96c54f48a1fd3be8c626dd9c9cbaa9ec.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 Modeling Read-Out for Solid-State Quantum Computers in Silicon Vincent Conrad Supervisors: C. Pakes & L. Hollenberg
Modeling Read-Out for Solid-State Quantum Computers in Silicon Vincent Conrad Supervisors: C. Pakes & L. Hollenberg
 Introduction Solid-State Quantum Computers in Silicon Single Electron Transistors Modeling Read-Out Results & Conclusion Further Work
Introduction Solid-State Quantum Computers in Silicon Single Electron Transistors Modeling Read-Out Results & Conclusion Further Work
 Solid-State Quantum Computers in Silicon Scalable Hard Qubits Kane Quantum Computer Spin-Qubit Buried Donor Charge Qubit Quantum Computer Charge-Qubit
Solid-State Quantum Computers in Silicon Scalable Hard Qubits Kane Quantum Computer Spin-Qubit Buried Donor Charge Qubit Quantum Computer Charge-Qubit
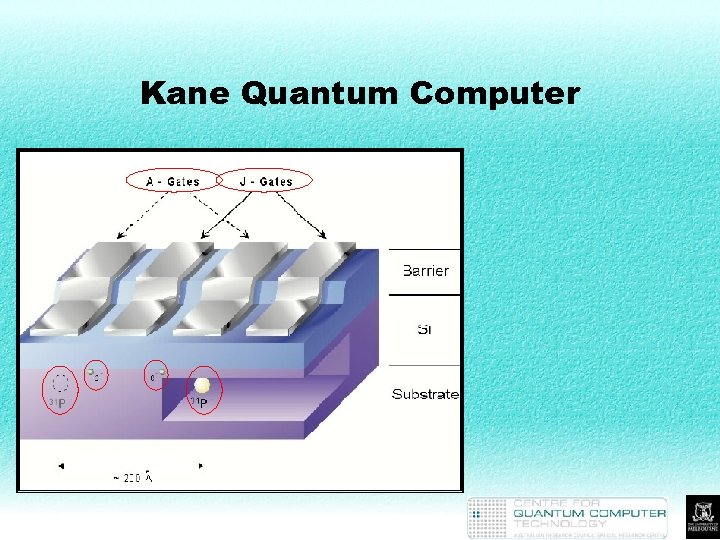 Kane Quantum Computer
Kane Quantum Computer
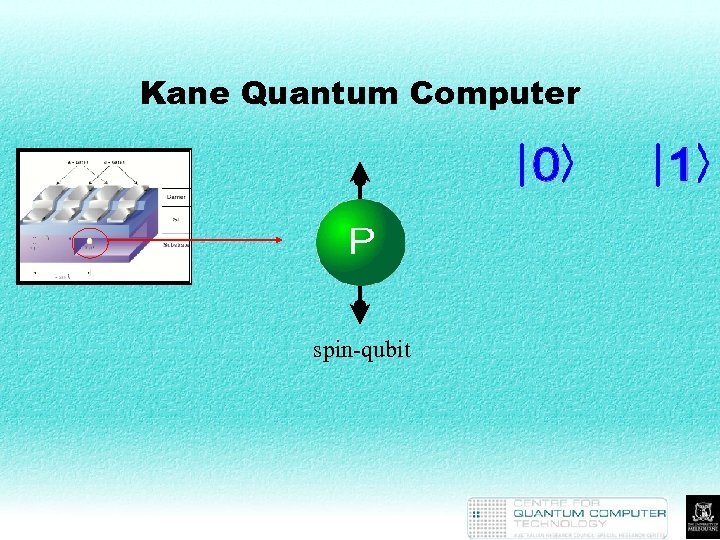 Kane Quantum Computer spin-qubit
Kane Quantum Computer spin-qubit
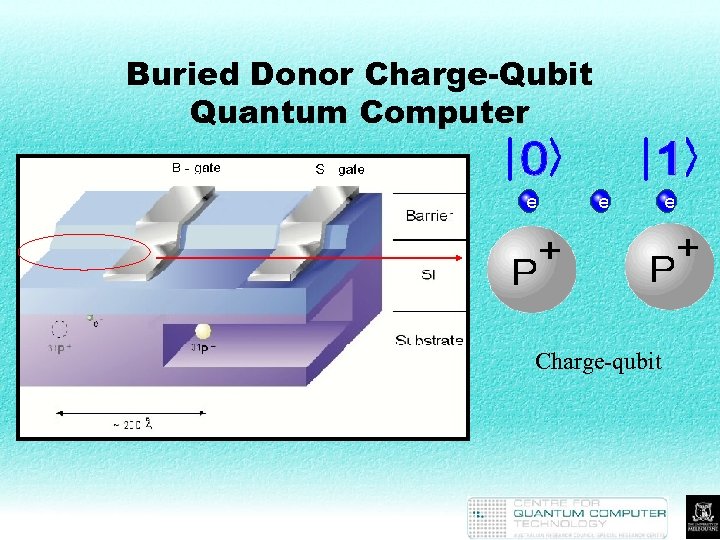 Buried Donor Charge-Qubit Quantum Computer Charge-qubit
Buried Donor Charge-Qubit Quantum Computer Charge-qubit
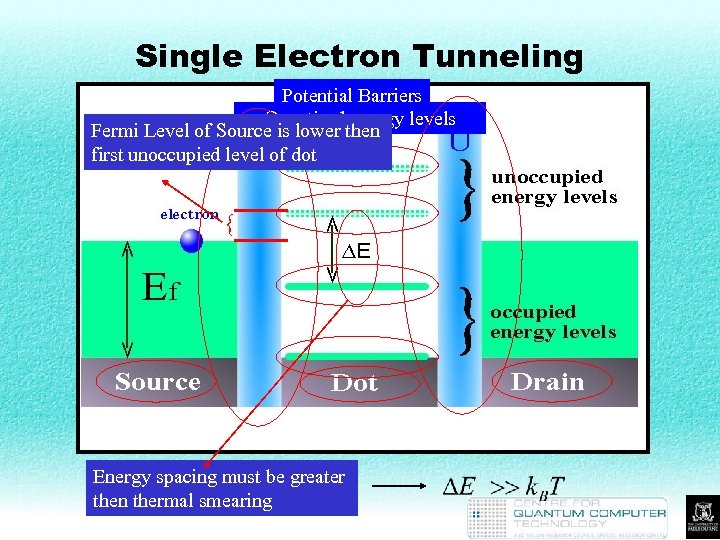 Single Electron Tunneling Potential Barriers Quantised energy levels Fermi Level of Source is lower then first unoccupied level of dot { Energy spacing must be greater then thermal smearing
Single Electron Tunneling Potential Barriers Quantised energy levels Fermi Level of Source is lower then first unoccupied level of dot { Energy spacing must be greater then thermal smearing
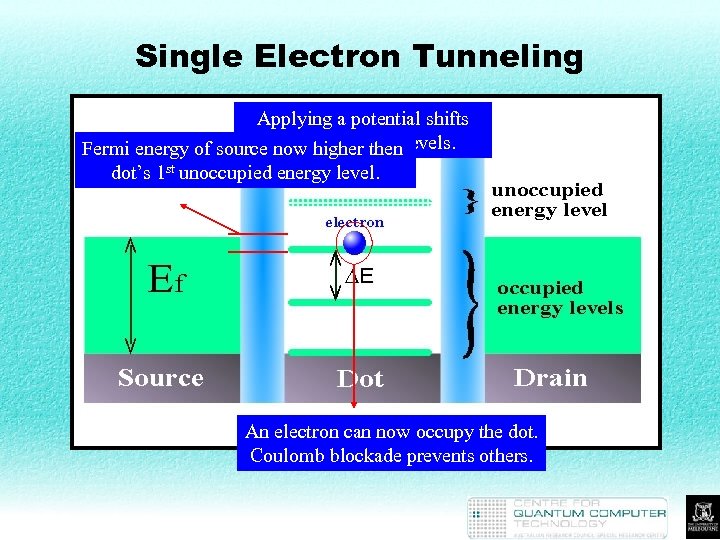 Single Electron Tunneling Applying a potential shifts Fermi energy of source the dot’s energy levels. now higher then dot’s 1 st unoccupied energy level. An electron can now occupy the dot. Coulomb blockade prevents others.
Single Electron Tunneling Applying a potential shifts Fermi energy of source the dot’s energy levels. now higher then dot’s 1 st unoccupied energy level. An electron can now occupy the dot. Coulomb blockade prevents others.
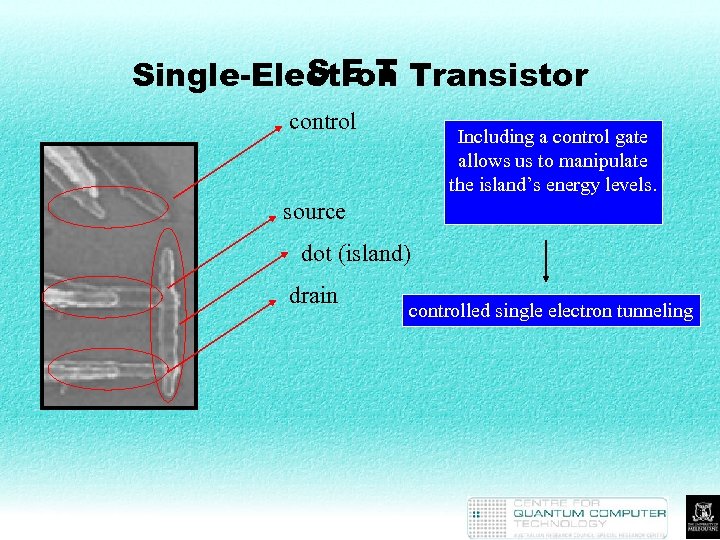 SET Single-Electron Transistor control Including a control gate allows us to manipulate the island’s energy levels. source dot (island) drain controlled single electron tunneling
SET Single-Electron Transistor control Including a control gate allows us to manipulate the island’s energy levels. source dot (island) drain controlled single electron tunneling
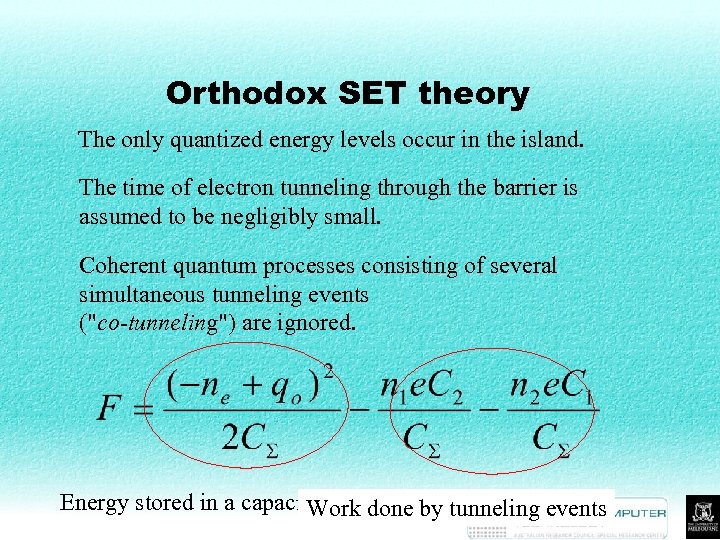 Orthodox SET theory The only quantized energy levels occur in the island. The time of electron tunneling through the barrier is assumed to be negligibly small. Coherent quantum processes consisting of several simultaneous tunneling events ("co-tunneling") are ignored. Energy stored in a capacitor Work done by tunneling events
Orthodox SET theory The only quantized energy levels occur in the island. The time of electron tunneling through the barrier is assumed to be negligibly small. Coherent quantum processes consisting of several simultaneous tunneling events ("co-tunneling") are ignored. Energy stored in a capacitor Work done by tunneling events
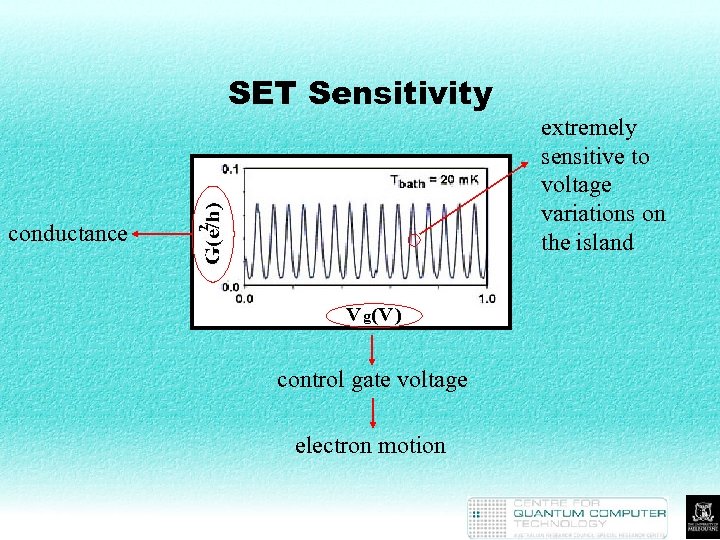 SET Sensitivity conductance control gate voltage electron motion extremely sensitive to voltage variations on the island
SET Sensitivity conductance control gate voltage electron motion extremely sensitive to voltage variations on the island
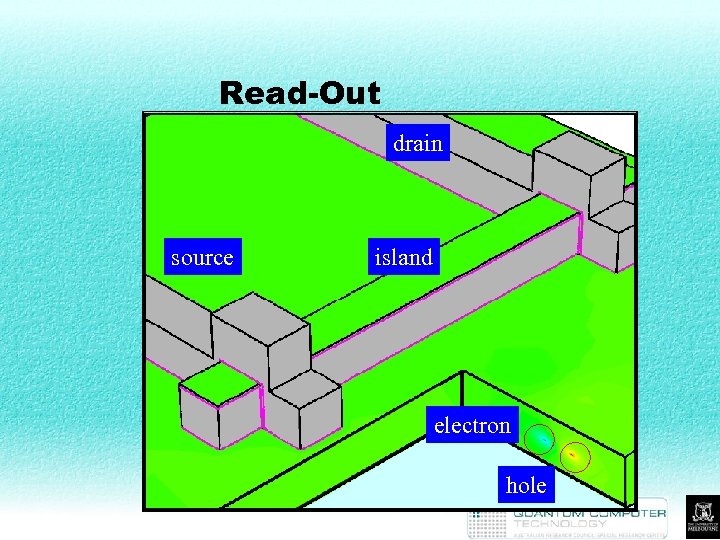 Read-Out drain Single electron’s motion between dopants. Vary potential on the source island (control gate). Induced island charge. Require induced charge > SET sensitivity. electron hole
Read-Out drain Single electron’s motion between dopants. Vary potential on the source island (control gate). Induced island charge. Require induced charge > SET sensitivity. electron hole
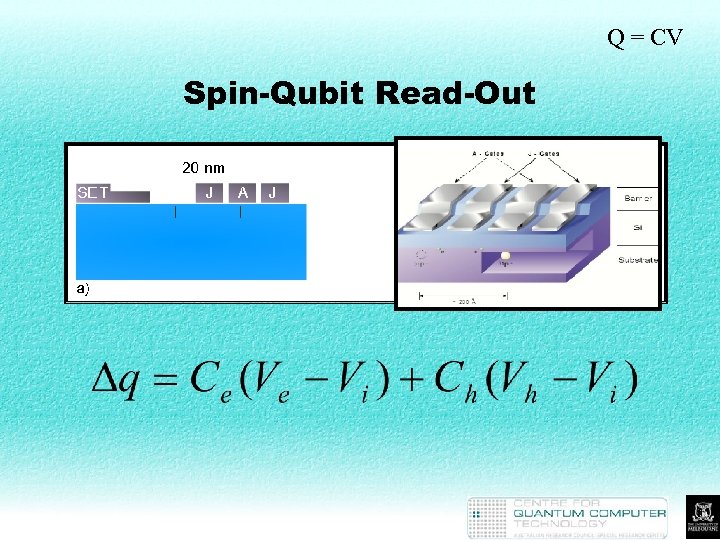 Q = CV Spin-Qubit Read-Out
Q = CV Spin-Qubit Read-Out
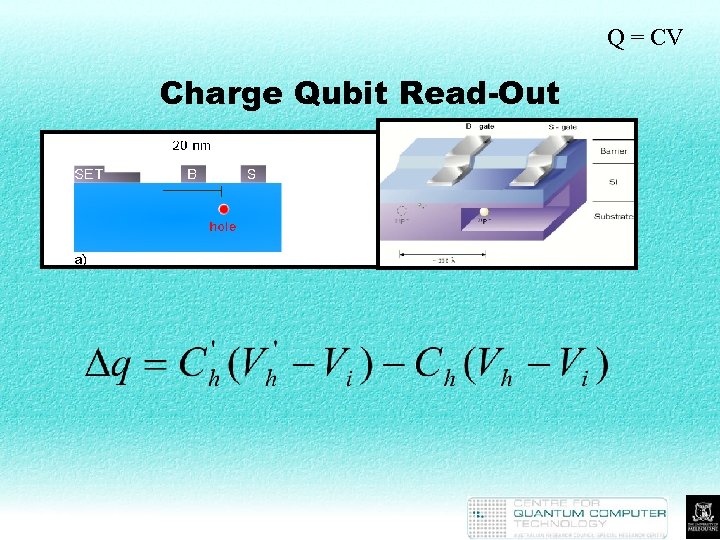 Q = CV Charge Qubit Read-Out
Q = CV Charge Qubit Read-Out
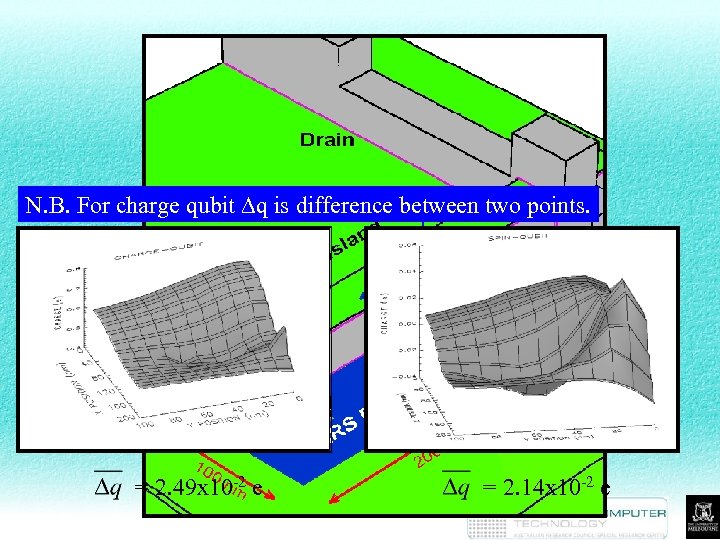 Results N. B. For charge qubit Dq is difference between two points. = 2. 49 x 10 -2 e = 2. 14 x 10 -2 e
Results N. B. For charge qubit Dq is difference between two points. = 2. 49 x 10 -2 e = 2. 14 x 10 -2 e
 Conclusions Induced island charge >> SET Sensitivity 2 x 10 -2 e >> 3. 2 x 10 -6 e Need an answer before information loss Electron-spin relaxation time (spin-qubit) Charge dissipation time (charge-qubit) Time given by shot-noise limit Well inside estimated times for both information loss mechanisms Both qubit types should produce measurable results using current technology made by the SRCQCT
Conclusions Induced island charge >> SET Sensitivity 2 x 10 -2 e >> 3. 2 x 10 -6 e Need an answer before information loss Electron-spin relaxation time (spin-qubit) Charge dissipation time (charge-qubit) Time given by shot-noise limit Well inside estimated times for both information loss mechanisms Both qubit types should produce measurable results using current technology made by the SRCQCT
 Further Work More complete architecture simulations. Full type 3 simulation ISE-TCAD input files prepared. Estimate 100 000 node points required. Accounts and ISE-TCAD setup at HPC. Beowulf in-house cluster under construction. Matching simulations to experiment. Convert type 3 simulation to replicate macroscopic charge-qubit experiment.
Further Work More complete architecture simulations. Full type 3 simulation ISE-TCAD input files prepared. Estimate 100 000 node points required. Accounts and ISE-TCAD setup at HPC. Beowulf in-house cluster under construction. Matching simulations to experiment. Convert type 3 simulation to replicate macroscopic charge-qubit experiment.

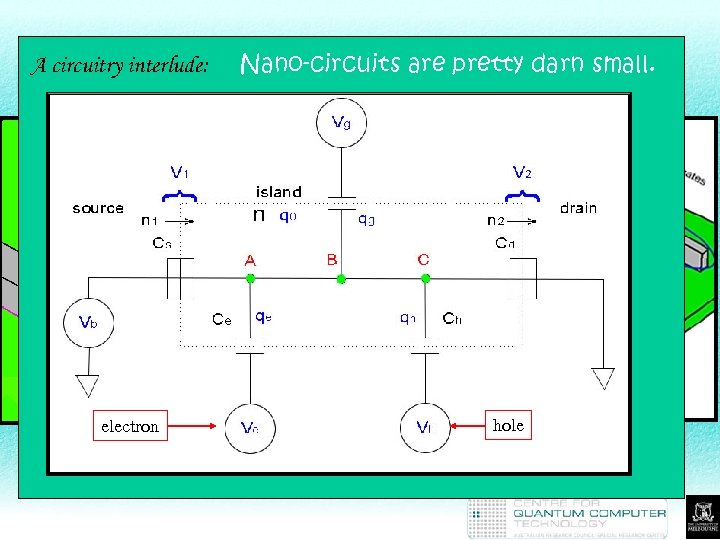 A circuitry interlude: Nano-circuits are pretty darn small. Type 3 Device hole electron and hole (spin-qubit)
A circuitry interlude: Nano-circuits are pretty darn small. Type 3 Device hole electron and hole (spin-qubit)
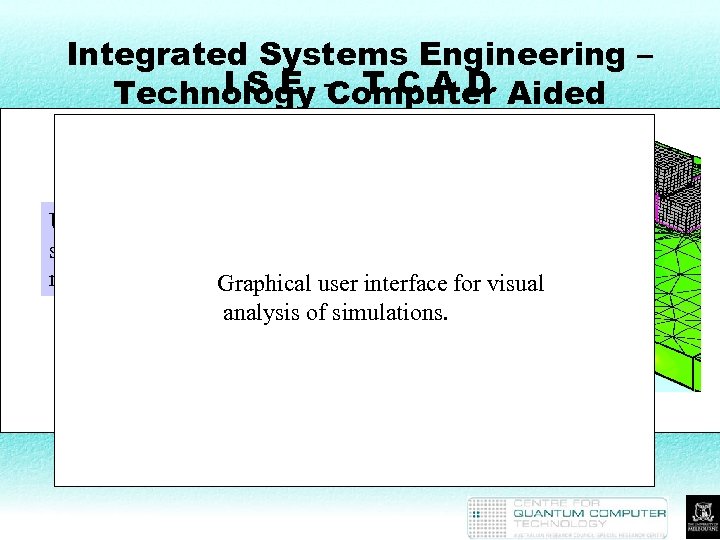 Integrated Systems Engineering – I S E Computer Technology – T C A D Aided Design coarse Poisson’s Equation Software package designed for microchip industry. User specifies mesh spacing to vary over MESH DESSIS PICASSO regions of interest. Graphical user interface for visual AC simulations. analysis of analysis Orthodox approach to single-electron tunneling. fine Extend ISE-TCAD to nanotech/mesoscopic devices.
Integrated Systems Engineering – I S E Computer Technology – T C A D Aided Design coarse Poisson’s Equation Software package designed for microchip industry. User specifies mesh spacing to vary over MESH DESSIS PICASSO regions of interest. Graphical user interface for visual AC simulations. analysis of analysis Orthodox approach to single-electron tunneling. fine Extend ISE-TCAD to nanotech/mesoscopic devices.


