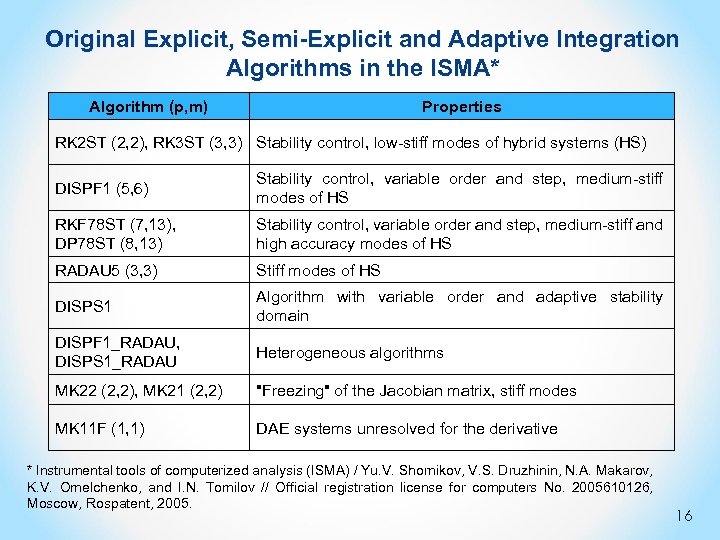 Original Explicit, Semi-Explicit and Adaptive Integration Algorithms in the ISMA* Algorithm (p, m) Properties RK 2 ST (2, 2), RK 3 ST (3, 3) Stability control, low-stiff modes of hybrid systems (HS) DISPF 1 (5, 6) Stability control, variable order and step, medium-stiff modes of HS RKF 78 ST (7, 13), DP 78 ST (8, 13) Stability control, variable order and step, medium-stiff and high accuracy modes of HS RADAU 5 (3, 3) Stiff modes of HS DISPS 1 Algorithm with variable order and adaptive stability domain DISPF 1_RADAU, DISPS 1_RADAU Heterogeneous algorithms MK 22 (2, 2), MK 21 (2, 2) "Freezing" of the Jacobian matrix, stiff modes MK 11 F (1, 1) DAE systems unresolved for the derivative * Instrumental tools of computerized analysis (ISMA) / Yu. V. Shornikov, V. S. Druzhinin, N. А. Makarov, K. V. Omelchenko, and I. N. Tomilov // Official registration license for computers No. 2005610126, Мoscow, Rospatent, 2005. 16
Original Explicit, Semi-Explicit and Adaptive Integration Algorithms in the ISMA* Algorithm (p, m) Properties RK 2 ST (2, 2), RK 3 ST (3, 3) Stability control, low-stiff modes of hybrid systems (HS) DISPF 1 (5, 6) Stability control, variable order and step, medium-stiff modes of HS RKF 78 ST (7, 13), DP 78 ST (8, 13) Stability control, variable order and step, medium-stiff and high accuracy modes of HS RADAU 5 (3, 3) Stiff modes of HS DISPS 1 Algorithm with variable order and adaptive stability domain DISPF 1_RADAU, DISPS 1_RADAU Heterogeneous algorithms MK 22 (2, 2), MK 21 (2, 2) "Freezing" of the Jacobian matrix, stiff modes MK 11 F (1, 1) DAE systems unresolved for the derivative * Instrumental tools of computerized analysis (ISMA) / Yu. V. Shornikov, V. S. Druzhinin, N. А. Makarov, K. V. Omelchenko, and I. N. Tomilov // Official registration license for computers No. 2005610126, Мoscow, Rospatent, 2005. 16
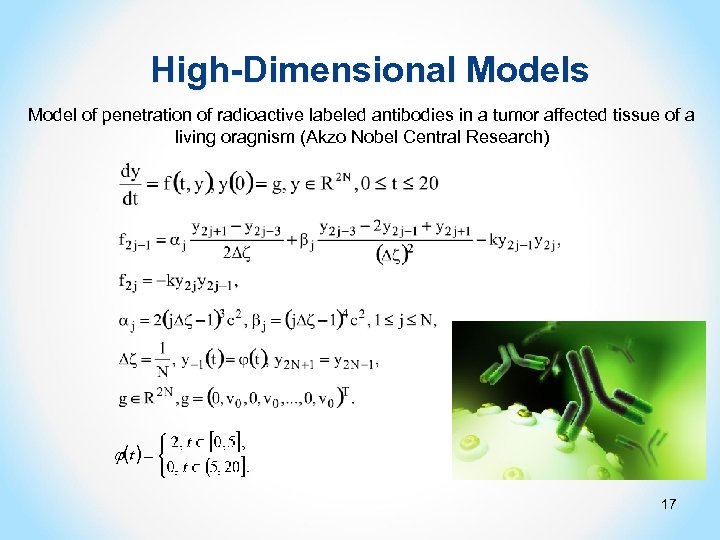 High-Dimensional Models Model of penetration of radioactive labeled antibodies in a tumor affected tissue of a living oragnism (Akzo Nobel Central Research) 17
High-Dimensional Models Model of penetration of radioactive labeled antibodies in a tumor affected tissue of a living oragnism (Akzo Nobel Central Research) 17
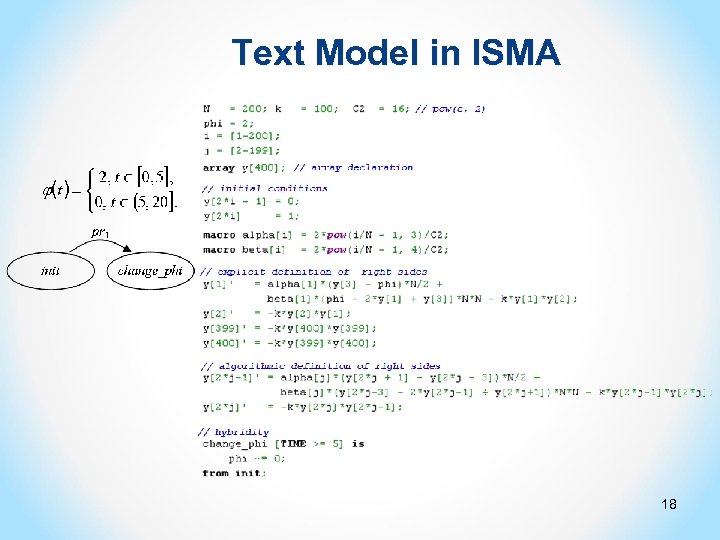 Text Model in ISMA 18
Text Model in ISMA 18
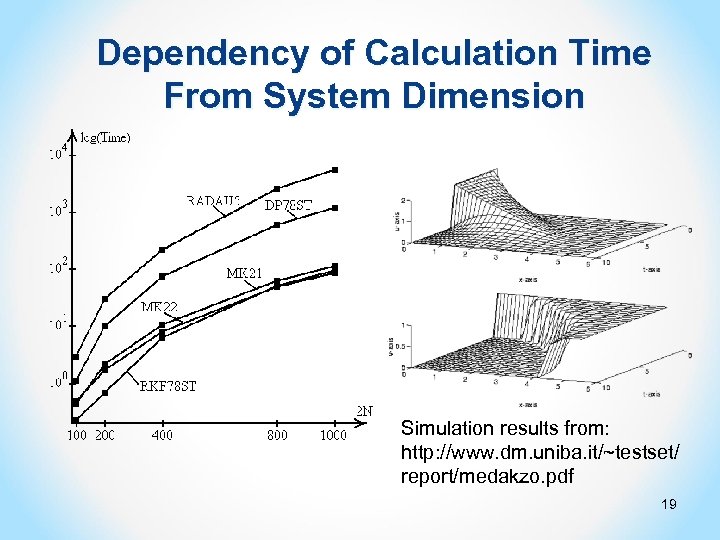 Dependency of Calculation Time From System Dimension Simulation results from: http: //www. dm. uniba. it/~testset/ report/medakzo. pdf 19
Dependency of Calculation Time From System Dimension Simulation results from: http: //www. dm. uniba. it/~testset/ report/medakzo. pdf 19
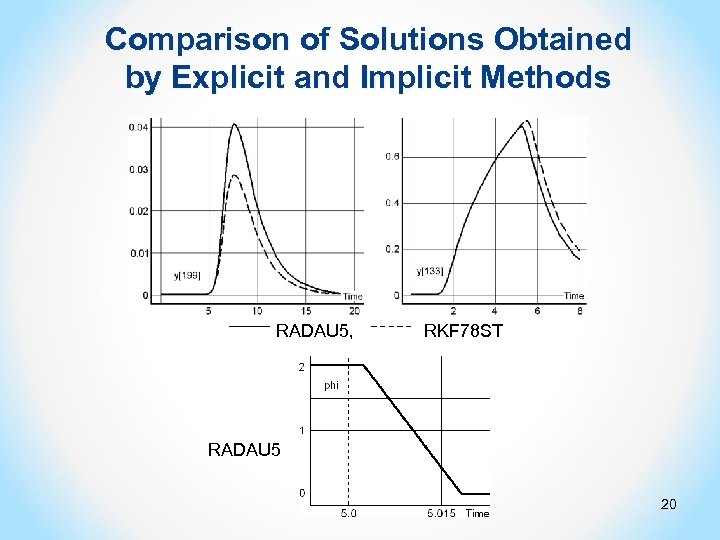 Comparison of Solutions Obtained by Explicit and Implicit Methods RADAU 5, RKF 78 ST RADAU 5 20
Comparison of Solutions Obtained by Explicit and Implicit Methods RADAU 5, RKF 78 ST RADAU 5 20
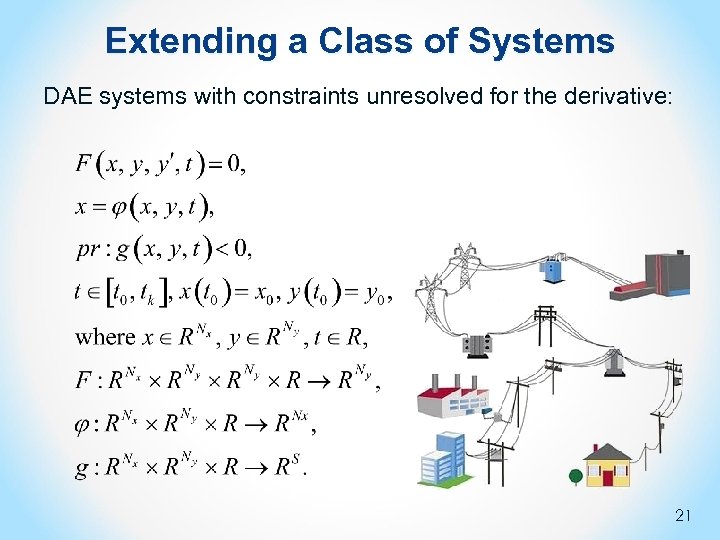 Extending a Class of Systems DAE systems with constraints unresolved for the derivative: 21
Extending a Class of Systems DAE systems with constraints unresolved for the derivative: 21
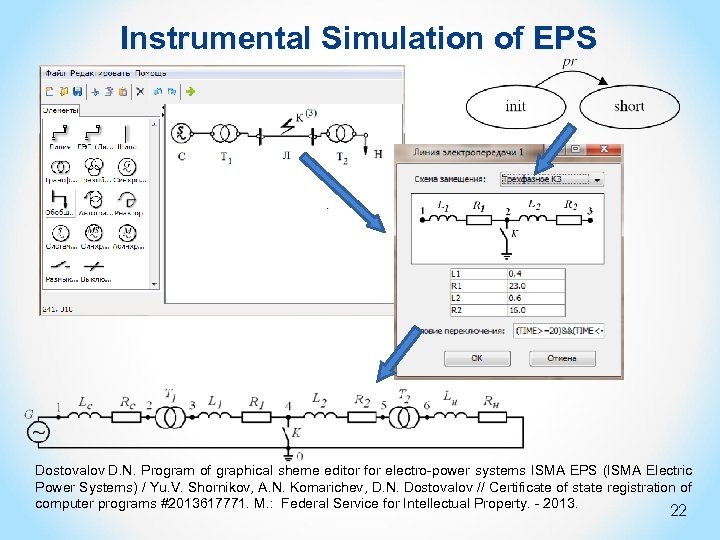 Instrumental Simulation of EPS Dostovalov D. N. Program of graphical sheme editor for electro-power systems ISMA EPS (ISMA Electric Power Systems) / Yu. V. Shornikov, A. N. Komarichev, D. N. Dostovalov // Certificate of state registration of computer programs #2013617771. M. : Federal Service for Intellectual Property. - 2013. 22
Instrumental Simulation of EPS Dostovalov D. N. Program of graphical sheme editor for electro-power systems ISMA EPS (ISMA Electric Power Systems) / Yu. V. Shornikov, A. N. Komarichev, D. N. Dostovalov // Certificate of state registration of computer programs #2013617771. M. : Federal Service for Intellectual Property. - 2013. 22
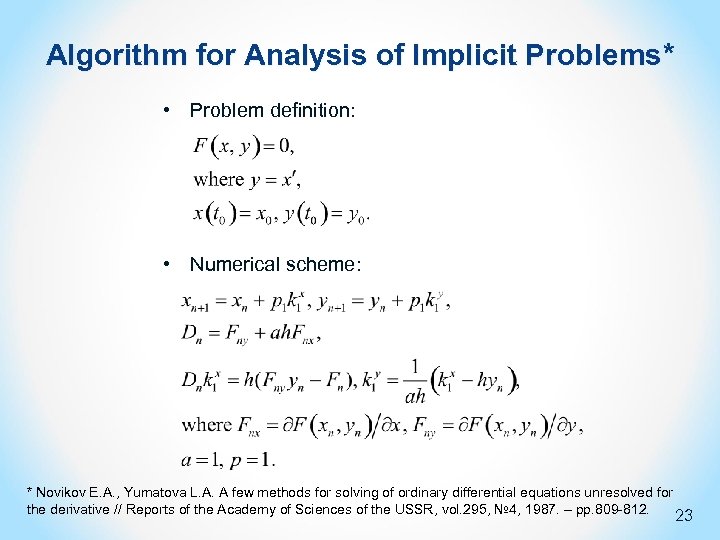 Algorithm for Analysis of Implicit Problems* • Problem definition: • Numerical scheme: * Novikov E. A. , Yumatova L. A. A few methods for solving of ordinary differential equations unresolved for the derivative // Reports of the Academy of Sciences of the USSR, vol. 295, № 4, 1987. – pp. 809 -812. 23
Algorithm for Analysis of Implicit Problems* • Problem definition: • Numerical scheme: * Novikov E. A. , Yumatova L. A. A few methods for solving of ordinary differential equations unresolved for the derivative // Reports of the Academy of Sciences of the USSR, vol. 295, № 4, 1987. – pp. 809 -812. 23
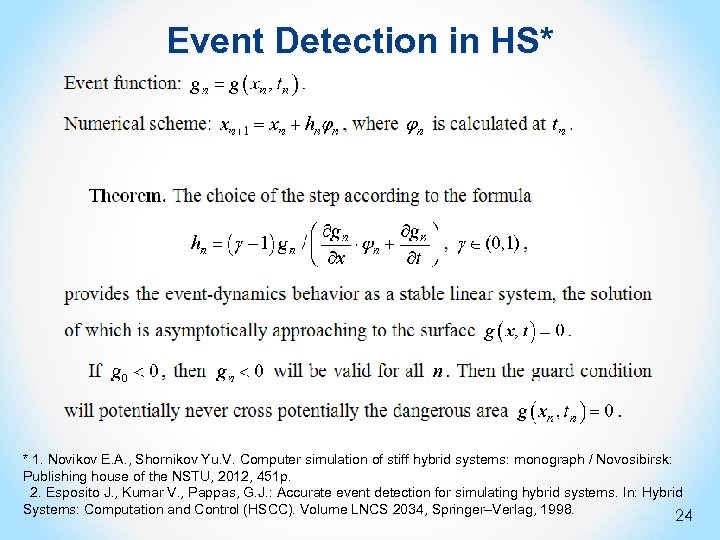 Event Detection in HS* * 1. Novikov E. A. , Shornikov Yu. V. Computer simulation of stiff hybrid systems: monograph / Novosibirsk: Publishing house of the NSTU, 2012, 451 p. 2. Esposito J. , Kumar V. , Pappas, G. J. : Accurate event detection for simulating hybrid systems. In: Hybrid Systems: Computation and Control (HSCC). Volume LNCS 2034, Springer–Verlag, 1998. 24
Event Detection in HS* * 1. Novikov E. A. , Shornikov Yu. V. Computer simulation of stiff hybrid systems: monograph / Novosibirsk: Publishing house of the NSTU, 2012, 451 p. 2. Esposito J. , Kumar V. , Pappas, G. J. : Accurate event detection for simulating hybrid systems. In: Hybrid Systems: Computation and Control (HSCC). Volume LNCS 2034, Springer–Verlag, 1998. 24
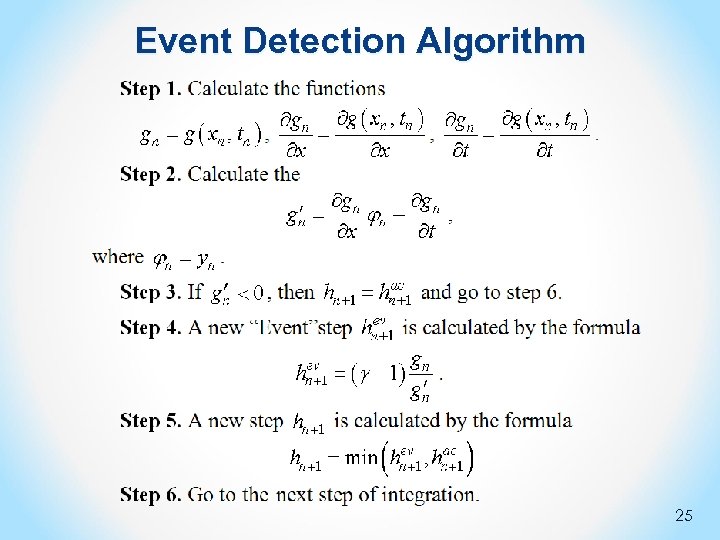 Event Detection Algorithm 25
Event Detection Algorithm 25
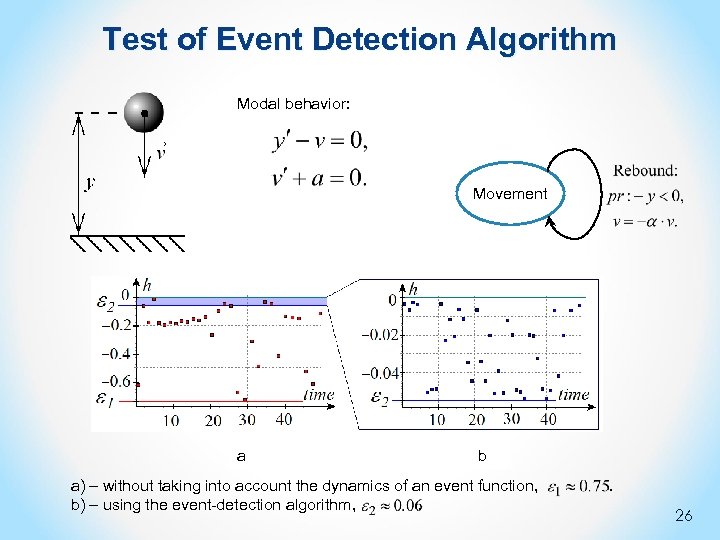 Test of Event Detection Algorithm Modal behavior: Movement a b a) – without taking into account the dynamics of an event function, . b) – using the event-detection algorithm, . 26
Test of Event Detection Algorithm Modal behavior: Movement a b a) – without taking into account the dynamics of an event function, . b) – using the event-detection algorithm, . 26
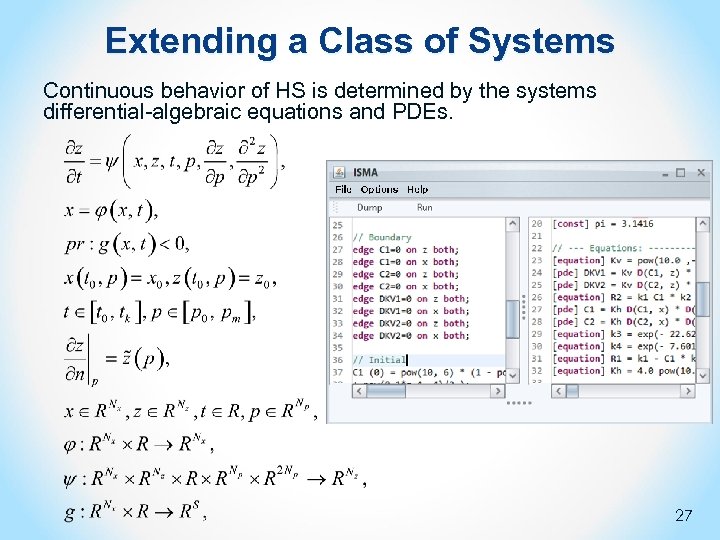 Extending a Class of Systems Continuous behavior of HS is determined by the systems differential-algebraic equations and PDEs. 27
Extending a Class of Systems Continuous behavior of HS is determined by the systems differential-algebraic equations and PDEs. 27
 Thank you for your attention! Yury Shornikov 1, Eugeny Novikov 2 Design Technological Institute of Digital Techniques SB RAS, Novosibirsk, Russia, shornikov@inbox. ru 1 Institute of Computational Modeling SB RAS, Krasnoyarsk, Russia, novikov@icm. krasn. ru 2 28
Thank you for your attention! Yury Shornikov 1, Eugeny Novikov 2 Design Technological Institute of Digital Techniques SB RAS, Novosibirsk, Russia, shornikov@inbox. ru 1 Institute of Computational Modeling SB RAS, Krasnoyarsk, Russia, novikov@icm. krasn. ru 2 28


